58104d67bd453887bfb66e02cda95b30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Investing 101 Part 1 : Creating a Diversified Portfolio Part 2 : Investing in the Stock Market, Indexing vs Active Management By: Bruce Mc. Nutt
Investing 101 Part 1 : Creating a Diversified Portfolio Part 2 : Investing in the Stock Market, Indexing vs Active Management By: Bruce Mc. Nutt
 The Goal of the Personal Investor n Your goal is to manage a well diversified portfolio through dollar cost averaging that meets your risk assessment needs through proper asset allocation in each of the asset classes.
The Goal of the Personal Investor n Your goal is to manage a well diversified portfolio through dollar cost averaging that meets your risk assessment needs through proper asset allocation in each of the asset classes.
 Investing vs. Saving n Saving: Holding onto the money you already have n Investing Using your money to make more money
Investing vs. Saving n Saving: Holding onto the money you already have n Investing Using your money to make more money
 Investing n Successful Investing requires time and a well thought out plan. n Successful investing requires a good understanding of the financial markets and investing strategy, unless you want to pay someone else to do it for you.
Investing n Successful Investing requires time and a well thought out plan. n Successful investing requires a good understanding of the financial markets and investing strategy, unless you want to pay someone else to do it for you.
 How Investments Grow n Investments grow for two reasons, through a process called compounding, and because you add money to them. n “The most powerful force in the Universe is Compounded Interest” Albert Einstein n Compounding means that not only does your original investment grow, but the interest you earn grows as well
How Investments Grow n Investments grow for two reasons, through a process called compounding, and because you add money to them. n “The most powerful force in the Universe is Compounded Interest” Albert Einstein n Compounding means that not only does your original investment grow, but the interest you earn grows as well
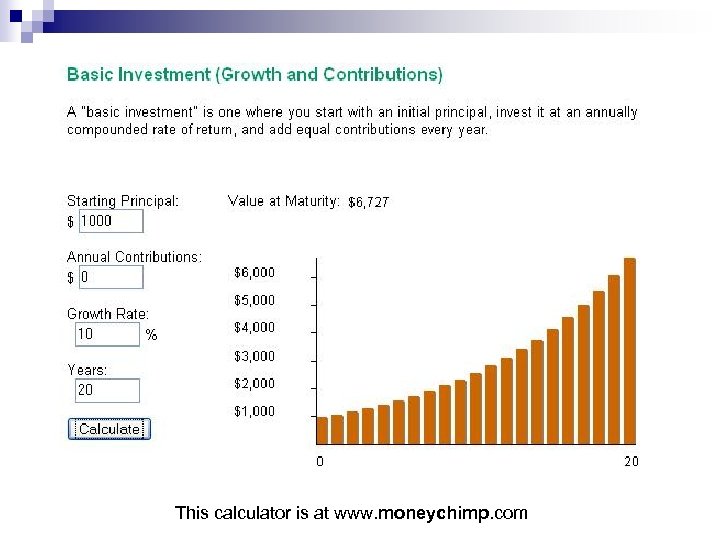 This calculator is at www. moneychimp. com
This calculator is at www. moneychimp. com
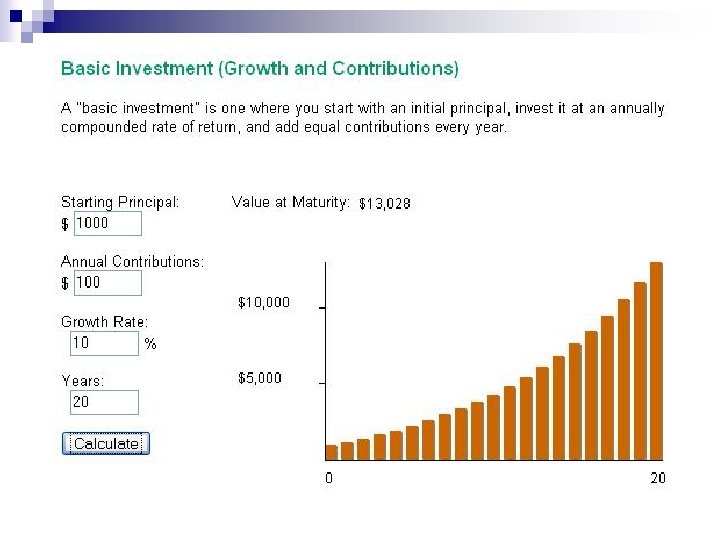
 A Word About Dollar Cost Averaging When an investor puts a little bit in his investment on a regular basis (i. e. every paycheck) he is said to be Dollar Cost Averaging. n The idea is to but more shares when the market is down and fewer shares when the market is up n
A Word About Dollar Cost Averaging When an investor puts a little bit in his investment on a regular basis (i. e. every paycheck) he is said to be Dollar Cost Averaging. n The idea is to but more shares when the market is down and fewer shares when the market is up n
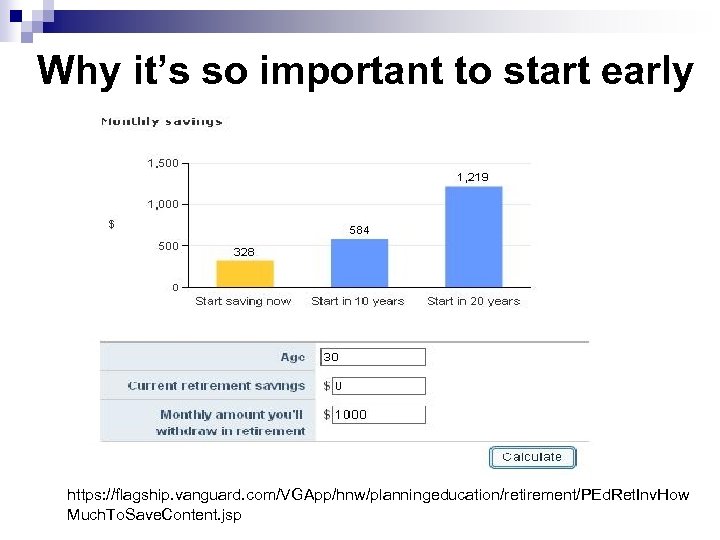 Why it’s so important to start early https: //flagship. vanguard. com/VGApp/hnw/planningeducation/retirement/PEd. Ret. Inv. How Much. To. Save. Content. jsp
Why it’s so important to start early https: //flagship. vanguard. com/VGApp/hnw/planningeducation/retirement/PEd. Ret. Inv. How Much. To. Save. Content. jsp
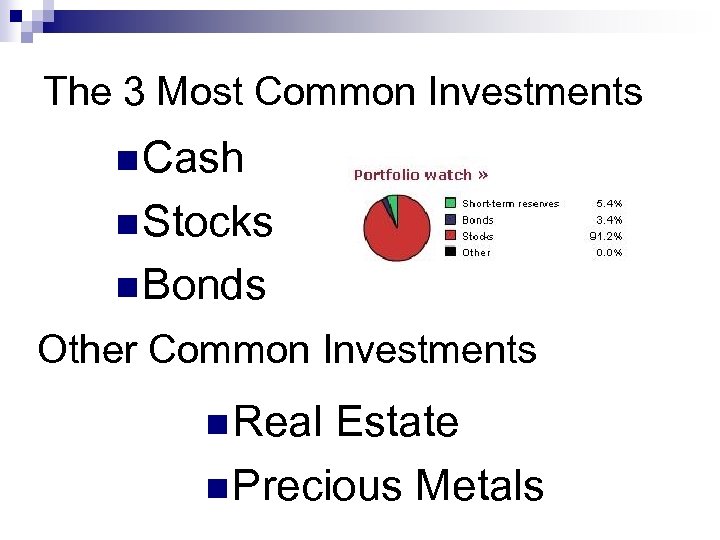 The 3 Most Common Investments n Cash n Stocks n Bonds Other Common Investments n Real Estate n Precious Metals
The 3 Most Common Investments n Cash n Stocks n Bonds Other Common Investments n Real Estate n Precious Metals
 Cash n Cash refers to money you have in a bank account, money market, or C. D. type of investment. n These accounts are virtually guaranteed to pay you the interest they promise. n They are considered very low risk, and usually low reward
Cash n Cash refers to money you have in a bank account, money market, or C. D. type of investment. n These accounts are virtually guaranteed to pay you the interest they promise. n They are considered very low risk, and usually low reward
 Bonds n When you purchase a bond, you are really loaning money to either a government or company and they are promising to pay you back with interest n There are MANY types of bonds.
Bonds n When you purchase a bond, you are really loaning money to either a government or company and they are promising to pay you back with interest n There are MANY types of bonds.
 The Stock Market n When you buy a stock, you are buying a piece of a company (a share) that someone else is selling OR n During an IPO (Initial Public Offering) you are still buying shares, but now you are giving money to the actual company.
The Stock Market n When you buy a stock, you are buying a piece of a company (a share) that someone else is selling OR n During an IPO (Initial Public Offering) you are still buying shares, but now you are giving money to the actual company.
 Risk vs. Reward n Risk : Anything that can cause your investment to go down in value n Reward : Your investment goes up in value
Risk vs. Reward n Risk : Anything that can cause your investment to go down in value n Reward : Your investment goes up in value
 Risk vs. Reward n There is no such thing as reward without risk in investing. n As a general rule, the higher the potential reward, the greater the risk Loan $20, 000 to a friend to go drill for oil n Put $20, 000 in a C. D. n
Risk vs. Reward n There is no such thing as reward without risk in investing. n As a general rule, the higher the potential reward, the greater the risk Loan $20, 000 to a friend to go drill for oil n Put $20, 000 in a C. D. n
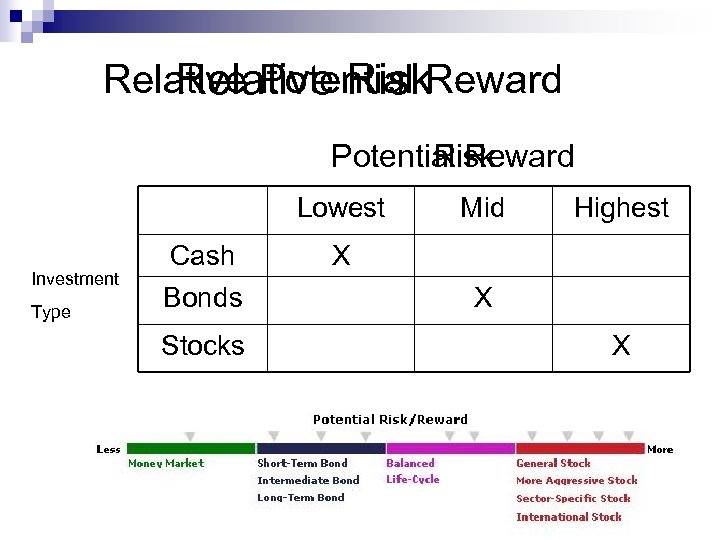 Relative Potential Reward Relative Risk Potential Reward Risk Lowest Investment Type Cash Bonds Stocks Mid Highest X X X
Relative Potential Reward Relative Risk Potential Reward Risk Lowest Investment Type Cash Bonds Stocks Mid Highest X X X
 Potential Reward when Investing in Cash n You will earn the percent the investment guarantees. n These percentages usually run in the 1%5% Range
Potential Reward when Investing in Cash n You will earn the percent the investment guarantees. n These percentages usually run in the 1%5% Range
 Types of Risks when Investing in Cash n Inflation Risk : The rate of inflation may outpace your rate of return n The Risk of the Unexpected:
Types of Risks when Investing in Cash n Inflation Risk : The rate of inflation may outpace your rate of return n The Risk of the Unexpected:
 Potential Reward when Investing in Bonds n The long term rate of return on Bonds is in the 6 -7% range.
Potential Reward when Investing in Bonds n The long term rate of return on Bonds is in the 6 -7% range.
 Types of Risks when Investing in Bonds n Call Risk : The issuer of the bond decides to pay off in full their obligation on their bonds n Credit Risk : The issuer of the bond fails to pay their interest or principal (default)(The federal government has never defaulted on a bond obligation) n Interest Rate Risk : changing interest rates cause bond prices to change
Types of Risks when Investing in Bonds n Call Risk : The issuer of the bond decides to pay off in full their obligation on their bonds n Credit Risk : The issuer of the bond fails to pay their interest or principal (default)(The federal government has never defaulted on a bond obligation) n Interest Rate Risk : changing interest rates cause bond prices to change
 Potential Reward when Investing in Stocks n The historical long term rate of return on Stocks is around 10%
Potential Reward when Investing in Stocks n The historical long term rate of return on Stocks is around 10%
 Types of Risks when Investing in Stocks n Market Risk : The Stock Market can (and will) go down over certain time intervals n Investment Style Risk : The specific types of stocks you invest in can (and will) go down n Manager Risk : the person you have picking your stocks picks bad ones n Expense Risk : The fees you pay cut into your gains
Types of Risks when Investing in Stocks n Market Risk : The Stock Market can (and will) go down over certain time intervals n Investment Style Risk : The specific types of stocks you invest in can (and will) go down n Manager Risk : the person you have picking your stocks picks bad ones n Expense Risk : The fees you pay cut into your gains
 The Million Dollar Question How do you know how much of my money to put in each type of investment?
The Million Dollar Question How do you know how much of my money to put in each type of investment?
 Asset Allocation n Your ASSET ALLOCATION is the answer to your million dollar question. n Asset Allocation means what percent of your money is invested in each type of investment.
Asset Allocation n Your ASSET ALLOCATION is the answer to your million dollar question. n Asset Allocation means what percent of your money is invested in each type of investment.
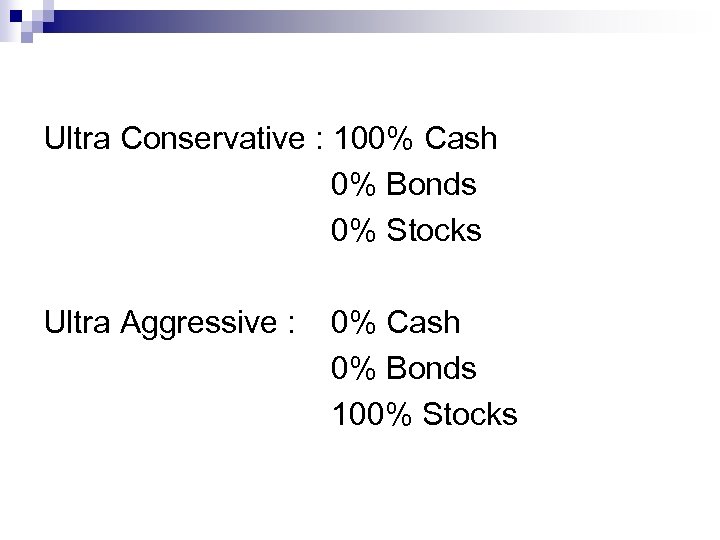 Ultra Conservative : 100% Cash 0% Bonds 0% Stocks Ultra Aggressive : 0% Cash 0% Bonds 100% Stocks
Ultra Conservative : 100% Cash 0% Bonds 0% Stocks Ultra Aggressive : 0% Cash 0% Bonds 100% Stocks
 What is your personal Asset Allocation n Your asset allocation is based on your risk tolerance, and there is no one size fits all formula n Your risk tolerance is a function of… ¨ Your age ¨ Your personal risk tolerance ¨ Your financial position
What is your personal Asset Allocation n Your asset allocation is based on your risk tolerance, and there is no one size fits all formula n Your risk tolerance is a function of… ¨ Your age ¨ Your personal risk tolerance ¨ Your financial position
 Marge: 24 years old. n No family yet n Has $100 per month to invest n
Marge: 24 years old. n No family yet n Has $100 per month to invest n
 Bill 45 years old n Has 14 years until retirement n Has $100 per month to invest and already has $70, 000 in his 403(b)(7) n
Bill 45 years old n Has 14 years until retirement n Has $100 per month to invest and already has $70, 000 in his 403(b)(7) n
 Jane 62 years old n Retiring next year n Already has $200, 000 in her 403(b)(7) n Will rely on this money for retirement income n
Jane 62 years old n Retiring next year n Already has $200, 000 in her 403(b)(7) n Will rely on this money for retirement income n
 The General Rule You should have a number of months worth of emergency money in cash. n The younger you are, the greater percentage of your money that should be in stocks. n The closer you get to needing your money for daily living, the more that should be in bonds and cash n
The General Rule You should have a number of months worth of emergency money in cash. n The younger you are, the greater percentage of your money that should be in stocks. n The closer you get to needing your money for daily living, the more that should be in bonds and cash n
 A Balanced Portfolio n A balanced portfolio is one that is adequately spread out within asset classes according to your asset allocation plan.
A Balanced Portfolio n A balanced portfolio is one that is adequately spread out within asset classes according to your asset allocation plan.
 Asset Allocation Over Time n Most advisors recommend that as you age, you want to adjust you asset allocation to have less in stocks and more in bonds over time. n That way, as you get closer to needing the money, bad years in the market won’t substantially deplete your nest egg
Asset Allocation Over Time n Most advisors recommend that as you age, you want to adjust you asset allocation to have less in stocks and more in bonds over time. n That way, as you get closer to needing the money, bad years in the market won’t substantially deplete your nest egg
 What you want in your Asset Allocation n You want Diversification n Diversification : your assets are spread out within your asset allocation plan
What you want in your Asset Allocation n You want Diversification n Diversification : your assets are spread out within your asset allocation plan
 Bad Plan on a 100, 000 Portfolio Stocks 40% Bonds 40% Cash 20% Stocks: Microsoft $25, 000 Wal-Mart $15, 000 Bonds: Ford Motor Company Corporate Bonds $40, 000 Cash: A 6 month C. D. $20, 000
Bad Plan on a 100, 000 Portfolio Stocks 40% Bonds 40% Cash 20% Stocks: Microsoft $25, 000 Wal-Mart $15, 000 Bonds: Ford Motor Company Corporate Bonds $40, 000 Cash: A 6 month C. D. $20, 000
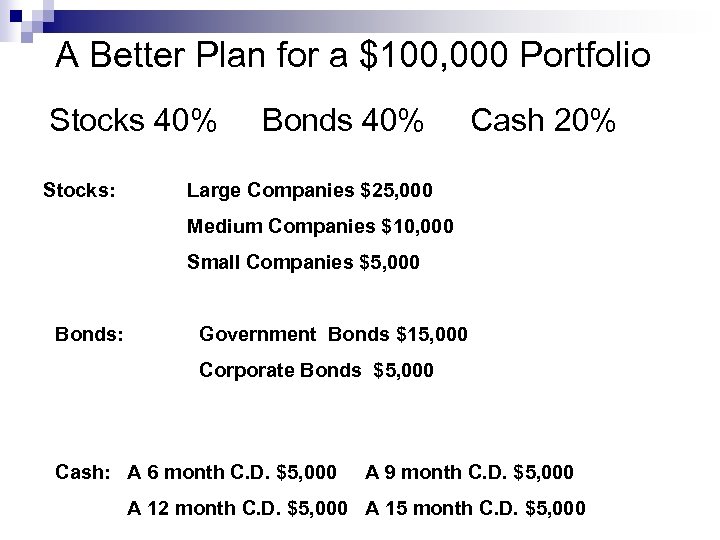 A Better Plan for a $100, 000 Portfolio Stocks 40% Stocks: Bonds 40% Cash 20% Large Companies $25, 000 Medium Companies $10, 000 Small Companies $5, 000 Bonds: Government Bonds $15, 000 Corporate Bonds $5, 000 Cash: A 6 month C. D. $5, 000 A 9 month C. D. $5, 000 A 12 month C. D. $5, 000 A 15 month C. D. $5, 000
A Better Plan for a $100, 000 Portfolio Stocks 40% Stocks: Bonds 40% Cash 20% Large Companies $25, 000 Medium Companies $10, 000 Small Companies $5, 000 Bonds: Government Bonds $15, 000 Corporate Bonds $5, 000 Cash: A 6 month C. D. $5, 000 A 9 month C. D. $5, 000 A 12 month C. D. $5, 000 A 15 month C. D. $5, 000
 What to Avoid n You want to avoid having too high a percentage of your money in any one place at any one time. n Enron
What to Avoid n You want to avoid having too high a percentage of your money in any one place at any one time. n Enron
 What a Professional Financial Advisor Does 1. 2. 3. Assess your risk tolerance Set up a diversified portfolio Manage your portfolio over time
What a Professional Financial Advisor Does 1. 2. 3. Assess your risk tolerance Set up a diversified portfolio Manage your portfolio over time
 Finding your own Asset Allocation n Go to almost any financial companies website and search asset allocation. n Try Vanguard, Fidelity, T. Rowe Price and then compare what each company says. n Google asset allocation, don’t do the ones you have to pay for.
Finding your own Asset Allocation n Go to almost any financial companies website and search asset allocation. n Try Vanguard, Fidelity, T. Rowe Price and then compare what each company says. n Google asset allocation, don’t do the ones you have to pay for.
 Summary of Part 1
Summary of Part 1
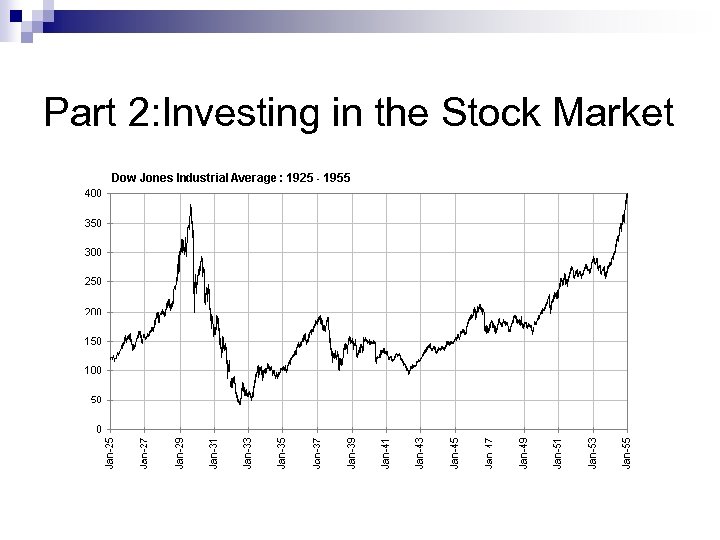 Part 2: Investing in the Stock Market
Part 2: Investing in the Stock Market
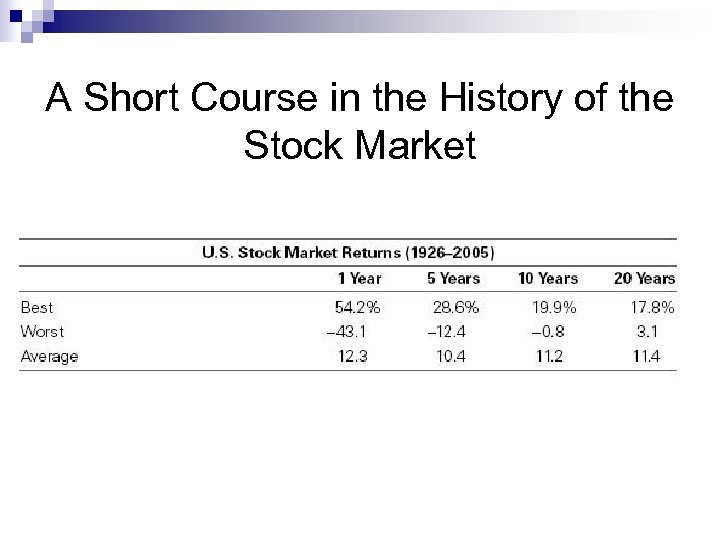 A Short Course in the History of the Stock Market
A Short Course in the History of the Stock Market
 Mutual Funds n Purchasing shares of a mutual fund means you are buying shares of many companies at one time n Example of a Vanguard Fund n Why buy Mutual Funds as opposed to buying individual stocks?
Mutual Funds n Purchasing shares of a mutual fund means you are buying shares of many companies at one time n Example of a Vanguard Fund n Why buy Mutual Funds as opposed to buying individual stocks?
 Diversify, Diversify n The point of buying many companies is to reduce risk, which of course reduces potential gain, but it keeps risk at a manageable level
Diversify, Diversify n The point of buying many companies is to reduce risk, which of course reduces potential gain, but it keeps risk at a manageable level
 The two main types of mutual funds n Index : An index is used to decide what stocks to hold in your fund : S&P 500, Wilshire 5000, Russell 2000, Dow Jones n Active : A fund manager, or a team of managers, decides what stocks to hold in your fund n American Fund Managers
The two main types of mutual funds n Index : An index is used to decide what stocks to hold in your fund : S&P 500, Wilshire 5000, Russell 2000, Dow Jones n Active : A fund manager, or a team of managers, decides what stocks to hold in your fund n American Fund Managers
 Fees and Expenses Expense Ratio n All Mutual Funds charge an expense ratio n Some mutual funds charge 12 b-1 (advertising) fees n Some funds are load funds that have a sales charge when you either buy or sell fund shares n
Fees and Expenses Expense Ratio n All Mutual Funds charge an expense ratio n Some mutual funds charge 12 b-1 (advertising) fees n Some funds are load funds that have a sales charge when you either buy or sell fund shares n
 Lets Compare Two Funds n The Vanguard Small Cap Index Fund n The Trend-Star Small Cap Fund
Lets Compare Two Funds n The Vanguard Small Cap Index Fund n The Trend-Star Small Cap Fund
 The Prospectus
The Prospectus
 Fund Strategies Active. Fund Index Fund n The strategy of an index fund is to mimic a particular index. n Vanguard 500 Fund
Fund Strategies Active. Fund Index Fund n The strategy of an index fund is to mimic a particular index. n Vanguard 500 Fund
 Who Manages the Active. Fund Index Fund n Nobody
Who Manages the Active. Fund Index Fund n Nobody
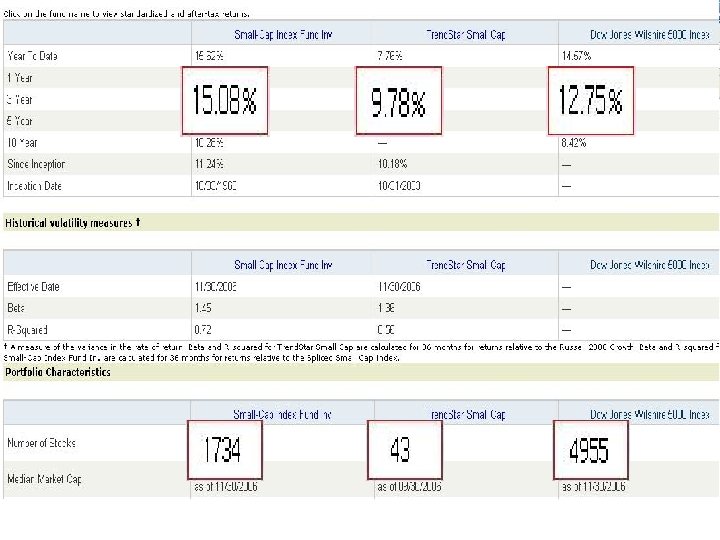 Judging Performance
Judging Performance
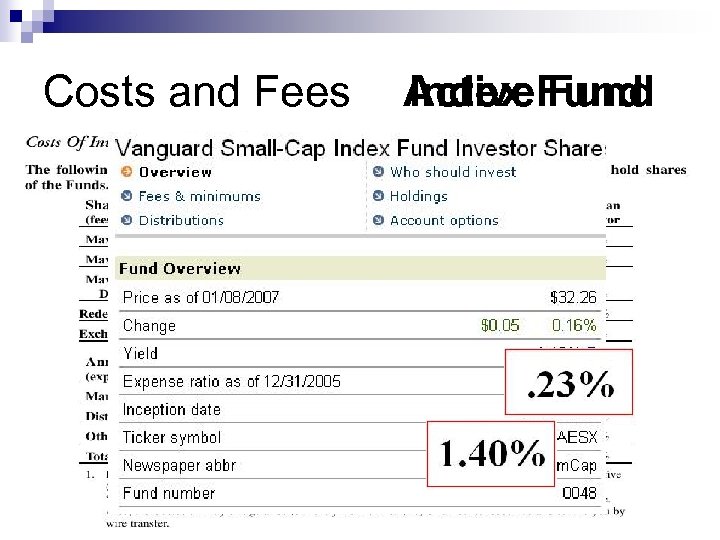 Costs and Fees Active. Fund Index Fund
Costs and Fees Active. Fund Index Fund
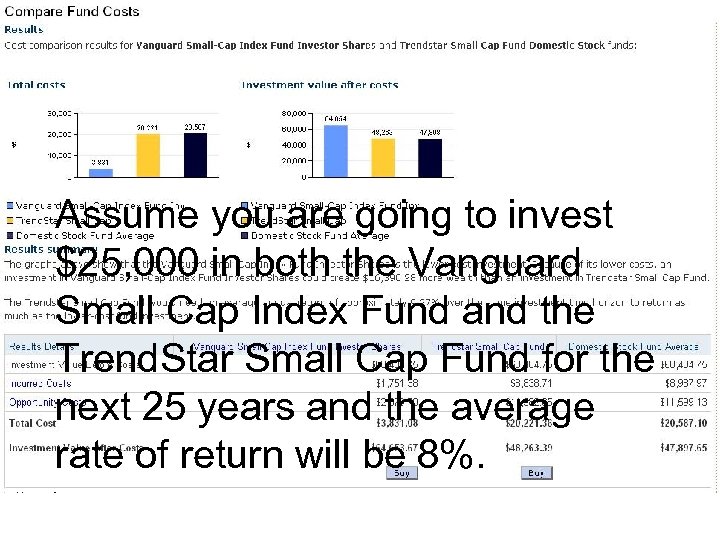 Do Expenses Really Matter? Assume you are going to invest $25, 000 in both the Vanguard Small Cap Index Fund and the Trend. Star Small Cap Fund for the next 25 years and the average rate of return will be 8%.
Do Expenses Really Matter? Assume you are going to invest $25, 000 in both the Vanguard Small Cap Index Fund and the Trend. Star Small Cap Fund for the next 25 years and the average rate of return will be 8%.
 David Serchuk and James M. Clash June 5 th, 2006 Forbes Magazine n There's a bracing logic to letting your money ride on an S&P 500 index fund. The most celebrated of them, the Vanguard 500 Index, has beaten 60% of all actively managed domestic stock funds over the past ten years. Buying an index fund means giving up on picking a smart money manager. But this saves you money management fees and also spares you the worry that your manager will do much worse than the averages.
David Serchuk and James M. Clash June 5 th, 2006 Forbes Magazine n There's a bracing logic to letting your money ride on an S&P 500 index fund. The most celebrated of them, the Vanguard 500 Index, has beaten 60% of all actively managed domestic stock funds over the past ten years. Buying an index fund means giving up on picking a smart money manager. But this saves you money management fees and also spares you the worry that your manager will do much worse than the averages.
 My Recommendations for Learning About Investing n Subscribe to Money Magazine (and read it). n Read Teach and Retire Rich by Dan Otter available at the www. 403 bwise. com website n Read the business section every day, especially the personal finance section n Find a friend to take the journey with you
My Recommendations for Learning About Investing n Subscribe to Money Magazine (and read it). n Read Teach and Retire Rich by Dan Otter available at the www. 403 bwise. com website n Read the business section every day, especially the personal finance section n Find a friend to take the journey with you


