70fd8765ea58c8ca162c1b18d6d22438.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 Introduction to the Programme: Part-1 : Overall Coverage and Assessing Export Readiness Dr. Vijaya Katti Chairperson (MDPs) Indian Institute of Foreign Trade New Delhi For Niryat Bandhu Scheme (Session on 25. 7. 2016)
Introduction to the Programme: Part-1 : Overall Coverage and Assessing Export Readiness Dr. Vijaya Katti Chairperson (MDPs) Indian Institute of Foreign Trade New Delhi For Niryat Bandhu Scheme (Session on 25. 7. 2016)
 Coverage • • What is meant by exports? Legal definition Why to export? Who can export? International trade scenario and India’s position in global trade Product specific specialties Demand of pattern of specific export market specific products Global market and possibilities of exports How to assess your export readiness?
Coverage • • What is meant by exports? Legal definition Why to export? Who can export? International trade scenario and India’s position in global trade Product specific specialties Demand of pattern of specific export market specific products Global market and possibilities of exports How to assess your export readiness?
 What is meant by export? - Legal definition
What is meant by export? - Legal definition
 Concept of Export • The term export derives from the conceptual meaning as to ship the goods and services out of the port of a country. • The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an “exporter” who is based in the country of export whereas the overseas based buyer is referred to as an “importer”. • In International Trade, “export” refers to selling goods and services produced in the home country to other markets. • In very simple terms, export may be defined as the selling of goods to a foreign country. However, As per Secion 2(e) of the India Foreign Trade (Development & Regulations) Act (1992), the term export may be defined as ‘an act of taking out of India any goods by land, sea or air and with proper transaction of money”.
Concept of Export • The term export derives from the conceptual meaning as to ship the goods and services out of the port of a country. • The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an “exporter” who is based in the country of export whereas the overseas based buyer is referred to as an “importer”. • In International Trade, “export” refers to selling goods and services produced in the home country to other markets. • In very simple terms, export may be defined as the selling of goods to a foreign country. However, As per Secion 2(e) of the India Foreign Trade (Development & Regulations) Act (1992), the term export may be defined as ‘an act of taking out of India any goods by land, sea or air and with proper transaction of money”.
 Why Export - Reasons for Export • There are many good reasons for exporting. Some of the motives of export are given below: • The first and the primary reason for export is to earn foreign exchange. The foreign exchange not only brings profit for the exporter but also improves the economic condition of the country. • Secondly, companies that export their goods are believed to be more reliable than their counterpart domestic companies assuming that exporting company has survived the test in meeting international standards. • Thirdly, free exchange of ideas and cultural knowledge opens up immense business and trade opportunities for a company. • Fourthly, as one starts visiting customers to sell one’s goods, he has an opportunity to start exploring for newer customers, state-of-the-art machines and vendors in foreign lands. • Fifthly, by exporting goods, an exporter also becomes safe from offset lack of demand for seasonal products. • Lastly, international trade keeps an exporter more competitive and less vulnerable to the market as the exporter may have a business boom in one area while simultaneously witnessing a bust in a different area.
Why Export - Reasons for Export • There are many good reasons for exporting. Some of the motives of export are given below: • The first and the primary reason for export is to earn foreign exchange. The foreign exchange not only brings profit for the exporter but also improves the economic condition of the country. • Secondly, companies that export their goods are believed to be more reliable than their counterpart domestic companies assuming that exporting company has survived the test in meeting international standards. • Thirdly, free exchange of ideas and cultural knowledge opens up immense business and trade opportunities for a company. • Fourthly, as one starts visiting customers to sell one’s goods, he has an opportunity to start exploring for newer customers, state-of-the-art machines and vendors in foreign lands. • Fifthly, by exporting goods, an exporter also becomes safe from offset lack of demand for seasonal products. • Lastly, international trade keeps an exporter more competitive and less vulnerable to the market as the exporter may have a business boom in one area while simultaneously witnessing a bust in a different area.
 Who can export? • Any one who wants to do something different • Anyone who wants to enter in a profit zone • Anyone who has assessed his readiness to enter in new field & try his luck • Anyone who is willing to take risk • Anyone who is constantly updating himself on global business environment
Who can export? • Any one who wants to do something different • Anyone who wants to enter in a profit zone • Anyone who has assessed his readiness to enter in new field & try his luck • Anyone who is willing to take risk • Anyone who is constantly updating himself on global business environment
 Planning for Export • The organization should plan well before exporting as to what product to be exported, where to be exported etc. The organization should also evaluate the export potential of a company. The main objective of a typical export plan should be to identify: – The objectives of exporting – Lists of activities to undertake to achieve those objectives – Mechanism for review and – Activities to help focus on goals
Planning for Export • The organization should plan well before exporting as to what product to be exported, where to be exported etc. The organization should also evaluate the export potential of a company. The main objective of a typical export plan should be to identify: – The objectives of exporting – Lists of activities to undertake to achieve those objectives – Mechanism for review and – Activities to help focus on goals
 Contd. . • Successful exporters agree that your ability to become an accomplished international traders depends largely on how you Target new business areas Identify and focus on markets, which consume products having the same competitive profile as the products you can supply Adopt appropriate export development strategy Have some idea of impact of the FTAs, WTO standards, SPS Measures, Intellectual Property Rights, domestic regulations on the products of interest Make every penny count Dig out every penny due to you from the system, by making best use of available opportunities, policies and schemes
Contd. . • Successful exporters agree that your ability to become an accomplished international traders depends largely on how you Target new business areas Identify and focus on markets, which consume products having the same competitive profile as the products you can supply Adopt appropriate export development strategy Have some idea of impact of the FTAs, WTO standards, SPS Measures, Intellectual Property Rights, domestic regulations on the products of interest Make every penny count Dig out every penny due to you from the system, by making best use of available opportunities, policies and schemes
 Contd. . • Information on the above subject is spread across numerous websites and documents produced by the Trade Ministries of various countries (For FTA, GSP, Customs duty), DGFT, Customs, RBI, Central Excise, Banks, WTO, Other international bodies. • You do not need to understand everything available, but how do you know what to miss. Information Overload makes impossible demand on your resources and time.
Contd. . • Information on the above subject is spread across numerous websites and documents produced by the Trade Ministries of various countries (For FTA, GSP, Customs duty), DGFT, Customs, RBI, Central Excise, Banks, WTO, Other international bodies. • You do not need to understand everything available, but how do you know what to miss. Information Overload makes impossible demand on your resources and time.
 Contd. . • The course you have enrolled provides straight answers to innumerable questions asked by the exporters as they launched, developed and grew their business. It is a one stop access to information scattered across 100 s of websites, manuals, and schemes : and covers basic essentials for starting your business endeavor.
Contd. . • The course you have enrolled provides straight answers to innumerable questions asked by the exporters as they launched, developed and grew their business. It is a one stop access to information scattered across 100 s of websites, manuals, and schemes : and covers basic essentials for starting your business endeavor.
 The course on “Export & Import Business” has 7 segments Basic steps for Exporting Marketing related issues (Identification of Product and Market) WTO Related Issues FTP related issues Finance/Risk Management issues Customs and Excise interface/Sales contract Preparation & Execution of Export Business Plan
The course on “Export & Import Business” has 7 segments Basic steps for Exporting Marketing related issues (Identification of Product and Market) WTO Related Issues FTP related issues Finance/Risk Management issues Customs and Excise interface/Sales contract Preparation & Execution of Export Business Plan
 Contents of the Program
Contents of the Program
 Session 1: Introduction to the Programme: Overall Coverage and Assessing Export Readiness Coverage • • • What is meant by exports? Legal definition Why to export? Who can export? Seven Segments involved in course
Session 1: Introduction to the Programme: Overall Coverage and Assessing Export Readiness Coverage • • • What is meant by exports? Legal definition Why to export? Who can export? Seven Segments involved in course
 Contd. . • Contents of the programme : – Different issues related with identification of products and markets, Exports and Imports, International Sales Contracts, Risk Management and Finance related issues • Foreign Trade Policy related issues • How to assess your export readiness (questionnaire…)
Contd. . • Contents of the programme : – Different issues related with identification of products and markets, Exports and Imports, International Sales Contracts, Risk Management and Finance related issues • Foreign Trade Policy related issues • How to assess your export readiness (questionnaire…)
 Session 2 : Basic Steps involved and Export Potential of States Coverage Basic steps involved in Exports Preparing the export plan. Applying for IEC Code – Online or Offline Understanding the purpose and procedure of various Incoterms for an international trade transaction and for decreasing the responsibilities and obligations of exporter. • Choosing the right shipping term keeping in mind the mode of payment affecting the responsibilities and obligations of exporter. • •
Session 2 : Basic Steps involved and Export Potential of States Coverage Basic steps involved in Exports Preparing the export plan. Applying for IEC Code – Online or Offline Understanding the purpose and procedure of various Incoterms for an international trade transaction and for decreasing the responsibilities and obligations of exporter. • Choosing the right shipping term keeping in mind the mode of payment affecting the responsibilities and obligations of exporter. • •
 Session 2 contd… : Knowledge about State’s export potential Coverage • • • Understanding requirements of state government. Rich heritage of various state – Natural endowment Product specific specialties Demand of pattern of specific export market in specific products. Tariff and non tariff barriers in international market
Session 2 contd… : Knowledge about State’s export potential Coverage • • • Understanding requirements of state government. Rich heritage of various state – Natural endowment Product specific specialties Demand of pattern of specific export market in specific products. Tariff and non tariff barriers in international market
 Session 3: How to Access Markets Coverage • Using trade data to identify the products with export potential • Adapting your product to meet government regulations, country conditions, or preferences • Modifying your product labeling and packaging • Planning for installation of your product overseas
Session 3: How to Access Markets Coverage • Using trade data to identify the products with export potential • Adapting your product to meet government regulations, country conditions, or preferences • Modifying your product labeling and packaging • Planning for installation of your product overseas
 Session 3 contd. : How to find buyers? Coverage • Marketing Strategy, Channel partners, Finding the Buyers & KYC • What is negotiation? Role of negotiation in business. How to convert buyers " No" to 'Yes" • How to price the product? Case study about the pricing. • How to draft a contract in International trade. • Dispute Resolution in contract
Session 3 contd. : How to find buyers? Coverage • Marketing Strategy, Channel partners, Finding the Buyers & KYC • What is negotiation? Role of negotiation in business. How to convert buyers " No" to 'Yes" • How to price the product? Case study about the pricing. • How to draft a contract in International trade. • Dispute Resolution in contract
 Session 4 : Sources of International market data (Online & Offline) Coverage • • • Step by step process flow and business decision indicators Sources of trade data collation followed by hands on experience of downloading the trade data Analyzing the data to apply it in real life business through mock case situations
Session 4 : Sources of International market data (Online & Offline) Coverage • • • Step by step process flow and business decision indicators Sources of trade data collation followed by hands on experience of downloading the trade data Analyzing the data to apply it in real life business through mock case situations
 Session 5 : INCOTERMS 2010 Coverage • INCOTERMS 2010 - Choosing the right delivery term
Session 5 : INCOTERMS 2010 Coverage • INCOTERMS 2010 - Choosing the right delivery term
 Session 6 : Introduction to ITC(HS) Codes. How to get IEC Code Coverage • • • What is an IEC? How to get an IEC online? How to make changes in IEC?
Session 6 : Introduction to ITC(HS) Codes. How to get IEC Code Coverage • • • What is an IEC? How to get an IEC online? How to make changes in IEC?
 Session 6 contd… Coverage • What is the basis of classification of policy • What is ITC (H S) CODE • What is product grouping • How to identify the product • Case Study pertaining to the above
Session 6 contd… Coverage • What is the basis of classification of policy • What is ITC (H S) CODE • What is product grouping • How to identify the product • Case Study pertaining to the above
 Session 7 : Free Trade Agreements Coverage • • • India’s emergence into FTA league; Subtle variation in focus of India’s FTAs with ASEAN vis-a-vis the Korea and Japan (CECAs); Actual trade Impact on India from the FTA and non-FTA Partners; How this difference can be explained? How to analyse an FTA effectively- using a product-Specific approach. Conclude
Session 7 : Free Trade Agreements Coverage • • • India’s emergence into FTA league; Subtle variation in focus of India’s FTAs with ASEAN vis-a-vis the Korea and Japan (CECAs); Actual trade Impact on India from the FTA and non-FTA Partners; How this difference can be explained? How to analyse an FTA effectively- using a product-Specific approach. Conclude
 Session 8 : Foreign Trade Policy (2015: 2020): Major highlights Coverage 1. 2. 3. Foreign Trade Policy (2015 -2020) – Major highlights DGFT and export promotion --- Role of RA, EPCs and RCMC Interface with Airports, Ports, ICDs, SEZs, ICE GATE
Session 8 : Foreign Trade Policy (2015: 2020): Major highlights Coverage 1. 2. 3. Foreign Trade Policy (2015 -2020) – Major highlights DGFT and export promotion --- Role of RA, EPCs and RCMC Interface with Airports, Ports, ICDs, SEZs, ICE GATE
 Session 8 contd. . : Export: Import Incentives Coverage • • • Objectives of Export Promotion Schemes MEIS SEIS Duty Exemption and Remission Scheme EPCG
Session 8 contd. . : Export: Import Incentives Coverage • • • Objectives of Export Promotion Schemes MEIS SEIS Duty Exemption and Remission Scheme EPCG
 Session 9 : SPS, TBT, NTB Coverage • Understanding types of Non tariff barriers • Quantitative Restrictions • Discussing dispute settlement cases on trade compliance • Quality compliance • Environmental compliance • Social compliance • Technology compliance
Session 9 : SPS, TBT, NTB Coverage • Understanding types of Non tariff barriers • Quantitative Restrictions • Discussing dispute settlement cases on trade compliance • Quality compliance • Environmental compliance • Social compliance • Technology compliance
 Session : 10 Coverage • Incorporating Sales Contract term
Session : 10 Coverage • Incorporating Sales Contract term
 Session 11 : Export Documentation Coverage • Understanding the role of trade documentation & procedure in international trade transactions. • Knowing what are the documentation practices & procedure in India for making export/import from the country. • Understanding the commercial and regulatory documentation practices in order to avoid any kind of non-compliance in international documents which may result in penalty or loss of incentives or benefits such as duty drawback.
Session 11 : Export Documentation Coverage • Understanding the role of trade documentation & procedure in international trade transactions. • Knowing what are the documentation practices & procedure in India for making export/import from the country. • Understanding the commercial and regulatory documentation practices in order to avoid any kind of non-compliance in international documents which may result in penalty or loss of incentives or benefits such as duty drawback.
 Session 12 : Duty Draw Back and claims procedures Coverage Excise & Customs Interface. Online filing of custom documents. Ease for doing exports. Factory Stuffing / Excise Sealing / Self Sealing Permission for container stuffing. • Various Checkpoints to avoid hassles. • •
Session 12 : Duty Draw Back and claims procedures Coverage Excise & Customs Interface. Online filing of custom documents. Ease for doing exports. Factory Stuffing / Excise Sealing / Self Sealing Permission for container stuffing. • Various Checkpoints to avoid hassles. • •
 Session : 13 Coverage • Understanding Logistics Value Chain in Export operations
Session : 13 Coverage • Understanding Logistics Value Chain in Export operations
 Session 14 : Letter of Credit and implication of UCP: 600 rules Coverage • • • Management of international payments to ensure full and on-time payments Letter of Credit Implication of UCP-600 rules.
Session 14 : Letter of Credit and implication of UCP: 600 rules Coverage • • • Management of international payments to ensure full and on-time payments Letter of Credit Implication of UCP-600 rules.
 Session 15 : Financial schemes Coverage • • • Export transaction schemes of import finance. How to do more export business with less money Case study
Session 15 : Financial schemes Coverage • • • Export transaction schemes of import finance. How to do more export business with less money Case study
 Session 16 : Understanding RBI guidelines Coverage Export and Import regulations by Reserve Bank of India
Session 16 : Understanding RBI guidelines Coverage Export and Import regulations by Reserve Bank of India
 Session 17 : Currency Management Coverage • • Understanding change in value of Foreign Currencies (USD, STG, YEN and EURO) Basics of Currency Risk Managements to protect profit margin – Export-Import transactions.
Session 17 : Currency Management Coverage • • Understanding change in value of Foreign Currencies (USD, STG, YEN and EURO) Basics of Currency Risk Managements to protect profit margin – Export-Import transactions.
 Session 18 : Risk Management Coverage • What is Risk? Various types of Risks in trade- specially International trade • Risk Management viz. Identification , quantification, analysis, & transfer of risk • What is credit & sovereignty risk • Role of ECGC & Credit risk agencies in the promotion of Export Trade • Procedures & settlement of claims
Session 18 : Risk Management Coverage • What is Risk? Various types of Risks in trade- specially International trade • Risk Management viz. Identification , quantification, analysis, & transfer of risk • What is credit & sovereignty risk • Role of ECGC & Credit risk agencies in the promotion of Export Trade • Procedures & settlement of claims
 Session 19 : Preparation & Execution of Export Business Plan Coverage • • How to write export business plan Contents of this plan Role of DGFT and RAs in export facilitation Financial & Product considerations Market identification Challenges and opportunities in selected markets Negotiating skill for marketing Economic diplomacy and role of Embassies
Session 19 : Preparation & Execution of Export Business Plan Coverage • • How to write export business plan Contents of this plan Role of DGFT and RAs in export facilitation Financial & Product considerations Market identification Challenges and opportunities in selected markets Negotiating skill for marketing Economic diplomacy and role of Embassies
 Session 20 : PANEL DISCUSSION • Interaction of IIFT PROFESSORS & DGFT OFFICIALS with all participants to sort out various issues regarding export and import business.
Session 20 : PANEL DISCUSSION • Interaction of IIFT PROFESSORS & DGFT OFFICIALS with all participants to sort out various issues regarding export and import business.
 Export Preliminaries • Export-Import is totally free with very limited restriction (96% items are free items) • To find Buyers-Seller is your decision • To decide Product and its Price-Qty are your decision • You must prepare Export Business Plan
Export Preliminaries • Export-Import is totally free with very limited restriction (96% items are free items) • To find Buyers-Seller is your decision • To decide Product and its Price-Qty are your decision • You must prepare Export Business Plan
 Export • • Take Order Find CHA (Custom House Agent) Find mode of export (Sea/Air) Find Carrier Fill Shipping Bill Take payment Request for Bank Realisation Certificate Register for Export Scheme
Export • • Take Order Find CHA (Custom House Agent) Find mode of export (Sea/Air) Find Carrier Fill Shipping Bill Take payment Request for Bank Realisation Certificate Register for Export Scheme
 Marketing related issues
Marketing related issues
 Marketing – The Concept • Marketing, in the simplest of terms, can be defined as the process which profitably meets the need for products. • The more formal definition of marketing" is that it is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.
Marketing – The Concept • Marketing, in the simplest of terms, can be defined as the process which profitably meets the need for products. • The more formal definition of marketing" is that it is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.
 Contd. . • Marketing activities have been traditionally depicted in terms of a marketing mix, which can be defined as the set of marketing tools needed to pursue marketing objectives. The marketing mix consists of four broad groups, popularly referred to as the four Ps of marketing. These are: • Product • Price • Place • Promotion
Contd. . • Marketing activities have been traditionally depicted in terms of a marketing mix, which can be defined as the set of marketing tools needed to pursue marketing objectives. The marketing mix consists of four broad groups, popularly referred to as the four Ps of marketing. These are: • Product • Price • Place • Promotion
 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING • Marketing as a concept is universal, but the markets and behaviour of consumers vary across countries and can be quite different. This makes it essential for any student of international marketing to gain knowledge in three critical areas: • Cross-cultural knowledge • Country/regional knowledge • Cross-border transactions knowledge
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING • Marketing as a concept is universal, but the markets and behaviour of consumers vary across countries and can be quite different. This makes it essential for any student of international marketing to gain knowledge in three critical areas: • Cross-cultural knowledge • Country/regional knowledge • Cross-border transactions knowledge
 EXPORT MARKETING-GOING GLOBAL This section addresses the all-important question: Why should a firm enter the international market? Some of the more obvious reasons for firms to enter overseas markets are: • Profitability • Growth • Achieving economies of scale • Risk spread • Access to imported inputs • Uniqueness of products and services • Marketing opportunities due to life cycle • Spreading R&D costs
EXPORT MARKETING-GOING GLOBAL This section addresses the all-important question: Why should a firm enter the international market? Some of the more obvious reasons for firms to enter overseas markets are: • Profitability • Growth • Achieving economies of scale • Risk spread • Access to imported inputs • Uniqueness of products and services • Marketing opportunities due to life cycle • Spreading R&D costs
 Find Buyer • • Experience Business Promotion: Website Distributor, Dealers, Commission Agents Reference Visits, Exhibition, Event Participation Advertise and Marketing Surfing
Find Buyer • • Experience Business Promotion: Website Distributor, Dealers, Commission Agents Reference Visits, Exhibition, Event Participation Advertise and Marketing Surfing
 Deciding on Pricing • Price and Pricing Strategies • Profit-Oriented Pricing Objectives • Sales-Oriented Pricing Objectives
Deciding on Pricing • Price and Pricing Strategies • Profit-Oriented Pricing Objectives • Sales-Oriented Pricing Objectives
 Product Specific Issues
Product Specific Issues
 Find Item for Export • Your background : Education, Job Experience, Family Business • Understand Export/Import Database • Supply/Demand • Price • Profitability • Example: Embroidery Machine, Pressing Machine, spinning machine
Find Item for Export • Your background : Education, Job Experience, Family Business • Understand Export/Import Database • Supply/Demand • Price • Profitability • Example: Embroidery Machine, Pressing Machine, spinning machine
 Find HS Code • • • HS Code – Harmonised System Code Type in google : Find (item) HS Code Example : Vitrified Tiles (69071010) See Chapters, sub heading Match with your item Match with 8 digit HS Code
Find HS Code • • • HS Code – Harmonised System Code Type in google : Find (item) HS Code Example : Vitrified Tiles (69071010) See Chapters, sub heading Match with your item Match with 8 digit HS Code
 Find your Item Type • Three type of items : Free, Prohibitive, Restrictive • Free : Without any restriction, no license, no certificate • Prohibitive: Total ban – Example: All wild animal, animal articles including their products and Derivatives • Restrictive : Under specific condition – Example : Live Horses – Kathiawari, Marwari and Manipuri breeds 96% items are free items ITEM Free Prohibited Restrictive Total 10915 55 443 11413
Find your Item Type • Three type of items : Free, Prohibitive, Restrictive • Free : Without any restriction, no license, no certificate • Prohibitive: Total ban – Example: All wild animal, animal articles including their products and Derivatives • Restrictive : Under specific condition – Example : Live Horses – Kathiawari, Marwari and Manipuri breeds 96% items are free items ITEM Free Prohibited Restrictive Total 10915 55 443 11413
 Foreign Trade Policy related issues
Foreign Trade Policy related issues
 INDIA’S FTP 2015 - 2020 • India’s new five year FTP 2015 – 2020 provides a stable and sustainable policy environment ; overarching framework and architecture to catalyse exports and facilitate nay rationalise imports; generate employment and increase value addition in the country. • India’s FTP – Domestic Trade Policy is anchored in the Domestic Policy framework (symbiotic relationship and synergy) Export Promotion Mission to be created that would be synergised with the National Missions of ‘Make in India’; ‘Digital India’ – e Governance - Improve the ‘ease of doing business’ index; ‘Skill India’.
INDIA’S FTP 2015 - 2020 • India’s new five year FTP 2015 – 2020 provides a stable and sustainable policy environment ; overarching framework and architecture to catalyse exports and facilitate nay rationalise imports; generate employment and increase value addition in the country. • India’s FTP – Domestic Trade Policy is anchored in the Domestic Policy framework (symbiotic relationship and synergy) Export Promotion Mission to be created that would be synergised with the National Missions of ‘Make in India’; ‘Digital India’ – e Governance - Improve the ‘ease of doing business’ index; ‘Skill India’.
 INDIA’S FTP 2015 – 2020 – SUPER ORDINATE GOAL (b. HAG) • India’s FTP Statement explains the Vision , Mission. Objectives and Goals ; Market and Product strategy; Structure and Architecture to achieve the goals. • VISION - Super Ordinate Goal – big Hairy Audacious Goal (b HAG ) of doubling India’s exports of merchandise and services from about USD 450 Billion in FY 2013 -14 to USD 900 Billion in FY 2019 – 2020 and to raise India’s share in world exports from 2% to 3. 5%. • Every thing hangs together in International Trade – so ‘Whole of Government’ approach - State Governments ; Other Central Government Ministries to be also involved rather than just the role of Department of Commerce in the export value chain (both up stream and down stream activities in terms of Michael Porter’s value chain)
INDIA’S FTP 2015 – 2020 – SUPER ORDINATE GOAL (b. HAG) • India’s FTP Statement explains the Vision , Mission. Objectives and Goals ; Market and Product strategy; Structure and Architecture to achieve the goals. • VISION - Super Ordinate Goal – big Hairy Audacious Goal (b HAG ) of doubling India’s exports of merchandise and services from about USD 450 Billion in FY 2013 -14 to USD 900 Billion in FY 2019 – 2020 and to raise India’s share in world exports from 2% to 3. 5%. • Every thing hangs together in International Trade – so ‘Whole of Government’ approach - State Governments ; Other Central Government Ministries to be also involved rather than just the role of Department of Commerce in the export value chain (both up stream and down stream activities in terms of Michael Porter’s value chain)
 INDIA’S FOREIGN TRADE POLICY (FTP) 2015 – 2020 • FTP 2015 – 2020 IS THE MICRO TRADE POLICY AND THE MACRO TRADE POLICY – INTERFACE WITH WORLD TRADE ORGANISATION (WTO); PTAs AND FTAs WITH VARIOUS COUNTRIES AND TRADE BLOCKS IS THE DOMAIN OF DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE.
INDIA’S FOREIGN TRADE POLICY (FTP) 2015 – 2020 • FTP 2015 – 2020 IS THE MICRO TRADE POLICY AND THE MACRO TRADE POLICY – INTERFACE WITH WORLD TRADE ORGANISATION (WTO); PTAs AND FTAs WITH VARIOUS COUNTRIES AND TRADE BLOCKS IS THE DOMAIN OF DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE.
 MARKET STRATEGY • Market Strategy – Market Penetration and Market Development (Diversification). India has signed 5 limited PTAs ; 11 FTAs and is negotiating 17 FTAs. Some of the issues being addressed are Rules of Origin; Inversion in Duty Structure; Capturing preferential export data; FTA outreach and information dissemination and setting up a Trade Portal. Under MEIS (Chapter – 3 – Export Reward Scrips), countries have been grouped into three categories – A – Traditional Markets ; B – Emerging & Focus Markets; C – Other Markets.
MARKET STRATEGY • Market Strategy – Market Penetration and Market Development (Diversification). India has signed 5 limited PTAs ; 11 FTAs and is negotiating 17 FTAs. Some of the issues being addressed are Rules of Origin; Inversion in Duty Structure; Capturing preferential export data; FTA outreach and information dissemination and setting up a Trade Portal. Under MEIS (Chapter – 3 – Export Reward Scrips), countries have been grouped into three categories – A – Traditional Markets ; B – Emerging & Focus Markets; C – Other Markets.
 Contd. . • NAFTA Countries – USA , Canada and Mexico – negotiating a FTA with Canada. • European Union (EU) – negotiating a BTIA. • Australia and New Zealand – negotiating a CECA/CEPA • South Asia – Sri Lanka FTA and discussions with Pakistan. • Focus on Iran. • SE Asia under the Look/ Act East Policy – ASEAN – India Trade in Goods/Services/ Investment Agreement. • Future Focus on CLMV (Cambodia; Lao PDR; Myanmar; Vietnam) and India – Myanmar – Thailand Trilateral Highway.
Contd. . • NAFTA Countries – USA , Canada and Mexico – negotiating a FTA with Canada. • European Union (EU) – negotiating a BTIA. • Australia and New Zealand – negotiating a CECA/CEPA • South Asia – Sri Lanka FTA and discussions with Pakistan. • Focus on Iran. • SE Asia under the Look/ Act East Policy – ASEAN – India Trade in Goods/Services/ Investment Agreement. • Future Focus on CLMV (Cambodia; Lao PDR; Myanmar; Vietnam) and India – Myanmar – Thailand Trilateral Highway.
 Contd. . • NE Asia – Focus on China , Japan and South Korea. • Focus on Africa ; West Asia & North Africa (WANA) particularly UAE; Latin American and Caribbean region - India – Chile/ Peru PTA being negotiated ; India – MERCOSUR (Argentina , Brazil , Paraguay, Venezuela and Uruguay) PTA already in place. • Focus on 12 countries of Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) – negotiating a RTA with the Customs Union of Russian Federation, Kazakistan and Belarus. Connecting India with the CIS – the International North South Transport Corridor.
Contd. . • NE Asia – Focus on China , Japan and South Korea. • Focus on Africa ; West Asia & North Africa (WANA) particularly UAE; Latin American and Caribbean region - India – Chile/ Peru PTA being negotiated ; India – MERCOSUR (Argentina , Brazil , Paraguay, Venezuela and Uruguay) PTA already in place. • Focus on 12 countries of Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) – negotiating a RTA with the Customs Union of Russian Federation, Kazakistan and Belarus. Connecting India with the CIS – the International North South Transport Corridor.
 PRODUCT STRATEGY • PRODUCT STRATEGY – Focus on moving up the value chain – Value added products (more domestic value in sync with Make in India) – Engineering Products ; Electronics and Drugs and Pharmaceuticals. • Focus on labour intensive products (create employment opportunities so that our demographic dividend does not become a demographic disaster) – handicrafts , leather, textiles, gems and jewellery; agro and plantation products; marine products. • Focus on new , innovative and high tech products and Project Exports.
PRODUCT STRATEGY • PRODUCT STRATEGY – Focus on moving up the value chain – Value added products (more domestic value in sync with Make in India) – Engineering Products ; Electronics and Drugs and Pharmaceuticals. • Focus on labour intensive products (create employment opportunities so that our demographic dividend does not become a demographic disaster) – handicrafts , leather, textiles, gems and jewellery; agro and plantation products; marine products. • Focus on new , innovative and high tech products and Project Exports.
 Contd. . • Move towards ‘World Class Products’- transforming India into a manufacturing and exporting hub. Build ‘Brand India’. • Facilitating and encouraging export of Dual use items – Special Chemicals , Organisms, Materials , Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET) items – validity of SCOMET authorisation has been extended from 12 to 24 months to help industry to plan their activity in an orderly manner and obviate the need to seek re validation or relaxation from DGFT.
Contd. . • Move towards ‘World Class Products’- transforming India into a manufacturing and exporting hub. Build ‘Brand India’. • Facilitating and encouraging export of Dual use items – Special Chemicals , Organisms, Materials , Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET) items – validity of SCOMET authorisation has been extended from 12 to 24 months to help industry to plan their activity in an orderly manner and obviate the need to seek re validation or relaxation from DGFT.
 Contd. . • Facilitating and encouraging export of defence items – normal export obligation period under Advance Authorisation is 18 months which has been extended to 24 months. A list of military stores requiring NOC of Department of Defence Production has been notified by DGFT recently. A committee has been formed to create ITC (HS) codes for defence and security items for which industrial licenses are issued by DIPP.
Contd. . • Facilitating and encouraging export of defence items – normal export obligation period under Advance Authorisation is 18 months which has been extended to 24 months. A list of military stores requiring NOC of Department of Defence Production has been notified by DGFT recently. A committee has been formed to create ITC (HS) codes for defence and security items for which industrial licenses are issued by DIPP.
 Contd. . • E – COMMERCE EXPORTS • Goods falling in the category of handloom products, books/periodicals, leather footwear, toys and customised fashion garments, having FOB value up to Rs 25, 000 per consignment (finalised using e – commerce platform) shall be eligible for benefits under FTP. Such goods can be exported in manual mode through Foreign Post Offices at New Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai.
Contd. . • E – COMMERCE EXPORTS • Goods falling in the category of handloom products, books/periodicals, leather footwear, toys and customised fashion garments, having FOB value up to Rs 25, 000 per consignment (finalised using e – commerce platform) shall be eligible for benefits under FTP. Such goods can be exported in manual mode through Foreign Post Offices at New Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai.
 PRODUCT STRATEGY – BOOST TO MAKE IN INDIA • Reduced Export Obligation (EO) for domestic procurement under EPCG scheme – specific EO under EPCG scheme in case capital goods are procured from indigenous manufacturers which is currently 90% of the normal EO (6 times the duty saved amount) has been reduced to 75% in order to boost ‘Make in India’. • Higher level of reward DCSs under MEIS for export items with high domestic content and value addition. • In order to encourage manufacturing of indigenous capital goods, imports under EPCG authorisation shall not be eligible for exemption from payment of Anti Dumping Duty, Safeguard Duty and Transitional Product Specific Safeguard Duty.
PRODUCT STRATEGY – BOOST TO MAKE IN INDIA • Reduced Export Obligation (EO) for domestic procurement under EPCG scheme – specific EO under EPCG scheme in case capital goods are procured from indigenous manufacturers which is currently 90% of the normal EO (6 times the duty saved amount) has been reduced to 75% in order to boost ‘Make in India’. • Higher level of reward DCSs under MEIS for export items with high domestic content and value addition. • In order to encourage manufacturing of indigenous capital goods, imports under EPCG authorisation shall not be eligible for exemption from payment of Anti Dumping Duty, Safeguard Duty and Transitional Product Specific Safeguard Duty.
 SYSTEMS • Online filing of documents/applications and paperless trade in 24 x 7 environment -: • 70% of applications filed in DGFT relate to Chapter 3 and Chapter 4. Henceforth hard copies of applications and specified documents under these chapters would not be required to be submitted to the Regional Authorities (RAs) under DGFT. Applications under Chapter – 5 would be taken in the next phase. • Certificates issued by C A s / Cost A s/ C S s to be enabled to be digitally signed and uploaded in the new system.
SYSTEMS • Online filing of documents/applications and paperless trade in 24 x 7 environment -: • 70% of applications filed in DGFT relate to Chapter 3 and Chapter 4. Henceforth hard copies of applications and specified documents under these chapters would not be required to be submitted to the Regional Authorities (RAs) under DGFT. Applications under Chapter – 5 would be taken in the next phase. • Certificates issued by C A s / Cost A s/ C S s to be enabled to be digitally signed and uploaded in the new system.
 Contd. . • Landing documents of export consignments as proofs for notified markets to be enabled to be digitally up loaded by any exporter / Three , Four , Five Star Export Houses. • SIMPLIFICATION OF PROCEDURES /PROCESSES -: • Under Para 2. 06 of FTP only 3 mandatory documents are required for - : • Export of goods from India - : Bill of Lading/ Airway Bill ; Commercial Invoice cum Packing List ; Shipping Bill /Bill of Export.
Contd. . • Landing documents of export consignments as proofs for notified markets to be enabled to be digitally up loaded by any exporter / Three , Four , Five Star Export Houses. • SIMPLIFICATION OF PROCEDURES /PROCESSES -: • Under Para 2. 06 of FTP only 3 mandatory documents are required for - : • Export of goods from India - : Bill of Lading/ Airway Bill ; Commercial Invoice cum Packing List ; Shipping Bill /Bill of Export.
 Contd. . • Import of goods into India – Bill of Lading/ Airway Bill ; Commercial Invoice cum Packing List ; Bill of Entry. • Exporter Importer Profile (EIP) has been created to upload documents and there would be no need to submit copies of permanent records/ documents like IEC, PAN , RCMC, Manufacturing Licence etc with each application once uploaded. • Online Inter Ministerial Consultations for approval of export of SCOMET items , Norms fixation, Import and Export Authorisations in a phased manner.
Contd. . • Import of goods into India – Bill of Lading/ Airway Bill ; Commercial Invoice cum Packing List ; Bill of Entry. • Exporter Importer Profile (EIP) has been created to upload documents and there would be no need to submit copies of permanent records/ documents like IEC, PAN , RCMC, Manufacturing Licence etc with each application once uploaded. • Online Inter Ministerial Consultations for approval of export of SCOMET items , Norms fixation, Import and Export Authorisations in a phased manner.
 Contd. . • FORTHCOMING E – GOVERNANCE INITIATIVES -: • Message exchange for transmission of chapter 3 export reward Duty Credit Scrips from DGFT to Customs. • Message exchange for transmission of Bills Of Entry (Import details) from Customs to DGFT. • Online issuance of Export Obligation Discharge Certificate (EODC). • Message exchange with CBDT for PAN. • Message exchange with Ministry of Corporate Affairs for CIN & DIN.
Contd. . • FORTHCOMING E – GOVERNANCE INITIATIVES -: • Message exchange for transmission of chapter 3 export reward Duty Credit Scrips from DGFT to Customs. • Message exchange for transmission of Bills Of Entry (Import details) from Customs to DGFT. • Online issuance of Export Obligation Discharge Certificate (EODC). • Message exchange with CBDT for PAN. • Message exchange with Ministry of Corporate Affairs for CIN & DIN.
 Contd. . • Facility to pay application fee using Debit/ Credit Card. • Open API (Application Programme Interface) for submission of IEC application. • Mobile applications for FTP.
Contd. . • Facility to pay application fee using Debit/ Credit Card. • Open API (Application Programme Interface) for submission of IEC application. • Mobile applications for FTP.
 SKILLS • Capacity building of the relevant stakeholders and institutions is of utmost importance in order to fully realise the potential of various Trade Agreements and FTP measures. The focus areas would be as follows -: • Training of Officers of the Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Export Development Authorities. • Establishment of a trade research/Analysis cell in these institutions. • Creation of an internal team for soliciting value added inputs from stakeholders. • Development and regular up dation of the web portals of institutions.
SKILLS • Capacity building of the relevant stakeholders and institutions is of utmost importance in order to fully realise the potential of various Trade Agreements and FTP measures. The focus areas would be as follows -: • Training of Officers of the Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Export Development Authorities. • Establishment of a trade research/Analysis cell in these institutions. • Creation of an internal team for soliciting value added inputs from stakeholders. • Development and regular up dation of the web portals of institutions.
 Contd. . • BOOST TO ‘SKILL INDIA’ -: • Under Para 1. 08 of FTP , DGFT is implementing Niryat Bandhu Scheme (NBS) for mentoring new and potential exporters on the intricacies of foreign trade through counselling , training and outreach programmes. • Considering the strategic significance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the manufacturing sector and employment generation, SME Clusters have been identified for focused interventions to boost exports.
Contd. . • BOOST TO ‘SKILL INDIA’ -: • Under Para 1. 08 of FTP , DGFT is implementing Niryat Bandhu Scheme (NBS) for mentoring new and potential exporters on the intricacies of foreign trade through counselling , training and outreach programmes. • Considering the strategic significance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the manufacturing sector and employment generation, SME Clusters have been identified for focused interventions to boost exports.
 STYLE AND SHARED VALUES • Under para 1. 07 of the FTP , DGFT Officers have to work not as Controllers but as Facilitators of exports / imports (Niryat Bandhus). Focus would be on good governance ; efficient, transparent and accountable delivery systems.
STYLE AND SHARED VALUES • Under para 1. 07 of the FTP , DGFT Officers have to work not as Controllers but as Facilitators of exports / imports (Niryat Bandhus). Focus would be on good governance ; efficient, transparent and accountable delivery systems.
 EASE OF DOING BUSINESS Recent initiatives of the Govt. of India for speedy disposal of work of SEZs : - q Work Disposal Timelines have been implemented in the SEZs across the country w. e. f. 14. 08. 2014. q Online modules have been implemented w. e. f. 01. 11. 2014 for more effective digitization and online processing of applications. q Harmonization of procedures, simplification of practices & standardization of Forms in all SEZs has been implemented w. e. f. 28. 10. 2014. q Govt. of India vide GSR(5) dated 2 nd January, 2015 has issued notification allowing dual-use of infrastructure in NPA in SEZs by both SEZ and DTA entities, by amending Rule 11(10) of SEZ Rules, 2006. Department of Commerce, Govt. of India 71
EASE OF DOING BUSINESS Recent initiatives of the Govt. of India for speedy disposal of work of SEZs : - q Work Disposal Timelines have been implemented in the SEZs across the country w. e. f. 14. 08. 2014. q Online modules have been implemented w. e. f. 01. 11. 2014 for more effective digitization and online processing of applications. q Harmonization of procedures, simplification of practices & standardization of Forms in all SEZs has been implemented w. e. f. 28. 10. 2014. q Govt. of India vide GSR(5) dated 2 nd January, 2015 has issued notification allowing dual-use of infrastructure in NPA in SEZs by both SEZ and DTA entities, by amending Rule 11(10) of SEZ Rules, 2006. Department of Commerce, Govt. of India 71
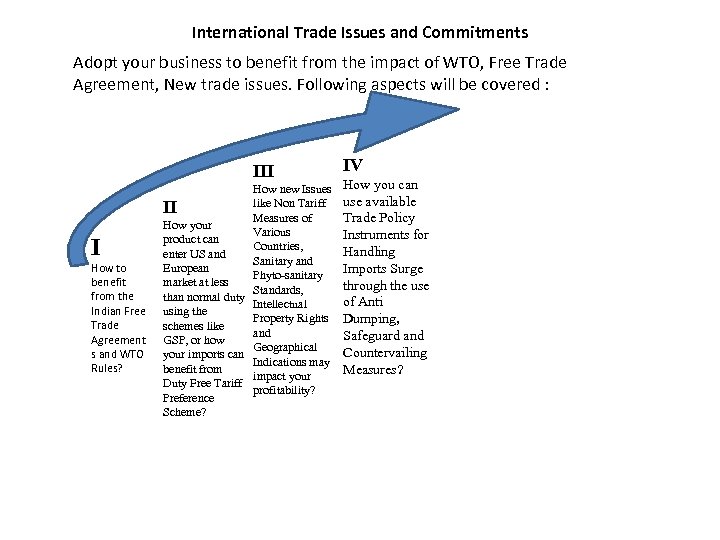 International Trade Issues and Commitments Adopt your business to benefit from the impact of WTO, Free Trade Agreement, New trade issues. Following aspects will be covered : III I How to benefit from the Indian Free Trade Agreement s and WTO Rules? How new Issues like Non Tariff II Measures of How your Various product can Countries, enter US and Sanitary and European Phyto-sanitary market at less Standards, than normal duty Intellectual using the Property Rights schemes like and GSP, or how Geographical your imports can Indications may benefit from impact your Duty Free Tariff profitability? Preference Scheme? IV How you can use available Trade Policy Instruments for Handling Imports Surge through the use of Anti Dumping, Safeguard and Countervailing Measures?
International Trade Issues and Commitments Adopt your business to benefit from the impact of WTO, Free Trade Agreement, New trade issues. Following aspects will be covered : III I How to benefit from the Indian Free Trade Agreement s and WTO Rules? How new Issues like Non Tariff II Measures of How your Various product can Countries, enter US and Sanitary and European Phyto-sanitary market at less Standards, than normal duty Intellectual using the Property Rights schemes like and GSP, or how Geographical your imports can Indications may benefit from impact your Duty Free Tariff profitability? Preference Scheme? IV How you can use available Trade Policy Instruments for Handling Imports Surge through the use of Anti Dumping, Safeguard and Countervailing Measures?
 Incoterm International Commerce Term • A formalized international Term of Trade regulated by the International Chamber of Commerce • Specifies the responsibilities of the exporter and the responsibilities of the importer in an international transaction – Which tasks will be performed by the exporter – Which tasks will be performed by the importer – Which activities will be paid by the exporter – Which activities will be paid by the importer – When the transfer of responsibility for the goods will take place • First codified by the International Chamber of Commerce in 1953. The latest revision is dated 2000
Incoterm International Commerce Term • A formalized international Term of Trade regulated by the International Chamber of Commerce • Specifies the responsibilities of the exporter and the responsibilities of the importer in an international transaction – Which tasks will be performed by the exporter – Which tasks will be performed by the importer – Which activities will be paid by the exporter – Which activities will be paid by the importer – When the transfer of responsibility for the goods will take place • First codified by the International Chamber of Commerce in 1953. The latest revision is dated 2000
 Finance/ Risk Management
Finance/ Risk Management
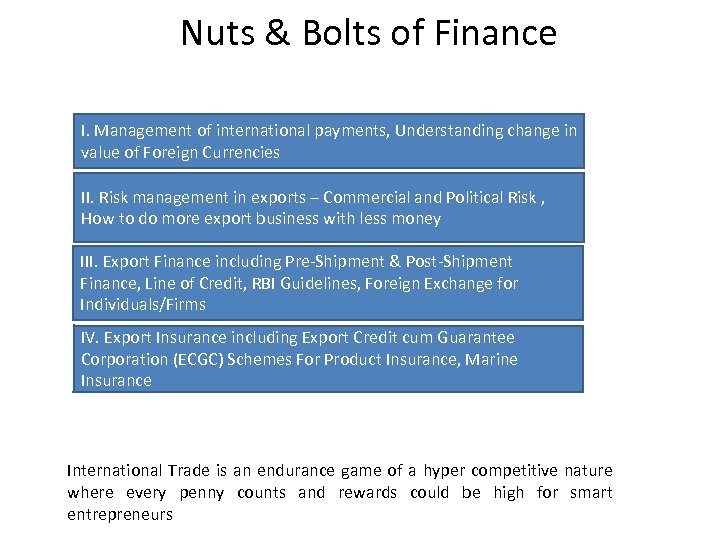 Nuts & Bolts of Finance I. Management of international payments, Understanding change in value of Foreign Currencies II. Risk management in exports – Commercial and Political Risk , How to do more export business with less money III. Export Finance including Pre-Shipment & Post-Shipment Finance, Line of Credit, RBI Guidelines, Foreign Exchange for Individuals/Firms IV. Export Insurance including Export Credit cum Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) Schemes For Product Insurance, Marine Insurance International Trade is an endurance game of a hyper competitive nature where every penny counts and rewards could be high for smart entrepreneurs
Nuts & Bolts of Finance I. Management of international payments, Understanding change in value of Foreign Currencies II. Risk management in exports – Commercial and Political Risk , How to do more export business with less money III. Export Finance including Pre-Shipment & Post-Shipment Finance, Line of Credit, RBI Guidelines, Foreign Exchange for Individuals/Firms IV. Export Insurance including Export Credit cum Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) Schemes For Product Insurance, Marine Insurance International Trade is an endurance game of a hyper competitive nature where every penny counts and rewards could be high for smart entrepreneurs
 PRE-SHIPMENT FINANCE • Financial assistance extended to the exporter prior to the shipment of goods is termed pre-shipment finance. • An exporter can avail pre-shipment finance either in the form of: • packing credit in local currency (e. g. , packing credit in rupees), or • pre-shipment credit foreign currency (PCFC).
PRE-SHIPMENT FINANCE • Financial assistance extended to the exporter prior to the shipment of goods is termed pre-shipment finance. • An exporter can avail pre-shipment finance either in the form of: • packing credit in local currency (e. g. , packing credit in rupees), or • pre-shipment credit foreign currency (PCFC).
 POST-SHIPMENT EXPORT ADVANCE • Banks give short-term finance to exporters against the exports receivable up to 120 days. The following are the primary types of advances: • Exports Bills Negotiation • Exports Bills Purchase • Exports against Bills Sent for Collection • Post-shipment finance is available at concessional rate to the exporters.
POST-SHIPMENT EXPORT ADVANCE • Banks give short-term finance to exporters against the exports receivable up to 120 days. The following are the primary types of advances: • Exports Bills Negotiation • Exports Bills Purchase • Exports against Bills Sent for Collection • Post-shipment finance is available at concessional rate to the exporters.
 Risk Management in Exportimport Business Commercial Risks: The risks arising from suitability of the product for the market or otherwise change in supply and demand conditions and changes in price. Commercial risks arise due to: • (i) Lack of Knowledge • (ii) Inability to adapt to the environment • (iii) Different kinds of situations to be dealt with • (iv) Greater transit time involved
Risk Management in Exportimport Business Commercial Risks: The risks arising from suitability of the product for the market or otherwise change in supply and demand conditions and changes in price. Commercial risks arise due to: • (i) Lack of Knowledge • (ii) Inability to adapt to the environment • (iii) Different kinds of situations to be dealt with • (iv) Greater transit time involved
 Risk Management in Export-import Business Cargo Risk: • Transit disasters are an ever present hazard for those engaged in Export-Import business. • Every shipment runs the risk of a long list of hazards such as storm, collision, theft, leakage, explosion, spoilage etc. It is possible to transfer the financial losses resulting from perils of and in transit to professional risk bearers known as underwriters. • As most goods are transported by marine transport, every exporter should have an elementary knowledge of marine insurance to get the protection at the minimum cost.
Risk Management in Export-import Business Cargo Risk: • Transit disasters are an ever present hazard for those engaged in Export-Import business. • Every shipment runs the risk of a long list of hazards such as storm, collision, theft, leakage, explosion, spoilage etc. It is possible to transfer the financial losses resulting from perils of and in transit to professional risk bearers known as underwriters. • As most goods are transported by marine transport, every exporter should have an elementary knowledge of marine insurance to get the protection at the minimum cost.
 Sales Contract • The major advantage of incorporation for a seller is that, where the rules are incorporated, he will know in advance the criteria against which the banks will examine the shipping documents in deciding whether or not to pay under the credit. The major advantage of incorporation for a buyer is that he will know in advance the criteria against which the price for the goods will be paid against tender of documents. However, for the buyer to be under an obligation to open a letter of credit governed by the UCP 600, the sale contract needs to include an express condition imposing such an obligation on the buyer. Only with such a condition in place can the seller object if the buyer were to open a letter of credit that is not governed by the UCP, e. g. 'Payment by irrevocable letter of credit, incorporating UCP 600'.
Sales Contract • The major advantage of incorporation for a seller is that, where the rules are incorporated, he will know in advance the criteria against which the banks will examine the shipping documents in deciding whether or not to pay under the credit. The major advantage of incorporation for a buyer is that he will know in advance the criteria against which the price for the goods will be paid against tender of documents. However, for the buyer to be under an obligation to open a letter of credit governed by the UCP 600, the sale contract needs to include an express condition imposing such an obligation on the buyer. Only with such a condition in place can the seller object if the buyer were to open a letter of credit that is not governed by the UCP, e. g. 'Payment by irrevocable letter of credit, incorporating UCP 600'.
 Contd. . • However, buyers may still stipulate in the credit that certain aspects of the UCP rules are excluded, provided of course this was laid down in the sales contract.
Contd. . • However, buyers may still stipulate in the credit that certain aspects of the UCP rules are excluded, provided of course this was laid down in the sales contract.
 Exporter’s Questionnaire
Exporter’s Questionnaire
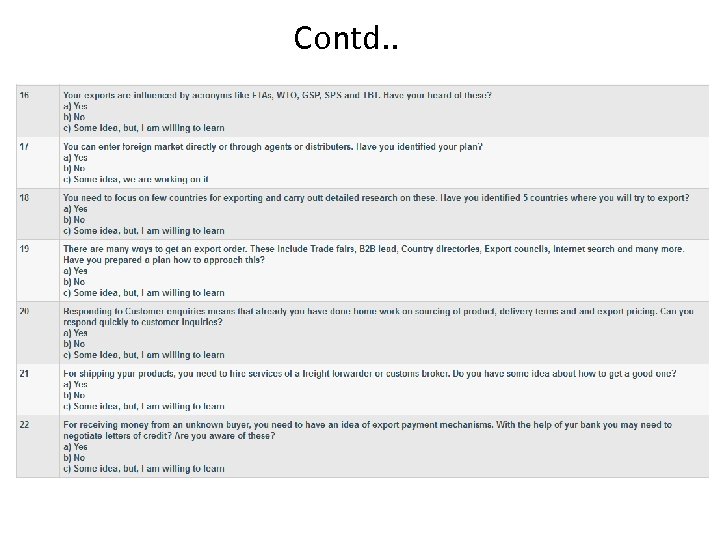
 For a proper export planning following questions need to answered : • • • Which products are selected for export development? What modifications, if any, must be made to adapt them for overseas markets? Which countries are targeted sales development? In each country, what is the basic customer profile ? What marketing and distribution channels should be used to reach customers? What special challenges pertain to each market (competition, cultural differences, import controls, etc. ), and what strategy will be used to address them? How will the product’s export sale price be determined? What specific operational steps must be taken and when? What will be the time frame for implementing each element of the plan? What personnel and company resources will be dedicated to exporting? What will be the cost in time and money for each element? How will results be evaluated and used to modify the plan?
For a proper export planning following questions need to answered : • • • Which products are selected for export development? What modifications, if any, must be made to adapt them for overseas markets? Which countries are targeted sales development? In each country, what is the basic customer profile ? What marketing and distribution channels should be used to reach customers? What special challenges pertain to each market (competition, cultural differences, import controls, etc. ), and what strategy will be used to address them? How will the product’s export sale price be determined? What specific operational steps must be taken and when? What will be the time frame for implementing each element of the plan? What personnel and company resources will be dedicated to exporting? What will be the cost in time and money for each element? How will results be evaluated and used to modify the plan?
 Export Readiness Assessment (ERA) Questionnaire For filling up this questionnaire, please register and Login at http: //indiabr. com/
Export Readiness Assessment (ERA) Questionnaire For filling up this questionnaire, please register and Login at http: //indiabr. com/
 Contd. .
Contd. .
 Contd….
Contd….
 Contd. .
Contd. .
 Thank You. .
Thank You. .


