operative.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Introduction to restorative dentistry Dr. samer. d. azrai : BDS(j. u. s. t), JOB( cons)
Introduction to restorative dentistry Dr. samer. d. azrai : BDS(j. u. s. t), JOB( cons)
 Operative dentistry Its that branch of dentistry concerned with restoration of part of the teeth that are defective through diseases (caries), trauma, developmental anomalies into the state of normal function and esthetic Including prevention
Operative dentistry Its that branch of dentistry concerned with restoration of part of the teeth that are defective through diseases (caries), trauma, developmental anomalies into the state of normal function and esthetic Including prevention
 Dental caries • It’s disease characterized by dissolution of non organic component of the tooth and subsequent disintegration of organic component. • Dynamic process. . Episodes of demineralization and re-mineralization occur depending on plaque ph.
Dental caries • It’s disease characterized by dissolution of non organic component of the tooth and subsequent disintegration of organic component. • Dynamic process. . Episodes of demineralization and re-mineralization occur depending on plaque ph.
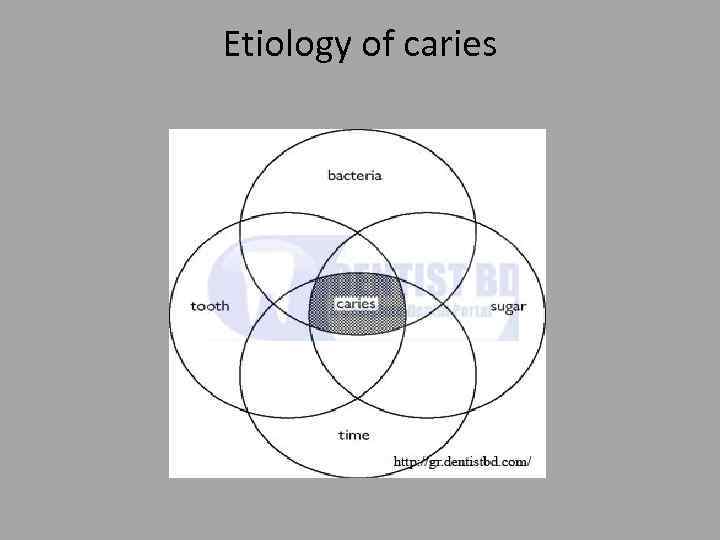 Etiology of caries
Etiology of caries
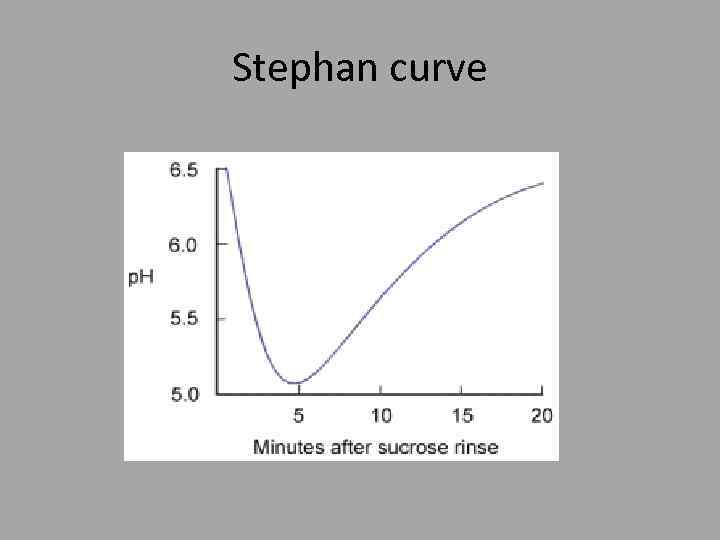 Stephan curve
Stephan curve
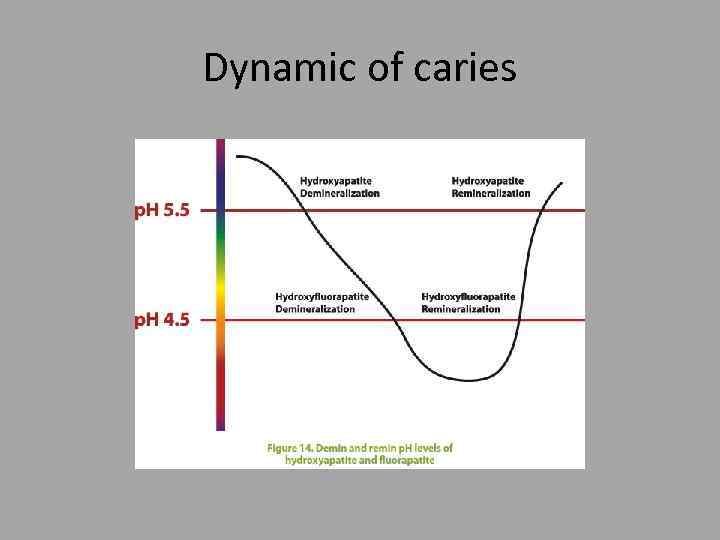 Dynamic of caries
Dynamic of caries
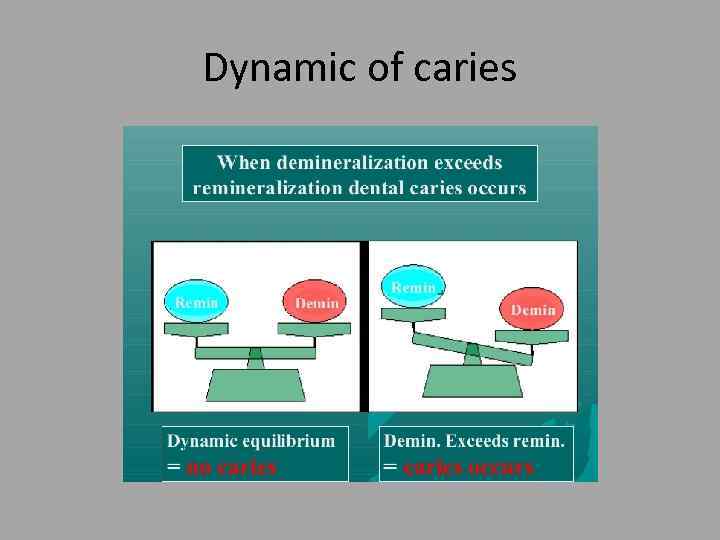 Dynamic of caries
Dynamic of caries
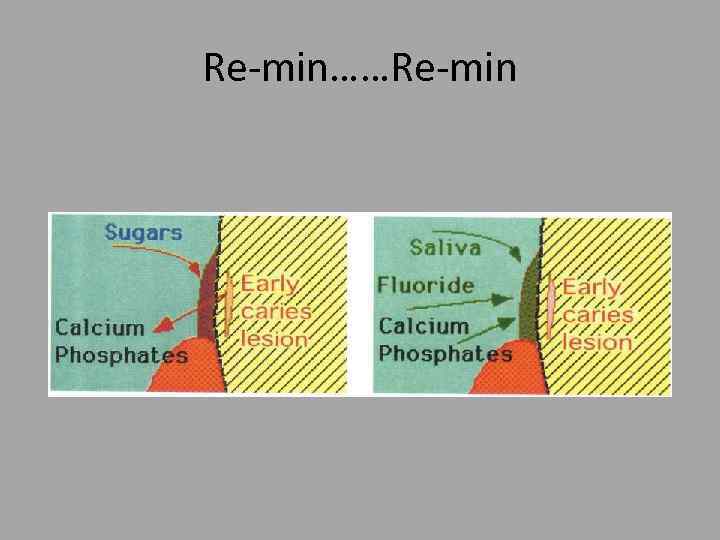 Re-min……Re-min
Re-min……Re-min
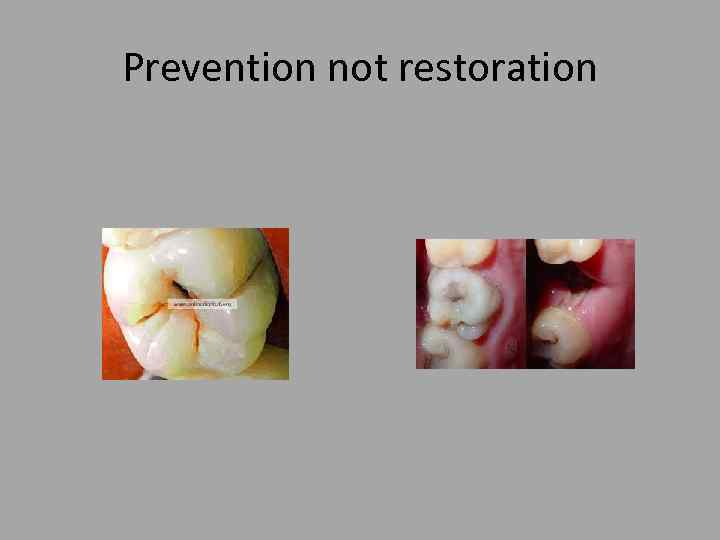 Prevention not restoration
Prevention not restoration
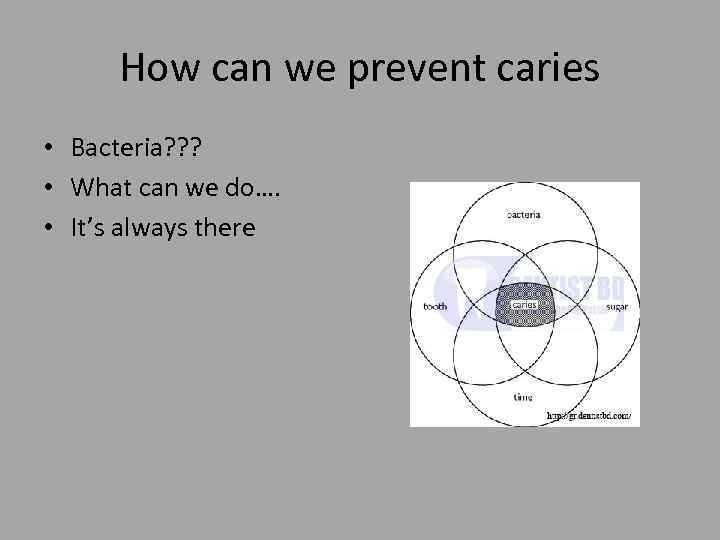 How can we prevent caries • Bacteria? ? ? • What can we do…. • It’s always there
How can we prevent caries • Bacteria? ? ? • What can we do…. • It’s always there
 bacteria • Tooth brushing • Regular use of mouth wash containing CHX. • By Disturbing dental plaque…non pathogenic bacteria faster in occupying tooth surface than pathogenic bacteria (m. striptococcus)
bacteria • Tooth brushing • Regular use of mouth wash containing CHX. • By Disturbing dental plaque…non pathogenic bacteria faster in occupying tooth surface than pathogenic bacteria (m. striptococcus)
 Bacteria…. tooth it self Key word…increase the tooth resistance to caries • Fluoridation of drinking water…reduced smooth surface caries. • Tooth brushing and local fluoride application …. . re min by fluoroappitite (more resistant to acid)
Bacteria…. tooth it self Key word…increase the tooth resistance to caries • Fluoridation of drinking water…reduced smooth surface caries. • Tooth brushing and local fluoride application …. . re min by fluoroappitite (more resistant to acid)
 Bacteria …. Tooth it self… • Increasing resistance • Fissure sealants Dramatic reduction in caries affecting fissures
Bacteria …. Tooth it self… • Increasing resistance • Fissure sealants Dramatic reduction in caries affecting fissures
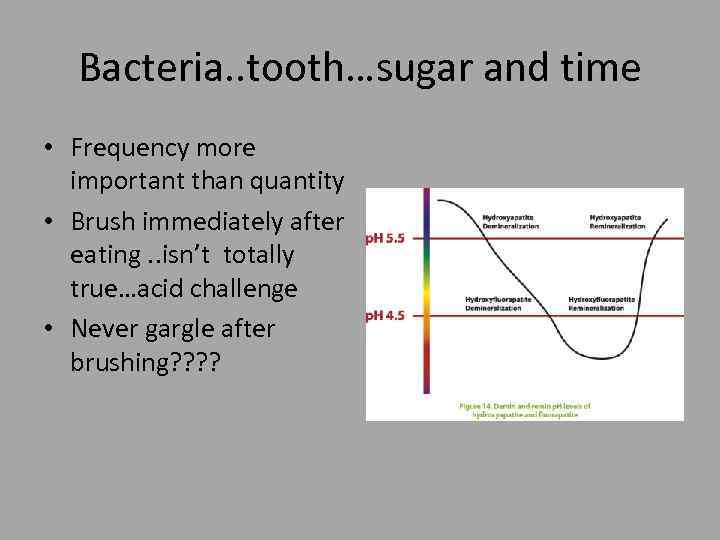 Bacteria. . tooth…sugar and time • Frequency more important than quantity • Brush immediately after eating. . isn’t totally true…acid challenge • Never gargle after brushing? ?
Bacteria. . tooth…sugar and time • Frequency more important than quantity • Brush immediately after eating. . isn’t totally true…acid challenge • Never gargle after brushing? ?
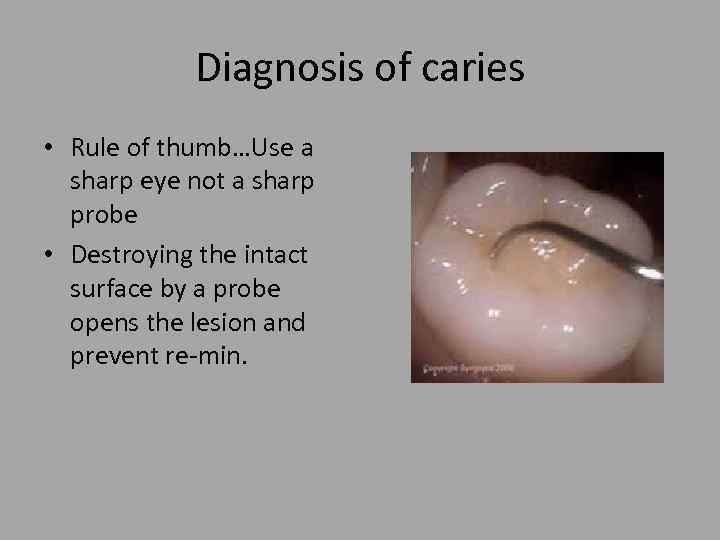 Diagnosis of caries • Rule of thumb…Use a sharp eye not a sharp probe • Destroying the intact surface by a probe opens the lesion and prevent re-min.
Diagnosis of caries • Rule of thumb…Use a sharp eye not a sharp probe • Destroying the intact surface by a probe opens the lesion and prevent re-min.
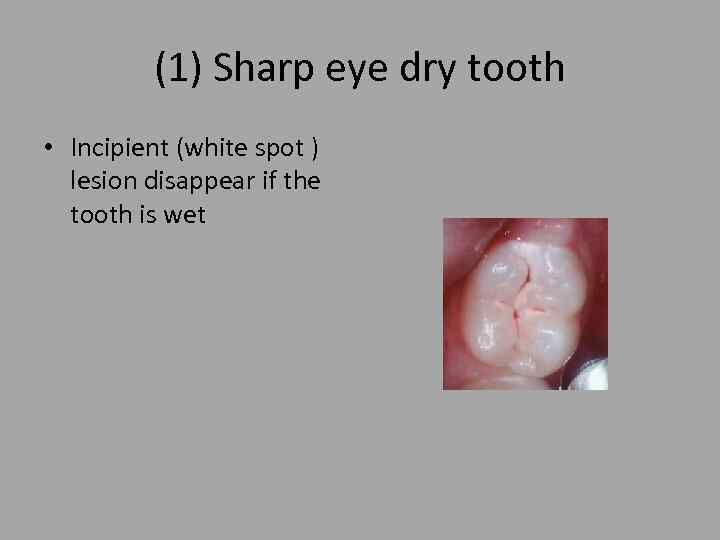 (1) Sharp eye dry tooth • Incipient (white spot ) lesion disappear if the tooth is wet
(1) Sharp eye dry tooth • Incipient (white spot ) lesion disappear if the tooth is wet
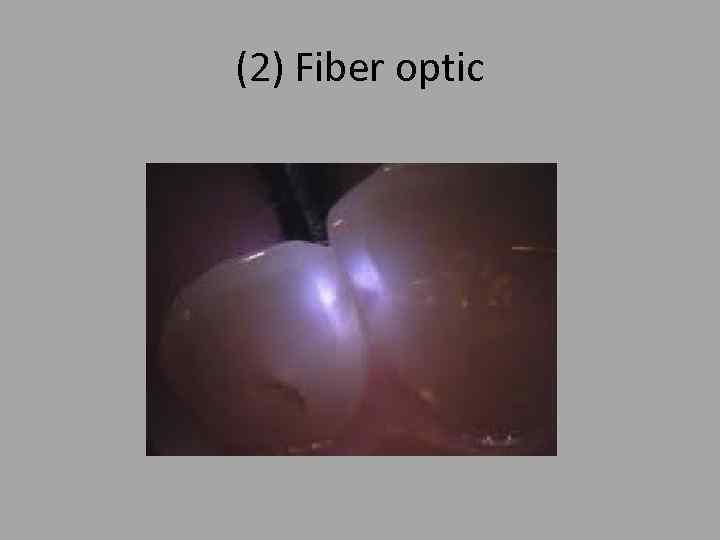 (2) Fiber optic
(2) Fiber optic
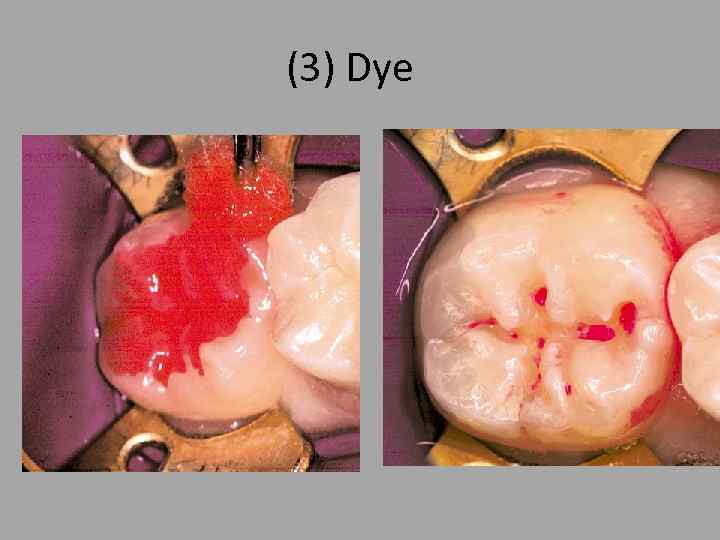 (3) Dye
(3) Dye
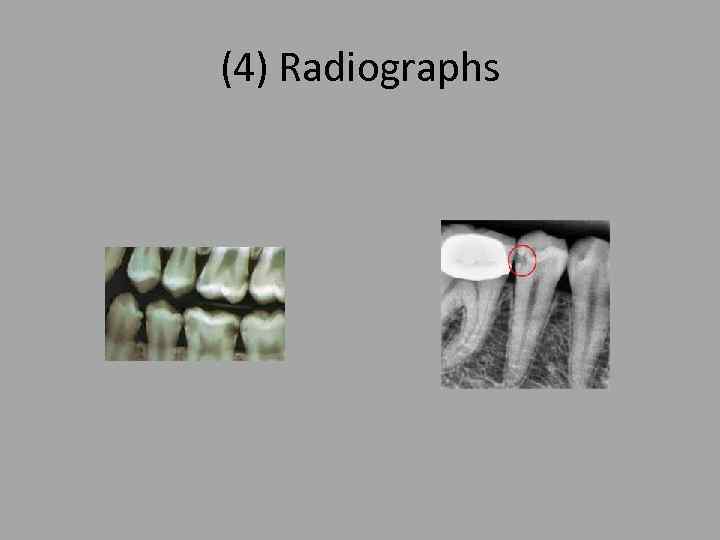 (4) Radiographs
(4) Radiographs
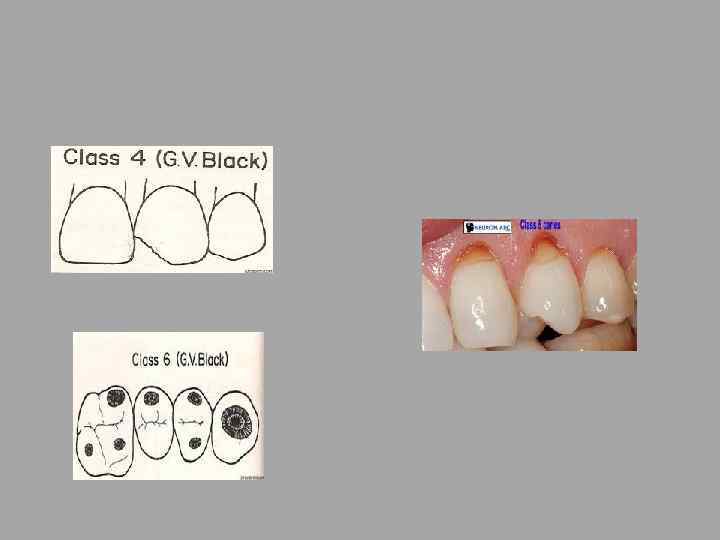
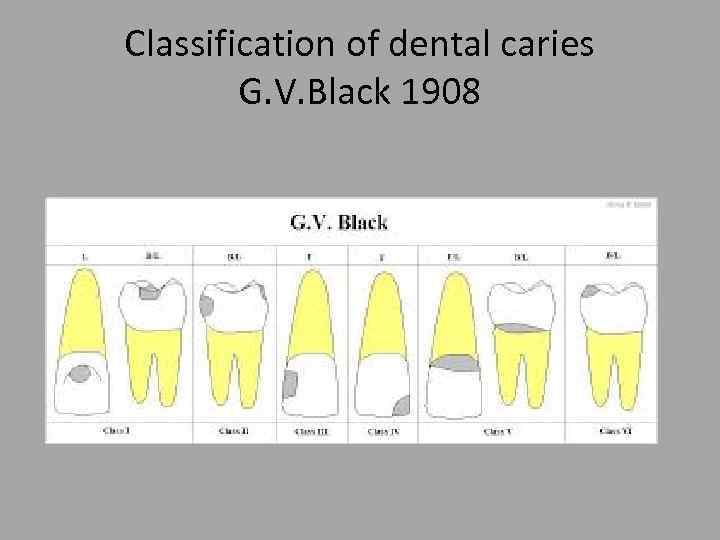 Classification of dental caries G. V. Black 1908
Classification of dental caries G. V. Black 1908
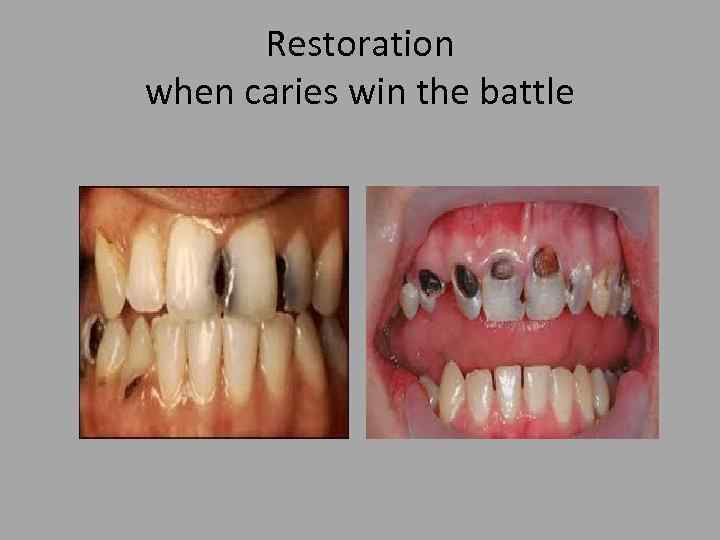 Restoration when caries win the battle
Restoration when caries win the battle
 Restorative material • • • Amalgam Composite resin G. I Polyacid modified composite resin (dyract) Resin modified G. I (RMGI) Giomer
Restorative material • • • Amalgam Composite resin G. I Polyacid modified composite resin (dyract) Resin modified G. I (RMGI) Giomer
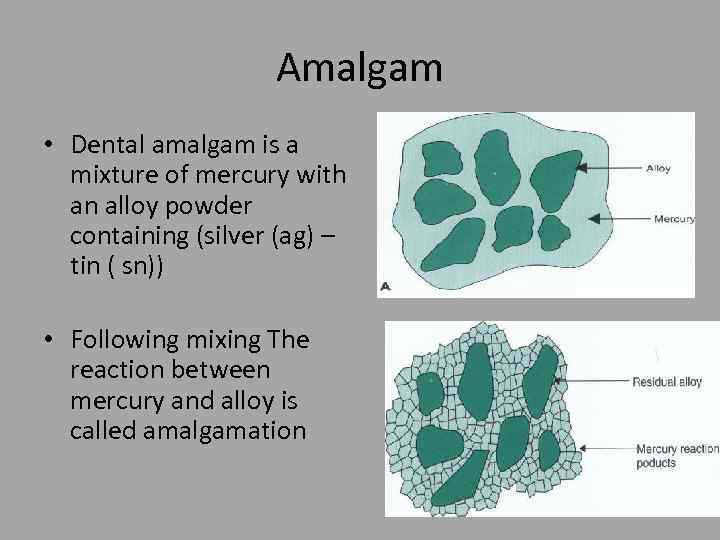 Amalgam • Dental amalgam is a mixture of mercury with an alloy powder containing (silver (ag) – tin ( sn)) • Following mixing The reaction between mercury and alloy is called amalgamation
Amalgam • Dental amalgam is a mixture of mercury with an alloy powder containing (silver (ag) – tin ( sn)) • Following mixing The reaction between mercury and alloy is called amalgamation
 Amalgam • Also contains a small amount of zinc (zn) almost 1% . . works as a scavenger Zn + H 2 O → Zn. O + H 2 • Responsible for delayed expansion of amalgam. . (3%5%) • Moisture control is mandatory
Amalgam • Also contains a small amount of zinc (zn) almost 1% . . works as a scavenger Zn + H 2 O → Zn. O + H 2 • Responsible for delayed expansion of amalgam. . (3%5%) • Moisture control is mandatory
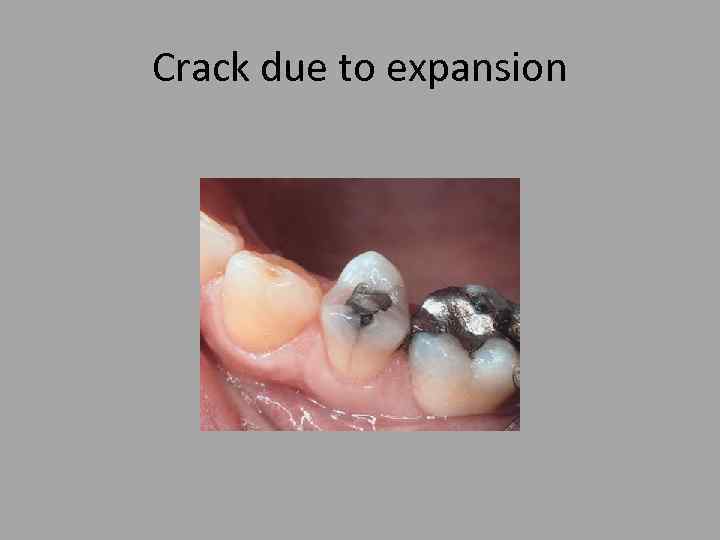 Crack due to expansion
Crack due to expansion
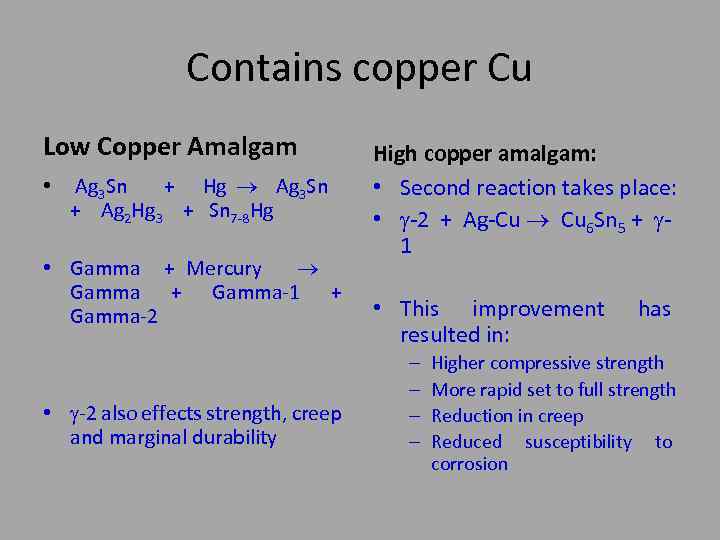 Contains copper Cu Low Copper Amalgam • Ag 3 Sn + Hg Ag 3 Sn + Ag 2 Hg 3 + Sn 7 -8 Hg • Gamma + Mercury Gamma + Gamma-1 + Gamma-2 • -2 also effects strength, creep and marginal durability High copper amalgam: • Second reaction takes place: • -2 + Ag-Cu Cu 6 Sn 5 + 1 • This improvement resulted in: – – has Higher compressive strength More rapid set to full strength Reduction in creep Reduced susceptibility to corrosion
Contains copper Cu Low Copper Amalgam • Ag 3 Sn + Hg Ag 3 Sn + Ag 2 Hg 3 + Sn 7 -8 Hg • Gamma + Mercury Gamma + Gamma-1 + Gamma-2 • -2 also effects strength, creep and marginal durability High copper amalgam: • Second reaction takes place: • -2 + Ag-Cu Cu 6 Sn 5 + 1 • This improvement resulted in: – – has Higher compressive strength More rapid set to full strength Reduction in creep Reduced susceptibility to corrosion
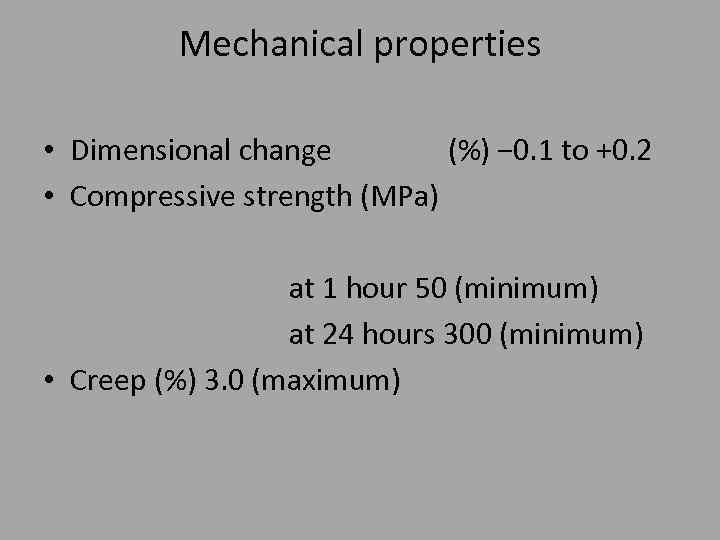 Mechanical properties • Dimensional change (%) − 0. 1 to +0. 2 • Compressive strength (MPa) at 1 hour 50 (minimum) at 24 hours 300 (minimum) • Creep (%) 3. 0 (maximum)
Mechanical properties • Dimensional change (%) − 0. 1 to +0. 2 • Compressive strength (MPa) at 1 hour 50 (minimum) at 24 hours 300 (minimum) • Creep (%) 3. 0 (maximum)
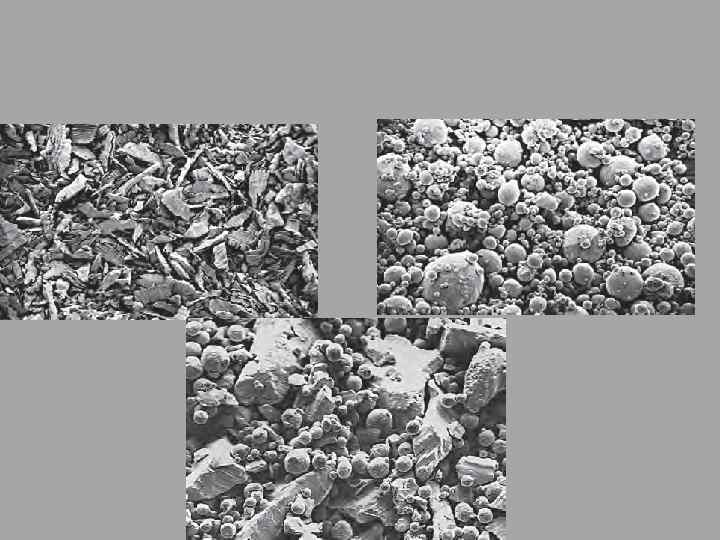
 Lath cut (filing). . spherical…mixed
Lath cut (filing). . spherical…mixed

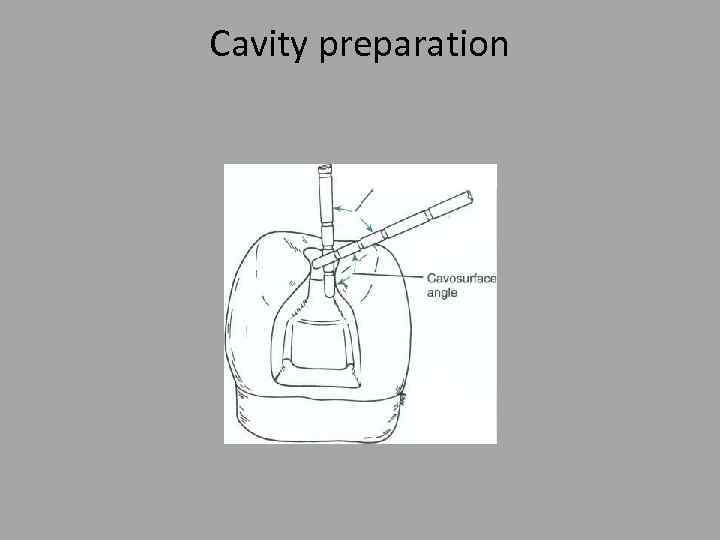 Cavity preparation
Cavity preparation
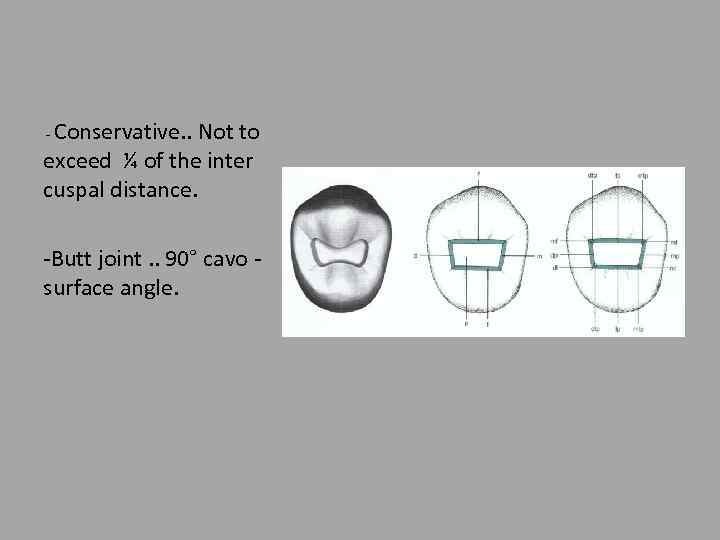 Conservative. . Not to exceed ¼ of the inter cuspal distance. - -Butt joint. . 90° cavo surface angle.
Conservative. . Not to exceed ¼ of the inter cuspal distance. - -Butt joint. . 90° cavo surface angle.
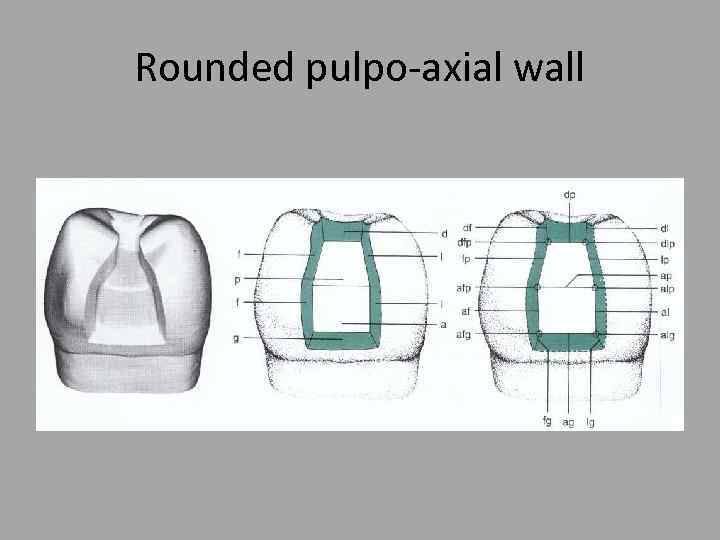 Rounded pulpo-axial wall
Rounded pulpo-axial wall
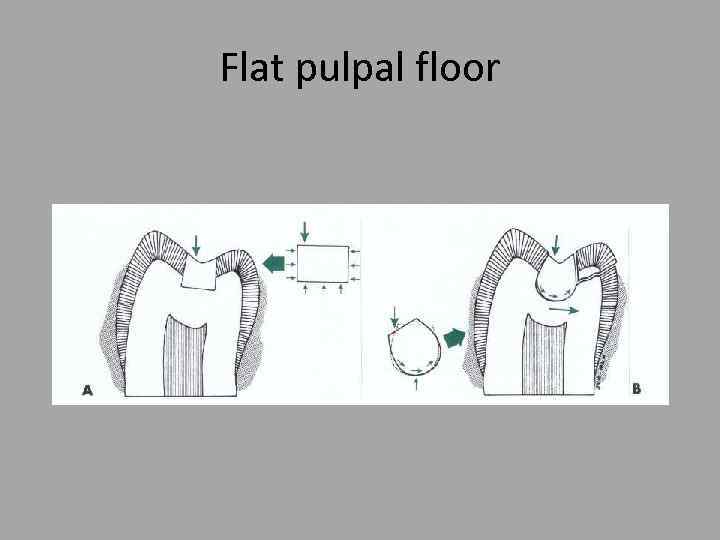 Flat pulpal floor
Flat pulpal floor
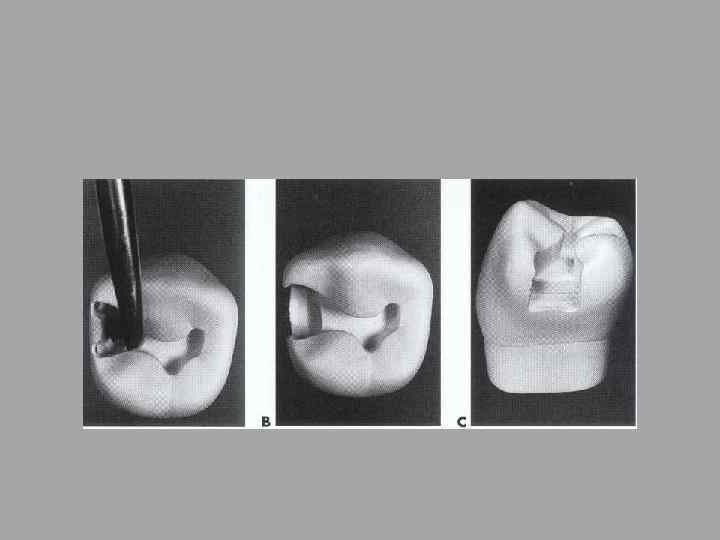
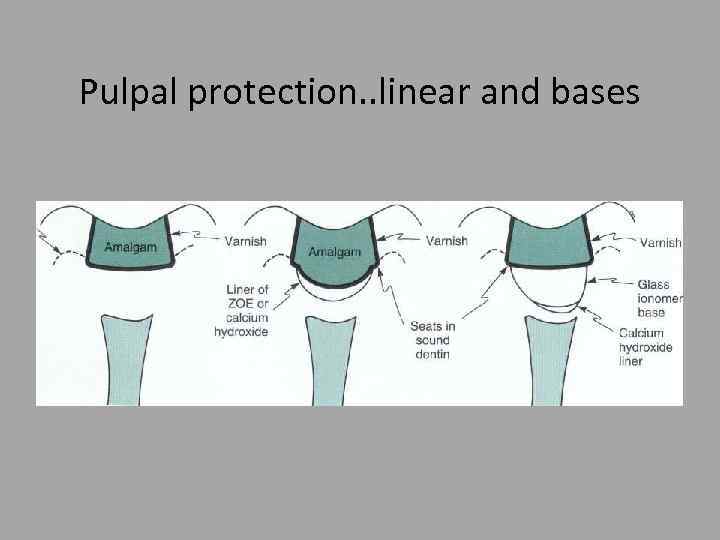 Pulpal protection. . linear and bases
Pulpal protection. . linear and bases
 Matrix band mandatory for missing walls
Matrix band mandatory for missing walls

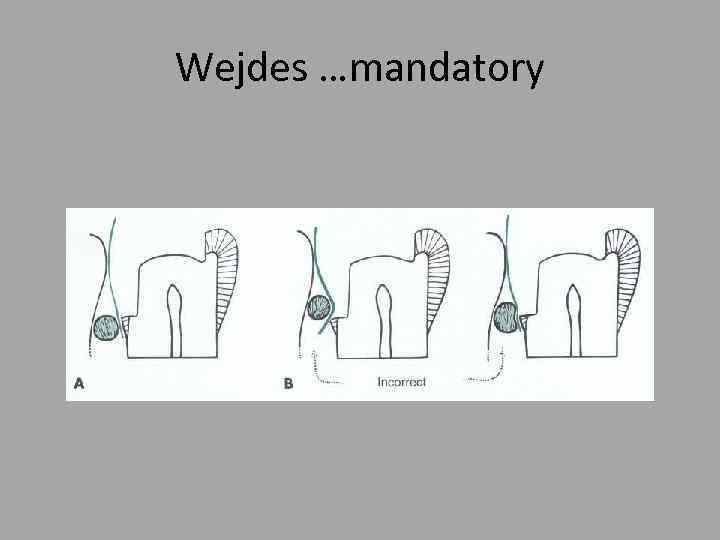 Wejdes …mandatory
Wejdes …mandatory
 Advantages of amalgam for restoring posterior teeth • • Less technique sensitive. More durable. Less costly. Time for placement is less. Cheaper. Excellent wear resistance. Self sealing against leakage. Surface not as adherent with bacteria.
Advantages of amalgam for restoring posterior teeth • • Less technique sensitive. More durable. Less costly. Time for placement is less. Cheaper. Excellent wear resistance. Self sealing against leakage. Surface not as adherent with bacteria.
 Composite • Dental composite is a physical blend between a resin and an inorganic filler • Resin usually is BIS-GMA or UDMA • TEGMA… a co-monomer used to reduce the viscosity of resin. • Filler usually quartz or alumino silicate glass
Composite • Dental composite is a physical blend between a resin and an inorganic filler • Resin usually is BIS-GMA or UDMA • TEGMA… a co-monomer used to reduce the viscosity of resin. • Filler usually quartz or alumino silicate glass
 In organic filler • Filler content • Reduces polymerization shrinkage • Reduced LCOE • Increases strength
In organic filler • Filler content • Reduces polymerization shrinkage • Reduced LCOE • Increases strength
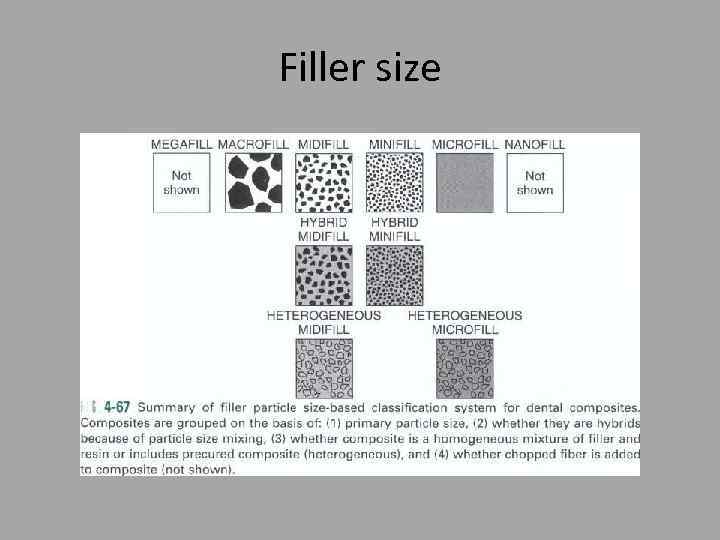 Filler size
Filler size
 Classification according to filler content
Classification according to filler content
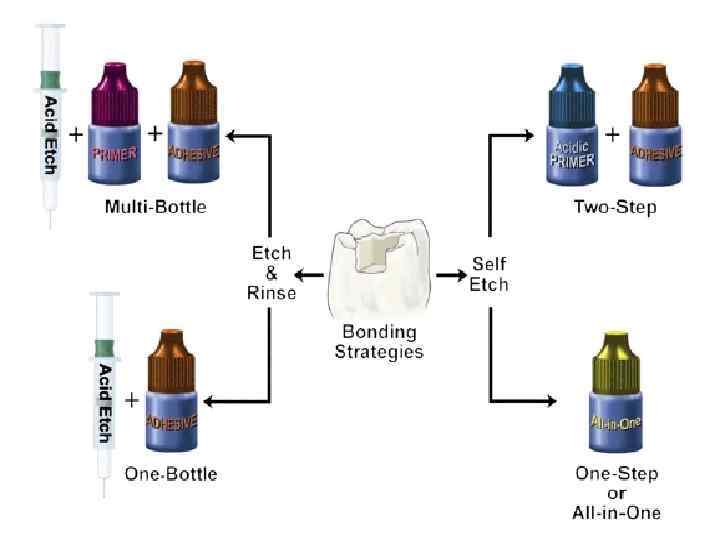
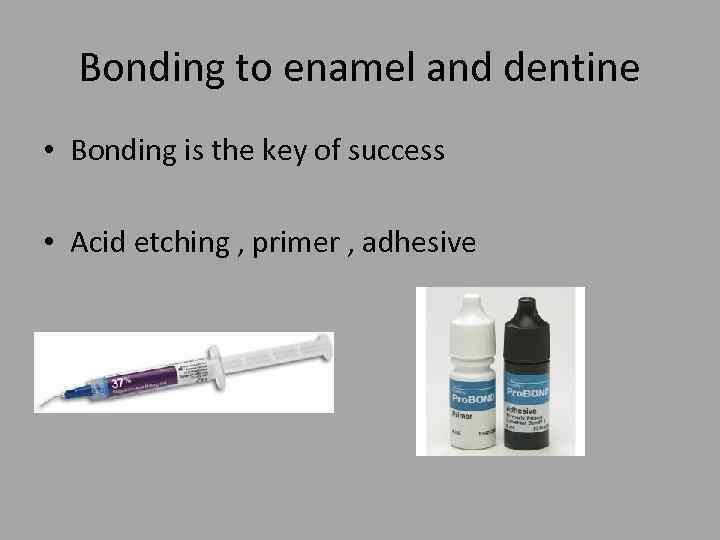 Bonding to enamel and dentine • Bonding is the key of success • Acid etching , primer , adhesive
Bonding to enamel and dentine • Bonding is the key of success • Acid etching , primer , adhesive
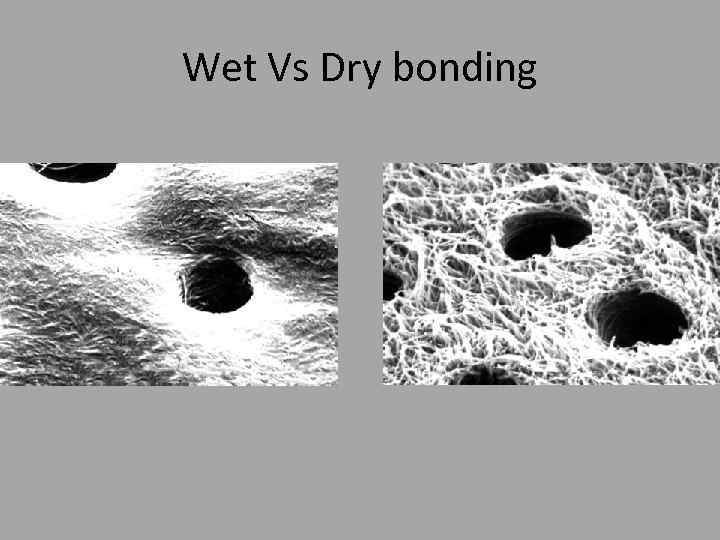 Wet Vs Dry bonding
Wet Vs Dry bonding
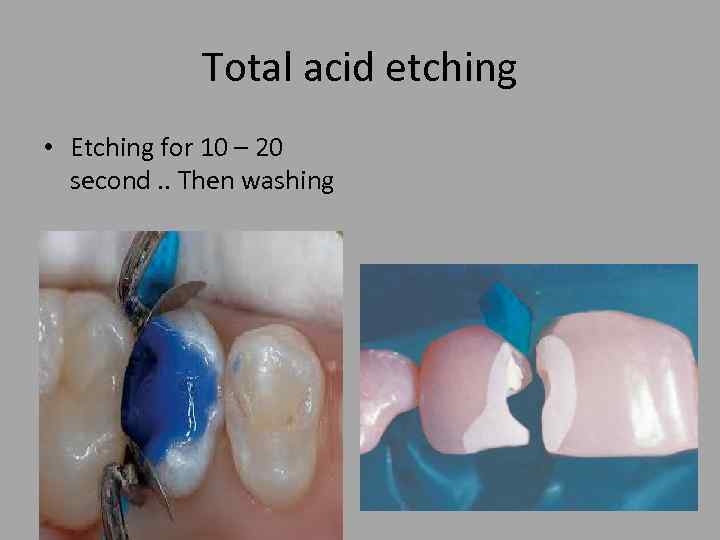 Total acid etching • Etching for 10 – 20 second. . Then washing
Total acid etching • Etching for 10 – 20 second. . Then washing
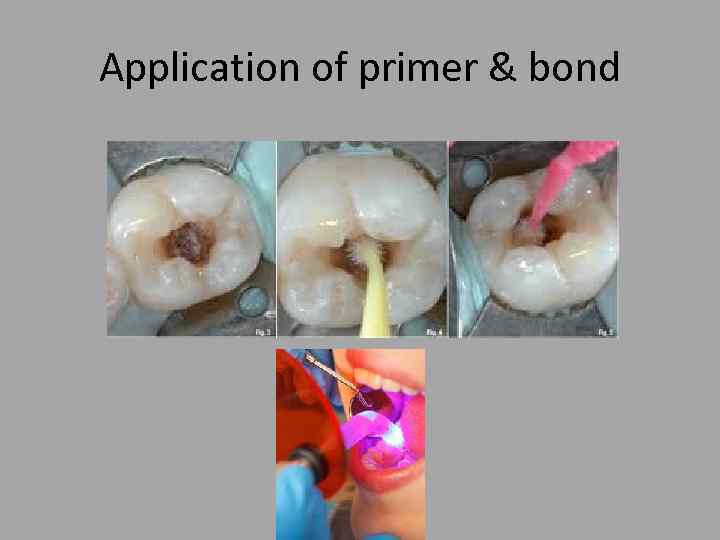 Application of primer & bond
Application of primer & bond
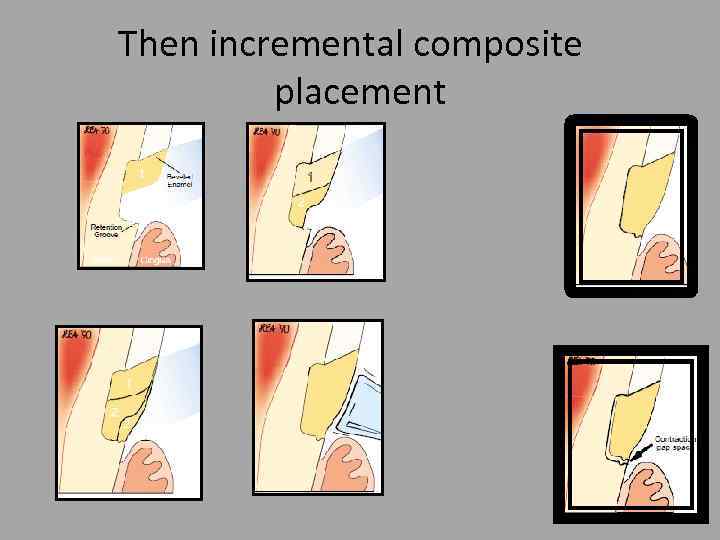 Then incremental composite placement
Then incremental composite placement
 Disadvantages of composite • • • Poor In wear resistance. Lacks appropriate proximal contact. Exhibited micro leakage & secondary caries. Post operative sensitivity Technique sensitive compared to amalgam
Disadvantages of composite • • • Poor In wear resistance. Lacks appropriate proximal contact. Exhibited micro leakage & secondary caries. Post operative sensitivity Technique sensitive compared to amalgam
 Glass ionomer (G. i) • In none load areas • Releases fluoride • Chemically bond to enamel and dentine • The closest in COE to tooth structure • Can be etched and bonded to receive composite …. sandwich technique
Glass ionomer (G. i) • In none load areas • Releases fluoride • Chemically bond to enamel and dentine • The closest in COE to tooth structure • Can be etched and bonded to receive composite …. sandwich technique
 • Resin modified glass ionomer 80% G. I Releases fluoride Light cured • Polyacid modified composite • 80% composite • Claimed to release flouride • Light cured • Used mostly with deciduous teeth •
• Resin modified glass ionomer 80% G. I Releases fluoride Light cured • Polyacid modified composite • 80% composite • Claimed to release flouride • Light cured • Used mostly with deciduous teeth •
 Thank you Dr. Samer. D. Azrai
Thank you Dr. Samer. D. Azrai


