f356ecd2293edd23e8861d9479a388b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 INTRODUCTION TO PC ARCHITECTURE
INTRODUCTION TO PC ARCHITECTURE
 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER 5 main components Motherboard The central processing unit ( CPU ) Memory I/O ports Hard Disc
MAIN COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER 5 main components Motherboard The central processing unit ( CPU ) Memory I/O ports Hard Disc
 MOTHERBOARD
MOTHERBOARD
 MOTHERBOARDS A big, flat circuit board that covers the entire floor of the PC casing. The heart of the computer as all of its connections leading out from itself into every device in the machine Everything has to be compatible to it. The motherboard design fixes the maximum speed of CPU that you can use.
MOTHERBOARDS A big, flat circuit board that covers the entire floor of the PC casing. The heart of the computer as all of its connections leading out from itself into every device in the machine Everything has to be compatible to it. The motherboard design fixes the maximum speed of CPU that you can use.
 CPU
CPU
 CPU Now CPU is the ‘brain’ of the computer It processes data and coordinate tasks among different components works in direct harmony if the motherboard has a slow bus speed, it will reduce the performance of new processor that has better speed. NOTE: BUS • collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another. You can think of a bus as a highway on which data travels within a computer • Every bus has a clock speed measured in MHz.
CPU Now CPU is the ‘brain’ of the computer It processes data and coordinate tasks among different components works in direct harmony if the motherboard has a slow bus speed, it will reduce the performance of new processor that has better speed. NOTE: BUS • collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another. You can think of a bus as a highway on which data travels within a computer • Every bus has a clock speed measured in MHz.
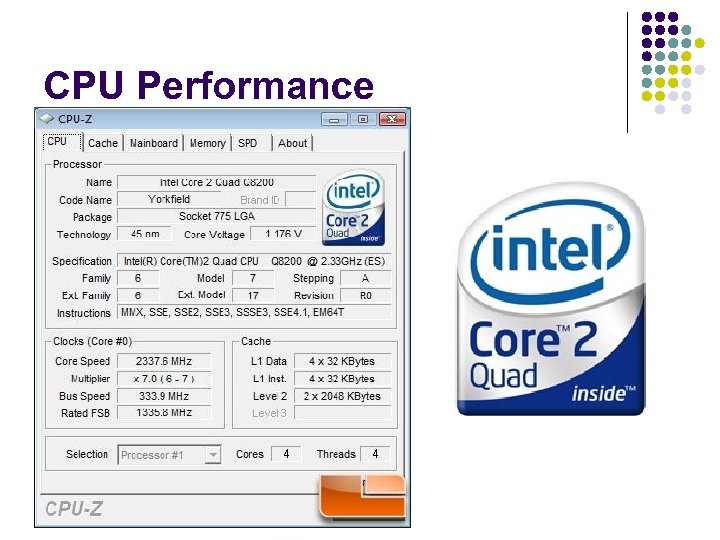 CPU Performance
CPU Performance
 CPU performance CPU speed is not a reliable indicator of CPU performance. Many factors inside and outside of the CPU exert a significant impact on CPU performance, and on overall system performance. CPU speed is measure in megahertz. A 1 MHz CPU = 1 million cycles per second.
CPU performance CPU speed is not a reliable indicator of CPU performance. Many factors inside and outside of the CPU exert a significant impact on CPU performance, and on overall system performance. CPU speed is measure in megahertz. A 1 MHz CPU = 1 million cycles per second.
 CPU performance – c’tnd Does this mean that a 2 MHz CPU is twice as fast as a 1 Mhz CPU? Not necessarily. This depends on how much work each CPU accomplishes in each clock cycle. The 1 MHz CPU might very well be faster, in practice, than the 2 Mhz CPU - if it is more efficient or can process more tasks in each CPU cycle.
CPU performance – c’tnd Does this mean that a 2 MHz CPU is twice as fast as a 1 Mhz CPU? Not necessarily. This depends on how much work each CPU accomplishes in each clock cycle. The 1 MHz CPU might very well be faster, in practice, than the 2 Mhz CPU - if it is more efficient or can process more tasks in each CPU cycle.
 CPU - The Cache The purpose of a cache is to enable the CPU to access recently used information very quickly and will significantly affect CPU performance. Some caches are bigger than others. A typical L 1 cache is 256 Kb and a typical L 2 cache is 1 MB. Generally speaking, the larger the cache, the better the system performance boost. However, this is not always the case. A cache operates at a certain speed, just like the core of the CPU. Some caches operate at the full speed of the CPU, while others operate at half that speed or less.
CPU - The Cache The purpose of a cache is to enable the CPU to access recently used information very quickly and will significantly affect CPU performance. Some caches are bigger than others. A typical L 1 cache is 256 Kb and a typical L 2 cache is 1 MB. Generally speaking, the larger the cache, the better the system performance boost. However, this is not always the case. A cache operates at a certain speed, just like the core of the CPU. Some caches operate at the full speed of the CPU, while others operate at half that speed or less.
 The Front Side Bus (FSB) is the connection between the CPU and system memory. The Front Side Bus operates at a speed which is a percentage of the CPU clock speed. The faster the speed at which the Front Side Bus allows data transfer, the better the performance of the CPU.
The Front Side Bus (FSB) is the connection between the CPU and system memory. The Front Side Bus operates at a speed which is a percentage of the CPU clock speed. The faster the speed at which the Front Side Bus allows data transfer, the better the performance of the CPU.
 CPU - System Memory RAM has an access speed. Faster RAM will mean the CPU has to wait less often for data. This will, effectively, make the CPU faster.
CPU - System Memory RAM has an access speed. Faster RAM will mean the CPU has to wait less often for data. This will, effectively, make the CPU faster.
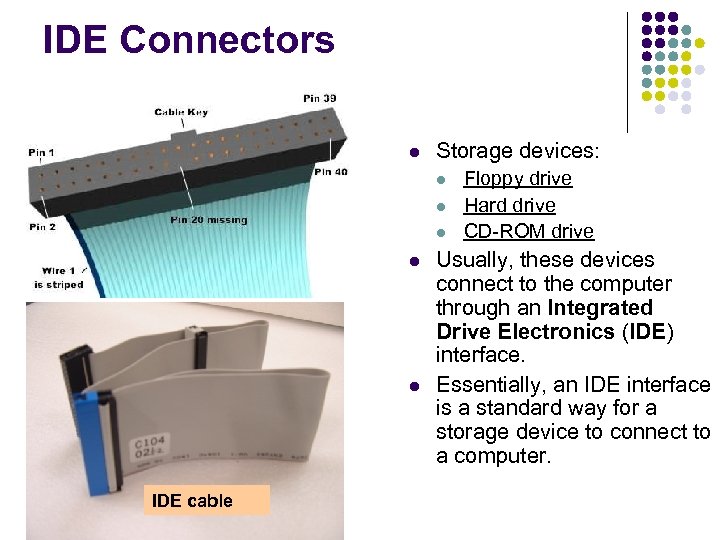 IDE Connectors Storage devices: IDE cable Floppy drive Hard drive CD-ROM drive Usually, these devices connect to the computer through an Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. Essentially, an IDE interface is a standard way for a storage device to connect to a computer.
IDE Connectors Storage devices: IDE cable Floppy drive Hard drive CD-ROM drive Usually, these devices connect to the computer through an Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. Essentially, an IDE interface is a standard way for a storage device to connect to a computer.
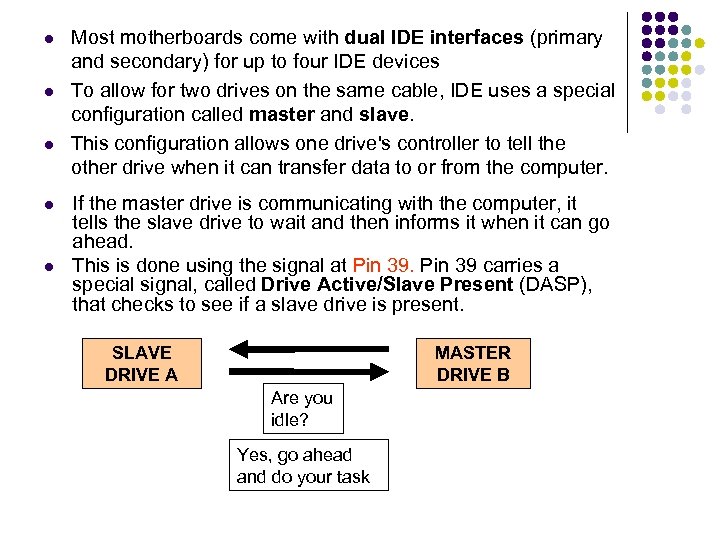 Most motherboards come with dual IDE interfaces (primary and secondary) for up to four IDE devices To allow for two drives on the same cable, IDE uses a special configuration called master and slave. This configuration allows one drive's controller to tell the other drive when it can transfer data to or from the computer. If the master drive is communicating with the computer, it tells the slave drive to wait and then informs it when it can go ahead. This is done using the signal at Pin 39 carries a special signal, called Drive Active/Slave Present (DASP), that checks to see if a slave drive is present. SLAVE DRIVE A MASTER DRIVE B Are you idle? Yes, go ahead and do your task
Most motherboards come with dual IDE interfaces (primary and secondary) for up to four IDE devices To allow for two drives on the same cable, IDE uses a special configuration called master and slave. This configuration allows one drive's controller to tell the other drive when it can transfer data to or from the computer. If the master drive is communicating with the computer, it tells the slave drive to wait and then informs it when it can go ahead. This is done using the signal at Pin 39 carries a special signal, called Drive Active/Slave Present (DASP), that checks to see if a slave drive is present. SLAVE DRIVE A MASTER DRIVE B Are you idle? Yes, go ahead and do your task
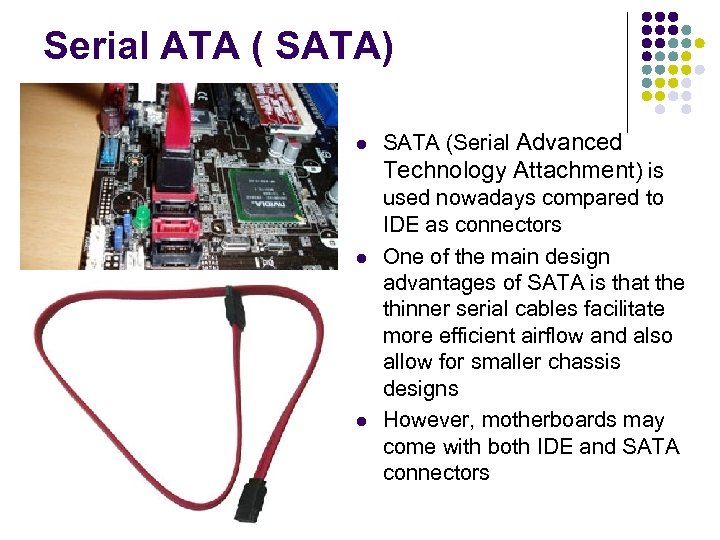 Serial ATA ( SATA) SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is used nowadays compared to IDE as connectors One of the main design advantages of SATA is that the thinner serial cables facilitate more efficient airflow and also allow for smaller chassis designs However, motherboards may come with both IDE and SATA connectors
Serial ATA ( SATA) SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is used nowadays compared to IDE as connectors One of the main design advantages of SATA is that the thinner serial cables facilitate more efficient airflow and also allow for smaller chassis designs However, motherboards may come with both IDE and SATA connectors
 MEMORY
MEMORY
 Two types of memory Random Access Memory (RAM) Temporary storage of the data takes place. The data in RAM will be lost when the PC is shut down Dynamic RAM and Static RAM Function: Read and Write Read Only Memory (ROM) Holds certain coding or information that controls certain things about the computer system. The content WILL NOT be cleared when the PC is shut down. Function: Read
Two types of memory Random Access Memory (RAM) Temporary storage of the data takes place. The data in RAM will be lost when the PC is shut down Dynamic RAM and Static RAM Function: Read and Write Read Only Memory (ROM) Holds certain coding or information that controls certain things about the computer system. The content WILL NOT be cleared when the PC is shut down. Function: Read
 I/O PORTS
I/O PORTS
 I/O Ports This covers all the socket especially at the back of the PC The intention of these ports are to plug in external hardware such as a printer or a mouse into your PC They work, for the most part, by being connected into the motherboard.
I/O Ports This covers all the socket especially at the back of the PC The intention of these ports are to plug in external hardware such as a printer or a mouse into your PC They work, for the most part, by being connected into the motherboard.
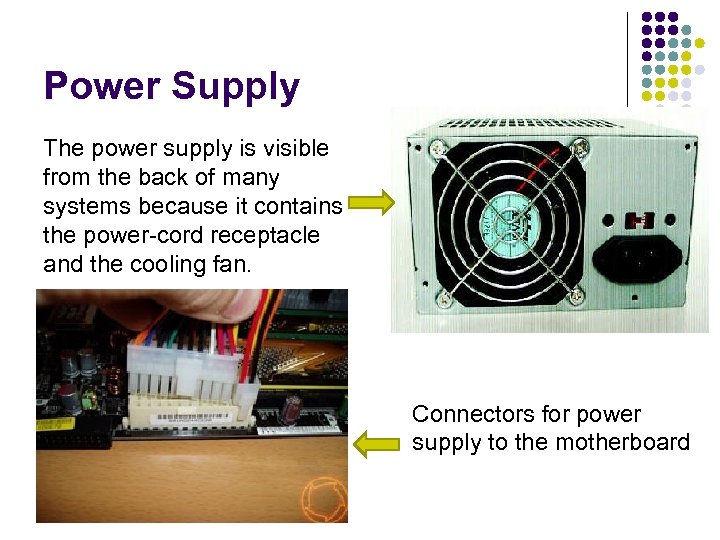 Power Supply The power supply is visible from the back of many systems because it contains the power-cord receptacle and the cooling fan. Connectors for power supply to the motherboard
Power Supply The power supply is visible from the back of many systems because it contains the power-cord receptacle and the cooling fan. Connectors for power supply to the motherboard
 HARD DISC
HARD DISC
 HARD DISC The main storage device, where it holds huge programs and file sizes. So, the bigger, the better. It stores data by magnetizing each section of the disc.
HARD DISC The main storage device, where it holds huge programs and file sizes. So, the bigger, the better. It stores data by magnetizing each section of the disc.
 HARD DISC Inside the hard disc: A read and write head and it performs the reading and writing from the disc. The heads do the work of converting bits to magnetic pulses and storing them on the sectors, and then reversing the process when the data needs to be read back. If a sector fills up then the head will move to another sector, no matter where. It has a special area that is allocated for File Allocation Table (FAT) It is a table that an operating system maintains on a hard disk that tells the read/write head where all the pieces of information it needs. Some parts of files get put in random places which are called fragments. So, a Disc Defragmenter can be use to put them in an orderly fashion and therefore, improves access time.
HARD DISC Inside the hard disc: A read and write head and it performs the reading and writing from the disc. The heads do the work of converting bits to magnetic pulses and storing them on the sectors, and then reversing the process when the data needs to be read back. If a sector fills up then the head will move to another sector, no matter where. It has a special area that is allocated for File Allocation Table (FAT) It is a table that an operating system maintains on a hard disk that tells the read/write head where all the pieces of information it needs. Some parts of files get put in random places which are called fragments. So, a Disc Defragmenter can be use to put them in an orderly fashion and therefore, improves access time.
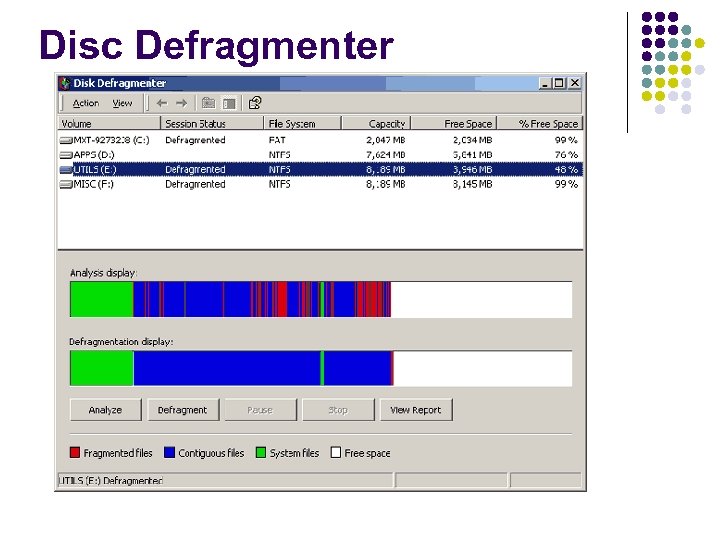 Disc Defragmenter
Disc Defragmenter
 HARD DISC Every hard disk must have a consistent "starting point" where key information is stored about the disk, such as the number of partitions and what type they are. There also must be someplace where the BIOS can load the initial boot program that starts the process of loading the operating system. The place where this information is stored is called the Master Boot Record (MBR) The MBR is located on the first sector of a disk
HARD DISC Every hard disk must have a consistent "starting point" where key information is stored about the disk, such as the number of partitions and what type they are. There also must be someplace where the BIOS can load the initial boot program that starts the process of loading the operating system. The place where this information is stored is called the Master Boot Record (MBR) The MBR is located on the first sector of a disk
 HARD DISC – Master Boot Record (MBR) The master boot record contains the following structures: Master Partition Table: This small bit of code that is referred to as a table contains a complete description of the partitions that are contained on the hard disk. ü FAT is stored in MASTER PARTITION TABLE Master Boot Code: The master boot code is the small bit of computer code that the BIOS loads and executes to start the boot process. This code, when fully executed, transfers control to the boot program stored on the boot (active) partition to load the operating system.
HARD DISC – Master Boot Record (MBR) The master boot record contains the following structures: Master Partition Table: This small bit of code that is referred to as a table contains a complete description of the partitions that are contained on the hard disk. ü FAT is stored in MASTER PARTITION TABLE Master Boot Code: The master boot code is the small bit of computer code that the BIOS loads and executes to start the boot process. This code, when fully executed, transfers control to the boot program stored on the boot (active) partition to load the operating system.
 Solid State Disk/Drive (SSD) Solid State Disk. Ø DRAM base. Ø No mechanical part thus no mechanical error. Ø Among the advantages, super faster boot time.
Solid State Disk/Drive (SSD) Solid State Disk. Ø DRAM base. Ø No mechanical part thus no mechanical error. Ø Among the advantages, super faster boot time.
 OTHERS Expansion cards Cards inside PC that gives it some features Eg: internal modems and graphic cards PCI = Peripheral Component Interconnect
OTHERS Expansion cards Cards inside PC that gives it some features Eg: internal modems and graphic cards PCI = Peripheral Component Interconnect
 Expansion card – PCI local bus Peripheral Component Interconnect Ø an industry-standard bus for attaching peripherals to computers Ø has displaced ISA and VESA Local Bus Ø It is now replaced by PCIe (PCI Express) Ø Ø Serial links: data can be sent over the bus in two directions at once. Ø Ø PCIe employs serial links whereas PCI uses parallel links Parallel links: data goes in one direction. Hence, for example, PCIe will provide much faster video than the PCI.
Expansion card – PCI local bus Peripheral Component Interconnect Ø an industry-standard bus for attaching peripherals to computers Ø has displaced ISA and VESA Local Bus Ø It is now replaced by PCIe (PCI Express) Ø Ø Serial links: data can be sent over the bus in two directions at once. Ø Ø PCIe employs serial links whereas PCI uses parallel links Parallel links: data goes in one direction. Hence, for example, PCIe will provide much faster video than the PCI.
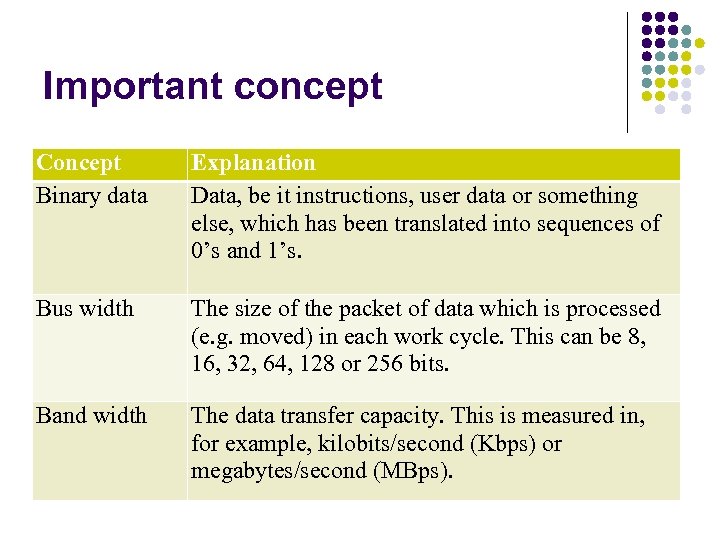 Important concept Concept Binary data Explanation Data, be it instructions, user data or something else, which has been translated into sequences of 0’s and 1’s. Bus width The size of the packet of data which is processed (e. g. moved) in each work cycle. This can be 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 or 256 bits. Band width The data transfer capacity. This is measured in, for example, kilobits/second (Kbps) or megabytes/second (MBps).
Important concept Concept Binary data Explanation Data, be it instructions, user data or something else, which has been translated into sequences of 0’s and 1’s. Bus width The size of the packet of data which is processed (e. g. moved) in each work cycle. This can be 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 or 256 bits. Band width The data transfer capacity. This is measured in, for example, kilobits/second (Kbps) or megabytes/second (MBps).
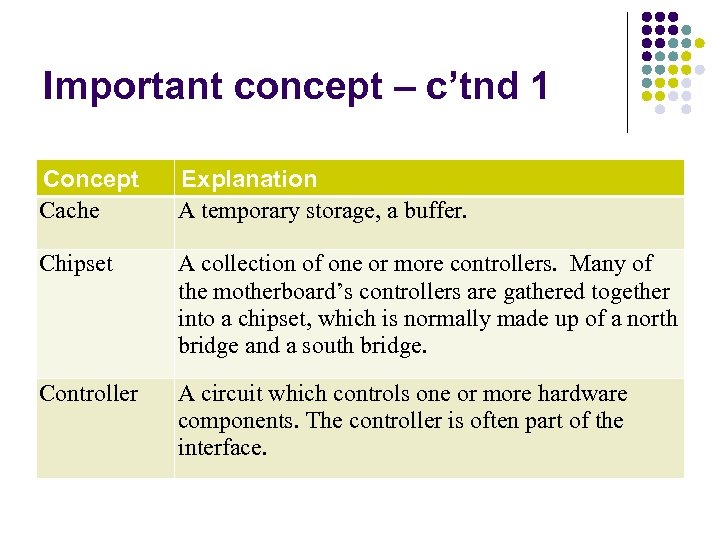 Important concept – c’tnd 1 Concept Cache Explanation A temporary storage, a buffer. Chipset A collection of one or more controllers. Many of the motherboard’s controllers are gathered together into a chipset, which is normally made up of a north bridge and a south bridge. Controller A circuit which controls one or more hardware components. The controller is often part of the interface.
Important concept – c’tnd 1 Concept Cache Explanation A temporary storage, a buffer. Chipset A collection of one or more controllers. Many of the motherboard’s controllers are gathered together into a chipset, which is normally made up of a north bridge and a south bridge. Controller A circuit which controls one or more hardware components. The controller is often part of the interface.
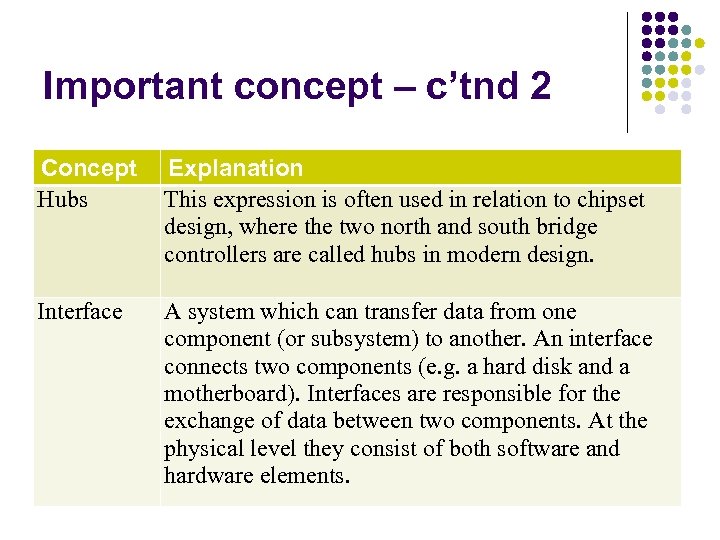 Important concept – c’tnd 2 Concept Hubs Explanation This expression is often used in relation to chipset design, where the two north and south bridge controllers are called hubs in modern design. Interface A system which can transfer data from one component (or subsystem) to another. An interface connects two components (e. g. a hard disk and a motherboard). Interfaces are responsible for the exchange of data between two components. At the physical level they consist of both software and hardware elements.
Important concept – c’tnd 2 Concept Hubs Explanation This expression is often used in relation to chipset design, where the two north and south bridge controllers are called hubs in modern design. Interface A system which can transfer data from one component (or subsystem) to another. An interface connects two components (e. g. a hard disk and a motherboard). Interfaces are responsible for the exchange of data between two components. At the physical level they consist of both software and hardware elements.
 Important concept – c’tnd 3 Concept I/O units Explanation Components like mice, keyboards, serial and parallel ports, screens, network and other cards, along with USB, firewire and SCSI controllers, etc. Clock frequency The rate at which data is transferred, which varies quite a lot between the various components of the PC. Usually measured in MHz.
Important concept – c’tnd 3 Concept I/O units Explanation Components like mice, keyboards, serial and parallel ports, screens, network and other cards, along with USB, firewire and SCSI controllers, etc. Clock frequency The rate at which data is transferred, which varies quite a lot between the various components of the PC. Usually measured in MHz.
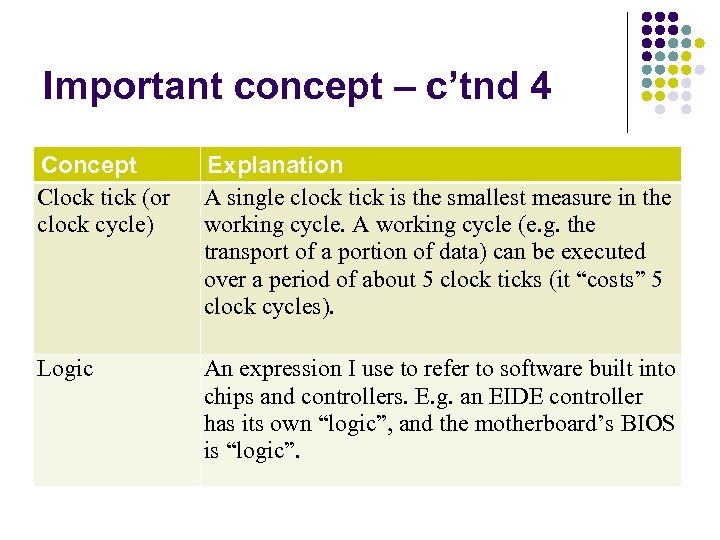 Important concept – c’tnd 4 Concept Clock tick (or clock cycle) Explanation A single clock tick is the smallest measure in the working cycle. A working cycle (e. g. the transport of a portion of data) can be executed over a period of about 5 clock ticks (it “costs” 5 clock cycles). Logic An expression I use to refer to software built into chips and controllers. E. g. an EIDE controller has its own “logic”, and the motherboard’s BIOS is “logic”.
Important concept – c’tnd 4 Concept Clock tick (or clock cycle) Explanation A single clock tick is the smallest measure in the working cycle. A working cycle (e. g. the transport of a portion of data) can be executed over a period of about 5 clock ticks (it “costs” 5 clock cycles). Logic An expression I use to refer to software built into chips and controllers. E. g. an EIDE controller has its own “logic”, and the motherboard’s BIOS is “logic”.
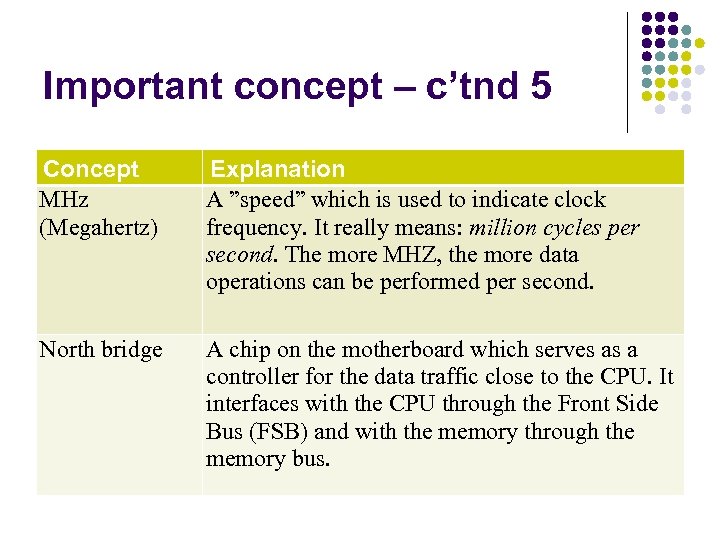 Important concept – c’tnd 5 Concept MHz (Megahertz) Explanation A ”speed” which is used to indicate clock frequency. It really means: million cycles per second. The more MHZ, the more data operations can be performed per second. North bridge A chip on the motherboard which serves as a controller for the data traffic close to the CPU. It interfaces with the CPU through the Front Side Bus (FSB) and with the memory through the memory bus.
Important concept – c’tnd 5 Concept MHz (Megahertz) Explanation A ”speed” which is used to indicate clock frequency. It really means: million cycles per second. The more MHZ, the more data operations can be performed per second. North bridge A chip on the motherboard which serves as a controller for the data traffic close to the CPU. It interfaces with the CPU through the Front Side Bus (FSB) and with the memory through the memory bus.
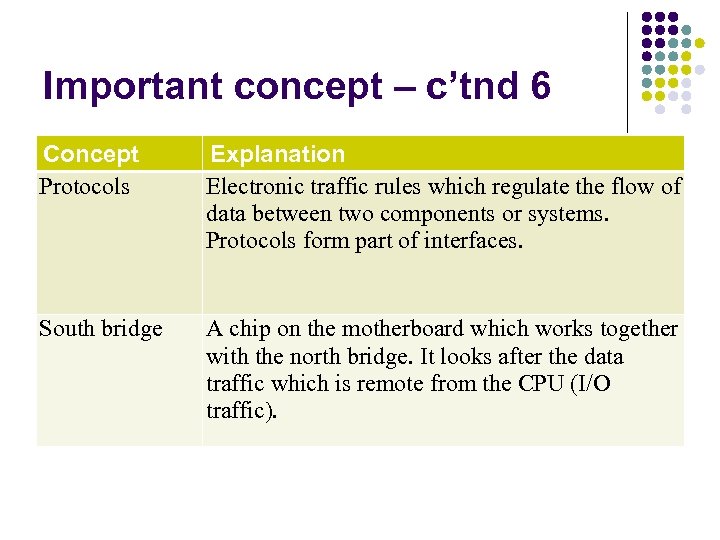 Important concept – c’tnd 6 Concept Protocols Explanation Electronic traffic rules which regulate the flow of data between two components or systems. Protocols form part of interfaces. South bridge A chip on the motherboard which works together with the north bridge. It looks after the data traffic which is remote from the CPU (I/O traffic).
Important concept – c’tnd 6 Concept Protocols Explanation Electronic traffic rules which regulate the flow of data between two components or systems. Protocols form part of interfaces. South bridge A chip on the motherboard which works together with the north bridge. It looks after the data traffic which is remote from the CPU (I/O traffic).


