77007f1886f2be44bd413f26d5cfcc01.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Introduction to Semicon SCM Thomas Chen/Allan Chen June 16, 2001 THE MISSING LINK FOR E-BUSINESS
Introduction to Semicon SCM Thomas Chen/Allan Chen June 16, 2001 THE MISSING LINK FOR E-BUSINESS
 Agenda • Supply Chain Management (SCM) in Semicon • Semicon SCM Components • Why Supply Chain Management • Implementation • Trend and Strategy
Agenda • Supply Chain Management (SCM) in Semicon • Semicon SCM Components • Why Supply Chain Management • Implementation • Trend and Strategy
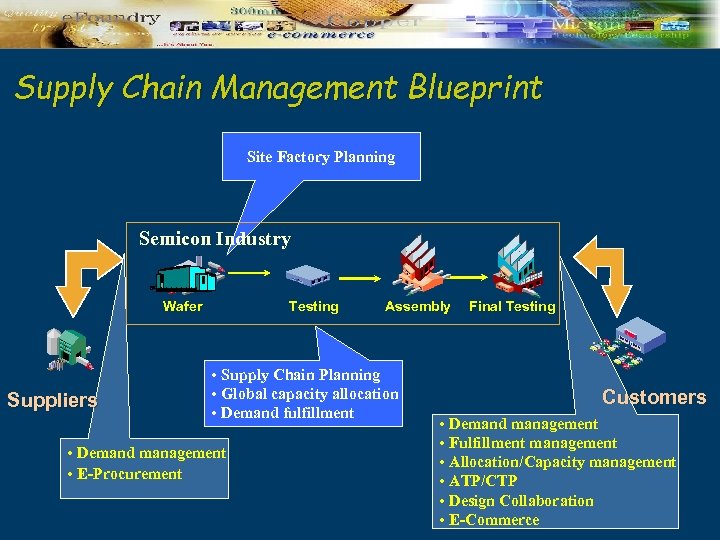 Supply Chain Management Blueprint Site Factory Planning Semicon Industry Wafer Suppliers Testing Assembly • Supply Chain Planning • Global capacity allocation • Demand fulfillment • Demand management • E-Procurement Final Testing Customers • Demand management • Fulfillment management • Allocation/Capacity management • ATP/CTP • Design Collaboration • E-Commerce
Supply Chain Management Blueprint Site Factory Planning Semicon Industry Wafer Suppliers Testing Assembly • Supply Chain Planning • Global capacity allocation • Demand fulfillment • Demand management • E-Procurement Final Testing Customers • Demand management • Fulfillment management • Allocation/Capacity management • ATP/CTP • Design Collaboration • E-Commerce
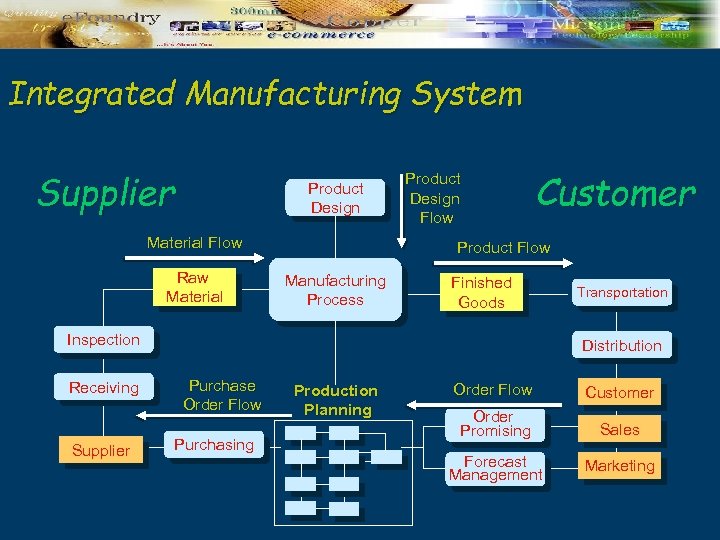 Integrated Manufacturing System Supplier Product Design Material Flow Raw Material Product Design Flow Customer Product Flow Manufacturing Process Finished Goods Inspection Receiving Supplier Transportation Distribution Purchase Order Flow Purchasing Production Planning Order Flow Customer Order Promising Sales Forecast Management Marketing
Integrated Manufacturing System Supplier Product Design Material Flow Raw Material Product Design Flow Customer Product Flow Manufacturing Process Finished Goods Inspection Receiving Supplier Transportation Distribution Purchase Order Flow Purchasing Production Planning Order Flow Customer Order Promising Sales Forecast Management Marketing
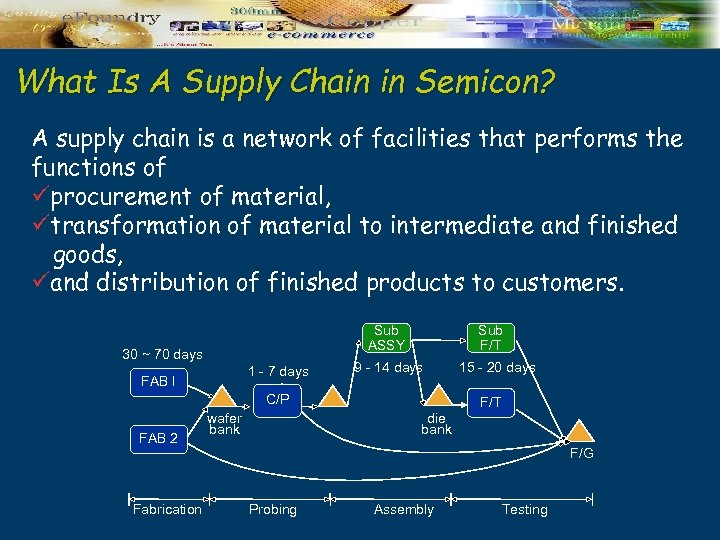 What Is A Supply Chain in Semicon? A supply chain is a network of facilities that performs the functions of üprocurement of material, ütransformation of material to intermediate and finished goods, üand distribution of finished products to customers. Sub ASSY 30 ~ 70 days 1 - 7 days FAB I Sub F/T 9 - 14 days C/P FAB 2 Fabrication wafer bank 15 - 20 days F/T die bank F/G Probing Assembly Testing
What Is A Supply Chain in Semicon? A supply chain is a network of facilities that performs the functions of üprocurement of material, ütransformation of material to intermediate and finished goods, üand distribution of finished products to customers. Sub ASSY 30 ~ 70 days 1 - 7 days FAB I Sub F/T 9 - 14 days C/P FAB 2 Fabrication wafer bank 15 - 20 days F/T die bank F/G Probing Assembly Testing
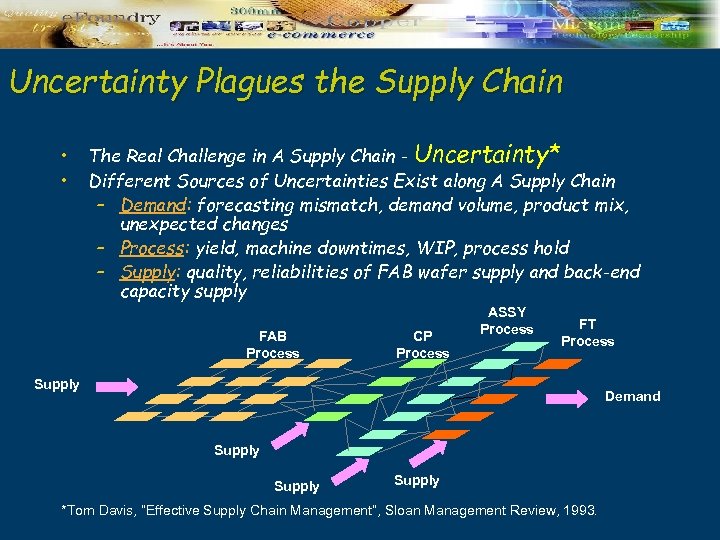 Uncertainty Plagues the Supply Chain • • The Real Challenge in A Supply Chain - Uncertainty* Different Sources of Uncertainties Exist along A Supply Chain – Demand: forecasting mismatch, demand volume, product mix, unexpected changes – Process: yield, machine downtimes, WIP, process hold – Supply: quality, reliabilities of FAB wafer supply and back-end capacity supply FAB Process CP Process ASSY Process FT Process Supply Demand Supply *Tom Davis, “Effective Supply Chain Management”, Sloan Management Review, 1993.
Uncertainty Plagues the Supply Chain • • The Real Challenge in A Supply Chain - Uncertainty* Different Sources of Uncertainties Exist along A Supply Chain – Demand: forecasting mismatch, demand volume, product mix, unexpected changes – Process: yield, machine downtimes, WIP, process hold – Supply: quality, reliabilities of FAB wafer supply and back-end capacity supply FAB Process CP Process ASSY Process FT Process Supply Demand Supply *Tom Davis, “Effective Supply Chain Management”, Sloan Management Review, 1993.
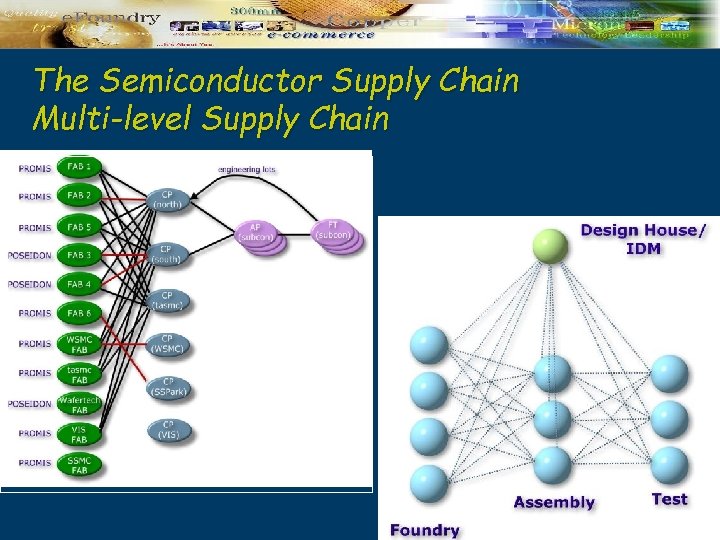 The Semiconductor Supply Chain Multi-level Supply Chain
The Semiconductor Supply Chain Multi-level Supply Chain
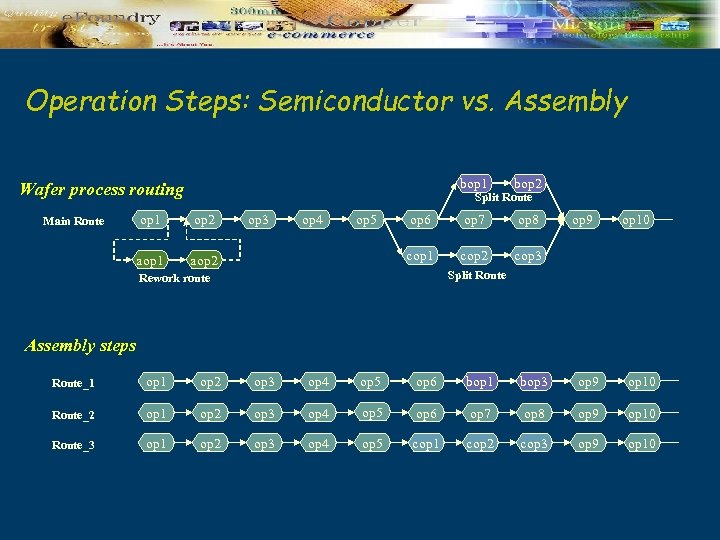 Operation Steps: Semiconductor vs. Assembly bop 1 bop 2 op 6 op 7 op 8 cop 1 cop 2 cop 3 Wafer process routing Split Route op 1 op 2 aop 1 Main Route op 3 op 4 op 5 aop 2 op 9 op 10 Split Route Rework route Assembly steps Route_1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 op 6 bop 1 bop 3 op 9 op 10 Route_2 op 1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 op 6 op 7 op 8 op 9 op 10 Route_3 op 1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 cop 1 cop 2 cop 3 op 9 op 10
Operation Steps: Semiconductor vs. Assembly bop 1 bop 2 op 6 op 7 op 8 cop 1 cop 2 cop 3 Wafer process routing Split Route op 1 op 2 aop 1 Main Route op 3 op 4 op 5 aop 2 op 9 op 10 Split Route Rework route Assembly steps Route_1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 op 6 bop 1 bop 3 op 9 op 10 Route_2 op 1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 op 6 op 7 op 8 op 9 op 10 Route_3 op 1 op 2 op 3 op 4 op 5 cop 1 cop 2 cop 3 op 9 op 10
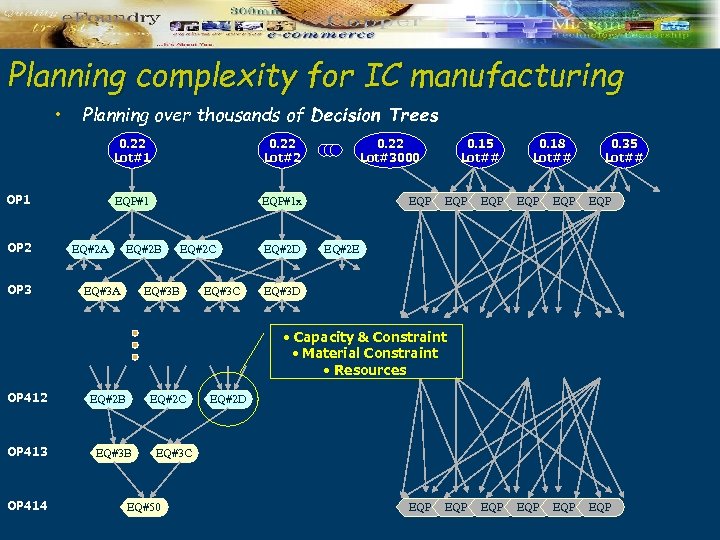 Planning complexity for IC manufacturing • Planning over thousands of Decision Trees 0. 22 Lot#1 EQP#1 OP 2 OP 3 0. 22 Lot#2 EQP#1 x EQ#2 A EQ#2 B EQ#3 A EQ#2 C EQ#3 B EQ#3 C EQ#2 D 0. 22 Lot#3000 EQP 0. 15 Lot## EQP 0. 18 Lot## 0. 35 Lot## EQP EQP EQ#2 E EQ#3 D • Capacity & Constraint • Material Constraint • Resources OP 412 OP 413 OP 414 EQ#2 B EQ#2 C EQ#3 B EQ#2 D EQ#3 C EQ#50 EQP
Planning complexity for IC manufacturing • Planning over thousands of Decision Trees 0. 22 Lot#1 EQP#1 OP 2 OP 3 0. 22 Lot#2 EQP#1 x EQ#2 A EQ#2 B EQ#3 A EQ#2 C EQ#3 B EQ#3 C EQ#2 D 0. 22 Lot#3000 EQP 0. 15 Lot## EQP 0. 18 Lot## 0. 35 Lot## EQP EQP EQ#2 E EQ#3 D • Capacity & Constraint • Material Constraint • Resources OP 412 OP 413 OP 414 EQ#2 B EQ#2 C EQ#3 B EQ#2 D EQ#3 C EQ#50 EQP
 Semiconductor SCM Components
Semiconductor SCM Components
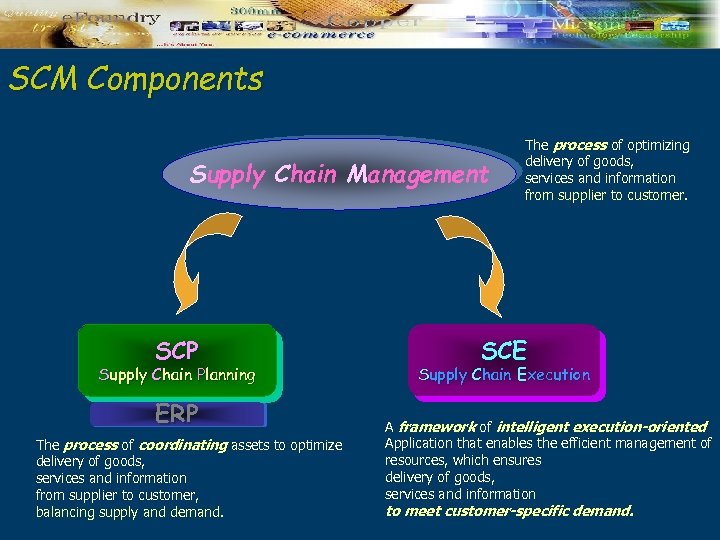 SCM Components Supply Chain Management SCP Supply Chain Planning ERP The process of coordinating assets to optimize delivery of goods, services and information from supplier to customer, balancing supply and demand. The process of optimizing delivery of goods, services and information from supplier to customer. SCE Supply Chain Execution A framework of intelligent execution-oriented Application that enables the efficient management of resources, which ensures delivery of goods, services and information to meet customer-specific demand.
SCM Components Supply Chain Management SCP Supply Chain Planning ERP The process of coordinating assets to optimize delivery of goods, services and information from supplier to customer, balancing supply and demand. The process of optimizing delivery of goods, services and information from supplier to customer. SCE Supply Chain Execution A framework of intelligent execution-oriented Application that enables the efficient management of resources, which ensures delivery of goods, services and information to meet customer-specific demand.
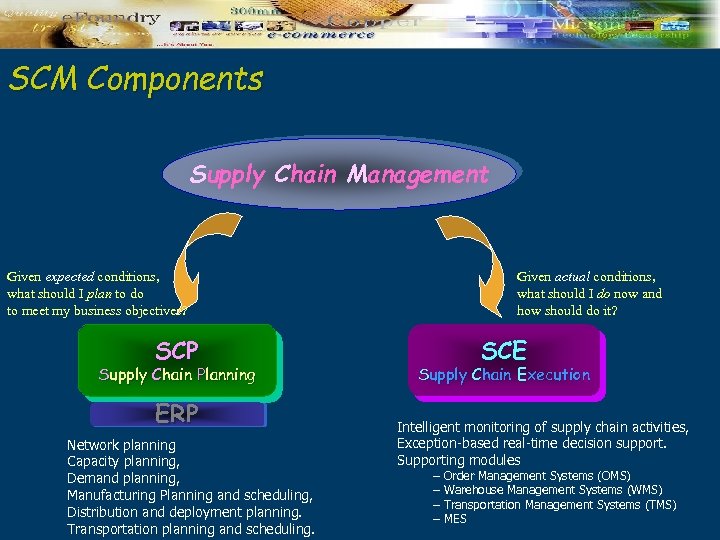 SCM Components Supply Chain Management Given expected conditions, what should I plan to do to meet my business objectives? SCP Supply Chain Planning ERP Network planning Capacity planning, Demand planning, Manufacturing Planning and scheduling, Distribution and deployment planning. Transportation planning and scheduling. Given actual conditions, what should I do now and how should do it? SCE Supply Chain Execution Intelligent monitoring of supply chain activities, Exception-based real-time decision support. Supporting modules – – Order Management Systems (OMS) Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) Transportation Management Systems (TMS) MES
SCM Components Supply Chain Management Given expected conditions, what should I plan to do to meet my business objectives? SCP Supply Chain Planning ERP Network planning Capacity planning, Demand planning, Manufacturing Planning and scheduling, Distribution and deployment planning. Transportation planning and scheduling. Given actual conditions, what should I do now and how should do it? SCE Supply Chain Execution Intelligent monitoring of supply chain activities, Exception-based real-time decision support. Supporting modules – – Order Management Systems (OMS) Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) Transportation Management Systems (TMS) MES
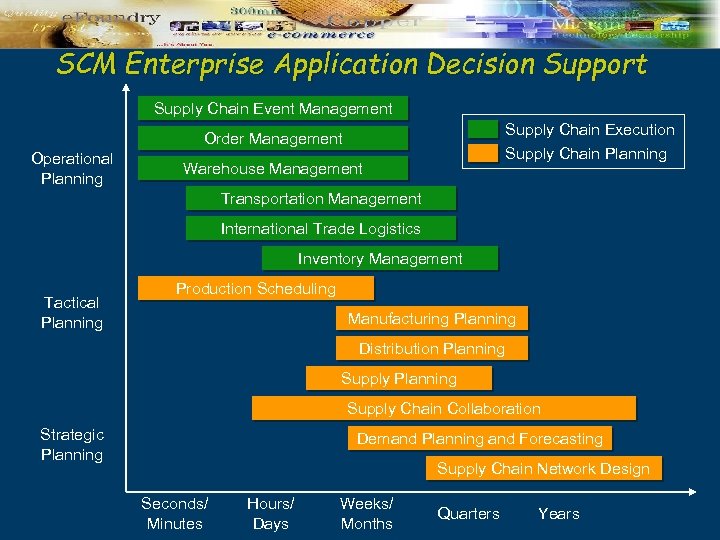 SCM Enterprise Application Decision Support Supply Chain Event Management Supply Chain Execution Order Management Operational Planning Supply Chain Planning Warehouse Management Transportation Management International Trade Logistics Inventory Management Tactical Planning Production Scheduling Manufacturing Planning Distribution Planning Supply Chain Collaboration Strategic Planning Demand Planning and Forecasting Supply Chain Network Design Seconds/ Minutes Hours/ Days Weeks/ Months Quarters Years
SCM Enterprise Application Decision Support Supply Chain Event Management Supply Chain Execution Order Management Operational Planning Supply Chain Planning Warehouse Management Transportation Management International Trade Logistics Inventory Management Tactical Planning Production Scheduling Manufacturing Planning Distribution Planning Supply Chain Collaboration Strategic Planning Demand Planning and Forecasting Supply Chain Network Design Seconds/ Minutes Hours/ Days Weeks/ Months Quarters Years
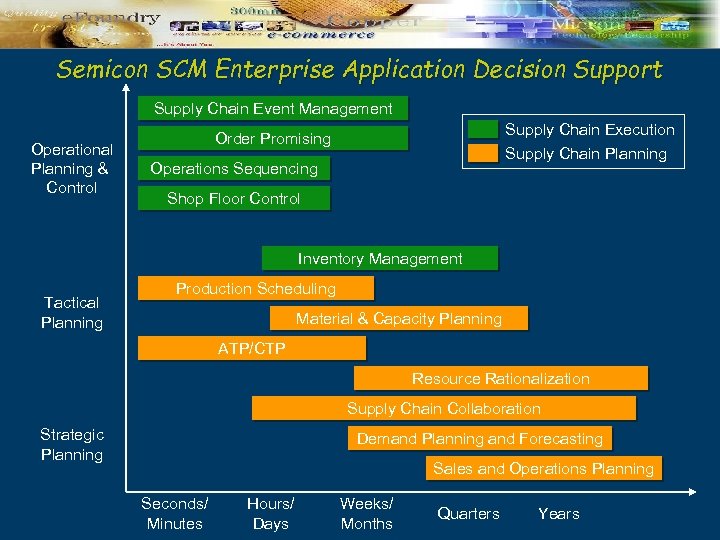 Semicon SCM Enterprise Application Decision Support Supply Chain Event Management Operational Planning & Control Supply Chain Execution Order Promising Supply Chain Planning Operations Sequencing Shop Floor Control Inventory Management Tactical Planning Production Scheduling Material & Capacity Planning ATP/CTP Resource Rationalization Supply Chain Collaboration Strategic Planning Demand Planning and Forecasting Sales and Operations Planning Seconds/ Minutes Hours/ Days Weeks/ Months Quarters Years
Semicon SCM Enterprise Application Decision Support Supply Chain Event Management Operational Planning & Control Supply Chain Execution Order Promising Supply Chain Planning Operations Sequencing Shop Floor Control Inventory Management Tactical Planning Production Scheduling Material & Capacity Planning ATP/CTP Resource Rationalization Supply Chain Collaboration Strategic Planning Demand Planning and Forecasting Sales and Operations Planning Seconds/ Minutes Hours/ Days Weeks/ Months Quarters Years
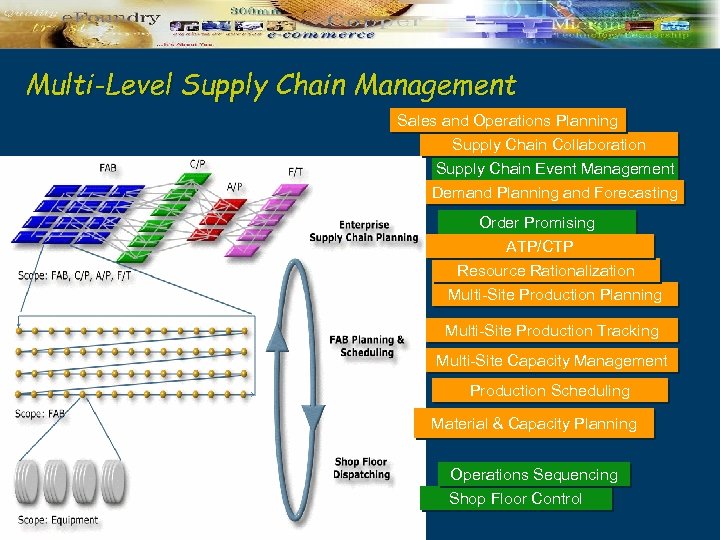 Multi-Level Supply Chain Management Sales and Operations Planning Supply Chain Collaboration Supply Chain Event Management Demand Planning and Forecasting Order Promising ATP/CTP Resource Rationalization Multi-Site Production Planning Multi-Site Production Tracking Multi-Site Capacity Management Production Scheduling Material & Capacity Planning Operations Sequencing Shop Floor Control
Multi-Level Supply Chain Management Sales and Operations Planning Supply Chain Collaboration Supply Chain Event Management Demand Planning and Forecasting Order Promising ATP/CTP Resource Rationalization Multi-Site Production Planning Multi-Site Production Tracking Multi-Site Capacity Management Production Scheduling Material & Capacity Planning Operations Sequencing Shop Floor Control
 Why Supply Chain Management?
Why Supply Chain Management?
 Fact Planning Issues Faced Needs • Weak integration between planning and execution • Enterprise visibility of planning process and multi-user access enable better process and convincing results • Lack of due date projection capability in foundry environment • Quickly generate ATP & CTP to customer • Limited visibility into capacity constraints • Concurrent planning & optimizations of all constraints. Problem windows and real-time simulation capabilities to react in a timely manner
Fact Planning Issues Faced Needs • Weak integration between planning and execution • Enterprise visibility of planning process and multi-user access enable better process and convincing results • Lack of due date projection capability in foundry environment • Quickly generate ATP & CTP to customer • Limited visibility into capacity constraints • Concurrent planning & optimizations of all constraints. Problem windows and real-time simulation capabilities to react in a timely manner
 Fact Planning Issues Faced Needs • Islands of data, multiple excel spreadsheets consuming vast amounts of planner time • Single entry of forecasting information, company-wide visibility • Manual Work with limited dimensional view (e. g. Total volume by Product) • Automatic tools with both planning and execution data inputs • Lack of rapid re-plan capability • Reduce planning cycle time allows daily planning and rapid re-planning • Lack of what-if analysis in variety product mix situation • Provide what-if analysis capability • Lack of detailed execution schedule • With proper modeling, provides detailed execution priority/schedule
Fact Planning Issues Faced Needs • Islands of data, multiple excel spreadsheets consuming vast amounts of planner time • Single entry of forecasting information, company-wide visibility • Manual Work with limited dimensional view (e. g. Total volume by Product) • Automatic tools with both planning and execution data inputs • Lack of rapid re-plan capability • Reduce planning cycle time allows daily planning and rapid re-planning • Lack of what-if analysis in variety product mix situation • Provide what-if analysis capability • Lack of detailed execution schedule • With proper modeling, provides detailed execution priority/schedule
 Future Business Process Changes • Reduce planning cycle from a weekly to daily • Integrate all fab areas as one team and quick response for capacity allocation. • Need a flexible system for start planners for dynamic capacity situations. • Solve problems from planning system instead of execution system. • Should integrate from customer to turnkey for Virtual Fab requirement.
Future Business Process Changes • Reduce planning cycle from a weekly to daily • Integrate all fab areas as one team and quick response for capacity allocation. • Need a flexible system for start planners for dynamic capacity situations. • Solve problems from planning system instead of execution system. • Should integrate from customer to turnkey for Virtual Fab requirement.
 Example: Business analysis and solution Customer order fulfillment performance • Scenario: Good individual site delivery performance but BAD overall delivery performance, due to lack of integrated manufacturing targets. • Issues – FABs’ MPS don’t meet CP/ATS’s delivery needs – Invisibility of FABs’ planning/execution changes to CP/ATS – Lack of Push/Pull mechanism for Fab lots under defined target • Current Status – MPS just cover Fabs only, CP/ATS MPS were generated based on current WIP – Replace projected out date with scheduled out date when lots were delayed – Managed manually • System Solution – – – Manage overall capacity for FABs, CPs, ATS, EBO, PC & IE Generate integrated target for Fab, CP, ATS and EBO by backward planning Update lot schedule out date for back-end stages by daily Raise demand/supply changes to drive back-end re-planning Coordinate FABs/CP/ATS/EBO planning modules for Push/Pull decision Re-plan for execution violation by weekly
Example: Business analysis and solution Customer order fulfillment performance • Scenario: Good individual site delivery performance but BAD overall delivery performance, due to lack of integrated manufacturing targets. • Issues – FABs’ MPS don’t meet CP/ATS’s delivery needs – Invisibility of FABs’ planning/execution changes to CP/ATS – Lack of Push/Pull mechanism for Fab lots under defined target • Current Status – MPS just cover Fabs only, CP/ATS MPS were generated based on current WIP – Replace projected out date with scheduled out date when lots were delayed – Managed manually • System Solution – – – Manage overall capacity for FABs, CPs, ATS, EBO, PC & IE Generate integrated target for Fab, CP, ATS and EBO by backward planning Update lot schedule out date for back-end stages by daily Raise demand/supply changes to drive back-end re-planning Coordinate FABs/CP/ATS/EBO planning modules for Push/Pull decision Re-plan for execution violation by weekly
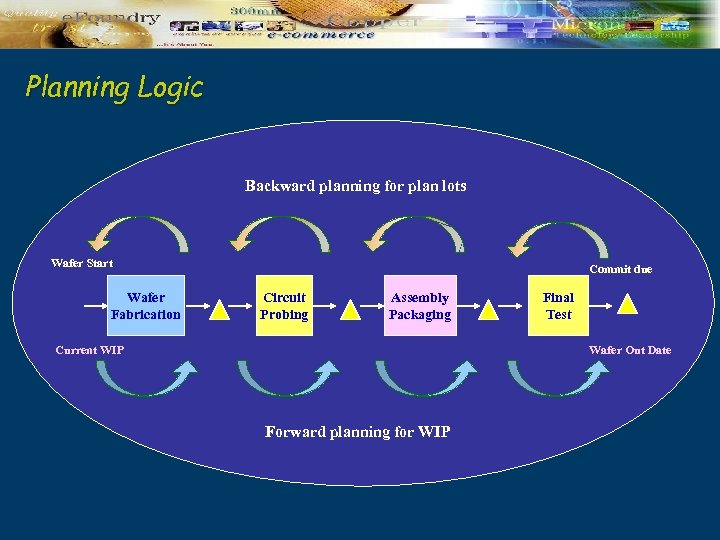 Planning Logic Backward planning for plan lots Wafer Start Wafer Fabrication Commit due Circuit Probing Assembly Packaging Current WIP Final Test Wafer Out Date Forward planning for WIP
Planning Logic Backward planning for plan lots Wafer Start Wafer Fabrication Commit due Circuit Probing Assembly Packaging Current WIP Final Test Wafer Out Date Forward planning for WIP
 Implementation
Implementation
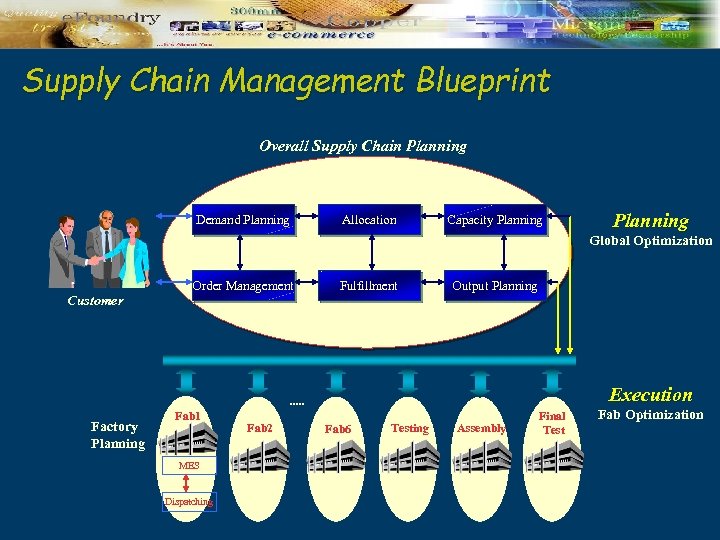 Supply Chain Management Blueprint Overall Supply Chain Planning Demand Planning Allocation Capacity Planning Global Optimization Order Management Fulfillment Output Planning Customer Execution . . . Factory Planning Fab 1 MES Dispatching Fab 2 Fab 6 Testing Assembly Final Test Fab Optimization
Supply Chain Management Blueprint Overall Supply Chain Planning Demand Planning Allocation Capacity Planning Global Optimization Order Management Fulfillment Output Planning Customer Execution . . . Factory Planning Fab 1 MES Dispatching Fab 2 Fab 6 Testing Assembly Final Test Fab Optimization
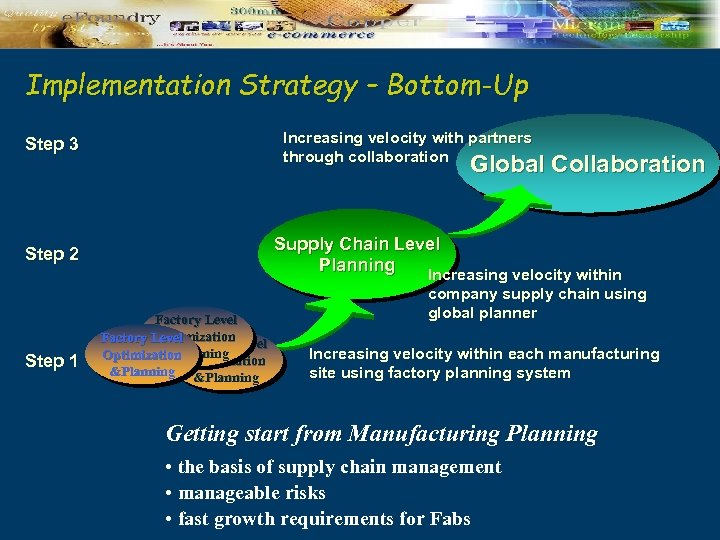 Implementation Strategy – Bottom-Up Increasing velocity with partners through collaboration Step 3 Global Collaboration Supply Chain Level Planning Increasing velocity within Step 2 Step 1 Factory Level Optimization Factory Level &Planning Optimization &Planning company supply chain using global planner Increasing velocity within each manufacturing site using factory planning system Getting start from Manufacturing Planning • the basis of supply chain management • manageable risks • fast growth requirements for Fabs
Implementation Strategy – Bottom-Up Increasing velocity with partners through collaboration Step 3 Global Collaboration Supply Chain Level Planning Increasing velocity within Step 2 Step 1 Factory Level Optimization Factory Level &Planning Optimization &Planning company supply chain using global planner Increasing velocity within each manufacturing site using factory planning system Getting start from Manufacturing Planning • the basis of supply chain management • manageable risks • fast growth requirements for Fabs
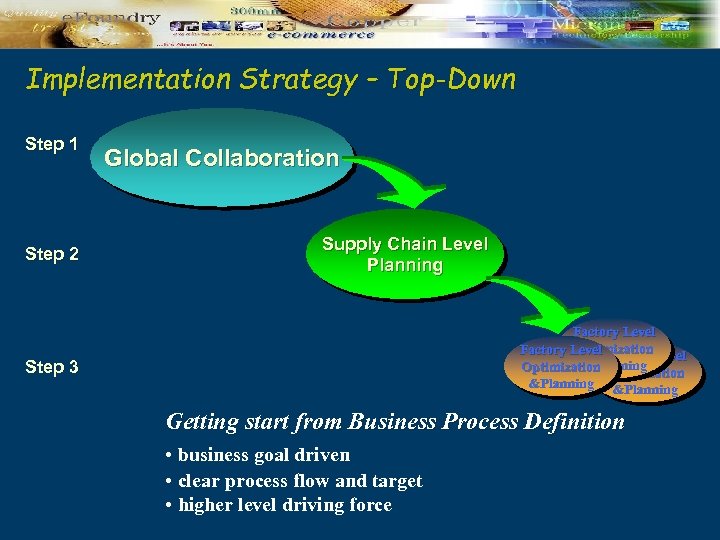 Implementation Strategy – Top-Down Step 1 Step 2 Global Collaboration Supply Chain Level Planning Factory Level Optimization Factory Level &Planning Optimization &Planning Step 3 Getting start from Business Process Definition • business goal driven • clear process flow and target • higher level driving force
Implementation Strategy – Top-Down Step 1 Step 2 Global Collaboration Supply Chain Level Planning Factory Level Optimization Factory Level &Planning Optimization &Planning Step 3 Getting start from Business Process Definition • business goal driven • clear process flow and target • higher level driving force
 Objectives • Provide a predictable customer capacity commitment • Improve visibility of capacity efficiency • Improve quality of decision process about allocation • Improve investment and resource utilization • Quick response to demand/supply variance • Improve accuracy of total projected out date • Enhance customer order tracking visibility • Improve global SC operation efficiency • Improve delivery deadline performance
Objectives • Provide a predictable customer capacity commitment • Improve visibility of capacity efficiency • Improve quality of decision process about allocation • Improve investment and resource utilization • Quick response to demand/supply variance • Improve accuracy of total projected out date • Enhance customer order tracking visibility • Improve global SC operation efficiency • Improve delivery deadline performance
 Solution development ? In-house design Enhance Legacy system!? Outsourcing Solution ? ! Outsourcing Solution !! • Efficiency - Solutions are ready now (6 months for a site) • Quality - Professional IT skills with domain knowledge • Expansion - More feasible functions were implemented • Maintenance - Easier to make upgrade by vendor • Market trend • Solution was verified by market • System development and maintenance outsourcing
Solution development ? In-house design Enhance Legacy system!? Outsourcing Solution ? ! Outsourcing Solution !! • Efficiency - Solutions are ready now (6 months for a site) • Quality - Professional IT skills with domain knowledge • Expansion - More feasible functions were implemented • Maintenance - Easier to make upgrade by vendor • Market trend • Solution was verified by market • System development and maintenance outsourcing
 Challenges • Resources – Resources consuming – Need more and more involvement and commitment from users for: • Data Collection and Validation • Model Design Input & Feedback • Functionality validation • Planning Scenario Development and checking • Legacy system adapting and interfacing • Tradeoff between a variety of objectives – Ex. Max Utilization vs. Customer Satisfaction – Requires management support to synchronize overall and each individual area’s KPIs or measures. • Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • PM and team capability
Challenges • Resources – Resources consuming – Need more and more involvement and commitment from users for: • Data Collection and Validation • Model Design Input & Feedback • Functionality validation • Planning Scenario Development and checking • Legacy system adapting and interfacing • Tradeoff between a variety of objectives – Ex. Max Utilization vs. Customer Satisfaction – Requires management support to synchronize overall and each individual area’s KPIs or measures. • Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • PM and team capability
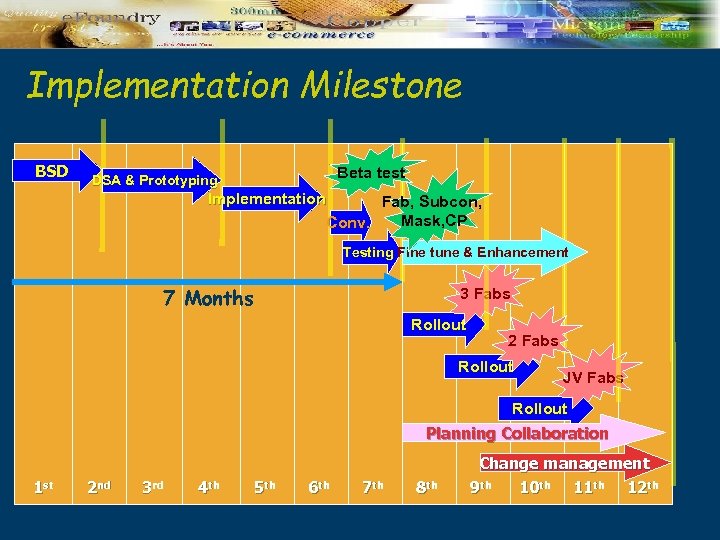 Implementation Milestone BSD Beta test DSA & Prototyping Implementation Fab, Subcon, Mask, CP Conv. Testing Fine tune & Enhancement 7 Months 3 Fabs Rollout 2 Fabs Rollout JV Fabs Rollout Planning Collaboration 1 st 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 7 th 8 th Change management 9 th 10 th 11 th 12 th
Implementation Milestone BSD Beta test DSA & Prototyping Implementation Fab, Subcon, Mask, CP Conv. Testing Fine tune & Enhancement 7 Months 3 Fabs Rollout 2 Fabs Rollout JV Fabs Rollout Planning Collaboration 1 st 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 7 th 8 th Change management 9 th 10 th 11 th 12 th
 Trend and Strategy
Trend and Strategy
 From ERP to SCM to Supply Chain Collaboration SCM ERP • Back-office functions alone • Automate functional processes • Ensure data consistency & integrity • provide a transactional backbone • support the planning, scheduling, and fulfillment • Allow cross-functional processes to coordinate activities across company departments • help companies interact better with their customers, suppliers, and employees. • Offered as hubs to support joint intra-enterprise and inter-enterprise planning and scheduling
From ERP to SCM to Supply Chain Collaboration SCM ERP • Back-office functions alone • Automate functional processes • Ensure data consistency & integrity • provide a transactional backbone • support the planning, scheduling, and fulfillment • Allow cross-functional processes to coordinate activities across company departments • help companies interact better with their customers, suppliers, and employees. • Offered as hubs to support joint intra-enterprise and inter-enterprise planning and scheduling
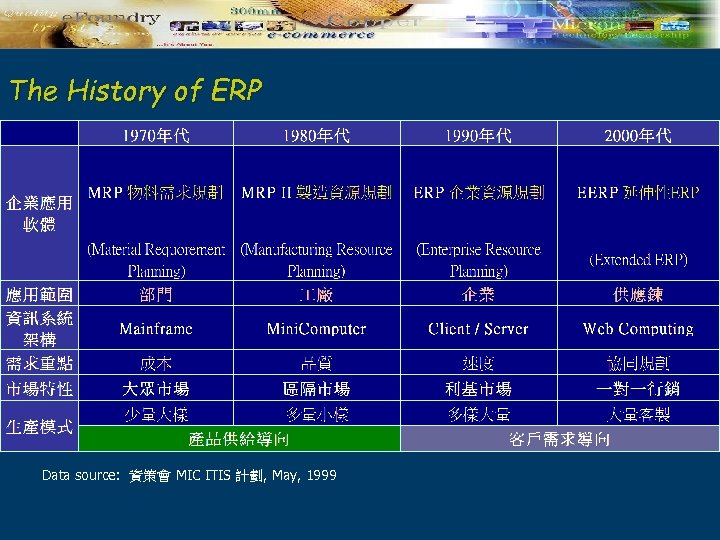 The History of ERP Data source: 資策會 MIC ITIS 計劃, May, 1999
The History of ERP Data source: 資策會 MIC ITIS 計劃, May, 1999
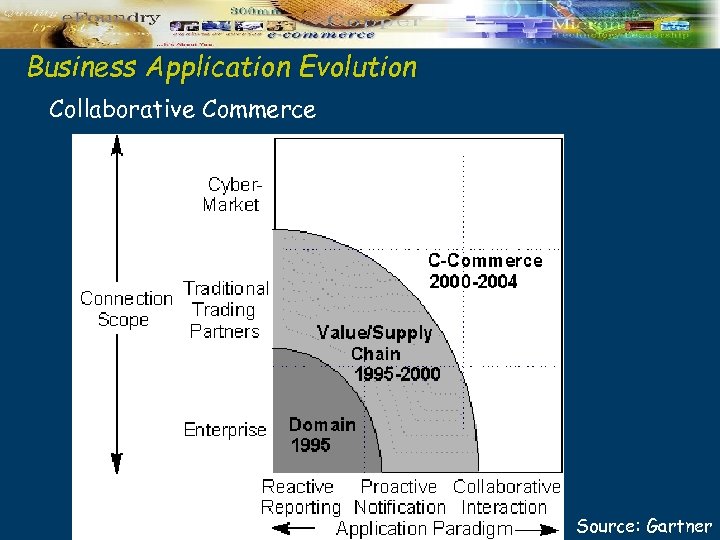 Business Application Evolution Collaborative Commerce Source: Gartner
Business Application Evolution Collaborative Commerce Source: Gartner
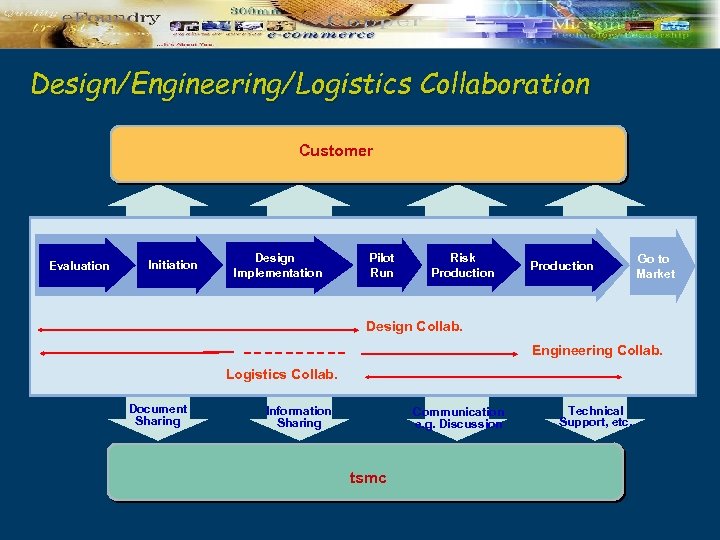 Design/Engineering/Logistics Collaboration Customer Evaluation Initiation Design Implementation Pilot Run Risk Production Go to Market Design Collab. Engineering Collab. Logistics Collab. Document Sharing Information Sharing Communication e. g. Discussion tsmc Technical Support, etc.
Design/Engineering/Logistics Collaboration Customer Evaluation Initiation Design Implementation Pilot Run Risk Production Go to Market Design Collab. Engineering Collab. Logistics Collab. Document Sharing Information Sharing Communication e. g. Discussion tsmc Technical Support, etc.
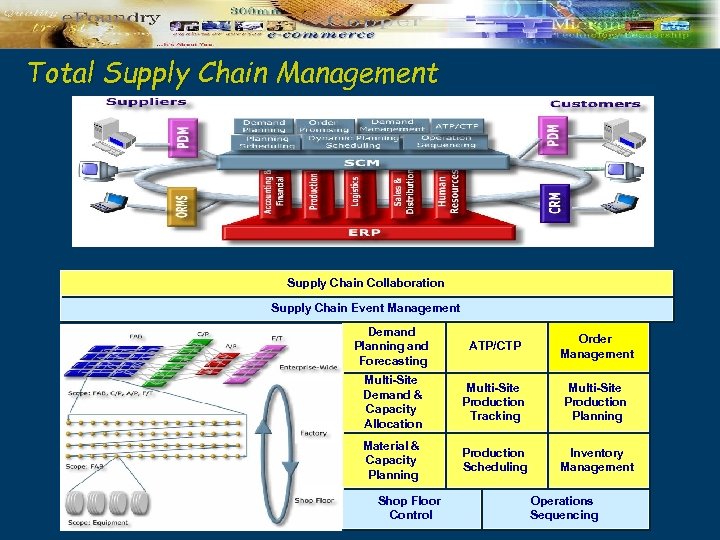 Total Supply Chain Management Supply Chain Collaboration Supply Chain Event Management Demand Planning and Forecasting ATP/CTP Order Management Multi-Site Demand & Capacity Allocation Multi-Site Production Tracking Multi-Site Production Planning Material & Capacity Planning Production Scheduling Inventory Management Shop Floor Control Operations Sequencing
Total Supply Chain Management Supply Chain Collaboration Supply Chain Event Management Demand Planning and Forecasting ATP/CTP Order Management Multi-Site Demand & Capacity Allocation Multi-Site Production Tracking Multi-Site Production Planning Material & Capacity Planning Production Scheduling Inventory Management Shop Floor Control Operations Sequencing
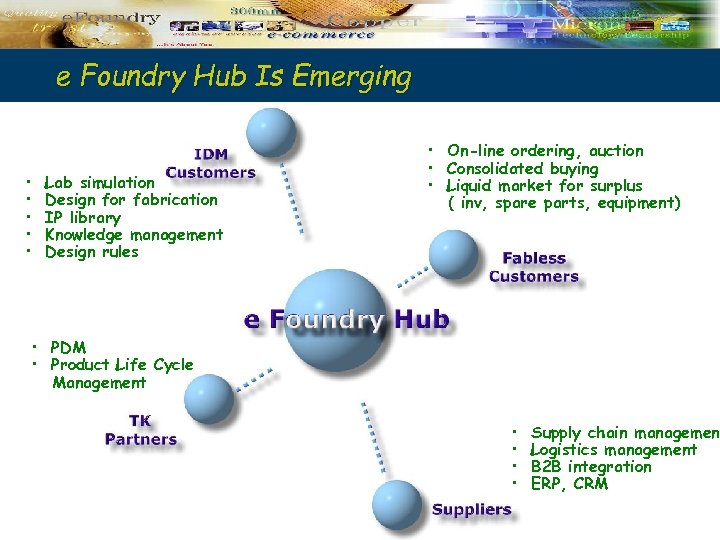 e Foundry Hub Is Emerging • • • Lab simulation Design for fabrication IP library Knowledge management Design rules • On-line ordering, auction • Consolidated buying • Liquid market for surplus ( inv, spare parts, equipment) • PDM • Product Life Cycle Management • • Supply chain management Logistics management B 2 B integration ERP, CRM
e Foundry Hub Is Emerging • • • Lab simulation Design for fabrication IP library Knowledge management Design rules • On-line ordering, auction • Consolidated buying • Liquid market for surplus ( inv, spare parts, equipment) • PDM • Product Life Cycle Management • • Supply chain management Logistics management B 2 B integration ERP, CRM
 A Global Collaborative Commerce Web
A Global Collaborative Commerce Web
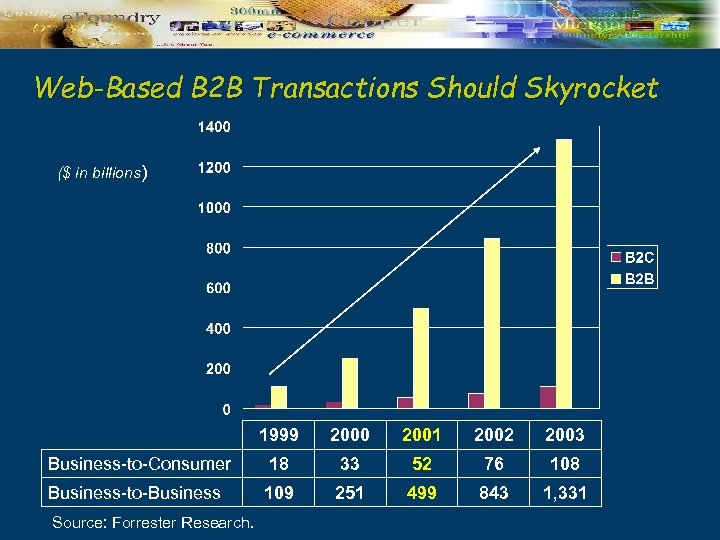 Web-Based B 2 B Transactions Should Skyrocket ($ in billions) 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Business-to-Consumer 18 33 52 76 108 Business-to-Business 109 251 499 843 1, 331 Source: Forrester Research.
Web-Based B 2 B Transactions Should Skyrocket ($ in billions) 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Business-to-Consumer 18 33 52 76 108 Business-to-Business 109 251 499 843 1, 331 Source: Forrester Research.
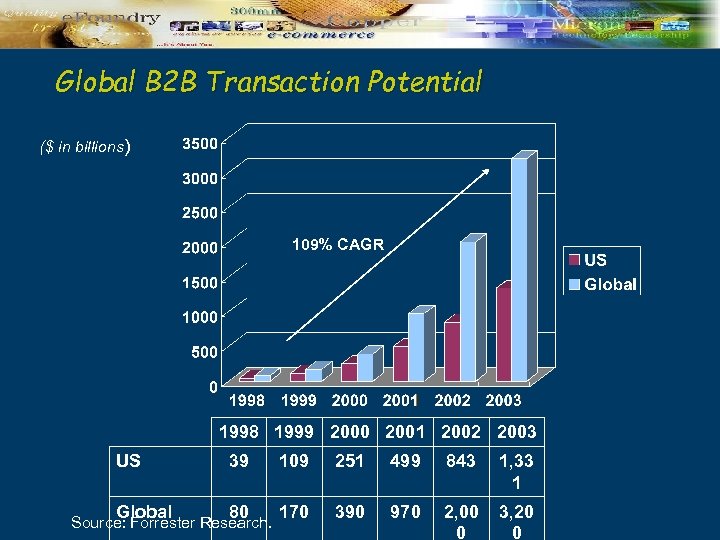 Global B 2 B Transaction Potential ($ in billions) 109% CAGR 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 US 39 109 251 499 843 1, 33 1 Global 80 170 390 970 2, 00 0 3, 20 0 Source: Forrester Research.
Global B 2 B Transaction Potential ($ in billions) 109% CAGR 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 US 39 109 251 499 843 1, 33 1 Global 80 170 390 970 2, 00 0 3, 20 0 Source: Forrester Research.
 Successful IT Strategies for Foundry • Put customers at the center of IT systems • Provide rapid access to fab information remotely • Cluster fab Manufacturing Execution Systems • Internet is the standard communication channel with customers • Integrate with upstream and downstream supply chain Source: Quincy Lin, Senior Vice President, TSMC
Successful IT Strategies for Foundry • Put customers at the center of IT systems • Provide rapid access to fab information remotely • Cluster fab Manufacturing Execution Systems • Internet is the standard communication channel with customers • Integrate with upstream and downstream supply chain Source: Quincy Lin, Senior Vice President, TSMC
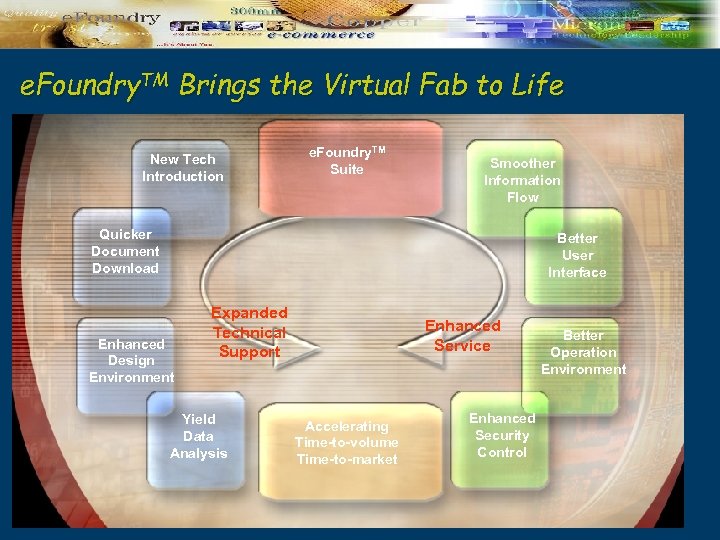 e. Foundry. TM Brings the Virtual Fab to Life New Tech Introduction e. Foundry. TM Suite Smoother Information Flow Quicker Document Download Better User Interface Enhanced Design Environment Expanded Technical Support Yield Data Analysis Enhanced Service Accelerating Time-to-volume Time-to-market Enhanced Security Control Better Operation Environment
e. Foundry. TM Brings the Virtual Fab to Life New Tech Introduction e. Foundry. TM Suite Smoother Information Flow Quicker Document Download Better User Interface Enhanced Design Environment Expanded Technical Support Yield Data Analysis Enhanced Service Accelerating Time-to-volume Time-to-market Enhanced Security Control Better Operation Environment
 Q&A
Q&A


