a9604dae911f703e5f706713e581f119.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Introduction to the ca. DSR Presented to HL 7 Vocab SIG January 24, 2005 Denise Warzel National Cancer Institute, Center for Bioinformatics ca. DSR Project Officer, Software Development 1
Introduction to the ca. DSR Presented to HL 7 Vocab SIG January 24, 2005 Denise Warzel National Cancer Institute, Center for Bioinformatics ca. DSR Project Officer, Software Development 1
 Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 2
Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 2
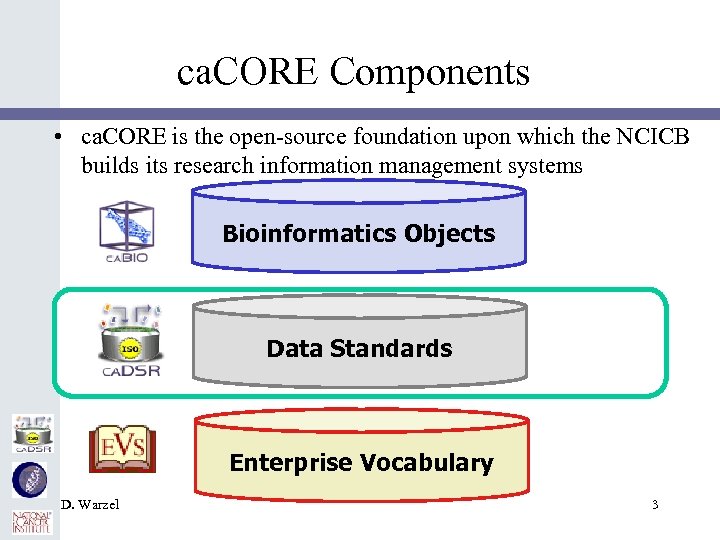 ca. CORE Components • ca. CORE is the open-source foundation upon which the NCICB builds its research information management systems Bioinformatics Objects Data Standards Enterprise Vocabulary D. Warzel 3
ca. CORE Components • ca. CORE is the open-source foundation upon which the NCICB builds its research information management systems Bioinformatics Objects Data Standards Enterprise Vocabulary D. Warzel 3
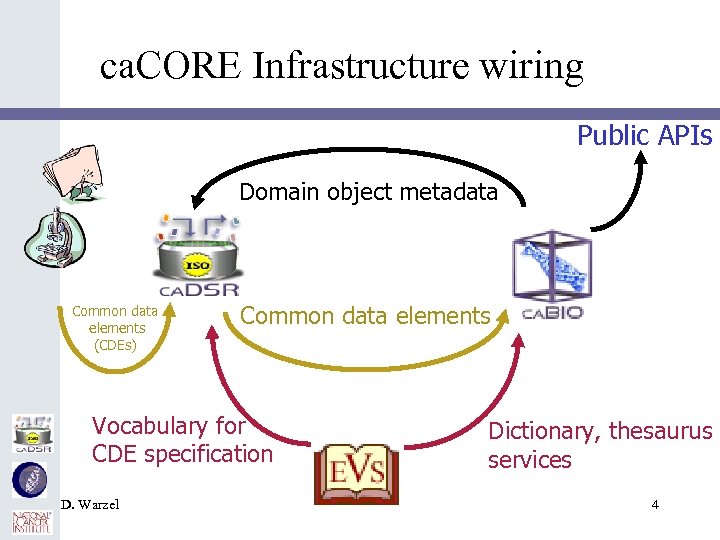 ca. CORE Infrastructure wiring Public APIs Domain object metadata Common data elements (CDEs) Common data elements Vocabulary for CDE specification D. Warzel Dictionary, thesaurus services 4
ca. CORE Infrastructure wiring Public APIs Domain object metadata Common data elements (CDEs) Common data elements Vocabulary for CDE specification D. Warzel Dictionary, thesaurus services 4
 Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 5
Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 5
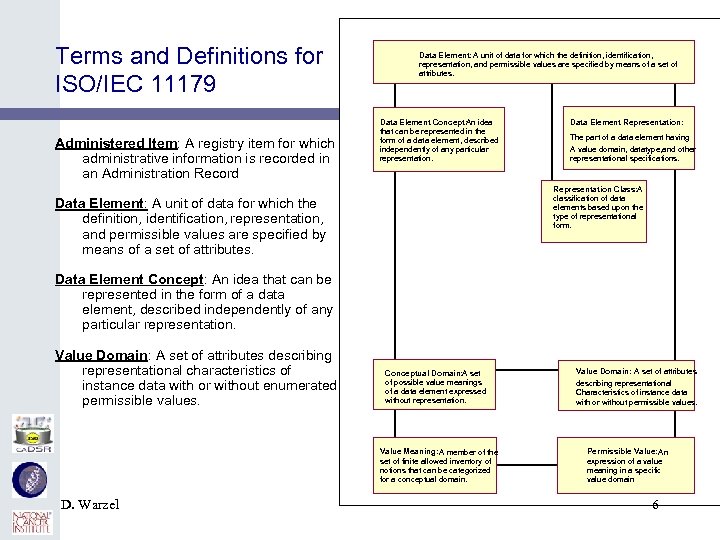 Terms and Definitions for ISO/IEC 11179 Administered Item: A registry item for which administrative information is recorded in an Administration Record Data Element: A unit of data for which the definition, identification, representation, and permissible values are specified by means of a set of attributes. Data Element Concept: An idea that can be represented in the form of a data element, described independently of any particular representation. Data Element Representation: The part of a data element having A value domain, datatype, and other representational specifications. Representation Class: A classification of data elements based upon the type of representational form. Data Element: A unit of data for which the definition, identification, representation, and permissible values are specified by means of a set of attributes. Data Element Concept: An idea that can be represented in the form of a data element, described independently of any particular representation. Value Domain: A set of attributes describing representational characteristics of instance data with or without enumerated permissible values. Conceptual Domain: A set of possible value meanings of a data element expressed without representation. Value Meaning: A member of the set of finite allowed inventory of notions that can be categorized for a conceptual domain. D. Warzel Value Domain: A set of attributes describing representational Characteristics of instance data with or without permissible values. Permissible Value: An expression of a value meaning in a specific value domain 6
Terms and Definitions for ISO/IEC 11179 Administered Item: A registry item for which administrative information is recorded in an Administration Record Data Element: A unit of data for which the definition, identification, representation, and permissible values are specified by means of a set of attributes. Data Element Concept: An idea that can be represented in the form of a data element, described independently of any particular representation. Data Element Representation: The part of a data element having A value domain, datatype, and other representational specifications. Representation Class: A classification of data elements based upon the type of representational form. Data Element: A unit of data for which the definition, identification, representation, and permissible values are specified by means of a set of attributes. Data Element Concept: An idea that can be represented in the form of a data element, described independently of any particular representation. Value Domain: A set of attributes describing representational characteristics of instance data with or without enumerated permissible values. Conceptual Domain: A set of possible value meanings of a data element expressed without representation. Value Meaning: A member of the set of finite allowed inventory of notions that can be categorized for a conceptual domain. D. Warzel Value Domain: A set of attributes describing representational Characteristics of instance data with or without permissible values. Permissible Value: An expression of a value meaning in a specific value domain 6
 What is ISO/IEC 11179? • ISO/IEC 11179 Parts 1 -6: Information technology – Specification and Standardization of data elements – A metamodel for ‘data element’ metadata – Standard by which to convey semantic, syntactic and lexical meaning • Human and machine understandable • Unambiguous D. Warzel 7
What is ISO/IEC 11179? • ISO/IEC 11179 Parts 1 -6: Information technology – Specification and Standardization of data elements – A metamodel for ‘data element’ metadata – Standard by which to convey semantic, syntactic and lexical meaning • Human and machine understandable • Unambiguous D. Warzel 7
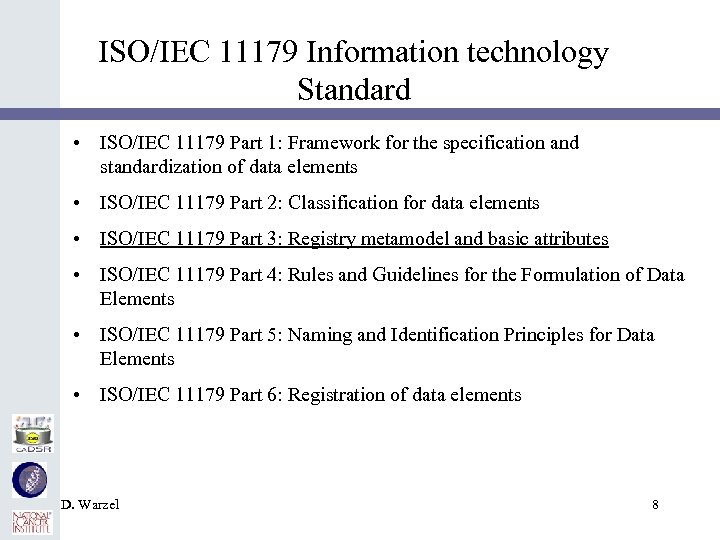 ISO/IEC 11179 Information technology Standard • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 1: Framework for the specification and standardization of data elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 2: Classification for data elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 3: Registry metamodel and basic attributes • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 4: Rules and Guidelines for the Formulation of Data Elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 5: Naming and Identification Principles for Data Elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 6: Registration of data elements D. Warzel 8
ISO/IEC 11179 Information technology Standard • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 1: Framework for the specification and standardization of data elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 2: Classification for data elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 3: Registry metamodel and basic attributes • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 4: Rules and Guidelines for the Formulation of Data Elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 5: Naming and Identification Principles for Data Elements • ISO/IEC 11179 Part 6: Registration of data elements D. Warzel 8
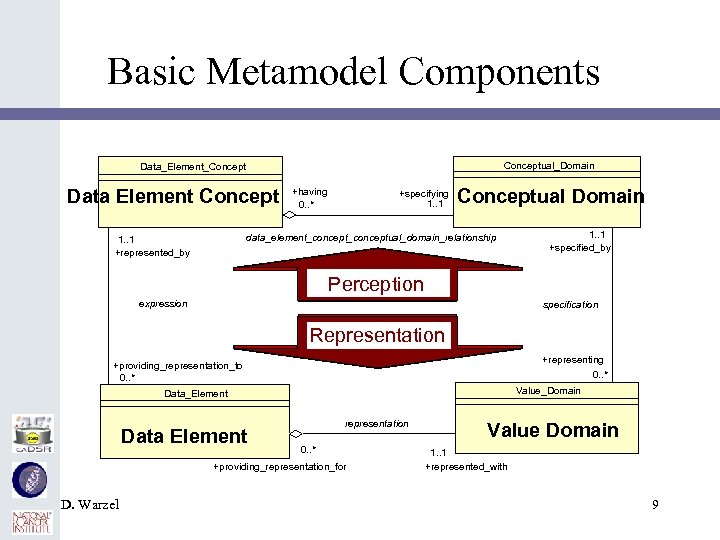 Basic Metamodel Components Conceptual_Domain Data_Element_Concept Data Element Concept +having 0. . * +specifying 1. . 1 Conceptual Domain data_element_conceptual_domain_relationship 1. . 1 +represented_by 1. . 1 +specified_by Perception expression specification Representation +representing 0. . * +providing_representation_to 0. . * Value_Domain Data_Element Data Element representation 0. . * +providing_representation_for D. Warzel Value Domain 1. . 1 +represented_with 9
Basic Metamodel Components Conceptual_Domain Data_Element_Concept Data Element Concept +having 0. . * +specifying 1. . 1 Conceptual Domain data_element_conceptual_domain_relationship 1. . 1 +represented_by 1. . 1 +specified_by Perception expression specification Representation +representing 0. . * +providing_representation_to 0. . * Value_Domain Data_Element Data Element representation 0. . * +providing_representation_for D. Warzel Value Domain 1. . 1 +represented_with 9
 Why ISO/IEC 11179? • “What is this datum? ” – Provides concrete guidance on the creation and maintenance of discrete data element attributes and metadata (semantics) enabling the formulation of data elements in a consistent, standard manner – • “Metadata Repository/Registry” – Framework for Data element standardization and registration allow the creation of a shared data environment in much less time and with much less effort than it takes for conventional data management methodologies. • Adoption of 1179 Allowed us to “Get on with it” D. Warzel 10
Why ISO/IEC 11179? • “What is this datum? ” – Provides concrete guidance on the creation and maintenance of discrete data element attributes and metadata (semantics) enabling the formulation of data elements in a consistent, standard manner – • “Metadata Repository/Registry” – Framework for Data element standardization and registration allow the creation of a shared data environment in much less time and with much less effort than it takes for conventional data management methodologies. • Adoption of 1179 Allowed us to “Get on with it” D. Warzel 10
 ISO/IEC 11179 Administered Items Derivation_Rule D. Warzel 11
ISO/IEC 11179 Administered Items Derivation_Rule D. Warzel 11
 ISO/IEC Administered Item Administration Record and Common Attributes • • • Unique Identifier Administrative Status Registration Status Creation Date Administrative Note(s) Effective Date Change Date(s) Change Description(s) Origin Until Date D. Warzel • • Created By Modified By Name(s) Definition(s) Stewardship Information Submitter Information Reference Document(s) Classifications 12
ISO/IEC Administered Item Administration Record and Common Attributes • • • Unique Identifier Administrative Status Registration Status Creation Date Administrative Note(s) Effective Date Change Date(s) Change Description(s) Origin Until Date D. Warzel • • Created By Modified By Name(s) Definition(s) Stewardship Information Submitter Information Reference Document(s) Classifications 12
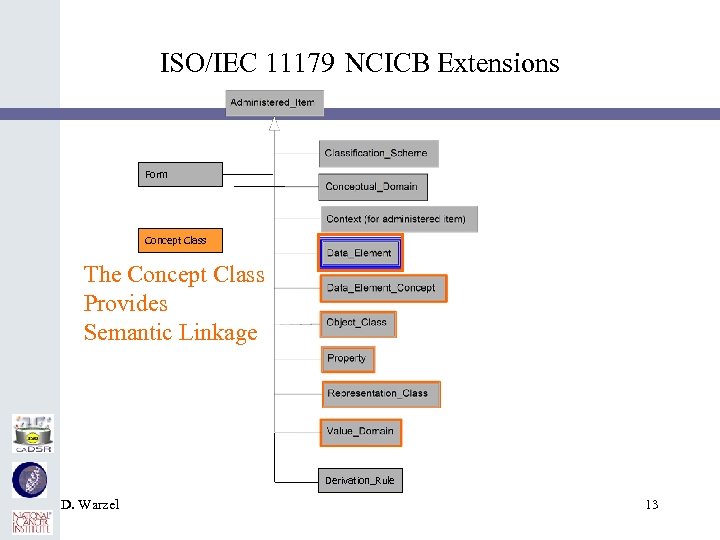 ISO/IEC 11179 NCICB Extensions Form Concept Class The Concept Class Provides Semantic Linkage Derivation_Rule D. Warzel 13
ISO/IEC 11179 NCICB Extensions Form Concept Class The Concept Class Provides Semantic Linkage Derivation_Rule D. Warzel 13
 NCICB Concept Class Common Attributes • Concept Class • Administered Item attributes + • Concept Unique Identifier • Pointer to an externally defined concept • Concept Definition Source • Names the source terminology/ontology/vocabulary • Concept Relationship • Semantic Order of the concepts • NOTE: ISO describes a ‘Concept Relationship’ as a semantic link among two or more concepts. There is a subtlety in our implementation. In ca. DSR use the concept relationships as more of a derivation rule, naming the order of the concepts - not semantic relationships in an ontologic or object model sense of ‘relationship’. • Object Class, Property, Representation term, Qualifier terms, Value Domains D. Warzel 14
NCICB Concept Class Common Attributes • Concept Class • Administered Item attributes + • Concept Unique Identifier • Pointer to an externally defined concept • Concept Definition Source • Names the source terminology/ontology/vocabulary • Concept Relationship • Semantic Order of the concepts • NOTE: ISO describes a ‘Concept Relationship’ as a semantic link among two or more concepts. There is a subtlety in our implementation. In ca. DSR use the concept relationships as more of a derivation rule, naming the order of the concepts - not semantic relationships in an ontologic or object model sense of ‘relationship’. • Object Class, Property, Representation term, Qualifier terms, Value Domains D. Warzel 14
 Why vocabularies/ontology important? • Goal: “Semantically unambiguous, interoperability” • Data Element curators are not necessarily vocabulary experts • NCI had a terminology and vocabulary services group: EVS • Semantic integration is achieved by tying Standard vocabulary identifier codes to the ca. DSR metadata • The ISO 11179 provides the framework – we were looking for something that could be computed without a human having to read and interpret definitions • By abstracting the curation of concepts in ca. DSR and instead relying on external vocabularies D. Warzel 15
Why vocabularies/ontology important? • Goal: “Semantically unambiguous, interoperability” • Data Element curators are not necessarily vocabulary experts • NCI had a terminology and vocabulary services group: EVS • Semantic integration is achieved by tying Standard vocabulary identifier codes to the ca. DSR metadata • The ISO 11179 provides the framework – we were looking for something that could be computed without a human having to read and interpret definitions • By abstracting the curation of concepts in ca. DSR and instead relying on external vocabularies D. Warzel 15
 EVS and ca. DSR Distinctions • ca. DSR is a metadata repository – maintains metadata to permit a user to locate the correct data element defining the characteristics of a piece of datum, an instance of a specific concept, in sufficient detail to be collected and stored on a computer • EVS is a terminology server – provides services for synonymy, mapping between vocabularies, hierarchical structures, Subconcepts, Superconcepts, Roles, Semantic type, etc. D. Warzel 16
EVS and ca. DSR Distinctions • ca. DSR is a metadata repository – maintains metadata to permit a user to locate the correct data element defining the characteristics of a piece of datum, an instance of a specific concept, in sufficient detail to be collected and stored on a computer • EVS is a terminology server – provides services for synonymy, mapping between vocabularies, hierarchical structures, Subconcepts, Superconcepts, Roles, Semantic type, etc. D. Warzel 16
 Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 17
Presentation Outline • ca. CORE Overview • ISO/IEC 11179 Overview • ca. DSR Implementation and tooling D. Warzel 17
 ca. DSR Overview • NCI Data Element Metadata repository and registry • Based on the ISO/IEC 11179 • Designed to integrate ca. CORE infrastructure • Supports the development and deployment of Data Elements that are used as metadata descriptors, primarily for NCI-sponsored research, with an ever widening girth of end users • Available as an open-source download D. Warzel 18
ca. DSR Overview • NCI Data Element Metadata repository and registry • Based on the ISO/IEC 11179 • Designed to integrate ca. CORE infrastructure • Supports the development and deployment of Data Elements that are used as metadata descriptors, primarily for NCI-sponsored research, with an ever widening girth of end users • Available as an open-source download D. Warzel 18
 ca. DSR Tools • Goals of ca. DSR Tools development: – Simplify development and creation of ISO/IEC 11179 compliant metadata by Data Element Curators and UML Modelers – Simplify consumption of Data Elements by end users and application developers – Enhance reuse of Data Elements for all – Enable semantic consistency across research domains – Support metadata life-cycle and governance processes D. Warzel 19
ca. DSR Tools • Goals of ca. DSR Tools development: – Simplify development and creation of ISO/IEC 11179 compliant metadata by Data Element Curators and UML Modelers – Simplify consumption of Data Elements by end users and application developers – Enhance reuse of Data Elements for all – Enable semantic consistency across research domains – Support metadata life-cycle and governance processes D. Warzel 19
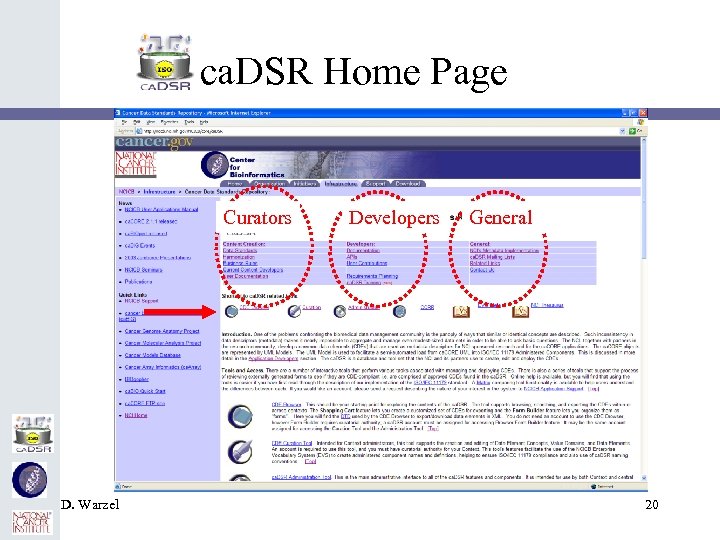 ca. DSR Home Page Curators D. Warzel Developers General 20
ca. DSR Home Page Curators D. Warzel Developers General 20
 Introduction to ca. DSR Tools – CDE Browser to Search for and Download – Form Builder to Create user specified collections of CDEs – CDE Curation Tool to Create Data Elements – Admin Tool to Curate and Administer ca. DSR - “Power Users” – Batch Load to import Administered Items • Excel Loader (MS Excel) • UML Loader (XMI) • Case Report Form Loader (MS Excel) – Sentinel Tool (3. 0) • Generates end user ‘Alerts’ triggered by metadata changes Access, Develop, Manage, Consume D. Warzel 21
Introduction to ca. DSR Tools – CDE Browser to Search for and Download – Form Builder to Create user specified collections of CDEs – CDE Curation Tool to Create Data Elements – Admin Tool to Curate and Administer ca. DSR - “Power Users” – Batch Load to import Administered Items • Excel Loader (MS Excel) • UML Loader (XMI) • Case Report Form Loader (MS Excel) – Sentinel Tool (3. 0) • Generates end user ‘Alerts’ triggered by metadata changes Access, Develop, Manage, Consume D. Warzel 21
 CDE Browser “CONTEXT Browsing” • View, Search, Download – Shopping cart feature • Form. Builder to Build / Download Forms and Data Elements • “Context Browsing” Tree – By Classification Schemes – By Forms • CDE Basic Search Criteria Basic Search D. Warzel – Google-like search – Sortable search results by clicking on column headings 22
CDE Browser “CONTEXT Browsing” • View, Search, Download – Shopping cart feature • Form. Builder to Build / Download Forms and Data Elements • “Context Browsing” Tree – By Classification Schemes – By Forms • CDE Basic Search Criteria Basic Search D. Warzel – Google-like search – Sortable search results by clicking on column headings 22
 CDE Browser • Advanced Search Criteria – Leverages ISO attributes • Find all with “ 18254 -3” permissible value • Find all with “Gene*” • Find all with “Released” workflow status • Find all with “Standard” Registration status • Etc. Advanced Search D. Warzel 23
CDE Browser • Advanced Search Criteria – Leverages ISO attributes • Find all with “ 18254 -3” permissible value • Find all with “Gene*” • Find all with “Released” workflow status • Find all with “Standard” Registration status • Etc. Advanced Search D. Warzel 23
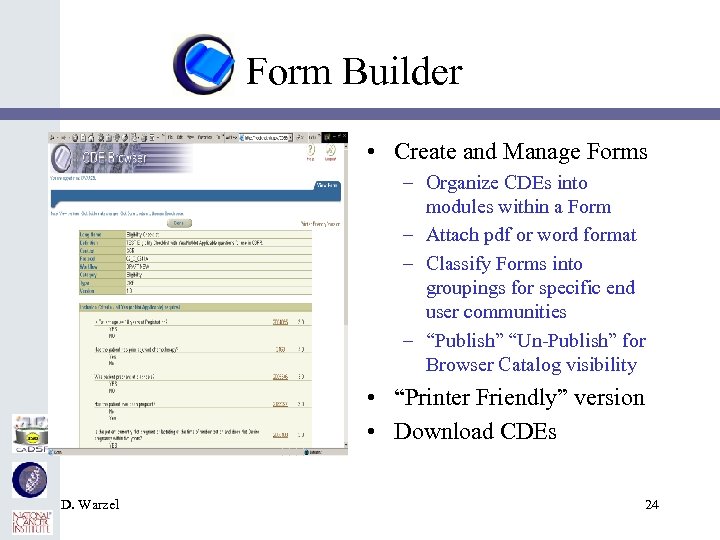 Form Builder • Create and Manage Forms – Organize CDEs into modules within a Form – Attach pdf or word format – Classify Forms into groupings for specific end user communities – “Publish” “Un-Publish” for Browser Catalog visibility • “Printer Friendly” version • Download CDEs D. Warzel 24
Form Builder • Create and Manage Forms – Organize CDEs into modules within a Form – Attach pdf or word format – Classify Forms into groupings for specific end user communities – “Publish” “Un-Publish” for Browser Catalog visibility • “Printer Friendly” version • Download CDEs D. Warzel 24
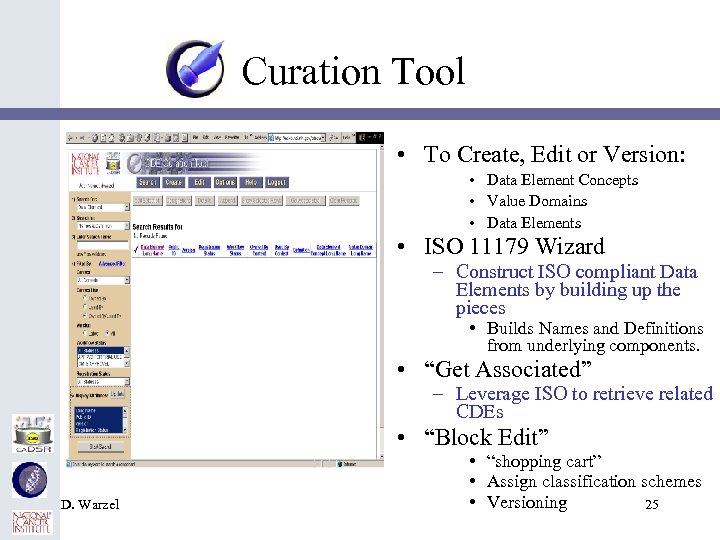 Curation Tool • To Create, Edit or Version: • Data Element Concepts • Value Domains • Data Elements • ISO 11179 Wizard – Construct ISO compliant Data Elements by building up the pieces • Builds Names and Definitions from underlying components. • “Get Associated” – Leverage ISO to retrieve related CDEs • “Block Edit” D. Warzel • “shopping cart” • Assign classification schemes • Versioning 25
Curation Tool • To Create, Edit or Version: • Data Element Concepts • Value Domains • Data Elements • ISO 11179 Wizard – Construct ISO compliant Data Elements by building up the pieces • Builds Names and Definitions from underlying components. • “Get Associated” – Leverage ISO to retrieve related CDEs • “Block Edit” D. Warzel • “shopping cart” • Assign classification schemes • Versioning 25
 Administration Tool • System Administration • User Accounts and Security • Lists of Values (LOVs) used in content creation • Create “Framework”: • Conceptual Domains • Classification Schemes (basis for organizing CDEs in Browser) • Protocols D. Warzel 26
Administration Tool • System Administration • User Accounts and Security • Lists of Values (LOVs) used in content creation • Create “Framework”: • Conceptual Domains • Classification Schemes (basis for organizing CDEs in Browser) • Protocols D. Warzel 26
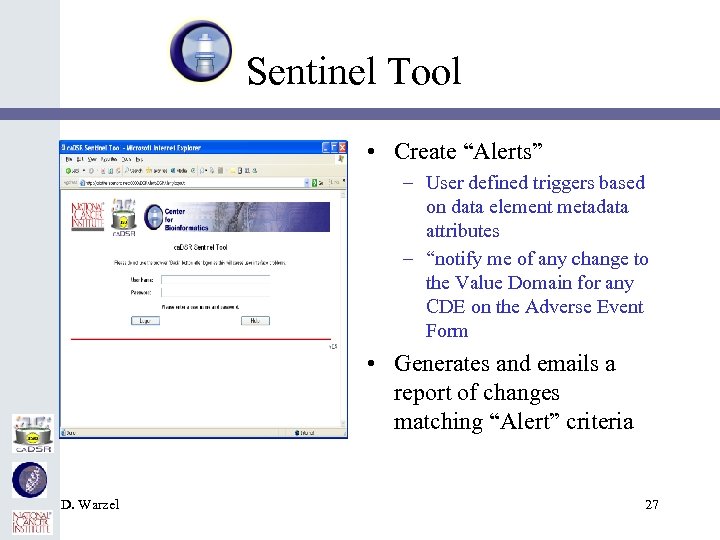 Sentinel Tool • Create “Alerts” – User defined triggers based on data element metadata attributes – “notify me of any change to the Value Domain for any CDE on the Adverse Event Form • Generates and emails a report of changes matching “Alert” criteria D. Warzel 27
Sentinel Tool • Create “Alerts” – User defined triggers based on data element metadata attributes – “notify me of any change to the Value Domain for any CDE on the Adverse Event Form • Generates and emails a report of changes matching “Alert” criteria D. Warzel 27
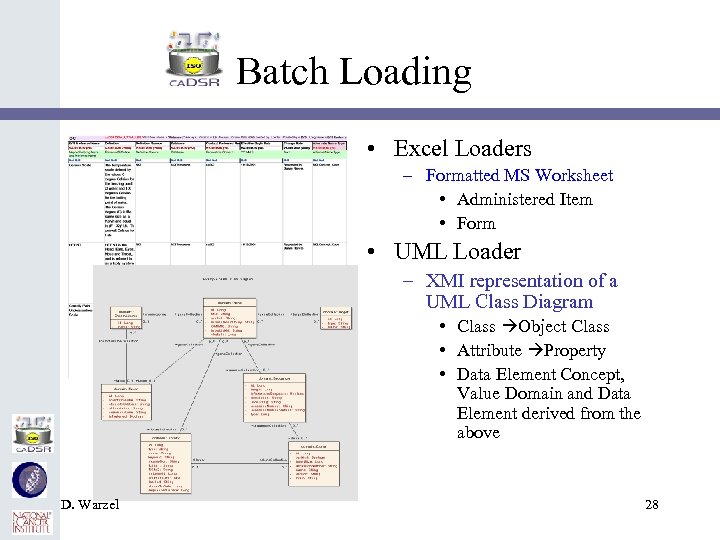 Batch Loading • Excel Loaders – Formatted MS Worksheet • Administered Item • Form • UML Loader – XMI representation of a UML Class Diagram • Class Object Class • Attribute Property • Data Element Concept, Value Domain and Data Element derived from the above D. Warzel 28
Batch Loading • Excel Loaders – Formatted MS Worksheet • Administered Item • Form • UML Loader – XMI representation of a UML Class Diagram • Class Object Class • Attribute Property • Data Element Concept, Value Domain and Data Element derived from the above D. Warzel 28
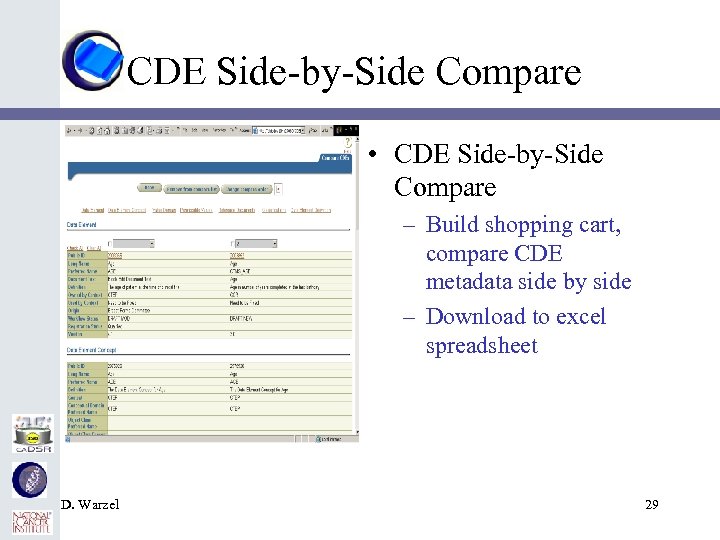 CDE Side-by-Side Compare • CDE Side-by-Side Compare – Build shopping cart, compare CDE metadata side by side – Download to excel spreadsheet D. Warzel 29
CDE Side-by-Side Compare • CDE Side-by-Side Compare – Build shopping cart, compare CDE metadata side by side – Download to excel spreadsheet D. Warzel 29
 Current User Base • • • Cancer Biomedical Informatics Grid (ca. BIG) – 820/466 * Center for Cancer Research (CCR) – 821/573 Clinical Data Interchange Standard Consortium (CDISC) - 3/0 Center for Cancer Imaging (CIP) - 238/151 Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP) – 8027/2410 Division of Cancer Prevention (DCP) – 427/321 National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) – 0/0 Early Detection Research Network (EDRN) – 121/1 Divisions of Population Sciences and Cancer Control (PS & CC) 85/9 Specialized Programs of Research Excellence (SPOREs) – 719/197 Cancer Ontologic Research Environment (ca. CORE) – 1028/810 * Total CDEs/”Released” CDEs D. Warzel 30
Current User Base • • • Cancer Biomedical Informatics Grid (ca. BIG) – 820/466 * Center for Cancer Research (CCR) – 821/573 Clinical Data Interchange Standard Consortium (CDISC) - 3/0 Center for Cancer Imaging (CIP) - 238/151 Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP) – 8027/2410 Division of Cancer Prevention (DCP) – 427/321 National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) – 0/0 Early Detection Research Network (EDRN) – 121/1 Divisions of Population Sciences and Cancer Control (PS & CC) 85/9 Specialized Programs of Research Excellence (SPOREs) – 719/197 Cancer Ontologic Research Environment (ca. CORE) – 1028/810 * Total CDEs/”Released” CDEs D. Warzel 30
 Exploring • National Institute of Neurological and Disorders and Syndromes (NINDS) • National Icelandic Center for Oncology • Cancergrid – UK D. Warzel 31
Exploring • National Institute of Neurological and Disorders and Syndromes (NINDS) • National Icelandic Center for Oncology • Cancergrid – UK D. Warzel 31
 Operating Environments • Database Repository – Oracle 98 i • Administration Tool – Oracle PL/SQL, Oracle 9 i Application Server • CDE Browser – Java, Oracle 9 i Application Server • CDE Curation Tool – Jakarta Tomcat D. Warzel 32
Operating Environments • Database Repository – Oracle 98 i • Administration Tool – Oracle PL/SQL, Oracle 9 i Application Server • CDE Browser – Java, Oracle 9 i Application Server • CDE Curation Tool – Jakarta Tomcat D. Warzel 32
 Contact Information • ca. DSR Home Page – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/core/ca. DSR • ca. DSR Training Home Page – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Tr aining • ca. DSR Training List. Serve – ca. DSR_Training-L@list. nih. gov D. Warzel 33
Contact Information • ca. DSR Home Page – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/core/ca. DSR • ca. DSR Training Home Page – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Tr aining • ca. DSR Training List. Serve – ca. DSR_Training-L@list. nih. gov D. Warzel 33
 Documentation/Recommended Reading Materials • ca. DSR Homepage: – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/core/ca. DSR • ca. CORE User Application Manual: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/NCICBapplications/NCICBApp. Manual. pdf • ca. CORE Technical Guide: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/ca. CORE 2. 0_Tech_Guide. pdf – ca. DSR APIs • ca. DSR API Guide: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/ca. DSR/ca. CORE 2. 0_ca. DSR_API. pdf • ca. DSR Business Rules – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Business. Rules • ca. DSR Content Meetings – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Content • ca. DSR_Users List serv subscribe: – http: //list. nih. gov – Send Request for ca. DSR Account to: ncicb@pop. nci. nih. gov D. Warzel 34
Documentation/Recommended Reading Materials • ca. DSR Homepage: – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/core/ca. DSR • ca. CORE User Application Manual: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/NCICBapplications/NCICBApp. Manual. pdf • ca. CORE Technical Guide: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/ca. CORE 2. 0_Tech_Guide. pdf – ca. DSR APIs • ca. DSR API Guide: – ftp: //ftp 1. nci. nih. gov/pub/cacore/ca. DSR/ca. CORE 2. 0_ca. DSR_API. pdf • ca. DSR Business Rules – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Business. Rules • ca. DSR Content Meetings – http: //ncicb. nci. nih. gov/NCICB/core/ca. DSR/Content • ca. DSR_Users List serv subscribe: – http: //list. nih. gov – Send Request for ca. DSR Account to: ncicb@pop. nci. nih. gov D. Warzel 34
 ca. DSR Tools Team • NCICB – Peter Covitz – Denise Warzel • Scen. Pro – – – Bill Mc. Curry Tom Phillips Robert Harding Jennifer Brush Larry Hebel Smita Hastak D. Warzel • Oracle – – – – Edmond Mulaire Ram Chilukuri Prerna Aggarwal Dan Ladino Christophe Ludet Shaji Kakkodi Jane Jiang • SAIC – Kathleen Gundry – Tommie Curtis – Brenda Maeske 35
ca. DSR Tools Team • NCICB – Peter Covitz – Denise Warzel • Scen. Pro – – – Bill Mc. Curry Tom Phillips Robert Harding Jennifer Brush Larry Hebel Smita Hastak D. Warzel • Oracle – – – – Edmond Mulaire Ram Chilukuri Prerna Aggarwal Dan Ladino Christophe Ludet Shaji Kakkodi Jane Jiang • SAIC – Kathleen Gundry – Tommie Curtis – Brenda Maeske 35


