de4f23555a74c4118a9203903632a2a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Introduction to QUERI Implementation Research for VHA Operations Staff: What It is and Why It is Helpful Richard R. Owen, MD Director, Mental Health QUERI Jeffrey L. Smith, Ph. D(c) Implementation Research Coordinator, Mental Health QUERI April 28, 2009 Quality Enhancement Research Initiative
Introduction to QUERI Implementation Research for VHA Operations Staff: What It is and Why It is Helpful Richard R. Owen, MD Director, Mental Health QUERI Jeffrey L. Smith, Ph. D(c) Implementation Research Coordinator, Mental Health QUERI April 28, 2009 Quality Enhancement Research Initiative
 Overview • Clinical Research Translation Roadblocks and the Quality Chasm • Introduction to QUERI and Implementation Science • Examples of QUERI Projects • Barriers to and Opportunities for Greater Involvement of Policymakers and Managers • Discussion
Overview • Clinical Research Translation Roadblocks and the Quality Chasm • Introduction to QUERI and Implementation Science • Examples of QUERI Projects • Barriers to and Opportunities for Greater Involvement of Policymakers and Managers • Discussion
 The problem • Clinical research translational roadblocks Significant barriers impede timely progression of innovations from basic science to clinical application to routine use and population benefit • The healthcare quality chasm Pervasive gaps exist in the quality, safety, equity, efficiency, timeliness and patient-centeredness of healthcare
The problem • Clinical research translational roadblocks Significant barriers impede timely progression of innovations from basic science to clinical application to routine use and population benefit • The healthcare quality chasm Pervasive gaps exist in the quality, safety, equity, efficiency, timeliness and patient-centeredness of healthcare
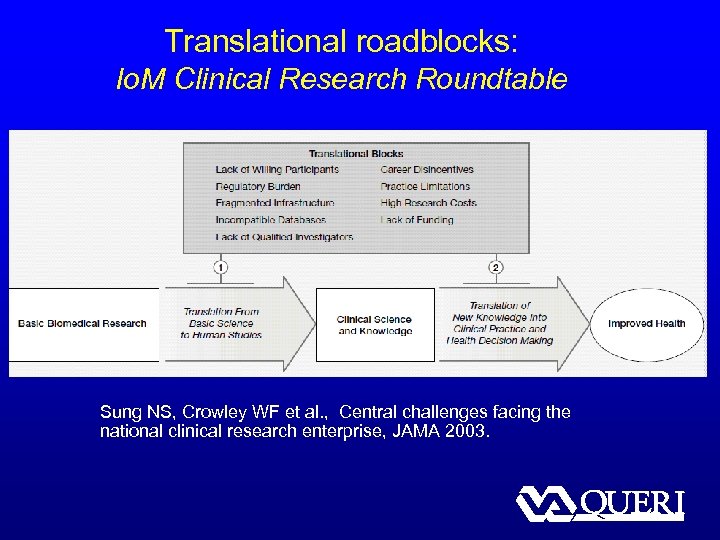 Translational roadblocks: Io. M Clinical Research Roundtable Sung NS, Crowley WF et al. , Central challenges facing the national clinical research enterprise, JAMA 2003.
Translational roadblocks: Io. M Clinical Research Roundtable Sung NS, Crowley WF et al. , Central challenges facing the national clinical research enterprise, JAMA 2003.
 Implementation gaps and the quality chasm Most healthcare quality gaps result from insufficient implementation of evidence-based practices Strategies and programs to accelerate implementation and to improve quality are similar and generally involve organizational and professional behavior change
Implementation gaps and the quality chasm Most healthcare quality gaps result from insufficient implementation of evidence-based practices Strategies and programs to accelerate implementation and to improve quality are similar and generally involve organizational and professional behavior change
 Possible Solutions • “Push” research into practice – researchers get involved in implementation of research findings • “Pull” research into practice – policymakers, managers get involved in prioritization and planning of research
Possible Solutions • “Push” research into practice – researchers get involved in implementation of research findings • “Pull” research into practice – policymakers, managers get involved in prioritization and planning of research
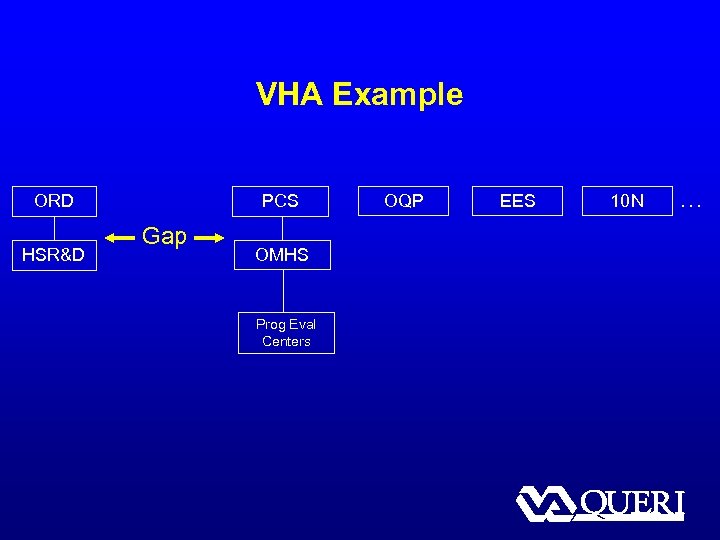 VHA Example ORD HSR&D PCS Gap OMHS Prog Eval Centers OQP EES 10 N …
VHA Example ORD HSR&D PCS Gap OMHS Prog Eval Centers OQP EES 10 N …
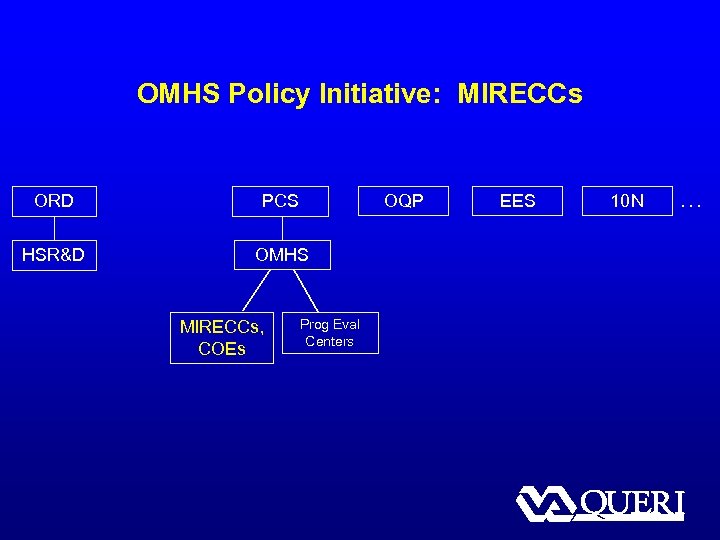 OMHS Policy Initiative: MIRECCs ORD PCS HSR&D OMHS MIRECCs, COEs OQP Prog Eval Centers EES 10 N …
OMHS Policy Initiative: MIRECCs ORD PCS HSR&D OMHS MIRECCs, COEs OQP Prog Eval Centers EES 10 N …
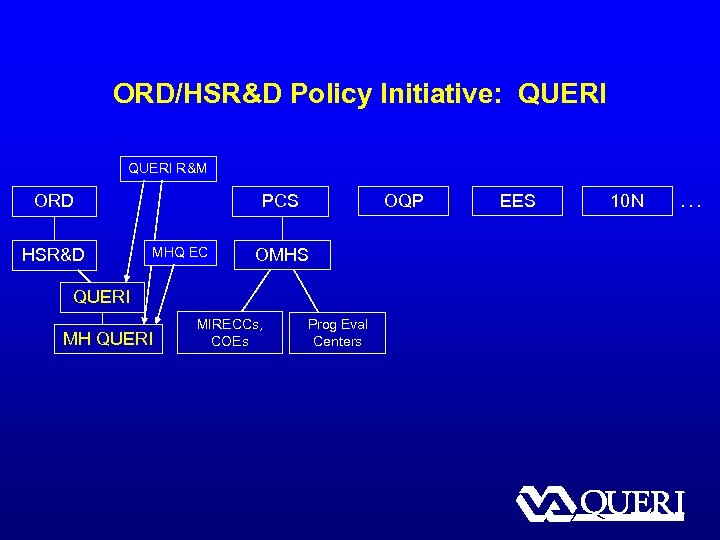 ORD/HSR&D Policy Initiative: QUERI R&M ORD HSR&D OQP PCS MHQ EC OMHS QUERI MH QUERI MIRECCs, COEs Prog Eval Centers EES 10 N …
ORD/HSR&D Policy Initiative: QUERI R&M ORD HSR&D OQP PCS MHQ EC OMHS QUERI MH QUERI MIRECCs, COEs Prog Eval Centers EES 10 N …
 US Department of Veterans Affairs Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) QUERI Mission To enhance the quality, outcomes and efficiency of VA health care by systematically implementing evidencebased clinical guidelines and innovations into routine clinical practice
US Department of Veterans Affairs Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) QUERI Mission To enhance the quality, outcomes and efficiency of VA health care by systematically implementing evidencebased clinical guidelines and innovations into routine clinical practice
 Nine QUERI coordinating centers • Chronic Heart Failure • Diabetes • HIV/AIDS • Ischemic Heart Disease • Mental Health • Polytrauma/Blast-Related Injuries • Spinal Cord Injury • Stroke • Substance Use Disorders
Nine QUERI coordinating centers • Chronic Heart Failure • Diabetes • HIV/AIDS • Ischemic Heart Disease • Mental Health • Polytrauma/Blast-Related Injuries • Spinal Cord Injury • Stroke • Substance Use Disorders
 “Implementation research in health” Implementation research is the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice, and, hence, to improve the quality and effectiveness of health services. It includes the study of influences on healthcare professional and organizational behavior. -- Eccles and Mittman, Implementation Science 2006
“Implementation research in health” Implementation research is the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice, and, hence, to improve the quality and effectiveness of health services. It includes the study of influences on healthcare professional and organizational behavior. -- Eccles and Mittman, Implementation Science 2006
 Implementation research policy/practice goals • Develop effective strategies for improving health-related processes and outcomes • Improve health-related processes and outcomes within participating study sites • Facilitate widespread adoption (or ‘spread’) of these strategies
Implementation research policy/practice goals • Develop effective strategies for improving health-related processes and outcomes • Improve health-related processes and outcomes within participating study sites • Facilitate widespread adoption (or ‘spread’) of these strategies
 Implementation research science goals • Generate new insights and generalizable knowledge regarding implementation processes, barriers, facilitators, strategies • Develop, test and refine implementation theories, hypotheses, models and principles • Develop improved approaches and methods for studying implementation
Implementation research science goals • Generate new insights and generalizable knowledge regarding implementation processes, barriers, facilitators, strategies • Develop, test and refine implementation theories, hypotheses, models and principles • Develop improved approaches and methods for studying implementation
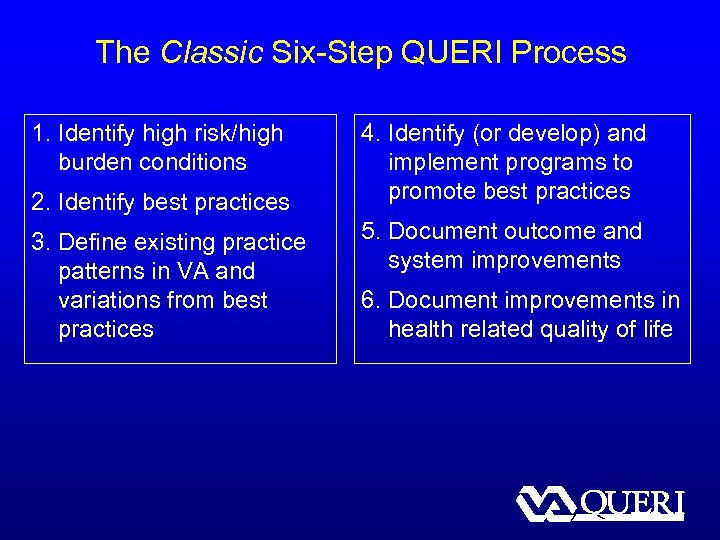 The Classic Six-Step QUERI Process 1. Identify high risk/high burden conditions 2. Identify best practices 3. Define existing practice patterns in VA and variations from best practices 4. Identify (or develop) and implement programs to promote best practices 5. Document outcome and system improvements 6. Document improvements in health related quality of life
The Classic Six-Step QUERI Process 1. Identify high risk/high burden conditions 2. Identify best practices 3. Define existing practice patterns in VA and variations from best practices 4. Identify (or develop) and implement programs to promote best practices 5. Document outcome and system improvements 6. Document improvements in health related quality of life
 Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 1: Select Diseases/Conditions/Patient Populations 1 A. identify and prioritize high risk/high burden clinical conditions 1 B. identify high priority outcomes and areas of practice within a selected condition Step 2: Identify Evidence-Based Guidelines, Practices 2 A. identify evidence-based clinical practice guidelines and recommendations 2 B. identify evidence-based clinical practices, care models Prioritize recommendations for implementation (based on gap, importance for outcomes, feasibility of improvement)
Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 1: Select Diseases/Conditions/Patient Populations 1 A. identify and prioritize high risk/high burden clinical conditions 1 B. identify high priority outcomes and areas of practice within a selected condition Step 2: Identify Evidence-Based Guidelines, Practices 2 A. identify evidence-based clinical practice guidelines and recommendations 2 B. identify evidence-based clinical practices, care models Prioritize recommendations for implementation (based on gap, importance for outcomes, feasibility of improvement)
 Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 3: Measure and Diagnose Quality/Performance Gaps 3 A. measure existing practice patterns and outcomes and identify variations from evidence-based practices and benchmark outcomes (quality, outcome and performance gaps) 3 B. identify determinants of current practices 3 C. diagnose quality gaps 3 D. identify barriers and facilitators to improvement
Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 3: Measure and Diagnose Quality/Performance Gaps 3 A. measure existing practice patterns and outcomes and identify variations from evidence-based practices and benchmark outcomes (quality, outcome and performance gaps) 3 B. identify determinants of current practices 3 C. diagnose quality gaps 3 D. identify barriers and facilitators to improvement
 Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 4: Implement Improvement Programs 4 A. identify implementation/quality improvement strategies, programs and program components or tools (e. g. , via literature reviews, formative evaluation techniques) 4 B. develop implementation/quality improvement strategies, program components or tools 4 C. implement quality improvement strategies and programs Step 5/6: Evaluate Improvement Programs 5. assess improvement program feasibility, implementation and impacts on patient, family and system outcomes 6. assess improvement program impacts on health-related quality of life (HRQOL)
Expanded QUERI Six-Step Process Step 4: Implement Improvement Programs 4 A. identify implementation/quality improvement strategies, programs and program components or tools (e. g. , via literature reviews, formative evaluation techniques) 4 B. develop implementation/quality improvement strategies, program components or tools 4 C. implement quality improvement strategies and programs Step 5/6: Evaluate Improvement Programs 5. assess improvement program feasibility, implementation and impacts on patient, family and system outcomes 6. assess improvement program impacts on health-related quality of life (HRQOL)
 Implementing evidence-based depression treatment model in VA primary care (Example of Clinical-Research Partnerships at VISN- / National-Level)
Implementing evidence-based depression treatment model in VA primary care (Example of Clinical-Research Partnerships at VISN- / National-Level)
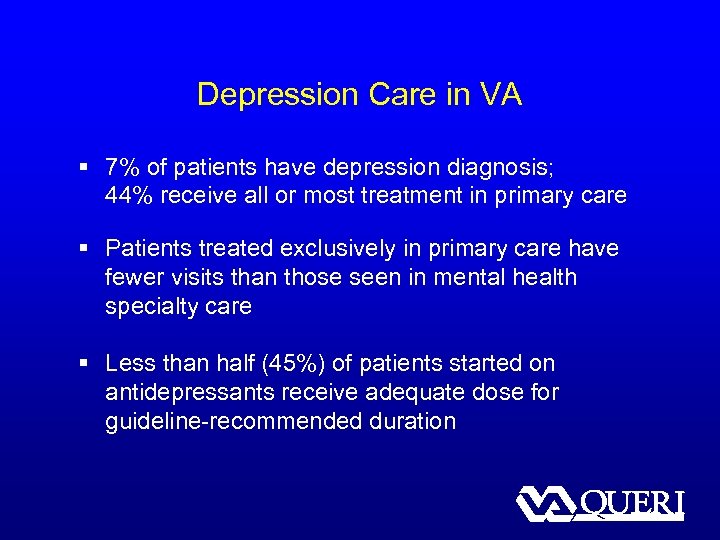 Depression Care in VA § 7% of patients have depression diagnosis; 44% receive all or most treatment in primary care § Patients treated exclusively in primary care have fewer visits than those seen in mental health specialty care § Less than half (45%) of patients started on antidepressants receive adequate dose for guideline-recommended duration
Depression Care in VA § 7% of patients have depression diagnosis; 44% receive all or most treatment in primary care § Patients treated exclusively in primary care have fewer visits than those seen in mental health specialty care § Less than half (45%) of patients started on antidepressants receive adequate dose for guideline-recommended duration
 Collaborative Care for Depression § Integrated package of intervention tools / strategies, including… – Clinician education and decision support – Care management – Active collaboration between primary care and mental health specialists – Patient education and self-management support § Consistent with Chronic Care Model (Wagner)
Collaborative Care for Depression § Integrated package of intervention tools / strategies, including… – Clinician education and decision support – Care management – Active collaboration between primary care and mental health specialists – Patient education and self-management support § Consistent with Chronic Care Model (Wagner)
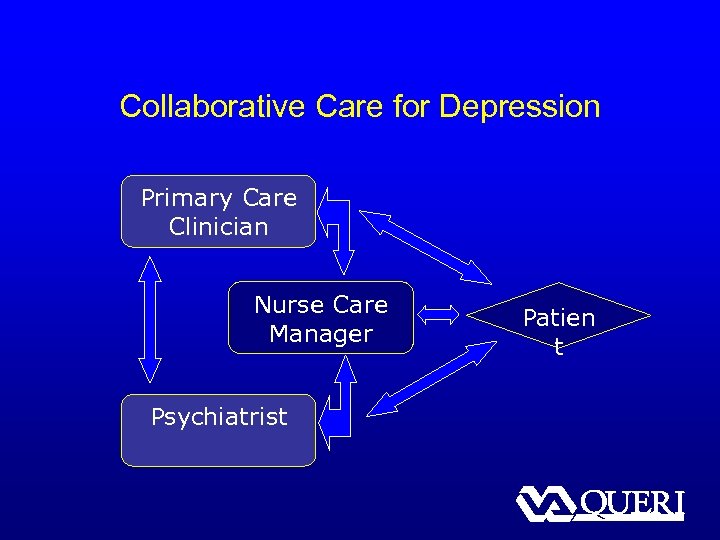 Collaborative Care for Depression Primary Care Clinician Nurse Care Manager Psychiatrist Patien t
Collaborative Care for Depression Primary Care Clinician Nurse Care Manager Psychiatrist Patien t
 Collaborative Care for Depression § Improves depression treatment, symptoms, functioning, work-related outcomes, qualityof-life, and is cost-effective § Achieving the Promise: Transforming Mental Health Care in VA – “Develop… a VA-adapted collaborative care model dissemination package as the basis for national rollout”
Collaborative Care for Depression § Improves depression treatment, symptoms, functioning, work-related outcomes, qualityof-life, and is cost-effective § Achieving the Promise: Transforming Mental Health Care in VA – “Develop… a VA-adapted collaborative care model dissemination package as the basis for national rollout”
 Translating Initiatives for Depression into Effective Solutions (TIDES) § PI’s: Lisa Rubenstein, Ed Chaney § Implement collaborative care for depression in VAMCs from 3 VISNs (VISNs 10, 16 & 23) § Use evidence-based quality improvement (EBQI) processes for tailored implementation § Findings – Patients kept 90% of follow-up appointments – Twice as many patients receiving collaborative care were treatment adherent – Depression symptoms significantly improved at 8 -12 weeks – Improved work/social functioning at 6 months
Translating Initiatives for Depression into Effective Solutions (TIDES) § PI’s: Lisa Rubenstein, Ed Chaney § Implement collaborative care for depression in VAMCs from 3 VISNs (VISNs 10, 16 & 23) § Use evidence-based quality improvement (EBQI) processes for tailored implementation § Findings – Patients kept 90% of follow-up appointments – Twice as many patients receiving collaborative care were treatment adherent – Depression symptoms significantly improved at 8 -12 weeks – Improved work/social functioning at 6 months
 Regional TIDES Spread (Re. TIDES) § PI’s: Rubenstein, Chaney § Sustainability in 1 st generation TIDES sites (VISNs 10, 16, 23) § Spread collaborative care to new sites (VISN 22) § Evaluate impact of implementation on patient care, clinical outcomes, and costs § Build and leverage system support for further spread
Regional TIDES Spread (Re. TIDES) § PI’s: Rubenstein, Chaney § Sustainability in 1 st generation TIDES sites (VISNs 10, 16, 23) § Spread collaborative care to new sites (VISN 22) § Evaluate impact of implementation on patient care, clinical outcomes, and costs § Build and leverage system support for further spread
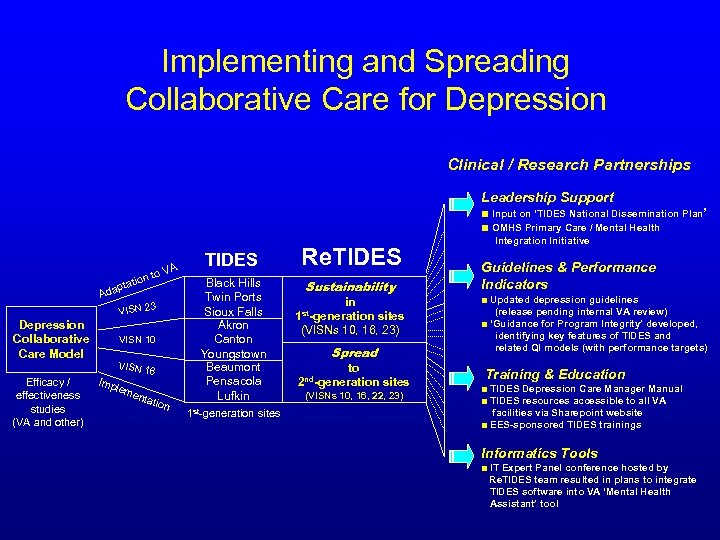 Implementing and Spreading Collaborative Care for Depression Clinical / Research Partnerships Leadership Support ■ Input on ‘TIDES National Dissemination Plan’ ■ OMHS Primary Care / Mental Health A i ptat Ada o. V on t VISN 23 Depression Collaborative Care Model Efficacy / effectiveness studies (VA and other) VISN 10 VISN 1 Imp 6 lem enta tion TIDES Black Hills Twin Ports Sioux Falls Akron Canton Youngstown Beaumont Pensacola Lufkin 1 st-generation sites Re. TIDES Sustainability in st-generation sites 1 (VISNs 10, 16, 23) Spread to 2 nd-generation sites (VISNs 10, 16, 22, 23) Integration Initiative Guidelines & Performance Indicators ■ Updated depression guidelines (release pending internal VA review) ■ ‘Guidance for Program Integrity’ developed, identifying key features of TIDES and related QI models (with performance targets) Training & Education ■ TIDES Depression Care Manager Manual ■ TIDES resources accessible to all VA facilities via Sharepoint website ■ EES-sponsored TIDES trainings Informatics Tools ■ IT Expert Panel conference hosted by Re. TIDES team resulted in plans to integrate TIDES software into VA ‘Mental Health Assistant’ tool
Implementing and Spreading Collaborative Care for Depression Clinical / Research Partnerships Leadership Support ■ Input on ‘TIDES National Dissemination Plan’ ■ OMHS Primary Care / Mental Health A i ptat Ada o. V on t VISN 23 Depression Collaborative Care Model Efficacy / effectiveness studies (VA and other) VISN 10 VISN 1 Imp 6 lem enta tion TIDES Black Hills Twin Ports Sioux Falls Akron Canton Youngstown Beaumont Pensacola Lufkin 1 st-generation sites Re. TIDES Sustainability in st-generation sites 1 (VISNs 10, 16, 23) Spread to 2 nd-generation sites (VISNs 10, 16, 22, 23) Integration Initiative Guidelines & Performance Indicators ■ Updated depression guidelines (release pending internal VA review) ■ ‘Guidance for Program Integrity’ developed, identifying key features of TIDES and related QI models (with performance targets) Training & Education ■ TIDES Depression Care Manager Manual ■ TIDES resources accessible to all VA facilities via Sharepoint website ■ EES-sponsored TIDES trainings Informatics Tools ■ IT Expert Panel conference hosted by Re. TIDES team resulted in plans to integrate TIDES software into VA ‘Mental Health Assistant’ tool
 Improving metabolic side effect monitoring for veterans taking antipsychotic medications (Example of Clinical-Research Partnership at VISN- / Facility-Level)
Improving metabolic side effect monitoring for veterans taking antipsychotic medications (Example of Clinical-Research Partnership at VISN- / Facility-Level)
 Background • Psychotic disorders highly disabling and burdensome in VA – 1. 3% prevalence of schizophrenia; over 90, 000 vets treated annually – Vets w/ schizophrenia account for 12% of annual VA healthcare costs • Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) are a key component of treatment – Prescribed to over 80% of veterans with psychosis • SGAs can cause adverse metabolic side effects – Weight gain – Diabetes – Dyslipidemia • VA guidelines and ADA/APA consensus statement recommend monitoring and management of metabolic side effects for patients started on new antipsychotic
Background • Psychotic disorders highly disabling and burdensome in VA – 1. 3% prevalence of schizophrenia; over 90, 000 vets treated annually – Vets w/ schizophrenia account for 12% of annual VA healthcare costs • Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) are a key component of treatment – Prescribed to over 80% of veterans with psychosis • SGAs can cause adverse metabolic side effects – Weight gain – Diabetes – Dyslipidemia • VA guidelines and ADA/APA consensus statement recommend monitoring and management of metabolic side effects for patients started on new antipsychotic
 A Study of Strategies to Improve Schizophrenia Treatment (ASSIST) § Objectives: Develop and test intervention strategies/tools to improve metabolic side effect monitoring for patients taking APs • Increase baseline monitoring for weight gain, diabetes onset, dyslipidemia § ASSIST Tools / Strategies • Educational tools (for clinicians and patients) • Clinical support tools • Pocket-sized booklet with AP side effect monitoring recommendations • CPRS clinical reminder for side effect monitoring • Performance monitoring tools • Monthly site-level performance reports • Weekly provider-specific feedback on side effect monitoring • Facilitated Team QI and Opinion Leader strategies
A Study of Strategies to Improve Schizophrenia Treatment (ASSIST) § Objectives: Develop and test intervention strategies/tools to improve metabolic side effect monitoring for patients taking APs • Increase baseline monitoring for weight gain, diabetes onset, dyslipidemia § ASSIST Tools / Strategies • Educational tools (for clinicians and patients) • Clinical support tools • Pocket-sized booklet with AP side effect monitoring recommendations • CPRS clinical reminder for side effect monitoring • Performance monitoring tools • Monthly site-level performance reports • Weekly provider-specific feedback on side effect monitoring • Facilitated Team QI and Opinion Leader strategies
 External Facilitation in ASSIST • Facilitator – Maintained regular contact w/ local QI team • Email communication • Participate in monthly ASSIST Team meetings – Monitored implementation of project tools/strategies; performance on AP side effect monitoring and dosing – Identified and problem-solved barriers to implementation – Assisted in adapting tools/strategies as needed or suggested by local QI team to meet project goals
External Facilitation in ASSIST • Facilitator – Maintained regular contact w/ local QI team • Email communication • Participate in monthly ASSIST Team meetings – Monitored implementation of project tools/strategies; performance on AP side effect monitoring and dosing – Identified and problem-solved barriers to implementation – Assisted in adapting tools/strategies as needed or suggested by local QI team to meet project goals
 External Facilitation ‘Products’ (Facility A) • Collaborative research-clinical partnership • Placement of recommendations for antipsychotic side effect monitoring on medication order screens • Enhanced monthly performance reports, tailored to clinician preferences and specifications • Development of weekly reporting system identifying patients in need of metabolic side effect monitoring – Provider name, patient identifier, AP fill date, medication name, info on monitoring parameters – Now fully automated
External Facilitation ‘Products’ (Facility A) • Collaborative research-clinical partnership • Placement of recommendations for antipsychotic side effect monitoring on medication order screens • Enhanced monthly performance reports, tailored to clinician preferences and specifications • Development of weekly reporting system identifying patients in need of metabolic side effect monitoring – Provider name, patient identifier, AP fill date, medication name, info on monitoring parameters – Now fully automated
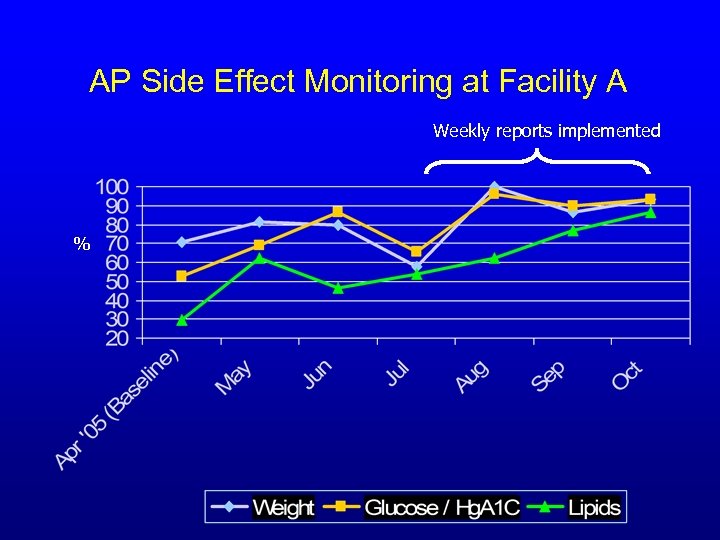 AP Side Effect Monitoring at Facility A Weekly reports implemented %
AP Side Effect Monitoring at Facility A Weekly reports implemented %
 VISN 16 Performance Measures – FY 06
VISN 16 Performance Measures – FY 06
 Clinical-Research Partnerships: Barriers and Opportunities
Clinical-Research Partnerships: Barriers and Opportunities
 Barriers to “Clinical-Research Partnerships” • As part of the Re. TIDES project, we interviewed 26 VHA leaders and key staff about perspectives on EBP implementation. • Barriers: – Research takes too long – Research isn’t practical • Researchers’ pursue their own career goals • Research tends to focus on single diseases – Managers have to balance available evidence with clinical needs
Barriers to “Clinical-Research Partnerships” • As part of the Re. TIDES project, we interviewed 26 VHA leaders and key staff about perspectives on EBP implementation. • Barriers: – Research takes too long – Research isn’t practical • Researchers’ pursue their own career goals • Research tends to focus on single diseases – Managers have to balance available evidence with clinical needs
 Opportunities for Enhanced Collaboration and Partnerships • QUERI centers and other initiatives to bridge the gap, while being recognized for their impact, haven’t solved the problem • Clinical-research partnership should include early and active involvement of managers in research prioritization and design • Clinical-research partnership should include capacity for rapid research response to high priority needs of managers
Opportunities for Enhanced Collaboration and Partnerships • QUERI centers and other initiatives to bridge the gap, while being recognized for their impact, haven’t solved the problem • Clinical-research partnership should include early and active involvement of managers in research prioritization and design • Clinical-research partnership should include capacity for rapid research response to high priority needs of managers
 QUESTIONS? Contact: Rick Owen (Richard. Owen 2@va. gov) Jeff Smith (Jeffrey. Smith 6@va. gov) VA Mental Health QUERI http: //www. queri. research. va. gov/mh/default. cfm
QUESTIONS? Contact: Rick Owen (Richard. Owen 2@va. gov) Jeff Smith (Jeffrey. Smith 6@va. gov) VA Mental Health QUERI http: //www. queri. research. va. gov/mh/default. cfm


