54c1f4a0d018f3f3f495c40b2f52d66f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Introduction to Project Management Project Planning Overview Lecture a This material (Comp 19_Unit 4 a) was developed by Johns Hopkins University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology under Award Number IU 24 OC 000013.
Introduction to Project Management Project Planning Overview Lecture a This material (Comp 19_Unit 4 a) was developed by Johns Hopkins University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology under Award Number IU 24 OC 000013.
 Project Planning Overview Learning Objectives—Lecture a • Identify the importance and purpose of effective planning. • Identify and describe each component of the project management plan. • Define and prepare project planning documents. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 2
Project Planning Overview Learning Objectives—Lecture a • Identify the importance and purpose of effective planning. • Identify and describe each component of the project management plan. • Define and prepare project planning documents. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 2
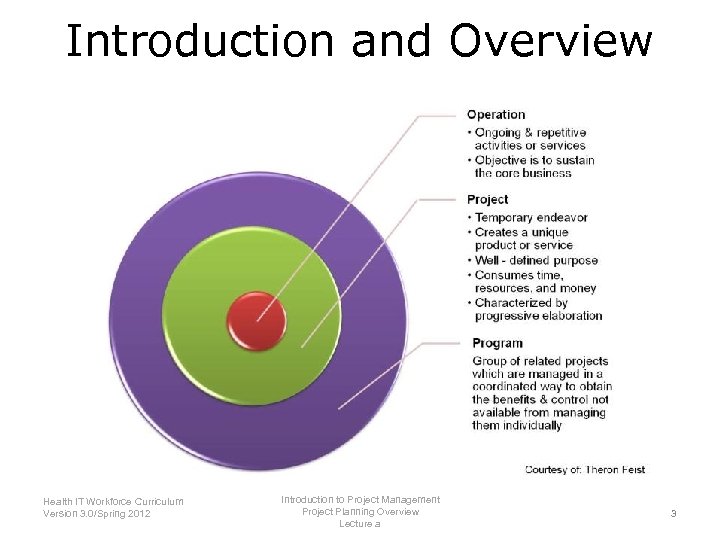 Introduction and Overview Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 3
Introduction and Overview Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 3
 Why Are Projects Initiated? The reasons for selecting a project may include, but are not limited to: • Customer requests • Market demand • Organizational need • Legal requirement • Technological advance • Social needs Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 4
Why Are Projects Initiated? The reasons for selecting a project may include, but are not limited to: • Customer requests • Market demand • Organizational need • Legal requirement • Technological advance • Social needs Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 4
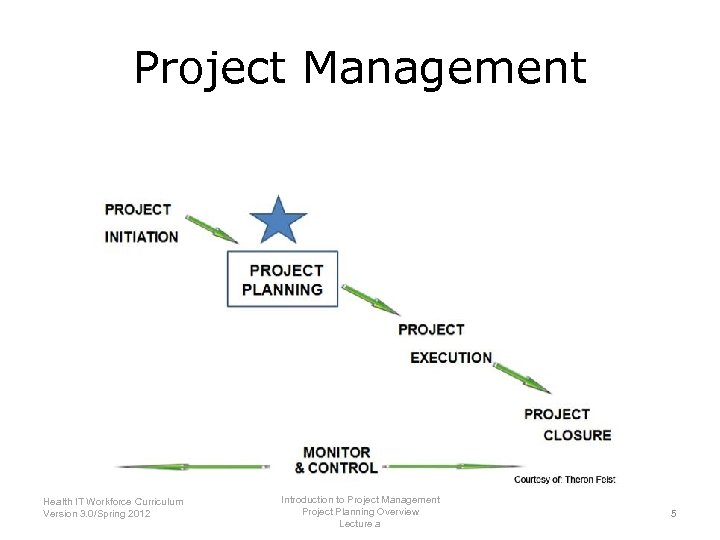 Project Management Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 5
Project Management Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 5
 Five Process Groups Initiating – Define a new project or new phase of an existing project Planning – Define the scope and objectives of the project – Develop plans to accomplish the objectives. Executing – Accomplish the work of the project and satisfy the project objectives. Monitoring & Controlling – Tracking, reviewing, and controlling progress and performance – Identify required changes – Preventive or corrective steps Closing – Finalize all activities – Formally close the project or phase. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 6
Five Process Groups Initiating – Define a new project or new phase of an existing project Planning – Define the scope and objectives of the project – Develop plans to accomplish the objectives. Executing – Accomplish the work of the project and satisfy the project objectives. Monitoring & Controlling – Tracking, reviewing, and controlling progress and performance – Identify required changes – Preventive or corrective steps Closing – Finalize all activities – Formally close the project or phase. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 6
 Planning a Project Activities during project planning include, but not limited to: • • • Collecting requirements Defining project scope Developing a project management plan Defining activities Creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) Developing a schedule Identifying and assessing risks Developing risk response plans Developing a communications management plan Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 7
Planning a Project Activities during project planning include, but not limited to: • • • Collecting requirements Defining project scope Developing a project management plan Defining activities Creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) Developing a schedule Identifying and assessing risks Developing risk response plans Developing a communications management plan Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 7
 Planning a Project • • • Estimate costs Determine the budget Make procurement decisions Estimate resource requirements Define project roles & responsibilities Develop a communications management plan Determine how performance will be measured Plan quality Conduct a kickoff meeting Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 8
Planning a Project • • • Estimate costs Determine the budget Make procurement decisions Estimate resource requirements Define project roles & responsibilities Develop a communications management plan Determine how performance will be measured Plan quality Conduct a kickoff meeting Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 8
 Factors That Lead to Project Success or Project Failure Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 9
Factors That Lead to Project Success or Project Failure Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 9
 Learning Activity: Project Success • Reflect on a project you have worked on that you consider successful. • List five contributing factors that led to that success. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 10
Learning Activity: Project Success • Reflect on a project you have worked on that you consider successful. • List five contributing factors that led to that success. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 10
 Project Success A project is successful: • If it is completed on time • If it is finished within its budget • If it produces deliverables that meet customer’s expectations Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 11
Project Success A project is successful: • If it is completed on time • If it is finished within its budget • If it produces deliverables that meet customer’s expectations Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 11
 Attributes of a Successful Project Success factors include, but are not limited to: • Proper project documentation • Clearly defined and assigned roles & responsibilities • Senior management or executive support • Stakeholder buy-in • Periodic team meetings held • Periodic meetings with the customer • Competent project manager & team Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 12
Attributes of a Successful Project Success factors include, but are not limited to: • Proper project documentation • Clearly defined and assigned roles & responsibilities • Senior management or executive support • Stakeholder buy-in • Periodic team meetings held • Periodic meetings with the customer • Competent project manager & team Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 12
 Attributes of a Successful Project • Risks are identified, assessed for severity and impact, and a risk response plan exists • Project baselines (schedule, budget, scope) • Project is monitored & controlled • Change control system • Well-defined scope • Effective communication • Acceptance criteria is documented & understood • Team members understand the criteria for measuring project success Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 13
Attributes of a Successful Project • Risks are identified, assessed for severity and impact, and a risk response plan exists • Project baselines (schedule, budget, scope) • Project is monitored & controlled • Change control system • Well-defined scope • Effective communication • Acceptance criteria is documented & understood • Team members understand the criteria for measuring project success Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 13
 Learning Activity: Project Failure • Reflect on a project you have worked on that was not successful. • List five contributing factors that led to the project’s failure. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 14
Learning Activity: Project Failure • Reflect on a project you have worked on that was not successful. • List five contributing factors that led to the project’s failure. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 14
 Factors Leading to Project Failure Factors leading to failure include, but are not limited to: • Poor project communications • Not managing stakeholder expectations • Inadequate & insufficient project planning • Lack of project documentation (charter, project management plan, etc), • Lack of stakeholder buy-in • Lack of management support • Resource constraints (human resources are unavailable when needed & / or incompetent) • Unrealistic schedule • Poor risk management (risks not identified or assessed, and lack of, or poorly prepared risk response plans) Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 15
Factors Leading to Project Failure Factors leading to failure include, but are not limited to: • Poor project communications • Not managing stakeholder expectations • Inadequate & insufficient project planning • Lack of project documentation (charter, project management plan, etc), • Lack of stakeholder buy-in • Lack of management support • Resource constraints (human resources are unavailable when needed & / or incompetent) • Unrealistic schedule • Poor risk management (risks not identified or assessed, and lack of, or poorly prepared risk response plans) Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 15
 Factors Leading to Project Failure Factors leading to failure include, but are not limited to (cont. ): • Unnecessary & / or unapproved scope changes • Lack of a change control management • Not using or improperly following change procedures • Not following the project management plan • Poor project monitoring & controlling • Continuously gathering requirements • Requirements that are poorly defined and are not understood • Undefined or poorly defined scope • Over-optimistic or unrealistic assumptions • Unclear project roles & responsibilities Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 16
Factors Leading to Project Failure Factors leading to failure include, but are not limited to (cont. ): • Unnecessary & / or unapproved scope changes • Lack of a change control management • Not using or improperly following change procedures • Not following the project management plan • Poor project monitoring & controlling • Continuously gathering requirements • Requirements that are poorly defined and are not understood • Undefined or poorly defined scope • Over-optimistic or unrealistic assumptions • Unclear project roles & responsibilities Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 16
 Project Managers’ Roles & Responsibilities in Project Planning Project managers plan, lead, and control project activities. Their responsibilities include, but are not limited to: • • • Identifying & documenting project requirements Identifying team members Establishing clear & obtainable project objectives Understanding stakeholders’ expectations Preventing unnecessary scope changes Monitoring & measuring project progress Communicating project performance & progress Ensuring team understands project objectives Working with team in developing project plans Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 17
Project Managers’ Roles & Responsibilities in Project Planning Project managers plan, lead, and control project activities. Their responsibilities include, but are not limited to: • • • Identifying & documenting project requirements Identifying team members Establishing clear & obtainable project objectives Understanding stakeholders’ expectations Preventing unnecessary scope changes Monitoring & measuring project progress Communicating project performance & progress Ensuring team understands project objectives Working with team in developing project plans Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 17
 PMBOK® Guide Knowledge Areas Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 18
PMBOK® Guide Knowledge Areas Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 18
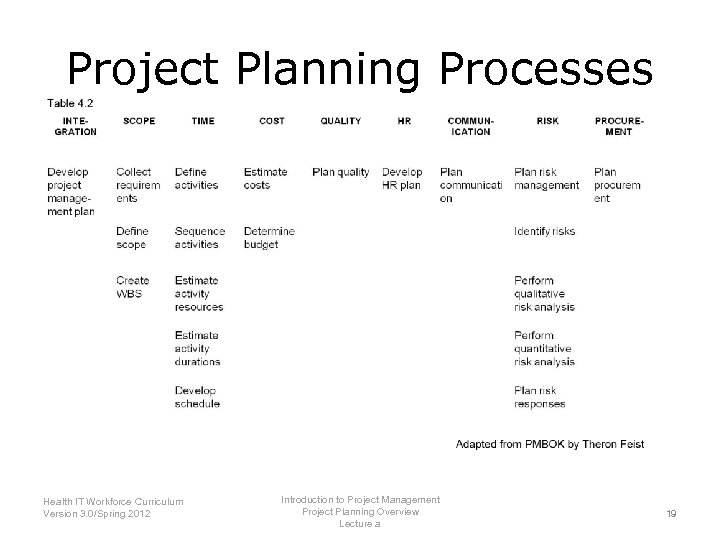 Project Planning Processes Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 19
Project Planning Processes Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 19
 Planning for Project Integration Management During project planning the project team develops a project management plan. This comprehensive document is the “master plan” for the project and is used by the project team to guide them through project execution. Although it is finalized and approved in planning, the document is continuously updated when new information is acquired as the project is executed and controlled. Project Integration Planning Process: Develop Project Management Plan Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 20
Planning for Project Integration Management During project planning the project team develops a project management plan. This comprehensive document is the “master plan” for the project and is used by the project team to guide them through project execution. Although it is finalized and approved in planning, the document is continuously updated when new information is acquired as the project is executed and controlled. Project Integration Planning Process: Develop Project Management Plan Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 20
 What Is the Project Management Plan? A project management plan is a comprehensive and essential document that: • Provides a justification for the project being undertaken • Captures the project objectives • Describes the approach for managing the project • Summarizes what the project must accomplish, how the work will be performed, who will perform the work, and how the work will be measured, monitored, and controlled Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 21
What Is the Project Management Plan? A project management plan is a comprehensive and essential document that: • Provides a justification for the project being undertaken • Captures the project objectives • Describes the approach for managing the project • Summarizes what the project must accomplish, how the work will be performed, who will perform the work, and how the work will be measured, monitored, and controlled Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 21
 How Is the Project Management Plan Developed? • Collaborative effort between the project manager and project team members is important. Teams’ participation in the developing this plan is beneficial because it helps strengthen their commitment to the project. The overall effort is aimed at developing a plan that can be followed to successfully accomplish the project objectives. • In addition to SME input, the project charter, outputs from planning processes, enterprise environmental factors, and organizational process assets are used to develop the project management plan. • The plan evolves in incremental steps in an ongoing process known as progressive elaboration. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 22
How Is the Project Management Plan Developed? • Collaborative effort between the project manager and project team members is important. Teams’ participation in the developing this plan is beneficial because it helps strengthen their commitment to the project. The overall effort is aimed at developing a plan that can be followed to successfully accomplish the project objectives. • In addition to SME input, the project charter, outputs from planning processes, enterprise environmental factors, and organizational process assets are used to develop the project management plan. • The plan evolves in incremental steps in an ongoing process known as progressive elaboration. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 22
 What Essential Information Is in a Project Management Plan? Cumulative document containing: • Scope management plan • Requirements management plan • Schedule management plan • Cost management plan • Quality management plan • Process improvement plan • HR management plan • Communication management plan • Risk management plan • Procurement management plan • Change management plan • Cost, schedule, performance, and scope baselines Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 23
What Essential Information Is in a Project Management Plan? Cumulative document containing: • Scope management plan • Requirements management plan • Schedule management plan • Cost management plan • Quality management plan • Process improvement plan • HR management plan • Communication management plan • Risk management plan • Procurement management plan • Change management plan • Cost, schedule, performance, and scope baselines Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 23
 How Is the Project Management Plan Used? • Roadmap used by the project team members to guide them through project execution • Serves as a communication document for stakeholders to inform them as to how the project will be performed and managed • Integrates strategic & other planning processes into a consistent & coherent document Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 24
How Is the Project Management Plan Used? • Roadmap used by the project team members to guide them through project execution • Serves as a communication document for stakeholders to inform them as to how the project will be performed and managed • Integrates strategic & other planning processes into a consistent & coherent document Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 24
 Planning for Project Scope Management Planning Processes: • Collect requirements • Create a project scope statement • Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 25
Planning for Project Scope Management Planning Processes: • Collect requirements • Create a project scope statement • Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 25
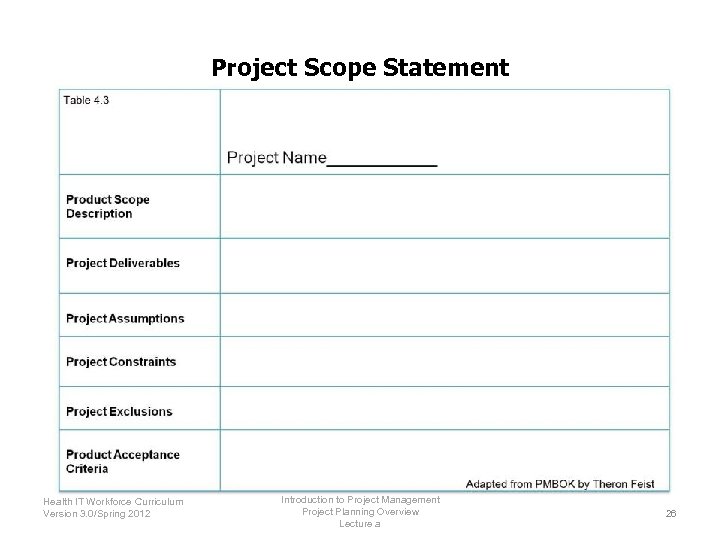 Project Scope Statement Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 26
Project Scope Statement Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 26
 Project Planning Overview Summary—Lecture a We have reviewed the need for effective planning in health IT projects, and have detailed the components and purposes of the project management plan. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 27
Project Planning Overview Summary—Lecture a We have reviewed the need for effective planning in health IT projects, and have detailed the components and purposes of the project management plan. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture a 27
 Project Planning Overview References—Lecture a References • Health Information and Management System Society. Chicago, IL. 2010. Available from: http: //www. himss. org • Highsmith JA. (2009). Agile Project Management: Creating Innovative Products. 2 nd ed. ; Boston: Addison-Wesley. • HITECH Answers. 2010. Available from: http: //hitechanswers. net/ • Houston S, Bove LA. (2010) Project Management for Healthcare Informatics. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, LLC. • Kerzner H. (2009) Project Management: a Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling. 10 th ed. Hoboken, NJ. : Wiley. m. Health Initiative. Boston, MA. 2009. Available from: http: //www. mobih. org/ • Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. 4 th ed (2008). Newtown Square, PA: PMI. • Scwalbe K. (2009) Information Technology Project Management (with Microsoft Project 2007 CD-ROM). 6 th ed. ; Boston: Cenage Learning. • Stackpole C. (2009). A Project Manager’s Book of Forms: A Companion to the PMBOK Guide. Hoboken, N. J. : Wiley; • Whitten N. Neal (2007). Whitten's Let's Talk! More No-nonsense Advice for Project Success. Vienna, VA. : Management Concepts Inc. • Wiefling K. (2007) Scrappy Project Management: The 12 Predictable and Avoidable Pitfalls Every Project Faces 1 st ed. Happy About; • Wysocki, RK. (2009). Effective Project Management: traditional, agile, extreme. 5 th Edition. New York: Wiley. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture b 28
Project Planning Overview References—Lecture a References • Health Information and Management System Society. Chicago, IL. 2010. Available from: http: //www. himss. org • Highsmith JA. (2009). Agile Project Management: Creating Innovative Products. 2 nd ed. ; Boston: Addison-Wesley. • HITECH Answers. 2010. Available from: http: //hitechanswers. net/ • Houston S, Bove LA. (2010) Project Management for Healthcare Informatics. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, LLC. • Kerzner H. (2009) Project Management: a Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling. 10 th ed. Hoboken, NJ. : Wiley. m. Health Initiative. Boston, MA. 2009. Available from: http: //www. mobih. org/ • Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. 4 th ed (2008). Newtown Square, PA: PMI. • Scwalbe K. (2009) Information Technology Project Management (with Microsoft Project 2007 CD-ROM). 6 th ed. ; Boston: Cenage Learning. • Stackpole C. (2009). A Project Manager’s Book of Forms: A Companion to the PMBOK Guide. Hoboken, N. J. : Wiley; • Whitten N. Neal (2007). Whitten's Let's Talk! More No-nonsense Advice for Project Success. Vienna, VA. : Management Concepts Inc. • Wiefling K. (2007) Scrappy Project Management: The 12 Predictable and Avoidable Pitfalls Every Project Faces 1 st ed. Happy About; • Wysocki, RK. (2009). Effective Project Management: traditional, agile, extreme. 5 th Edition. New York: Wiley. Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture b 28
 Project Planning Overview References—Lecture a Tables, Charts, Figures Table 4. 1. Knowledge Areas. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Table 4. 2. Project Planning Process. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Table 4. 3 Project Scope Statement. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Images Slide 3: An Overview of Project management detailing Projects, Operations and Programs. Courtesy of Theron Feist Slide 5: Project Planning. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Slide 9: The Hindenberg. Creative Commons: Wikipedia. Available from: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Hindenburg_disaster Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture b 29
Project Planning Overview References—Lecture a Tables, Charts, Figures Table 4. 1. Knowledge Areas. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Table 4. 2. Project Planning Process. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Table 4. 3 Project Scope Statement. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Images Slide 3: An Overview of Project management detailing Projects, Operations and Programs. Courtesy of Theron Feist Slide 5: Project Planning. Courtesy of Theron Feist. Slide 9: The Hindenberg. Creative Commons: Wikipedia. Available from: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Hindenburg_disaster Introduction to Project Management Health IT Workforce Curriculum Project Planning Overview Version 3. 0/Spring 2012 Lecture b 29


