0eb8a47e9f860af705156d92d61a0703.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Introduction To ® Windows NT Server And Internet Information Server
Introduction To ® Windows NT Server And Internet Information Server
 Agenda l l l Basic security principles ® Basics of Windows NT security Basics of Internet Information Server security How the two relate Top tips
Agenda l l l Basic security principles ® Basics of Windows NT security Basics of Internet Information Server security How the two relate Top tips
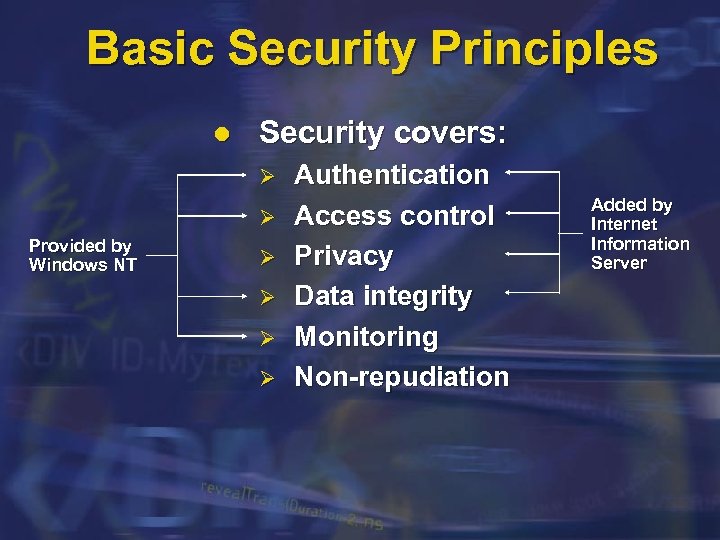 Basic Security Principles l Security covers: Ø Ø Provided by Windows NT Ø Ø Authentication Access control Privacy Data integrity Monitoring Non-repudiation Added by Internet Information Server
Basic Security Principles l Security covers: Ø Ø Provided by Windows NT Ø Ø Authentication Access control Privacy Data integrity Monitoring Non-repudiation Added by Internet Information Server
 Basics Of Windows NT Security
Basics Of Windows NT Security
 A Simple Fact To understand Internet Information Server Security you must understand Windows NT Security!
A Simple Fact To understand Internet Information Server Security you must understand Windows NT Security!
 Authentication l Windows NT requires “authenticated” users Ø Ø l A user must present his/her “credentials” Ø User name/password No notion of an anonymous user Ø Insecure Each user has a unique security ID (SID)
Authentication l Windows NT requires “authenticated” users Ø Ø l A user must present his/her “credentials” Ø User name/password No notion of an anonymous user Ø Insecure Each user has a unique security ID (SID)
 How Applications Work l Windows NT applications must run in the “context” of a user Ø When an application runs, the user’s security information is tagged onto the application Ø Called a “token” Ø A token identifies the user by their SID and group membership Ø Group SIDs
How Applications Work l Windows NT applications must run in the “context” of a user Ø When an application runs, the user’s security information is tagged onto the application Ø Called a “token” Ø A token identifies the user by their SID and group membership Ø Group SIDs
 How Applications Work l When an application attempts to use a resource the token is used to determine if that user has access Ø Ø l All secure resources have “access control lists”ACLs) ( ACLs are a list of SIDs and associated access rights Windows NT is very pessimistic Ø Ø Access denies are performed first Do not set everyone (no access)!
How Applications Work l When an application attempts to use a resource the token is used to determine if that user has access Ø Ø l All secure resources have “access control lists”ACLs) ( ACLs are a list of SIDs and associated access rights Windows NT is very pessimistic Ø Ø Access denies are performed first Do not set everyone (no access)!
 A Side Bar What does a SID look like? Windows NT Domain S-1 -5 -21 -2127521184 -1604012920 -1887927527 - 1001 Windows NT User ID on this domain
A Side Bar What does a SID look like? Windows NT Domain S-1 -5 -21 -2127521184 -1604012920 -1887927527 - 1001 Windows NT User ID on this domain
 Services Are Applications l Windows NT has special applications called “services” Ø Ø Ø Start when Windows NT starts Run in the background No UI Similar to UNIX daemons Examples: Ø Internet Information Server Ø SQL Server™ Ø Event log
Services Are Applications l Windows NT has special applications called “services” Ø Ø Ø Start when Windows NT starts Run in the background No UI Similar to UNIX daemons Examples: Ø Internet Information Server Ø SQL Server™ Ø Event log
 Services Are Applications l l l Because they are applications, they must run in a user context But they run before anyone logs on! You can configure a service to run as an account Ø Ø Ø Usually localsystem No password Limited access beyond the current server
Services Are Applications l l l Because they are applications, they must run in a user context But they run before anyone logs on! You can configure a service to run as an account Ø Ø Ø Usually localsystem No password Limited access beyond the current server
 Principle Of Least Privilege l l A process always runs in the context of user account If the account is privileged then the application has those privileges too Ø Ø Always run a process in the lowestpossible user context Remember the famous unix sendmailbug?
Principle Of Least Privilege l l A process always runs in the context of user account If the account is privileged then the application has those privileges too Ø Ø Always run a process in the lowestpossible user context Remember the famous unix sendmailbug?
 Impersonation l Most services run as localsystem hence they , access resources aslocalsystem Ø Ø Ø Not as the user account Impersonation lets the service impersonate the user before accessing the resource In fact is swaps out thelocalsystem token for the user’s token Ø On a thread-by-thread basis
Impersonation l Most services run as localsystem hence they , access resources aslocalsystem Ø Ø Ø Not as the user account Impersonation lets the service impersonate the user before accessing the resource In fact is swaps out thelocalsystem token for the user’s token Ø On a thread-by-thread basis
 Impersonation l l All servers must impersonate before accessing a resource Also, impersonation reduces the number of times a user needs to enter their credentials
Impersonation l l All servers must impersonate before accessing a resource Also, impersonation reduces the number of times a user needs to enter their credentials
 Basics Of Internet Information Server Security
Basics Of Internet Information Server Security
 Internet Information Server Authentication l Internet Information Server is a Windows NT service Ø Ø l Hence it must run as a user account By default Local. System Ø Don’t change! Every user request must be authenticated and then impersonated
Internet Information Server Authentication l Internet Information Server is a Windows NT service Ø Ø l Hence it must run as a user account By default Local. System Ø Don’t change! Every user request must be authenticated and then impersonated
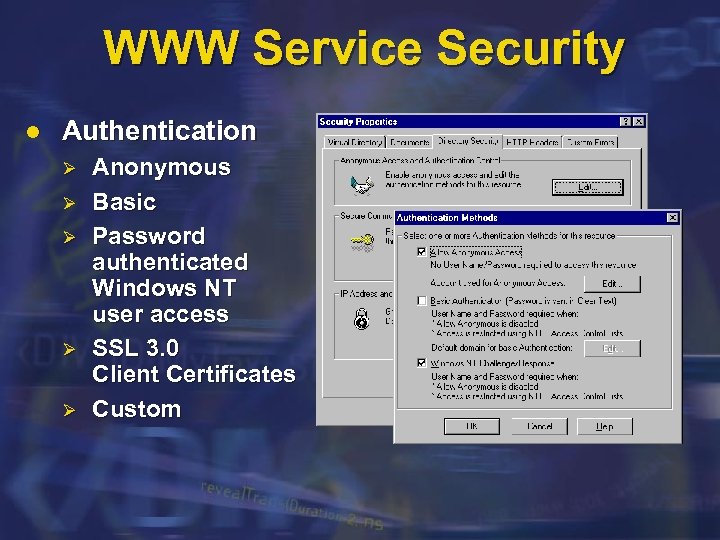 WWW Service Security l Authentication Ø Ø Ø Anonymous Basic Password authenticated Windows NT user access SSL 3. 0 Client Certificates Custom
WWW Service Security l Authentication Ø Ø Ø Anonymous Basic Password authenticated Windows NT user access SSL 3. 0 Client Certificates Custom
 Authentication Models l Anonymous Ø Ø l Basic Ø l Map onto IUSR_machinename account Guest account Base 64 encoded password/username NTLM Ø Ø Uses Windows NT network authentication No password
Authentication Models l Anonymous Ø Ø l Basic Ø l Map onto IUSR_machinename account Guest account Base 64 encoded password/username NTLM Ø Ø Uses Windows NT network authentication No password
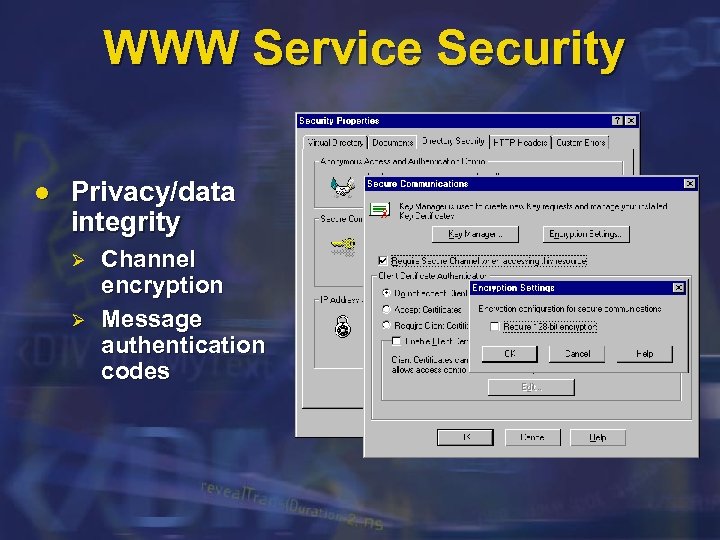 WWW Service Security l Privacy/data integrity Ø Ø Channel encryption Message authentication codes
WWW Service Security l Privacy/data integrity Ø Ø Channel encryption Message authentication codes
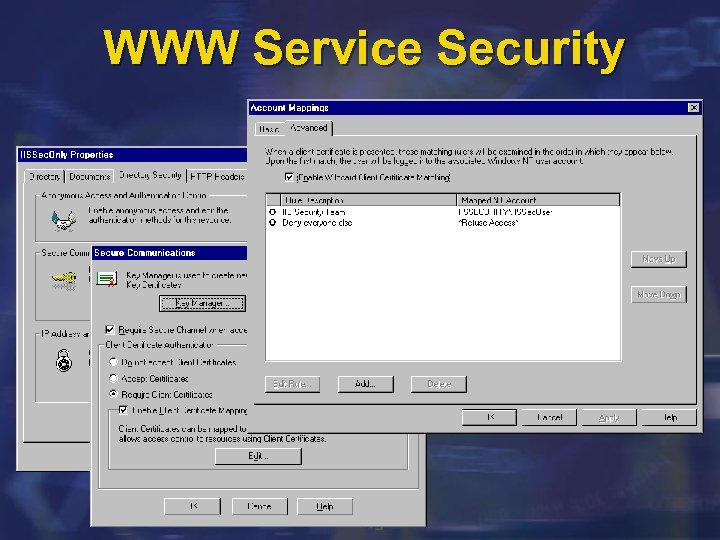
 WWW Service Security l Access control restricted by: Ø Ø Ø Ø Client TCP/IP address (or range) Client domain name Mapping Client Authentication Certificates Publishing point access permissions Designated site operators NTFS access control Custom ISAPI/CGI/ASP/component
WWW Service Security l Access control restricted by: Ø Ø Ø Ø Client TCP/IP address (or range) Client domain name Mapping Client Authentication Certificates Publishing point access permissions Designated site operators NTFS access control Custom ISAPI/CGI/ASP/component
 WWW Service Security
WWW Service Security
 WWW Service Security l System integrity Ø Ø Ø Process isolation Bandwidth limiting Application mapping CGI/script time-outs Connection time-out
WWW Service Security l System integrity Ø Ø Ø Process isolation Bandwidth limiting Application mapping CGI/script time-outs Connection time-out
 Custom Security l Custom: Ø Ø l Implement via: Ø Ø Ø l Authentication Access control ISAPI and CGI ASP and Perl Scripts Server-side components Requires understanding of: Ø Ø HTTP Protocol Authentication methods
Custom Security l Custom: Ø Ø l Implement via: Ø Ø Ø l Authentication Access control ISAPI and CGI ASP and Perl Scripts Server-side components Requires understanding of: Ø Ø HTTP Protocol Authentication methods
 Using Certificates On The Web l Authenticated access Ø Ø l l Servers Clients Secure access using SSL/TLS Examples Ø Ø Ø Departmental access control Interenterpriseaccess via Internet Certificate authority operation Ø E. g. , software publishing
Using Certificates On The Web l Authenticated access Ø Ø l l Servers Clients Secure access using SSL/TLS Examples Ø Ø Ø Departmental access control Interenterpriseaccess via Internet Certificate authority operation Ø E. g. , software publishing
 What Is A Certificate? Signed document Ø Ø Signed by a “trusted” certifying authority Binds subject to a public key Credential ties a name or identity to a public key Usage-specific attributes Credential expiration Subject Name: “Internet, Organization, Jane Doe” Public l Public key: Serial #: 29483756 Other data: 10236283025273 Expires: 6/18/98 Signed: CA’s signature Private
What Is A Certificate? Signed document Ø Ø Signed by a “trusted” certifying authority Binds subject to a public key Credential ties a name or identity to a public key Usage-specific attributes Credential expiration Subject Name: “Internet, Organization, Jane Doe” Public l Public key: Serial #: 29483756 Other data: 10236283025273 Expires: 6/18/98 Signed: CA’s signature Private
 Using Certificates On The Web l Why do it? Ø Ø Ø Better security than passwords Better scalability than passwords Ø No need to distribute password databases Use emerging technologies Ø Smart Cards Ø Crypto accelerators
Using Certificates On The Web l Why do it? Ø Ø Ø Better security than passwords Better scalability than passwords Ø No need to distribute password databases Use emerging technologies Ø Smart Cards Ø Crypto accelerators
 Top Tips And Rules Of Thumb
Top Tips And Rules Of Thumb
 Top Tips 10. NTFS is the last bastion 9. If you must use basic authentication then use SSL! 8. Seriously consider certificates 7. Create a company security policy 6. Use the Windows NT Option Pack Resource Kit (shameless plug!)
Top Tips 10. NTFS is the last bastion 9. If you must use basic authentication then use SSL! 8. Seriously consider certificates 7. Create a company security policy 6. Use the Windows NT Option Pack Resource Kit (shameless plug!)
 Top Tips 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Lock down your server Lock away your server! Restrict components at the server Do not allow Execute permission! Use the Windows NT Audit Log!
Top Tips 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Lock down your server Lock away your server! Restrict components at the server Do not allow Execute permission! Use the Windows NT Audit Log!


