f762bd77a4e93dda950a367736bd874e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69

Introduction to the RADIUS protocol
Module Objetives · Identify the elements and architecture of remote access to networks · Understand the way the RADIUS protocol works · Get to know the attributes that control different type of access technologies (dial-up, ADSL, GPRS/UMTS, CDMA 2000, etc) · Way to code attributes and RADIUS packets, and the sense of a dictionary · Cover the standard statistical information provided over SNMP · View the extensions added to the RADIUS protocol 2 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
AAA ·Authentication § Verify that a user really is who (s)he claims to be: Password, Token Cards, Calling number, X. 509 digital certificate, SIM card, etc. ·Authorization § Check that the user can access the service (s)he is trying to: Checking against a database, a file, etc. what the user can do, and restrict his/her access to the network ·Accounting § Write down what the user has done during his connection Connection time, bytes sent/received, access service, etc. § To get statistics about user accesses, billing, etc 3 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
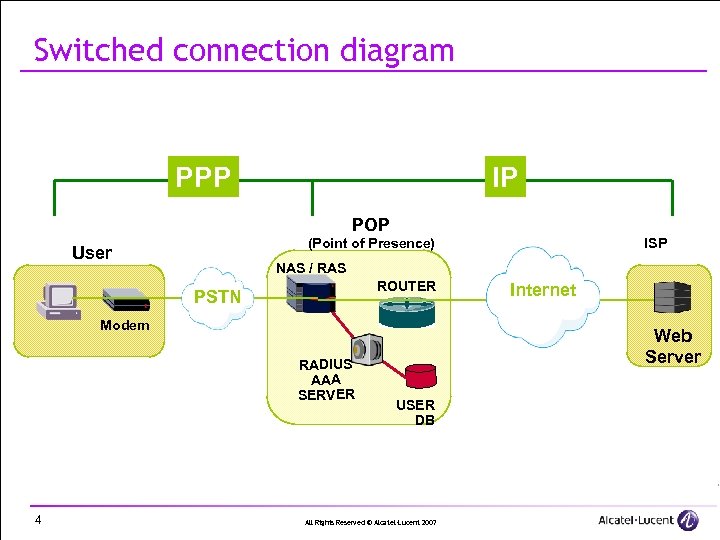
Switched connection diagram PPP IP POP NAS / RAS ROUTER PSTN Modem RADIUS AAA SERVER 4 ISP (Point of Presence) User Internet Web Server USER DB All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
Different ways for the AAA · Local accounts in the NAS/RAS § Only valid for small number of users § Not valid if any user can connect at any NAS We would have to provision all users in all NAS's · Proprietary software between NAS and an external server · Protocol RADIUS for a NAS to ask the server with centralized information about all users § Or its evolution: Diameter NASREQ application · Protocol TACACS (tacacs, tacacs+, xtacacs) § Not widely implemented, apart from Cisco 5 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
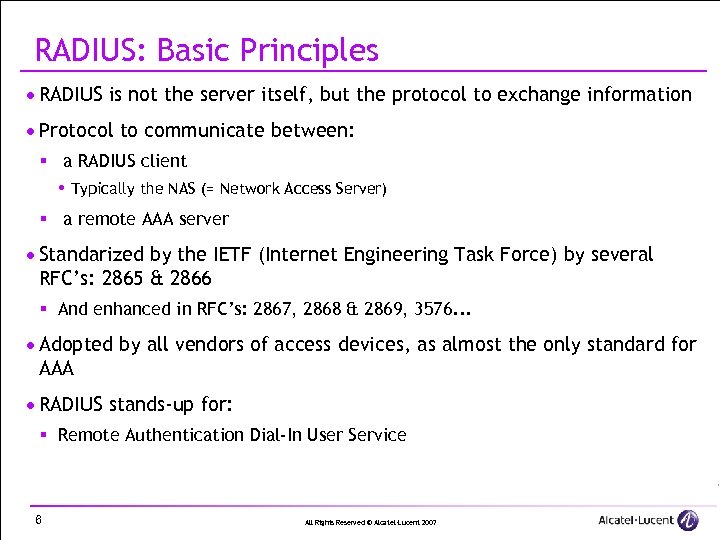
RADIUS: Basic Principles · RADIUS is not the server itself, but the protocol to exchange information · Protocol to communicate between: § a RADIUS client Typically the NAS (= Network Access Server) § a remote AAA server · Standarized by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) by several RFC’s: 2865 & 2866 § And enhanced in RFC’s: 2867, 2868 & 2869, 3576. . . · Adopted by all vendors of access devices, as almost the only standard for AAA · RADIUS stands-up for: § Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service 6 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
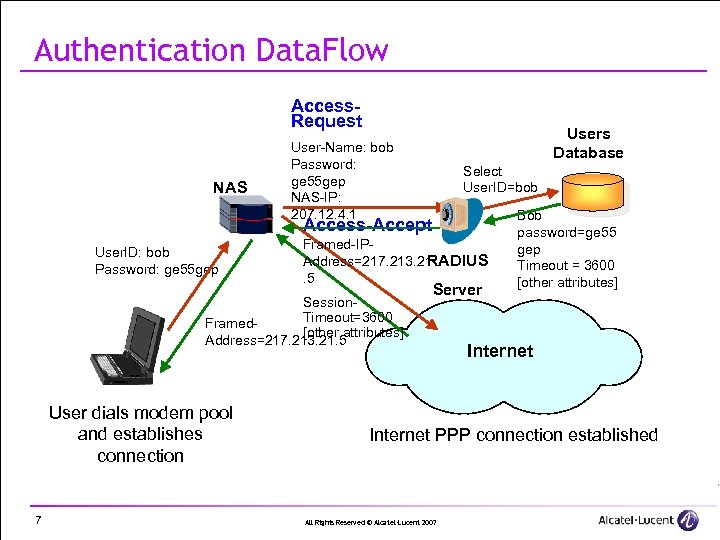
Authentication Data. Flow Access. Request NAS Users Database User-Name: bob Password: ge 55 gep NAS-IP: 207. 12. 4. 1 Select User. ID=bob Access-Accept User. ID: bob Password: ge 55 gep Framed-IPAddress=217. 213. 21 RADIUS. 5 Session. Timeout=3600 Framed[other attributes] Address=217. 213. 21. 5 User dials modem pool and establishes connection 7 Server Bob password=ge 55 gep Timeout = 3600 [other attributes] Internet PPP connection established All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
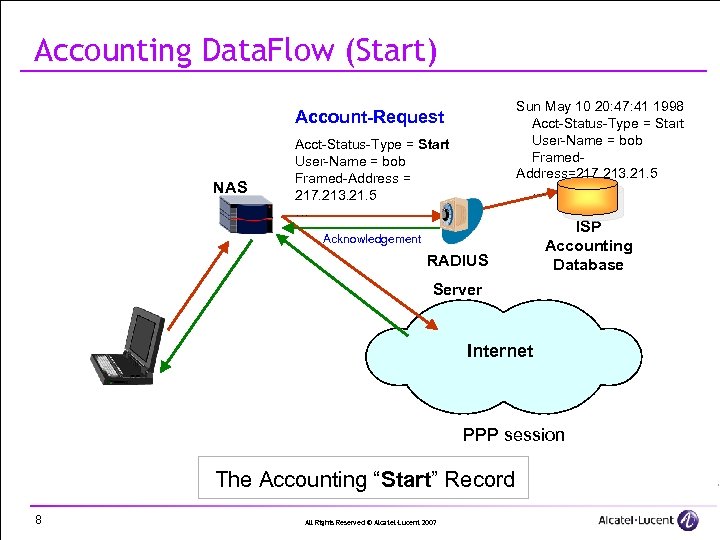
Accounting Data. Flow (Start) Sun May 10 20: 47: 41 1998 Acct-Status-Type = Start User-Name = bob Framed. Address=217. 213. 21. 5 … Account-Request NAS Acct-Status-Type = Start User-Name = bob Framed-Address = 217. 213. 21. 5 … Acknowledgement RADIUS ISP Accounting Database Server Internet PPP session The Accounting “Start” Record 8 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
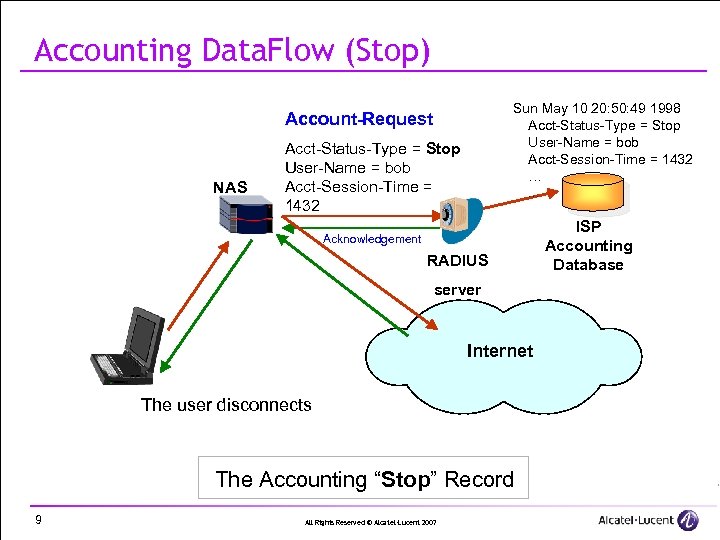
Accounting Data. Flow (Stop) Sun May 10 20: 50: 49 1998 Acct-Status-Type = Stop User-Name = bob Acct-Session-Time = 1432 …. . . Account-Request NAS Acct-Status-Type = Stop User-Name = bob Acct-Session-Time = 1432 Acknowledgement RADIUS server Internet The user disconnects The Accounting “Stop” Record 9 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 ISP Accounting Database
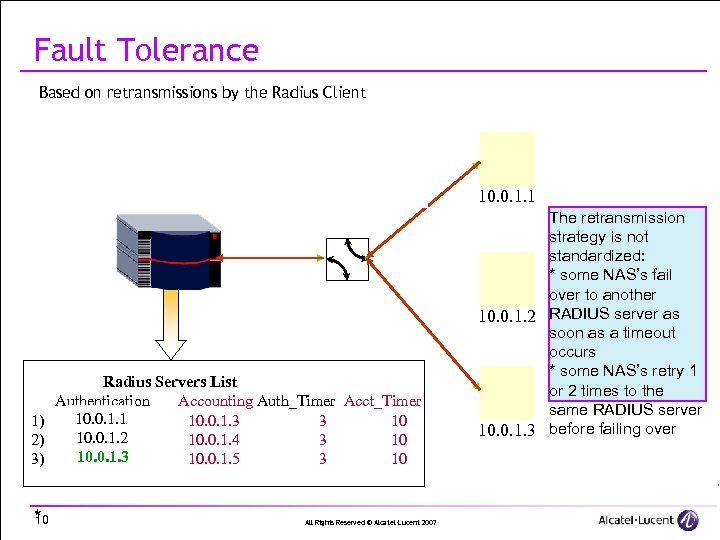
Fault Tolerance • Based on retransmissions by the Radius Client The first RADIUS server The NAS selectsrouterand The reply selects thethe The NAS is the third The NAS received get request does not replies but selects first RADIUSserver second. RADIUS ends list to the server onserver the transaction the RADIUS server drops the reply Radius Servers List Authentication Accounting Auth_Timer Acct_Timer 10. 0. 1. 1 1) 10. 0. 1. 3 3 10 10. 0. 1. 2 2) 10. 0. 1. 4 3 10 10. 0. 1. 3 3) 10. 0. 1. 5 3 10 * 10 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 10. 0. 1. 1 The retransmission strategy is not standardized: * some NAS’s fail over to another 10. 0. 1. 2 RADIUS server as soon as a timeout occurs * some NAS’s retry 1 or 2 times to the same RADIUS server 10. 0. 1. 3 before failing over
Information from NAS -> server for authentication · Information related to RADIUS client (NAS) § NAS-Ip-Address, or unique identification (NAS-Id) · Information to authenticate the user connecting: § User-Name & Password · Information about the connection itself (for authorization): § Calling number, called number (or APN for GPRS/UMTS), § Modem/port taking the connection (NAS-Port) § Type of session (PPP, SLIP, . . . ) § Type of connection (POTS, ISDN, ADSL, UMTS, GPRS, etc. ) 11 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
Authentication process in the server (I) · 1. - Decode the user's password (it travels encrypted) § Using the "shared secret key", known both by client and server · 2. - Search the user connection profile in: § § § Plain text file External SQL database LDAP server /etc/passwd file in UNIX User accounts in Windows Domains Etc. · 3. - Authenticate the user 12 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
Authentication process in the server (& II) · 4. - Optionally, check extra data (check-items) § § Type of connection (POTS, ISDN, ADSL, cable, UMTS, etc. ) Time of day Calling number, called number etc. · 5. - Send Accept/Reject to the NAS with the right attibutes for this user session (reply-items) § § § 13 Idle and session timeout IP filters for this user Indication of IP address to assign to user For ISDN, max. number of channels to bond together (MLPPP) etc. All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
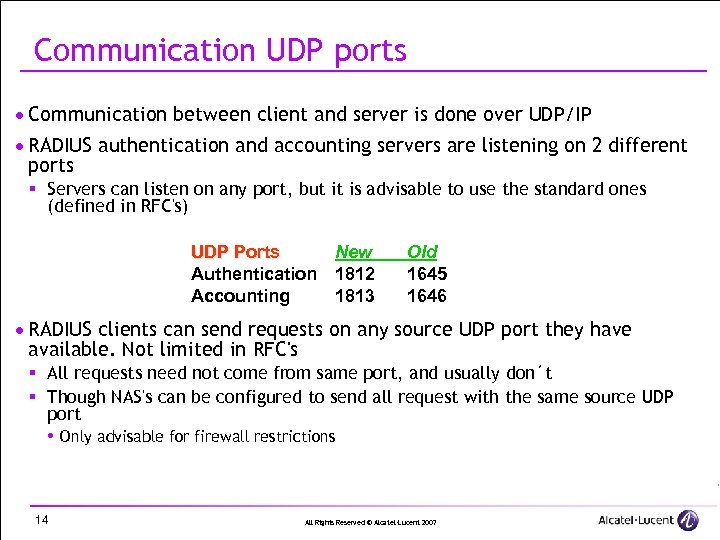
Communication UDP ports · Communication between client and server is done over UDP/IP · RADIUS authentication and accounting servers are listening on 2 different ports § Servers can listen on any port, but it is advisable to use the standard ones (defined in RFC's) UDP Ports Authentication Accounting New 1812 1813 Old 1645 1646 · RADIUS clients can send requests on any source UDP port they have available. Not limited in RFC's § All requests need not come from same port, and usually don´t § Though NAS's can be configured to send all request with the same source UDP port Only advisable for firewall restrictions 14 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
¿Why UDP? · In RADIUS it is not necessary the retransmision feature provided by TCP § If client doesn´t get an answer, it sends another one to a secondary server § The response to a retransmitted TCP request, could arrive too late · Simplifies server implementation § Specially for multi-threaded servers · Reduces network traffic § UDP has less overhead than TCP § UDP needs not establish a session before sending data 15 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5

PPP overview and traditional authentication methods · This Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) allows sending several protocols above its headers · The establishment of the PPP link requires certain handshaking. § LCP - Link Control Messages To determine MLPPP, the MTU and decide the authentication algorithm for the user § Authentication - It will depend on the protocol used: PAP, CHAP, MSCHAPv 2, EAP During this stage, the RADIUS server is contacted by the NAS § NCP - Network Control Protocol, to negotiate extra parameters IPCP, the IP address assigned to the user CCP, if the data is going to be compressed ECP, if the data is going to be encrypted 16 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
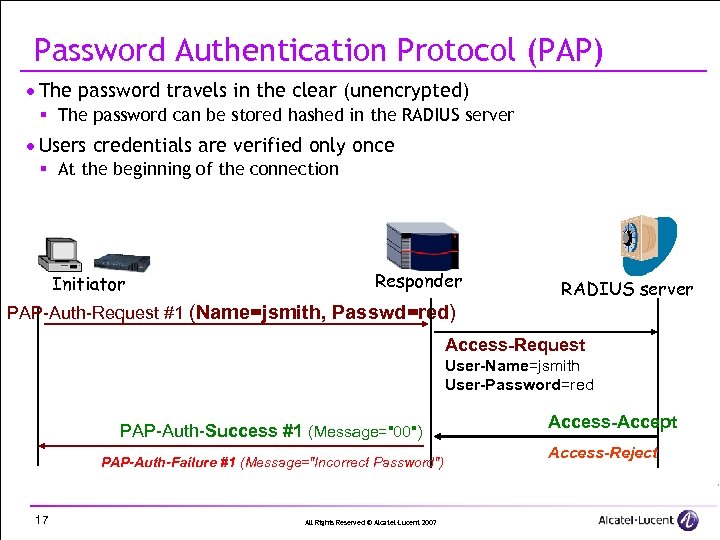
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) · The password travels in the clear (unencrypted) § The password can be stored hashed in the RADIUS server · Users credentials are verified only once § At the beginning of the connection Initiator Responder RADIUS server PAP-Auth-Request #1 (Name=jsmith, Passwd=red) Access-Request User-Name=jsmith User-Password=red PAP-Auth-Success #1 (Message="00") PAP-Auth-Failure #1 (Message="Incorrect Password") 17 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Access-Accept Access-Reject
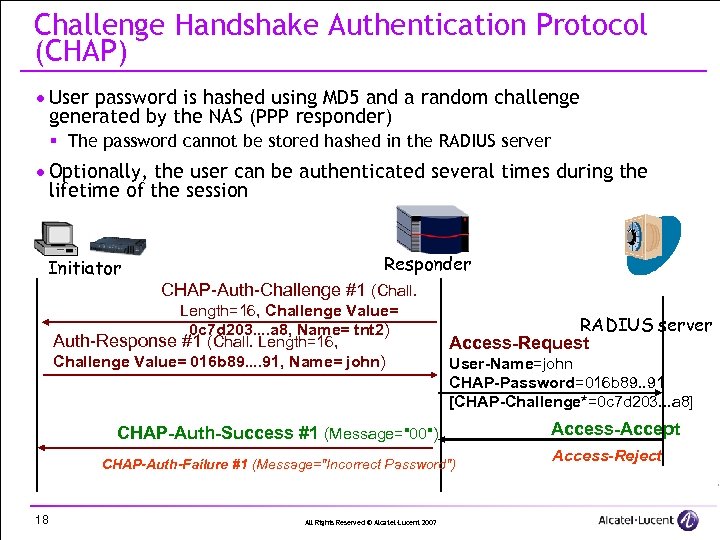
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) · User password is hashed using MD 5 and a random challenge generated by the NAS (PPP responder) § The password cannot be stored hashed in the RADIUS server · Optionally, the user can be authenticated several times during the lifetime of the session Initiator Responder CHAP-Auth-Challenge #1 (Chall. Length=16, Challenge Value= 0 c 7 d 203. . a 8, Name= tnt 2) Auth-Response #1 (Chall. Length=16, Challenge Value= 016 b 89. . 91, Name= john) RADIUS server Access-Request User-Name=john CHAP-Password=016 b 89. . 91 [CHAP-Challenge*=0 c 7 d 203. . . a 8] CHAP-Auth-Success #1 (Message="00") CHAP-Auth-Failure #1 (Message="Incorrect Password") 18 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Access-Accept Access-Reject
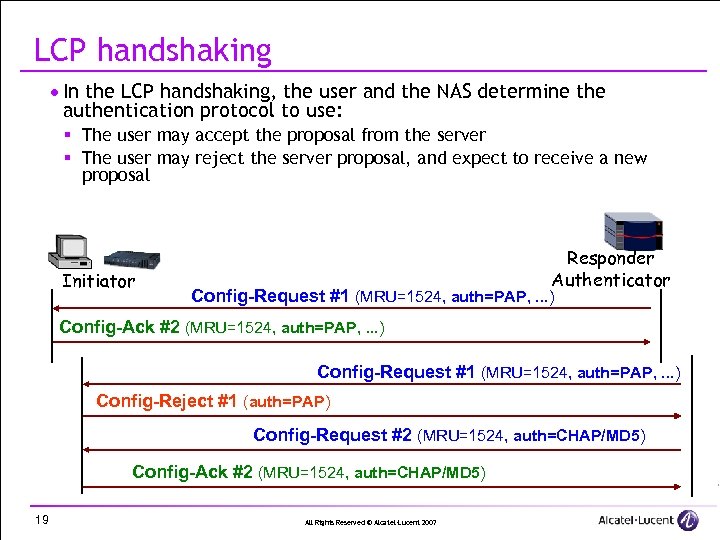
LCP handshaking · In the LCP handshaking, the user and the NAS determine the authentication protocol to use: § The user may accept the proposal from the server § The user may reject the server proposal, and expect to receive a new proposal Initiator Responder Authenticator Config-Request #1 (MRU=1524, auth=PAP, . . . ) Config-Ack #2 (MRU=1524, auth=PAP, . . . ) Config-Request #1 (MRU=1524, auth=PAP, . . . ) Config-Reject #1 (auth=PAP) Config-Request #2 (MRU=1524, auth=CHAP/MD 5) Config-Ack #2 (MRU=1524, auth=CHAP/MD 5) 19 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
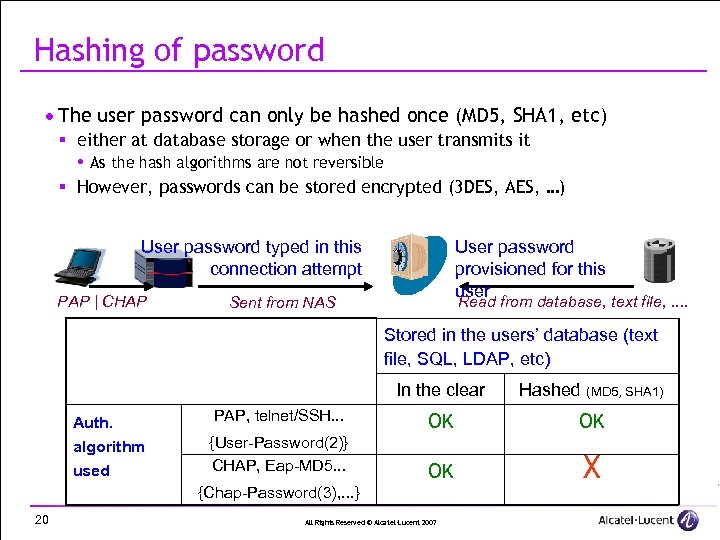
Hashing of password · The user password can only be hashed once (MD 5, SHA 1, etc) § either at database storage or when the user transmits it As the hash algorithms are not reversible § However, passwords can be stored encrypted (3 DES, AES, …) User password typed in this connection attempt PAP | CHAP User password provisioned for this user Read from database, text file, . . Sent from NAS Stored in the users’ database (text file, SQL, LDAP, etc) In the clear Auth. algorithm used PAP, telnet/SSH. . . {User-Password(2)} CHAP, Eap-MD 5. . . Hashed (MD 5, SHA 1) OK OK OK X {Chap-Password(3), . . . } 20 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
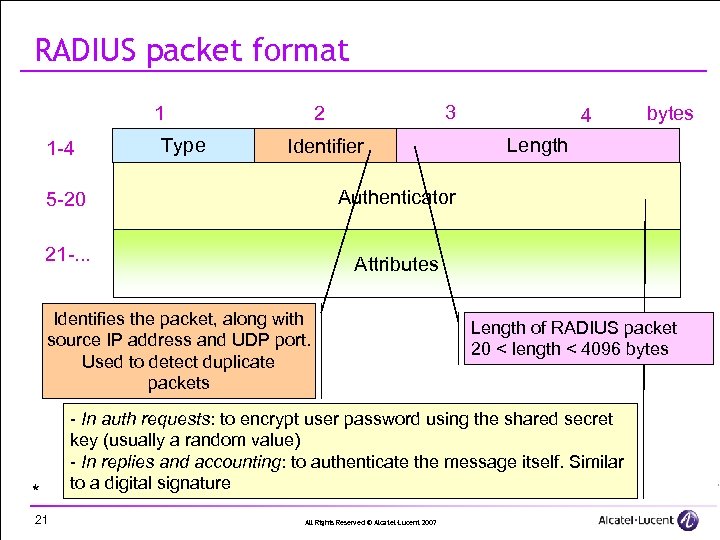
RADIUS packet format 1 -4 Type 3 2 1 Identifier 21 -. . . Length Attributes Identifies the packet, along with source IP address and UDP port. Used to detect duplicate packets 21 bytes Authenticator 5 -20 * 4 Length of RADIUS packet 20 < length < 4096 bytes - In auth requests: to encrypt user password using the shared secret key (usually a random value) - In replies and accounting: to authenticate the message itself. Similar to a digital signature All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
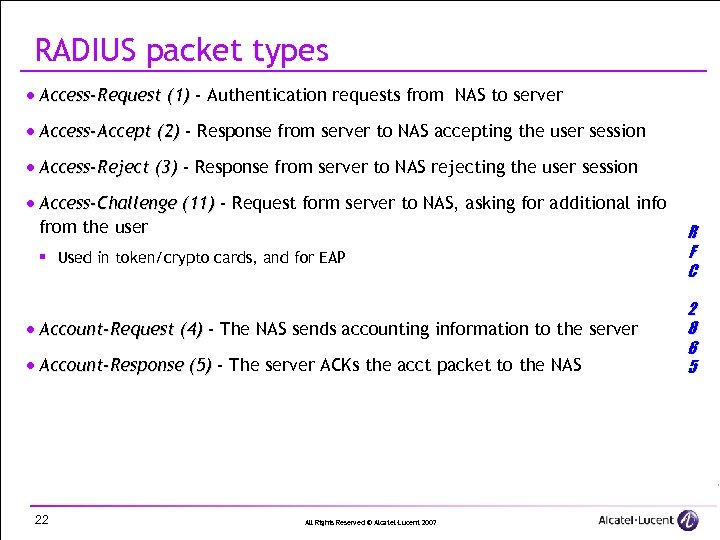
RADIUS packet types · Access-Request (1) - Authentication requests from NAS to server · Access-Accept (2) - Response from server to NAS accepting the user session · Access-Reject (3) - Response from server to NAS rejecting the user session · Access-Challenge (11) - Request form server to NAS, asking for additional info from the user § Used in token/crypto cards, and for EAP · Account-Request (4) - The NAS sends accounting information to the server · Account-Response (5) - The server ACKs the acct packet to the NAS 22 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
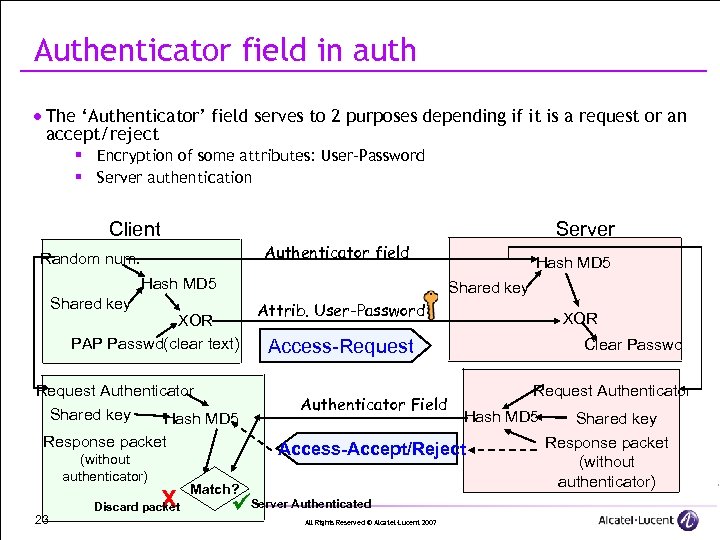
Authenticator field in auth · The ‘Authenticator’ field serves to 2 purposes depending if it is a request or an accept/reject § Encryption of some attributes: User-Password § Server authentication Client Server Authenticator field Random num. Hash MD 5 Shared key XOR PAP Passwd(clear text) Request Authenticator Shared key Hash MD 5 Response packet (without authenticator) 23 X Discard packet Hash MD 5 Attrib. User-Password XOR Access-Request Authenticator Field Clear Passwd Request Authenticator Hash MD 5 Access-Accept/Reject Match? Server Authenticated All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Shared key Response packet (without authenticator)
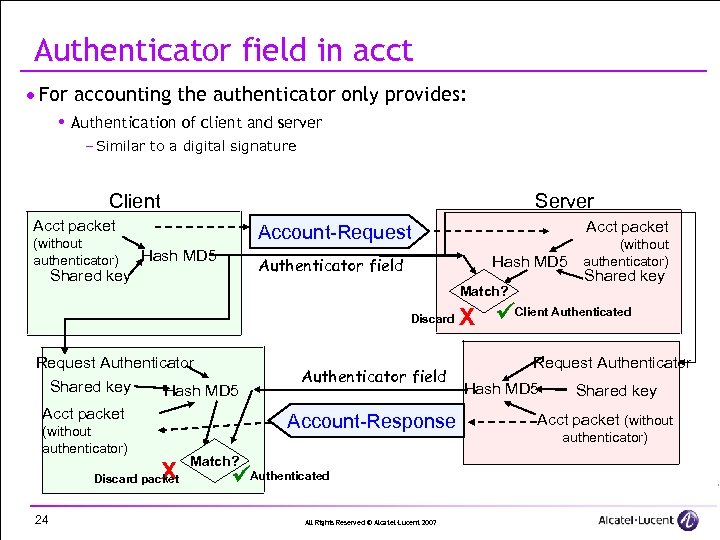
Authenticator field in acct · For accounting the authenticator only provides: Authentication of client and server – Similar to a digital signature Client Server Acct packet (without authenticator) Hash MD 5 Authenticator field Shared key Match? Discard Request Authenticator Shared key Hash MD 5 Acct packet (without authenticator) X Discard packet 24 Acct packet Account-Request Authenticator field Account-Response Match? Authenticated All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 (without authenticator) Shared key X Client Authenticated Request Authenticator Hash MD 5 Shared key Acct packet (without authenticator)

Example of successful auth: Dial-in user with PAP Access-Request (1) - ID=1 User-Name (1) = ”pepe" User-Password (2) = 5 E%&gn)8 NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 20 Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) NAS-Port-Type (61) = Async (0) Called-Station-Id (30) = 917529000 Calling-Station-Id (31) = 918078419 RADIUS client - NAS- PSTN POTS Modem IP RADIUS server Access-Accept (2) - ID=1 Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) Framed-IP-Address (8) = 255. 254 Framed-IP-Netmask (9) = 255 Framed-Routing (10) = None (0) Framed-Compression (13) = VJ TCP/IP (1) Framed-MTU (12) = 1500 Session-Timeout (27) = 7200 * 25 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007

Example of an PPPo. A (ADSL) connection Access-Request (1) - ID=1 For ADSL with PPPo. A, there is no Called-Station-Id or Calling-Station Id. For PPPo. E, they represent the Ethernet MAC addresses User-Name = "user 11@aunadsl" CHAP-Password = "�011266…303" CHAP-Challenge = "e241…�00" NAS-IP-Address = 1. 2. 3. 4 NAS-Port = 3329 Ascend-NAS-Port-Format = 2_4_5_5 NAS-Port-Type = Sync Service-Type = Framed-User Framed-Protocol = PPP Acct-Session-Id = "483015958" IP RADIUS server ATM ADSL line DSLAM PPPo. A Client * 26 RADIUS client -BRAS- Access-Accept (2) - ID=1 Service-Type = Framed-User Framed-Protocol = PPP Ascend-Source-IP-Check = Source-IP-Check-Y Ascend-IP-Source-If = "sip 100" Framed-Pool = 1 Filter-Id=Foo Ascend-Filter-Required=Required-Yes All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
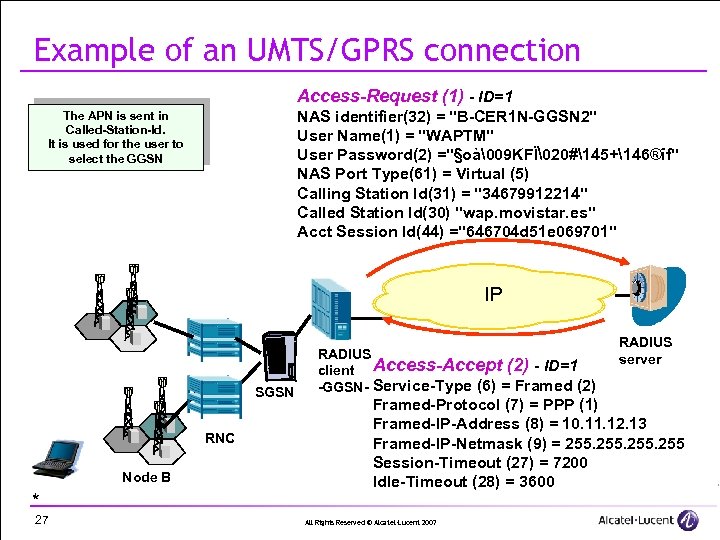
Example of an UMTS/GPRS connection Access-Request (1) - ID=1 NAS identifier(32) = "B-CER 1 N-GGSN 2" User Name(1) = "WAPTM" User Password(2) ="§oà�09 KFÏ�20#145+146®îf" NAS Port Type(61) = Virtual (5) Calling Station Id(31) = "34679912214" Called Station Id(30) "wap. movistar. es" Acct Session Id(44) ="646704 d 51 e 069701" The APN is sent in Called-Station-Id. It is used for the user to select the GGSN IP SGSN RNC Node B * 27 RADIUS client Access-Accept (2) - ID=1 -GGSN- Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) RADIUS server Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) Framed-IP-Address (8) = 10. 11. 12. 13 Framed-IP-Netmask (9) = 255 Session-Timeout (27) = 7200 Idle-Timeout (28) = 3600 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
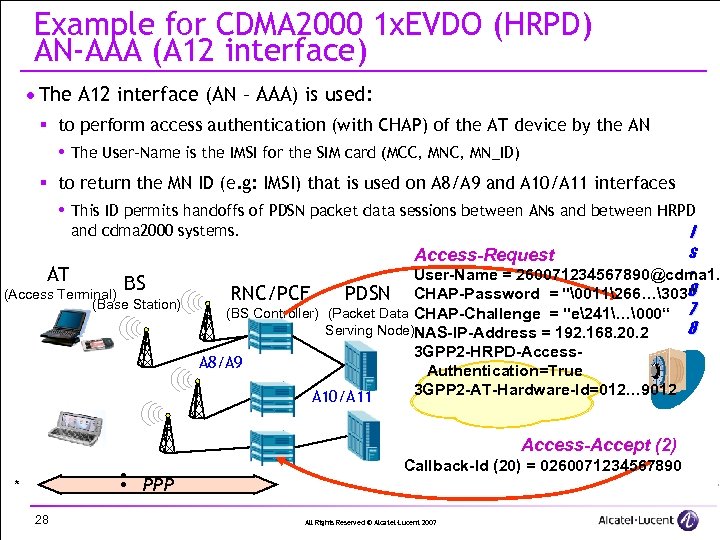
Example for CDMA 2000 1 x. EVDO (HRPD) AN-AAA (A 12 interface) · The A 12 interface (AN – AAA) is used: § to perform access authentication (with CHAP) of the AT device by the AN The User-Name is the IMSI for the SIM card (MCC, MN_ID) § to return the MN ID (e. g: IMSI) that is used on A 8/A 9 and A 10/A 11 interfaces This ID permits handoffs of PDSN packet data sessions between ANs and between HRPD and cdma 2000 systems. I s Access-Request User-Name = 260071234567890@cdma 1. AT BS 8 (Access Terminal) RNC/PCF PDSN CHAP-Password = "�011266…303" (Base Station) (BS Controller) (Packet Data CHAP-Challenge = "e241…�00“ 7 8 Serving Node)NAS-IP-Address = 192. 168. 20. 2 3 GPP 2 -HRPD-Access. A 8/A 9 Authentication=True 3 GPP 2 -AT-Hardware-Id=012… 9012 A 10/A 11 Access-Accept (2) PPP * 28 Callback-Id (20) = 0260071234567890 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
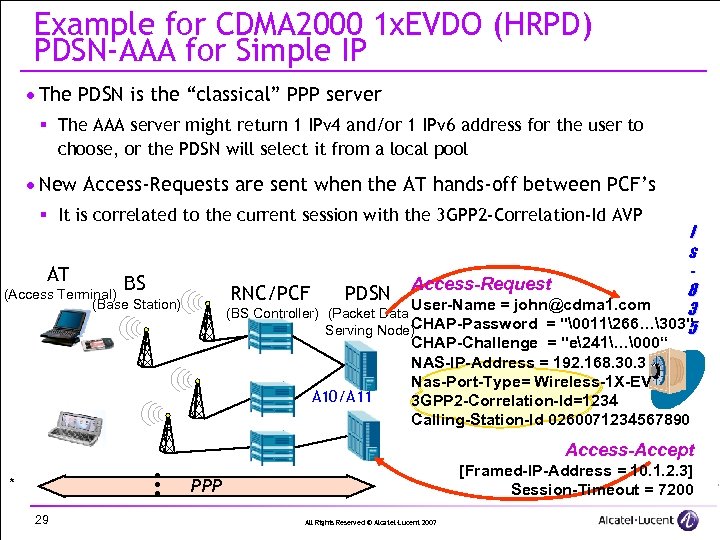
Example for CDMA 2000 1 x. EVDO (HRPD) PDSN-AAA for Simple IP · The PDSN is the “classical” PPP server § The AAA server might return 1 IPv 4 and/or 1 IPv 6 address for the user to choose, or the PDSN will select it from a local pool · New Access-Requests are sent when the AT hands-off between PCF’s § It is correlated to the current session with the 3 GPP 2 -Correlation-Id AVP AT I s Access-Request 8 RNC/PCF PDSN User-Name = john@cdma 1. com 3 (BS Controller) (Packet Data CHAP-Password = "�011266…303" 5 Serving Node) BS (Access Terminal) (Base Station) A 10/A 11 CHAP-Challenge = "e241…�00“ NAS-IP-Address = 192. 168. 30. 3 Nas-Port-Type= Wireless-1 X-EV 3 GPP 2 -Correlation-Id=1234 Calling-Station-Id 0260071234567890 Access-Accept * [Framed-IP-Address = 10. 1. 2. 3] Session-Timeout = 7200 PPP 29 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
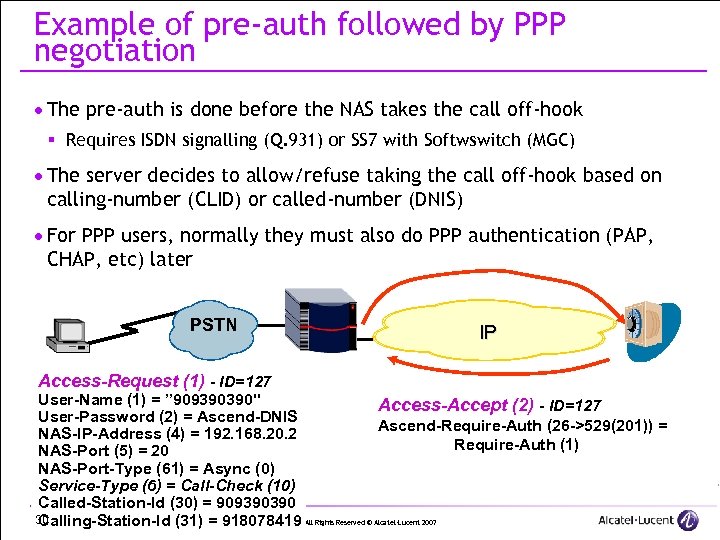
Example of pre-auth followed by PPP negotiation · The pre-auth is done before the NAS takes the call off-hook § Requires ISDN signalling (Q. 931) or SS 7 with Softwswitch (MGC) · The server decides to allow/refuse taking the call off-hook based on calling-number (CLID) or called-number (DNIS) · For PPP users, normally they must also do PPP authentication (PAP, CHAP, etc) later PSTN Access-Request (1) - ID=127 IP User-Name (1) = ” 909390390" Access-Accept (2) - ID=127 User-Password (2) = Ascend-DNIS Ascend-Require-Auth (26 ->529(201)) = NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 Require-Auth (1) NAS-Port (5) = 20 NAS-Port-Type (61) = Async (0) Service-Type (6) = Call-Check (10) Called-Station-Id (30) = 909390390 30 Calling-Station-Id (31) = 918078419 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
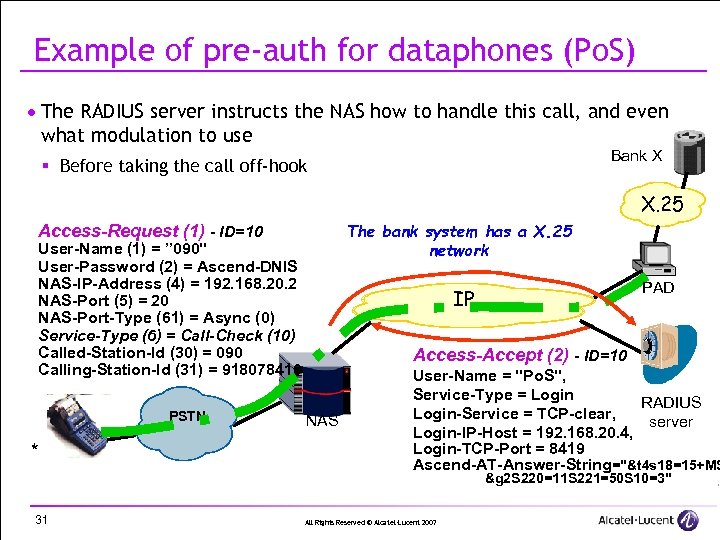
Example of pre-auth for dataphones (Po. S) · The RADIUS server instructs the NAS how to handle this call, and even what modulation to use Bank X § Before taking the call off-hook X. 25 The bank system has a X. 25 network Access-Request (1) - ID=10 User-Name (1) = ” 090" User-Password (2) = Ascend-DNIS NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 20 NAS-Port-Type (61) = Async (0) Service-Type (6) = Call-Check (10) Called-Station-Id (30) = 090 Calling-Station-Id (31) = 918078419 PSTN * PAD IP Access-Accept (2) - ID=10 NAS User-Name = "Po. S", Service-Type = Login RADIUS Login-Service = TCP-clear, server Login-IP-Host = 192. 168. 20. 4, Login-TCP-Port = 8419 Ascend-AT-Answer-String="&t 4 s 18=15+MS &g 2 S 220=11 S 221=50 S 10=3" 31 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
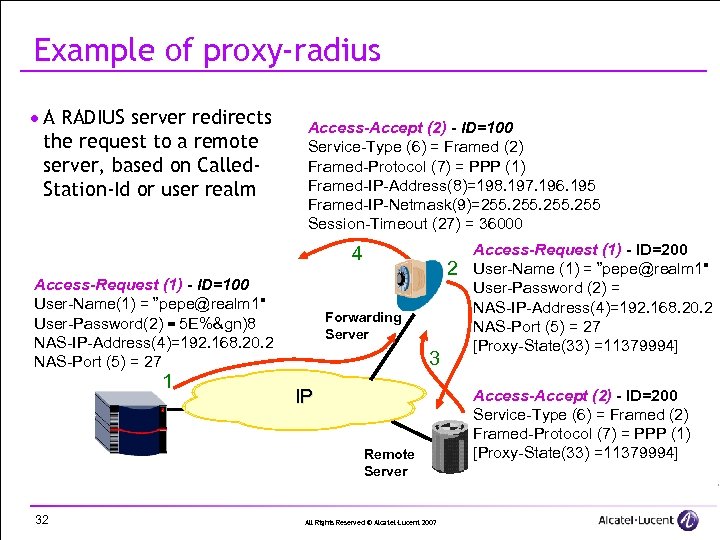
Example of proxy-radius · A RADIUS server redirects the request to a remote server, based on Called. Station-Id or user realm Access-Accept (2) - ID=100 Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) Framed-IP-Address(8)=198. 197. 196. 195 Framed-IP-Netmask(9)=255. 255 Session-Timeout (27) = 36000 4 Access-Request (1) - ID=100 User-Name(1) = ”pepe@realm 1" User-Password(2) = 5 E%&gn)8 NAS-IP-Address(4)=192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 27 1 2 Forwarding Server 3 IP Remote Server 32 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Access-Request (1) - ID=200 User-Name (1) = ”pepe@realm 1" User-Password (2) = NAS-IP-Address(4)=192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 27 [Proxy-State(33) =11379994] Access-Accept (2) - ID=200 Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) [Proxy-State(33) =11379994]
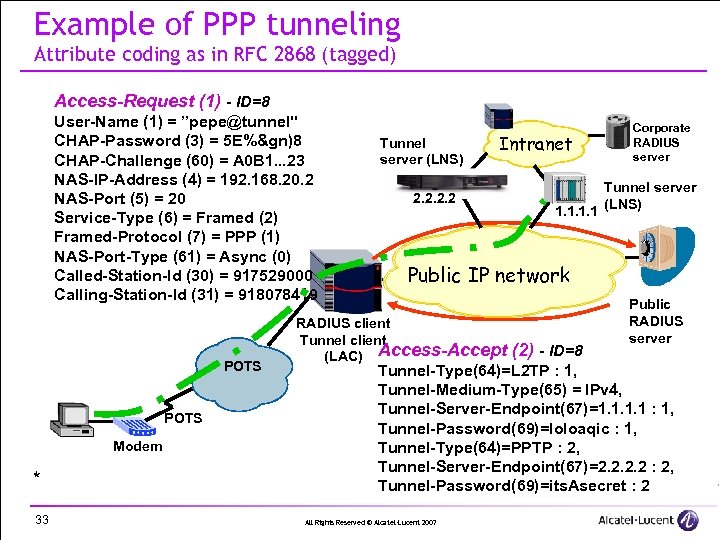
Example of PPP tunneling Attribute coding as in RFC 2868 (tagged) Access-Request (1) - ID=8 User-Name (1) = ”pepe@tunnel" CHAP-Password (3) = 5 E%&gn)8 CHAP-Challenge (60) = A 0 B 1. . . 23 NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 20 Service-Type (6) = Framed (2) Framed-Protocol (7) = PPP (1) NAS-Port-Type (61) = Async (0) Called-Station-Id (30) = 917529000 Calling-Station-Id (31) = 918078419 POTS Modem * 33 Tunnel server (LNS) Intranet 2. 2 1. 1 Corporate RADIUS server Tunnel server (LNS) Public IP network RADIUS client Tunnel client (LAC) Access-Accept (2) - ID=8 Public RADIUS server Tunnel-Type(64)=L 2 TP : 1, Tunnel-Medium-Type(65) = IPv 4, Tunnel-Server-Endpoint(67)=1. 1 : 1, Tunnel-Password(69)=loloaqic : 1, Tunnel-Type(64)=PPTP : 2, Tunnel-Server-Endpoint(67)=2. 2 : 2, Tunnel-Password(69)=its. Asecret : 2 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
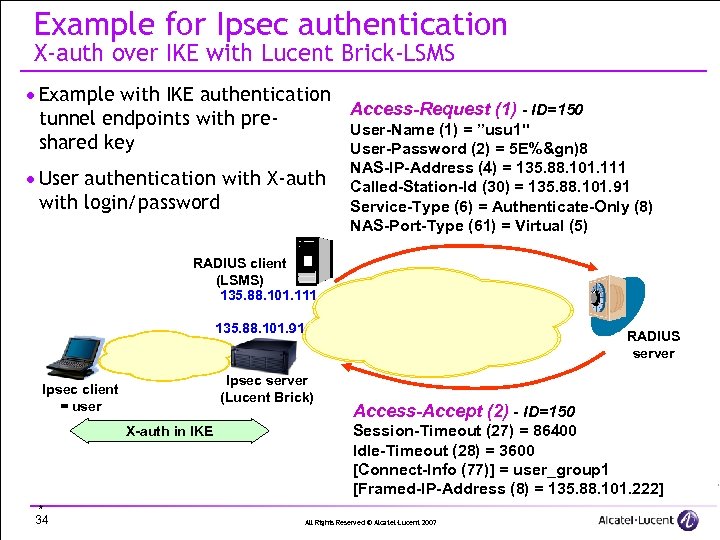
Example for Ipsec authentication X-auth over IKE with Lucent Brick-LSMS · Example with IKE authentication Access-Request (1) - ID=150 tunnel endpoints with pre. User-Name (1) = ”usu 1" shared key User-Password (2) = 5 E%&gn)8 · User authentication with X-auth with login/password NAS-IP-Address (4) = 135. 88. 101. 111 Called-Station-Id (30) = 135. 88. 101. 91 Service-Type (6) = Authenticate-Only (8) NAS-Port-Type (61) = Virtual (5) RADIUS client (LSMS) 135. 88. 101. 111 135. 88. 101. 91 Ipsec server (Lucent Brick) Ipsec client = user X-auth in IKE * 34 RADIUS server Access-Accept (2) - ID=150 Session-Timeout (27) = 86400 Idle-Timeout (28) = 3600 [Connect-Info (77)] = user_group 1 [Framed-IP-Address (8) = 135. 88. 101. 222] All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
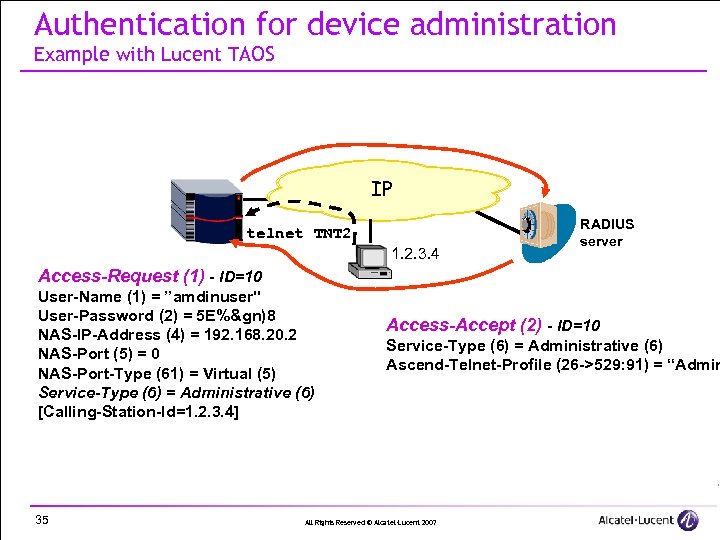
Authentication for device administration Example with Lucent TAOS IP telnet TNT 2 1. 2. 3. 4 RADIUS server Access-Request (1) - ID=10 User-Name (1) = ”amdinuser" User-Password (2) = 5 E%&gn)8 NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 0 NAS-Port-Type (61) = Virtual (5) Service-Type (6) = Administrative (6) [Calling-Station-Id=1. 2. 3. 4] 35 Access-Accept (2) - ID=10 Service-Type (6) = Administrative (6) Ascend-Telnet-Profile (26 ->529: 91) = “Admin All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
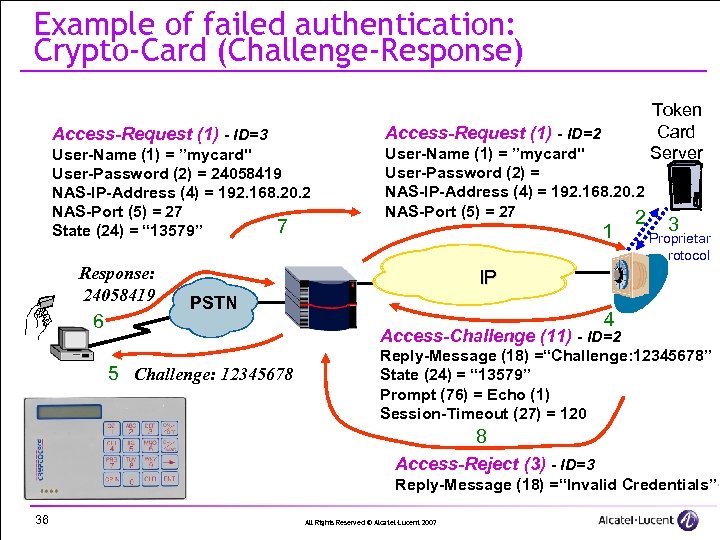
Example of failed authentication: Crypto-Card (Challenge-Response) Access-Request (1) - ID=3 Access-Request (1) - ID=2 User-Name (1) = ”mycard" User-Password (2) = 24058419 NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 27 7 State (24) = “ 13579” User-Name (1) = ”mycard" User-Password (2) = NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 NAS-Port (5) = 27 2 Response: 24058419 6 1 Token Card Server 3 Proprietar y protocol IP PSTN 4 Access-Challenge (11) - ID=2 5 Challenge: 12345678 Reply-Message (18) =“Challenge: 12345678” State (24) = “ 13579” Prompt (76) = Echo (1) Session-Timeout (27) = 120 8 Access-Reject (3) - ID=3 Reply-Message (18) =“Invalid Credentials” 36 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
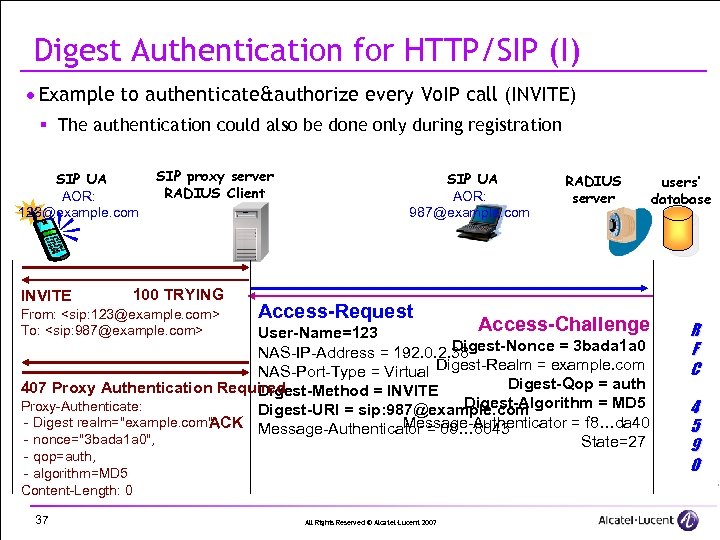
Digest Authentication for HTTP/SIP (I) · Example to authenticate&authorize every Vo. IP call (INVITE) § The authentication could also be done only during registration SIP UA AOR: 123@example. com SIP proxy server RADIUS Client 100 TRYING INVITE From: <sip: 123@example. com> To: <sip: 987@example. com> SIP UA AOR: 987@example. com Access-Request RADIUS server Access-Challenge User-Name=123 Digest-Nonce = 3 bada 1 a 0 NAS-IP-Address = 192. 0. 2. 38 NAS-Port-Type = Virtual Digest-Realm = example. com Digest-Qop = auth 407 Proxy Authentication Required Digest-Method = INVITE Digest-Algorithm = MD 5 Proxy-Authenticate: Digest-URI = sip: 987@example. com - Digest realm="example. com" , Message-Authenticator = f 8…da 40 ACK Message-Authenticator = 08… 8043 - nonce="3 bada 1 a 0", State=27 - qop=auth, - algorithm=MD 5 Content-Length: 0 37 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 users’ database R F C 4 5 9 0
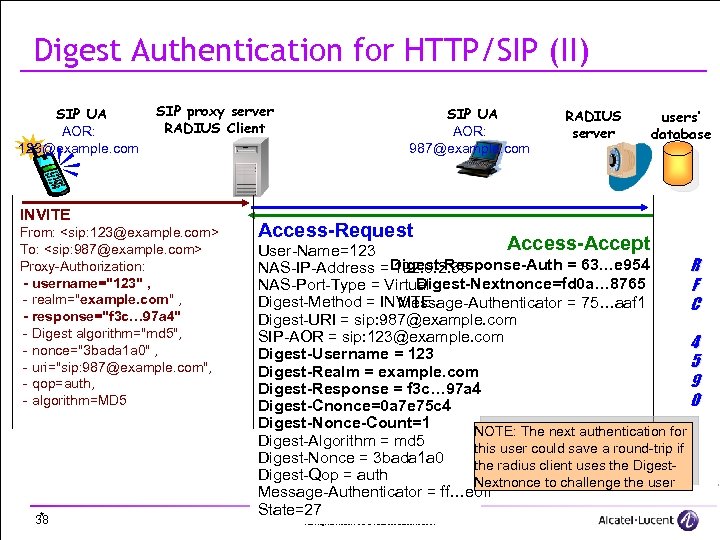
Digest Authentication for HTTP/SIP (II) SIP UA AOR: 123@example. com SIP proxy server RADIUS Client INVITE From: <sip: 123@example. com> To: <sip: 987@example. com> Proxy-Authorization: - username="123" , - realm="example. com" , - response="f 3 c… 97 a 4" - Digest algorithm="md 5", - nonce="3 bada 1 a 0" , - uri="sip: 987@example. com", - qop=auth, - algorithm=MD 5 * 38 SIP UA AOR: 987@example. com Access-Request RADIUS server users’ database Access-Accept User-Name=123 R NAS-IP-Address = Digest-Response-Auth = 63…e 954 192. 0. 2. 38 Digest-Nextnonce=fd 0 a… 8765 NAS-Port-Type = Virtual F Digest-Method = INVITE Message-Authenticator = 75…aaf 1 C Digest-URI = sip: 987@example. com SIP-AOR = sip: 123@example. com 4 Digest-Username = 123 5 Digest-Realm = example. com 9 Digest-Response = f 3 c… 97 a 4 0 Digest-Cnonce=0 a 7 e 75 c 4 Digest-Nonce-Count=1 NOTE: The next authentication for Digest-Algorithm = md 5 this user could save a round-trip if Digest-Nonce = 3 bada 1 a 0 the radius client uses the Digest-Qop = auth Nextnonce to challenge the user Message-Authenticator = ff…e 0 ff State=27 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
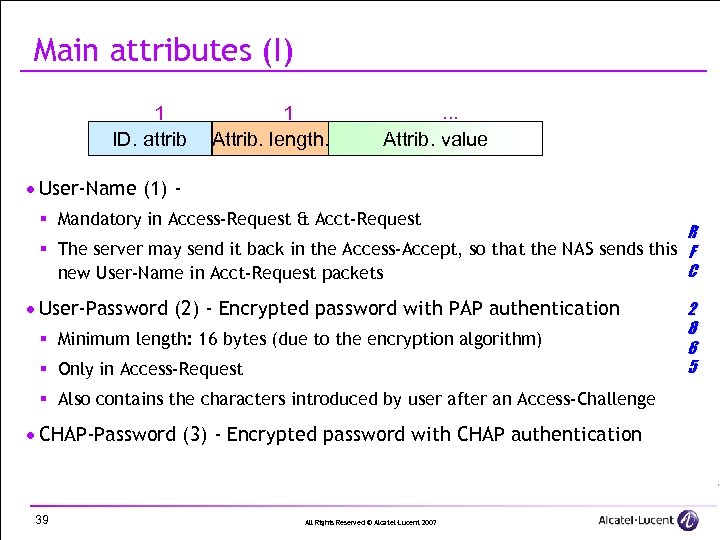
Main attributes (I) 1 ID. attrib 1 Attrib. length. . Attrib. value · User-Name (1) § Mandatory in Access-Request & Acct-Request R § The server may send it back in the Access-Accept, so that the NAS sends this F C new User-Name in Acct-Request packets · User-Password (2) - Encrypted password with PAP authentication § Minimum length: 16 bytes (due to the encryption algorithm) § Only in Access-Request § Also contains the characters introduced by user after an Access-Challenge · CHAP-Password (3) - Encrypted password with CHAP authentication 39 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 2 8 6 5
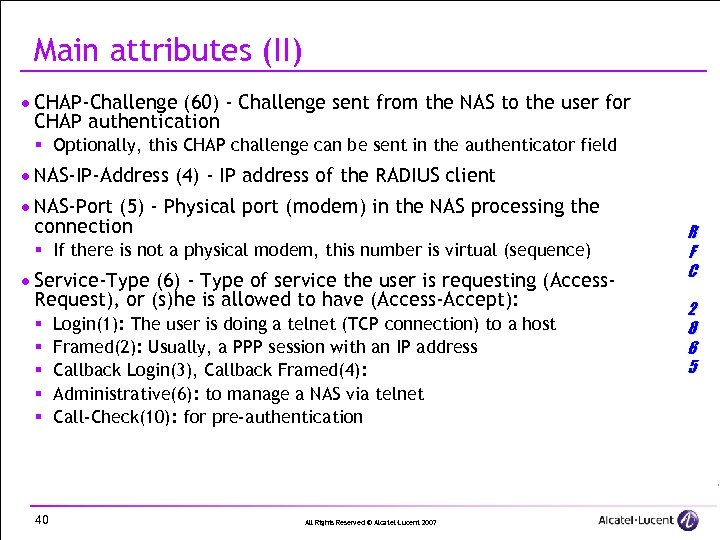
Main attributes (II) · CHAP-Challenge (60) - Challenge sent from the NAS to the user for CHAP authentication § Optionally, this CHAP challenge can be sent in the authenticator field · NAS-IP-Address (4) - IP address of the RADIUS client · NAS-Port (5) - Physical port (modem) in the NAS processing the connection § If there is not a physical modem, this number is virtual (sequence) · Service-Type (6) - Type of service the user is requesting (Access. Request), or (s)he is allowed to have (Access-Accept): § § § 40 Login(1): The user is doing a telnet (TCP connection) to a host Framed(2): Usually, a PPP session with an IP address Callback Login(3), Callback Framed(4): Administrative(6): to manage a NAS via telnet Call-Check(10): for pre-authentication All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
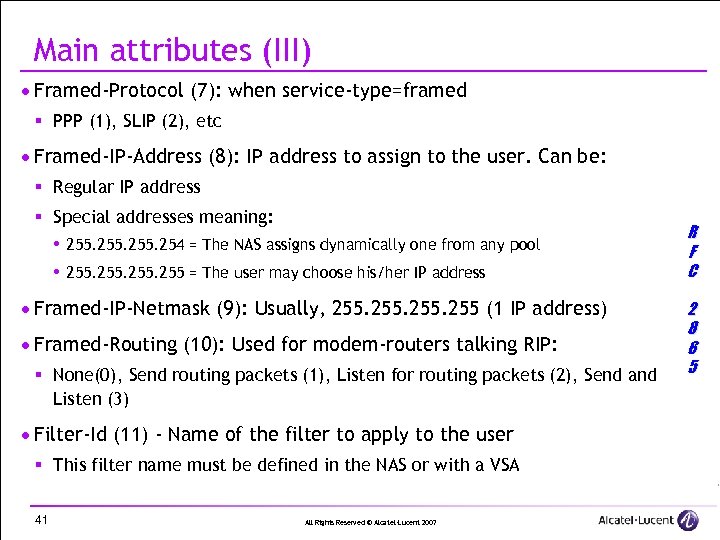
Main attributes (III) · Framed-Protocol (7): when service-type=framed § PPP (1), SLIP (2), etc · Framed-IP-Address (8): IP address to assign to the user. Can be: § Regular IP address § Special addresses meaning: 255. 254 = The NAS assigns dynamically one from any pool 255 = The user may choose his/her IP address · Framed-IP-Netmask (9): Usually, 255 (1 IP address) · Framed-Routing (10): Used for modem-routers talking RIP: § None(0), Send routing packets (1), Listen for routing packets (2), Send and Listen (3) · Filter-Id (11) - Name of the filter to apply to the user § This filter name must be defined in the NAS or with a VSA 41 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
Main attributes (IV) · Framed-MTU (12) - ‘Maximum Transmission Unit’ for layer 2 · Framed-Compression (13): § VJ TCP/IP header compression for PPP (1) · Login-IP-Host (14): In the Access-Accept the server instructs the NAS the IP address of a host to establish a TCP connection to § Used when IP Service-Type=Login, · Login-Service (15) – When Service-Type=Login: § Telnet (0), Rlogin (1), TCP Clear (2), etc · Reply-Message (18) – § For an Access-Challenge, the message to show to the user. § For an Access-Reject, may contain the cause to reject the connection 42 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
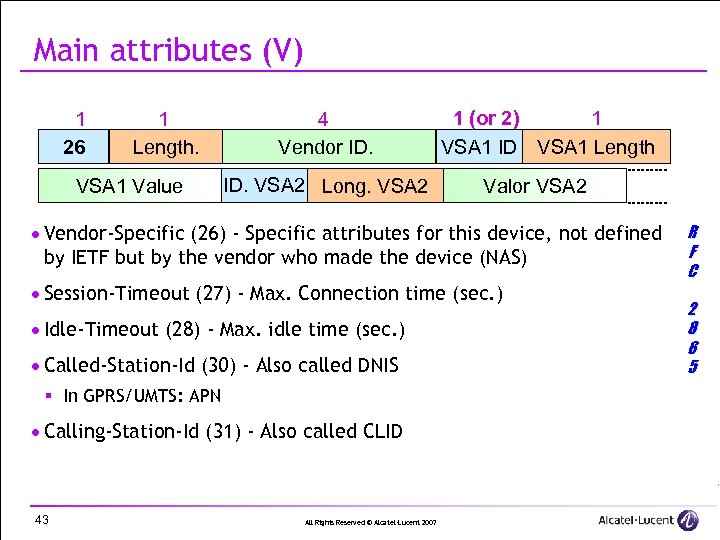
Main attributes (V) 1 26 1 Length. VSA 1 Value 4 Vendor ID. VSA 2 Long. VSA 2 1 (or 2) 1 VSA 1 ID VSA 1 Length Valor VSA 2 · Vendor-Specific (26) - Specific attributes for this device, not defined by IETF but by the vendor who made the device (NAS) · Session-Timeout (27) - Max. Connection time (sec. ) · Idle-Timeout (28) - Max. idle time (sec. ) · Called-Station-Id (30) - Also called DNIS § In GPRS/UMTS: APN · Calling-Station-Id (31) - Also called CLID 43 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
Main attributes (& VI) · NAS-Id (32) - Alternative to the attrib. NAS-IP-Address to identify the NAS sending the requests · Proxy-State (33) - May be used when a server is acting as proxy-RADIUS. § The NAS never receives this attribute · NAS-Port-Type (61) § Async/POTS (0), Sync (1), ISDN Sync (2), ISDN Async V. 120 (3), ISDN Async V. 110 (4) = Mobile § Virtual (5): ie, access via telnet § x. DSL (16), Cable (17) § GPRS (18), Wi-Fi=802. 11 (19), CDMA 2000 (22), UMTS (23) · Port-Limit (62) - To limit the max. number of calls that can be bonded together with MP (Multilink-Protocol), or concurrent sessions with the same User-Name 44 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 R F C 2 8 6 5
Protocol enhancement: RFC’s 2867 ->2869 · In RFC’s 2867 and 2868 new attributes are defined for tunneled connections (mainly L 2 TP) · RFC 2869 defines some general user attributes: § Prompt (76) - In a Challenge-Response to tell the NAS if it has to echo user response § Connect-Info (77) - May show info about user connection and speed. The format is NAS/vendor dependant: Ej: "28800 V 42 BIS/LAPM", "52000/31200 V 90", "9600 V 110/ISDN" § Acct-Interim-Interval (85) - The RADIUS server can order the NAS to send Interim acct packets with a certain periodicity R F C’ s 2 8 § Framed-Pool (88) - In the Access-Accept, to tell the NAS what pool to use for 6 7 user IP address assignment -> 9 This pool must be defined locally in NAS 45 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
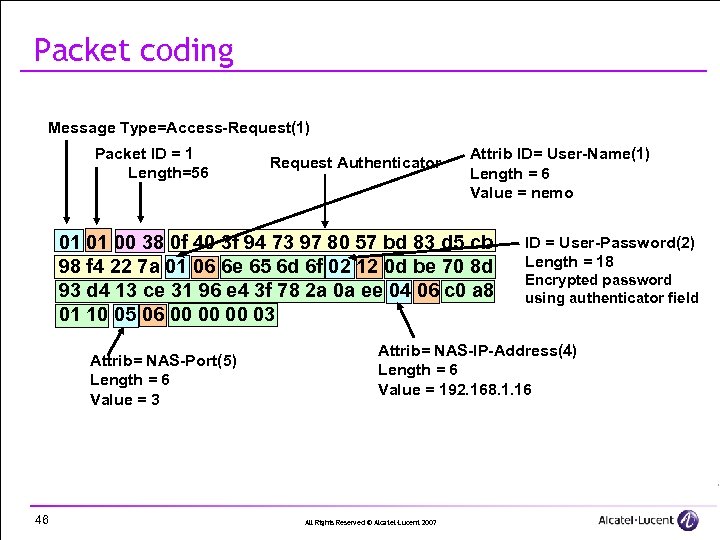
Packet coding Message Type=Access-Request(1) Packet ID = 1 Length=56 Request Authenticator Attrib ID= User-Name(1) Length = 6 Value = nemo 01 01 00 38 0 f 40 3 f 94 73 97 80 57 bd 83 d 5 cb 98 f 4 22 7 a 01 06 6 e 65 6 d 6 f 02 12 0 d be 70 8 d 93 d 4 13 ce 31 96 e 4 3 f 78 2 a 0 a ee 04 06 c 0 a 8 01 10 05 06 00 00 00 03 Attrib= NAS-Port(5) Length = 6 Value = 3 46 ID = User-Password(2) Length = 18 Encrypted password using authenticator field Attrib= NAS-IP-Address(4) Length = 6 Value = 192. 168. 1. 16 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
Accounting special attibutes (I) · Acct-Status-Type (40) - Type of accounting packet: § Start (1), Stop (2), Interim-Update (3), etc. § Accounting-On (7), Accounting-Off (8) The NAS is going to be/has been rebooted and won't send the Stop packets of users connected in that moment · Acct-Delay-Time (41) - # of seconds between the acct event time and the generation of this packet § Used mainly in retransmissions with a value != 0 · Acct-Input-Octets (42) - In Stop/interim, bytes tx by the user (input bytes for the NAS) from the beginning of the session = Upstream · Acct-Output-Octets (43) - Bytes received by the user = Downstream · Acct-Input-Packets (47) · Acct-Output-Packets (48) - 47 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
Accounting special attibutes (& II) · Acct-Session-Id (44) - Identifies a session in a unique manner in the NAS § This attribute may also be sent in the Access-Request packet (auth) § The value must be the same in Start, Stop and Interim (and in auth) · Acct-Authentic (45) - The way the user got authenticated § RADIUS (1), Local (2), Remote (3) · Acct-Session-Time (46) - How long (in seconds) the user was connected (Stop), has been connected up to the moment (interim) · Acct-Terminate-Cause (49) - General cause § User Request(1), Lost Carrier(2), Idle Timeout (4), Callback(16)… · Acct-Multi-Session-Id (50) - For MLPPP sessions, each call will have a different Acct-Session-Id, but the same Acct-Multi-Session-Id · Acct-Link-Count (51) - In MLPPP, the max number of channels that have been bonded together 48 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
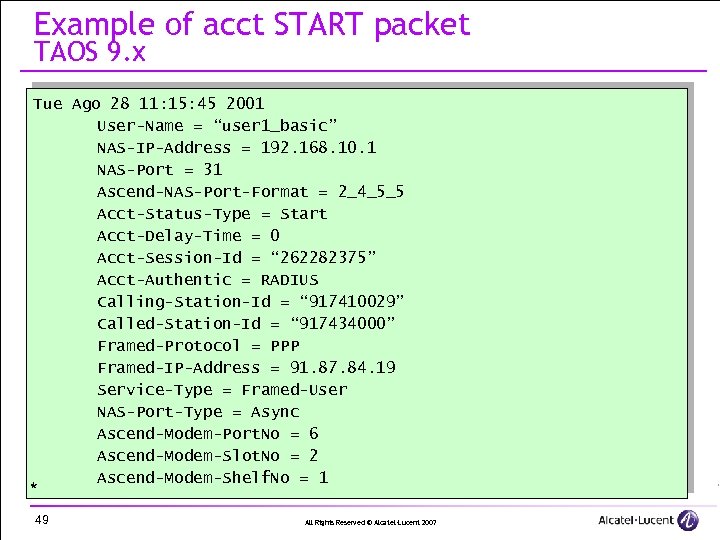
Example of acct START packet TAOS 9. x Tue Ago 28 11: 15: 45 2001 User-Name = “user 1_basic” NAS-IP-Address = 192. 168. 10. 1 NAS-Port = 31 Ascend-NAS-Port-Format = 2_4_5_5 Acct-Status-Type = Start Acct-Delay-Time = 0 Acct-Session-Id = “ 262282375” Acct-Authentic = RADIUS Calling-Station-Id = “ 917410029” Called-Station-Id = “ 917434000” Framed-Protocol = PPP Framed-IP-Address = 91. 87. 84. 19 Service-Type = Framed-User NAS-Port-Type = Async Ascend-Modem-Port. No = 6 Ascend-Modem-Slot. No = 2 Ascend-Modem-Shelf. No = 1 * 49 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
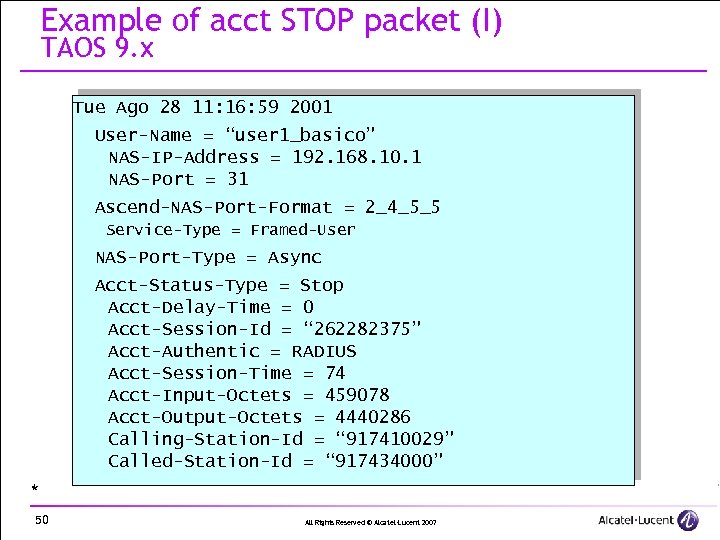
Example of acct STOP packet (I) TAOS 9. x Tue Ago 28 11: 16: 59 2001 User-Name = “user 1_basico” NAS-IP-Address = 192. 168. 10. 1 NAS-Port = 31 Ascend-NAS-Port-Format = 2_4_5_5 Service-Type = Framed-User NAS-Port-Type = Async Acct-Status-Type = Stop Acct-Delay-Time = 0 Acct-Session-Id = “ 262282375” Acct-Authentic = RADIUS Acct-Session-Time = 74 Acct-Input-Octets = 459078 Acct-Output-Octets = 4440286 Calling-Station-Id = “ 917410029” Called-Station-Id = “ 917434000” * 50 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
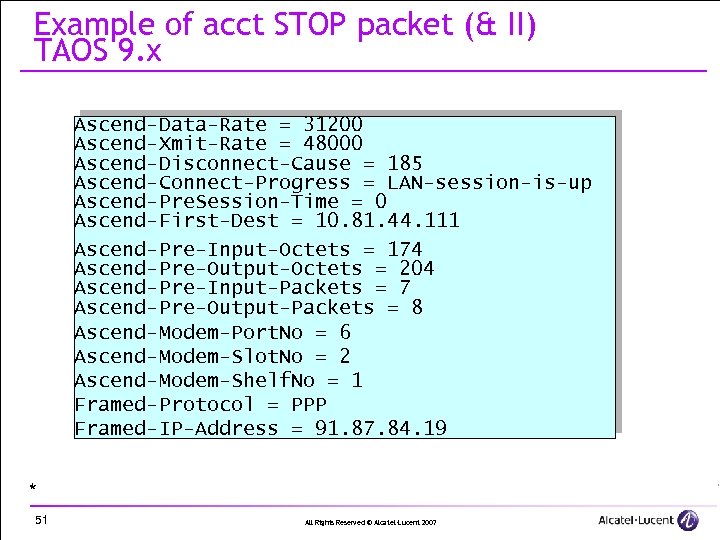
Example of acct STOP packet (& II) TAOS 9. x Ascend-Data-Rate = 31200 Ascend-Xmit-Rate = 48000 Ascend-Disconnect-Cause = 185 Ascend-Connect-Progress = LAN-session-is-up Ascend-Pre. Session-Time = 0 Ascend-First-Dest = 10. 81. 44. 111 Ascend-Pre-Input-Octets = 174 Ascend-Pre-Output-Octets = 204 Ascend-Pre-Input-Packets = 7 Ascend-Pre-Output-Packets = 8 Ascend-Modem-Port. No = 6 Ascend-Modem-Slot. No = 2 Ascend-Modem-Shelf. No = 1 Framed-Protocol = PPP Framed-IP-Address = 91. 87. 84. 19 * 51 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
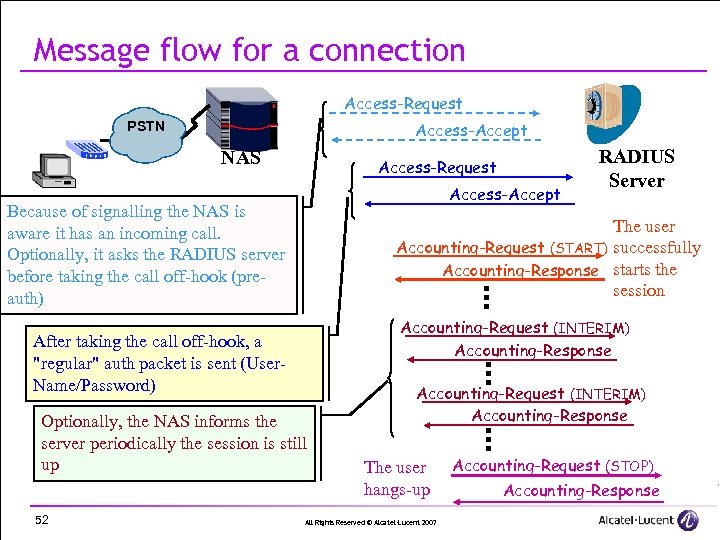
Message flow for a connection Access-Request Access-Accept PSTN NAS Access-Request Access-Accept Because of signalling the NAS is aware it has an incoming call. Optionally, it asks the RADIUS server before taking the call off-hook (preauth) The user Accounting-Request (START) successfully Accounting-Response starts the session Accounting-Request (INTERIM) Accounting-Response After taking the call off-hook, a "regular" auth packet is sent (User. Name/Password) Optionally, the NAS informs the server periodically the session is still up 52 RADIUS Server Accounting-Request (INTERIM) Accounting-Response The user hangs-up All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Accounting-Request (STOP) Accounting-Response
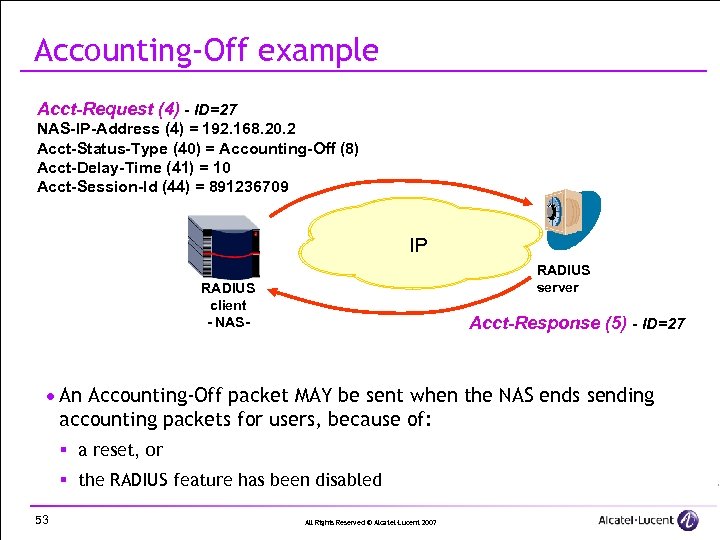
Accounting-Off example Acct-Request (4) - ID=27 NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 Acct-Status-Type (40) = Accounting-Off (8) Acct-Delay-Time (41) = 10 Acct-Session-Id (44) = 891236709 IP RADIUS server RADIUS client - NAS- Acct-Response (5) - ID=27 · An Accounting-Off packet MAY be sent when the NAS ends sending accounting packets for users, because of: § a reset, or § the RADIUS feature has been disabled 53 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
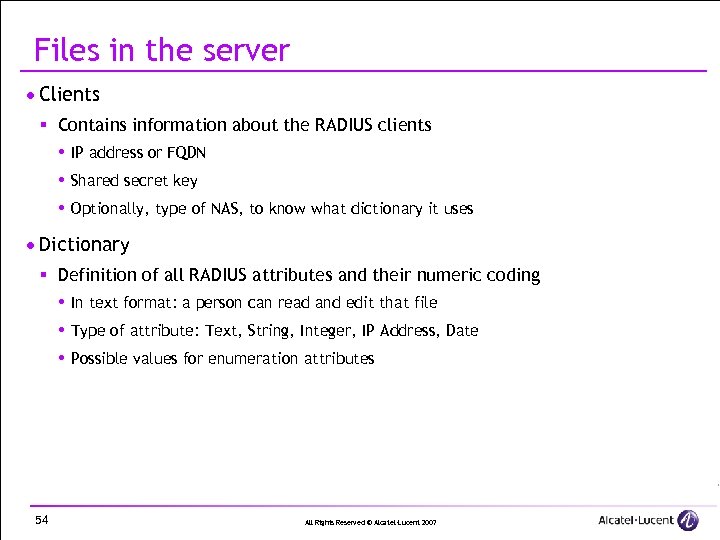
Files in the server · Clients § Contains information about the RADIUS clients IP address or FQDN Shared secret key Optionally, type of NAS, to know what dictionary it uses · Dictionary § Definition of all RADIUS attributes and their numeric coding In text format: a person can read and edit that file Type of attribute: Text, String, Integer, IP Address, Date Possible values for enumeration attributes 54 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
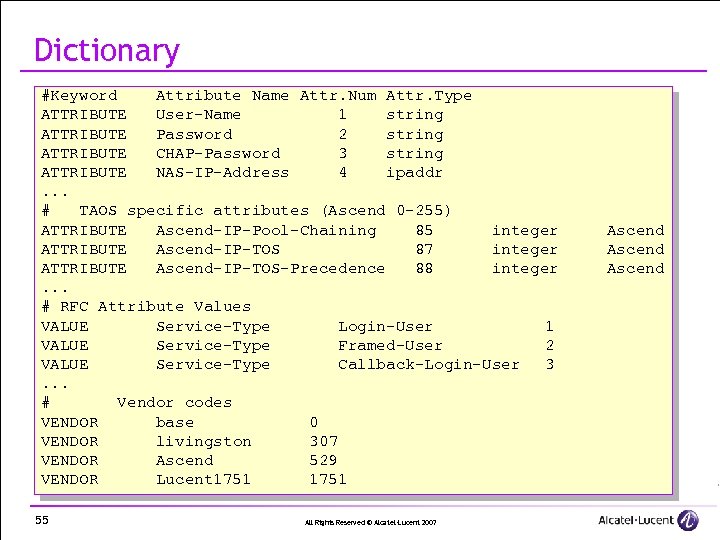
Dictionary #Keyword Attribute Name Attr. Num Attr. Type ATTRIBUTE User-Name 1 string ATTRIBUTE Password 2 string ATTRIBUTE CHAP-Password 3 string ATTRIBUTE NAS-IP-Address 4 ipaddr. . . # TAOS specific attributes (Ascend 0 -255) ATTRIBUTE Ascend-IP-Pool-Chaining 85 integer ATTRIBUTE Ascend-IP-TOS 87 integer ATTRIBUTE Ascend-IP-TOS-Precedence 88 integer. . . # RFC Attribute Values VALUE Service-Type Login-User 1 VALUE Service-Type Framed-User 2 VALUE Service-Type Callback-Login-User 3. . . # Vendor codes VENDOR base 0 VENDOR livingston 307 VENDOR Ascend 529 VENDOR Lucent 1751 55 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Ascend
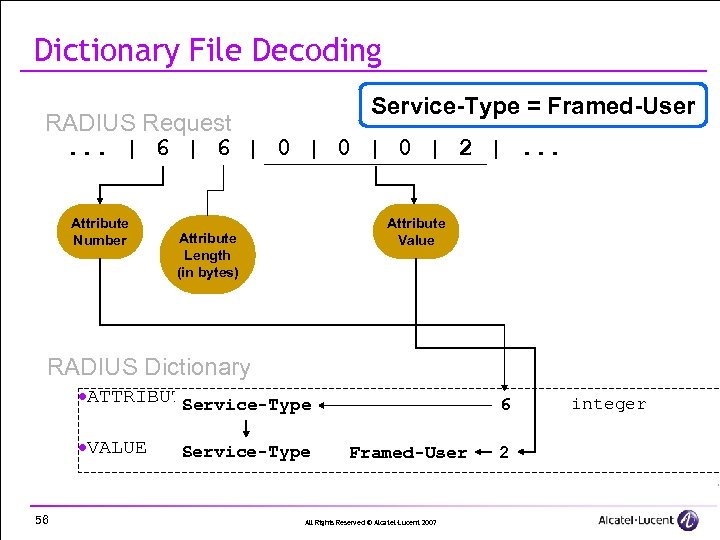
Dictionary File Decoding Service-Type = Framed-User RADIUS Request. . . | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 |. . . Attribute Number Attribute Value Attribute Length (in bytes) RADIUS Dictionary ·ATTRIBUTE Service-Type ·VALUE 56 Service-Type 6 Framed-User All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 2 integer
![Dictionary VSAs Example Dictionary entry: # Name VENDOR Ascend Number Type [Vendor] [(Modifiers)] 529 Dictionary VSAs Example Dictionary entry: # Name VENDOR Ascend Number Type [Vendor] [(Modifiers)] 529](https://present5.com/presentation/f762bd77a4e93dda950a367736bd874e/image-57.jpg)
Dictionary VSAs Example Dictionary entry: # Name VENDOR Ascend Number Type [Vendor] [(Modifiers)] 529 ATTRIBUTE Ascend-Secret 26 214 string Ascend (asecret, hidden) 529 | Attr. Number | Total Attr. Length | Vendor ID | data | VSA Attr. Number | VSA Attr. Length | VSA Attr. data 214 57 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
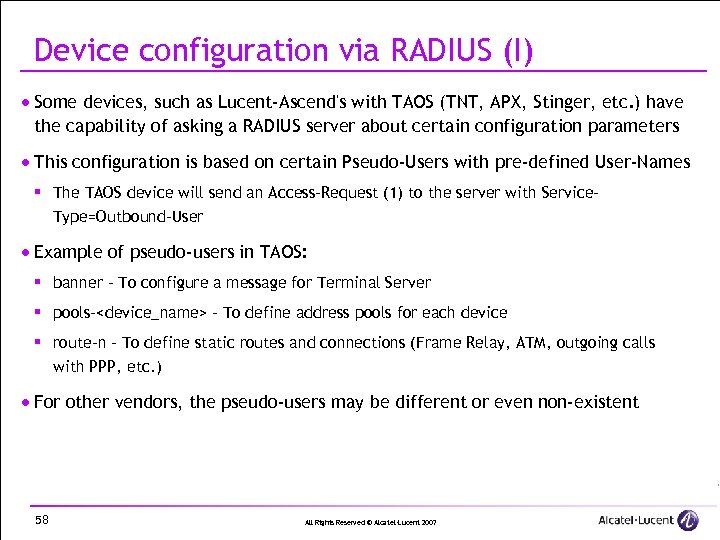
Device configuration via RADIUS (I) · Some devices, such as Lucent-Ascend's with TAOS (TNT, APX, Stinger, etc. ) have the capability of asking a RADIUS server about certain configuration parameters · This configuration is based on certain Pseudo-Users with pre-defined User-Names § The TAOS device will send an Access-Request (1) to the server with Service. Type=Outbound-User · Example of pseudo-users in TAOS: § banner - To configure a message for Terminal Server § pools-<device_name> - To define address pools for each device § route-n - To define static routes and connections (Frame Relay, ATM, outgoing calls with PPP, etc. ) · For other vendors, the pseudo-users may be different or even non-existent 58 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
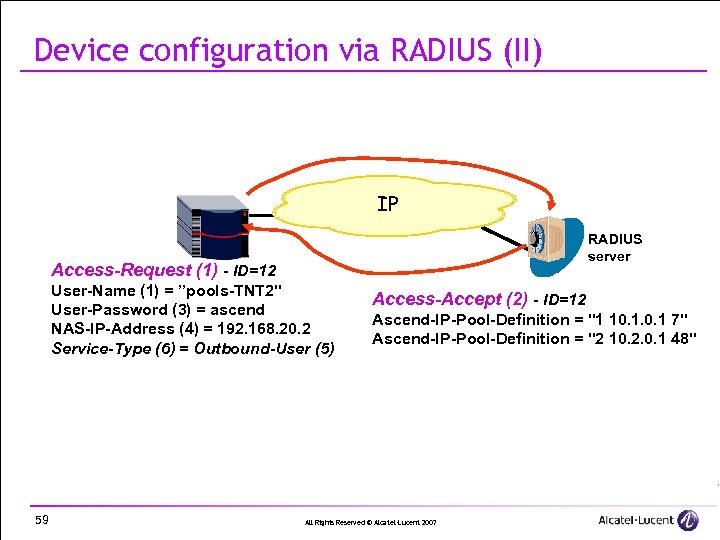
Device configuration via RADIUS (II) IP RADIUS server Access-Request (1) - ID=12 User-Name (1) = ”pools-TNT 2" User-Password (3) = ascend NAS-IP-Address (4) = 192. 168. 20. 2 Service-Type (6) = Outbound-User (5) 59 Access-Accept (2) - ID=12 Ascend-IP-Pool-Definition = "1 10. 1 7" Ascend-IP-Pool-Definition = "2 10. 2. 0. 1 48" All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
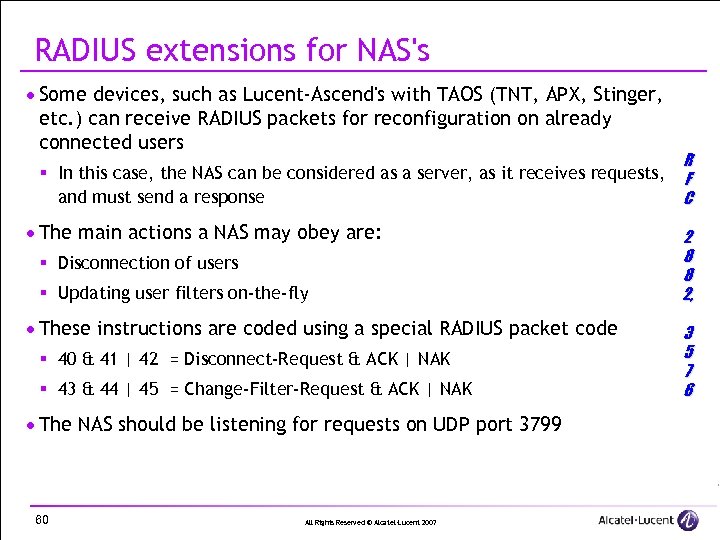
RADIUS extensions for NAS's · Some devices, such as Lucent-Ascend's with TAOS (TNT, APX, Stinger, etc. ) can receive RADIUS packets for reconfiguration on already connected users R § In this case, the NAS can be considered as a server, as it receives requests, F and must send a response C · The main actions a NAS may obey are: § Disconnection of users § Updating user filters on-the-fly · These instructions are coded using a special RADIUS packet code § 40 & 41 | 42 = Disconnect-Request & ACK | NAK § 43 & 44 | 45 = Change-Filter-Request & ACK | NAK · The NAS should be listening for requests on UDP port 3799 60 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 2 8 8 2, 3 5 7 6
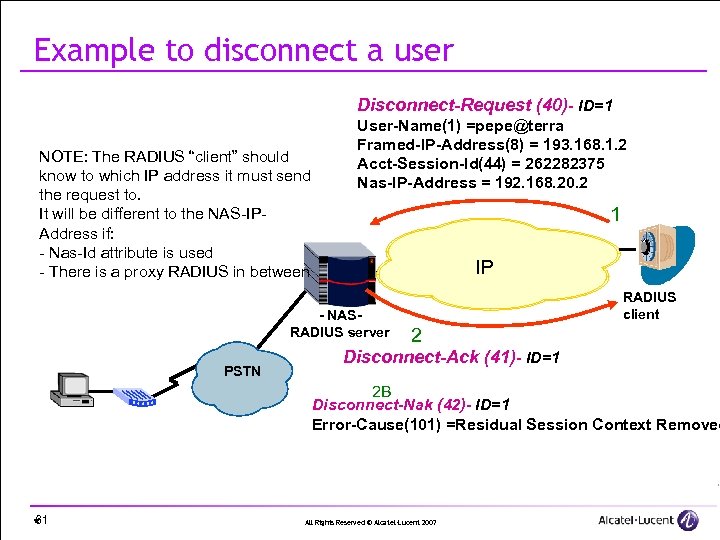
Example to disconnect a user Disconnect-Request (40)- ID=1 NOTE: The RADIUS “client” should know to which IP address it must send the request to. It will be different to the NAS-IPAddress if: - Nas-Id attribute is used - There is a proxy RADIUS in between User-Name(1) =pepe@terra Framed-IP-Address(8) = 193. 168. 1. 2 Acct-Session-Id(44) = 262282375 Nas-IP-Address = 192. 168. 20. 2 1 IP - NASRADIUS server PSTN RADIUS client 2 Disconnect-Ack (41)- ID=1 2 B Disconnect-Nak (42)- ID=1 Error-Cause(101) =Residual Session Context Removed 61 * All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
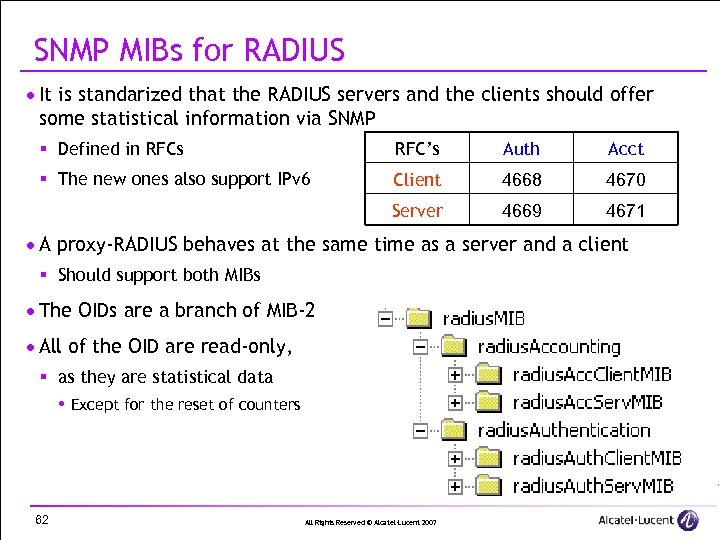
SNMP MIBs for RADIUS · It is standarized that the RADIUS servers and the clients should offer some statistical information via SNMP § Defined in RFCs RFC’s Auth Acct § The new ones also support IPv 6 Client 4668 4670 Server 4669 4671 · A proxy-RADIUS behaves at the same time as a server and a client § Should support both MIBs · The OIDs are a branch of MIB-2 · All of the OID are read-only, § as they are statistical data Except for the reset of counters 62 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
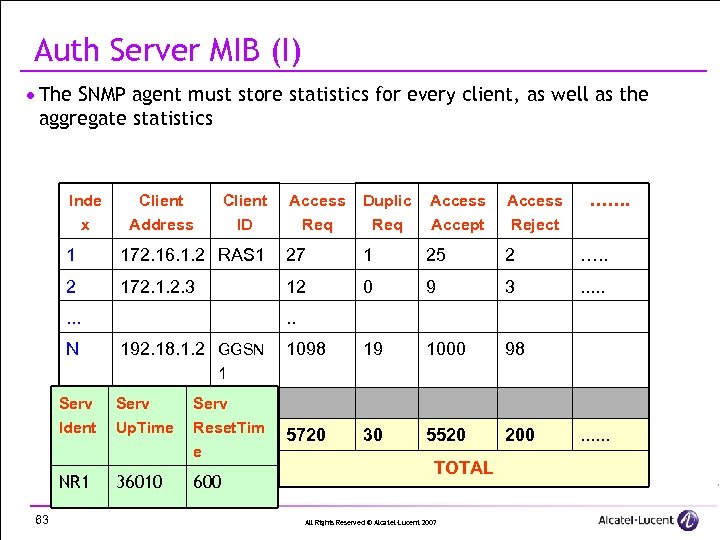
Auth Server MIB (I) · The SNMP agent must store statistics for every client, as well as the aggregate statistics Inde x Client Address Client ID Access Duplic Req Access Accept Access Reject . . . . 1 172. 16. 1. 2 RAS 1 27 1 25 2 …. . 2 172. 1. 2. 3 12 0 9 3 . . . 1098 19 1000 98 5720 30 5520 200 . . . N . . 192. 18. 1. 2 GGSN 1 Serv Ident Serv Up. Time Serv Reset. Tim e NR 1 63 36010 600 TOTAL All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 . . .
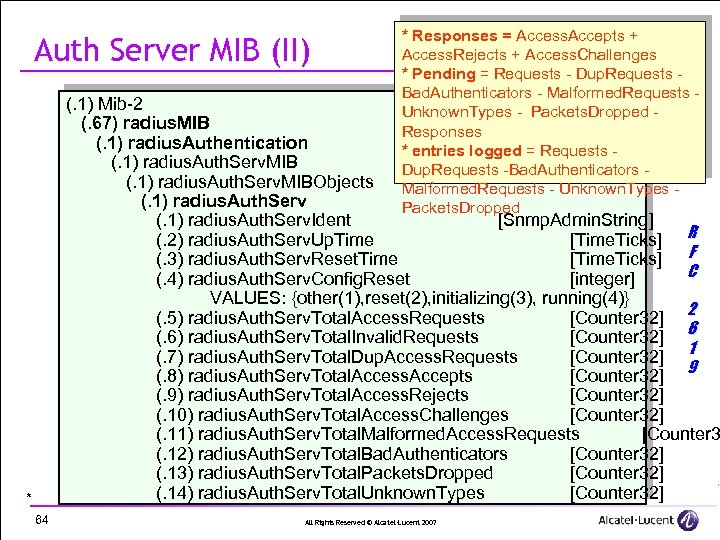
Auth Server MIB (II) * Responses = Access. Accepts + Access. Rejects + Access. Challenges * Pending = Requests - Dup. Requests Bad. Authenticators - Malformed. Requests Unknown. Types - Packets. Dropped Responses * entries logged = Requests Dup. Requests -Bad. Authenticators Malformed. Requests - Unknown. Types Packets. Dropped (. 1) Mib-2 (. 67) radius. MIB (. 1) radius. Authentication (. 1) radius. Auth. Serv. MIBObjects (. 1) radius. Auth. Serv. Ident [Snmp. Admin. String] (. 2) radius. Auth. Serv. Up. Time [Time. Ticks] R (. 3) radius. Auth. Serv. Reset. Time [Time. Ticks] F C (. 4) radius. Auth. Serv. Config. Reset [integer] VALUES: {other(1), reset(2), initializing(3), running(4)} (. 5) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Access. Requests [Counter 32] 2 (. 6) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Invalid. Requests [Counter 32] 6 1 (. 7) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Dup. Access. Requests [Counter 32] 9 (. 8) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Access. Accepts [Counter 32] (. 9) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Access. Rejects [Counter 32] (. 10) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Access. Challenges [Counter 32] (. 11) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Malformed. Access. Requests [Counter 3 (. 12) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Bad. Authenticators [Counter 32] (. 13) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Packets. Dropped [Counter 32] (. 14) radius. Auth. Serv. Total. Unknown. Types [Counter 32] • * 64 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
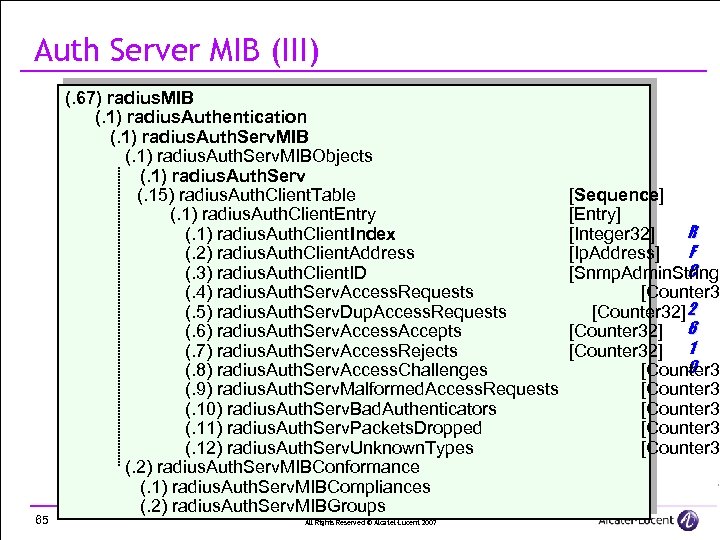
Auth Server MIB (III) 65 (. 67) radius. MIB (. 1) radius. Authentication (. 1) radius. Auth. Serv. MIBObjects (. 1) radius. Auth. Serv (. 15) radius. Auth. Client. Table (. 1) radius. Auth. Client. Entry (. 1) radius. Auth. Client. Index (. 2) radius. Auth. Client. Address (. 3) radius. Auth. Client. ID (. 4) radius. Auth. Serv. Access. Requests (. 5) radius. Auth. Serv. Dup. Access. Requests (. 6) radius. Auth. Serv. Access. Accepts (. 7) radius. Auth. Serv. Access. Rejects (. 8) radius. Auth. Serv. Access. Challenges (. 9) radius. Auth. Serv. Malformed. Access. Requests (. 10) radius. Auth. Serv. Bad. Authenticators (. 11) radius. Auth. Serv. Packets. Dropped (. 12) radius. Auth. Serv. Unknown. Types (. 2) radius. Auth. Serv. MIBConformance (. 1) radius. Auth. Serv. MIBCompliances (. 2) radius. Auth. Serv. MIBGroups All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 [Sequence] [Entry] R [Integer 32] F [Ip. Address] C [Snmp. Admin. String] [Counter 32] 2 [Counter 32] 6 [Counter 32] 1 9 [Counter 3 [Counter 3

Acct Client MIB 66 * Requests = Responses + Pending. Requests + Client. Timeouts * Successfully received = Responses Malformed. Responses - Bad. Authenticators Unknown. Types - Packets. Dropped (. 67) radius. MIB (. 2) radius. Accounting (. 2) radius. Acc. Client. MIB (. 1) radius. Acc. Client. MIBObjects (. 1) radius. Acc. Client. Invalid. Server. Addresses (. 2) radius. Acc. Client. Identifier (. 3) radius. Acc. Server. Table (. 1) radius. Acc. Server. Entry (. 1) radius. Acc. Server. Index (. 2) radius. Acc. Server. Address (. 3) radius. Acc. Client. Server. Port. Number (. 4) radius. Acc. Client. Round. Trip. Time (. 5) radius. Acc. Client. Requests (. 6) radius. Acc. Client. Retransmissions (. 7) radius. Acc. Client. Responses (. 8) radius. Acc. Client. Malformed. Responses (. 9) radius. Acc. Client. Bad. Authenticators (. 10) radius. Acc. Client. Pending. Requests (. 11) radius. Acc. Client. Timeouts (. 12) radius. Acc. Client. Unknown. Types (. 13) radius. Acc. Client. Packets. Dropped All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 [Counter 32] [Snmp. Admin. String [Sequence] R F [Entry] C [Integer 32] [Ip. Address] 2 [Integer 32] [Time. Ticks] 6 2 [Counter 32] 0 [Counter 32] [Gauge 32 [Counter 32] [Counter 3
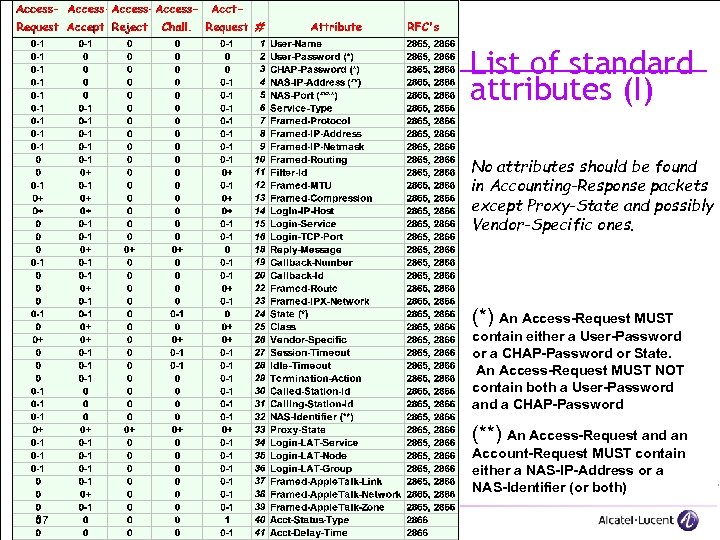
List of standard attributes (I) No attributes should be found in Accounting-Response packets except Proxy-State and possibly Vendor-Specific ones. (*) An Access-Request MUST contain either a User-Password or a CHAP-Password or State. An Access-Request MUST NOT contain both a User-Password and a CHAP-Password (**) An Access-Request and an Account-Request MUST contain either a NAS-IP-Address or a NAS-Identifier (or both) 67 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
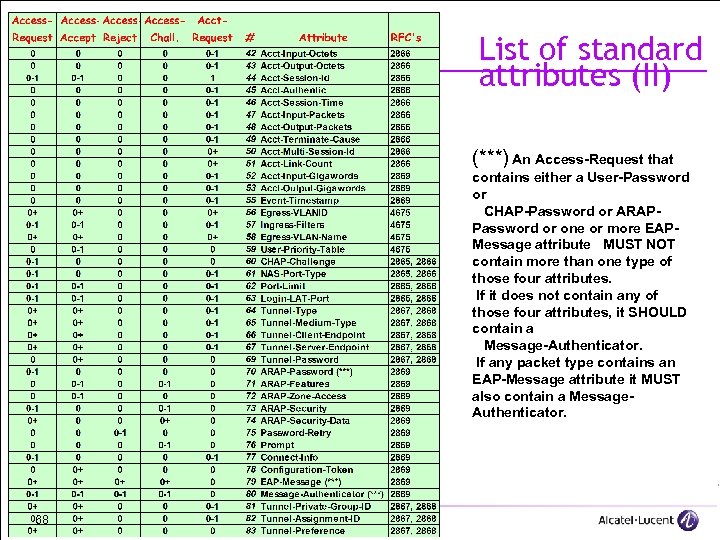
List of standard attributes (II) (***) An Access-Request that contains either a User-Password or CHAP-Password or ARAPPassword or one or more EAPMessage attribute MUST NOT contain more than one type of those four attributes. If it does not contain any of those four attributes, it SHOULD contain a Message-Authenticator. If any packet type contains an EAP-Message attribute it MUST also contain a Message. Authenticator. 68 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007
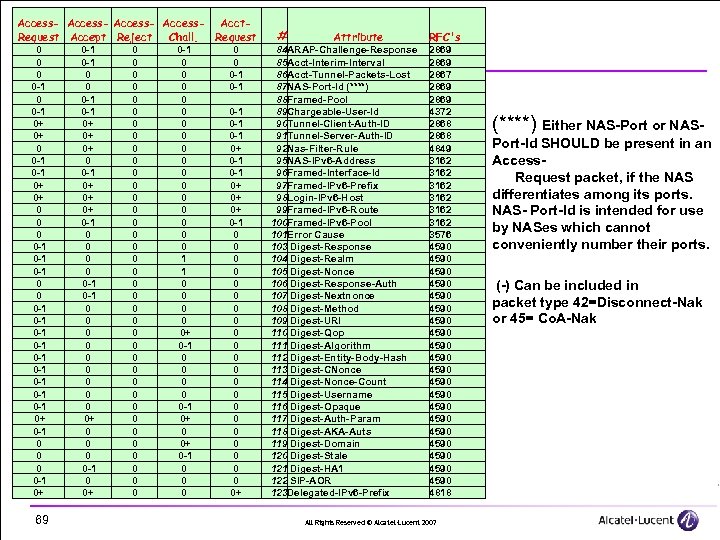
Access- Acct. Request Accept Reject Chall. Request 0 0 -1 0+ 0+ 0 0 -1 0 -1 0 0 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0+ 0 -1 0+ 69 0 -1 0 0 0 -1 0+ 0+ 0+ 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0+ 0 0 -1 0 0+ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0+ 0 -1 0 0 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0+ 0+ 0+ 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0+ # Attribute 84 ARAP-Challenge-Response 85 Acct-Interim-Interval 86 Acct-Tunnel-Packets-Lost 87 NAS-Port-Id (****) 88 Framed-Pool 89 Chargeable-User-Id 90 Tunnel-Client-Auth-ID 91 Tunnel-Server-Auth-ID 92 Nas-Filter-Rule 95 NAS-IPv 6 -Address 96 Framed-Interface-Id 97 Framed-IPv 6 -Prefix 98 Login-IPv 6 -Host 99 Framed-IPv 6 -Route 100 Framed-IPv 6 -Pool 101 Error Cause 103 Digest-Response 104 Digest-Realm 105 Digest-Nonce 106 Digest-Response-Auth 107 Digest-Nextnonce 108 Digest-Method 109 Digest-URI 110 Digest-Qop 111 Digest-Algorithm 112 Digest-Entity-Body-Hash 113 Digest-CNonce 114 Digest-Nonce-Count 115 Digest-Username 116 Digest-Opaque 117 Digest-Auth-Param 118 Digest-AKA-Auts 119 Digest-Domain 120 Digest-Stale 121 Digest-HA 1 122 SIP-AOR 123 Delegated-IPv 6 -Prefix RFC's 2869 2867 2869 4372 2868 4849 3162 3162 3576 4590 4590 4590 4590 4590 4818 All Rights Reserved © Alcatel-Lucent 2007 (****) Either NAS-Port or NASPort-Id SHOULD be present in an Access Request packet, if the NAS differentiates among its ports. NAS- Port-Id is intended for use by NASes which cannot conveniently number their ports. (-) Can be included in packet type 42=Disconnect-Nak or 45= Co. A-Nak
f762bd77a4e93dda950a367736bd874e.ppt