Inventory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Inventories Perpetual and periodic systems Done by Serik Akbota Sultanova Muldir

Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. Definition of Inventory systems Advantages and disadvantages of systems Perpetual vs. Periodic Inventory System Journal Entries

Defining Inventory 1. Assets held for resale purpose in a normal course of business. 2. Assets used to produce products for resale purpose. Merchandising Firms: merchandise Manufacturing Firms: raw materials Work-in-process Finished Goods

How to Account for Inventory Purchases, Sales and Reporting? Applying either the periodic inventory system or the perpetual inventory system and select a cost flow assumption to determine the value of inventories. Both inventory systems require a physical count of inventory at the end of a period to determine the units which can be included in the inventory count.

Inventory Systems Perpetual system -Inventory records are updated after each purchases or sale Periodic system -Inventory records are updated periodically based on physical inventory counts

Perpetual Inventory System Inventory subsidiary ledger is updated after each transaction. • Inventory quantities are updated continuously. •

Periodic Inventory System Inventory subsidiary ledger is not updated after each purchase or sale of inventory. • Inventory quantities are not updated continuously. • Inventory quantities are updated on a periodic basis. •

Advantages Perpetual The primary advantage of the perpetual system is that it allows companies to take an immediate measure of their inventory at any given time. Disadvantages The implementation and cost of maintaining the perpetual inventory system is the biggest disadvantage as it may require extra staffing and technology.

Advantages Periodic The main advantage of the periodic inventory system is that it is simple and easy to maintain. Disadvantages A disadvantage of the periodic system is that companies are not aware of how much inventory is on hand until the end of the accounting period.
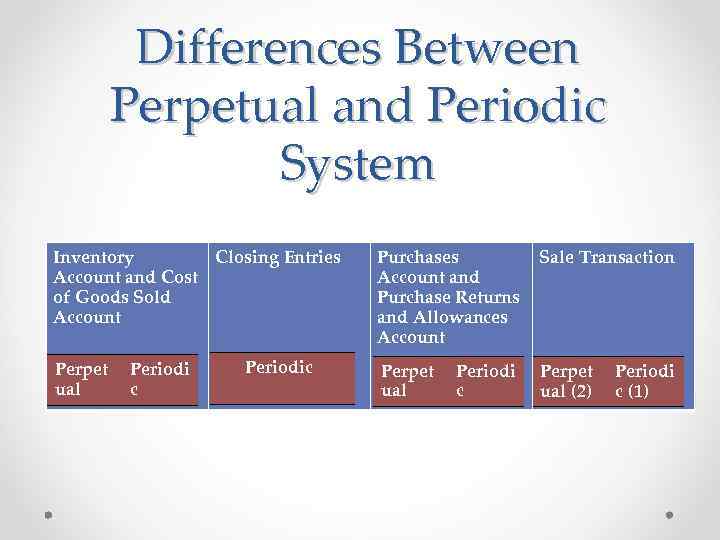
Differences Between Perpetual and Periodic System Inventory Closing Entries Account and Cost of Goods Sold Account Perpet ual Periodi c Periodic Purchases Account and Purchase Returns and Allowances Account Sale Transaction Perpet ual (2) Periodi c (1)

Inventory Account and Cost of Goods Sold Account Example: (Unit cost is held constant to avoid the necessity of a using a cost flow assumption) Beginning inventory 100 units @ $6 = $600 Purchases 900 units @ $6 = $5, 400 Sales 600 units @ $12 = $7, 200 Ending inventory 400 units @ $6 =$2, 400
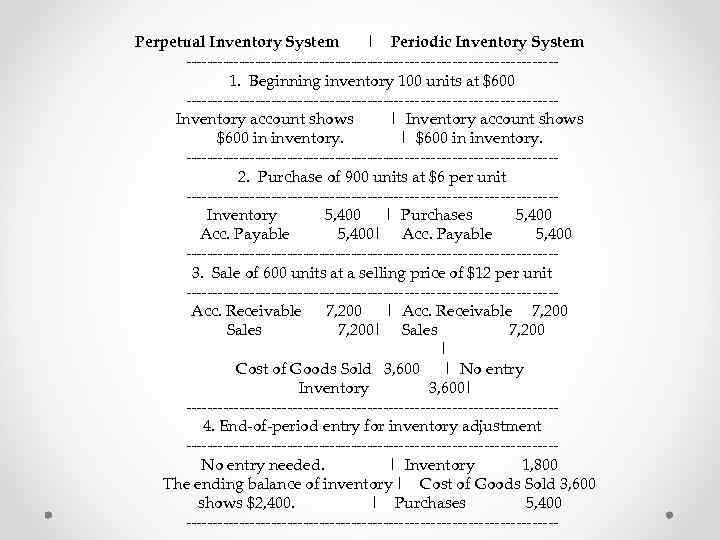
Perpetual Inventory System | Periodic Inventory System -----------------------------------1. Beginning inventory 100 units at $600 -----------------------------------Inventory account shows | Inventory account shows $600 in inventory. | $600 in inventory. -----------------------------------2. Purchase of 900 units at $6 per unit -----------------------------------Inventory 5, 400 | Purchases 5, 400 Acc. Payable 5, 400| Acc. Payable 5, 400 -----------------------------------3. Sale of 600 units at a selling price of $12 per unit -----------------------------------Acc. Receivable 7, 200 | Acc. Receivable 7, 200 Sales 7, 200| Sales 7, 200 | Cost of Goods Sold 3, 600 | No entry Inventory 3, 600| -----------------------------------4. End-of-period entry for inventory adjustment -----------------------------------No entry needed. | Inventory 1, 800 The ending balance of inventory | Cost of Goods Sold 3, 600 shows $2, 400. | Purchases 5, 400 -----------------------------------
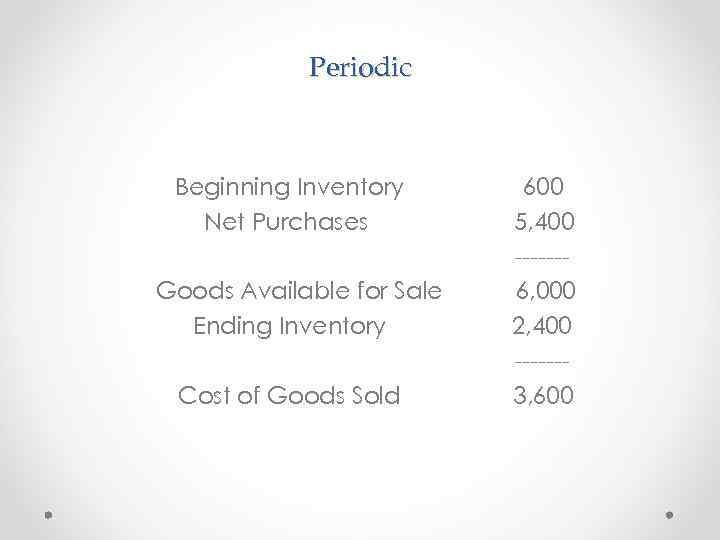
Periodic Beginning Inventory Net Purchases Goods Available for Sale Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold 600 5, 400 ------6, 000 2, 400 ------3, 600

Allowances Account Perpetual Inventory System | Periodic Inventory System -----------------------------------1. Ace Company returned $600 of damaged merchandise and received a price reduction allowance of $100 on the portion of the merchandise they retained. -----------------------------------Acc. Payable 700 | Acc. Payable 700 Inventory 700 | Purch. R&A 700 -----------------------------------2. In a previous transaction, Ace purchased merchandise on account at a cost of $1, 000. The credit terms were 2/10, n/30. Ace paid for the merchandise within the discount period. -----------------------------------Acc. Payable 1, 000 | Acc. Payable 1, 000 Inventory 20 | Purch. Disc. 20 Cash 980 | Cash 980 ------------------------------------

Sale Transaction Perpetual Inventory System | Periodic Inventory System -----------------------------------1. Sam Company received $600 of damaged merchandise from their customer Ace. They also gave Ace a $100 allowance for some of the damaged merchandise that Ace retained. The original cost of the merchandise returned to Sam was $400. -----------------------------------Sales R&A 700 | Sales R&A 700 Acc. Receivable 700 | Inventory 400 | No entry Cost of Goods Sold 400 | -----------------------------------2. Sam received a customer payment for a prior sale on account of $1, 000 subject to credit terms of 2/10, n/30. The customer made payment within the discount period. -----------------------------------Cash 980 | Cash 980 Sales Disc. 20 | Sales Disc. 20 Acc. Receivable 1, 000| Acc. Receivable 1, 000 ------------------------------------

Thank you!
Inventory.ppt