8cfce69c7d28786fae50866be6941075.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Introduction to the Grid: technologies and projects Oxana Smirnova Lund University October 28, 2003, Košice 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se
Introduction to the Grid: technologies and projects Oxana Smirnova Lund University October 28, 2003, Košice 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se
 Outlook n n Information Technology developments Grid solutions High Energy Physics challenges Development and deployment projects 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 2
Outlook n n Information Technology developments Grid solutions High Energy Physics challenges Development and deployment projects 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 2
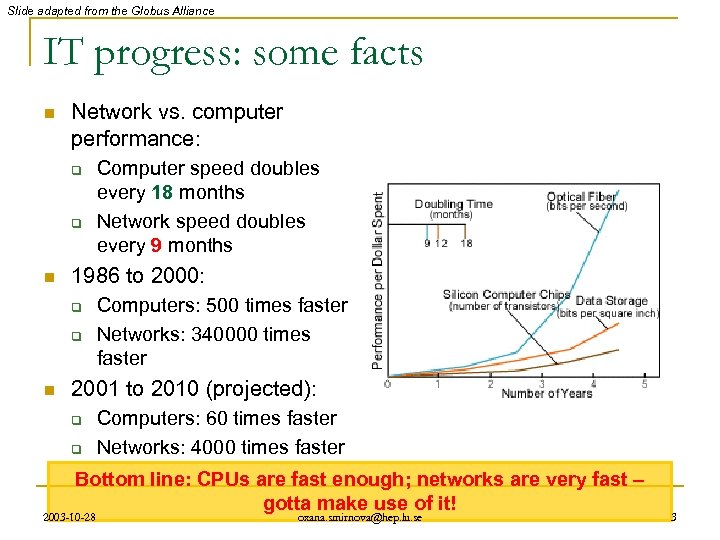 Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance IT progress: some facts n Network vs. computer performance: q q n 1986 to 2000: q q n Computer speed doubles every 18 months Network speed doubles every 9 months Computers: 500 times faster Networks: 340000 times faster 2001 to 2010 (projected): q q Computers: 60 times faster Networks: 4000 times faster Bottom line: CPUs are fast enough; networks are very fast – gotta make use of it! 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 3
Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance IT progress: some facts n Network vs. computer performance: q q n 1986 to 2000: q q n Computer speed doubles every 18 months Network speed doubles every 9 months Computers: 500 times faster Networks: 340000 times faster 2001 to 2010 (projected): q q Computers: 60 times faster Networks: 4000 times faster Bottom line: CPUs are fast enough; networks are very fast – gotta make use of it! 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 3
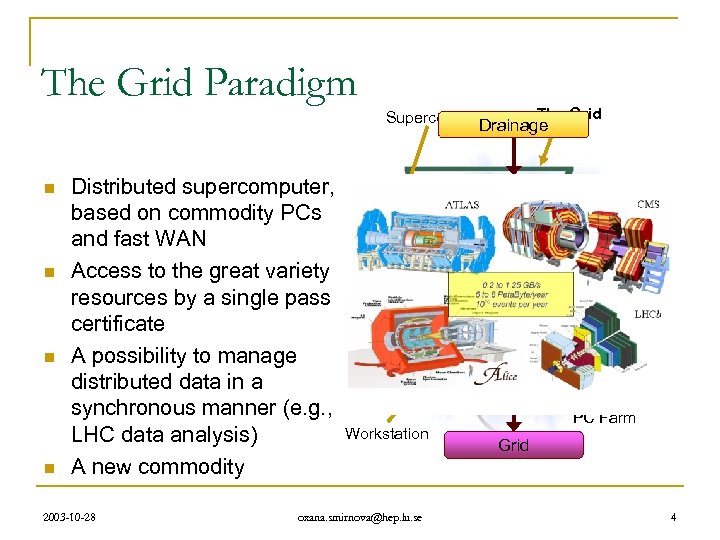 The Grid Paradigm The Grid Supercomputer Drainage n n Distributed supercomputer, based on commodity PCs and fast WAN Access to the great variety of resources by a single pass – certificate A possibility to manage distributed data in a synchronous manner (e. g. , Workstation LHC data analysis) A new commodity 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Water Electricity Radio/TV Internet PC Farm Grid 4
The Grid Paradigm The Grid Supercomputer Drainage n n Distributed supercomputer, based on commodity PCs and fast WAN Access to the great variety of resources by a single pass – certificate A possibility to manage distributed data in a synchronous manner (e. g. , Workstation LHC data analysis) A new commodity 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Water Electricity Radio/TV Internet PC Farm Grid 4
 Slide adapted from A. Grimshaw Wider scope: a Grid System A Grid system is a collection of distributed resources connected by a network Examples of Distributed Resources: n Desktop n Handheld hosts n Devices with embedded processing resources such as digital cameras and phones n Tera-scale supercomputers 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 5
Slide adapted from A. Grimshaw Wider scope: a Grid System A Grid system is a collection of distributed resources connected by a network Examples of Distributed Resources: n Desktop n Handheld hosts n Devices with embedded processing resources such as digital cameras and phones n Tera-scale supercomputers 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 5
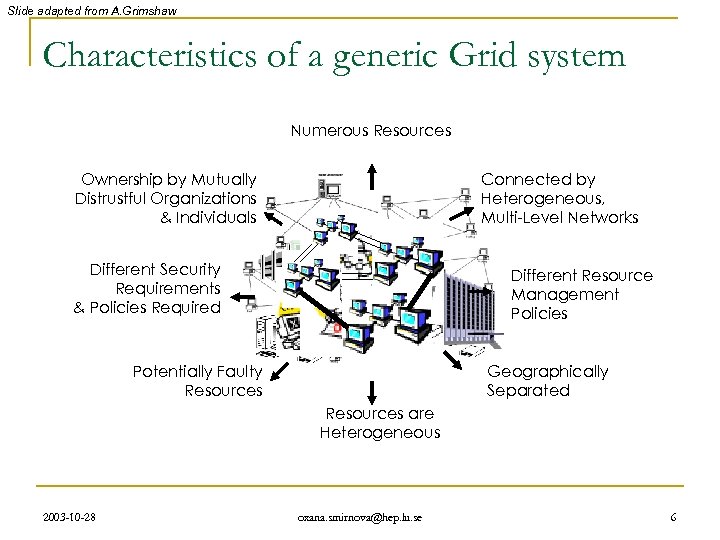 Slide adapted from A. Grimshaw Characteristics of a generic Grid system Numerous Resources Ownership by Mutually Distrustful Organizations & Individuals Connected by Heterogeneous, Multi-Level Networks Different Security Requirements & Policies Required Different Resource Management Policies Potentially Faulty Resources Geographically Separated Resources are Heterogeneous 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 6
Slide adapted from A. Grimshaw Characteristics of a generic Grid system Numerous Resources Ownership by Mutually Distrustful Organizations & Individuals Connected by Heterogeneous, Multi-Level Networks Different Security Requirements & Policies Required Different Resource Management Policies Potentially Faulty Resources Geographically Separated Resources are Heterogeneous 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 6
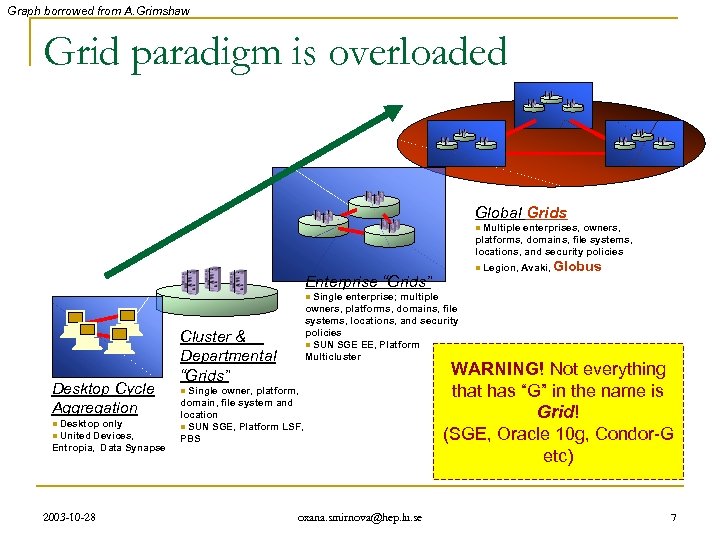 Graph borrowed from A. Grimshaw Grid paradigm is overloaded Global Grids Multiple enterprises, owners, platforms, domains, file systems, locations, and security policies n n Enterprise “Grids” Legion, Avaki, Globus Single enterprise; multiple owners, platforms, domains, file systems, locations, and security policies n SUN SGE EE, Platform Multicluster n Desktop Cycle Aggregation Desktop only United Devices, Entropia, Data Synapse n n 2003 -10 -28 Cluster & Departmental “Grids” Single owner, platform, domain, file system and location n SUN SGE, Platform LSF, PBS n oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se WARNING! Not everything that has “G” in the name is Grid! (SGE, Oracle 10 g, Condor-G etc) 7
Graph borrowed from A. Grimshaw Grid paradigm is overloaded Global Grids Multiple enterprises, owners, platforms, domains, file systems, locations, and security policies n n Enterprise “Grids” Legion, Avaki, Globus Single enterprise; multiple owners, platforms, domains, file systems, locations, and security policies n SUN SGE EE, Platform Multicluster n Desktop Cycle Aggregation Desktop only United Devices, Entropia, Data Synapse n n 2003 -10 -28 Cluster & Departmental “Grids” Single owner, platform, domain, file system and location n SUN SGE, Platform LSF, PBS n oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se WARNING! Not everything that has “G” in the name is Grid! (SGE, Oracle 10 g, Condor-G etc) 7
 Globus: the toolkit provider The first and only provider of a Grid toolkit (libraries and API) q q q An academic research project in USA and now Europe Free software, open code Supports Grid testbeds since late 90’s Grid features: • Heterogeneous • Non-interactive • Single logon • Optimized file transfer protocol • Information schema To do: • Global resource management • Data management • User management, accounting 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 8
Globus: the toolkit provider The first and only provider of a Grid toolkit (libraries and API) q q q An academic research project in USA and now Europe Free software, open code Supports Grid testbeds since late 90’s Grid features: • Heterogeneous • Non-interactive • Single logon • Optimized file transfer protocol • Information schema To do: • Global resource management • Data management • User management, accounting 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 8
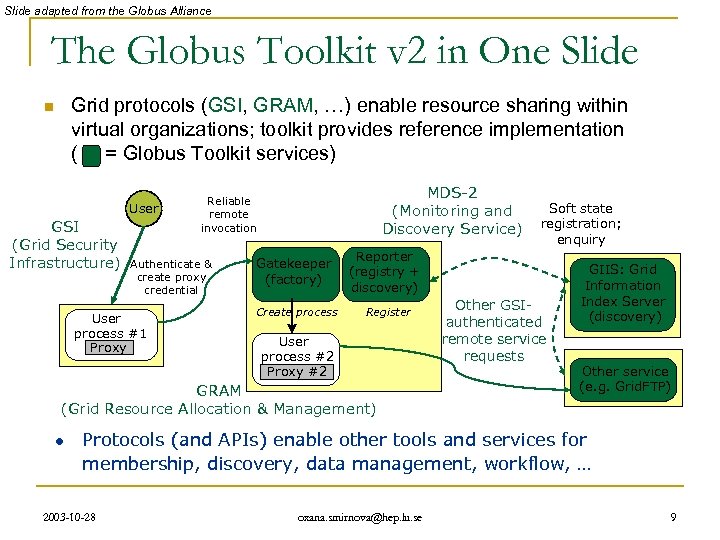 Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance The Globus Toolkit v 2 in One Slide Grid protocols (GSI, GRAM, …) enable resource sharing within virtual organizations; toolkit provides reference implementation ( = Globus Toolkit services) n User GSI (Grid Security Infrastructure) Authenticate & create proxy credential User process #1 Proxy MDS-2 (Monitoring and Discovery Service) Reliable remote invocation Gatekeeper (factory) Create process Reporter (registry + discovery) Register User process #2 Proxy #2 GRAM (Grid Resource Allocation & Management) l Soft state registration; enquiry Other GSIauthenticated remote service requests GIIS: Grid Information Index Server (discovery) Other service (e. g. Grid. FTP) Protocols (and APIs) enable other tools and services for membership, discovery, data management, workflow, … 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 9
Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance The Globus Toolkit v 2 in One Slide Grid protocols (GSI, GRAM, …) enable resource sharing within virtual organizations; toolkit provides reference implementation ( = Globus Toolkit services) n User GSI (Grid Security Infrastructure) Authenticate & create proxy credential User process #1 Proxy MDS-2 (Monitoring and Discovery Service) Reliable remote invocation Gatekeeper (factory) Create process Reporter (registry + discovery) Register User process #2 Proxy #2 GRAM (Grid Resource Allocation & Management) l Soft state registration; enquiry Other GSIauthenticated remote service requests GIIS: Grid Information Index Server (discovery) Other service (e. g. Grid. FTP) Protocols (and APIs) enable other tools and services for membership, discovery, data management, workflow, … 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 9
 Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance Globus-Based Grid Tools & Applications n n n Data Grids q Distributed management of large quantities of data: physics, astronomy, engineering High-throughput computing q Coordinated use of many computers Collaborative environments q Authentication, resource discovery, and resource access Portals q Thin client access to remote resources & services And combinations of the above 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 10
Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance Globus-Based Grid Tools & Applications n n n Data Grids q Distributed management of large quantities of data: physics, astronomy, engineering High-throughput computing q Coordinated use of many computers Collaborative environments q Authentication, resource discovery, and resource access Portals q Thin client access to remote resources & services And combinations of the above 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 10
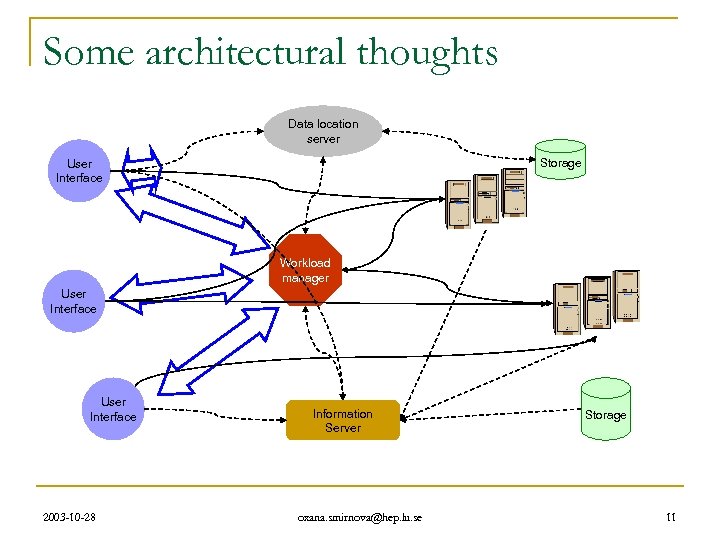 Some architectural thoughts Data location server Storage User Interface Workload manager User Interface 2003 -10 -28 Information Server oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Storage 11
Some architectural thoughts Data location server Storage User Interface Workload manager User Interface 2003 -10 -28 Information Server oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Storage 11
 Who needs Grid: High Energy Physics challenges n Data-intensive tasks q q n Very distributed user base q q q n Large datasets, large files Lengthy processing times Large memory consumption High throughput is necessary Distributed computing resources of modest size Produced and processed data are hence distributed, too Issues of coordination, synchronization and authorization are outstanding HEP is by no means unique in its demands, but they are first, they are many, and they badly need it 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 12
Who needs Grid: High Energy Physics challenges n Data-intensive tasks q q n Very distributed user base q q q n Large datasets, large files Lengthy processing times Large memory consumption High throughput is necessary Distributed computing resources of modest size Produced and processed data are hence distributed, too Issues of coordination, synchronization and authorization are outstanding HEP is by no means unique in its demands, but they are first, they are many, and they badly need it 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 12
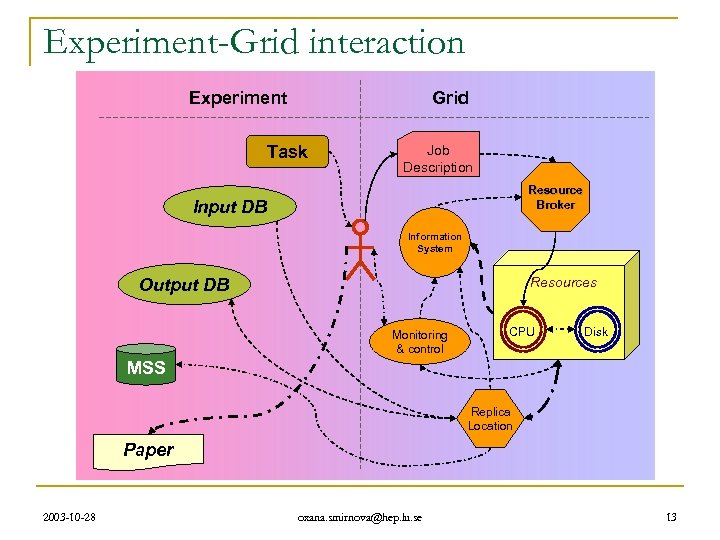 Experiment-Grid interaction Grid Experiment Task Job Description Resource Broker Input DB Information System Resources Output DB Monitoring & control CPU Disk MSS Replica Location Paper 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 13
Experiment-Grid interaction Grid Experiment Task Job Description Resource Broker Input DB Information System Resources Output DB Monitoring & control CPU Disk MSS Replica Location Paper 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 13
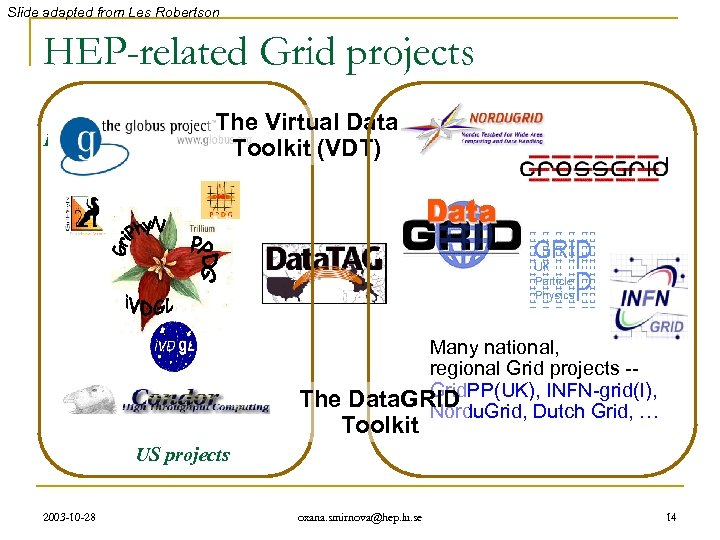 Slide adapted from Les Robertson HEP-related Grid projects European projects The Virtual Data Toolkit (VDT) Many national, regional Grid projects -Grid. PP(UK), INFN-grid(I), Data. GRID Nordu. Grid, Dutch Grid, … The Toolkit US projects 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 14
Slide adapted from Les Robertson HEP-related Grid projects European projects The Virtual Data Toolkit (VDT) Many national, regional Grid projects -Grid. PP(UK), INFN-grid(I), Data. GRID Nordu. Grid, Dutch Grid, … The Toolkit US projects 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 14
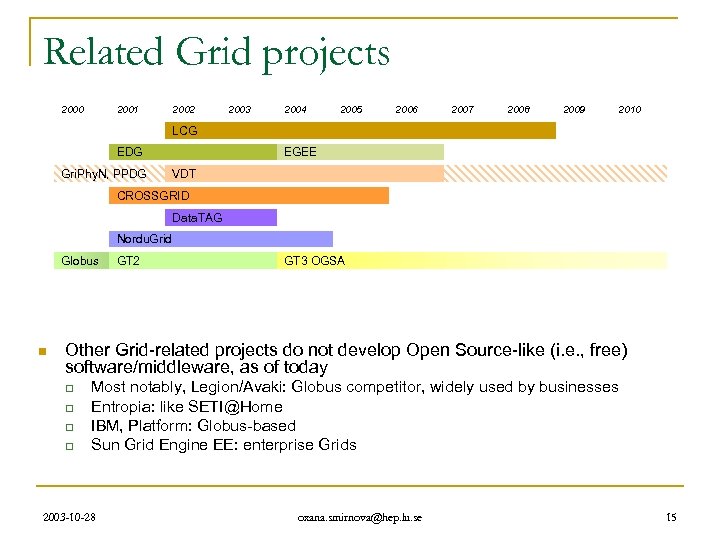 Related Grid projects 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 LCG EDG Gri. Phy. N, PPDG EGEE VDT CROSSGRID Data. TAG Nordu. Grid Globus n GT 2 GT 3 OGSA Other Grid-related projects do not develop Open Source-like (i. e. , free) software/middleware, as of today q q Most notably, Legion/Avaki: Globus competitor, widely used by businesses Entropia: like SETI@Home IBM, Platform: Globus-based Sun Grid Engine EE: enterprise Grids 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 15
Related Grid projects 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 LCG EDG Gri. Phy. N, PPDG EGEE VDT CROSSGRID Data. TAG Nordu. Grid Globus n GT 2 GT 3 OGSA Other Grid-related projects do not develop Open Source-like (i. e. , free) software/middleware, as of today q q Most notably, Legion/Avaki: Globus competitor, widely used by businesses Entropia: like SETI@Home IBM, Platform: Globus-based Sun Grid Engine EE: enterprise Grids 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 15
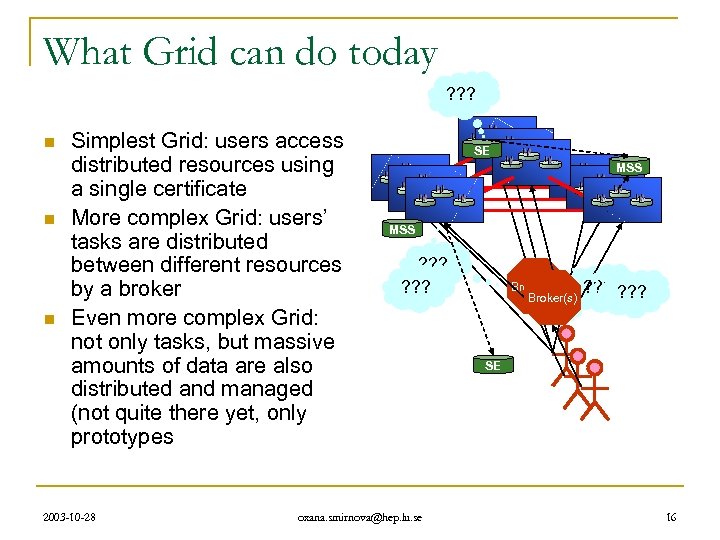 What Grid can do today ? ? ? n n n Simplest Grid: users access distributed resources using a single certificate More complex Grid: users’ tasks are distributed between different resources by a broker Even more complex Grid: not only tasks, but massive amounts of data are also distributed and managed (not quite there yet, only prototypes 2003 -10 -28 SE MSS ? ? ? oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Broker(s) ? ? ? SE 16
What Grid can do today ? ? ? n n n Simplest Grid: users access distributed resources using a single certificate More complex Grid: users’ tasks are distributed between different resources by a broker Even more complex Grid: not only tasks, but massive amounts of data are also distributed and managed (not quite there yet, only prototypes 2003 -10 -28 SE MSS ? ? ? oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se Broker(s) ? ? ? SE 16
 What is missing n n n Common policies, or ways of mutually respecting such Grid accounting systems and Grid economy Serious security solutions; role-based access control Full-blown distributed data management systems Tools and methods for system-wide applications environment deployment STANDARDS! 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 17
What is missing n n n Common policies, or ways of mutually respecting such Grid accounting systems and Grid economy Serious security solutions; role-based access control Full-blown distributed data management systems Tools and methods for system-wide applications environment deployment STANDARDS! 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 17
 The Grid or many Grids? n Globus Toolkit 2 is a basis for great many Grid solutions q q q Which use some common tools and utilities: GSI, Grid. FTP But they also differ a lot, architecturally and technologically There are several non-interoperable GT 2 -based Grid systems! n n Grid standards body: Global Grid Forum (GGF) q q n No satisfactory ready-made solutions developers invent their own Being financed from different sources, developers and users are not always encouraged to adopt rival project’s solution Instead of “How should I use Grid? ”, users ask “Which Grid should I use? ” Heavily oriented towards commercial implementations No effective standards since 2001 Meanwhile, Globus introduced the “Open Grid Services Architecture” (OGSA) q q q 2003 -10 -28 Globus Toolkit 3 is released Not yet used by any of the development projects Perhaps the first set of standards endorsed by GGF oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 18
The Grid or many Grids? n Globus Toolkit 2 is a basis for great many Grid solutions q q q Which use some common tools and utilities: GSI, Grid. FTP But they also differ a lot, architecturally and technologically There are several non-interoperable GT 2 -based Grid systems! n n Grid standards body: Global Grid Forum (GGF) q q n No satisfactory ready-made solutions developers invent their own Being financed from different sources, developers and users are not always encouraged to adopt rival project’s solution Instead of “How should I use Grid? ”, users ask “Which Grid should I use? ” Heavily oriented towards commercial implementations No effective standards since 2001 Meanwhile, Globus introduced the “Open Grid Services Architecture” (OGSA) q q q 2003 -10 -28 Globus Toolkit 3 is released Not yet used by any of the development projects Perhaps the first set of standards endorsed by GGF oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 18
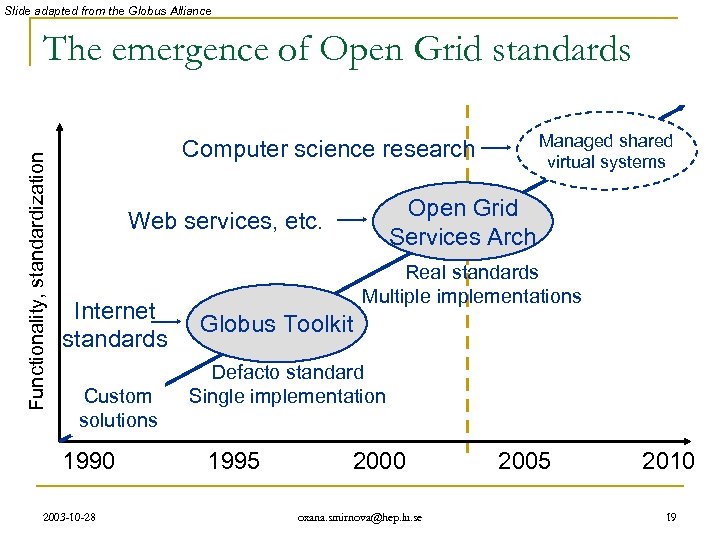 Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance Functionality, standardization The emergence of Open Grid standards Managed shared virtual systems Computer science research Open Grid Services Arch Web services, etc. Internet standards Custom solutions 1990 2003 -10 -28 Real standards Multiple implementations Globus Toolkit Defacto standard Single implementation 1995 2000 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 2005 2010 19
Slide adapted from the Globus Alliance Functionality, standardization The emergence of Open Grid standards Managed shared virtual systems Computer science research Open Grid Services Arch Web services, etc. Internet standards Custom solutions 1990 2003 -10 -28 Real standards Multiple implementations Globus Toolkit Defacto standard Single implementation 1995 2000 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 2005 2010 19
 Open Grid Services Architecture n n Standard interfaces & behaviors for distributed system management Service orientation: Grid Services, in analogy to Web Services q Web services: persistent q Grid services: transient (issues: e. g. , how are they discovered? ) q Extending WSDL to GSDL (work with W 3 C) Standard service specifications q Resource management q Data management q Workflow q Security q etc. Paves the road towards interoperability and true modularity of Grid structures 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 20
Open Grid Services Architecture n n Standard interfaces & behaviors for distributed system management Service orientation: Grid Services, in analogy to Web Services q Web services: persistent q Grid services: transient (issues: e. g. , how are they discovered? ) q Extending WSDL to GSDL (work with W 3 C) Standard service specifications q Resource management q Data management q Workflow q Security q etc. Paves the road towards interoperability and true modularity of Grid structures 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 20
 Conclusion n HEP community stirred a world-wide Grid interest q n Despite a slow start and much hype, some real work is under way q n Rather, the next big thing after the WWW ! Still, no complete solution exists q q n Next big thing after the dot-com? . . Data management? Accounting? Security? Standardization? With courage and patience, we should go Grid 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 21
Conclusion n HEP community stirred a world-wide Grid interest q n Despite a slow start and much hype, some real work is under way q n Rather, the next big thing after the WWW ! Still, no complete solution exists q q n Next big thing after the dot-com? . . Data management? Accounting? Security? Standardization? With courage and patience, we should go Grid 2003 -10 -28 oxana. smirnova@hep. lu. se 21


