4594a7758601b06c0bce9302f1e6aeda.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Introduction to the new mainframe Chapter 9: Batch processing and the Job Entry Subsystem (JES) Batch processing and JES © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved. jkettner@us. ibm. com

Introduction to the new mainframe Objectives Be able to: • Give an overview of batch processing and how work is initiated and managed in the system. • Explain how the job entry subsystem (JES) governs the flow of work through a z/OS system. • Workload Manager © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe Key terms in this chapter • batch processing • execution • initiator • job entry subsystem (JES) • output • procedure • purge • queue • spool • symbolic reference • workload manager (WLM) © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe What is batch processing? Much of the work running on z/OS consists of programs called batch jobs. Batch processing is used for programs that can be executed: • With minimal human interaction • At a scheduled time or on an as-needed basis. After a batch job is submitted to the system for execution, there is normally no further human interaction with the job until it is complete. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
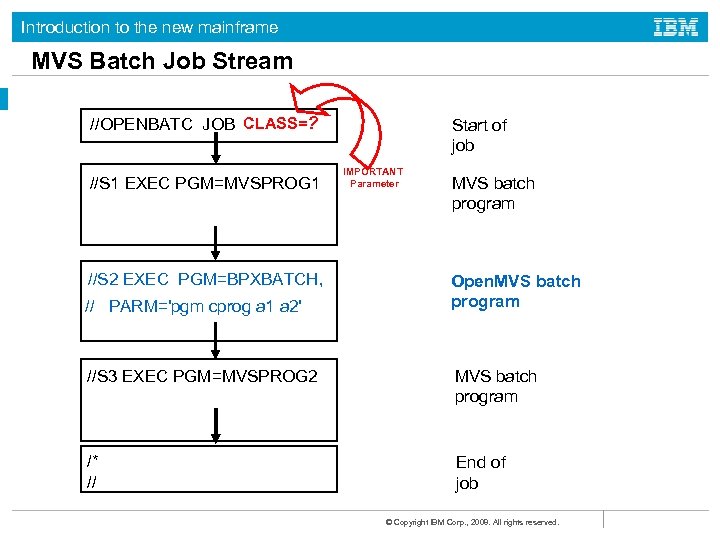
Introduction to the new mainframe MVS Batch Job Stream //OPENBATC JOB CLASS=? //S 1 EXEC PGM=MVSPROG 1 //S 2 EXEC PGM=BPXBATCH, // PARM='pgm cprog a 1 a 2' Start of job IMPORTANT Parameter MVS batch program Open. MVS batch program //S 3 EXEC PGM=MVSPROG 2 MVS batch program /* // End of job © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
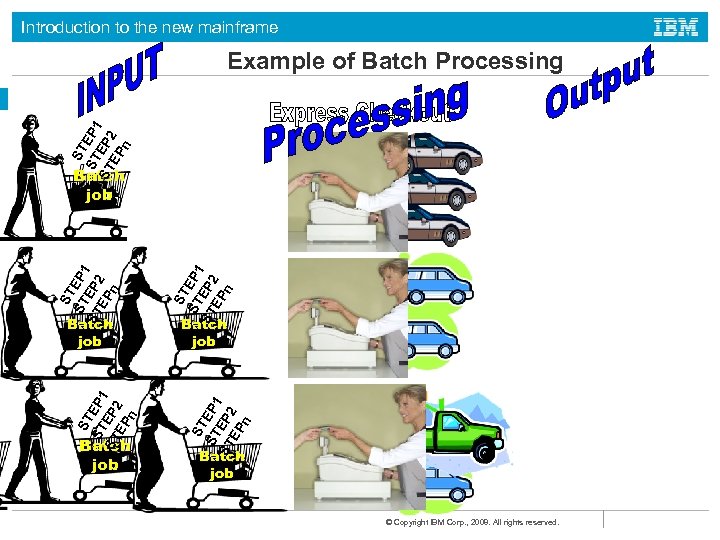
Introduction to the new mainframe ST ST EP 1 ST EP 2 EP n Example of Batch Processing Batch job ST ST EP 1 ST EP 2 EP n Batch job © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe What is JES? • In the z/OS operating system, JES manages the input and output job queues and data. • JES handles the following aspects of batch processing for z/OS: • Receives jobs into the operating system • Schedules them for processing by z/OS • Controls their output processing © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe What is JES? (continued) z/OS offers two types: JES 2 and JES 3 Some important differences, but both JES 2 and JES 3: • Accept and queue jobs submitted for execution • Queue jobs for an initiator -- a JES program that requests the next job in the queue • Accept output from a job while it is running and queue the output • Can print the output, or save it on spool for an output manager to retrieve. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe Job Management © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe Why do we need JES © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
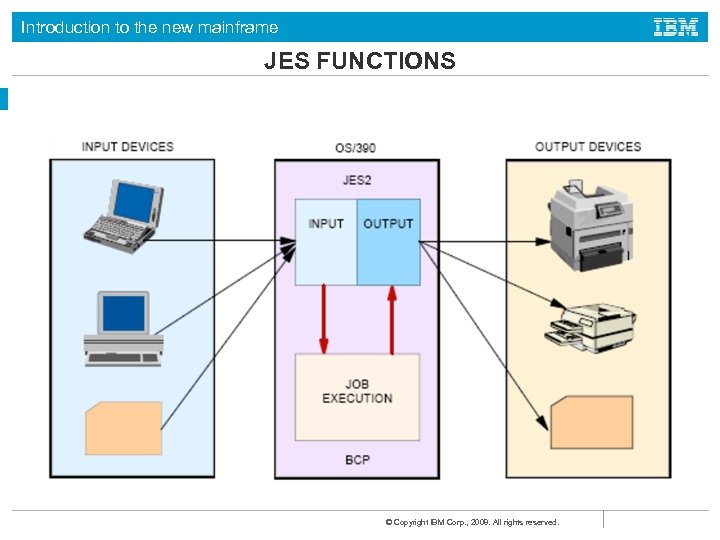
Introduction to the new mainframe JES FUNCTIONS © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
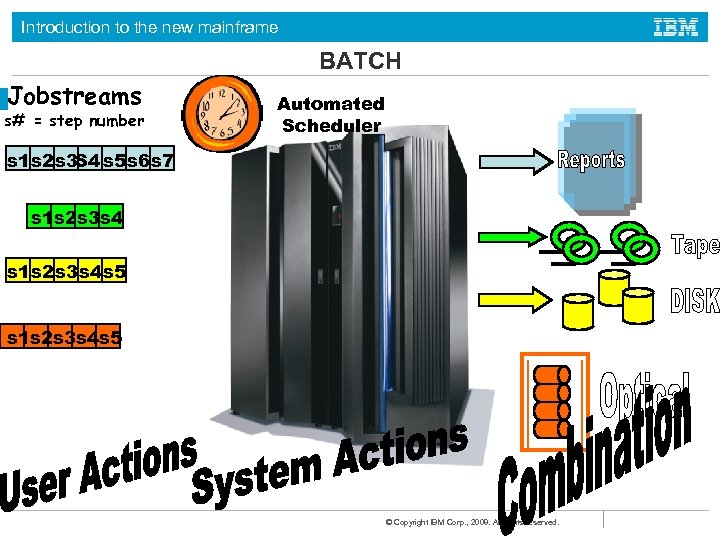
Introduction to the new mainframe BATCH Jobstreams s# = step number Automated Scheduler s 1 s 2 s 3 S 4 s 5 s 6 s 7 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
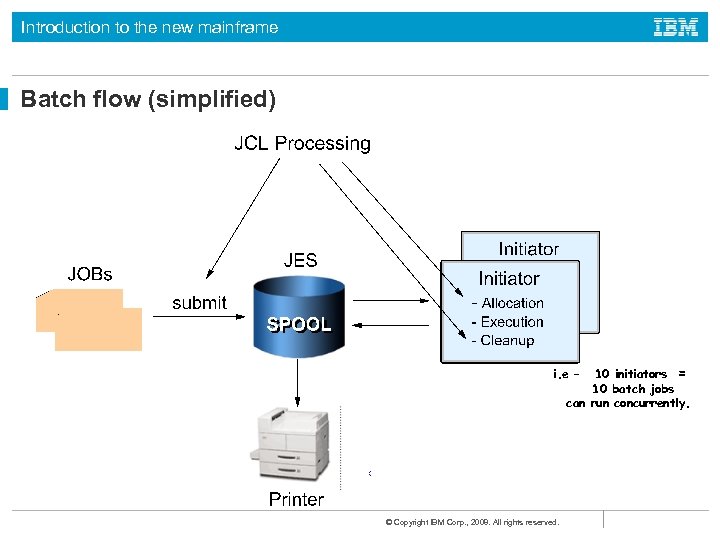
Introduction to the new mainframe Batch flow (simplified) 10 initiators = 10 batch jobs can run concurrently. i. e – © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
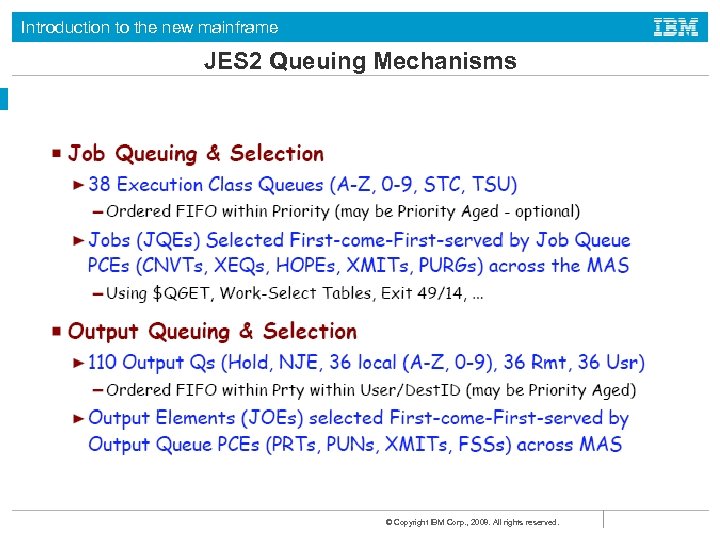
Introduction to the new mainframe JES 2 Queuing Mechanisms © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
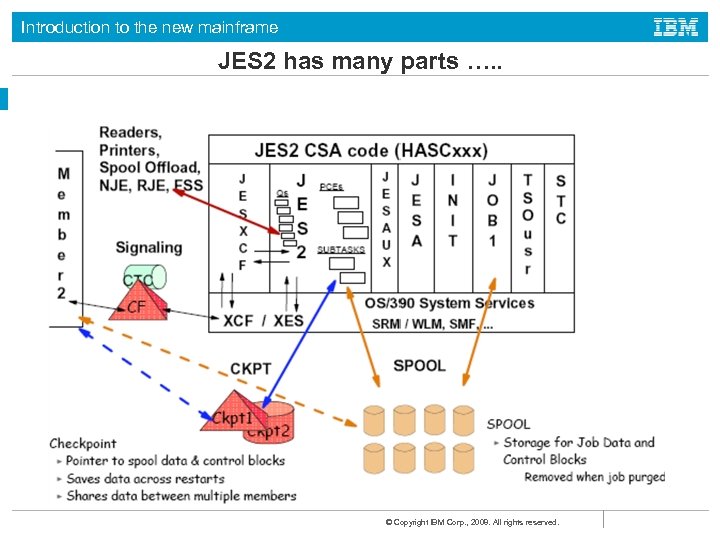
Introduction to the new mainframe JES 2 has many parts …. . © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
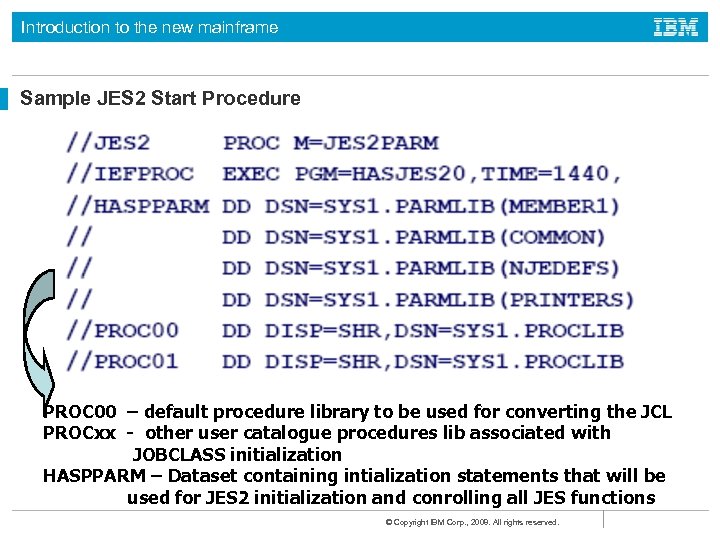
Introduction to the new mainframe Sample JES 2 Start Procedure PROC 00 – default procedure library to be used for converting the JCL PROCxx - other user catalogue procedures lib associated with JOBCLASS initialization HASPPARM – Dataset containing intialization statements that will be used for JES 2 initialization and conrolling all JES functions © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe What is spooling? (Simultaneous Peripheral Operations On. Line) Spooling is a method for queuing and holding data for input or output. JES uses one or more disk data sets for spooling. Input jobs and printed output from many jobs are stored in the single (conceptual) spool data set. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
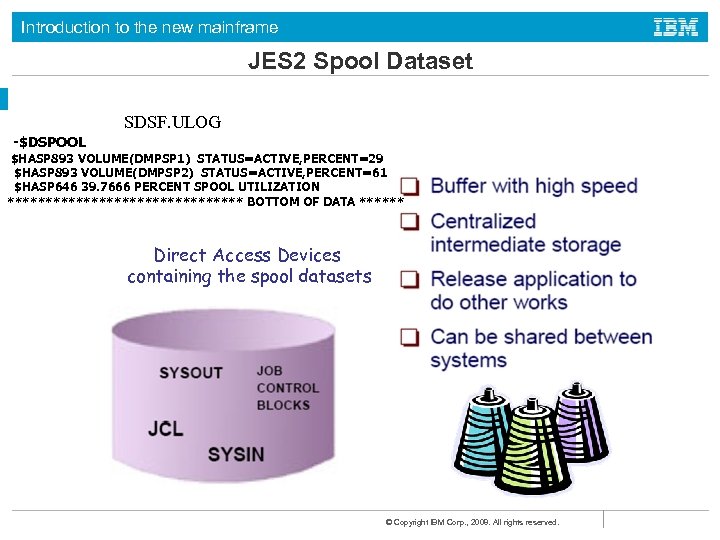
Introduction to the new mainframe JES 2 Spool Dataset SDSF. ULOG -$DSPOOL $HASP 893 VOLUME(DMPSP 1) STATUS=ACTIVE, PERCENT=29 $HASP 893 VOLUME(DMPSP 2) STATUS=ACTIVE, PERCENT=61 $HASP 646 39. 7666 PERCENT SPOOL UTILIZATION **************** BOTTOM OF DATA ****** Direct Access Devices containing the spool datasets © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe What an initiator does To run multiple jobs asynchronously, z/OS uses initiators to: • Ensure that jobs do not conflict in data set usage • Ensure that single-user devices (tape drives) are allocated correctly • Find executable programs requested by jobs • Clean up after the job ends and request the next job Preventing two users from accessing the same data at the same time is critical to z/OS and the ability to do this is one of the defining characteristics of the operating system. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
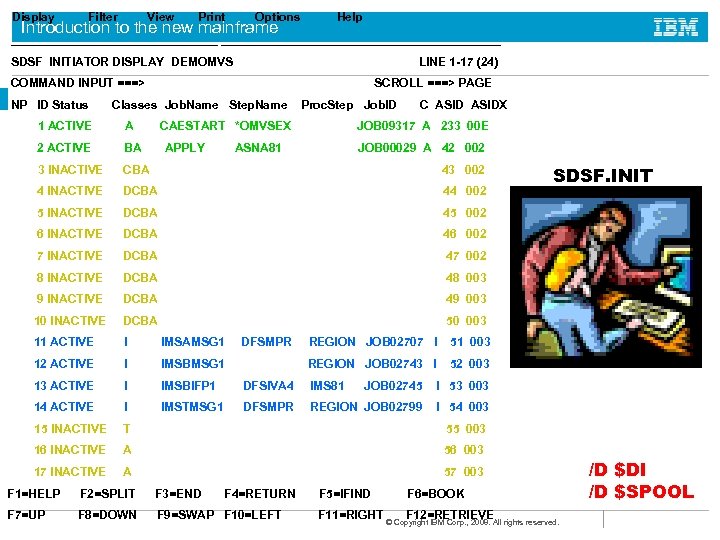
Display Filter View Print Options Introduction to the new mainframe Help _____________________________________ SDSF INITIATOR DISPLAY DEMOMVS LINE 1 -17 (24) COMMAND INPUT ===> NP ID Status SCROLL ===> PAGE Classes Job. Name Step. Name Proc. Step Job. ID CAESTART *OMVSEX C ASIDX 1 ACTIVE A 2 ACTIVE BA 3 INACTIVE CBA 43 002 4 INACTIVE DCBA 44 002 5 INACTIVE DCBA 45 002 6 INACTIVE DCBA 46 002 7 INACTIVE DCBA 47 002 8 INACTIVE DCBA 48 003 9 INACTIVE DCBA 49 003 10 INACTIVE DCBA 50 003 11 ACTIVE I IMSAMSG 1 12 ACTIVE I IMSBMSG 1 13 ACTIVE I IMSBIFP 1 DFSIVA 4 IMS 81 JOB 02745 I 53 003 14 ACTIVE I IMSTMSG 1 DFSMPR REGION JOB 02799 I 54 003 15 INACTIVE T 55 003 16 INACTIVE A 56 003 17 INACTIVE A 57 003 APPLY JOB 09317 A 233 00 E ASNA 81 DFSMPR JOB 00029 A 42 002 F 2=SPLIT F 3=END F 4=RETURN F 7=UP F 8=DOWN F 9=SWAP F 10=LEFT 51 003 REGION JOB 02743 I F 1=HELP REGION JOB 02707 I SDSF. INIT 52 003 F 5=IFIND F 6=BOOK F 11=RIGHT © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved. F 12=RETRIEVE /D $DI /D $SPOOL
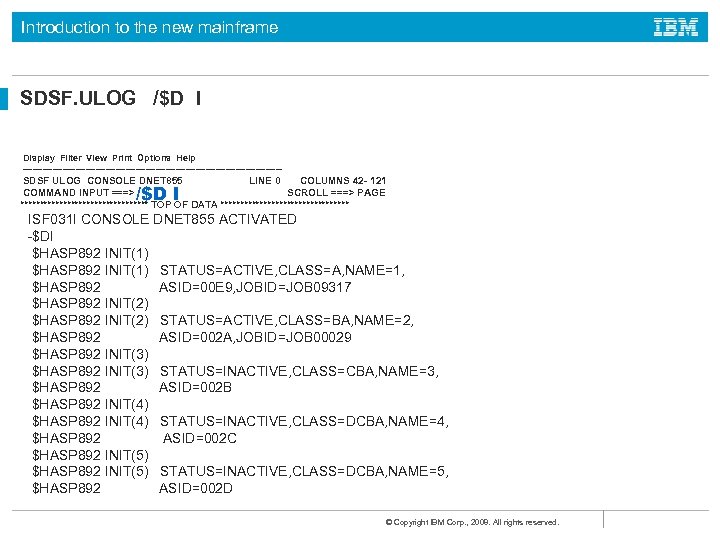
Introduction to the new mainframe SDSF. ULOG /$D I Display Filter View Print Options Help ---------------------------------------SDSF ULOG CONSOLE DNET 855 LINE 0 COLUMNS 42 - 121 COMMAND INPUT ===> SCROLL ===> PAGE ***************** TOP OF DATA ***************** /$D I ISF 031 I CONSOLE DNET 855 ACTIVATED -$DI $HASP 892 INIT(1) STATUS=ACTIVE, CLASS=A, NAME=1, $HASP 892 ASID=00 E 9, JOBID=JOB 09317 $HASP 892 INIT(2) STATUS=ACTIVE, CLASS=BA, NAME=2, $HASP 892 ASID=002 A, JOBID=JOB 00029 $HASP 892 INIT(3) STATUS=INACTIVE, CLASS=CBA, NAME=3, $HASP 892 ASID=002 B $HASP 892 INIT(4) STATUS=INACTIVE, CLASS=DCBA, NAME=4, $HASP 892 ASID=002 C $HASP 892 INIT(5) STATUS=INACTIVE, CLASS=DCBA, NAME=5, $HASP 892 ASID=002 D © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe Symbolic references to files z/OS normally uses symbolic references to files (data sets) rather than actual file names. The use of symbolic references provides a naming redirection between a data set-related name used in a program and the actual data set used during execution of that program. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
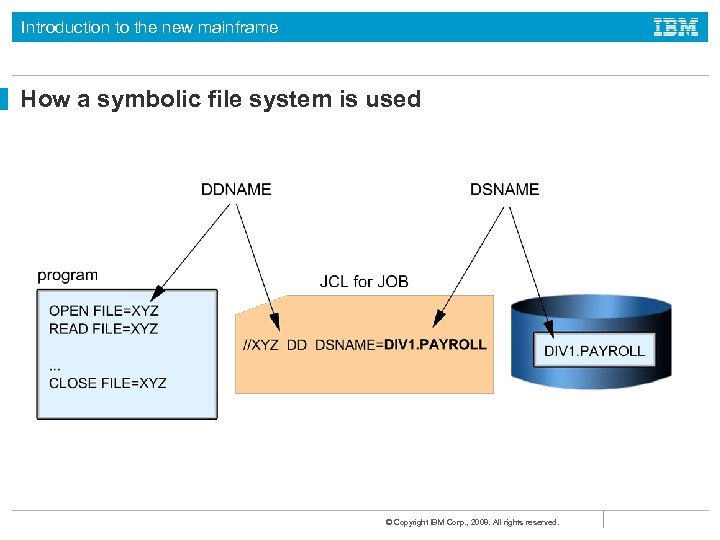
Introduction to the new mainframe How a symbolic file system is used © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe JES, job management, and JCL Job control language (JCL) is the language used by a batch job to request resources and services from the operating system. Through JCL, you specify: • Who you are (important for security reasons). • Which resources (programs, files, memory) and services are needed from the system to process your program. The use of JCL is covered in detail in the next module. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
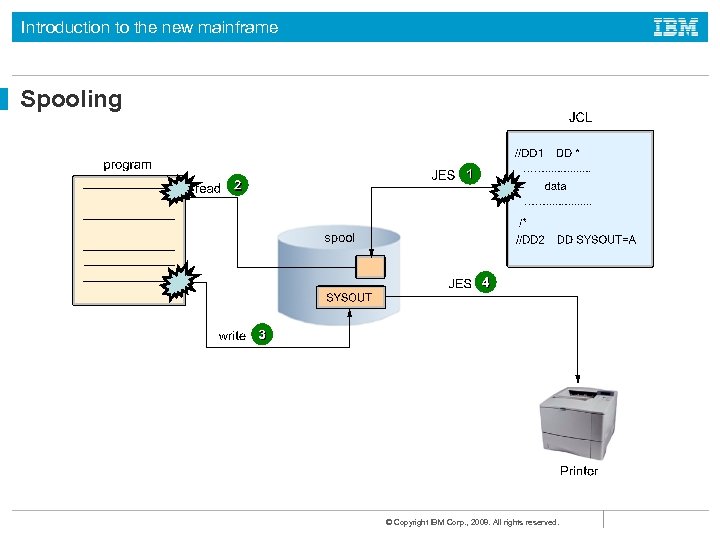
Introduction to the new mainframe Spooling © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
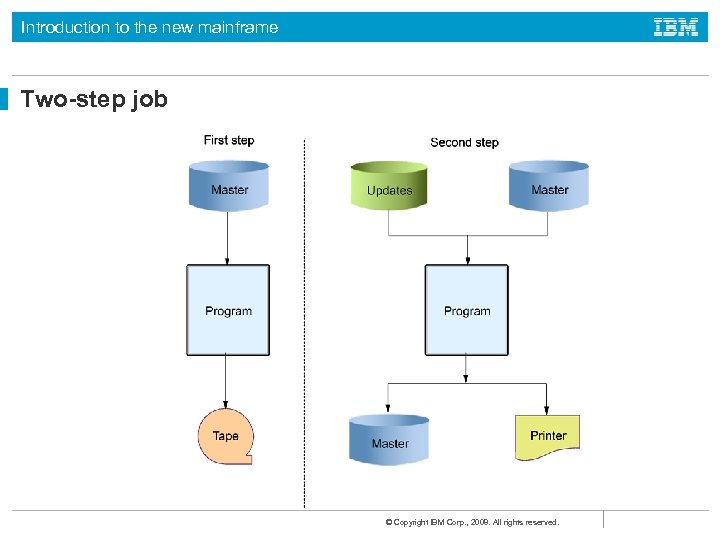
Introduction to the new mainframe Two-step job © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe Job flow through the system During execution, a job goes through the following phases: • • • Input Conversion Processing Output Print (to hardcopy or a console display) Purge © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
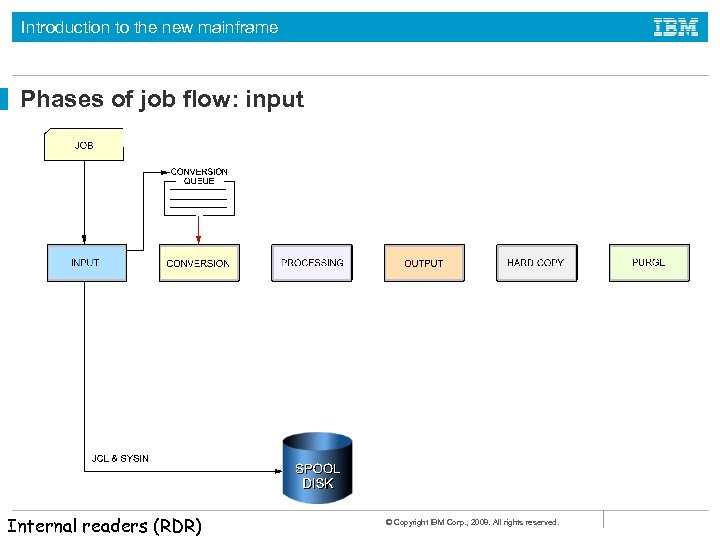
Introduction to the new mainframe Phases of job flow: input Internal readers (RDR) © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
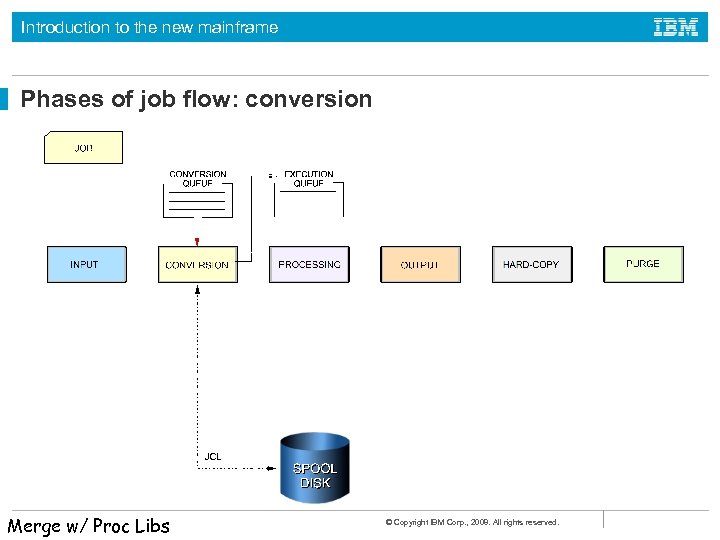
Introduction to the new mainframe Phases of job flow: conversion Merge w/ Proc Libs © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
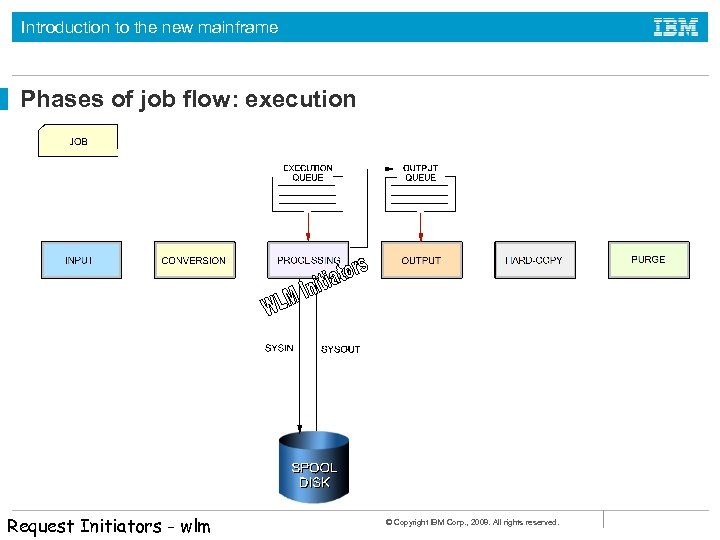
Introduction to the new mainframe Phases of job flow: execution Request Initiators - wlm © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
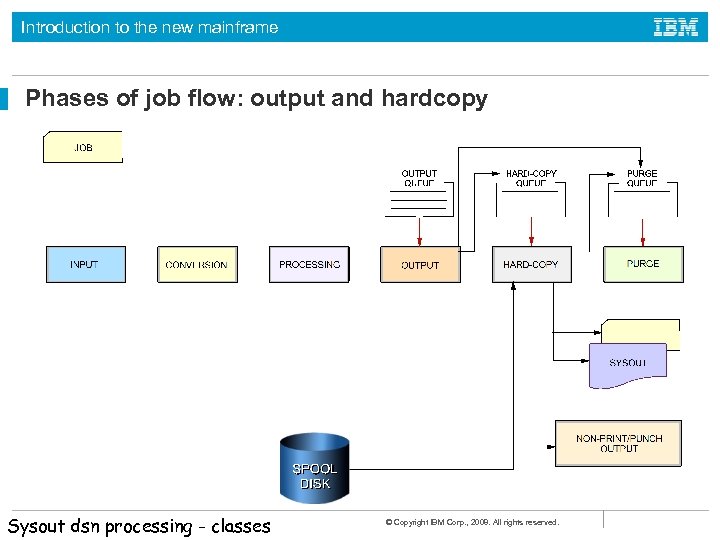
Introduction to the new mainframe Phases of job flow: output and hardcopy Sysout dsn processing - classes © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
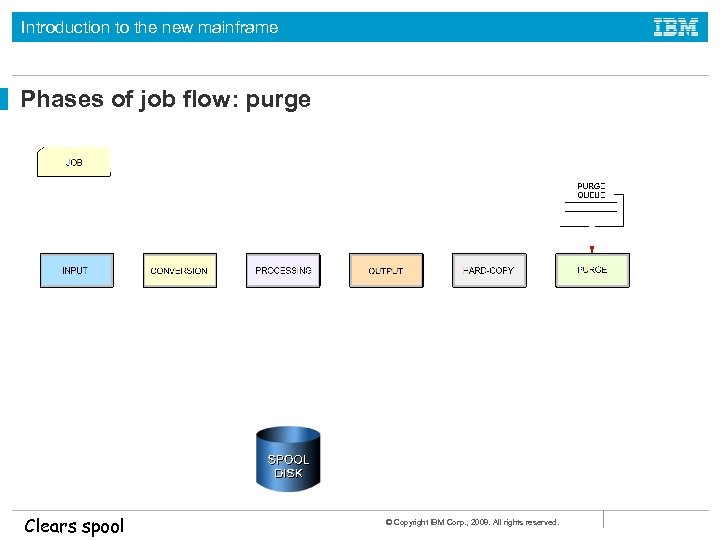
Introduction to the new mainframe Phases of job flow: purge Clears spool © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
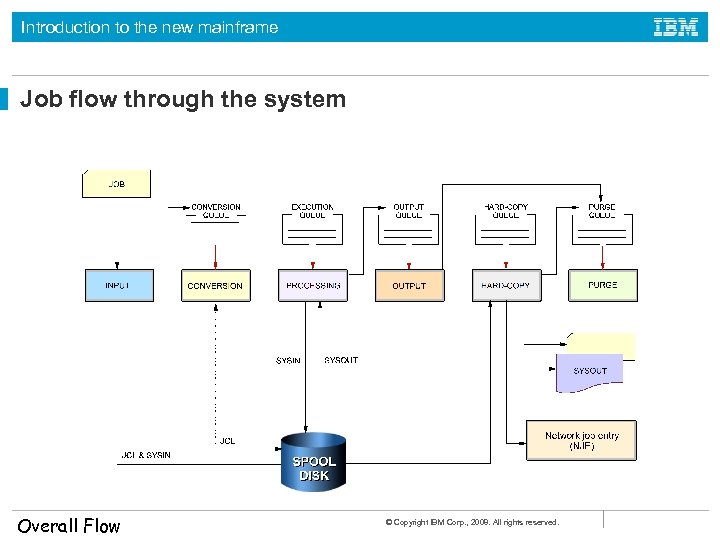
Introduction to the new mainframe Job flow through the system Overall Flow © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
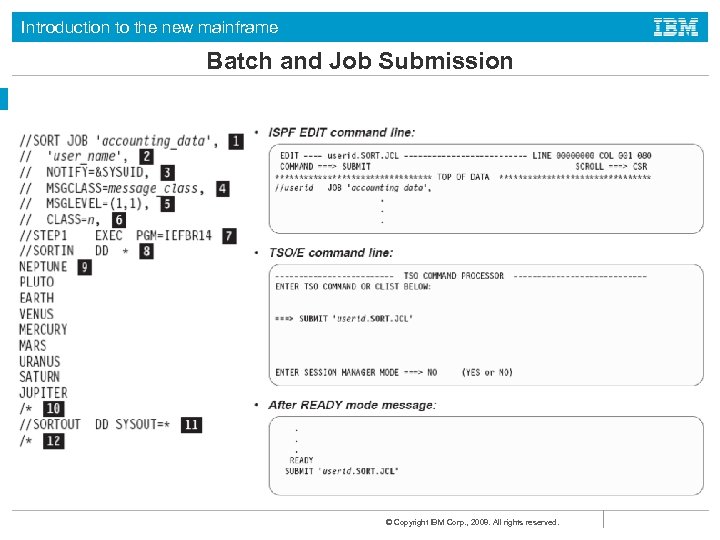
Introduction to the new mainframe Batch and Job Submission © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe JES END /* // © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe What is workload manager? Workload manager (WLM): The component of z/OS that manages the processing of workload in the system according to the company’s business goals, such as response time. Also manages the use of system resources, such as processors and storage, to accomplish these goals. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
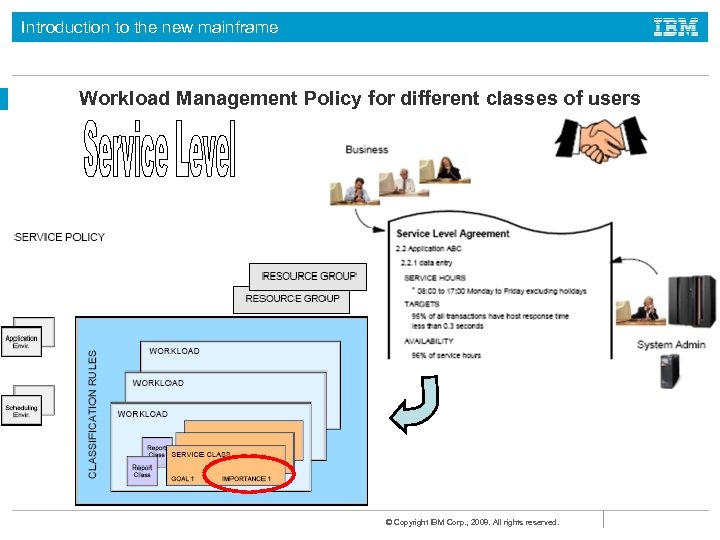
Introduction to the new mainframe Workload Management Policy for different classes of users © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
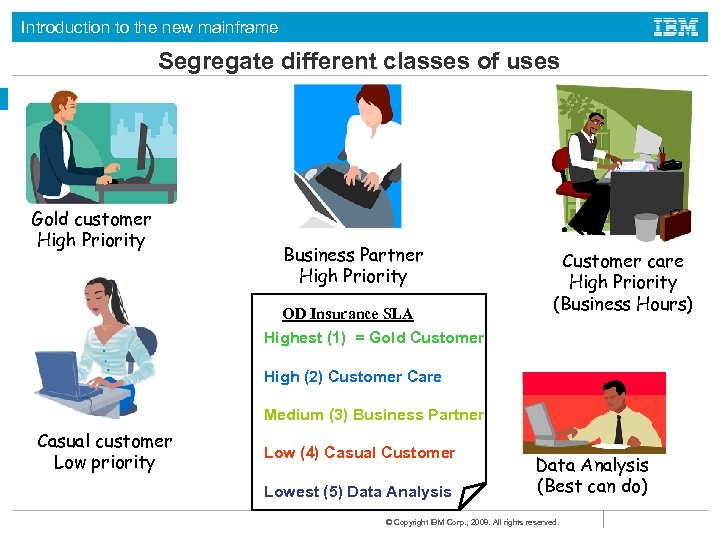
Introduction to the new mainframe Segregate different classes of uses Gold customer High Priority Business Partner High Priority OD Insurance SLA Customer care High Priority (Business Hours) Highest (1) = Gold Customer High (2) Customer Care Medium (3) Business Partner Casual customer Low priority Low (4) Casual Customer Lowest (5) Data Analysis (Best can do) © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.

Introduction to the new mainframe Summary Batch processing is a fundamental function of z/OS shares with JES the management of jobs and resources. JES receives jobs into the system, schedules them for processing, and controls their output. JES manages jobs in queues. An initiator sets up the necessary environment for running a batch job. Multiple initiators permit the parallel execution of batch jobs. During the life of a job, both JES and the z/OS base control program control different phases of the overall processing. © Copyright IBM Corp. , 2008. All rights reserved.
4594a7758601b06c0bce9302f1e6aeda.ppt