97dc115a532fa7c857316da6edeed30a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 IP Networking and MEDIACOM - 2004 Workshop / Geneva IP Management - Why, What and How - 25, April, 2001 Transport Systems Group,Fujitsu Ltd. Masayoshi Ejiri ejiri@jp. fujitsu. com
IP Networking and MEDIACOM - 2004 Workshop / Geneva IP Management - Why, What and How - 25, April, 2001 Transport Systems Group,Fujitsu Ltd. Masayoshi Ejiri ejiri@jp. fujitsu. com
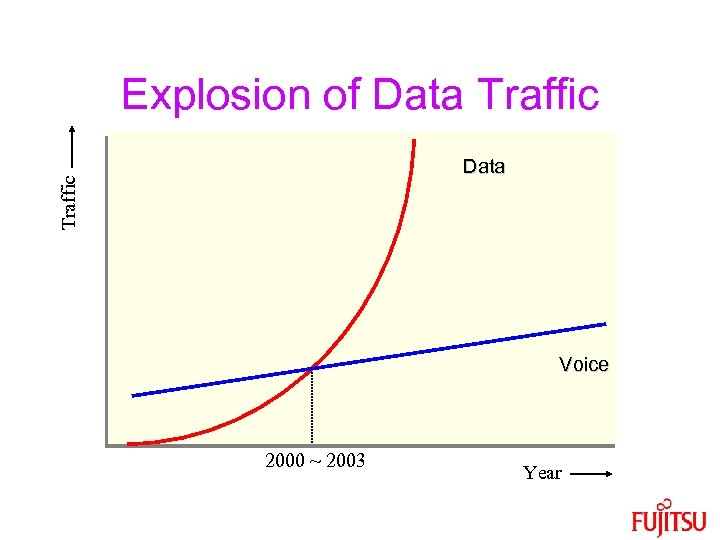 Explosion of Data Traffic Data Voice 2000 ~ 2003 Year
Explosion of Data Traffic Data Voice 2000 ~ 2003 Year
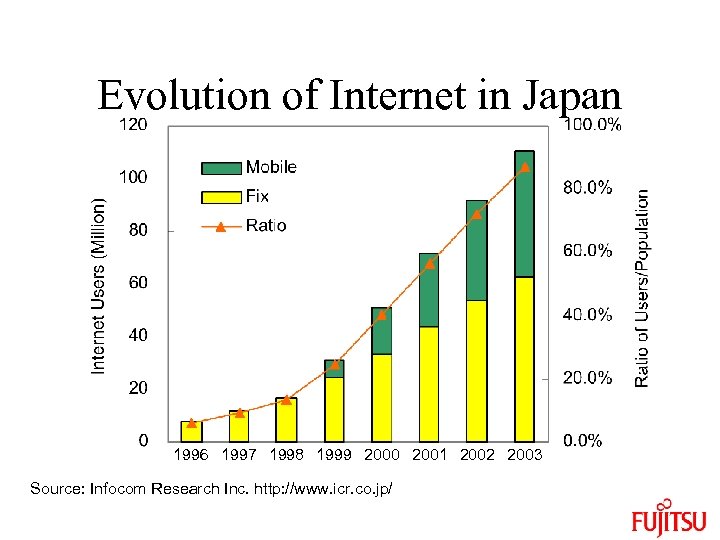 Evolution of Internet in Japan 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Source: Infocom Research Inc. http: //www. icr. co. jp/
Evolution of Internet in Japan 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Source: Infocom Research Inc. http: //www. icr. co. jp/
 Number of Subscribers in Japan ---March 2001 --- • Telephone : 129 M Fixed : 62 M ( Incl. ISDN : 10 M) Mobile : 67 M • Internet : 65 M Fixed : 30 M Mobile : 35 M Note: Population : 120 M color TV terminals: 100 M, PCs : 100 M
Number of Subscribers in Japan ---March 2001 --- • Telephone : 129 M Fixed : 62 M ( Incl. ISDN : 10 M) Mobile : 67 M • Internet : 65 M Fixed : 30 M Mobile : 35 M Note: Population : 120 M color TV terminals: 100 M, PCs : 100 M
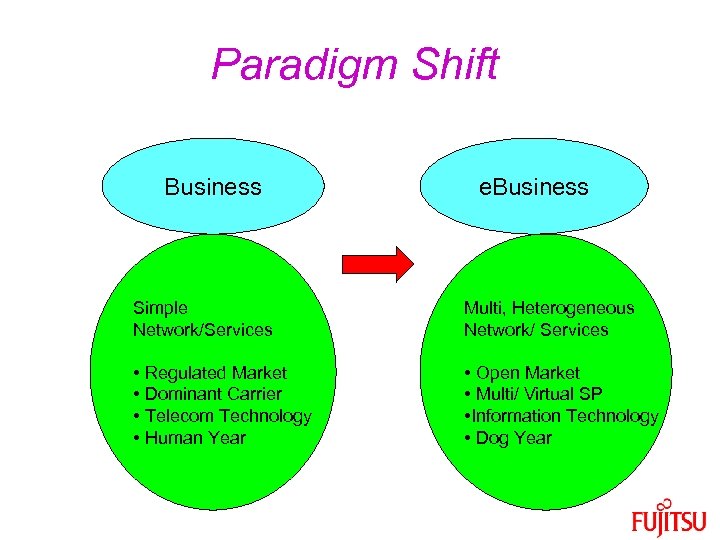 Paradigm Shift Business e. Business Simple Network/Services Multi, Heterogeneous Network/ Services • Regulated Market • Dominant Carrier • Telecom Technology • Human Year • Open Market • Multi/ Virtual SP • Information Technology • Dog Year
Paradigm Shift Business e. Business Simple Network/Services Multi, Heterogeneous Network/ Services • Regulated Market • Dominant Carrier • Telecom Technology • Human Year • Open Market • Multi/ Virtual SP • Information Technology • Dog Year
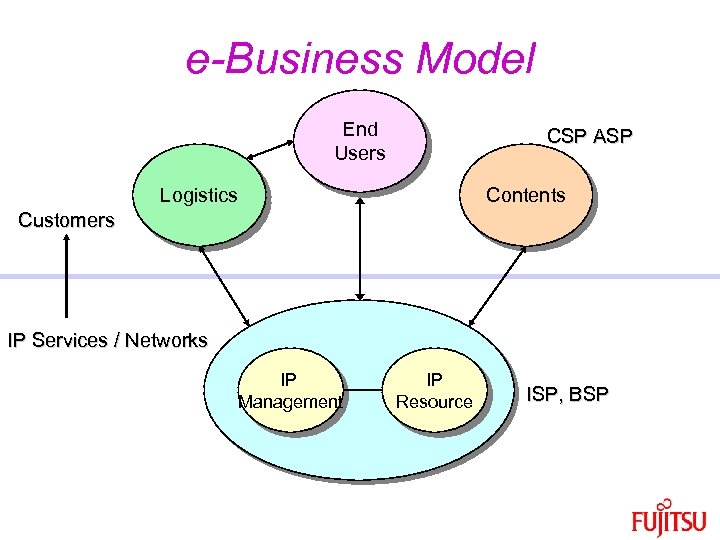 e-Business Model End Users CSP ASP Logistics Contents Customers IP Services / Networks IP Management IP Resource ISP, BSP
e-Business Model End Users CSP ASP Logistics Contents Customers IP Services / Networks IP Management IP Resource ISP, BSP
 IP Services --for Speed, Simple and Smile e. Business-Customers’ Demand Providers’ Solution • Speedy / Easy Subscription On Line, Real Time Provisioning • Non Stop Services Reliable & Scalable Networks / Systems • Quick Response High Throughput Mechanism • Secure Services Security Level Agreement • Price Performance Negotiation
IP Services --for Speed, Simple and Smile e. Business-Customers’ Demand Providers’ Solution • Speedy / Easy Subscription On Line, Real Time Provisioning • Non Stop Services Reliable & Scalable Networks / Systems • Quick Response High Throughput Mechanism • Secure Services Security Level Agreement • Price Performance Negotiation
 Target of IP Management Competitive Service Creation with • Low Price • Managed Quality for Customer Retention and Profit
Target of IP Management Competitive Service Creation with • Low Price • Managed Quality for Customer Retention and Profit
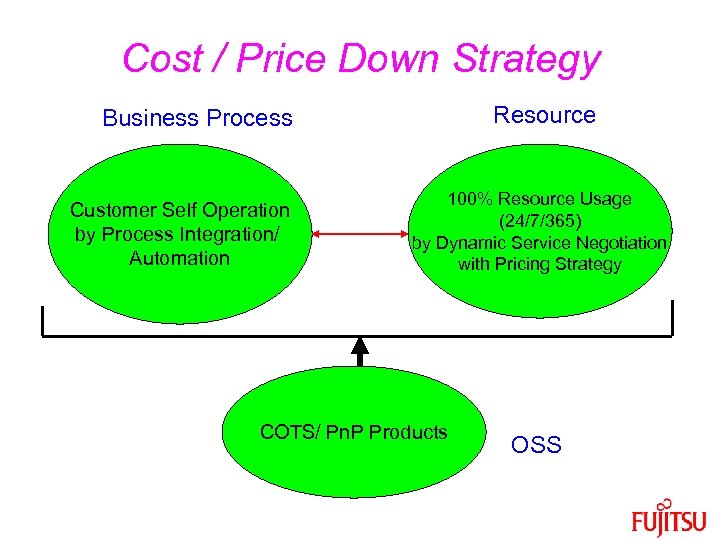 Cost / Price Down Strategy Resource Business Process Customer Self Operation by Process Integration/ Automation 100% Resource Usage (24/7/365) by Dynamic Service Negotiation with Pricing Strategy COTS/ Pn. P Products OSS
Cost / Price Down Strategy Resource Business Process Customer Self Operation by Process Integration/ Automation 100% Resource Usage (24/7/365) by Dynamic Service Negotiation with Pricing Strategy COTS/ Pn. P Products OSS
 SLA for IP Management Public Network / Services Fixed Qo. S Negotiated Co. S Network Performance Oriented Internal within SP IP network / Services Human Interface Oriented Open and Visible to Customers
SLA for IP Management Public Network / Services Fixed Qo. S Negotiated Co. S Network Performance Oriented Internal within SP IP network / Services Human Interface Oriented Open and Visible to Customers
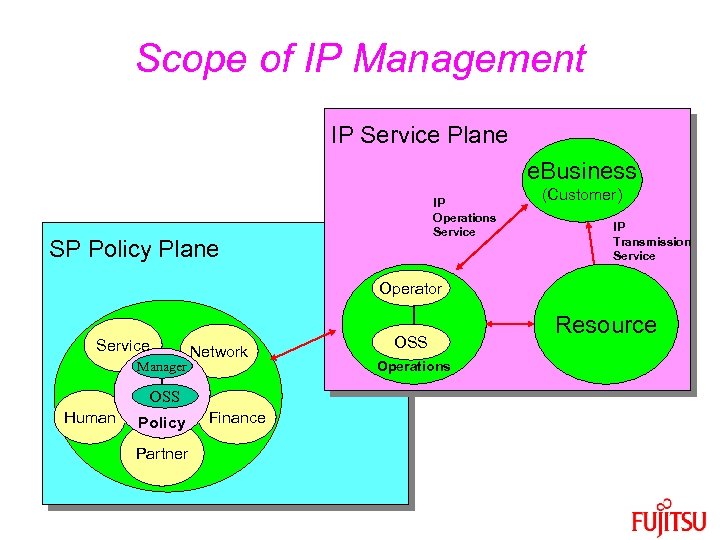 Scope of IP Management IP Service Plane e. Business IP Operations Service SP Policy Plane (Customer) IP Transmission Service Operator Service Manager Network OSS Human Policy Partner Finance OSS Operations Resource
Scope of IP Management IP Service Plane e. Business IP Operations Service SP Policy Plane (Customer) IP Transmission Service Operator Service Manager Network OSS Human Policy Partner Finance OSS Operations Resource
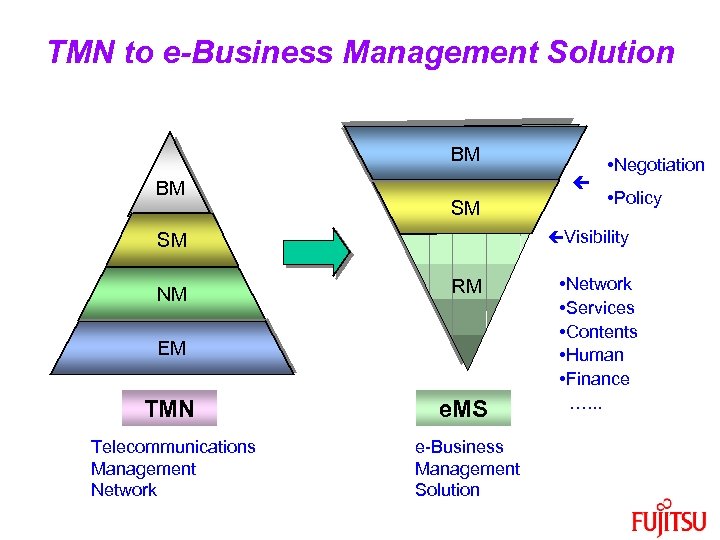 TMN to e-Business Management Solution BM NM BM SM • Policy Visibility SM NM • Negotiation RM EM TMN e. MS Telecommunications Management Network e-Business Management Solution • Network • Services • Contents • Human • Finance …. . .
TMN to e-Business Management Solution BM NM BM SM • Policy Visibility SM NM • Negotiation RM EM TMN e. MS Telecommunications Management Network e-Business Management Solution • Network • Services • Contents • Human • Finance …. . .
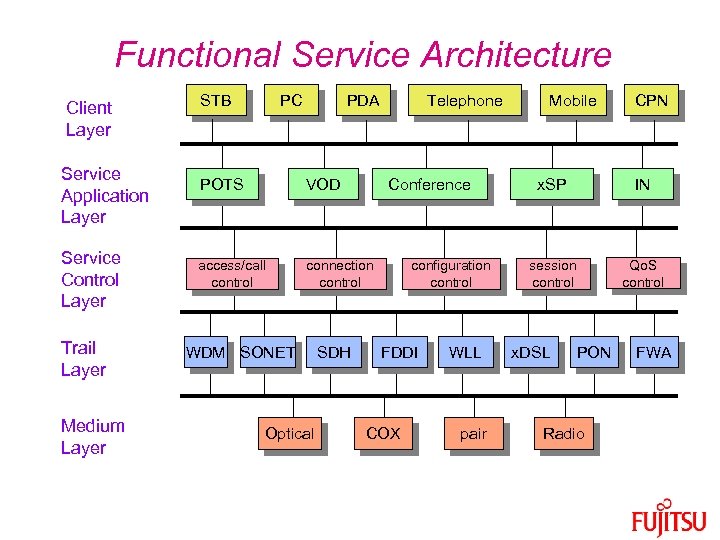 Functional Service Architecture Client Layer Service Application Layer Service Control Layer Trail Layer Medium Layer STB PC PDA POTS VOD access/call control Telephone connection control WDM SONET Optical SDH Conference configuration control FDDI COX WLL pair Mobile CPN x. SP IN session control Qo. S control x. DSL PON Radio FWA
Functional Service Architecture Client Layer Service Application Layer Service Control Layer Trail Layer Medium Layer STB PC PDA POTS VOD access/call control Telephone connection control WDM SONET Optical SDH Conference configuration control FDDI COX WLL pair Mobile CPN x. SP IN session control Qo. S control x. DSL PON Radio FWA
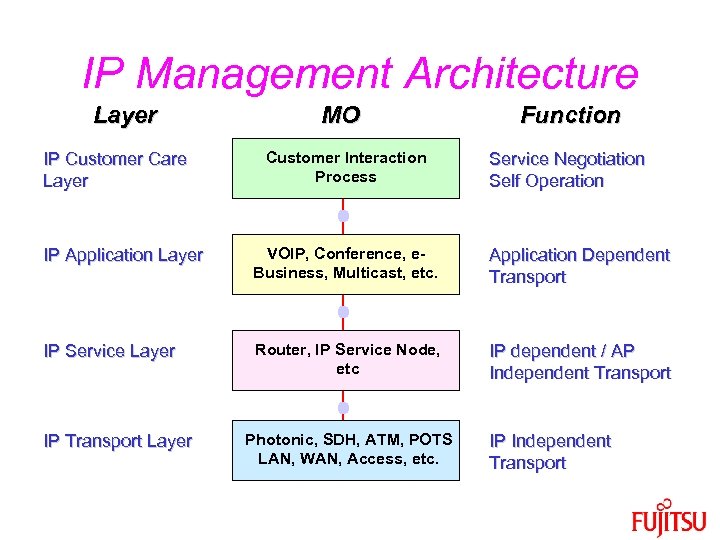 IP Management Architecture Layer IP Customer Care Layer MO Customer Interaction Process Function Service Negotiation Self Operation IP Application Layer VOIP, Conference, e. Business, Multicast, etc. Application Dependent Transport IP Service Layer Router, IP Service Node, etc IP dependent / AP Independent Transport IP Transport Layer Photonic, SDH, ATM, POTS LAN, WAN, Access, etc. IP Independent Transport
IP Management Architecture Layer IP Customer Care Layer MO Customer Interaction Process Function Service Negotiation Self Operation IP Application Layer VOIP, Conference, e. Business, Multicast, etc. Application Dependent Transport IP Service Layer Router, IP Service Node, etc IP dependent / AP Independent Transport IP Transport Layer Photonic, SDH, ATM, POTS LAN, WAN, Access, etc. IP Independent Transport
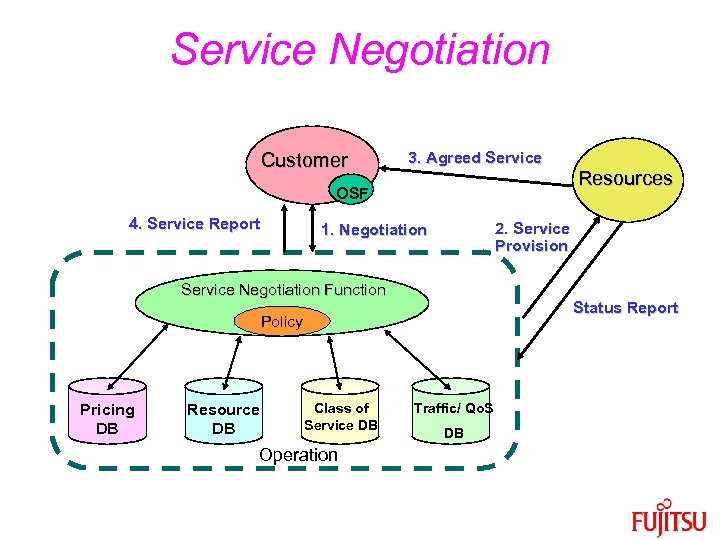 Service Negotiation Customer 3. Agreed Service OSF 4. Service Report 2. Service Provision 1. Negotiation Service Negotiation Function Status Report Policy Pricing DB Resource DB Class of Service DB Operation Resources Traffic/ Qo. S DB
Service Negotiation Customer 3. Agreed Service OSF 4. Service Report 2. Service Provision 1. Negotiation Service Negotiation Function Status Report Policy Pricing DB Resource DB Class of Service DB Operation Resources Traffic/ Qo. S DB
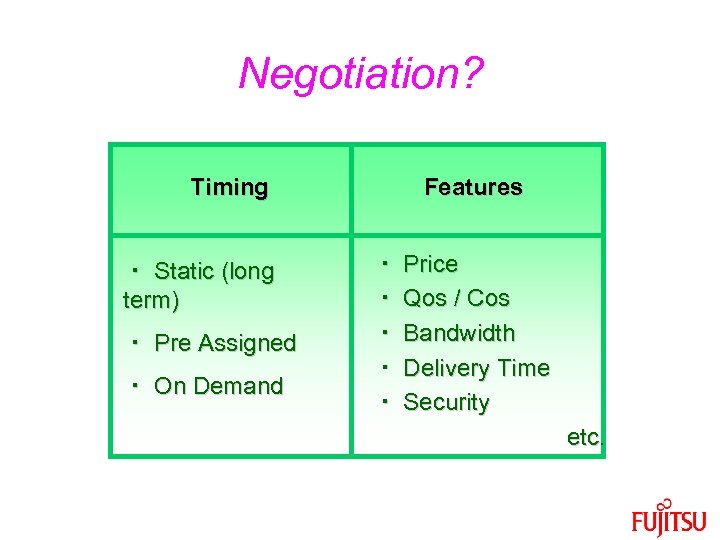 Negotiation? Timing ・ Static (long term) ・ Pre Assigned ・ On Demand Features ・ Price ・ Qos / Cos ・ Bandwidth ・ Delivery Time ・ Security etc.
Negotiation? Timing ・ Static (long term) ・ Pre Assigned ・ On Demand Features ・ Price ・ Qos / Cos ・ Bandwidth ・ Delivery Time ・ Security etc.
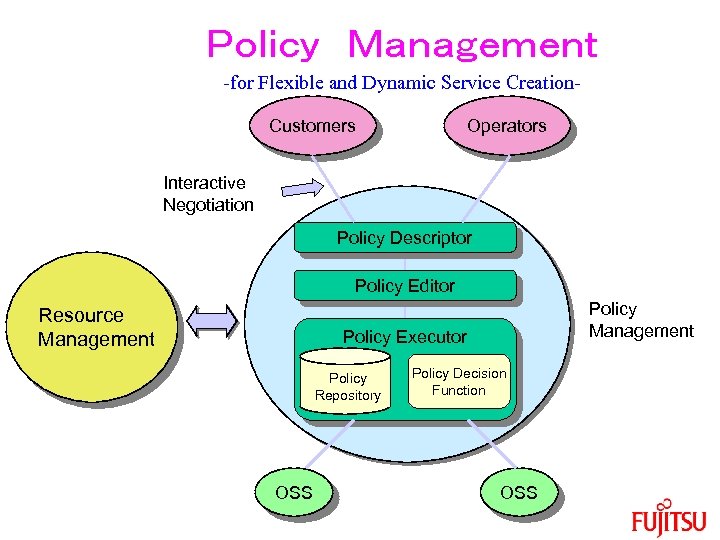 Policy Management -for Flexible and Dynamic Service Creation. Customers Operators Interactive Negotiation Policy Descriptor Policy Editor Resource Management Policy Executor Policy Repository OSS Policy Decision Function OSS
Policy Management -for Flexible and Dynamic Service Creation. Customers Operators Interactive Negotiation Policy Descriptor Policy Editor Resource Management Policy Executor Policy Repository OSS Policy Decision Function OSS
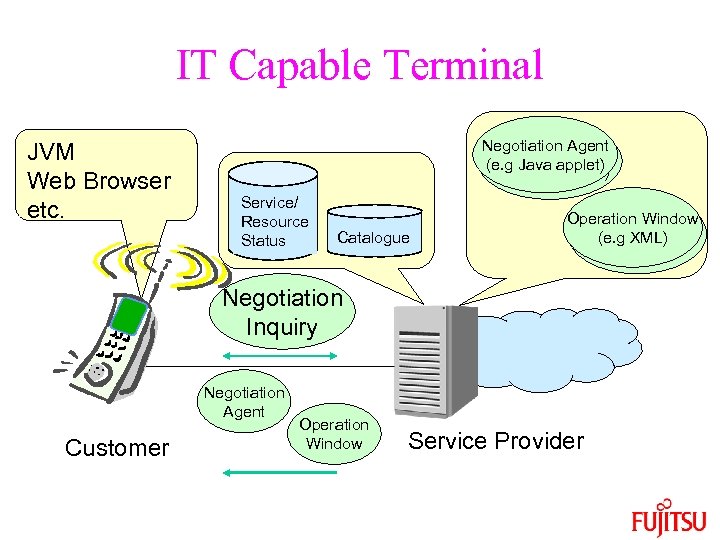 IT Capable Terminal JVM Web Browser etc. Negotiation Agent (e. g Java applet) Service/ Resource Status Catalogue Operation Window (e. g XML) Negotiation Inquiry Negotiation Agent Customer Operation Window Service Provider
IT Capable Terminal JVM Web Browser etc. Negotiation Agent (e. g Java applet) Service/ Resource Status Catalogue Operation Window (e. g XML) Negotiation Inquiry Negotiation Agent Customer Operation Window Service Provider
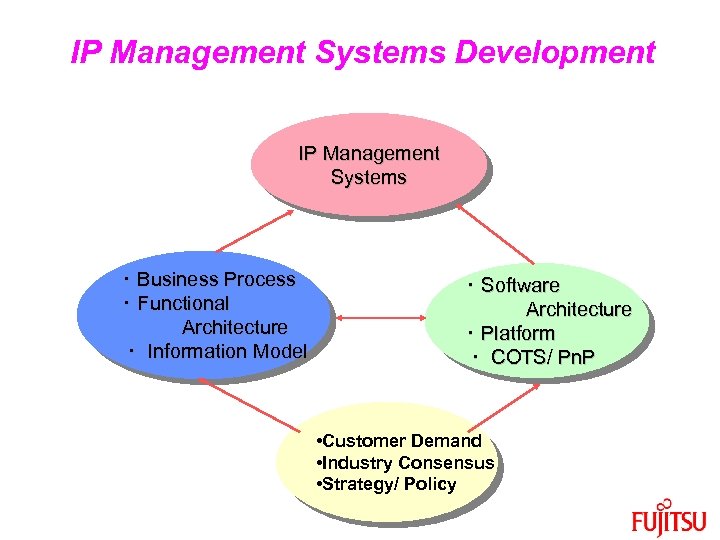 IP Management Systems Development IP Management Systems ・ Business Process ・ Functional Architecture ・ Information Model ・ Software Architecture ・ Platform ・ COTS/ Pn. P • Customer Demand • Industry Consensus • Strategy/ Policy
IP Management Systems Development IP Management Systems ・ Business Process ・ Functional Architecture ・ Information Model ・ Software Architecture ・ Platform ・ COTS/ Pn. P • Customer Demand • Industry Consensus • Strategy/ Policy
 For Faster, Cheaper and Better OSS Consensus of Business Process and OSS ・COTS: Commercial Off the Shelf Software ・Proof of Interoperability Plug and Play Software Packages and Management Systems in Global Market ----> Not Built but Buy
For Faster, Cheaper and Better OSS Consensus of Business Process and OSS ・COTS: Commercial Off the Shelf Software ・Proof of Interoperability Plug and Play Software Packages and Management Systems in Global Market ----> Not Built but Buy
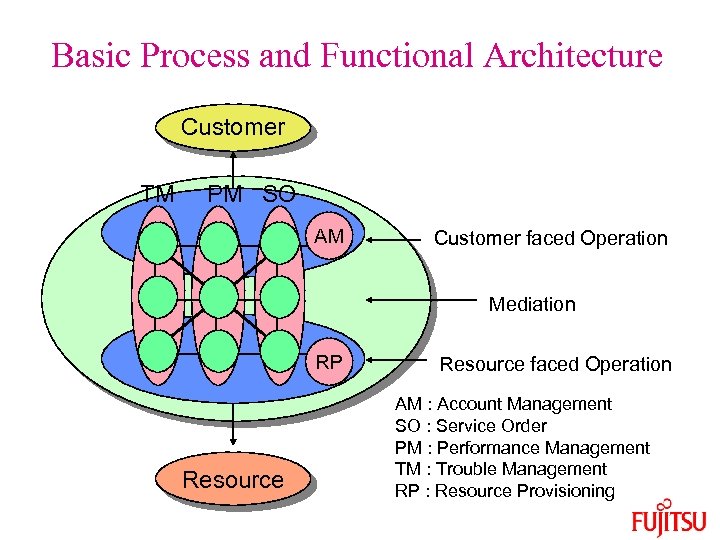 Basic Process and Functional Architecture Customer TM PM SO AM Customer faced Operation Mediation RP Resource faced Operation AM : Account Management SO : Service Order PM : Performance Management TM : Trouble Management RP : Resource Provisioning
Basic Process and Functional Architecture Customer TM PM SO AM Customer faced Operation Mediation RP Resource faced Operation AM : Account Management SO : Service Order PM : Performance Management TM : Trouble Management RP : Resource Provisioning
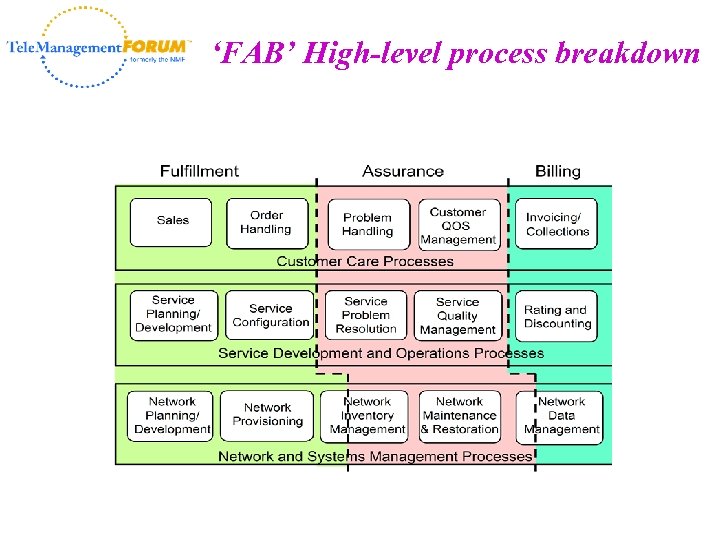 ‘FAB’ High-level process breakdown
‘FAB’ High-level process breakdown
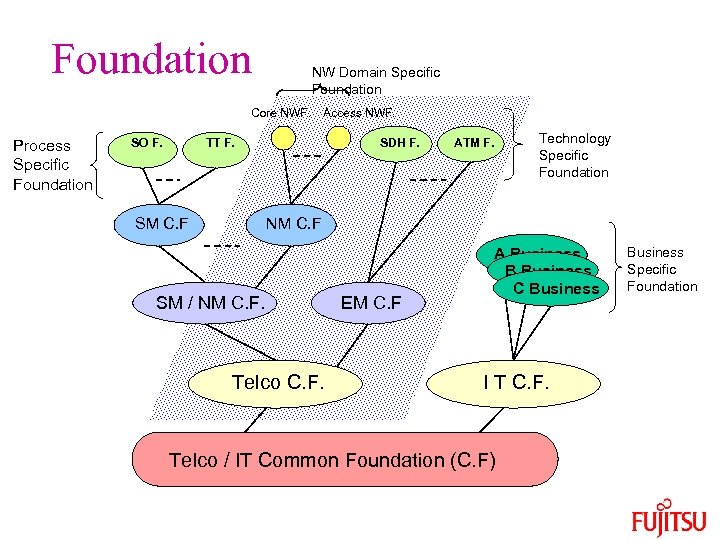 Foundation NW Domain Specific Foundation Core NWF. Process Specific Foundation SO F. Access NWF. TT F. SM C. F SDH F. ATM F. Technology Specific Foundation NM C. F SM / NM C. F. Telco C. F. EM C. F A Business B Business C Business I T C. F. Telco / IT Common Foundation (C. F) Business Specific Foundation
Foundation NW Domain Specific Foundation Core NWF. Process Specific Foundation SO F. Access NWF. TT F. SM C. F SDH F. ATM F. Technology Specific Foundation NM C. F SM / NM C. F. Telco C. F. EM C. F A Business B Business C Business I T C. F. Telco / IT Common Foundation (C. F) Business Specific Foundation
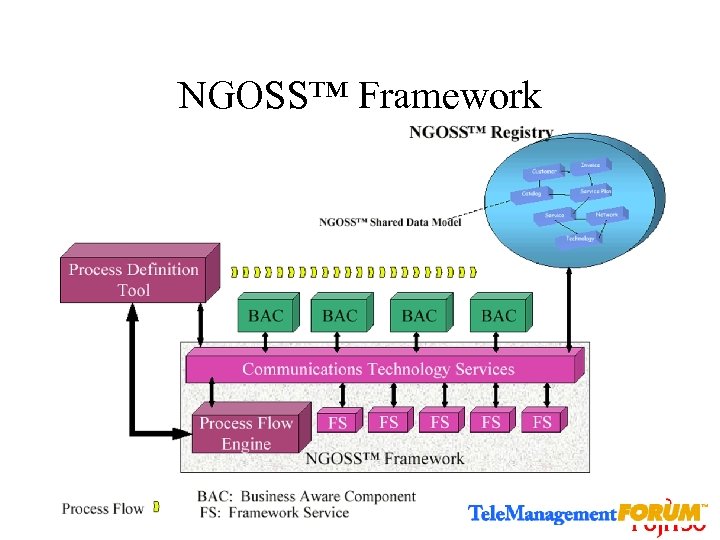 NGOSS™ Framework
NGOSS™ Framework
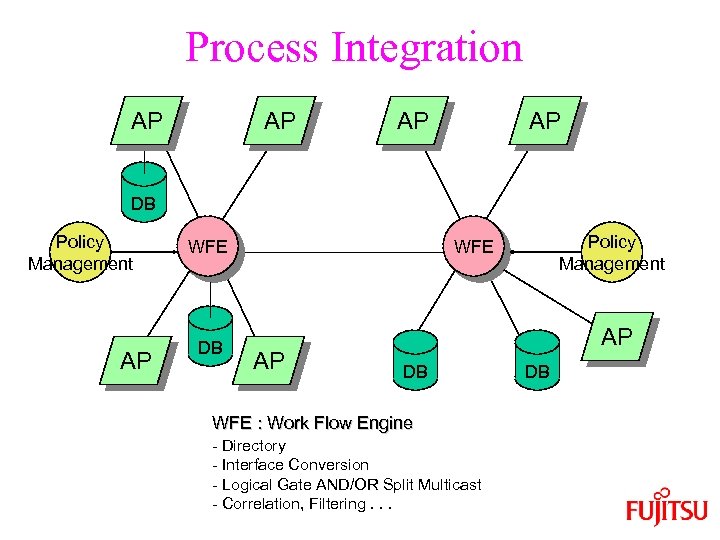 Process Integration AP AP DB Policy Management AP WFE DB Policy Management WFE AP AP DB WFE : Work Flow Engine - Directory - Interface Conversion - Logical Gate AND/OR Split Multicast - Correlation, Filtering. . . DB
Process Integration AP AP DB Policy Management AP WFE DB Policy Management WFE AP AP DB WFE : Work Flow Engine - Directory - Interface Conversion - Logical Gate AND/OR Split Multicast - Correlation, Filtering. . . DB
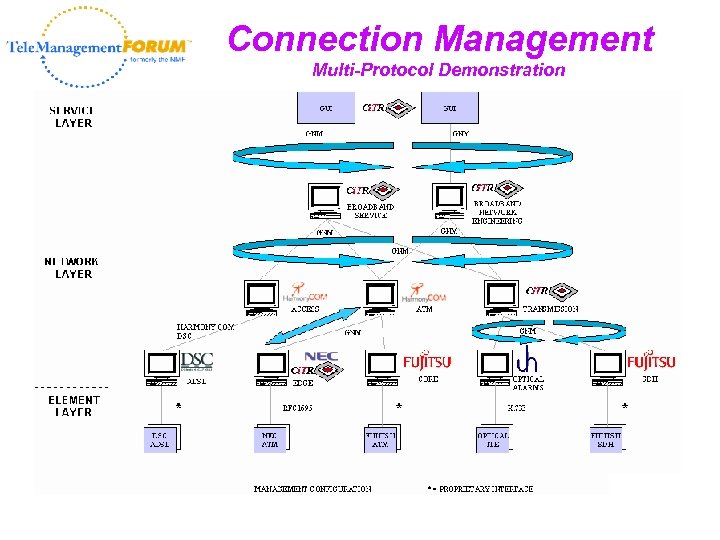 Connection Management Multi-Protocol Demonstration
Connection Management Multi-Protocol Demonstration
 Conclusion Why ? Support e. Business by Competitive Service Creation in New Paradigm What ? Negotiation for Customer Defined Services and SLA How ? Policy Based Management and COTS/ Pn. P OSS
Conclusion Why ? Support e. Business by Competitive Service Creation in New Paradigm What ? Negotiation for Customer Defined Services and SLA How ? Policy Based Management and COTS/ Pn. P OSS
 New Paradigm • TMN to e. Business Management Solution • Speed , Dynamic and Flexible Operations -Policy Based Management -Customer Self Operation • Negotiation( Customer Participated) based SLA • Consensus among Industries and Customers
New Paradigm • TMN to e. Business Management Solution • Speed , Dynamic and Flexible Operations -Policy Based Management -Customer Self Operation • Negotiation( Customer Participated) based SLA • Consensus among Industries and Customers
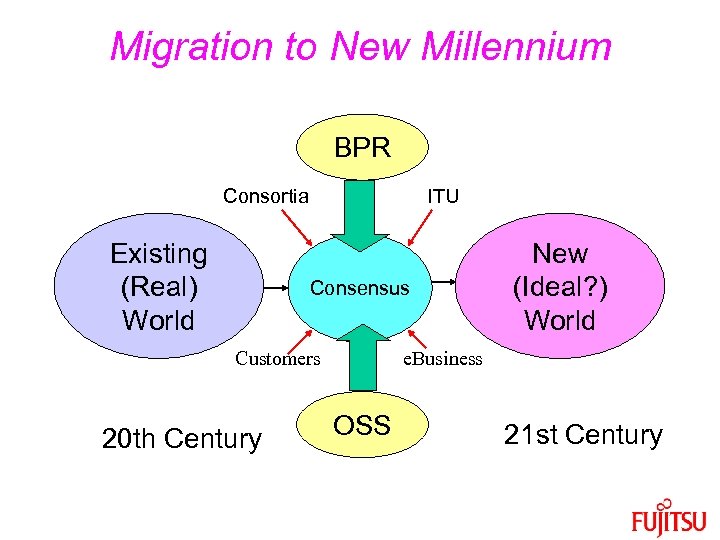 Migration to New Millennium BPR Consortia Existing (Real) World ITU Consensus Customers 20 th Century New (Ideal? ) World e. Business OSS 21 st Century
Migration to New Millennium BPR Consortia Existing (Real) World ITU Consensus Customers 20 th Century New (Ideal? ) World e. Business OSS 21 st Century
 “Excellence of Telecommunications Management is the Key Differentiater In 2000 s Telecom Business. ”
“Excellence of Telecommunications Management is the Key Differentiater In 2000 s Telecom Business. ”


