7f0f3190c111a2900d0f41f0cefddeb8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Ionic Liquids – Inherent sensing and transduction of metal ion complexation EMRS Spring Meeting Strasbourg, France 10 th June 2010 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Ionic Liquids – Inherent sensing and transduction of metal ion complexation EMRS Spring Meeting Strasbourg, France 10 th June 2010 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
 Me. . • Graduated with B. Sc (Hons) in Chemical & Pharmaceutical Sciences, Dublin City University (2008). • Ph. D. in “Ionic Liquids and their use in the development of potential chemical sensors”. Sept 08’ • Supervisors Dr. Aleksandar Radu & Prof. Dermot Diamond UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Me. . • Graduated with B. Sc (Hons) in Chemical & Pharmaceutical Sciences, Dublin City University (2008). • Ph. D. in “Ionic Liquids and their use in the development of potential chemical sensors”. Sept 08’ • Supervisors Dr. Aleksandar Radu & Prof. Dermot Diamond UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
 Outline • Ionic Liquids • Polymeric Optodes • Ionic Liquid – PVC Optodes UV/Vis Characterisation • Alternate Detection Techniques Wireless Radio Frequency Detection Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Portable X-Ray Fluorescence UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Outline • Ionic Liquids • Polymeric Optodes • Ionic Liquid – PVC Optodes UV/Vis Characterisation • Alternate Detection Techniques Wireless Radio Frequency Detection Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Portable X-Ray Fluorescence UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
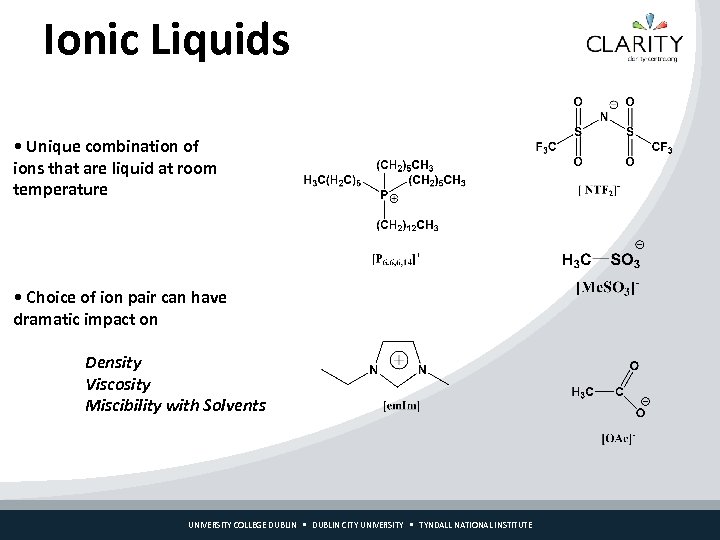 Ionic Liquids • Unique combination of ions that are liquid at room temperature • Choice of ion pair can have dramatic impact on Density Viscosity Miscibility with Solvents UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Ionic Liquids • Unique combination of ions that are liquid at room temperature • Choice of ion pair can have dramatic impact on Density Viscosity Miscibility with Solvents UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
 Applications • Synthesis & Catalysis in Organic Chemistry => Good thermal stability • Electrochemistry => Good Conductivity and a large electrochemical window • Analytical Chemistry => Stable stationary phase for separations UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Applications • Synthesis & Catalysis in Organic Chemistry => Good thermal stability • Electrochemistry => Good Conductivity and a large electrochemical window • Analytical Chemistry => Stable stationary phase for separations UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
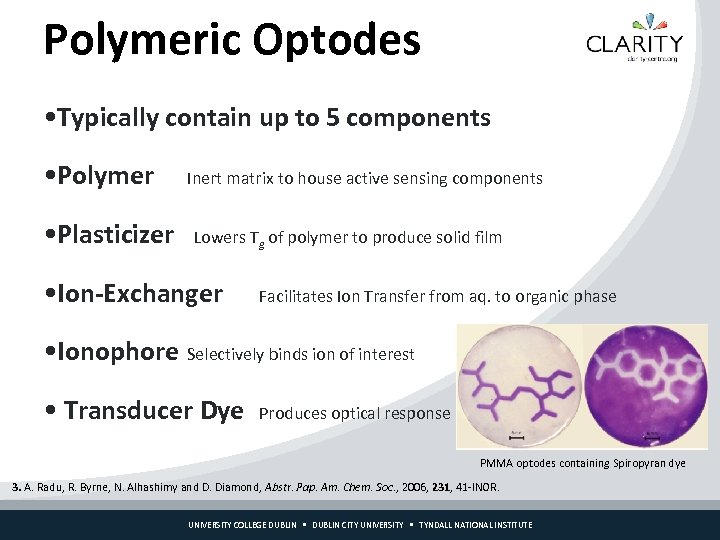 Polymeric Optodes • Typically contain up to 5 components • Polymer • Plasticizer Inert matrix to house active sensing components Lowers Tg of polymer to produce solid film • Ion-Exchanger Facilitates Ion Transfer from aq. to organic phase • Ionophore Selectively binds ion of interest • Transducer Dye Produces optical response PMMA optodes containing Spiropyran dye 3. A. Radu, R. Byrne, N. Alhashimy and D. Diamond, Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2006, 231, 41 -INOR. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Polymeric Optodes • Typically contain up to 5 components • Polymer • Plasticizer Inert matrix to house active sensing components Lowers Tg of polymer to produce solid film • Ion-Exchanger Facilitates Ion Transfer from aq. to organic phase • Ionophore Selectively binds ion of interest • Transducer Dye Produces optical response PMMA optodes containing Spiropyran dye 3. A. Radu, R. Byrne, N. Alhashimy and D. Diamond, Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2006, 231, 41 -INOR. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
![Simple, 2 -component optodes Cu 2+ Co 2+ • [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] Simple, 2 -component optodes Cu 2+ Co 2+ • [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA]](https://present5.com/presentation/7f0f3190c111a2900d0f41f0cefddeb8/image-7.jpg) Simple, 2 -component optodes Cu 2+ Co 2+ • [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] acts as plasticizer ion-exchanger ligand transducer dye Cu 2+/Co 2+ Upon exposure to Cu 2+ and Co 2+ UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Simple, 2 -component optodes Cu 2+ Co 2+ • [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] acts as plasticizer ion-exchanger ligand transducer dye Cu 2+/Co 2+ Upon exposure to Cu 2+ and Co 2+ UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
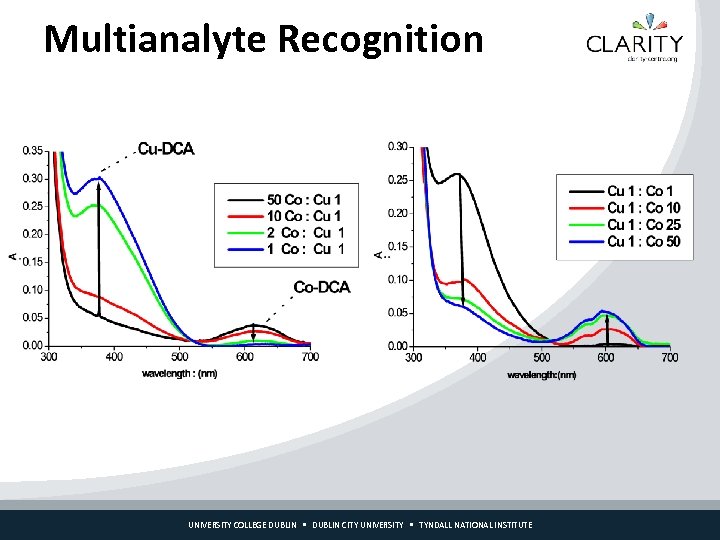 Multianalyte Recognition UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Multianalyte Recognition UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
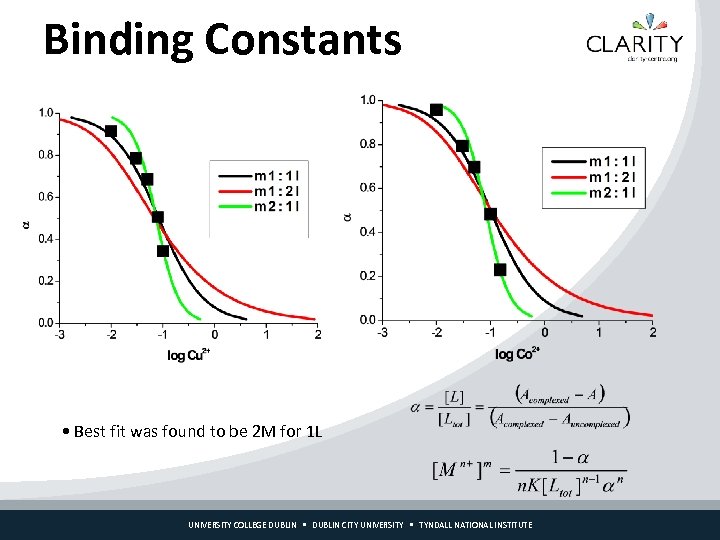 Binding Constants • Best fit was found to be 2 M for 1 L UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Binding Constants • Best fit was found to be 2 M for 1 L UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
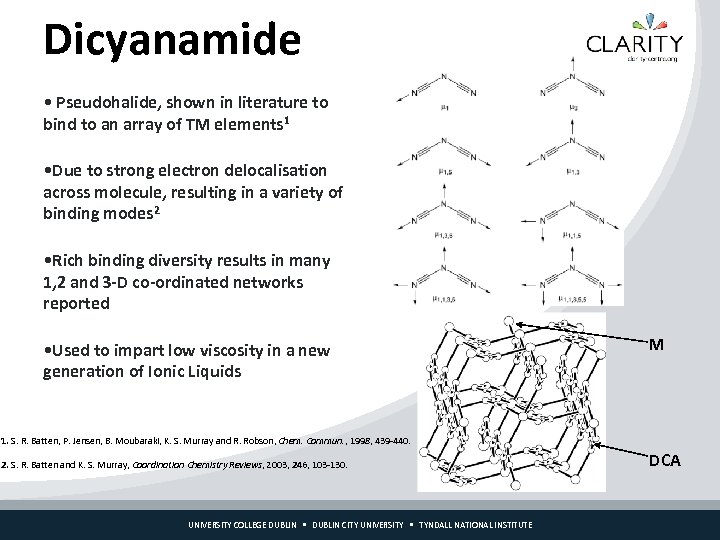 Dicyanamide • Pseudohalide, shown in literature to bind to an array of TM elements 1 • Due to strong electron delocalisation across molecule, resulting in a variety of binding modes 2 • Rich binding diversity results in many 1, 2 and 3 -D co-ordinated networks reported • Used to impart low viscosity in a new generation of Ionic Liquids M 1. S. R. Batten, P. Jensen, B. Moubaraki, K. S. Murray and R. Robson, Chem. Commun. , 1998, 439 -440. 2. S. R. Batten and K. S. Murray, Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2003, 246, 103 -130. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE DCA
Dicyanamide • Pseudohalide, shown in literature to bind to an array of TM elements 1 • Due to strong electron delocalisation across molecule, resulting in a variety of binding modes 2 • Rich binding diversity results in many 1, 2 and 3 -D co-ordinated networks reported • Used to impart low viscosity in a new generation of Ionic Liquids M 1. S. R. Batten, P. Jensen, B. Moubaraki, K. S. Murray and R. Robson, Chem. Commun. , 1998, 439 -440. 2. S. R. Batten and K. S. Murray, Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2003, 246, 103 -130. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE DCA
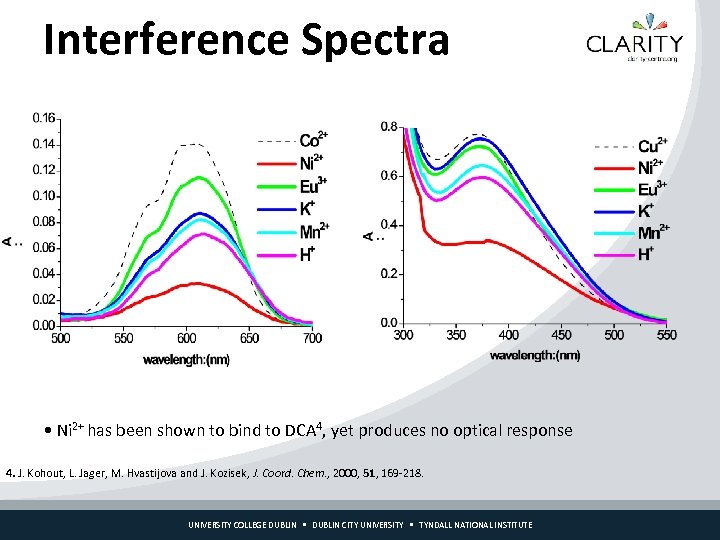 Interference Spectra • Ni 2+ has been shown to bind to DCA 4, yet produces no optical response 4. J. Kohout, L. Jager, M. Hvastijova and J. Kozisek, J. Coord. Chem. , 2000, 51, 169 -218. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Interference Spectra • Ni 2+ has been shown to bind to DCA 4, yet produces no optical response 4. J. Kohout, L. Jager, M. Hvastijova and J. Kozisek, J. Coord. Chem. , 2000, 51, 169 -218. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
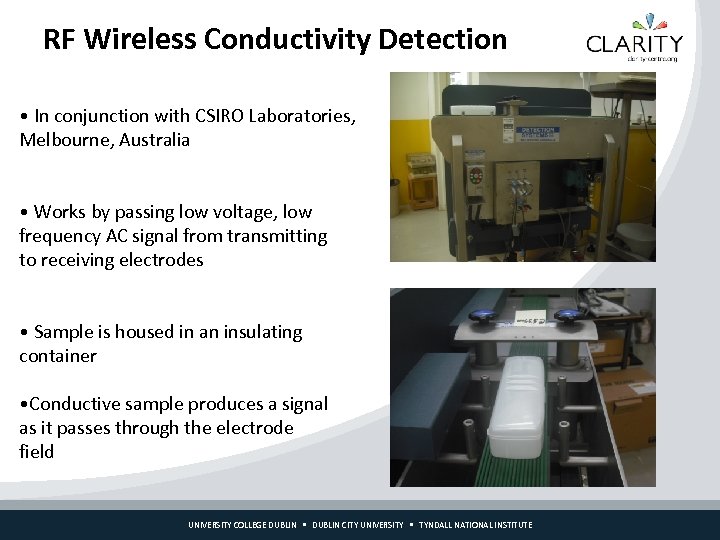 RF Wireless Conductivity Detection • In conjunction with CSIRO Laboratories, Melbourne, Australia • Works by passing low voltage, low frequency AC signal from transmitting to receiving electrodes • Sample is housed in an insulating container • Conductive sample produces a signal as it passes through the electrode field UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
RF Wireless Conductivity Detection • In conjunction with CSIRO Laboratories, Melbourne, Australia • Works by passing low voltage, low frequency AC signal from transmitting to receiving electrodes • Sample is housed in an insulating container • Conductive sample produces a signal as it passes through the electrode field UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
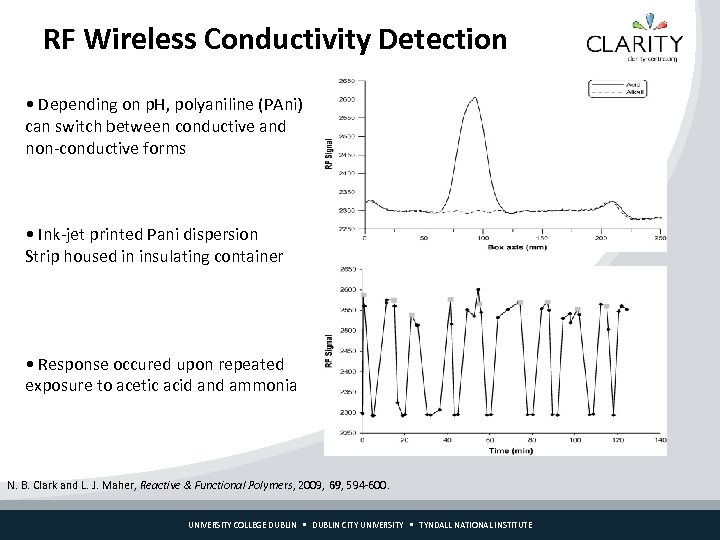 RF Wireless Conductivity Detection • Depending on p. H, polyaniline (PAni) can switch between conductive and non-conductive forms • Ink-jet printed Pani dispersion Strip housed in insulating container • Response occured upon repeated exposure to acetic acid and ammonia N. B. Clark and L. J. Maher, Reactive & Functional Polymers, 2009, 69, 594 -600. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
RF Wireless Conductivity Detection • Depending on p. H, polyaniline (PAni) can switch between conductive and non-conductive forms • Ink-jet printed Pani dispersion Strip housed in insulating container • Response occured upon repeated exposure to acetic acid and ammonia N. B. Clark and L. J. Maher, Reactive & Functional Polymers, 2009, 69, 594 -600. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
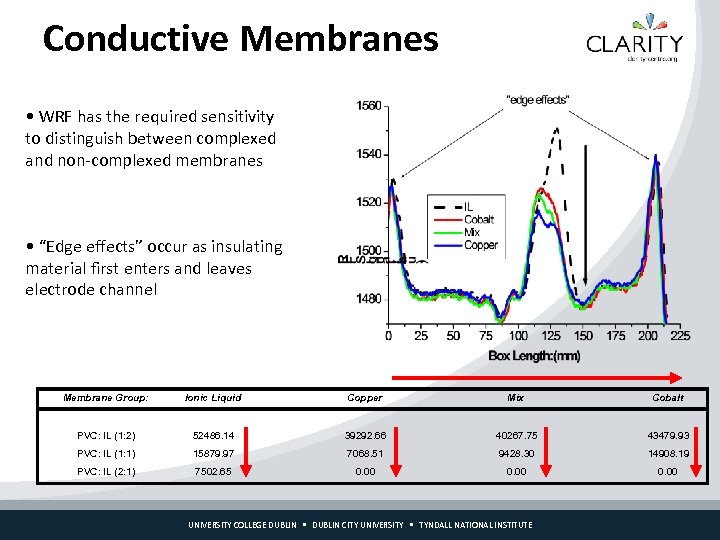 Conductive Membranes • WRF has the required sensitivity to distinguish between complexed and non-complexed membranes • “Edge effects” occur as insulating material first enters and leaves electrode channel Membrane Group: Ionic Liquid Copper Mix Cobalt PVC: IL (1: 2) 52486. 14 39292. 66 40267. 75 43479. 93 PVC: IL (1: 1) 15879. 97 7068. 51 9428. 30 14908. 19 PVC: IL (2: 1) 7502. 65 0. 00 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Conductive Membranes • WRF has the required sensitivity to distinguish between complexed and non-complexed membranes • “Edge effects” occur as insulating material first enters and leaves electrode channel Membrane Group: Ionic Liquid Copper Mix Cobalt PVC: IL (1: 2) 52486. 14 39292. 66 40267. 75 43479. 93 PVC: IL (1: 1) 15879. 97 7068. 51 9428. 30 14908. 19 PVC: IL (2: 1) 7502. 65 0. 00 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
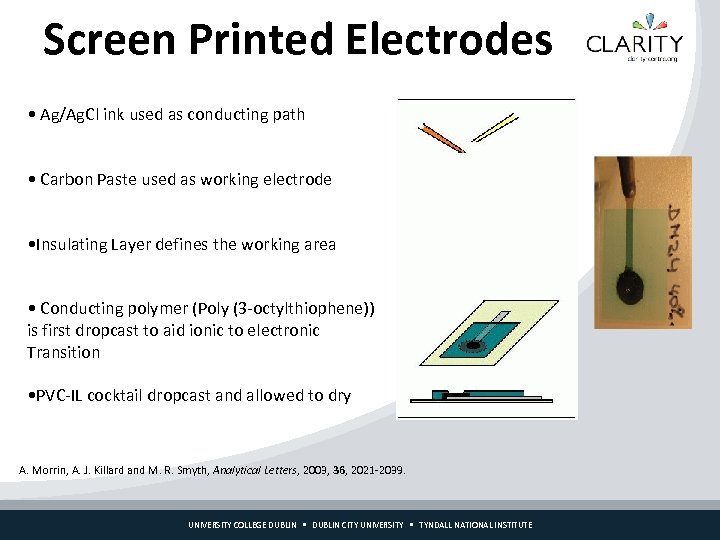 Screen Printed Electrodes • Ag/Ag. Cl ink used as conducting path • Carbon Paste used as working electrode • Insulating Layer defines the working area • Conducting polymer (Poly (3 -octylthiophene)) is first dropcast to aid ionic to electronic Transition • PVC-IL cocktail dropcast and allowed to dry A. Morrin, A. J. Killard and M. R. Smyth, Analytical Letters, 2003, 36, 2021 -2039. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Screen Printed Electrodes • Ag/Ag. Cl ink used as conducting path • Carbon Paste used as working electrode • Insulating Layer defines the working area • Conducting polymer (Poly (3 -octylthiophene)) is first dropcast to aid ionic to electronic Transition • PVC-IL cocktail dropcast and allowed to dry A. Morrin, A. J. Killard and M. R. Smyth, Analytical Letters, 2003, 36, 2021 -2039. UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
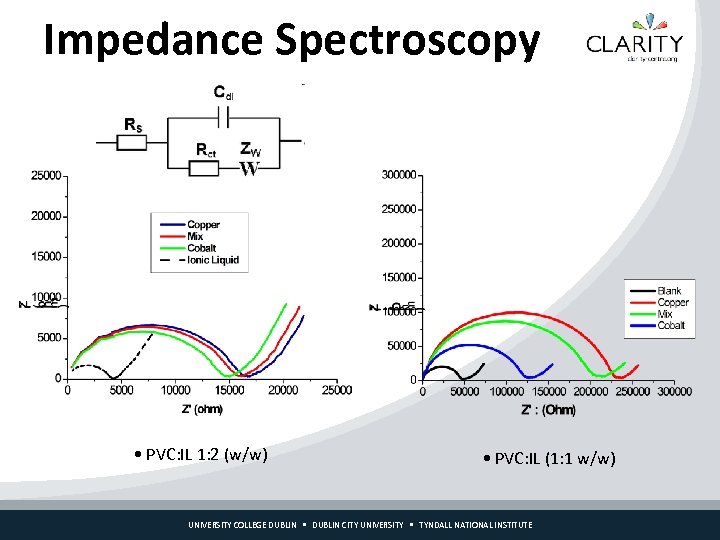 Impedance Spectroscopy • PVC: IL 1: 2 (w/w) • PVC: IL (1: 1 w/w) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Impedance Spectroscopy • PVC: IL 1: 2 (w/w) • PVC: IL (1: 1 w/w) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
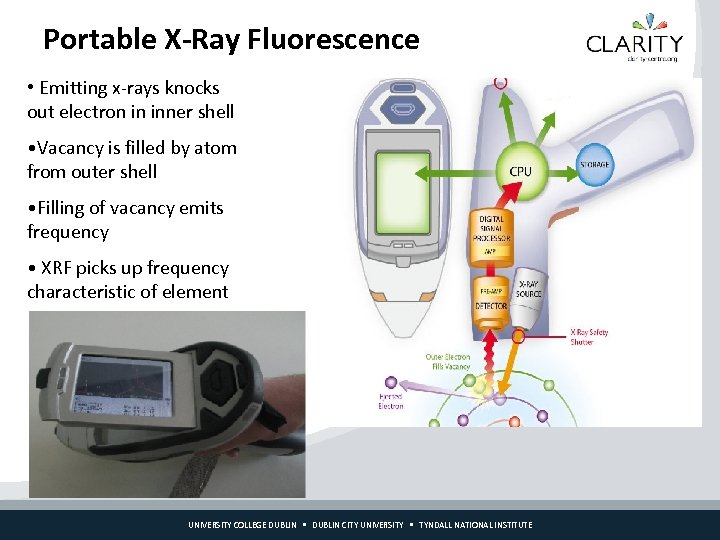 Portable X-Ray Fluorescence • Emitting x-rays knocks out electron in inner shell • Vacancy is filled by atom from outer shell • Filling of vacancy emits frequency • XRF picks up frequency characteristic of element UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Portable X-Ray Fluorescence • Emitting x-rays knocks out electron in inner shell • Vacancy is filled by atom from outer shell • Filling of vacancy emits frequency • XRF picks up frequency characteristic of element UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
![XRF Results • Used to quantify [DCA]binding preferentiality • Co levels were found to XRF Results • Used to quantify [DCA]binding preferentiality • Co levels were found to](https://present5.com/presentation/7f0f3190c111a2900d0f41f0cefddeb8/image-18.jpg) XRF Results • Used to quantify [DCA]binding preferentiality • Co levels were found to be 45% lower • Even as a mixture (2: 1 Co: Cu (vol. )) Co levels are 88% lower! Membrane Copper: Cobalt: Composition: Mixture Blank Copper: Cobalt: 2551. 91 (164. 43) 272. 17 (83. 39) 80. 98 (21. 56) 69. 59 ( 168. 57) 1559. 59 (179. 21) 192. 55 (81. 51) < LOD 202. 62 (88. 09) < LOD 1. PVC: IL (1: 1 w/w) 2642. 14 (165. 73) 1207. 55 (153. 38) 2. PVC: IL (1: 2 w/w) 16996. 25 (424. 75) 7652. 11 (371. 17) 12866. 82 (357. 98) 3. PVC: IL (2: 1 w/w) 222. 53 (77. 79) < LOD 294. 12 (90. 91) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
XRF Results • Used to quantify [DCA]binding preferentiality • Co levels were found to be 45% lower • Even as a mixture (2: 1 Co: Cu (vol. )) Co levels are 88% lower! Membrane Copper: Cobalt: Composition: Mixture Blank Copper: Cobalt: 2551. 91 (164. 43) 272. 17 (83. 39) 80. 98 (21. 56) 69. 59 ( 168. 57) 1559. 59 (179. 21) 192. 55 (81. 51) < LOD 202. 62 (88. 09) < LOD 1. PVC: IL (1: 1 w/w) 2642. 14 (165. 73) 1207. 55 (153. 38) 2. PVC: IL (1: 2 w/w) 16996. 25 (424. 75) 7652. 11 (371. 17) 12866. 82 (357. 98) 3. PVC: IL (2: 1 w/w) 222. 53 (77. 79) < LOD 294. 12 (90. 91) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
![Conclusions • The Ionic Liquids [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] fulfils multiple roles in Conclusions • The Ionic Liquids [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] fulfils multiple roles in](https://present5.com/presentation/7f0f3190c111a2900d0f41f0cefddeb8/image-19.jpg) Conclusions • The Ionic Liquids [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] fulfils multiple roles in polymeric optodes • Conductive membranes allow for detection via an array of techniques • The relative ease of synthesis and diversity allows for the possibility of new IL’s with greater selectivity UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Conclusions • The Ionic Liquids [P 6, 6, 6, 14][DCA] fulfils multiple roles in polymeric optodes • Conductive membranes allow for detection via an array of techniques • The relative ease of synthesis and diversity allows for the possibility of new IL’s with greater selectivity UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
 Acknowledgements • Dr’s. Aleksandar Radu, Robert Byrne and Professor Dermot Diamond • Michele Zanoni, Bartosz Ziolkowski, Larisa Florea and Caroline Barry • Dr’s. Noel Clarke and Matthius Hilder at CSIRO • Cytec Industries • DCU Research Career Start Fellowship 2008 • Science Foundation Ireland (grant 07/CE/I 1147) • Enterprise Ireland (grant 07/RFP/MASF 812) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
Acknowledgements • Dr’s. Aleksandar Radu, Robert Byrne and Professor Dermot Diamond • Michele Zanoni, Bartosz Ziolkowski, Larisa Florea and Caroline Barry • Dr’s. Noel Clarke and Matthius Hilder at CSIRO • Cytec Industries • DCU Research Career Start Fellowship 2008 • Science Foundation Ireland (grant 07/CE/I 1147) • Enterprise Ireland (grant 07/RFP/MASF 812) UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
 • Thanks for listening! UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE
• Thanks for listening! UNIVERSITY COLLEGE DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY TYNDALL NATIONAL INSTITUTE


