b285d30f76d9559db7fae9b0f9d6a4c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Introductions to the Metrological Control System of Japan and Roles of NMIJ in AIST Dr. Tsuyoshi Matsumoto Chair of APLMF WG on Quality Measurements of Agricultural Products (QMAP) National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) at APLMF Training Course on Traceability in Rice Moisture Measurement 25 - 29 November, 2013 Chiang Mai, Thailand 1
Introductions to the Metrological Control System of Japan and Roles of NMIJ in AIST Dr. Tsuyoshi Matsumoto Chair of APLMF WG on Quality Measurements of Agricultural Products (QMAP) National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) at APLMF Training Course on Traceability in Rice Moisture Measurement 25 - 29 November, 2013 Chiang Mai, Thailand 1
 1. Basic Metrological System of Japan 1. 1 Measurement Act (Law) History of Measurement Act • 701: The origin of legal metrology is found in “Taiho Code”. • 1885: Japan participated in the Meter Convention. • 1891: “Act of Weight and Measures” was enforced, and a transition to SI system started. • 1951: “Measurement Act” was enforced. Use of SI was required. • 1992: The act was largely amended to correspond the needs from society, industries and international organizations. Outline of the Act • Supported with cabinet orders and ministerial ordinances. • Aims establishing measurement standard, and accurate measurement for transaction / certification in legal units. • Defines specified measuring instruments, and initial / periodic verification system for legal control. 2 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
1. Basic Metrological System of Japan 1. 1 Measurement Act (Law) History of Measurement Act • 701: The origin of legal metrology is found in “Taiho Code”. • 1885: Japan participated in the Meter Convention. • 1891: “Act of Weight and Measures” was enforced, and a transition to SI system started. • 1951: “Measurement Act” was enforced. Use of SI was required. • 1992: The act was largely amended to correspond the needs from society, industries and international organizations. Outline of the Act • Supported with cabinet orders and ministerial ordinances. • Aims establishing measurement standard, and accurate measurement for transaction / certification in legal units. • Defines specified measuring instruments, and initial / periodic verification system for legal control. 2 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
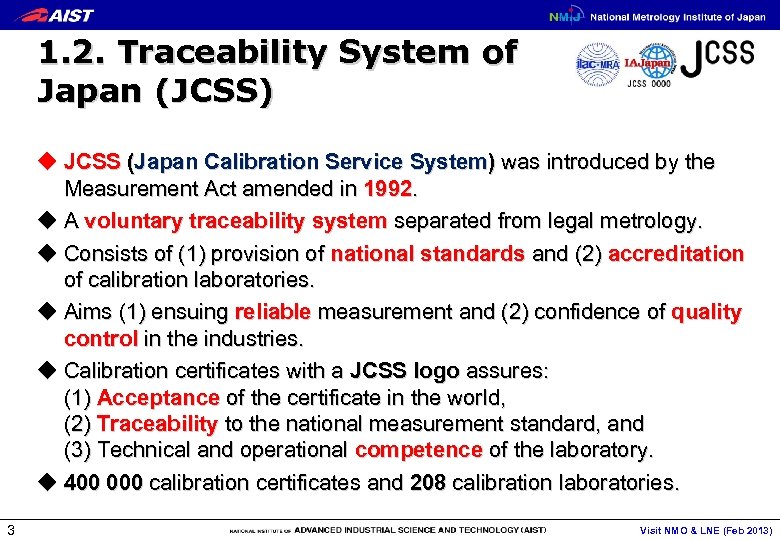 1. 2. Traceability System of Japan (JCSS) u JCSS (Japan Calibration Service System) was introduced by the Measurement Act amended in 1992. u A voluntary traceability system separated from legal metrology. u Consists of (1) provision of national standards and (2) accreditation of calibration laboratories. u Aims (1) ensuing reliable measurement and (2) confidence of quality control in the industries. u Calibration certificates with a JCSS logo assures: (1) Acceptance of the certificate in the world, (2) Traceability to the national measurement standard, and (3) Technical and operational competence of the laboratory. u 400 000 calibration certificates and 208 calibration laboratories. 3 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
1. 2. Traceability System of Japan (JCSS) u JCSS (Japan Calibration Service System) was introduced by the Measurement Act amended in 1992. u A voluntary traceability system separated from legal metrology. u Consists of (1) provision of national standards and (2) accreditation of calibration laboratories. u Aims (1) ensuing reliable measurement and (2) confidence of quality control in the industries. u Calibration certificates with a JCSS logo assures: (1) Acceptance of the certificate in the world, (2) Traceability to the national measurement standard, and (3) Technical and operational competence of the laboratory. u 400 000 calibration certificates and 208 calibration laboratories. 3 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
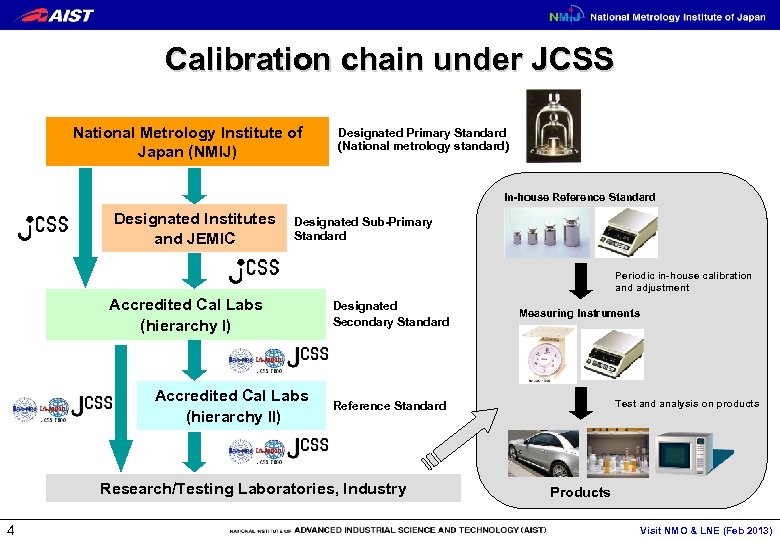 Calibration chain under JCSS National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) Designated Primary Standard (National metrology standard) In-house Reference Standard Designated Institutes and JEMIC Designated Sub-Primary Standard Periodic in-house calibration and adjustment Accredited Cal Labs (hierarchy I) Accredited Cal Labs (hierarchy II) Designated Secondary Standard Test and analysis on products Reference Standard Research/Testing Laboratories, Industry 4 Measuring Instruments Products Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Calibration chain under JCSS National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) Designated Primary Standard (National metrology standard) In-house Reference Standard Designated Institutes and JEMIC Designated Sub-Primary Standard Periodic in-house calibration and adjustment Accredited Cal Labs (hierarchy I) Accredited Cal Labs (hierarchy II) Designated Secondary Standard Test and analysis on products Reference Standard Research/Testing Laboratories, Industry 4 Measuring Instruments Products Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
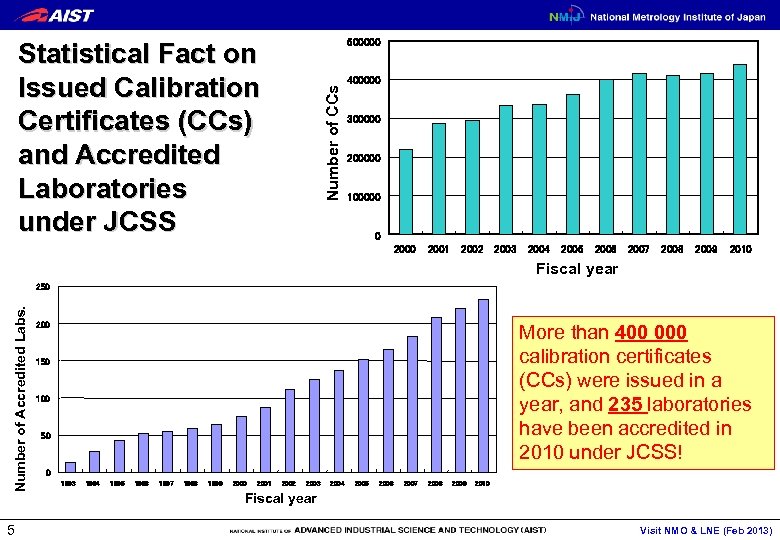 500000 Number of CCs Statistical Fact on Issued Calibration Certificates (CCs) and Accredited Laboratories under JCSS 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Fiscal year Number of Accredited Labs. 250 5 200 More than 400 000 calibration certificates (CCs) were issued in a year, and 235 laboratories have been accredited in 2010 under JCSS! 150 100 50 0 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Fiscal year Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
500000 Number of CCs Statistical Fact on Issued Calibration Certificates (CCs) and Accredited Laboratories under JCSS 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Fiscal year Number of Accredited Labs. 250 5 200 More than 400 000 calibration certificates (CCs) were issued in a year, and 235 laboratories have been accredited in 2010 under JCSS! 150 100 50 0 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Fiscal year Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 1. 2 Legal Metrology in Japan Measuring instruments under legal control Special measuring instruments controlled under legal metrology those are closely connected to safety and benefit of individuals and/or society used for: • Trade measurements, • Public health & safety, and • Environmental measurement 6 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
1. 2 Legal Metrology in Japan Measuring instruments under legal control Special measuring instruments controlled under legal metrology those are closely connected to safety and benefit of individuals and/or society used for: • Trade measurements, • Public health & safety, and • Environmental measurement 6 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
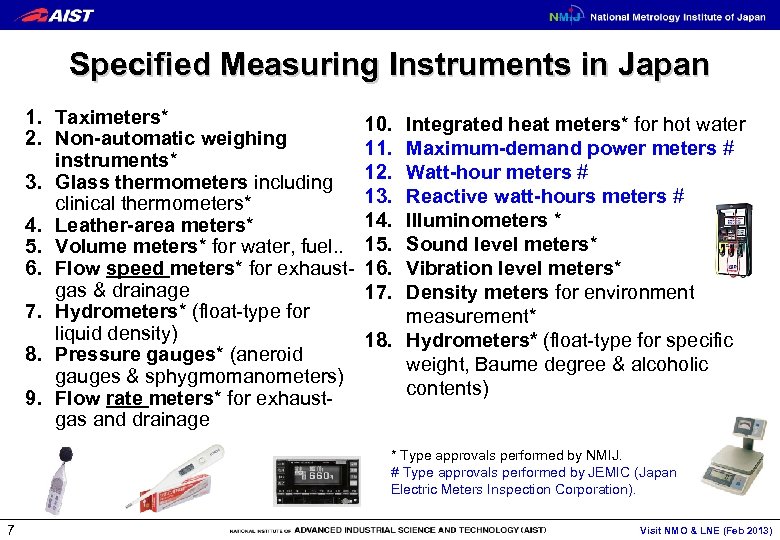 Specified Measuring Instruments in Japan 1. Taximeters* 2. Non-automatic weighing instruments* 3. Glass thermometers including clinical thermometers* 4. Leather-area meters* 5. Volume meters* for water, fuel. . 6. Flow speed meters* for exhaustgas & drainage 7. Hydrometers* (float-type for liquid density) 8. Pressure gauges* (aneroid gauges & sphygmomanometers) 9. Flow rate meters* for exhaustgas and drainage 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Integrated heat meters* for hot water Maximum-demand power meters # Watt-hour meters # Reactive watt-hours meters # Illuminometers * Sound level meters* Vibration level meters* Density meters for environment measurement* 18. Hydrometers* (float-type for specific weight, Baume degree & alcoholic contents) * Type approvals performed by NMIJ. # Type approvals performed by JEMIC (Japan Electric Meters Inspection Corporation). 7 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Specified Measuring Instruments in Japan 1. Taximeters* 2. Non-automatic weighing instruments* 3. Glass thermometers including clinical thermometers* 4. Leather-area meters* 5. Volume meters* for water, fuel. . 6. Flow speed meters* for exhaustgas & drainage 7. Hydrometers* (float-type for liquid density) 8. Pressure gauges* (aneroid gauges & sphygmomanometers) 9. Flow rate meters* for exhaustgas and drainage 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Integrated heat meters* for hot water Maximum-demand power meters # Watt-hour meters # Reactive watt-hours meters # Illuminometers * Sound level meters* Vibration level meters* Density meters for environment measurement* 18. Hydrometers* (float-type for specific weight, Baume degree & alcoholic contents) * Type approvals performed by NMIJ. # Type approvals performed by JEMIC (Japan Electric Meters Inspection Corporation). 7 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
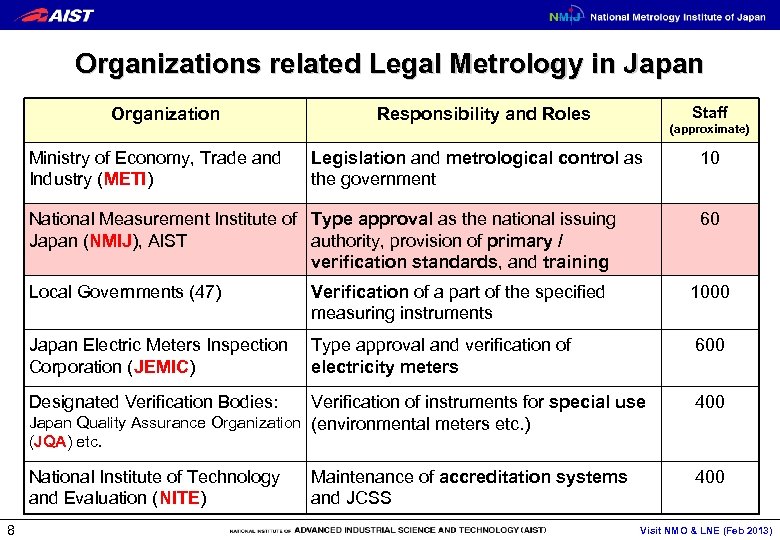 Organizations related Legal Metrology in Japan Organization Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) Staff Responsibility and Roles (approximate) Legislation and metrological control as the government National Measurement Institute of Type approval as the national issuing Japan (NMIJ), AIST authority, provision of primary / verification standards, and training 10 60 Local Governments (47) Verification of a part of the specified measuring instruments 1000 Japan Electric Meters Inspection Corporation (JEMIC) Type approval and verification of electricity meters 600 Designated Verification Bodies: Verification of instruments for special use Japan Quality Assurance Organization (environmental meters etc. ) 400 National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE) 400 (JQA) etc. 8 Maintenance of accreditation systems and JCSS Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Organizations related Legal Metrology in Japan Organization Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) Staff Responsibility and Roles (approximate) Legislation and metrological control as the government National Measurement Institute of Type approval as the national issuing Japan (NMIJ), AIST authority, provision of primary / verification standards, and training 10 60 Local Governments (47) Verification of a part of the specified measuring instruments 1000 Japan Electric Meters Inspection Corporation (JEMIC) Type approval and verification of electricity meters 600 Designated Verification Bodies: Verification of instruments for special use Japan Quality Assurance Organization (environmental meters etc. ) 400 National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE) 400 (JQA) etc. 8 Maintenance of accreditation systems and JCSS Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
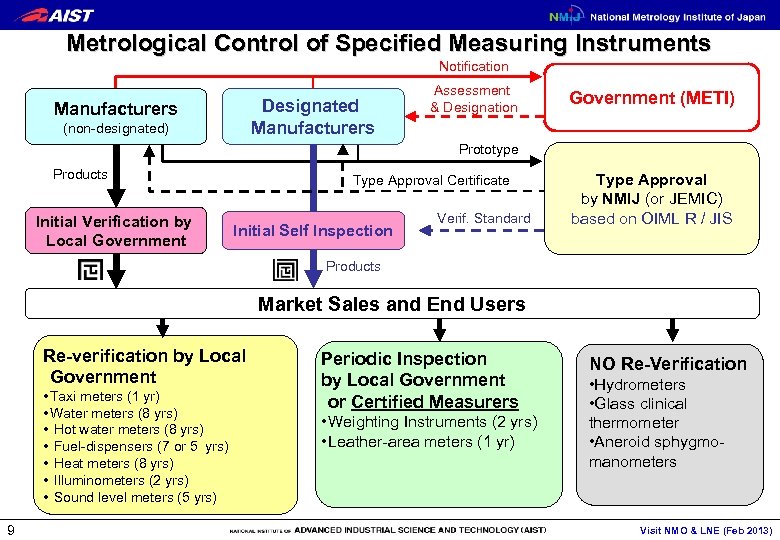 Metrological Control of Specified Measuring Instruments Notification Designated Manufacturers (non-designated) Assessment & Designation Government (METI) Prototype Products Initial Verification by Local Government Type Approval Certificate Initial Self Inspection Verif. Standard Type Approval by NMIJ (or JEMIC) based on OIML R / JIS Products Market Sales and End Users Re-verification by Local Government • Taxi meters (1 yr) • Water meters (8 yrs) • Hot water meters (8 yrs) • Fuel-dispensers (7 or 5 yrs) • Heat meters (8 yrs) • Illuminometers (2 yrs) • Sound level meters (5 yrs) 9 Periodic Inspection by Local Government or Certified Measurers • Weighting Instruments (2 yrs) • Leather-area meters (1 yr) NO Re-Verification • Hydrometers • Glass clinical thermometer • Aneroid sphygmomanometers Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Metrological Control of Specified Measuring Instruments Notification Designated Manufacturers (non-designated) Assessment & Designation Government (METI) Prototype Products Initial Verification by Local Government Type Approval Certificate Initial Self Inspection Verif. Standard Type Approval by NMIJ (or JEMIC) based on OIML R / JIS Products Market Sales and End Users Re-verification by Local Government • Taxi meters (1 yr) • Water meters (8 yrs) • Hot water meters (8 yrs) • Fuel-dispensers (7 or 5 yrs) • Heat meters (8 yrs) • Illuminometers (2 yrs) • Sound level meters (5 yrs) 9 Periodic Inspection by Local Government or Certified Measurers • Weighting Instruments (2 yrs) • Leather-area meters (1 yr) NO Re-Verification • Hydrometers • Glass clinical thermometer • Aneroid sphygmomanometers Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 1. 3 Certified Measurers System in Japan Two Types of Certified Measurers: (1) General measurers Roles: periodical inspection of NAWI and meteorological control in factories, laboratories, market, etc. (2) Environmental measurers Roles: environmental control of pollution (air / water) and sound / vibration level. Process for qualification: (1) National uniform examination (1170 examinee passed in 2010) + practical experience (2) Finish the training course in NMIJ + practical experience + approval by the Administrative Council. 10 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
1. 3 Certified Measurers System in Japan Two Types of Certified Measurers: (1) General measurers Roles: periodical inspection of NAWI and meteorological control in factories, laboratories, market, etc. (2) Environmental measurers Roles: environmental control of pollution (air / water) and sound / vibration level. Process for qualification: (1) National uniform examination (1170 examinee passed in 2010) + practical experience (2) Finish the training course in NMIJ + practical experience + approval by the Administrative Council. 10 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 2. Outline of AIST and NMIJ 2. 1 What is AIST? AIST: National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Independent administrative institution established by the integration of 15 national research institutes under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) in 2001 AIST has…. About 3, 000 employees plus over 4, 000 visiting researchers The largest research organization in the area of industrial science and technology in Japan AIST Tsukuba Headquarters / AIST Tsukuba 11 http: //www. aist. go. jp/index_en. html Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
2. Outline of AIST and NMIJ 2. 1 What is AIST? AIST: National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Independent administrative institution established by the integration of 15 national research institutes under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) in 2001 AIST has…. About 3, 000 employees plus over 4, 000 visiting researchers The largest research organization in the area of industrial science and technology in Japan AIST Tsukuba Headquarters / AIST Tsukuba 11 http: //www. aist. go. jp/index_en. html Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
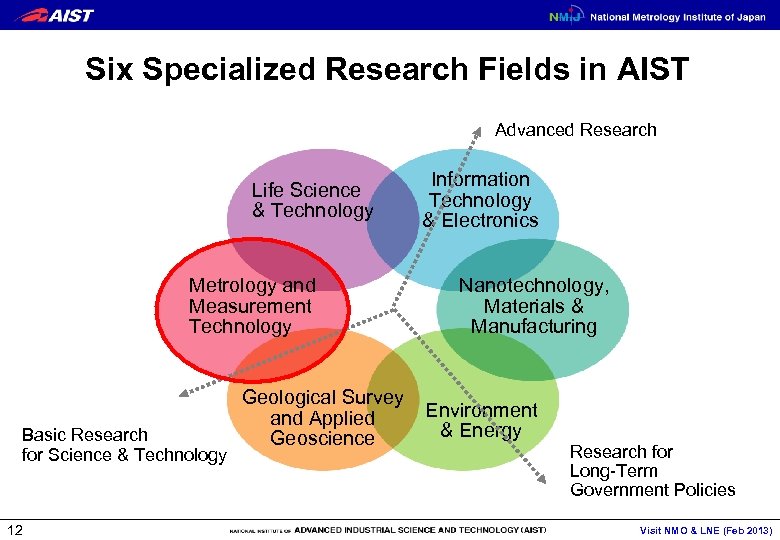 Six Specialized Research Fields in AIST Advanced Research Life Science & Technology Metrology and Measurement Technology Basic Research for Science & Technology 12 Geological Survey and Applied Geoscience Information Technology & Electronics Nanotechnology, Materials & Manufacturing Environment & Energy Research for Long-Term Government Policies Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Six Specialized Research Fields in AIST Advanced Research Life Science & Technology Metrology and Measurement Technology Basic Research for Science & Technology 12 Geological Survey and Applied Geoscience Information Technology & Electronics Nanotechnology, Materials & Manufacturing Environment & Energy Research for Long-Term Government Policies Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
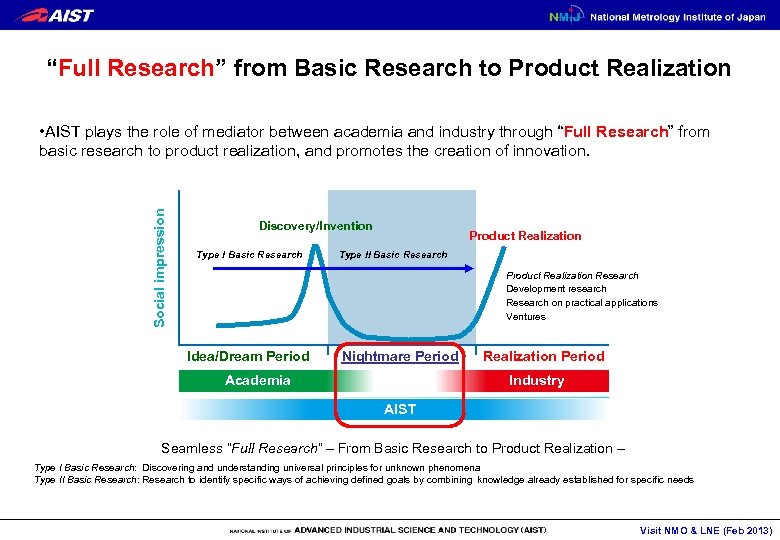 “Full Research” from Basic Research to Product Realization Social impression • AIST plays the role of mediator between academia and industry through “Full Research” from basic research to product realization, and promotes the creation of innovation. Discovery/Invention Type I Basic Research Product Realization Type II Basic Research Product Realization Research Development research Research on practical applications Ventures Idea/Dream Period Nightmare Period Academia Realization Period Industry AIST Seamless “Full Research” – From Basic Research to Product Realization – Type I Basic Research: Discovering and understanding universal principles for unknown phenomena Type II Basic Research: Research to identify specific ways of achieving defined goals by combining knowledge already established for specific needs Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
“Full Research” from Basic Research to Product Realization Social impression • AIST plays the role of mediator between academia and industry through “Full Research” from basic research to product realization, and promotes the creation of innovation. Discovery/Invention Type I Basic Research Product Realization Type II Basic Research Product Realization Research Development research Research on practical applications Ventures Idea/Dream Period Nightmare Period Academia Realization Period Industry AIST Seamless “Full Research” – From Basic Research to Product Realization – Type I Basic Research: Discovering and understanding universal principles for unknown phenomena Type II Basic Research: Research to identify specific ways of achieving defined goals by combining knowledge already established for specific needs Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
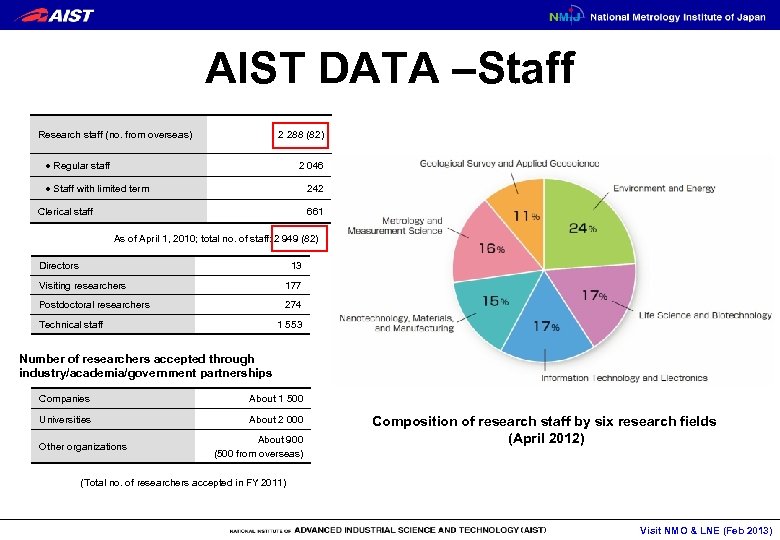 AIST DATA –Staff 2 288 (82) Research staff (no. from overseas) 2 046 ● Regular staff ● Staff with limited term 242 Clerical staff 661 As of April 1, 2010; total no. of staff: 2 949 (82) Directors 13 Visiting researchers 177 Postdoctoral researchers 274 Technical staff 1 553 Number of researchers accepted through industry/academia/government partnerships Companies About 1 500 Universities About 2 000 Other organizations About 900 (500 from overseas) Composition of research staff by six research fields (April 2012) (Total no. of researchers accepted in FY 2011) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
AIST DATA –Staff 2 288 (82) Research staff (no. from overseas) 2 046 ● Regular staff ● Staff with limited term 242 Clerical staff 661 As of April 1, 2010; total no. of staff: 2 949 (82) Directors 13 Visiting researchers 177 Postdoctoral researchers 274 Technical staff 1 553 Number of researchers accepted through industry/academia/government partnerships Companies About 1 500 Universities About 2 000 Other organizations About 900 (500 from overseas) Composition of research staff by six research fields (April 2012) (Total no. of researchers accepted in FY 2011) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
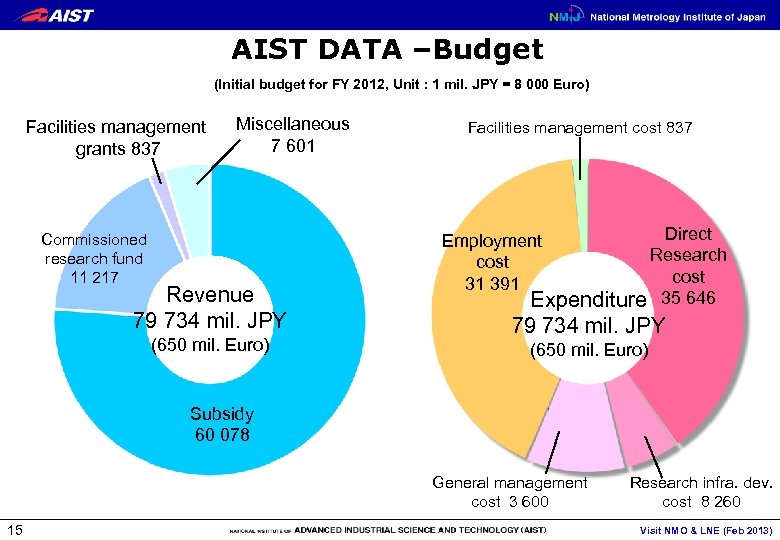 AIST DATA –Budget (Initial budget for FY 2012, Unit : 1 mil. JPY = 8 000 Euro) Facilities management grants 837 Miscellaneous 7 601 Commissioned research fund 11 217 Revenue 79 734 mil. JPY (650 mil. Euro) Facilities management cost 837 Direct Research cost Expenditure 35 646 Employment cost 31 391 79 734 mil. JPY (650 mil. Euro) Subsidy 60 078 General management cost 3 600 15 Research infra. dev. cost 8 260 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
AIST DATA –Budget (Initial budget for FY 2012, Unit : 1 mil. JPY = 8 000 Euro) Facilities management grants 837 Miscellaneous 7 601 Commissioned research fund 11 217 Revenue 79 734 mil. JPY (650 mil. Euro) Facilities management cost 837 Direct Research cost Expenditure 35 646 Employment cost 31 391 79 734 mil. JPY (650 mil. Euro) Subsidy 60 078 General management cost 3 600 15 Research infra. dev. cost 8 260 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
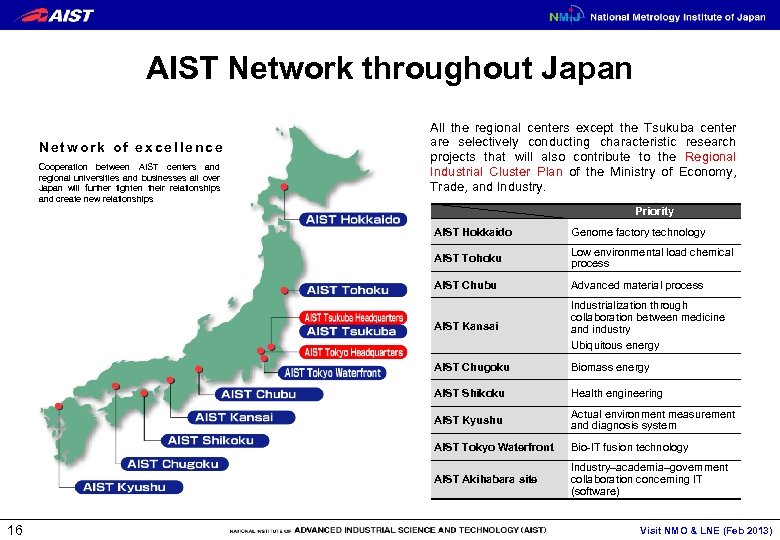 AIST Network throughout Japan Network of excellence Cooperation between AIST centers and regional universities and businesses all over Japan will further tighten their relationships and create new relationships All the regional centers except the Tsukuba center are selectively conducting characteristic research projects that will also contribute to the Regional Industrial Cluster Plan of the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry. Priority AIST Hokkaido Genome factory technology AIST Tohoku Low environmental load chemical process AIST Chubu Advanced material process AIST Kansai Industrialization through collaboration between medicine and industry Ubiquitous energy AIST Chugoku AIST Shikoku Health engineering AIST Kyushu Actual environment measurement and diagnosis system AIST Tokyo Waterfront Bio-IT fusion technology AIST Akihabara site 16 Biomass energy Industry–academia–government collaboration concerning IT (software) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
AIST Network throughout Japan Network of excellence Cooperation between AIST centers and regional universities and businesses all over Japan will further tighten their relationships and create new relationships All the regional centers except the Tsukuba center are selectively conducting characteristic research projects that will also contribute to the Regional Industrial Cluster Plan of the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry. Priority AIST Hokkaido Genome factory technology AIST Tohoku Low environmental load chemical process AIST Chubu Advanced material process AIST Kansai Industrialization through collaboration between medicine and industry Ubiquitous energy AIST Chugoku AIST Shikoku Health engineering AIST Kyushu Actual environment measurement and diagnosis system AIST Tokyo Waterfront Bio-IT fusion technology AIST Akihabara site 16 Biomass energy Industry–academia–government collaboration concerning IT (software) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 AIST Research Bases NMIJ AIST Hokkaido AIST Chugoku AIST Shikoku AIST Tsukuba Headquarters / AIST Tsukuba AIST Tohoku NMIJ AIST Kyushu 17 AIST Kansai AIST Chubu AIST Tokyo Waterfront Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
AIST Research Bases NMIJ AIST Hokkaido AIST Chugoku AIST Shikoku AIST Tsukuba Headquarters / AIST Tsukuba AIST Tohoku NMIJ AIST Kyushu 17 AIST Kansai AIST Chubu AIST Tokyo Waterfront Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 2. 2. Outline of NMIJ in AIST NMIJ: National Metrology Institute of Japan National Research Laboratory of Metrology (NRLM) Physical and Mechanical Standards Electrotechnical Laboratory (ETL) Electrical Standards National Metrology Institute of Japan ( found in 2001 ) http: //www. nmij. jp/english/ National Institute of Materials and Chemical Research (NIMC) Reference Materials Metrology Training Center NMIJ Headquarters Training 18 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
2. 2. Outline of NMIJ in AIST NMIJ: National Metrology Institute of Japan National Research Laboratory of Metrology (NRLM) Physical and Mechanical Standards Electrotechnical Laboratory (ETL) Electrical Standards National Metrology Institute of Japan ( found in 2001 ) http: //www. nmij. jp/english/ National Institute of Materials and Chemical Research (NIMC) Reference Materials Metrology Training Center NMIJ Headquarters Training 18 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
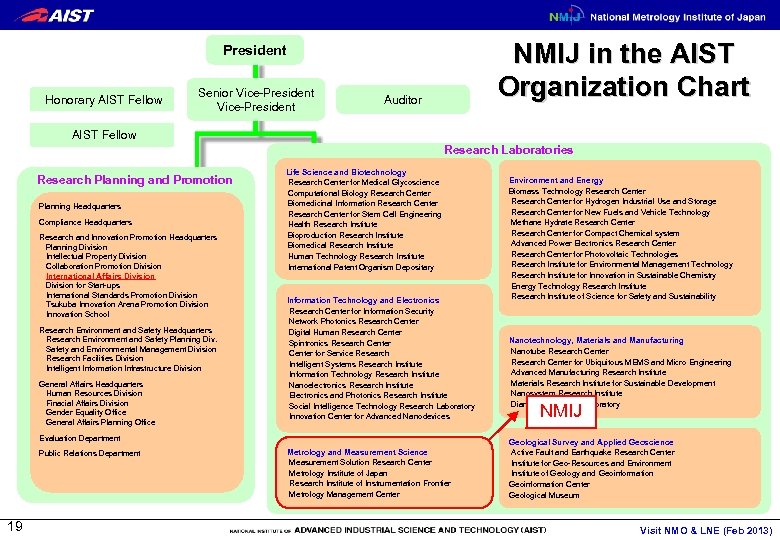 NMIJ in the AIST Organization Chart President Honorary AIST Fellow Senior Vice-President Auditor AIST Fellow Research Laboratories Research Planning and Promotion Planning Headquarters Compliance Headquarters Research and Innovation Promotion Headquarters Planning Division Intellectual Property Division Collaboration Promotion Division International Affairs Division for Start-ups International Standards Promotion Division Tsukuba Innovation Arena Promotion Division Innovation School Research Environment and Safety Headquarters Research Environment and Safety Planning Div. Safety and Environmental Management Division Research Facilities Division Intelligent Information Infrastructure Division General Affairs Headquarters Human Resources Division Finacial Affairs Division Gender Equality Office General Affairs Planning Office Life Science and Biotechnology Research Center for Medical Glycoscience Computational Biology Research Center Biomedicinal Information Research Center for Stem Cell Engineering Health Research Institute Bioproduction Research Institute Biomedical Research Institute Human Technology Research Institute International Patent Organism Depositary Information Technology and Electronics Research Center for Information Security Network Photonics Research Center Digital Human Research Center Spintronics Research Center for Service Research Intelligent Systems Research Institute Information Technology Research Institute Nanoelectronics Research Institute Electronics and Photonics Research Institute Social Intelligence Technology Research Laboratory Innovation Center for Advanced Nanodevices Evaluation Department Public Relations Department 19 Metrology and Measurement Science Measurement Solution Research Center Metrology Institute of Japan Research Institute of Instrumentation Frontier Metrology Management Center Environment and Energy Biomass Technology Research Center for Hydrogen Industrial Use and Storage Research Center for New Fuels and Vehicle Technology Methane Hydrate Research Center for Compact Chemical system Advanced Power Electronics Research Center for Photovoltaic Technologies Research Institute for Environmental Management Technology Research Institute for Innovation in Sustainable Chemistry Energy Technology Research Institute of Science for Safety and Sustainability Nanotechnology, Materials and Manufacturing Nanotube Research Center for Ubiquitous MEMS and Micro Engineering Advanced Manufacturing Research Institute Materials Research Institute for Sustainable Development Nanosystem Research Institute Diamond Research Laboratory NMIJ Geological Survey and Applied Geoscience Active Fault and Earthquake Research Center Institute for Geo-Resources and Environment Institute of Geology and Geoinformation Center Geological Museum Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
NMIJ in the AIST Organization Chart President Honorary AIST Fellow Senior Vice-President Auditor AIST Fellow Research Laboratories Research Planning and Promotion Planning Headquarters Compliance Headquarters Research and Innovation Promotion Headquarters Planning Division Intellectual Property Division Collaboration Promotion Division International Affairs Division for Start-ups International Standards Promotion Division Tsukuba Innovation Arena Promotion Division Innovation School Research Environment and Safety Headquarters Research Environment and Safety Planning Div. Safety and Environmental Management Division Research Facilities Division Intelligent Information Infrastructure Division General Affairs Headquarters Human Resources Division Finacial Affairs Division Gender Equality Office General Affairs Planning Office Life Science and Biotechnology Research Center for Medical Glycoscience Computational Biology Research Center Biomedicinal Information Research Center for Stem Cell Engineering Health Research Institute Bioproduction Research Institute Biomedical Research Institute Human Technology Research Institute International Patent Organism Depositary Information Technology and Electronics Research Center for Information Security Network Photonics Research Center Digital Human Research Center Spintronics Research Center for Service Research Intelligent Systems Research Institute Information Technology Research Institute Nanoelectronics Research Institute Electronics and Photonics Research Institute Social Intelligence Technology Research Laboratory Innovation Center for Advanced Nanodevices Evaluation Department Public Relations Department 19 Metrology and Measurement Science Measurement Solution Research Center Metrology Institute of Japan Research Institute of Instrumentation Frontier Metrology Management Center Environment and Energy Biomass Technology Research Center for Hydrogen Industrial Use and Storage Research Center for New Fuels and Vehicle Technology Methane Hydrate Research Center for Compact Chemical system Advanced Power Electronics Research Center for Photovoltaic Technologies Research Institute for Environmental Management Technology Research Institute for Innovation in Sustainable Chemistry Energy Technology Research Institute of Science for Safety and Sustainability Nanotechnology, Materials and Manufacturing Nanotube Research Center for Ubiquitous MEMS and Micro Engineering Advanced Manufacturing Research Institute Materials Research Institute for Sustainable Development Nanosystem Research Institute Diamond Research Laboratory NMIJ Geological Survey and Applied Geoscience Active Fault and Earthquake Research Center Institute for Geo-Resources and Environment Institute of Geology and Geoinformation Center Geological Museum Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
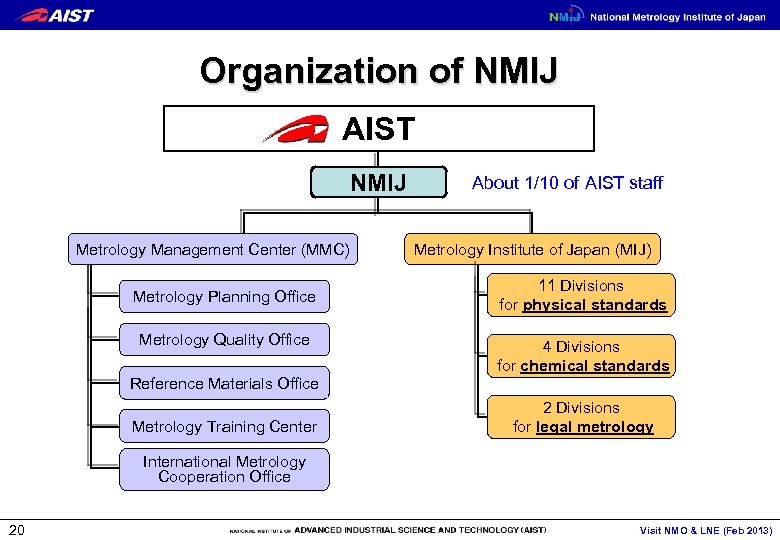 Organization of NMIJ AIST NMIJ Metrology Management Center (MMC) Metrology Planning Office Metrology Quality Office Reference Materials Office Metrology Training Center About 1/10 of AIST staff Metrology Institute of Japan (MIJ) 11 Divisions for physical standards 4 Divisions for chemical standards 2 Divisions for legal metrology International Metrology Cooperation Office 20 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Organization of NMIJ AIST NMIJ Metrology Management Center (MMC) Metrology Planning Office Metrology Quality Office Reference Materials Office Metrology Training Center About 1/10 of AIST staff Metrology Institute of Japan (MIJ) 11 Divisions for physical standards 4 Divisions for chemical standards 2 Divisions for legal metrology International Metrology Cooperation Office 20 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
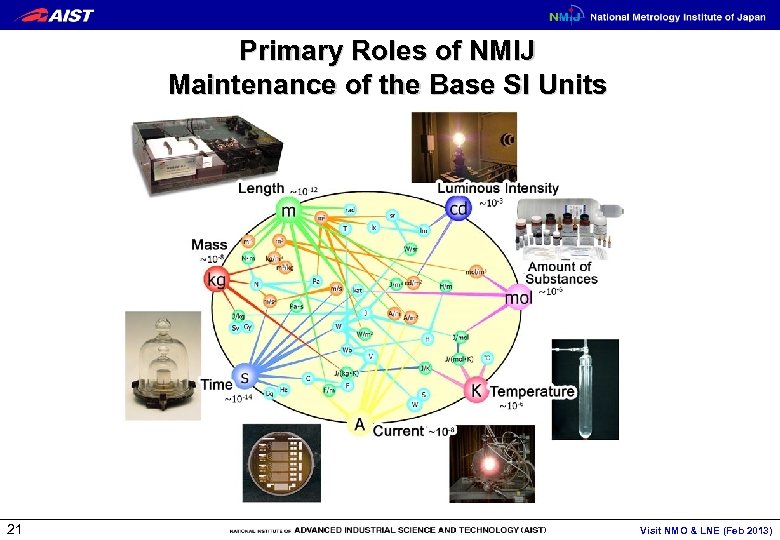 Primary Roles of NMIJ Maintenance of the Base SI Units 21 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Primary Roles of NMIJ Maintenance of the Base SI Units 21 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
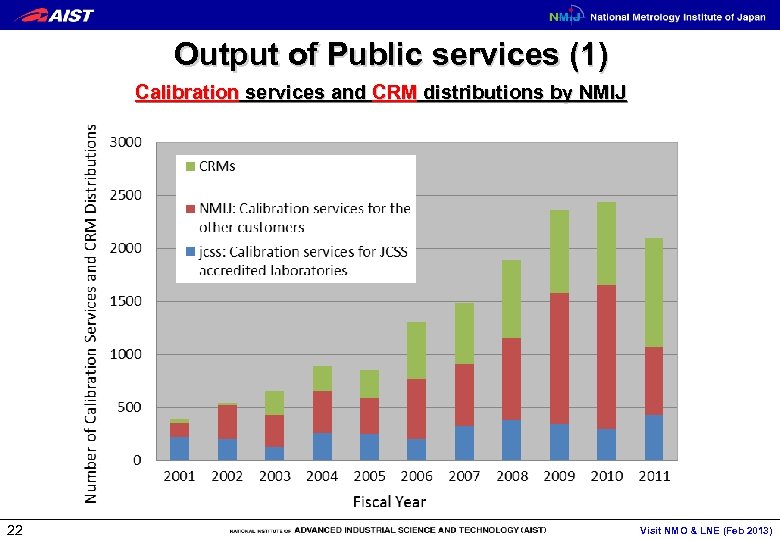 Output of Public services (1) Calibration services and CRM distributions by NMIJ 22 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Output of Public services (1) Calibration services and CRM distributions by NMIJ 22 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
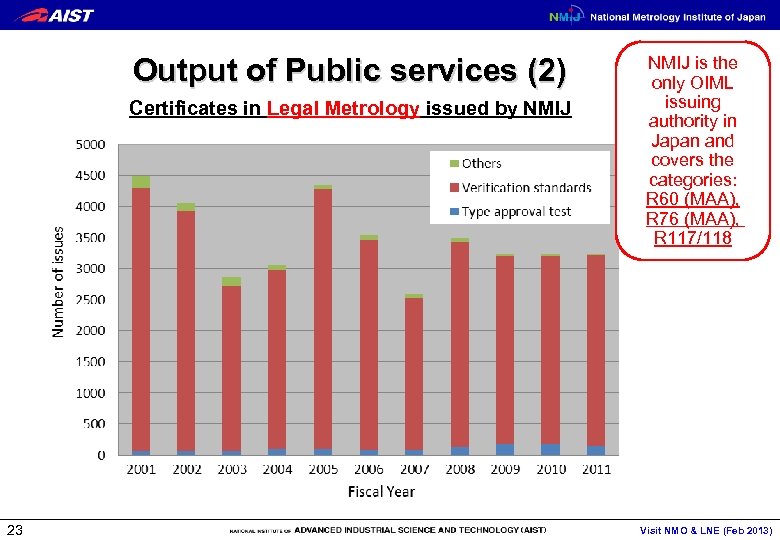 Output of Public services (2) Certificates in Legal Metrology issued by NMIJ 23 NMIJ is the only OIML issuing authority in Japan and covers the categories: R 60 (MAA), R 76 (MAA), R 117/118 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Output of Public services (2) Certificates in Legal Metrology issued by NMIJ 23 NMIJ is the only OIML issuing authority in Japan and covers the categories: R 60 (MAA), R 76 (MAA), R 117/118 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
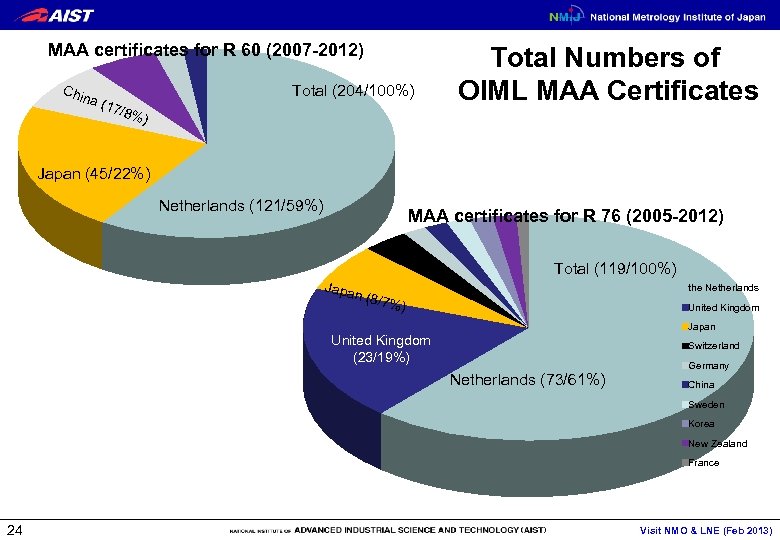 MAA certificates for R 60 (2007 -2012) Chi na Total (204/100%) ( 17 /8% Total Numbers of OIML MAA Certificates ) Japan (45/22%) Netherlands (121/59%) MAA certificates for R 76 (2005 -2012) Total (119/100%) Japa the Netherlands n (8/ 7%) United Kingdom Japan United Kingdom (23/19%) Switzerland Netherlands (73/61%) Germany China Sweden Korea New Zealand France 24 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
MAA certificates for R 60 (2007 -2012) Chi na Total (204/100%) ( 17 /8% Total Numbers of OIML MAA Certificates ) Japan (45/22%) Netherlands (121/59%) MAA certificates for R 76 (2005 -2012) Total (119/100%) Japa the Netherlands n (8/ 7%) United Kingdom Japan United Kingdom (23/19%) Switzerland Netherlands (73/61%) Germany China Sweden Korea New Zealand France 24 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
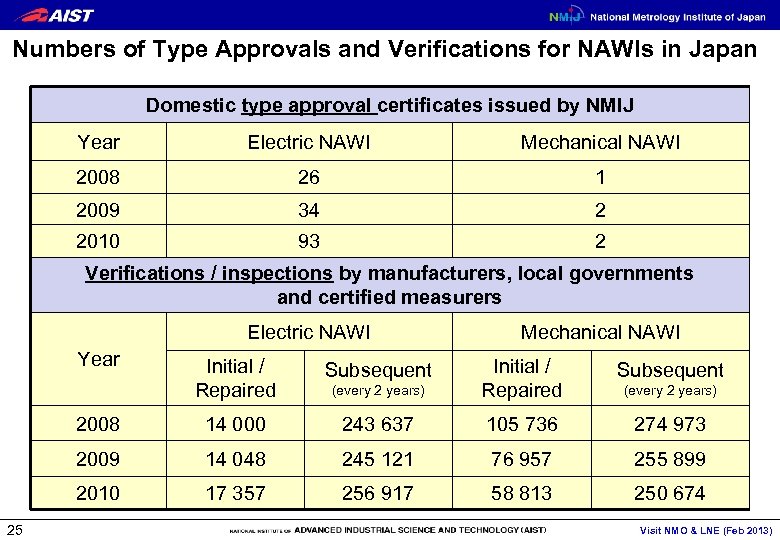 Numbers of Type Approvals and Verifications for NAWIs in Japan Domestic type approval certificates issued by NMIJ Year Electric NAWI Mechanical NAWI 2008 26 1 2009 34 2 2010 93 2 Verifications / inspections by manufacturers, local governments and certified measurers Electric NAWI Year Subsequent 2008 Subsequent (every 2 years) Initial / Repaired 14 000 243 637 105 736 274 973 2009 14 048 245 121 76 957 255 899 2010 25 Initial / Repaired Mechanical NAWI 17 357 256 917 58 813 250 674 (every 2 years) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Numbers of Type Approvals and Verifications for NAWIs in Japan Domestic type approval certificates issued by NMIJ Year Electric NAWI Mechanical NAWI 2008 26 1 2009 34 2 2010 93 2 Verifications / inspections by manufacturers, local governments and certified measurers Electric NAWI Year Subsequent 2008 Subsequent (every 2 years) Initial / Repaired 14 000 243 637 105 736 274 973 2009 14 048 245 121 76 957 255 899 2010 25 Initial / Repaired Mechanical NAWI 17 357 256 917 58 813 250 674 (every 2 years) Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. International Cooperation Activities in Metrology Meter Convention, OIML, APMP & APLMF 26 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. International Cooperation Activities in Metrology Meter Convention, OIML, APMP & APLMF 26 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
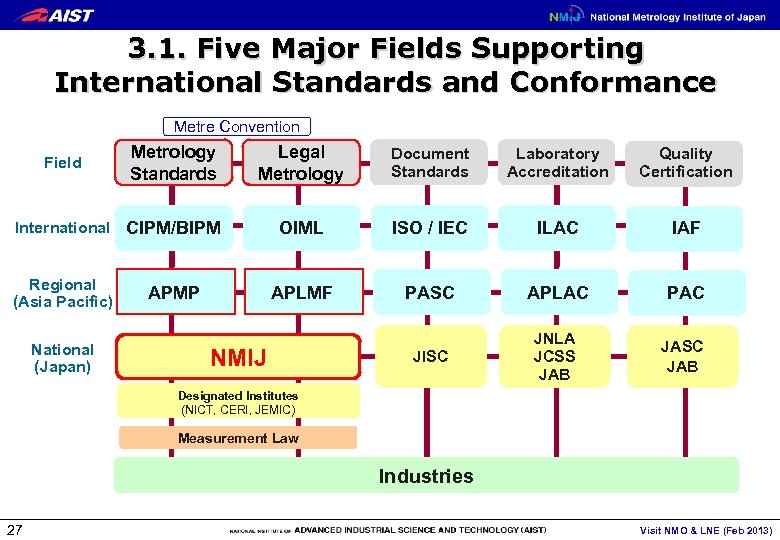 3. 1. Five Major Fields Supporting International Standards and Conformance Metre Convention Field Legal Metrology Document Standards Laboratory Accreditation Quality Certification OIML ISO / IEC ILAC IAF APLMF Metrology Standards PASC APLAC PAC JISC JNLA JCSS JAB JASC JAB International CIPM/BIPM Regional (Asia Pacific) National (Japan) APMP NMIJ Designated Institutes (NICT, CERI, JEMIC) Measurement Law Industries 27 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 1. Five Major Fields Supporting International Standards and Conformance Metre Convention Field Legal Metrology Document Standards Laboratory Accreditation Quality Certification OIML ISO / IEC ILAC IAF APLMF Metrology Standards PASC APLAC PAC JISC JNLA JCSS JAB JASC JAB International CIPM/BIPM Regional (Asia Pacific) National (Japan) APMP NMIJ Designated Institutes (NICT, CERI, JEMIC) Measurement Law Industries 27 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. 2. Cooperation with Meter Convention and BIPM • Japan participated in the Meter Convention in 1885. • Since 1907, Japan has been a member of CIPM (Dr. Usuda of NMIJ in present). • Japan is also responsible for the chair (Dr. Fujii of NMIJ) of WGD on density in CCM. • Japan signed CIPM-MRA in 1999, and has been actively contributing the development and properation of the arrangement. 28 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 2. Cooperation with Meter Convention and BIPM • Japan participated in the Meter Convention in 1885. • Since 1907, Japan has been a member of CIPM (Dr. Usuda of NMIJ in present). • Japan is also responsible for the chair (Dr. Fujii of NMIJ) of WGD on density in CCM. • Japan signed CIPM-MRA in 1999, and has been actively contributing the development and properation of the arrangement. 28 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
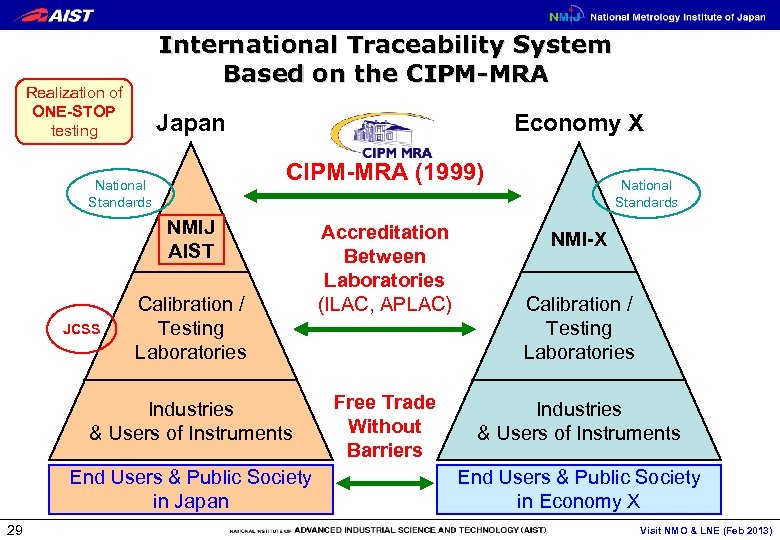 International Traceability System Based on the CIPM-MRA Realization of ONE-STOP testing Japan Economy X CIPM-MRA (1999) National Standards NMIJ AIST JCSS Calibration / Testing Laboratories Industries & Users of Instruments End Users & Public Society in Japan 29 Accreditation Between Laboratories (ILAC, APLAC) Free Trade Without Barriers National Standards NMI-X Calibration / Testing Laboratories Industries & Users of Instruments End Users & Public Society in Economy X Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
International Traceability System Based on the CIPM-MRA Realization of ONE-STOP testing Japan Economy X CIPM-MRA (1999) National Standards NMIJ AIST JCSS Calibration / Testing Laboratories Industries & Users of Instruments End Users & Public Society in Japan 29 Accreditation Between Laboratories (ILAC, APLAC) Free Trade Without Barriers National Standards NMI-X Calibration / Testing Laboratories Industries & Users of Instruments End Users & Public Society in Economy X Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
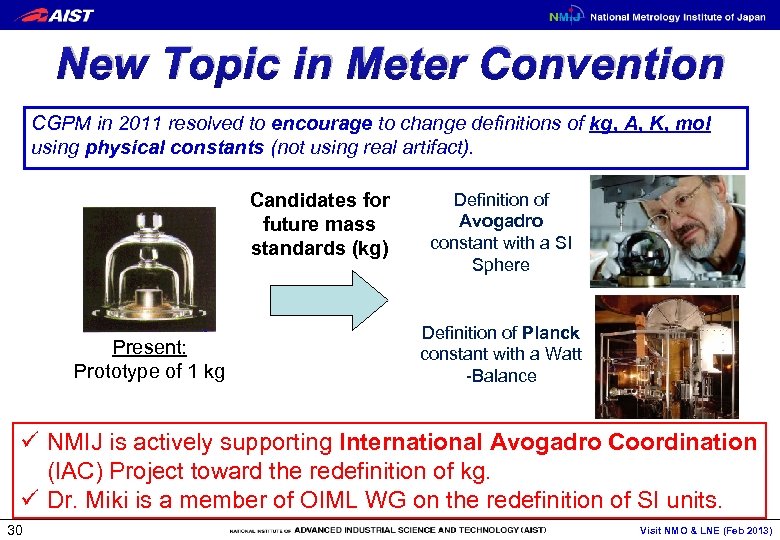 New Topic in Meter Convention CGPM in 2011 resolved to encourage to change definitions of kg, A, K, mol using physical constants (not using real artifact). Candidates for future mass standards (kg) Present: Prototype of 1 kg Definition of Avogadro constant with a SI Sphere Definition of Planck constant with a Watt -Balance ü NMIJ is actively supporting International Avogadro Coordination (IAC) Project toward the redefinition of kg. ü Dr. Miki is a member of OIML WG on the redefinition of SI units. 30 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
New Topic in Meter Convention CGPM in 2011 resolved to encourage to change definitions of kg, A, K, mol using physical constants (not using real artifact). Candidates for future mass standards (kg) Present: Prototype of 1 kg Definition of Avogadro constant with a SI Sphere Definition of Planck constant with a Watt -Balance ü NMIJ is actively supporting International Avogadro Coordination (IAC) Project toward the redefinition of kg. ü Dr. Miki is a member of OIML WG on the redefinition of SI units. 30 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. 3. Cooperation with OIML (International Organization of Legal Metrology) • Japan signed the OIML Treaty in 1961 and has been participating OIML Conferences and CIML Meetings. • CIML member has been provided by NMIJ (NRLM before 2001). • Japan is actively supporting OIML; (1) as a PC (Presidential Council) member, (2) submitting comments and votes to the OIML draft documents (about 30 items / year), (3) as an issuing authority in the OIML certificate system including MAA (R 60 & R 76), and (4) as a chair of TC 8 (measurement of quantities of fluids). 31 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 3. Cooperation with OIML (International Organization of Legal Metrology) • Japan signed the OIML Treaty in 1961 and has been participating OIML Conferences and CIML Meetings. • CIML member has been provided by NMIJ (NRLM before 2001). • Japan is actively supporting OIML; (1) as a PC (Presidential Council) member, (2) submitting comments and votes to the OIML draft documents (about 30 items / year), (3) as an issuing authority in the OIML certificate system including MAA (R 60 & R 76), and (4) as a chair of TC 8 (measurement of quantities of fluids). 31 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. 4. Introduction of APMP Asia-Pacific Metrology Programme (A regional organization in scientific metrology) 1978: 1980: 1999: 2003: 2004: 2007: 2009: 2011: 2012: 32 “Old APMP” was established under the commonwealth of UK. “New APMP” was reorganized. NMIJ served as the Chairperson and Secretariat. Singapore served as the Chairperson. New Zealand served as the Chairperson. KRISS in R. Korea served as the Chair and Secretariat. NIM in PR. China serves as the Chair and Secretariat. General Assembly was held in Kobe, Japan. General Assembly was held in New Zealand. Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 4. Introduction of APMP Asia-Pacific Metrology Programme (A regional organization in scientific metrology) 1978: 1980: 1999: 2003: 2004: 2007: 2009: 2011: 2012: 32 “Old APMP” was established under the commonwealth of UK. “New APMP” was reorganized. NMIJ served as the Chairperson and Secretariat. Singapore served as the Chairperson. New Zealand served as the Chairperson. KRISS in R. Korea served as the Chair and Secretariat. NIM in PR. China serves as the Chair and Secretariat. General Assembly was held in Kobe, Japan. General Assembly was held in New Zealand. Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
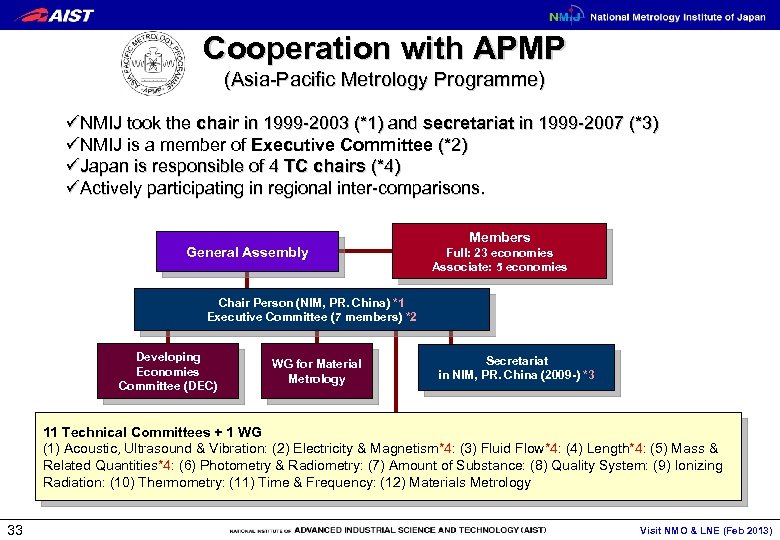 Cooperation with APMP (Asia-Pacific Metrology Programme) üNMIJ took the chair in 1999 -2003 (*1) and secretariat in 1999 -2007 (*3) üNMIJ is a member of Executive Committee (*2) üJapan is responsible of 4 TC chairs (*4) üActively participating in regional inter-comparisons. General Assembly Members Full: 23 economies Associate: 5 economies Chair Person (NIM, PR. China) *1 Executive Committee (7 members) *2 Developing Economies Committee (DEC) WG for Material Metrology Secretariat in NIM, PR. China (2009 -) *3 11 Technical Committees + 1 WG (1) Acoustic, Ultrasound & Vibration: (2) Electricity & Magnetism*4: (3) Fluid Flow*4: (4) Length*4: (5) Mass & Related Quantities*4: (6) Photometry & Radiometry: (7) Amount of Substance: (8) Quality System: (9) Ionizing Radiation: (10) Thermometry: (11) Time & Frequency: (12) Materials Metrology 33 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Cooperation with APMP (Asia-Pacific Metrology Programme) üNMIJ took the chair in 1999 -2003 (*1) and secretariat in 1999 -2007 (*3) üNMIJ is a member of Executive Committee (*2) üJapan is responsible of 4 TC chairs (*4) üActively participating in regional inter-comparisons. General Assembly Members Full: 23 economies Associate: 5 economies Chair Person (NIM, PR. China) *1 Executive Committee (7 members) *2 Developing Economies Committee (DEC) WG for Material Metrology Secretariat in NIM, PR. China (2009 -) *3 11 Technical Committees + 1 WG (1) Acoustic, Ultrasound & Vibration: (2) Electricity & Magnetism*4: (3) Fluid Flow*4: (4) Length*4: (5) Mass & Related Quantities*4: (6) Photometry & Radiometry: (7) Amount of Substance: (8) Quality System: (9) Ionizing Radiation: (10) Thermometry: (11) Time & Frequency: (12) Materials Metrology 33 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. 5. Introduction of APLMF Asia-Pacific Legal Metrology Forum (A regional organization in legal metrology) • A group of legal metrology authorities on the Pacific rim. • 26 member economies (20 full+6 correspondence) in 2010. • Has following main objectives: Remove technical barriers to trade Encourage mutual confidence. Provide a forum for exchange of information. Coordinate training courses for capacity building and communication. Cooperate with OIML and APEC. Cooperate with RLMOs (regional legal metrology organizations) • Established in November 1994, with 14 member economies in the APEC region with president and secretariat in Australia. • In 2002, Japan succeeded the presidency and the secretariat. • In 2007, PR China succeeded the presidency and secretariat. 34 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 5. Introduction of APLMF Asia-Pacific Legal Metrology Forum (A regional organization in legal metrology) • A group of legal metrology authorities on the Pacific rim. • 26 member economies (20 full+6 correspondence) in 2010. • Has following main objectives: Remove technical barriers to trade Encourage mutual confidence. Provide a forum for exchange of information. Coordinate training courses for capacity building and communication. Cooperate with OIML and APEC. Cooperate with RLMOs (regional legal metrology organizations) • Established in November 1994, with 14 member economies in the APEC region with president and secretariat in Australia. • In 2002, Japan succeeded the presidency and the secretariat. • In 2007, PR China succeeded the presidency and secretariat. 34 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 Cooperation with APLMF (Asia-Pacific Legal Metrology Forum) üNMIJ took the chair and secretariat in 2001 -2007 (*1) üNMIJ is a member of Executive Committee (*2) üJapan is responsible for a WG chair on agricultural products (*3) Forum Meeting (every year) Full Members (20): Australia, Cambodia, Canada, PR China, Hong Kong China, Indonesia, Japan, DPR Korea, Rep. Korea, Malaysia, Mongolia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, U. S. A. , Vietnam Corresponding Members (6): Brunei Darussalam, Chile, Columbia, Lao PDR, Mexico, Peru Executive Committee Pres. & Sec. Former Pres. *2 Australia Canada ASEAN 35 President*1 Mr. Pu Changcheng Secretariat*1 ACCSQ, PR China Working Groups (WGs) WG on Training Coordination WG on Goods Packed by Measure WG on Utility Meters WG on Mutual Recognition Arrangements WG on Medical Measurements WG on Quality Measurement of Agricultural Products*3 WG on Metrological Control Systems Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
Cooperation with APLMF (Asia-Pacific Legal Metrology Forum) üNMIJ took the chair and secretariat in 2001 -2007 (*1) üNMIJ is a member of Executive Committee (*2) üJapan is responsible for a WG chair on agricultural products (*3) Forum Meeting (every year) Full Members (20): Australia, Cambodia, Canada, PR China, Hong Kong China, Indonesia, Japan, DPR Korea, Rep. Korea, Malaysia, Mongolia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, U. S. A. , Vietnam Corresponding Members (6): Brunei Darussalam, Chile, Columbia, Lao PDR, Mexico, Peru Executive Committee Pres. & Sec. Former Pres. *2 Australia Canada ASEAN 35 President*1 Mr. Pu Changcheng Secretariat*1 ACCSQ, PR China Working Groups (WGs) WG on Training Coordination WG on Goods Packed by Measure WG on Utility Meters WG on Mutual Recognition Arrangements WG on Medical Measurements WG on Quality Measurement of Agricultural Products*3 WG on Metrological Control Systems Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 3. 6. Summary of International Cooperation l. Cooperation with international/regional organizations: BIPM (CIPM), BIML (OIML), APMP, APLMF, EURAMET, SIM, etc. l. Cooperation with NMIs (National Metrology Institutes) through peer assessments / intercomparisons: NIST, PTB, KRISS, NIM, NMIA, NIMT, SIRIM, KIM-LIPI, Do. M, ITDI, VMI, A*STAR, CENAM, CMS/ITRI, etc. l. Took President/Secretariat of APMP and APLMF. NMIJ is still supporting activities of APMP and APLMF. l. NMIJ supported NIMT (NMI Thailand) in 2002 -2008 in cooperation with JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency). Cooperation with NIMT still continues. l. NMIJ supported JICA training courses in legal metrology in 1973 -2010. More than 300 trainees visited Japan from Asia, Central and South America and North Africa. (Project is temporarily suspended. ) l. NMIJ accepts trainees in metrology from other NMIs (with own fund). 36 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
3. 6. Summary of International Cooperation l. Cooperation with international/regional organizations: BIPM (CIPM), BIML (OIML), APMP, APLMF, EURAMET, SIM, etc. l. Cooperation with NMIs (National Metrology Institutes) through peer assessments / intercomparisons: NIST, PTB, KRISS, NIM, NMIA, NIMT, SIRIM, KIM-LIPI, Do. M, ITDI, VMI, A*STAR, CENAM, CMS/ITRI, etc. l. Took President/Secretariat of APMP and APLMF. NMIJ is still supporting activities of APMP and APLMF. l. NMIJ supported NIMT (NMI Thailand) in 2002 -2008 in cooperation with JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency). Cooperation with NIMT still continues. l. NMIJ supported JICA training courses in legal metrology in 1973 -2010. More than 300 trainees visited Japan from Asia, Central and South America and North Africa. (Project is temporarily suspended. ) l. NMIJ accepts trainees in metrology from other NMIs (with own fund). 36 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 4. Metrological control on grain moisture measurement in Japan (as a personal view by the presenter) l. Grain moisture meters are out of legal metrology under the Measurement Law of Japan. l. Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) provides another regulation system based on the ‘Agricultural Products Inspection Act’, which defines methodologies to evaluate qualities of agricultural products. l. The policy to control grain moisture meters is also covered by the act. However, this act seems not implemented strictly. Practical control activities including periodical inspections are delegated to the manufacturers of the meters. MAFF is responsible for supervision of the manufacturers. l. On the other hand, International cooperation in grain moisture measurement is actually taken care by METI and NMIJ. METI considers this is an important filed to support international trade. 37 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
4. Metrological control on grain moisture measurement in Japan (as a personal view by the presenter) l. Grain moisture meters are out of legal metrology under the Measurement Law of Japan. l. Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) provides another regulation system based on the ‘Agricultural Products Inspection Act’, which defines methodologies to evaluate qualities of agricultural products. l. The policy to control grain moisture meters is also covered by the act. However, this act seems not implemented strictly. Practical control activities including periodical inspections are delegated to the manufacturers of the meters. MAFF is responsible for supervision of the manufacturers. l. On the other hand, International cooperation in grain moisture measurement is actually taken care by METI and NMIJ. METI considers this is an important filed to support international trade. 37 Visit NMO & LNE (Feb 2013)
 We do our best effort to support international standard & conformance through metrology. Thank You for Your Attention! Contact: Tsuyoshi Matsumoto
We do our best effort to support international standard & conformance through metrology. Thank You for Your Attention! Contact: Tsuyoshi Matsumoto


