42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

IPR Acquisition and The Business Concentration Professor Huang Yong huangyong 1962@vip. sina. com UIBECLC Dalian , June 10, 2010
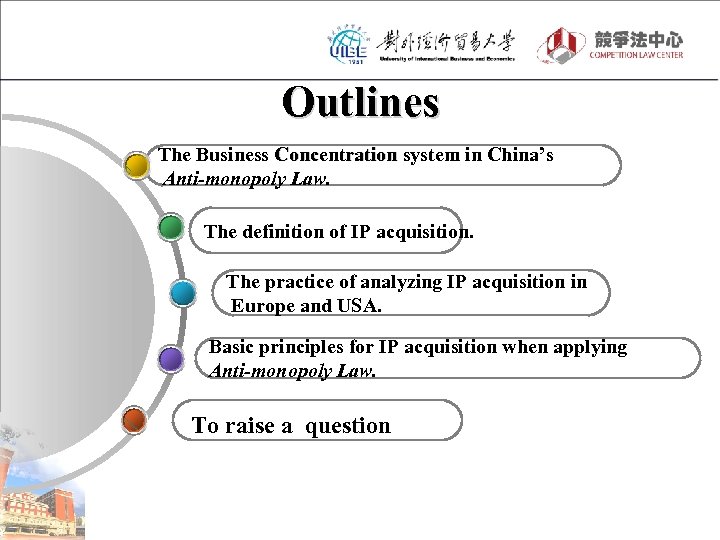
Outlines The Business Concentration system in China’s Anti-monopoly Law. The definition of IP acquisition. The practice of analyzing IP acquisition in Europe and USA. Basic principles for IP acquisition when applying Anti-monopoly Law. To raise a question
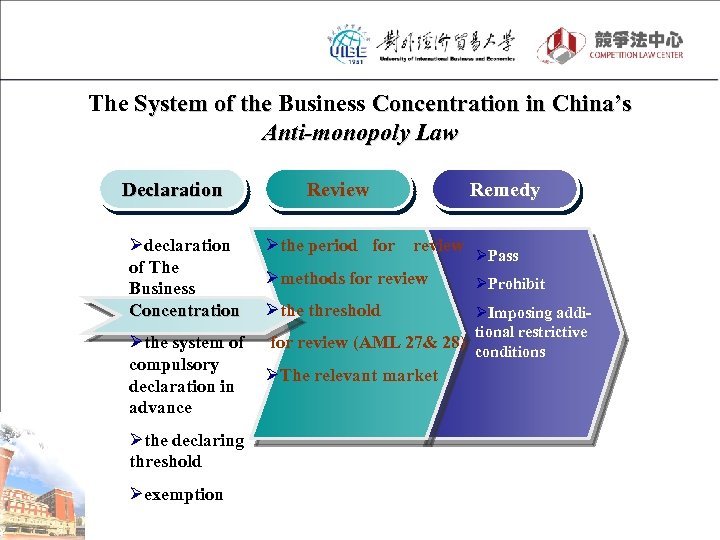
The System of the Business Concentration in China’s Anti-monopoly Law Declaration Ødeclaration of The Business Concentration Øthe system of compulsory declaration in advance Øthe declaring threshold Øexemption Review Øthe period for review Ømethods for review Øthe threshold Remedy ØPass ØProhibit ØImposing additional restrictive for review (AML 27& 28) conditions ØThe relevant market
![[The Business Concentration ] Definition and Forms Definition • Refers to merger of undertakings, [The Business Concentration ] Definition and Forms Definition • Refers to merger of undertakings,](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-4.jpg)
[The Business Concentration ] Definition and Forms Definition • Refers to merger of undertakings, or control over other undertakings gained by an undertaking through acquiring their shares or assets or signing contracts or other means, or the ability capable of exerting a decisive influence on other undertakings. Forms • Including: merger of undertakings, assets purchase, shares purchase, contractual stipulation, staff assignment, technical control, etc.
![[Definition of The Business Concentration ] Article 20 of Antimonopoly Law Merger of undertakings [Definition of The Business Concentration ] Article 20 of Antimonopoly Law Merger of undertakings](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-5.jpg)
[Definition of The Business Concentration ] Article 20 of Antimonopoly Law Merger of undertakings Control over other undertakings gained by an undertaking through acquiring their shares or assets Concentration of Undertakings Control over other undertakings or the ability capable of exerting a decisive influence on the same gained by an undertaking through signing contracts or other means.
![[The Business Concentration ] Classification Horizontal merger The acquiring and acquired parties are in [The Business Concentration ] Classification Horizontal merger The acquiring and acquired parties are in](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-6.jpg)
[The Business Concentration ] Classification Horizontal merger The acquiring and acquired parties are in the same industry. Vertical merger The merger between undertakings at different production and sales levels but have close connections on operating objects. Conglomerate merger The merger between undertakings in different industries which have almost no operating connections.
![[Declaration of The Business Concentration ] Threshold Levels of Declaration Ø Regulations of the [Declaration of The Business Concentration ] Threshold Levels of Declaration Ø Regulations of the](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-7.jpg)
[Declaration of The Business Concentration ] Threshold Levels of Declaration Ø Regulations of the State Council of P. R. China on the Threshold of Declaration of Concentration of Undertakings Ø Article 3 When their intended concentration reaches one of the following threshold levels, undertakings shall declare in advance to the commercial authority under the State Council; they shall not implement the concentration in the absence of such declaration: (1) the worldwide turnover in the previous fiscal year of all the undertakings involved in the concentration sums to over 10 billion RMB, and the turnover in China in the previous fiscal year of at least two of them sums to over 4 hundred million RMB each; or (2) the turnover in China in the previous fiscal year of all the undertakings involved in the concentration sums to over 2 billion RMB, and the turnover in China in the previous fiscal year of at least two of them sums to over 4 hundred million RMB each. Ø Ps: As for the calculation methods of the turnover, there are detailed regulations from article 4 to article 7 in Measures on Declaration of Concentration of Undertakings.

The Apply of the Declaration Threshold When judging whether a merger transaction needs to declare or not, turnover is the sole index in the existing declaration threshold in China. But the field of the undertaking and the specific situation of the industry shall also be considered. When calculating the turnover, the specific situation of bank, insurance, security, futures and other special industries and fields shall be considered. Details shall be formulated by the commercial authority and other relevant departments under the State Council.
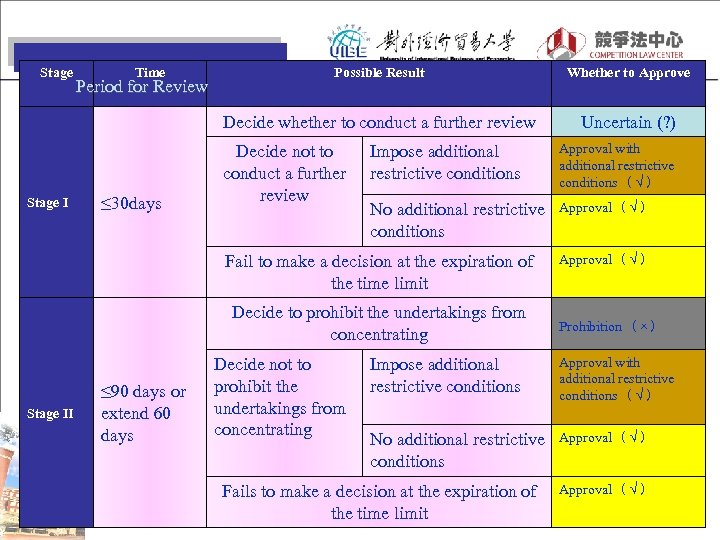
Stage Period for Review ≤ 30 days Possible Result Whether to Approve Decide whether to conduct a further review Stage Ⅰ Time Uncertain (? ) Decide not to conduct a further review Impose additional restrictive conditions Approval with additional restrictive conditions (√) No additional restrictive conditions Approval (√) Fail to make a decision at the expiration of the time limit Decide to prohibit the undertakings from concentrating Stage Ⅱ ≤ 90 days or extend 60 days Decide not to prohibit the undertakings from concentrating Approval (√) Prohibition (×) Impose additional restrictive conditions Approval with additional restrictive conditions (√) No additional restrictive conditions Approval (√) Fails to make a decision at the expiration of the time limit Approval (√)
![[Review of The Business Concentration ] Threshold for Review • Article 27 The following [Review of The Business Concentration ] Threshold for Review • Article 27 The following](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-10.jpg)
[Review of The Business Concentration ] Threshold for Review • Article 27 The following factors shall be taken into consideration in the review of concentration of undertakings: • (1) the market shares ; • (2) the degree of concentration in relevant market; • (3) assess to the market; • (4) the impact of their concentration on consumers and the other relevant undertakings concerned; • (5) the impact of their concentration on the development of the national economy. Ø Article 28 If the concentration of undertakings leads, or may lead, to elimination or restriction of competition, the authority for enforcement of the Anti-monopoly Law under the State Council shall make a decision to prohibit their concentration. However, if the undertakings concerned can prove that the advantages of such concentration to competition obviously outweigh the disadvantages, or that the concentration is in the public interest, the authority for enforcement of the Anti-monopoly Law under the State Council may decide not to prohibit their concentration.
![[Remedies for The Business Concentration ] Restrictive Conditions The lead to elimina-tion or restriction [Remedies for The Business Concentration ] Restrictive Conditions The lead to elimina-tion or restriction](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-11.jpg)
[Remedies for The Business Concentration ] Restrictive Conditions The lead to elimina-tion or restriction Business Concentration may of competition. To eliminate or reduce the aforesaid result, the undertakings concerned and the Ministry of Commerce may put forward some restrictive conditions to adjust the plan of the concentration. Constructive conditions, such as stripping some assets or businesses off the undertakings involved; Behavioral conditions, including opening their infrastructure such as network or platform, licensing key technologies (including patent, know-how and other IPR), terminating exclusive agreement by the undertakings involved. Comprehensive conditions, combining constructive conditions with behavioral conditions.
![[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of IPR Acquisition Original Acquisition ØApply for [The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of IPR Acquisition Original Acquisition ØApply for](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-12.jpg)
[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of IPR Acquisition Original Acquisition ØApply for and acquire IPR through independent R&D. Derivative Acquisition ØAcquire other’s IPR by authorization or purchase. ØThe Anti-monopoly Law can maintain market competition, and encourage enterprises to innovate independently by using their own business intelligence and technologies.
![[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of derivative acquisition 1 To merge enterprises [The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of derivative acquisition 1 To merge enterprises](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-13.jpg)
[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ways of derivative acquisition 1 To merge enterprises that own IPR. 2 3 To buy IPR directly. To acquire exclusive license of IPR.
![[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Exclusive License Prohibiting the licensor from licensing the [The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Exclusive License Prohibiting the licensor from licensing the](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-14.jpg)
[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Exclusive License Prohibiting the licensor from licensing the IPR to a third party, and even the licensor can’t use the IPR. Prohibiting the licensee from sublicensing or transferring the IPR, or prohibiting the licensee from using techniques which are competitive with the IPR.
![[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ø Anti-monopoly Law pays close attention to the [The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ø Anti-monopoly Law pays close attention to the](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-15.jpg)
[The definition of IPR Acquisition ] Ø Anti-monopoly Law pays close attention to the derivative acquisition of IPR: derivative acquisition is likely to be used by undertakings to obtain, maintain or strengthen their market monopoly position, so as to eliminate competition.
![[The practice of USA] Ø In 1995, Antitrust Guidelines for the Licensing of Intellectual [The practice of USA] Ø In 1995, Antitrust Guidelines for the Licensing of Intellectual](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-16.jpg)
[The practice of USA] Ø In 1995, Antitrust Guidelines for the Licensing of Intellectual Property (USA) provided that the merger analysis method and principle shall be applied to (derivative) acquisition of IPR. Ø It is appropriate to apply the merger analysis principle and standard to certain IPR transaction, especially the principles and standards stated in Guidelines for Horizontal Mergers 1992.
![[The practice of USA] Example Ø Company A invented a technique, which is competitive [The practice of USA] Example Ø Company A invented a technique, which is competitive](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-17.jpg)
[The practice of USA] Example Ø Company A invented a technique, which is competitive with the technique of Company B. Company A transferred the aforesaid technique to Company B, or exclusively licensed the technique to Company B. Then Anti-monopoly Law will pay attention to the transaction, the administrative authority will apply the merger analysis method to analyze the acquisition of the aforesaid IPR, because it is equivalent to the merger of a potential competitor.
![[The practice of EU] The classification of derivative acquisition of IPR 1 Elements of [The practice of EU] The classification of derivative acquisition of IPR 1 Elements of](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-18.jpg)
[The practice of EU] The classification of derivative acquisition of IPR 1 Elements of Concentration of Undertakings 2 Ancillary restraints of Concentration of Undertakings 3 Neither elements nor ancillary restraints of Concentration of Undertakings
![[The practice of EU] Ø How to judge whether the acquisition of IPR becomes [The practice of EU] Ø How to judge whether the acquisition of IPR becomes](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-19.jpg)
[The practice of EU] Ø How to judge whether the acquisition of IPR becomes the element of concentration of undertakings or not? Ø If the acquisition of IPR is the main purpose of concentration of undertakings, the acquisition shall be considered as the element of concentration.
![[Basic principles of IPR acquisition analysis] 1 To analyze within the framework of Anti-monopoly [Basic principles of IPR acquisition analysis] 1 To analyze within the framework of Anti-monopoly](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-20.jpg)
[Basic principles of IPR acquisition analysis] 1 To analyze within the framework of Anti-monopoly Law, just like other tangible assets. 2 3 The acquisition of IPR is helpful to realize resource complementation and to increase efficiency , rule of reason shall be applied. Market dominant position can’t be presumed from the fact of IPR acquisition.
![[To Raise a Question] Ø USA: the guidelines provide the method of analyzing IPR [To Raise a Question] Ø USA: the guidelines provide the method of analyzing IPR](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-21.jpg)
[To Raise a Question] Ø USA: the guidelines provide the method of analyzing IPR acquisition– merger analysis method, it is applied to IPR acquisition in the form of agreement and merger. Ø EU: Regulations on Technique Transfer Agreement and Guidelines for Technique Transfer Agreement are applied to IP license agreements; Regulations on Merger and Guidelines for Horizontal Merger are applied when judging whether the acquisition of IPR becomes the element of concentration of undertakings; even though different documents are applied, the law enforcement agencies are the same—European Commission, and it is convenient to coordinate.
![[To Raise a Question] Ø Cases in China: 1. There are three authorities for [To Raise a Question] Ø Cases in China: 1. There are three authorities for](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-22.jpg)
[To Raise a Question] Ø Cases in China: 1. There are three authorities for enforcement of the Anti-monopoly Law: Ministry of Commerce, National Development and Reform Commission, and State Administration for Industry &Commerce. 2. Guidelines for Applying Anti-monopoly Law to IP (draft) provides the methods of analyzing IPR acquisition.
![[To Raise a Question] The problem 3 2 1 As for an exclusive license [To Raise a Question] The problem 3 2 1 As for an exclusive license](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-23.jpg)
[To Raise a Question] The problem 3 2 1 As for an exclusive license agreement, shall concentration method or agreement method be applied? In China, the regulations are formulated by different agencies. If concentration method is to be applied, how to coordinate the administrative authorities? There is not regulation for license agreement in China. Shall the guidelines (draft) be used by law enforcement agencies and the judicial agencies? (there are only principles and methods in the guidelines, but no penalty provisions or remedies. Will the IPR sales agreement or exclusive license agreement be regarded as “control over other undertakings through acquiring their assets”? If so, shall it enter into the concentration review procedure or be dealt according to the agreement? How to coordinate the jurisdiction?
![[To Raise a Question] The problem Ø Remedies for concentration of undertakings concerning IPR [To Raise a Question] The problem Ø Remedies for concentration of undertakings concerning IPR](https://present5.com/presentation/42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f/image-24.jpg)
[To Raise a Question] The problem Ø Remedies for concentration of undertakings concerning IPR acquisition: 1. Constructive remedy: stripping off IPR 2. Behavioral remedy: non-exclusive license IPR to a third party Ø The problem: 1. What is the legal basis of compulsory license in Anti-monopoly Law? 2. How to coordinate with the compulsory license system in Patent Law?

Thanks Ø Q&A Ø Contact information: huangyong 1962@vip. sina. com
42ce5bf6e41a91337c603fb6601d816f.ppt