28c1b26fd26fef72a42fb601c556c135.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 INTRODUCTION TO SPATIAL ANALYSIS
INTRODUCTION TO SPATIAL ANALYSIS
 Four fundamental functions of GIS fall under the manipulation and analysis component (Martin, 1991): 1. 2. 3. 4. Reclassification operations Overlay operations Distance and connectivity measurements Neighbourhood characterisation Will be discussed in the next chapter.
Four fundamental functions of GIS fall under the manipulation and analysis component (Martin, 1991): 1. 2. 3. 4. Reclassification operations Overlay operations Distance and connectivity measurements Neighbourhood characterisation Will be discussed in the next chapter.
 1. Reclassification operations • these transform the attribute information associated with a single map coverage for example a map of population densities may be classified into classes such as 'sparsely populated' or 'overcrowded' without reference to other data. • This function can also be used to calculate densities of sales observations
1. Reclassification operations • these transform the attribute information associated with a single map coverage for example a map of population densities may be classified into classes such as 'sparsely populated' or 'overcrowded' without reference to other data. • This function can also be used to calculate densities of sales observations
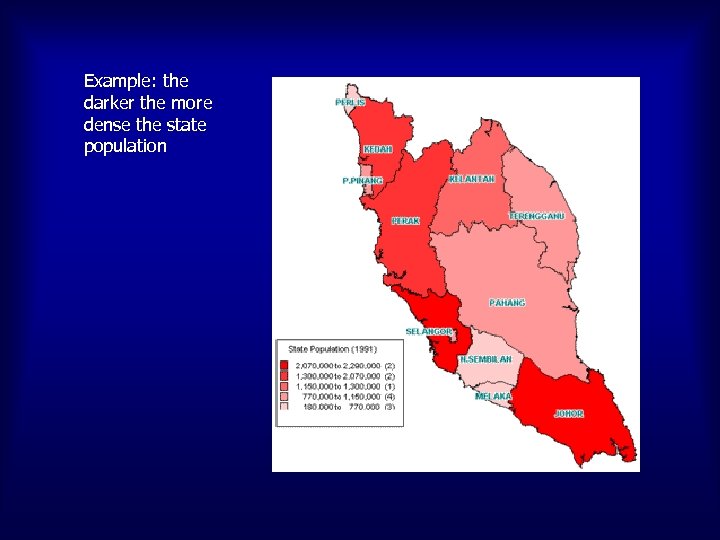 Example: the darker the more dense the state population MAP
Example: the darker the more dense the state population MAP
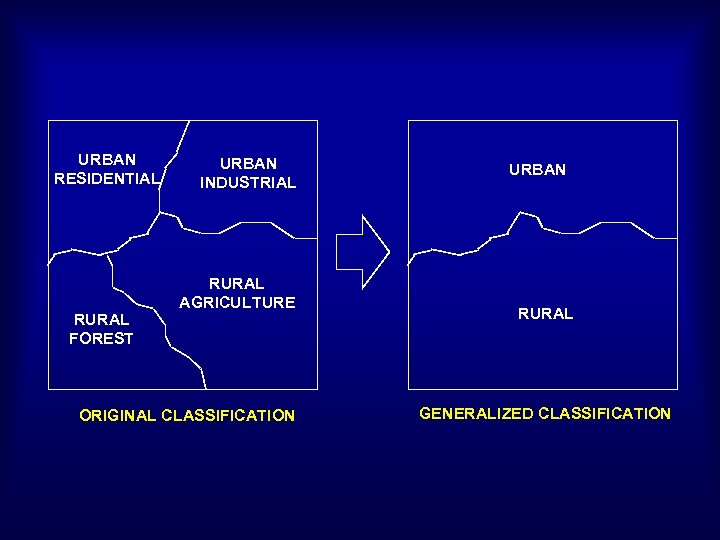
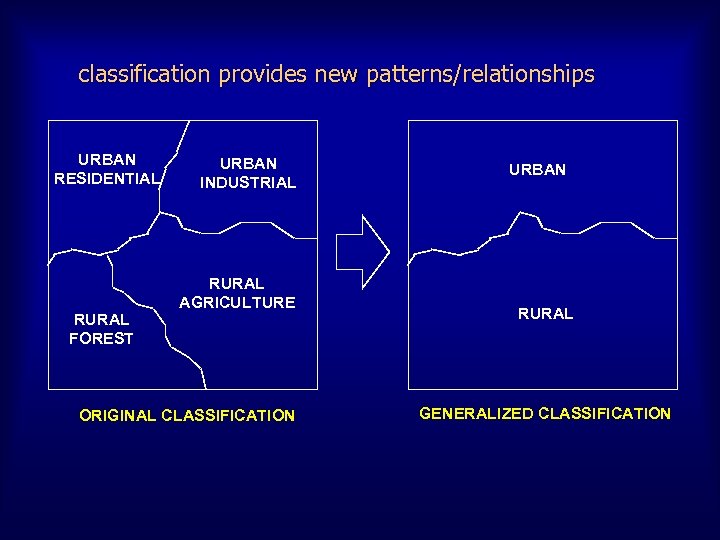 classification provides new patterns/relationships URBAN RESIDENTIAL RURAL FOREST URBAN INDUSTRIAL RURAL AGRICULTURE ORIGINAL CLASSIFICATION URBAN RURAL GENERALIZED CLASSIFICATION
classification provides new patterns/relationships URBAN RESIDENTIAL RURAL FOREST URBAN INDUSTRIAL RURAL AGRICULTURE ORIGINAL CLASSIFICATION URBAN RURAL GENERALIZED CLASSIFICATION
 Classification (cont. ) Classification: • Land parcels for housing are classed into • single storey terrace, • double storey terrace and • bungalow. Generalisation: • single storey terrace, double storey terrace and bungalow are generalised under housing lots
Classification (cont. ) Classification: • Land parcels for housing are classed into • single storey terrace, • double storey terrace and • bungalow. Generalisation: • single storey terrace, double storey terrace and bungalow are generalised under housing lots
 2. Overlay operations • involve the combination of two or more maps according to boolean conditions and may result in the delineation of new boundaries of housing market
2. Overlay operations • involve the combination of two or more maps according to boolean conditions and may result in the delineation of new boundaries of housing market
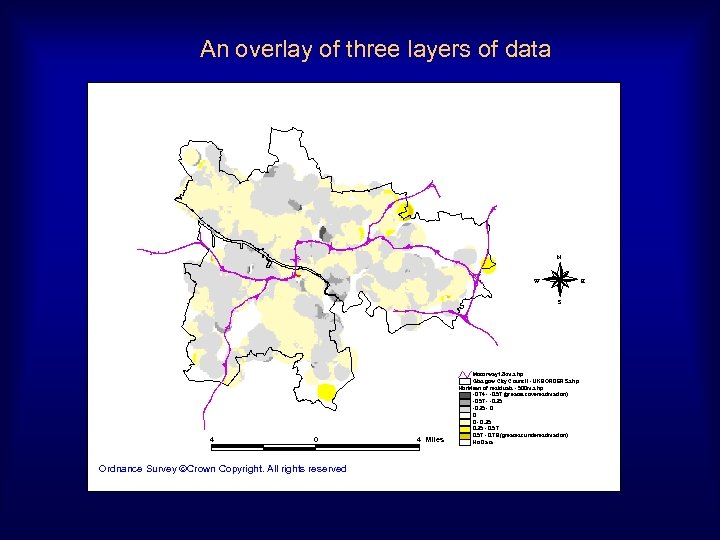 An overlay of three layers of data N W E S 4 0 Ordnance Survey Crown Copyright. All rights reserved 4 Miles Motorway 12 km. shp Glasgow City Cou ncil - UKBORDERS. shp Nb r. Mean of residuals - 500 m. shp -0. 74 - -0. 57 (great est overest imation) -0. 57 - -0. 35 - 0 0 0 - 0. 35 - 0. 57 - 0. 78 (greatest u nd erest imation) No Data
An overlay of three layers of data N W E S 4 0 Ordnance Survey Crown Copyright. All rights reserved 4 Miles Motorway 12 km. shp Glasgow City Cou ncil - UKBORDERS. shp Nb r. Mean of residuals - 500 m. shp -0. 74 - -0. 57 (great est overest imation) -0. 57 - -0. 35 - 0 0 0 - 0. 35 - 0. 57 - 0. 78 (greatest u nd erest imation) No Data
 3. Distance and connectivity measurements • include both simple measures of inter-point distance and more complex operations such as the construction of zones of increasing transport cost away from specified locations. • Distance measurement can be used to calculate straight line and network distance. • Includes perimeter and area measurements…
3. Distance and connectivity measurements • include both simple measures of inter-point distance and more complex operations such as the construction of zones of increasing transport cost away from specified locations. • Distance measurement can be used to calculate straight line and network distance. • Includes perimeter and area measurements…
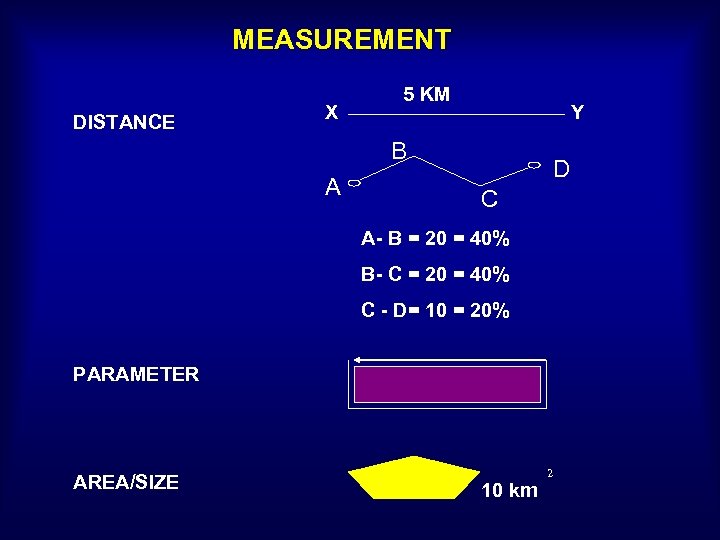 MEASUREMENT DISTANCE X 5 KM Y B A D C A- B = 20 = 40% B- C = 20 = 40% C - D= 10 = 20% PARAMETER AREA/SIZE 10 km 2
MEASUREMENT DISTANCE X 5 KM Y B A D C A- B = 20 = 40% B- C = 20 = 40% C - D= 10 = 20% PARAMETER AREA/SIZE 10 km 2
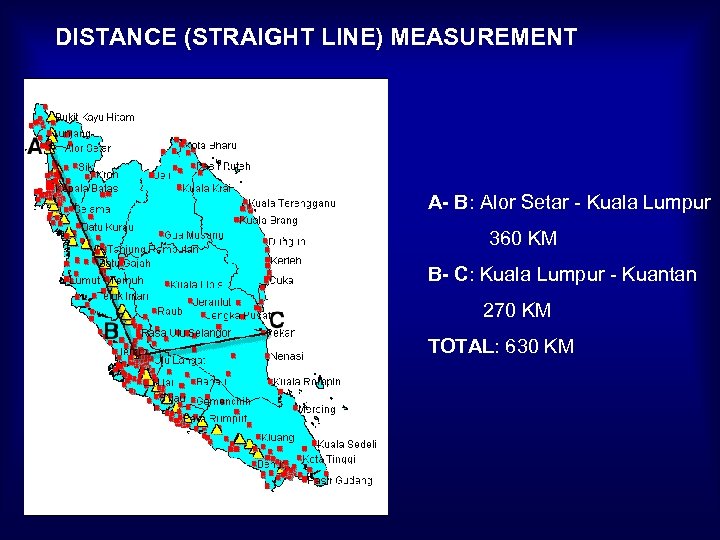 DISTANCE (STRAIGHT LINE) MEASUREMENT A- B: Alor Setar - Kuala Lumpur 360 KM B- C: Kuala Lumpur - Kuantan 270 KM TOTAL: 630 KM
DISTANCE (STRAIGHT LINE) MEASUREMENT A- B: Alor Setar - Kuala Lumpur 360 KM B- C: Kuala Lumpur - Kuantan 270 KM TOTAL: 630 KM
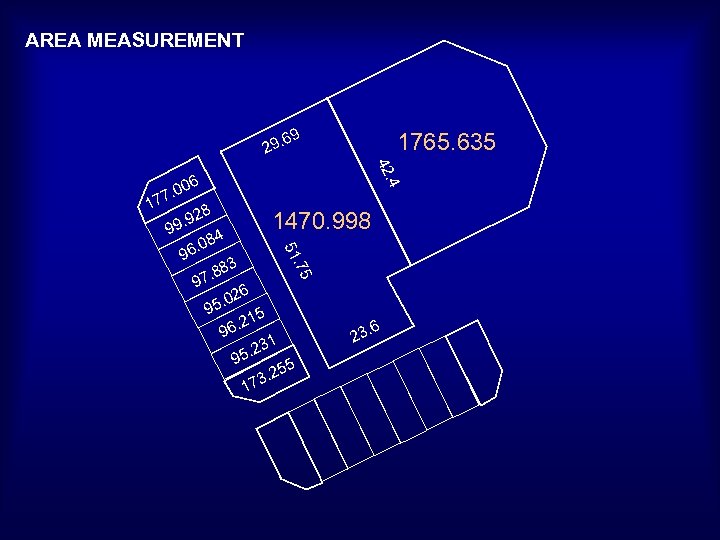 AREA MEASUREMENT 69 1765. 635 29. 42 1 . 4 06 . 0 77 28 . 9 99 . 0 9 . 75 3 8 7. 8 51 96 1470. 998 84 26 5. 0 9 5. 21 96 1. 23 95 5. 25 3 17 . 6 23
AREA MEASUREMENT 69 1765. 635 29. 42 1 . 4 06 . 0 77 28 . 9 99 . 0 9 . 75 3 8 7. 8 51 96 1470. 998 84 26 5. 0 9 5. 21 96 1. 23 95 5. 25 3 17 . 6 23
 4. Neighbourhood characterisation • involves ascribing values to location according to characteristics of the surrounding region. • Such operations may involve both summary and mean measures of a variable. • This can be used to examine positive and negative spatial autocorrelation house price hedonic models.
4. Neighbourhood characterisation • involves ascribing values to location according to characteristics of the surrounding region. • Such operations may involve both summary and mean measures of a variable. • This can be used to examine positive and negative spatial autocorrelation house price hedonic models.
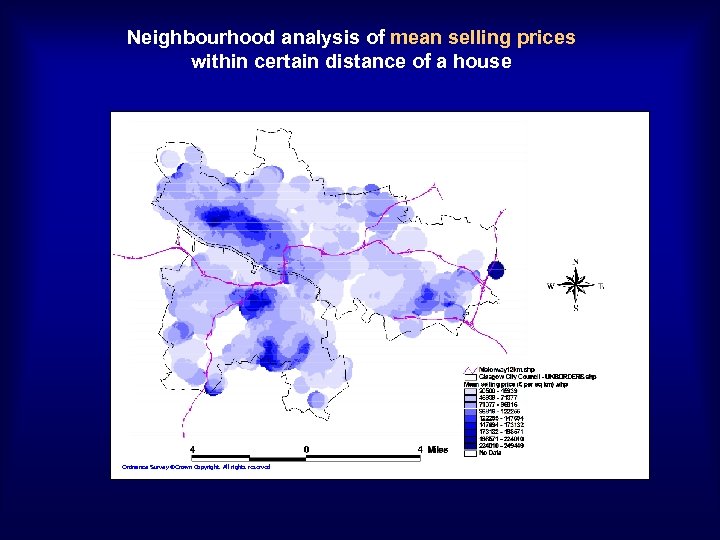 Neighbourhood analysis of mean selling prices within certain distance of a house Ordnance Survey Crown Copyright. All rights reserved
Neighbourhood analysis of mean selling prices within certain distance of a house Ordnance Survey Crown Copyright. All rights reserved
 Other View of GIS Functions • Anselin (1998) proposes that GIS functions can be classified as follows – Selection – Manipulation – Exploration – Confirmation
Other View of GIS Functions • Anselin (1998) proposes that GIS functions can be classified as follows – Selection – Manipulation – Exploration – Confirmation
 GIS functions • Selection: involves boolean queries and spatial sampling. This seems similar to the overlay operations function. • Manipulation: may be based on attribute data, map data, or integration of both, simultaneously. This means analysing data in an integrated manner where various data as available in the database can be combined in an analysis. • Exploration: for investigation of spatial structure and involves description and visualisation. This is relevant to spatial autocorrelation analysis of hedonic models using geostatistical method • Confirmation: for modelling spatial association and/or autocorrelation. This is also more relevant to spatial autocorrelation analysis using geostatistical method.
GIS functions • Selection: involves boolean queries and spatial sampling. This seems similar to the overlay operations function. • Manipulation: may be based on attribute data, map data, or integration of both, simultaneously. This means analysing data in an integrated manner where various data as available in the database can be combined in an analysis. • Exploration: for investigation of spatial structure and involves description and visualisation. This is relevant to spatial autocorrelation analysis of hedonic models using geostatistical method • Confirmation: for modelling spatial association and/or autocorrelation. This is also more relevant to spatial autocorrelation analysis using geostatistical method.
 DATA RECALL • can be invoke on spatial and attribute components • involves selective search • no new objects created • example: lots owned by foreigners • example: lots along the substation buffer
DATA RECALL • can be invoke on spatial and attribute components • involves selective search • no new objects created • example: lots owned by foreigners • example: lots along the substation buffer
 LOTS OWNED BY FOREIGNERS
LOTS OWNED BY FOREIGNERS
 CLASSIFICATION AND GENERALISATION • classification - identify a set of characteristics to group together objects. • in a vector system, classification involves addition of objects characteristics. • in a raster system, classification involves converting or coding cell values. • classification examples: Land parcels for housing are classed into single storey terras, double storey terras and bungalow. • classification provides new patterns/relationships • generalisation: single storey terras, double storey terras and bungalow are generalise under housing lots
CLASSIFICATION AND GENERALISATION • classification - identify a set of characteristics to group together objects. • in a vector system, classification involves addition of objects characteristics. • in a raster system, classification involves converting or coding cell values. • classification examples: Land parcels for housing are classed into single storey terras, double storey terras and bungalow. • classification provides new patterns/relationships • generalisation: single storey terras, double storey terras and bungalow are generalise under housing lots
 Housing Age Legend Before 1900 1901 -1930 1931 -1950 1951 to 1999 Map showing classification of buildings according to age
Housing Age Legend Before 1900 1901 -1930 1931 -1950 1951 to 1999 Map showing classification of buildings according to age
 URBAN RESIDENTIAL RURAL FOREST URBAN INDUSTRIAL RURAL AGRICULTURE ORIGINAL CLASSIFICATION URBAN RURAL GENERALIZED CLASSIFICATION
URBAN RESIDENTIAL RURAL FOREST URBAN INDUSTRIAL RURAL AGRICULTURE ORIGINAL CLASSIFICATION URBAN RURAL GENERALIZED CLASSIFICATION
 . . . • vector data – converting attribute values for polygon, line and point • raster data – converting attribute values of group cell
. . . • vector data – converting attribute values for polygon, line and point • raster data – converting attribute values of group cell
 MEASUREMENT • measurement functions includes distance, parameter and area • example: land parcels larger than 5 hectares • example: shortest distance from KLCC to Pudu bas station
MEASUREMENT • measurement functions includes distance, parameter and area • example: land parcels larger than 5 hectares • example: shortest distance from KLCC to Pudu bas station
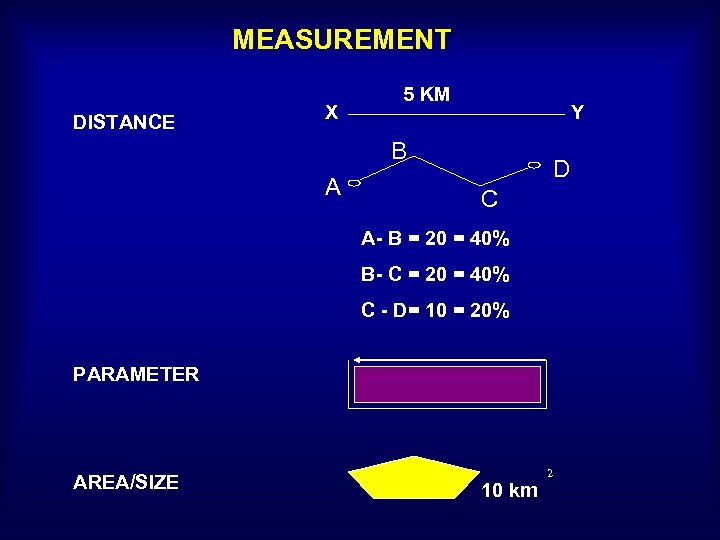 MEASUREMENT DISTANCE X 5 KM Y B A D C A- B = 20 = 40% B- C = 20 = 40% C - D= 10 = 20% PARAMETER AREA/SIZE 10 km 2
MEASUREMENT DISTANCE X 5 KM Y B A D C A- B = 20 = 40% B- C = 20 = 40% C - D= 10 = 20% PARAMETER AREA/SIZE 10 km 2
 DISTANCE MEASUREMENT A- B: Alor Setar - Kuala Lumpur 360 KM B- C: Kuala Lumpur - Kuantan 270 KM TOTAL: 630 KM
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT A- B: Alor Setar - Kuala Lumpur 360 KM B- C: Kuala Lumpur - Kuantan 270 KM TOTAL: 630 KM
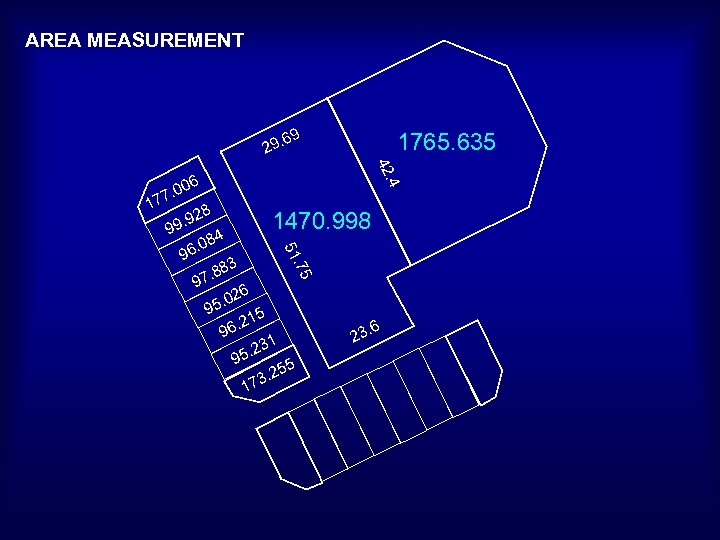 AREA MEASUREMENT 69 1765. 635 29. 42 1 . 4 06 . 0 77 28 . 9 99 . 0 9 . 75 3 8 7. 8 51 96 1470. 998 84 26 5. 0 9 5. 21 96 1. 23 95 5. 25 3 17 . 6 23
AREA MEASUREMENT 69 1765. 635 29. 42 1 . 4 06 . 0 77 28 . 9 99 . 0 9 . 75 3 8 7. 8 51 96 1470. 998 84 26 5. 0 9 5. 21 96 1. 23 95 5. 25 3 17 . 6 23
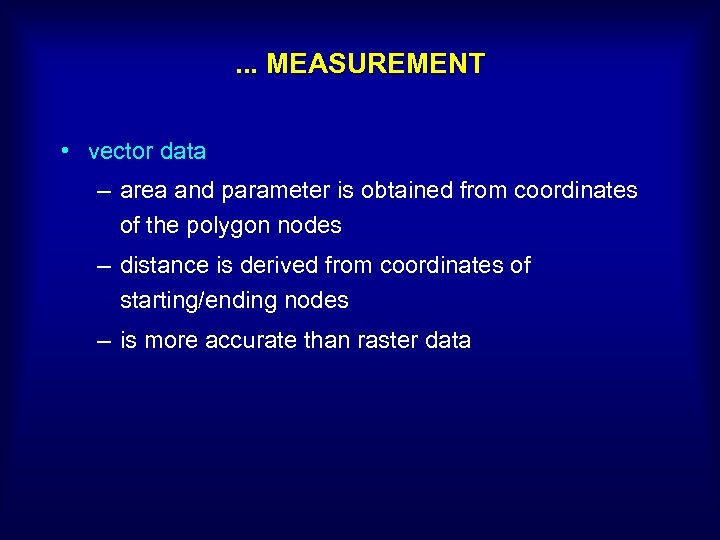 . . . MEASUREMENT • vector data – area and parameter is obtained from coordinates of the polygon nodes – distance is derived from coordinates of starting/ending nodes – is more accurate than raster data
. . . MEASUREMENT • vector data – area and parameter is obtained from coordinates of the polygon nodes – distance is derived from coordinates of starting/ending nodes – is more accurate than raster data
 SEARCHING • determine values against target object according to a neighbourhood characteristic • three parameters need to be identified – targets – neighbourhood around the targets – applied neighbourhood function for resultant values • example: total of households within 1 km of proposed shopping mall – target-shopping mall – neighborhood-in the radius of 1 km – function-total residential units
SEARCHING • determine values against target object according to a neighbourhood characteristic • three parameters need to be identified – targets – neighbourhood around the targets – applied neighbourhood function for resultant values • example: total of households within 1 km of proposed shopping mall – target-shopping mall – neighborhood-in the radius of 1 km – function-total residential units
 . . . SPATIAL SEARCH • operated as additional points in polygon, line in polygon and polygon in polygon • vector data – point, line or polygon analysed with neighbourhood polygon using coordinate nodes – involves complex calculation with overlapping and out-of-boundary neighbourhood • raster data – perform as overlay operations
. . . SPATIAL SEARCH • operated as additional points in polygon, line in polygon and polygon in polygon • vector data – point, line or polygon analysed with neighbourhood polygon using coordinate nodes – involves complex calculation with overlapping and out-of-boundary neighbourhood • raster data – perform as overlay operations
 NEIGHBOURHOOD • represents ‘distance’ between map features • ‘distance’ unit can be in measurement units or other units like travelling time, noise level, visibility distance etc. • requires 4 parameters – target location - schools, highways, etc. – ‘distance’ units - meter, d. B, ppm, etc. – function for calculation on distance, perimeter, travel time – location to be analysed
NEIGHBOURHOOD • represents ‘distance’ between map features • ‘distance’ unit can be in measurement units or other units like travelling time, noise level, visibility distance etc. • requires 4 parameters – target location - schools, highways, etc. – ‘distance’ units - meter, d. B, ppm, etc. – function for calculation on distance, perimeter, travel time – location to be analysed
 . . . NEIGHBOURHOOD • used to generate buffer zones • example: a 2 km zone along a proposed transmission line alignment; zones exceeds 50 d. B around the airport • neighbourhood is most often complex and involves data from various layers. For example, more than 50 d. B from noisy roads AND more than 1 km from factories AND 15 minutes walking time AND. . .
. . . NEIGHBOURHOOD • used to generate buffer zones • example: a 2 km zone along a proposed transmission line alignment; zones exceeds 50 d. B around the airport • neighbourhood is most often complex and involves data from various layers. For example, more than 50 d. B from noisy roads AND more than 1 km from factories AND 15 minutes walking time AND. . .
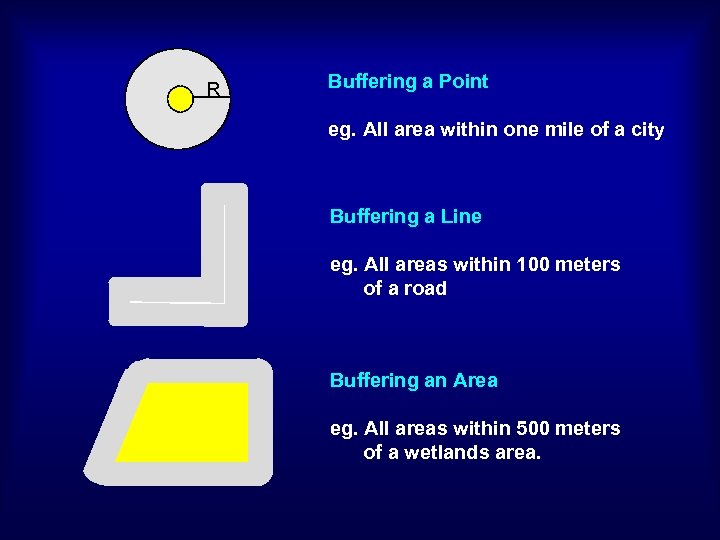 R Buffering a Point eg. All area within one mile of a city Buffering a Line eg. All areas within 100 meters of a road Buffering an Area eg. All areas within 500 meters of a wetlands area.
R Buffering a Point eg. All area within one mile of a city Buffering a Line eg. All areas within 100 meters of a road Buffering an Area eg. All areas within 500 meters of a wetlands area.
 OVERLAY • Involves two or more data layers • Produces new layers • Two types of overlay operation – arithmetic overlay – logical overlay • Arithmetic overlay involves mathematics operation such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
OVERLAY • Involves two or more data layers • Produces new layers • Two types of overlay operation – arithmetic overlay – logical overlay • Arithmetic overlay involves mathematics operation such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
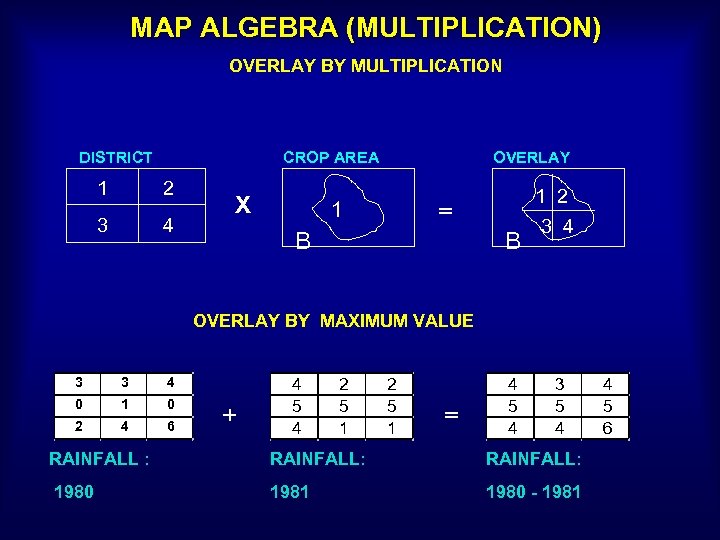 MAP ALGEBRA (MULTIPLICATION) OVERLAY BY MULTIPLICATION DISTRICT CROP AREA 1 2 3 4 X OVERLAY 1 = B B 1 2 3 4 OVERLAY BY MAXIMUM VALUE 3 3 4 0 1 0 2 4 6 + 4 5 4 2 5 1 = 4 5 4 3 5 4 RAINFALL : RAINFALL: 1980 1981 1980 - 1981 4 5 6
MAP ALGEBRA (MULTIPLICATION) OVERLAY BY MULTIPLICATION DISTRICT CROP AREA 1 2 3 4 X OVERLAY 1 = B B 1 2 3 4 OVERLAY BY MAXIMUM VALUE 3 3 4 0 1 0 2 4 6 + 4 5 4 2 5 1 = 4 5 4 3 5 4 RAINFALL : RAINFALL: 1980 1981 1980 - 1981 4 5 6
 . . . OVERLAY • vector data are sometimes more efficient than raster data if data are not dense. – vector data - operation based on the selected data only – raster data - operation on all cells - even null values
. . . OVERLAY • vector data are sometimes more efficient than raster data if data are not dense. – vector data - operation based on the selected data only – raster data - operation on all cells - even null values
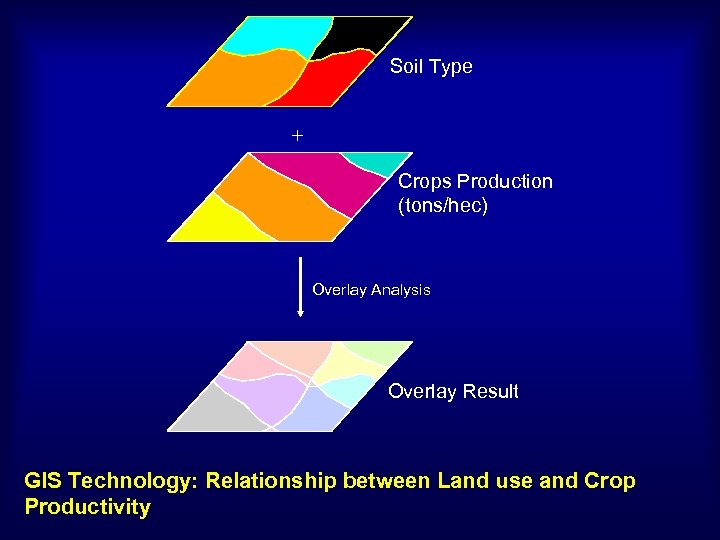 Soil Type + Crops Production (tons/hec) Overlay Analysis Overlay Result GIS Technology: Relationship between Land use and Crop Productivity
Soil Type + Crops Production (tons/hec) Overlay Analysis Overlay Result GIS Technology: Relationship between Land use and Crop Productivity
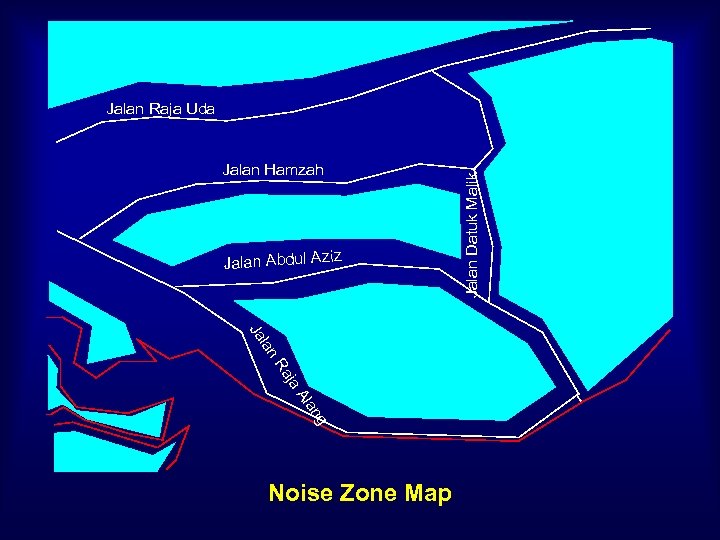 Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz lan Ja ja Ra Al g an Noise Zone Map Jalan Datuk Malik Jalan Raja Uda
Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz lan Ja ja Ra Al g an Noise Zone Map Jalan Datuk Malik Jalan Raja Uda
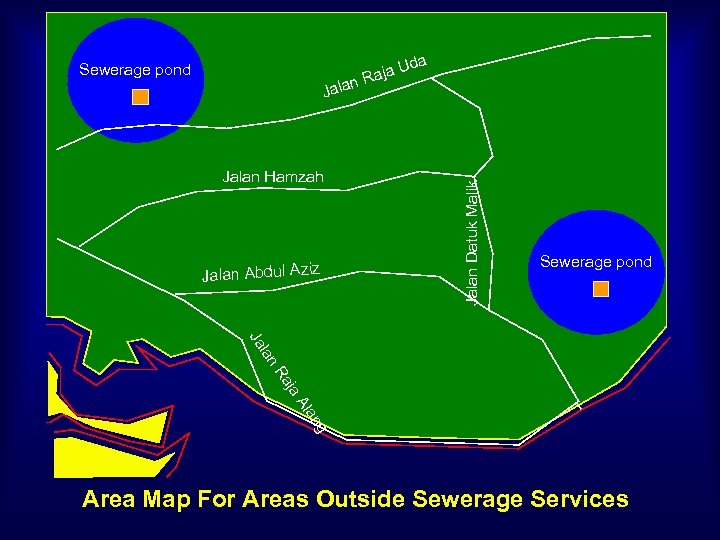 da Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz Jalan Datuk Malik U Raja n Jala Sewerage pond lan Ja ja Ra Al g an Area Map For Areas Outside Sewerage Services
da Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz Jalan Datuk Malik U Raja n Jala Sewerage pond lan Ja ja Ra Al g an Area Map For Areas Outside Sewerage Services
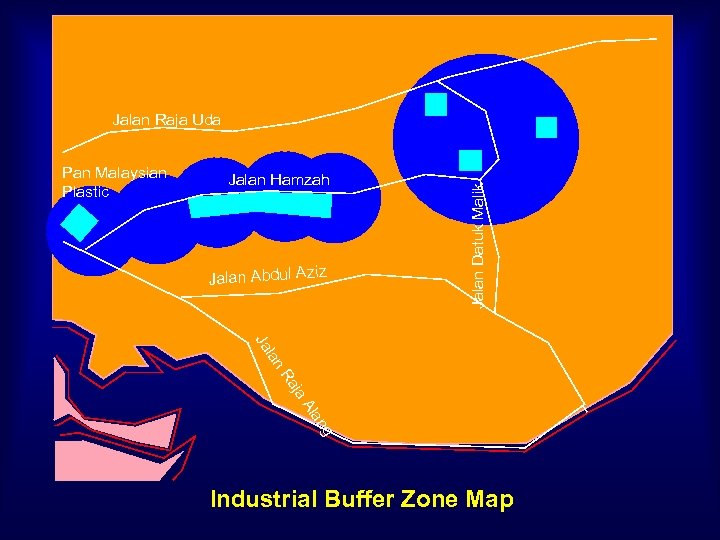 Pan Malaysian Plastic Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz Jalan Datuk Malik Jalan Raja Uda lan Ja ja Ra g an Al Industrial Buffer Zone Map
Pan Malaysian Plastic Jalan Hamzah Jalan Abdul Aziz Jalan Datuk Malik Jalan Raja Uda lan Ja ja Ra g an Al Industrial Buffer Zone Map


