79e50535a853f2131170c9d7ab1a5b7e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

IPM in Soybean Dr. Amar N. Sharma Principal Scientist (Entomology) Directorate of Soybean Research (ICAR) Indore 452 001 (MP) [amarnathsharma 2@gmail. com]

IPM !!!!!!

Integrated Pest Management Integrated use of all possible measures to keep insect-pest population below ETL

Limitations in adoption of IPM q Lack of awareness q Easy access to chemical insecticides q Inadequate production of bio-control agents q Farmers’ economic status q Lack of incentives q Limited area under IPM Then why IPM ? ? ?
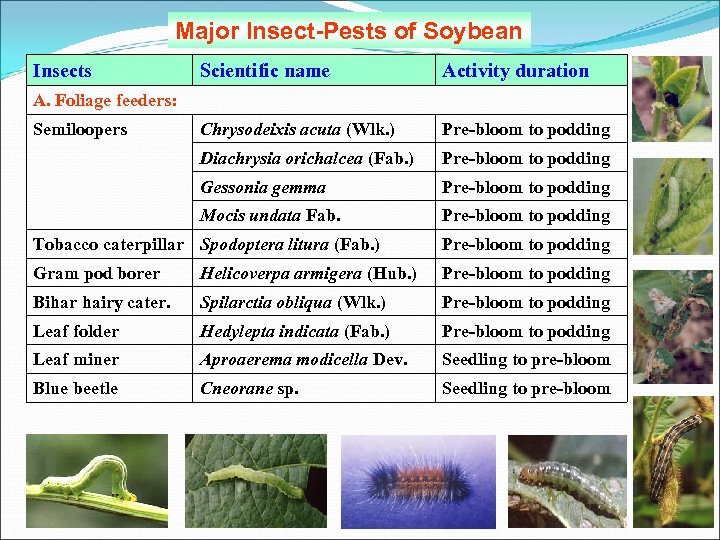
Major Insect-Pests of Soybean Insects Scientific name Activity duration A. Foliage feeders: Semiloopers Chrysodeixis acuta (Wlk. ) Pre-bloom to podding Diachrysia orichalcea (Fab. ) Pre-bloom to podding Gessonia gemma Pre-bloom to podding Mocis undata Fab. Pre-bloom to podding Tobacco caterpillar Spodoptera litura (Fab. ) Pre-bloom to podding Gram pod borer Helicoverpa armigera (Hub. ) Pre-bloom to podding Bihar hairy cater. Spilarctia obliqua (Wlk. ) Pre-bloom to podding Leaf folder Hedylepta indicata (Fab. ) Pre-bloom to podding Leaf miner Aproaerema modicella Dev. Seedling to pre-bloom Blue beetle Cneorane sp. Seedling to pre-bloom
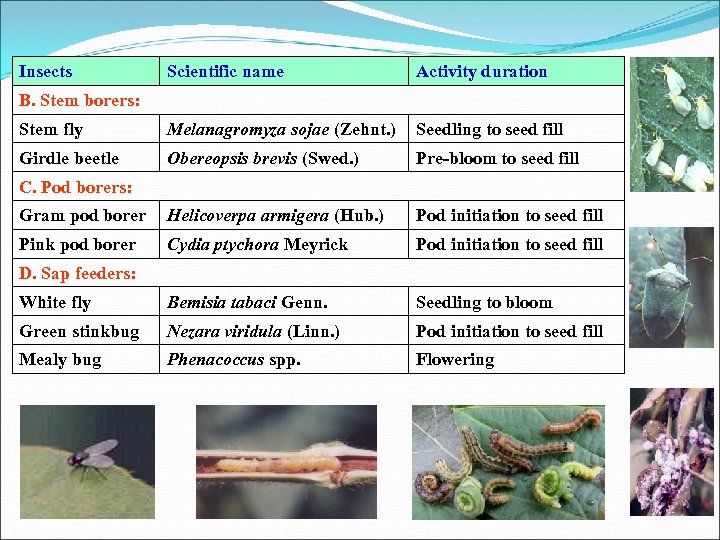
Insects Scientific name Activity duration Stem fly Melanagromyza sojae (Zehnt. ) Seedling to seed fill Girdle beetle Obereopsis brevis (Swed. ) Pre-bloom to seed fill B. Stem borers: C. Pod borers: Gram pod borer Helicoverpa armigera (Hub. ) Pod initiation to seed fill Pink pod borer Cydia ptychora Meyrick Pod initiation to seed fill White fly Bemisia tabaci Genn. Seedling to bloom Green stinkbug Nezara viridula (Linn. ) od initiation to seed fill P Mealy bug Phenacoccus spp. D. Sap feeders: Flowering

Damage Potential of Insects Leaf Miner Leaf Folder Stem Fly Girdle Beetle White Fly (YMV) Green Semilooper Bihar Hairy Caterpillar Grey Weevil Pod Borer Aphids : : : : : 40 - 60 % 8 -9% 19 - 40 % 58 % 80 % 46 % 42 % 10 % 95 % Pod damage 30 %

(AICRPS 2012 to 2014) Yield loss v/s Damage levels v/s Crop stage
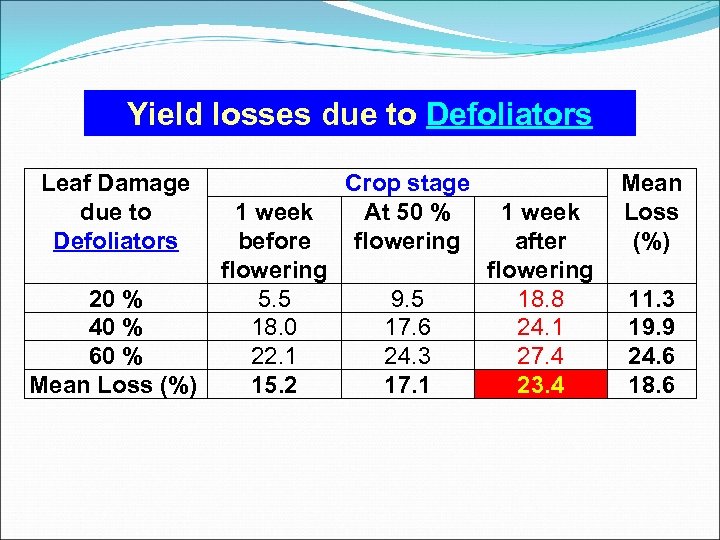
Yield losses due to Defoliators Leaf Damage due to Defoliators 1 week before flowering 20 % 5. 5 40 % 18. 0 60 % 22. 1 Mean Loss (%) 15. 2 Crop stage At 50 % flowering 9. 5 17. 6 24. 3 17. 1 1 week after flowering 18. 8 24. 1 27. 4 23. 4 Mean Loss (%) 11. 3 19. 9 24. 6 18. 6
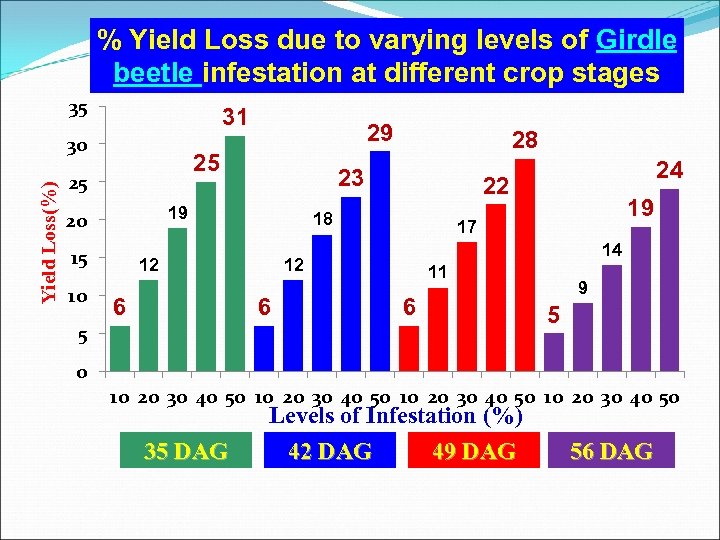
% Yield Loss due to varying levels of Girdle beetle infestation at different crop stages 35 31 Yield Loss(%) 30 25 25 15 19 17 14 12 6 24 22 18 12 6 28 23 19 20 10 29 11 6 5 9 5 0 10 20 30 40 50 35 DAG Levels of Infestation (%) 42 DAG 49 DAG 56 DAG
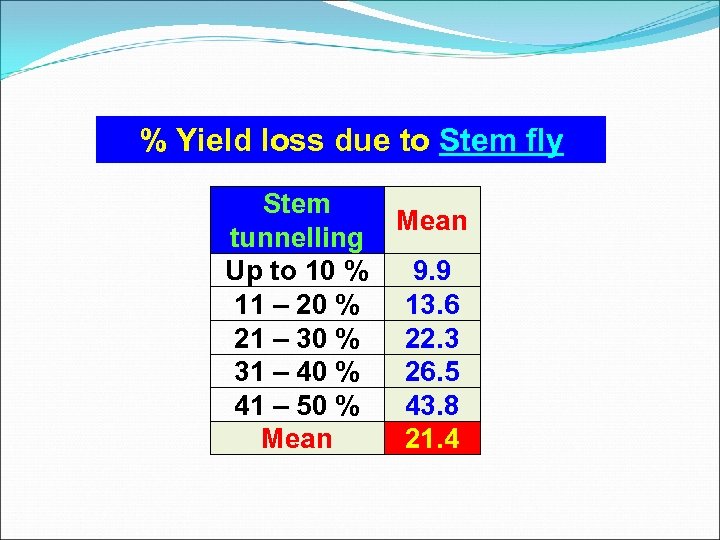
% Yield loss due to Stem fly Stem Mean tunnelling Up to 10 % 9. 9 11 – 20 % 13. 6 21 – 30 % 22. 3 31 – 40 % 26. 5 41 – 50 % 43. 8 Mean 21. 4
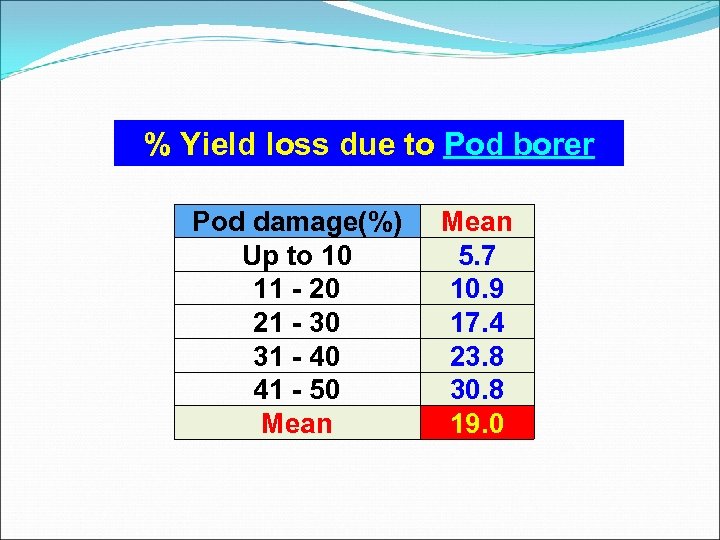
% Yield loss due to Pod borer Pod damage(%) Up to 10 11 - 20 21 - 30 31 - 40 41 - 50 Mean 5. 7 10. 9 17. 4 23. 8 30. 8 19. 0

Insect Outbreaks

Damage due to Outbreak of S. litura (Rajasthan, 1999)

Damage due to Outbreak of S. litura (MP, 2003)

Damage due to Outbreak of litura S. (Maharashtra- 2008)

Semilooper attack in Nagpur (2009) Crop condition on 30 th July 2009 Crop condition on 13 th August 2009

Demonstrated Feasibility and economics
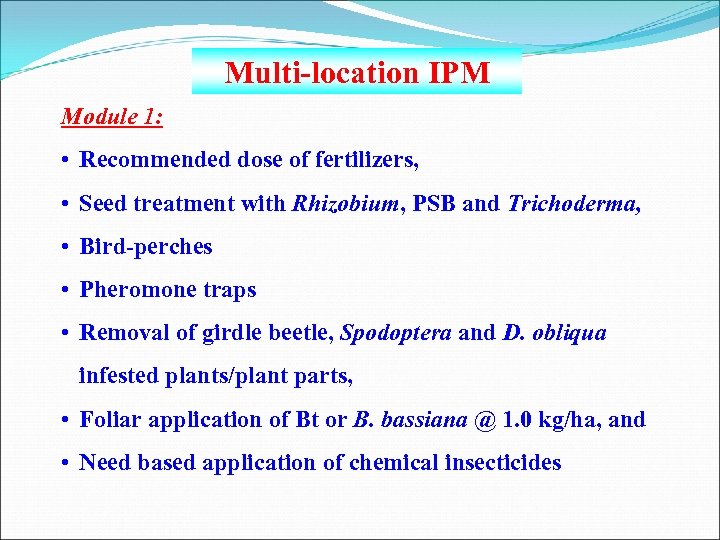
Multi-location IPM Module 1: • Recommended dose of fertilizers, • Seed treatment with Rhizobium, PSB and Trichoderma, • Bird-perches • Pheromone traps • Removal of girdle beetle, Spodoptera and D. obliqua infested plants/plant parts, • Foliar application of Bt or B. bassiana @ 1. 0 kg/ha, and • Need based application of chemical insecticides
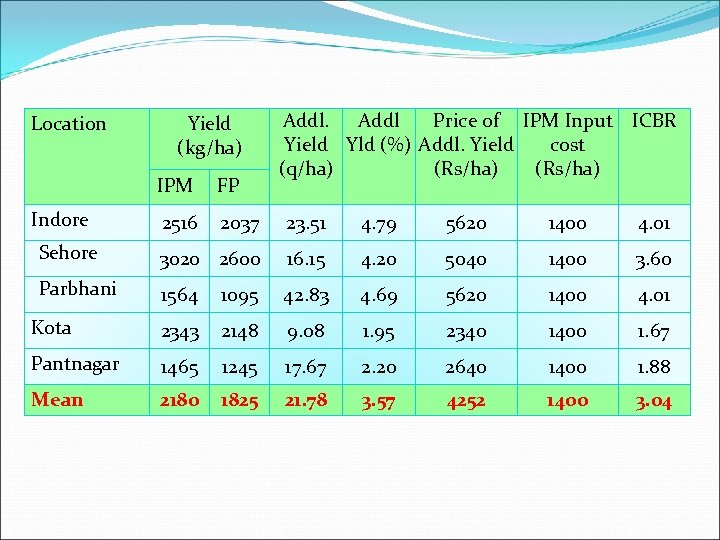
Location Yield (kg/ha) Addl Price of IPM Input ICBR Yield Yld (%) Addl. Yield cost (q/ha) (Rs/ha) IPM FP 2516 2037 23. 51 4. 79 5620 1400 4. 01 Sehore 3020 2600 16. 15 4. 20 5040 1400 3. 60 Parbhani 1564 1095 42. 83 4. 69 5620 1400 4. 01 Kota 2343 2148 9. 08 1. 95 2340 1400 1. 67 Pantnagar 1465 1245 17. 67 2. 20 2640 1400 1. 88 Mean 2180 1825 21. 78 3. 57 4252 1400 3. 04 Indore

Module 2: • Recommended dose of fertilizer, • Seed treatment with Rhizobium, PSB and Trichoderma, • Spray of Ha NPV or Sl NPV @ 250 LE/ha, • Spray of N. rileyi or Bt @ 1. 0 l/ha, • Spray of NSKE @ 5%, • Need based application of chemical insecticides

Location Mean Price of IPM Addl. Yield Addl Yld Addl. Input (q/ha) (%) Yield cost (Rs/ha) ICBR IPM FP Dharwad 2662 2182 4. 80 22. 00 5760 2300 2. 50 Bangalore 2578 2519 0. 59 2. 34 1770 2300 0. 77 Mean 2620 2350 2. 69 12. 17 3765 2300 1. 64

Measures to reduce insect infestation Deep summer ploughing Selection of proper variety Balanced nutrition Proper seed rate & spacing Use of Improved Light Traps

Use of Pheromone Traps

Bird perches

Management of Soybean insect-pests Removal of infested plants


Use of Microbial insecticides Bt based: Dipel, Biobit, Halt, Delfin @ 1. 0 kg/ha, or Bb based: Biorin, Biosoft, Larvocel, Dispel @ 1. 0 kg/ha, or Virus based: Ha. NPV / Sl. NPV @ 250 LE/ha
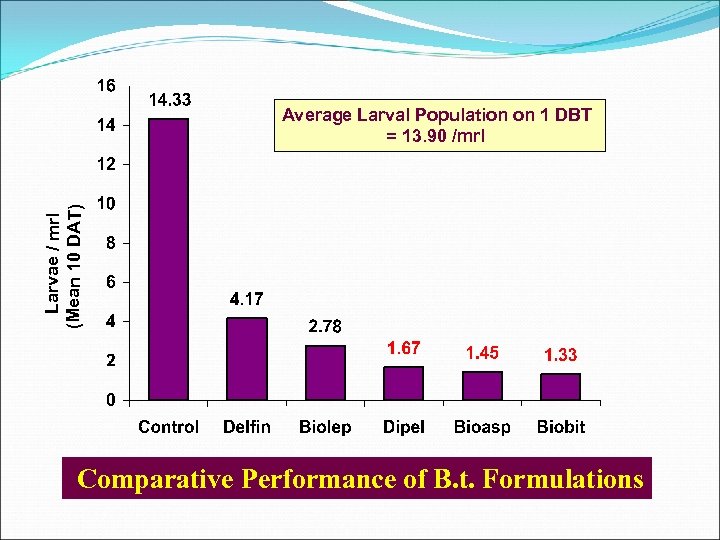
Larvae / mrl (Mean 10 DAT) Average Larval Population on 1 DBT = 13. 90 /mrl Comparative Performance of B. t. Formulations
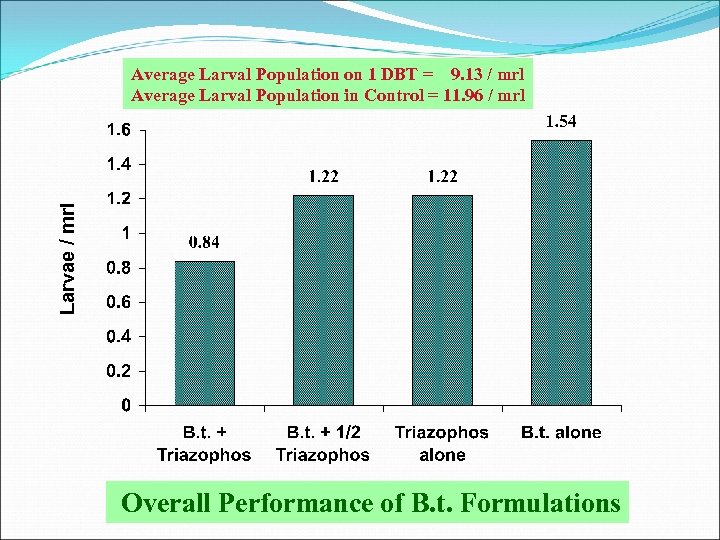
Larvae / mrl Average Larval Population on 1 DBT = 9. 13 / mrl Average Larval Population in Control = 11. 96 / mrl Overall Performance of B. t. Formulations
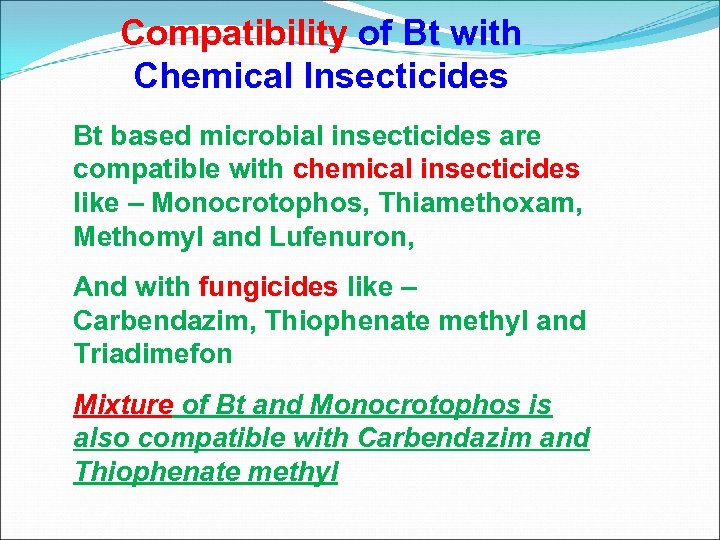
Compatibility of Bt with Chemical Insecticides Bt based microbial insecticides are compatible with chemical insecticides like – Monocrotophos, Thiamethoxam, Methomyl and Lufenuron, And with fungicides like – Carbendazim, Thiophenate methyl and Triadimefon Mixture of Bt and Monocrotophos is also compatible with Carbendazim and Thiophenate methyl

Exploitation of Natural Enemies
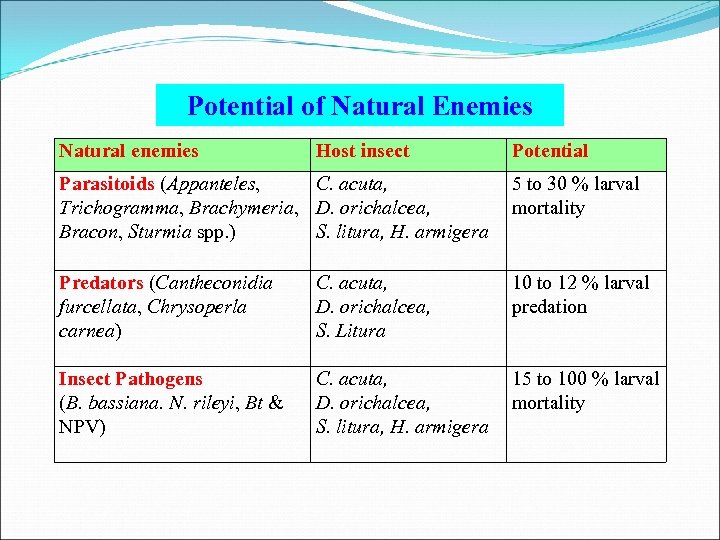
Potential of Natural Enemies Natural enemies Host insect Potential Parasitoids (Appanteles, C. acuta, Trichogramma, Brachymeria, D. orichalcea, Bracon, Sturmia spp. ) S. litura, H. armigera 5 to 30 % larval mortality Predators (Cantheconidia furcellata, Chrysoperla carnea) C. acuta, D. orichalcea, S. Litura 10 to 12 % larval predation Insect Pathogens (B. bassiana. N. rileyi, Bt & NPV) C. acuta, D. orichalcea, S. litura, H. armigera 15 to 100 % larval mortality



Success Stories in biological control • Papaya mealy bug (Paracoccus marginatus) control through Acerophagus papayae) • Sugarcane woolly aphid (Ceratovacuna lanigera) control through predators (Dipha aphidivora or Micromus igorotus)
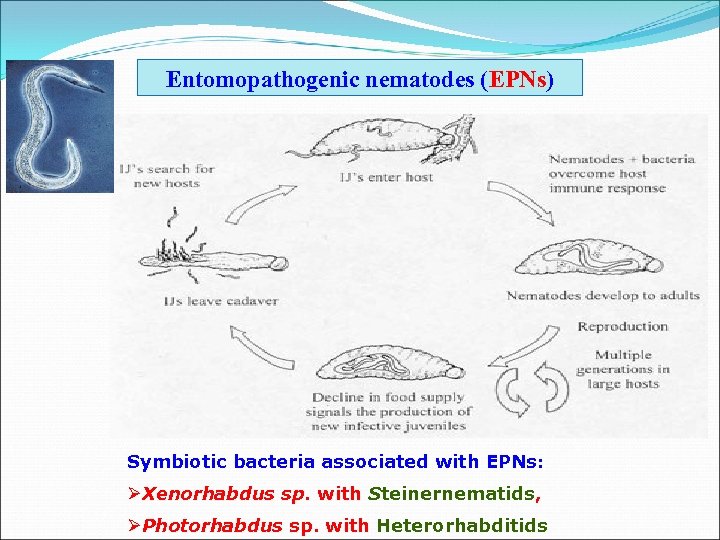
Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) Symbiotic bacteria associated with EPNs: ØXenorhabdus sp. with Steinernematids, ØPhotorhabdus sp. with Heterorhabditids
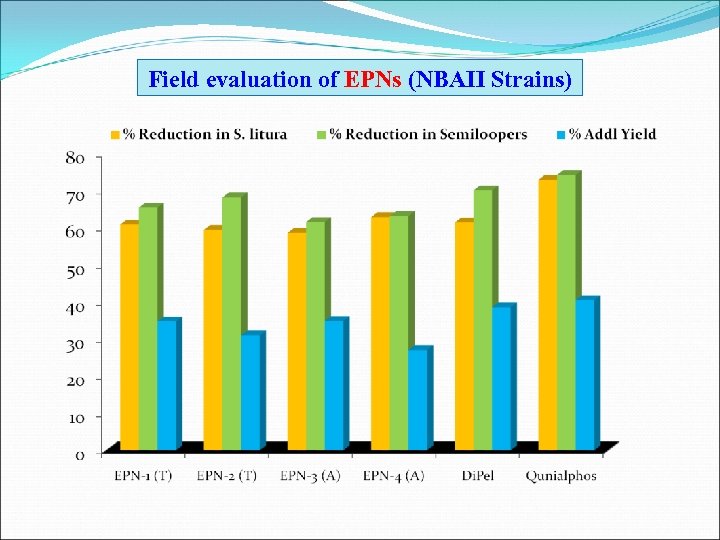
Field evaluation of EPNs (NBAII Strains)

Use of Chitin inhibitors Diflubenzuron 25 WP @ 400 -600 g/ha, or Lufenuron 10 EC @ 300 -400 ml/ha

Use of Botanicals Acacia arabica (leaves & seeds) Annona squamosa (leaves & seeds) Datura stramonium (leaves & seeds) Eucalyptus globulus (leaves) Ipomoea carnea (leaves) Lantana camara (leaves) Nicotiana tabacum (leaves) Pongamia pinnata (leaves) 1. Bio-efficacy : Aqueous extract @ 25, 50, 75 and 100% Ethanol extract @ 5, 7. 5 and 10 % 2. Preference Index 3. Compatibility & Synergism 4. Utilization Indices 5. Mode of Action

Contact Poisons : Annona leaves Ipomoea leaves Itg Stomach Poisons : Lantana leaves Nicotiana leaves Pongamia leaves Acacia seed Annona seed Datura seed Mv Itg Contact and Stomach Poisons : Acacia leaves Datura leaves Eucalyptus leaves Pm MEL

Use of Chemical insecticides • Judicious / Need based • Recommended insecticides • With proper dose and dilution • Careful and safe application • Proper Time of application

ETL of some major Insect-Pests Blue beetle : 4 adults / mrl upto 10 DAG. Green semilooper : 3 larvae / mrl at flowering, or 4 larvae / mrl at podding. Tobacco caterpillar : 10 larvae / mrl at pre-flowering. Pod borer : 10 larvae / mrl at pod development. Leaf folder : 8 -9 folded leaves / mrl. Stem fly : 26 per cent stem tunnelling.

Recommended Insecticides and precautions ¤ Selection of suitable insecticide For Stem fly, Blue beetle and Linseed caterpillar • Phorate 10 G @ 10 kg/ha • Thiamethoxam 30 FS @ 10 ml/kg seed • Thiamethoxam 25 WG @ 100 g/ha • Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1. 5 l/ha

For Girdle beetle Ø Triazophos 40 EC @ 800 ml/ha Ø Thiacloprid 21. 7 SC @ 650 ml/ha Ø Ethofenprox 10 EC @ 1. 0 l/ha

For Defoliators Ø Chlorpyrifos 20 EC @ 1. 5 l/ha Ø Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1. 5 l/ha Ø Triazophos 40 EC @ 800 ml/ha Ø Profenophos 50 EC @ 1. 25 l/ha Ø Rynaxypyre 20 SC @ 100 ml/ha Ø Methomyl 40 SP @ 1. 0 kg/ha Ø Lembda cyhalothrin 5 EC @ 300 ml/ha Ø Indoxacarb 14. 5 SC @ 300 ml/ha Ø Spinosad 45 SC @ 125 ml/ha

For Pod borers Ø Profenophos 50 EC @ 1. 25 l/ha Ø Emamectin benzoate 5 SG @ 0. 18 kg/ha Ø Rynaxypyre 20 SC @ 100 ml/ha Ø Indoxacarb 14. 5 SC @ 300 ml/ha Ø Methomyl 40 SP @ 1. 0 kg/ha Ø Lembda cyhalothrin 5 EC @ 300 ml/ha Ø Spinosad 45 SC @ 125 ml/ha

For Sap sucking insects Ø Ethofenprox 10 EC @ 1. 0 l/ha Ø Difenthiuron 50 WP @ 0. 50 kg/ha Ø Thiamethoxam 30 FS @ 10 ml/kg seed Ø Imidacloprid 48 FS @ 1. 25 ml/kg seed Ø Imidacloprid 17. 8 SL @ 600 ml/ha

For Red Spider Mite Ø Ethion 50 EC @ 1. 5 l/ha For Mealy bug Ø Ø Ø Profenophos 50 EC Quinalphos 25 EC Acephate 75 SP Chlorpyriphos 20 EC Thiamethoxam 25 WG 1. 25 lit 2. 0 kg 1. 50 lit 100 ml

Compatible combinations of Insecticides and Herbicides for effective management of major insects and weeds in Soybean Insect(s) Weed(s) Combination Stem fly Monocot + Dicot Monocot 1. Rynaxypyr + Imazethapyr 2. Rynaxypyr + Quizalofop Ethyl Semiloopers Monocot + Dicot 1. Rynaxypyr + Imazethapyr 2. Rynaxypyr + Quizalofop Ethyl 3. Indoxacarb + Imazethapyr S. litura Monocot + Dicot Monocot 1. Rynaxypyr + Imazethapyr 2. Quinalphos + Imazethapyr 3. Quinalphos + Quizalofop Ethyl Girdle beetle Monocot + Dicot 1. Rynaxypyr + Imazethapyr 2. Indoxacarb + Imazethapyr

¤ Proper dilution of insecticide ¤ Proper Spray time ¤ Protective clothing

¤ Proper spray equipment

क स न क सझबझ




FEASIBILITY OF PLANT EXTRACTS Stock solution : 0. 2 kg in 1 lit to give 100 % stock soln. With Power sprayer – For 100 % conc. – 24. 0 kg crushed in 120 lit of water For 75 % conc. – 18. 0 kg crushed in 120 lit of water For 50 % conc. – 12. 0 kg crushed in 120 lit of water For 25 % conc. – 6. 0 kg crushed in 120 lit of water
79e50535a853f2131170c9d7ab1a5b7e.ppt