cfe7bac51451970cccfcebb7a594b922.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

IPC REFORM Objectives and principal Features Antonios Farassopoulos World Intellectual Property Organization IPC Forum 2006 Geneva

Modern History of the IPC u 1956 - Council of Europe initiates work on European Patent Classification u 1968 - 1 st edition of the IPC u 1971 - Strasbourg Agreement concerning the IPC u 1975 - Strasbourg Agreement entered into force u Every five years - a new edition of the IPC u 2000 - 7 th edition of the IPC

Purposes of the IPC u Primary purpose: effective search tool for the retrieval of patent information u Other purposes: – selective dissemination of information – investigation of the state of the art – preparation of industrial property statistics

Worldwide Application of the IPC u 55 States-members of the Strasbourg Union u IPC is applied: – in more than 100 countries – by five international organizations

IPC Crisis at the end of the XX century u IPC - a tool for manual searching u IPC - a compromise between large and small patent offices – not sufficiently detailed for large offices – too complex for small offices u IPC - need to consult several editions

IPC Advanced Seminar (December 1998) Discussions about the IPC future

Seminar Conclusions u IPC retains its value as the only worldwide patent classification u Methods of revision and use of the IPC should be radically changed u IPC should become a tool for searching electronic information

Launch of the reform u In March 1999 the IPC Committee of Experts decides to start reform of the Classification u In March 2000 the strategic plan for the development of the IPC is approved

Strategic Goals of the Reform u Integration of the IPC with the systems of electronic information u Creation of a universal search tool for all patent offices u Establishment of a global system of generation, processing and distribution of classification data

Principal objectives of the reform u Division of the IPC into core and advanced levels u Creation of the Master Classification Database u Reclassification of search files according to revision changes u Introduction in the IPC of electronic information and tools facilitating classification and search u Accommodate the IPC to an electronic environment

Core level u Volume - 18, 000 groups (all main groups and some 1, 2 dot gr. based on file size) u Use: - search in small national patent files - dissemination of patent information - patent statistics u Revision according to the traditional procedure (IPC/CE) u Revision cycle - three years > more stable

Advanced level u Initial volume in 2006 - 70, 000 groups u Revision by a Special Subcommittee according to accelerated procedure u Use - search in international patent files (PCT minimum documentation) u Continuous revision > accelerated revision, more dynamic

Core and advanced levels u May be used on the choice of patent offices u Are fully compatible

Electronic information in the reformed IPC u Classification definitions – subclass definition – Interrelations with other subclasses – classification rules within the subclass – informative references – definitions of technical terms u Chemical formulae; drawings u Standardized sequence of main groups

Master Classification Database u Hosted by EPO; extension of existing Doc. DB u Classification data on the worldwide patent collections u Complete IPC data according to current version u Complete information of the core level by rollingup of advanced level symbols u Bridge to full text databases u Access via Espacenet, Epoque, national systems
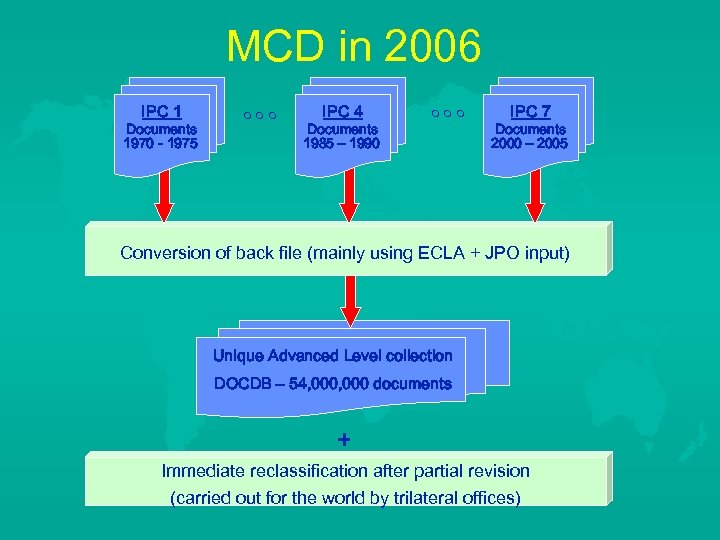
MCD in 2006 IPC 1 Documents 1970 - 1975 IPC 4 Documents 1985 – 1990 IPC 7 Documents 2000 – 2005 Conversion of back file (mainly using ECLA + JPO input) Unique Advanced Level collection DOCDB – 54, 000 documents + Immediate reclassification after partial revision (carried out for the world by trilateral offices)

Electronic exchange of data u Reclassification for each new AL version – PCT min by trilateral offices – propagation of reclassification to all family members – lists of remaining documents to be reclassified by respective offices u Delivery of reclassification data to the Master Classification Database

New ST. 8: Recording IPC data New ST. 8 F new symbol length – old: A 01 B 123/12345 – new: A 01 B 0123/123456 F version indicator – attribute: YYYYMMDD F invention / additional ~ non-invention – attribute: (I) or (N) F advanced / core – attribute: (A) or (C) F original / reclassified – attribute: (B) or (R) F action date – attribute: YYYYMMDD F human / machine propagated / generated by computer – attribute: (H), (M) or (G)

New ST. 10/C Document classified in the advanced level: (51) Int. Cl. B 28 B 5/00 (2006. 01) B 28 B 1/29 (2007. 04) H 05 B 3/18 (2008. 07) Italics Advanced Level Bold Invention Information Version Indicator Non-bold Additional Information Document classified in the core level: (51) Int. Cl. (2006) B 28 B 5/00 B 28 B 1/00 H 05 B 3/10 Regular Core Level
Publications of the IPC u u Printed publication - only the core level Internet publication - on the user’s choice, display is possible: – only to the core level or to the complete text of the Classification (advanced level) – only tо the official text or with the inclusion of electronic information u XML files (scheme, validity file, RCL , Catchword Index)

cfe7bac51451970cccfcebb7a594b922.ppt