1c3ea776dbecbfc7940ad19781c92514.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Introductions 1. Context for CSM is Business Success 2. Begin with the end in mind – reporting results 3. Survey design 4. Data analysis 5. Other issues A Step-by-Step Approach to Survey Design, Validation and Implementation agenda

Section 5 Other Issues Section 5: Other Issues Slide 2 Topics • • • Outsourcing vs. in-house Selecting the right vendor Writing the Professional Services Agreement (PSA) Vendor management Sampling issues Data collection Questionnaire design Global issues Segmentation Communicating the research results Causes of survey failure Linking your results to other research and operational data • Case study – outline survey design based on customer lifecycle touch points • HP’s Total Customer Experience Measurement Program • Networking and resources for further development

Section 5 Other Issues Outsourcing vs. in-house Slide 3 Program Manager vs. “Expert” • Internal staff • Training • Experience • Credibility • Need for speed • Management’s outsourcing philosophy • Management’s philosophy about internal consultants • Is this position a career path? • Entry level vs. experienced • Need for additional sources of competitive differentiation • Why would you hire out strategy development? • Market research vs. customer research • Tactical vs. strategic • Out-of-pocket vs. ongoing costs • Short term vs. long term needs

Section 5 Other Issues Outsourcing vs. in-house Slide 4 • Class discussion – articulate your situation and your short/long term proposal.

Section 5 Other Issues Selecting the right vendor Slide 5 • • • Consultant expertise vs. low cost Training Methodological expertise Fielding expertise – e. g. data quality issues Knows my industry • Written proposal • Presentation content Credibility • WOM, references, credentials, papers, books • Presentation professionalism • Willingness/ability to answer your difficult questions Relationship and trust Responsiveness Previous experience Cost

Section 5 Other Issues Selecting the right vendor Slide 6 • Class discussion – what are some of your selection criteria?

Section 5 Other Issues Writing the PSA (Professional Services Agreement) Slide 7 • • Detailed definition of the “work product” Intellectual Property – who owns the work product Who owns the data Detailed sampling/quota plan with contingencies • Assumed response rate • Name list sources, size, cost • Detailed timeline for each phase (e. g. development, fielding, reporting) • Detailed cost breakdown • Timeline for each phase showing labor rates and time/cost for each job type and output

Section 5 Other Issues Writing the PSA Slide 8 • Class discussion – PSA best practices and “war stories”.

Section 5 Other Issues Vendor management Slide 9 • Bottom line: your vendor works for you. • Set expectations before the contract is signed. If they are not sufficiently responsive, work with them to resolve the problem. If problems persist, fire them. • Employees want to be treated as a partner, not as a competitor • Like a good employee, they want to feel valued, that their contribution is having an impact. They want an inclusive relationship with you. • They desire regular communication.

Section 5 Other Issues Vendor management Slide 10 • Class discussion – best practices and “war stories”.

Section 5 Other Issues Sampling issues Slide 11 • Who should be interviewed? • Current/past/competitors’ customers • Sample frame (name lists) reflects target population (and segments). • Internal vs. purchased name lists • Target population must be large enough • E. g. top 100 global customers • Types of sampling • Random (probabilistic) sampling • Quota sampling • Declining response rates • Incentives – monetary and other • Customer “Over-touching” issues

Section 5 Other Issues Sampling issues Slide 12 • Increasing privacy concerns, standards, law • Phone – “opt-out” • Email, mail – “opt-in” • Blind surveys • Sample size • Judgment or history • Budget • Statistical precision – One must know a priori the variance in order to determine sample size N for a given desired degree of precision • Analytical considerations – E. g. driver analysis

Section 5 Other Issues Sampling issues Slide 13 • Standards committees you should become familiar with • ESOMAR http: //www. esomar. nl/ • CASRO http: //www. casro. org/ • CMOR http: //www. cmor. org/

Section 5 Other Issues Data collection Slide 14 • In-house vs. outsourced • Types – generally prefer not to mix • In-person • Mail • Telephone • FAX • Email • Internet • hybrid

Section 5 Other Issues Data collection Slide 15 • • Qualitative versus quantitative Complex surveys - skip patterns Survey length Global vs. regional Senior executives “state of mind” issue Data quality and cleanup • Not enough attention is paid to this • CATI programming • Interviewer training, monitoring • Allow - not applicable, DK, refused

Section 5 Other Issues Data collection Slide 16 • Class discussion – what is your approach and why?

Section 5 Other Issues Questionnaire design addendum Slide 17 • Who to include on the team… • Using the concept of an integrated measurement system and customer experience lifecycle mapping to frame the discussion • Criteria for cutting unnecessary detail… • The review process…

Section 5 Other Issues Questionnaire design Slide 18 • Class discussion – best practices and “war stories”.
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 19 Concept • Market segmentation involves viewing a heterogeneous market as a number of smaller homogeneous market segments that have different customer demand characteristics. That is, the drivers of business success are different.

Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 20 Criteria for Usefulness • • • Identifiable Substantial Accessible Responsive (unique response to marketing mix) Stable Actionable (firm competitiveness)
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 21 Many potential segments • There is not a single correct segmentation. • Segmentation is dependent on bases, methods, markets and the purpose of the study
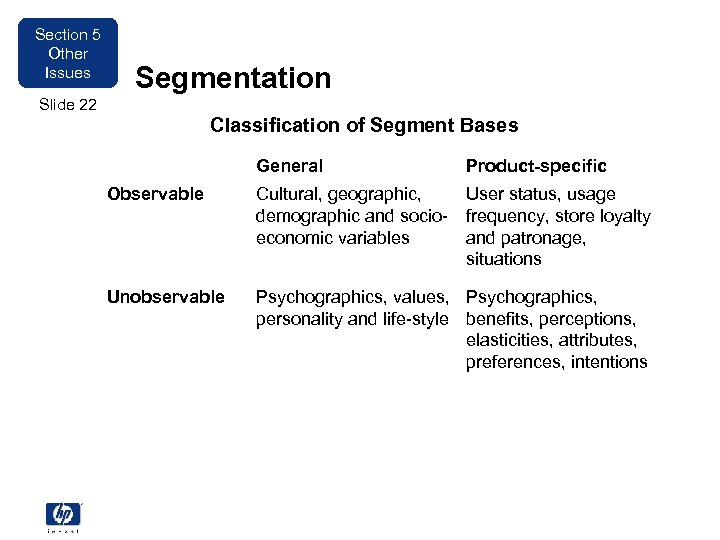
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 22 Classification of Segment Bases General Product-specific Observable Cultural, geographic, demographic and socioeconomic variables User status, usage frequency, store loyalty and patronage, situations Unobservable Psychographics, values, Psychographics, personality and life-style benefits, perceptions, elasticities, attributes, preferences, intentions
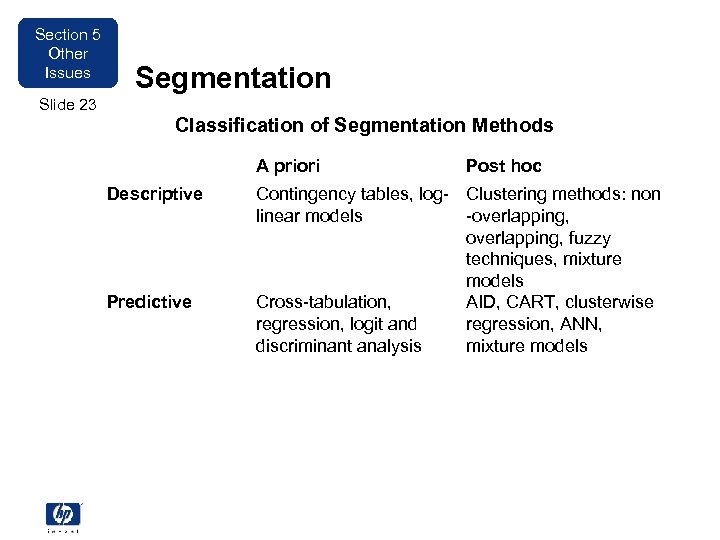
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 23 Classification of Segmentation Methods A priori Descriptive Predictive Post hoc Contingency tables, log- Clustering methods: non linear models -overlapping, fuzzy techniques, mixture models Cross-tabulation, AID, CART, clusterwise regression, logit and regression, ANN, discriminant analysis mixture models
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 24 Purpose of study • • Pricing New product development Media selection Customer loyalty • Your customers • Competitor A customers • Competitor B customers Other bases
Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 25 Common Segmentation Schemes • Consumer • VALS http: //www. sric-bi. com/VALS • Business • SIC codes • Company size

Section 5 Other Issues Segmentation Slide 26 • Class discussion • What is an obvious hotel segmentation? • Be careful of “scale usage” segmentation • What segmentation are you using?

Section 5 Other Issues Communicating research results Addendum Slide 27 • Identify audience and information needs • Senior management, middle management, individual contributors • Region, entity, department • Process owner • Have management “take the survey” first • Facts versus opinions • Triangulation – survey is only once source of recommendations, it does not alone set strategy • The role of graphics and customer quotes • Presenting complex statistics to senior management • Preview of results before general roll-out

Section 5 Other Issues Communicating research results Slide 28 • Class discussion – best practices and “war stories”.

Section 5 Other Issues Some causes of survey failure Slide 29 • • Lack of partnership with stakeholders Lack of actionability Lack of “needle” movement Lack of integration with other customer research Lack of modularity Lack of flexibility Lack of credibility • It doesn’t tell senior management what they want to hear

Section 5 Other Issues Communicating research results Slide 30 • Class discussion – best practices and “war stories”.

Section 5 Other Issues Linking your results to market share Slide 31 • Discussion…
1c3ea776dbecbfc7940ad19781c92514.ppt