2b23e0b376bc470df72fac4b00198082.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Ionization 24 March 2003 Astronomy G 9001 - Spring 2003 Prof. Mordecai-Mark Mac Low
Ionization 24 March 2003 Astronomy G 9001 - Spring 2003 Prof. Mordecai-Mark Mac Low
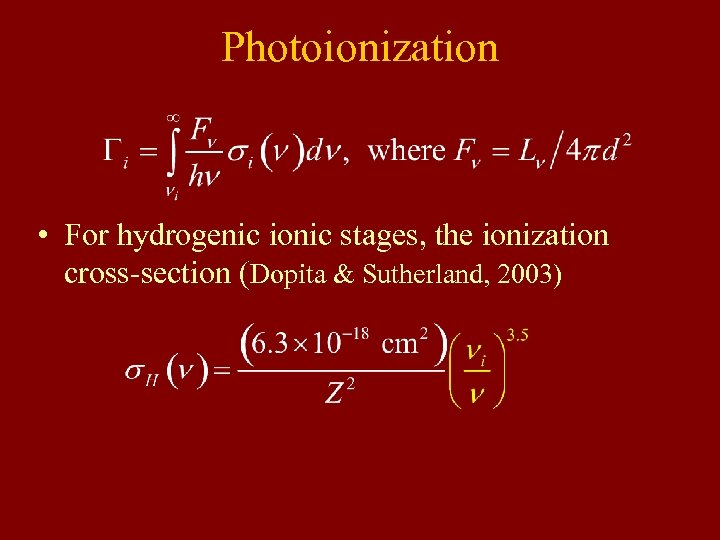 Photoionization • For hydrogenic ionic stages, the ionization cross-section (Dopita & Sutherland, 2003)
Photoionization • For hydrogenic ionic stages, the ionization cross-section (Dopita & Sutherland, 2003)
 Recombination • σrec can be derived from σi using detailed balance. • For hydrogenic ions, the Gaunt factor gmf is evaluated approximately in PPISM
Recombination • σrec can be derived from σi using detailed balance. • For hydrogenic ions, the Gaunt factor gmf is evaluated approximately in PPISM
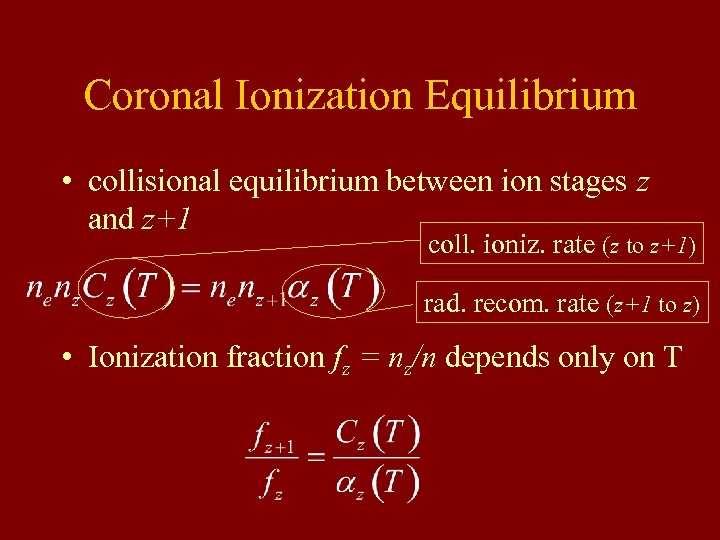 Coronal Ionization Equilibrium • collisional equilibrium between ion stages z and z+1 coll. ioniz. rate (z to z+1) rad. recom. rate (z+1 to z) • Ionization fraction fz = nz/n depends only on T
Coronal Ionization Equilibrium • collisional equilibrium between ion stages z and z+1 coll. ioniz. rate (z to z+1) rad. recom. rate (z+1 to z) • Ionization fraction fz = nz/n depends only on T
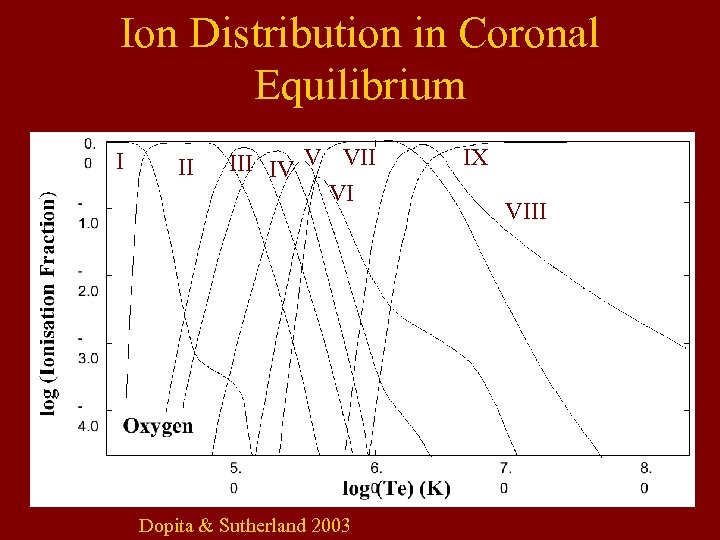 Ion Distribution in Coronal Equilibrium I II IV V VII VI Dopita & Sutherland 2003 IX VIII
Ion Distribution in Coronal Equilibrium I II IV V VII VI Dopita & Sutherland 2003 IX VIII
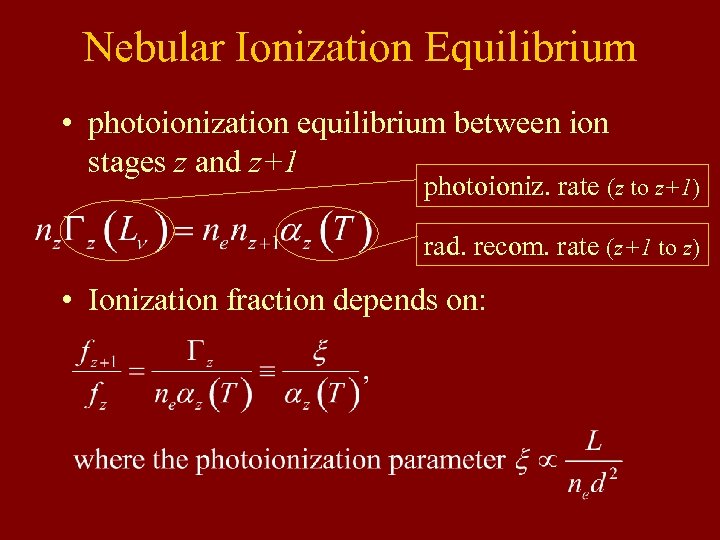 Nebular Ionization Equilibrium • photoionization equilibrium between ion stages z and z+1 photoioniz. rate (z to z+1) rad. recom. rate (z+1 to z) • Ionization fraction depends on:
Nebular Ionization Equilibrium • photoionization equilibrium between ion stages z and z+1 photoioniz. rate (z to z+1) rad. recom. rate (z+1 to z) • Ionization fraction depends on:
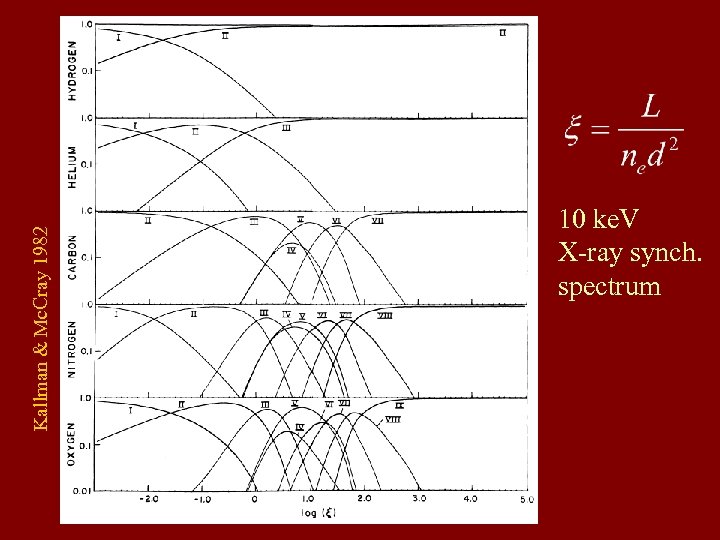 Kallman & Mc. Cray 1982 10 ke. V X-ray synch. spectrum
Kallman & Mc. Cray 1982 10 ke. V X-ray synch. spectrum
 H II Regions • Observed H II regions limited: – ionization bounded: all photons contained – density bounded: all atoms ionized • The optical depth for ionization is tiny. – At edge, σ = 6. 3 10 -18 cm 2, so if n = 1 cm-3 • Thus, density bounded H II regions have sharp edges
H II Regions • Observed H II regions limited: – ionization bounded: all photons contained – density bounded: all atoms ionized • The optical depth for ionization is tiny. – At edge, σ = 6. 3 10 -18 cm 2, so if n = 1 cm-3 • Thus, density bounded H II regions have sharp edges
 Strömgren Spheres • Two components to local ionizing flux near a star – direct ionizing flux – diffuse flux from recombinations to ground state • Calculate radius of ionized sphere in uniform ρ: – balance flux of ionizing photons through sphere S(r) against recombinations to levels above ground α(2): – Integrate over r until S(r) = 0 at r = r. S
Strömgren Spheres • Two components to local ionizing flux near a star – direct ionizing flux – diffuse flux from recombinations to ground state • Calculate radius of ionized sphere in uniform ρ: – balance flux of ionizing photons through sphere S(r) against recombinations to levels above ground α(2): – Integrate over r until S(r) = 0 at r = r. S
 Dynamical Solutions • Temperature increases upon photoionization – Resulting pressure differential can only be equalized by expansion of photoionized gas – When pressures balance, photoionized gas far less dense than neutral gas • Propagation of ionization front can be calculated by examining conservation equations, taking ΔT across front into account.
Dynamical Solutions • Temperature increases upon photoionization – Resulting pressure differential can only be equalized by expansion of photoionized gas – When pressures balance, photoionized gas far less dense than neutral gas • Propagation of ionization front can be calculated by examining conservation equations, taking ΔT across front into account.
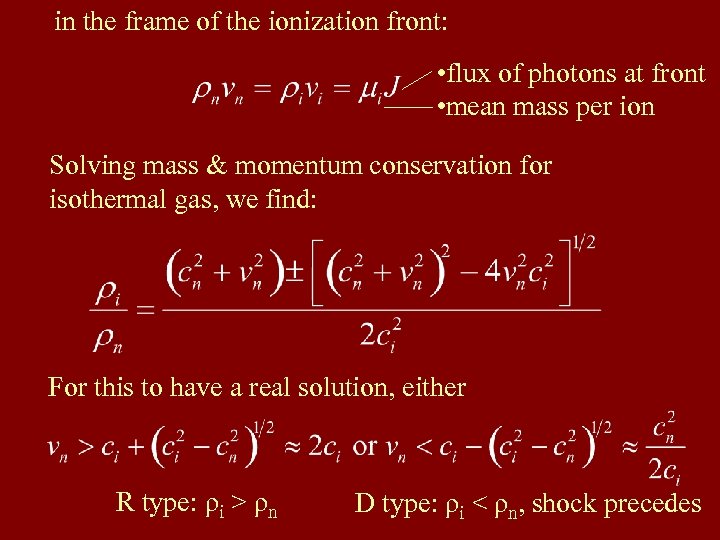 in the frame of the ionization front: • flux of photons at front • mean mass per ion Solving mass & momentum conservation for isothermal gas, we find: For this to have a real solution, either R type: ρi > ρn D type: ρi < ρn, shock precedes
in the frame of the ionization front: • flux of photons at front • mean mass per ion Solving mass & momentum conservation for isothermal gas, we find: For this to have a real solution, either R type: ρi > ρn D type: ρi < ρn, shock precedes
 Stages of Growth • Ultracompact – less than 10”, associated with young stars • Compact – more evolved, but still not nebular • Standard – single stars or groups, show structure • Giant – OB associations, early stages of superbubbles
Stages of Growth • Ultracompact – less than 10”, associated with young stars • Compact – more evolved, but still not nebular • Standard – single stars or groups, show structure • Giant – OB associations, early stages of superbubbles
 Ultracompact HII Regions • Defined to be less than about 10” in size • Should be rare if H II regions expand at roughly 10 km/s • Wood & Churchwell (1989) found 10 x more than expected.
Ultracompact HII Regions • Defined to be less than about 10” in size • Should be rare if H II regions expand at roughly 10 km/s • Wood & Churchwell (1989) found 10 x more than expected.
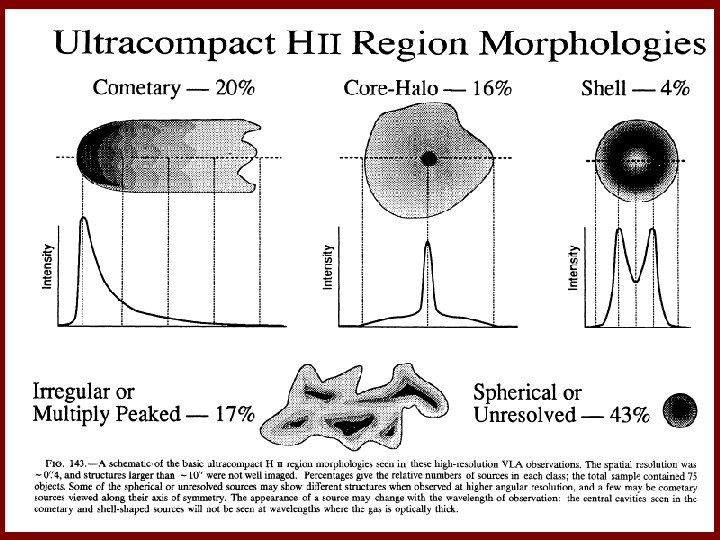
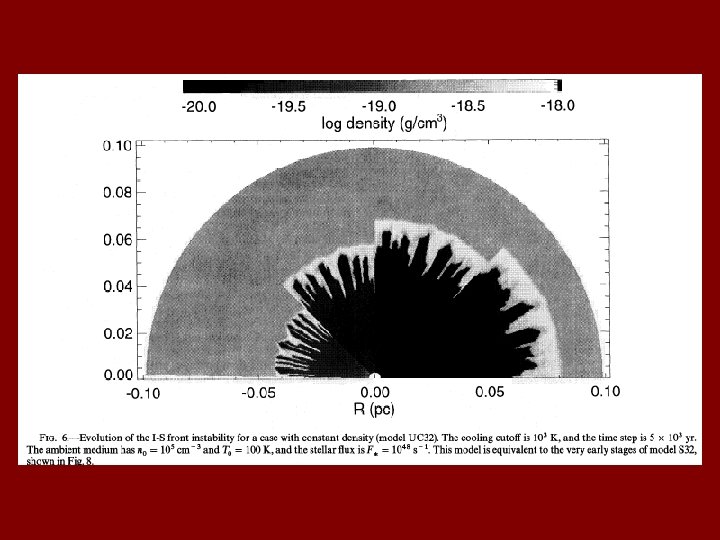
 Confinement • Three major mechanisms proposed – Bow shocks (Van Buren et al. 1990): ram pressure of motion confines cometary regions. – Disk photoevaporation (Hollenbach et al. 1994): dense disk provides mass source for core-halo – Pressure confinement (García-Segura & Franco, 1996): self-gravity increases core pressure, confining very small regions
Confinement • Three major mechanisms proposed – Bow shocks (Van Buren et al. 1990): ram pressure of motion confines cometary regions. – Disk photoevaporation (Hollenbach et al. 1994): dense disk provides mass source for core-halo – Pressure confinement (García-Segura & Franco, 1996): self-gravity increases core pressure, confining very small regions
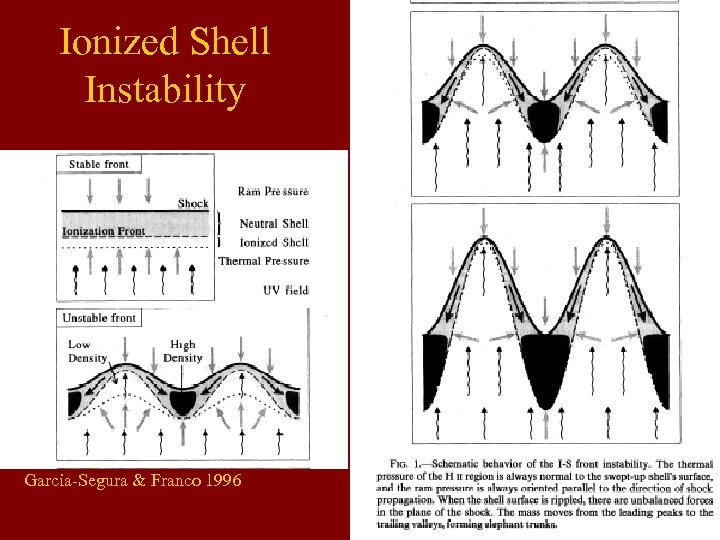 Ionized Shell Instability Garcia-Segura & Franco 1996
Ionized Shell Instability Garcia-Segura & Franco 1996

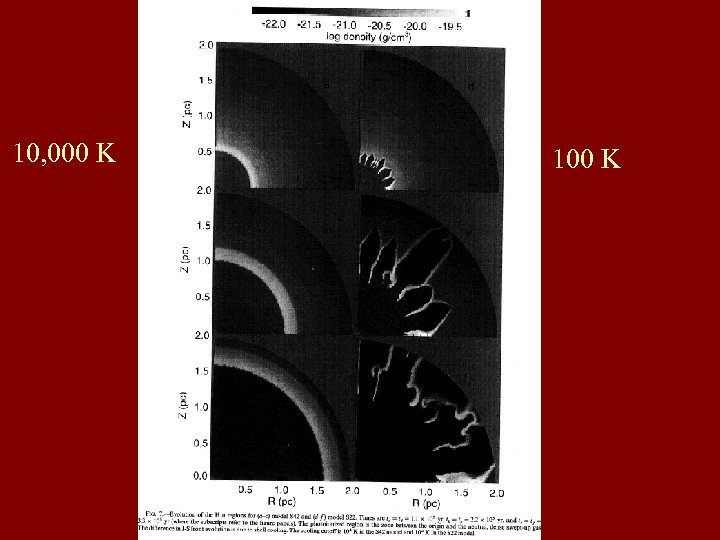 10, 000 K 100 K
10, 000 K 100 K
 Escape of Ionizing Radiation from Galaxy • Direct measurements (Hα) require a screen – High velocity clouds (Tufte et al. 1998, Bland. Hawthorn et al. 1998) – Magellanic Stream gas (Weiner & Williams 1996) • Optical depth to ionizing radiation τ = 3 – about 4% escape fraction – consistent with theoretical model of Domgörgen & Mathis (1994)
Escape of Ionizing Radiation from Galaxy • Direct measurements (Hα) require a screen – High velocity clouds (Tufte et al. 1998, Bland. Hawthorn et al. 1998) – Magellanic Stream gas (Weiner & Williams 1996) • Optical depth to ionizing radiation τ = 3 – about 4% escape fraction – consistent with theoretical model of Domgörgen & Mathis (1994)
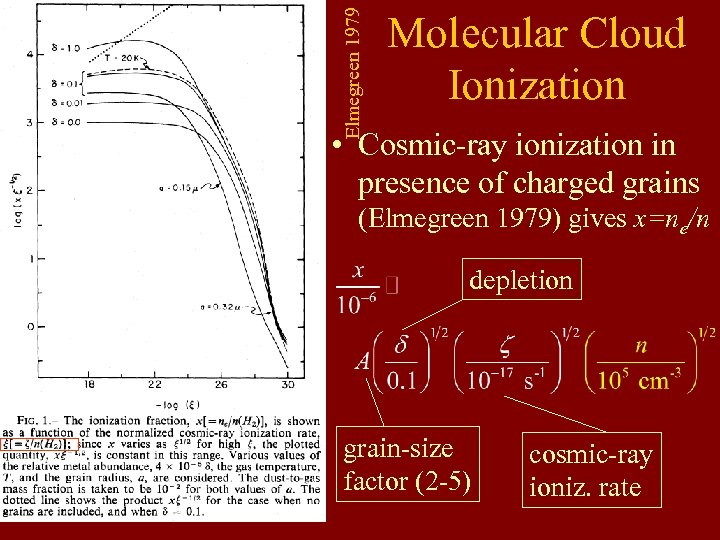 Elmegreen 1979 Molecular Cloud Ionization • Cosmic-ray ionization in presence of charged grains (Elmegreen 1979) gives x=ne/n depletion grain-size factor (2 -5) cosmic-ray ioniz. rate
Elmegreen 1979 Molecular Cloud Ionization • Cosmic-ray ionization in presence of charged grains (Elmegreen 1979) gives x=ne/n depletion grain-size factor (2 -5) cosmic-ray ioniz. rate
 Assignments • Flashcode registration • Read sections 1 -4 (quick start), and start looking at rest of manual • Read sections I, II, VII, and one other (to be summarized) of Hollenbach & Tielens, Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, 173
Assignments • Flashcode registration • Read sections 1 -4 (quick start), and start looking at rest of manual • Read sections I, II, VII, and one other (to be summarized) of Hollenbach & Tielens, Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, 173
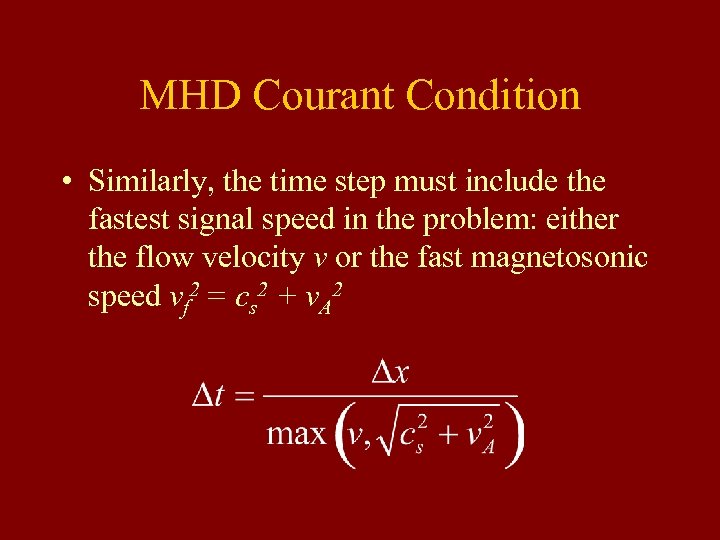 MHD Courant Condition • Similarly, the time step must include the fastest signal speed in the problem: either the flow velocity v or the fast magnetosonic speed vf 2 = cs 2 + v. A 2
MHD Courant Condition • Similarly, the time step must include the fastest signal speed in the problem: either the flow velocity v or the fast magnetosonic speed vf 2 = cs 2 + v. A 2
 Lorentz Forces • Update pressure term during source step • Tension term drives Alfvén waves – Must be updated at same time as induction equation to ensure correct propagation speeds – operator splitting of two terms
Lorentz Forces • Update pressure term during source step • Tension term drives Alfvén waves – Must be updated at same time as induction equation to ensure correct propagation speeds – operator splitting of two terms
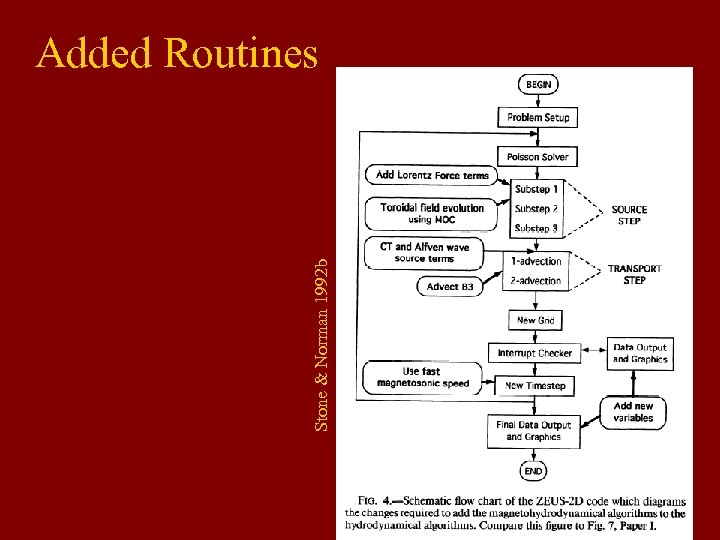 Stone & Norman 1992 b Added Routines
Stone & Norman 1992 b Added Routines
 Flashcode History • Politics – world historical – political – internal • Components • Coding philosophy – spaghetti (Fortran IV/66) – structured (Fortran 77) – modular (Fortran 90)
Flashcode History • Politics – world historical – political – internal • Components • Coding philosophy – spaghetti (Fortran IV/66) – structured (Fortran 77) – modular (Fortran 90)
 Flashcode Structure • setup preprocessor script – reads configuration files • setups/ - problem specific – Config file to generate Modules – init_block. F 90 to initialize one block • source/sites/ - location specific – sets up makefiles and code for a particular problem, and a particular site. • Compilation with gmake (can be parallel) • Runtime input parameters in flash. par
Flashcode Structure • setup preprocessor script – reads configuration files • setups/ - problem specific – Config file to generate Modules – init_block. F 90 to initialize one block • source/sites/ - location specific – sets up makefiles and code for a particular problem, and a particular site. • Compilation with gmake (can be parallel) • Runtime input parameters in flash. par


