089f9e4845421ba8a6ff9416bf695cee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Introduction to Packet Sniffing using Ethereal 0. 10. 9 Rob Bergin Network Engineer The Timberland Company
Introduction to Packet Sniffing using Ethereal 0. 10. 9 Rob Bergin Network Engineer The Timberland Company
 Non-Technical Currently Data just travels around your network like a train. With a packet sniffer, get the ability to capture the data and look inside the packets to see what is actually moving long the tracks.
Non-Technical Currently Data just travels around your network like a train. With a packet sniffer, get the ability to capture the data and look inside the packets to see what is actually moving long the tracks.
 Technical
Technical
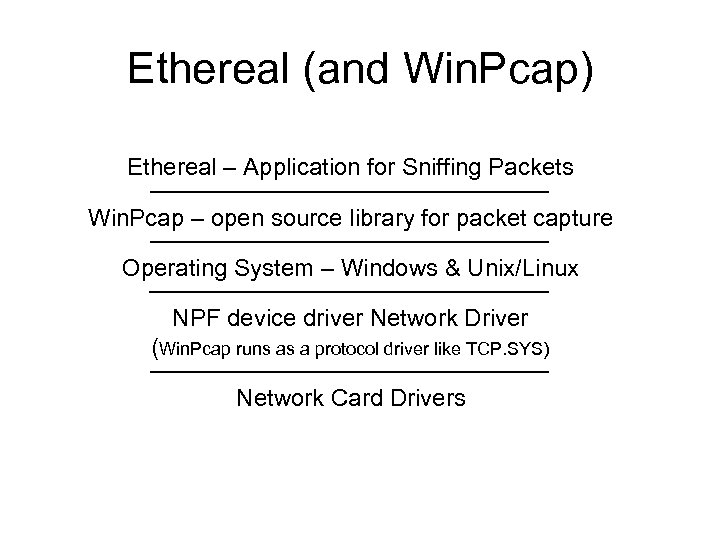 Ethereal (and Win. Pcap) Ethereal – Application for Sniffing Packets Win. Pcap – open source library for packet capture Operating System – Windows & Unix/Linux NPF device driver Network Driver (Win. Pcap runs as a protocol driver like TCP. SYS) Network Card Drivers
Ethereal (and Win. Pcap) Ethereal – Application for Sniffing Packets Win. Pcap – open source library for packet capture Operating System – Windows & Unix/Linux NPF device driver Network Driver (Win. Pcap runs as a protocol driver like TCP. SYS) Network Card Drivers
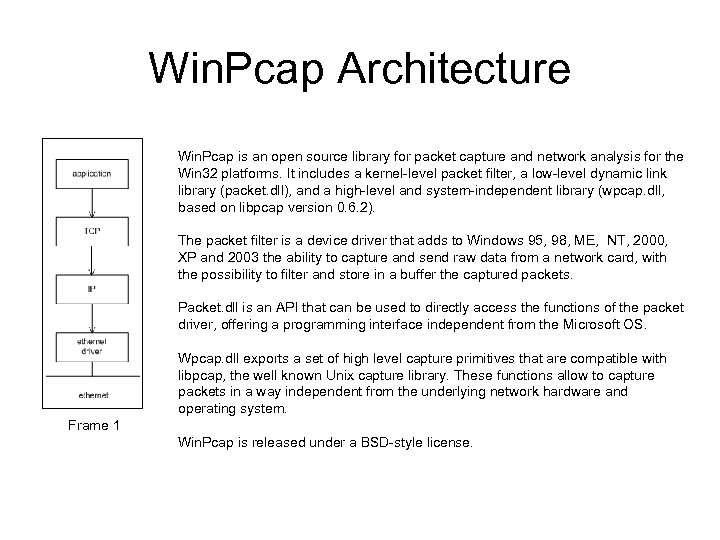 Win. Pcap Architecture Win. Pcap is an open source library for packet capture and network analysis for the Win 32 platforms. It includes a kernel-level packet filter, a low-level dynamic link library (packet. dll), and a high-level and system-independent library (wpcap. dll, based on libpcap version 0. 6. 2). The packet filter is a device driver that adds to Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, 2000, XP and 2003 the ability to capture and send raw data from a network card, with the possibility to filter and store in a buffer the captured packets. Packet. dll is an API that can be used to directly access the functions of the packet driver, offering a programming interface independent from the Microsoft OS. Wpcap. dll exports a set of high level capture primitives that are compatible with libpcap, the well known Unix capture library. These functions allow to capture packets in a way independent from the underlying network hardware and operating system. Frame 1 Win. Pcap is released under a BSD-style license.
Win. Pcap Architecture Win. Pcap is an open source library for packet capture and network analysis for the Win 32 platforms. It includes a kernel-level packet filter, a low-level dynamic link library (packet. dll), and a high-level and system-independent library (wpcap. dll, based on libpcap version 0. 6. 2). The packet filter is a device driver that adds to Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, 2000, XP and 2003 the ability to capture and send raw data from a network card, with the possibility to filter and store in a buffer the captured packets. Packet. dll is an API that can be used to directly access the functions of the packet driver, offering a programming interface independent from the Microsoft OS. Wpcap. dll exports a set of high level capture primitives that are compatible with libpcap, the well known Unix capture library. These functions allow to capture packets in a way independent from the underlying network hardware and operating system. Frame 1 Win. Pcap is released under a BSD-style license.
 Ethereal Application • Requires Win. Pcap for Captures • Can run standalone to examine captures
Ethereal Application • Requires Win. Pcap for Captures • Can run standalone to examine captures
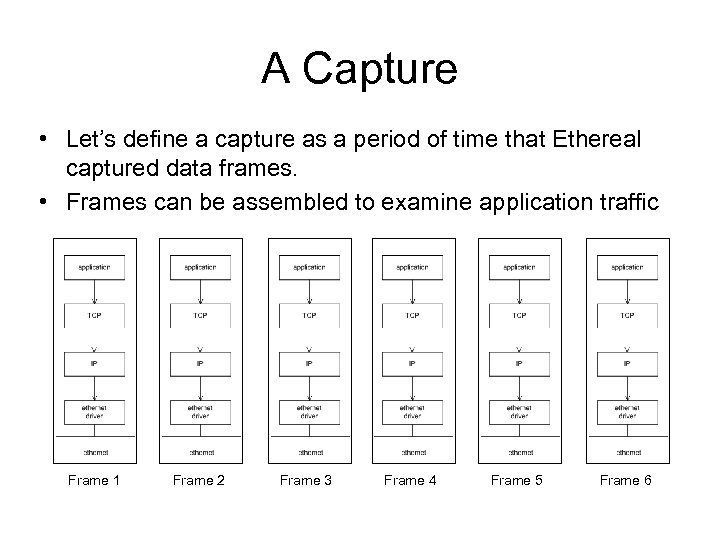 A Capture • Let’s define a capture as a period of time that Ethereal captured data frames. • Frames can be assembled to examine application traffic Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4 Frame 5 Frame 6
A Capture • Let’s define a capture as a period of time that Ethereal captured data frames. • Frames can be assembled to examine application traffic Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4 Frame 5 Frame 6
 Recap • • • Packet Sniffing Ethereal Data Frame Architecture Win. Pcap Network Capture
Recap • • • Packet Sniffing Ethereal Data Frame Architecture Win. Pcap Network Capture
 Basic TCP/IP Stuff
Basic TCP/IP Stuff
 Interoperable TCP/IP • TCP/IP is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a suite of network protocols. • TCP and IP are two separate protocols • TCP handles the data (HTTP vs. FTP vs. Telnet) • IP handles the data transmission (i. e. between routers). • TCP/IP protocols were designed to allow different applications running on dissimilar operating systems to communicate across a network.
Interoperable TCP/IP • TCP/IP is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a suite of network protocols. • TCP and IP are two separate protocols • TCP handles the data (HTTP vs. FTP vs. Telnet) • IP handles the data transmission (i. e. between routers). • TCP/IP protocols were designed to allow different applications running on dissimilar operating systems to communicate across a network.
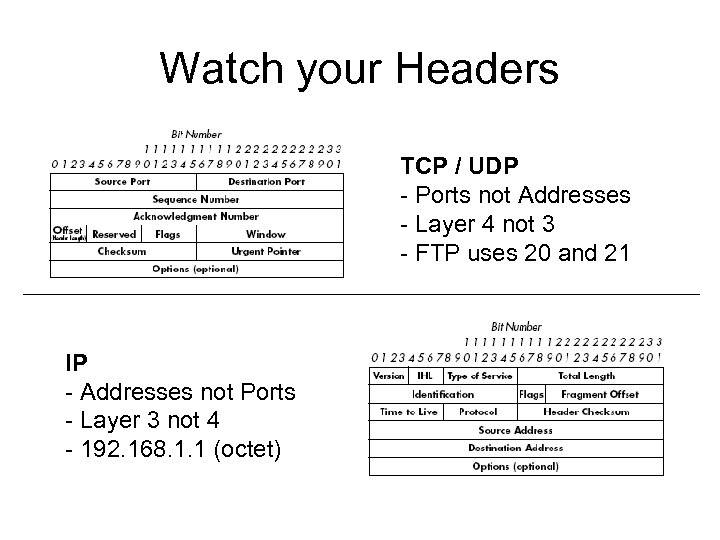 Watch your Headers TCP / UDP - Ports not Addresses - Layer 4 not 3 - FTP uses 20 and 21 IP - Addresses not Ports - Layer 3 not 4 - 192. 168. 1. 1 (octet)
Watch your Headers TCP / UDP - Ports not Addresses - Layer 4 not 3 - FTP uses 20 and 21 IP - Addresses not Ports - Layer 3 not 4 - 192. 168. 1. 1 (octet)
 TCP • TCP is connection-oriented transport layer protocol designed to provide a reliable connection for data exchange between two systems. • TCP ensures that all packets are properly sequenced and acknowledged and that a connection is established before data is sent. • TCP provides it reliability through the use of an acknowledgement or ACK.
TCP • TCP is connection-oriented transport layer protocol designed to provide a reliable connection for data exchange between two systems. • TCP ensures that all packets are properly sequenced and acknowledged and that a connection is established before data is sent. • TCP provides it reliability through the use of an acknowledgement or ACK.
 TCP • If a receiving system had to send an ACK for every packet, the result would be an incredible amount of overhead for the network. • To reduce the overhead, a mechanism called windowing is used. • Windowing is a method of flow control.
TCP • If a receiving system had to send an ACK for every packet, the result would be an incredible amount of overhead for the network. • To reduce the overhead, a mechanism called windowing is used. • Windowing is a method of flow control.
 TCP • The receiving system advertises a certain number of packets that it can receive at a time (input buffer size. ) • The sending system watches for an ACK after the designated number of packets is sent. • If an ACK is not received, data will be retransmitted from the point of the last ACK.
TCP • The receiving system advertises a certain number of packets that it can receive at a time (input buffer size. ) • The sending system watches for an ACK after the designated number of packets is sent. • If an ACK is not received, data will be retransmitted from the point of the last ACK.
 UDP • UDP (User Datagram Protocol) provides an unreliable, connectionless protocol to deliver packets. • This protocol allows messages, called datagrams, to be sent without the overhead of ACKs, established connections, and sequencing. • Applications that use UDP as their communications mechanism include NFS (2049), TFTP (79), DNS (53) and Unreal Tournament (7777).
UDP • UDP (User Datagram Protocol) provides an unreliable, connectionless protocol to deliver packets. • This protocol allows messages, called datagrams, to be sent without the overhead of ACKs, established connections, and sequencing. • Applications that use UDP as their communications mechanism include NFS (2049), TFTP (79), DNS (53) and Unreal Tournament (7777).
 IPv 4 • IP (Internet Protocol) is used to handle datagram services between hosts. • IP handles the addressing, routing, and reassembly • IP addresses are 32 bits long, are organized into 4 octets (8 bits) separated by periods • IPv 4 address examples: 192. 168. 10. 20. • IPv 6 is a next generation form of addressing.
IPv 4 • IP (Internet Protocol) is used to handle datagram services between hosts. • IP handles the addressing, routing, and reassembly • IP addresses are 32 bits long, are organized into 4 octets (8 bits) separated by periods • IPv 4 address examples: 192. 168. 10. 20. • IPv 6 is a next generation form of addressing.
 IPv 6 • IP (Internet Protocol) is used to handle datagram services between hosts. • IP handles the addressing, routing, and reassembly • IP addresses are 32 bits long, are organized into 4 octets (8 bits) separated by periods • IPv 4 address examples: 192. 168. 10. 20. • IPv 6 is a next generation form of addressing.
IPv 6 • IP (Internet Protocol) is used to handle datagram services between hosts. • IP handles the addressing, routing, and reassembly • IP addresses are 32 bits long, are organized into 4 octets (8 bits) separated by periods • IPv 4 address examples: 192. 168. 10. 20. • IPv 6 is a next generation form of addressing.
 What will IPv 6 look like? IPv 6 Addresses: CDFE: 910 A: 2356: 5709: 8475: 1024: 3911: 2021 2080: 0000: 0090: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Combo IPv 4 and IPv 6 1800: 0000: 7 AEF: 0000: 16. 114. 67. 16 Compacted IPv 6 Address: 2080: 0: 90: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Legal compaction 2080: : 90: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Legal compaction 1800: : 7 AEF: 0: 0: 1072: 4310 Legal compaction
What will IPv 6 look like? IPv 6 Addresses: CDFE: 910 A: 2356: 5709: 8475: 1024: 3911: 2021 2080: 0000: 0090: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Combo IPv 4 and IPv 6 1800: 0000: 7 AEF: 0000: 16. 114. 67. 16 Compacted IPv 6 Address: 2080: 0: 90: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Legal compaction 2080: : 90: 7 AEB: 1000: 123 A Legal compaction 1800: : 7 AEF: 0: 0: 1072: 4310 Legal compaction
 IPv 4 vs. IPv 6 • IPv 4 RFC came out in 1981. Mobile Subscribers PCs Connected to Web Mobile Internet Users Sources: ABN AMRO/IDC/Ovum • IPv 6 RFC came out in 1998.
IPv 4 vs. IPv 6 • IPv 4 RFC came out in 1981. Mobile Subscribers PCs Connected to Web Mobile Internet Users Sources: ABN AMRO/IDC/Ovum • IPv 6 RFC came out in 1998.
 Recap • • • TCP vs. IP Headers TCP UDP IP IPv 4 vs. IPv 6
Recap • • • TCP vs. IP Headers TCP UDP IP IPv 4 vs. IPv 6
 Ethereal Overview
Ethereal Overview
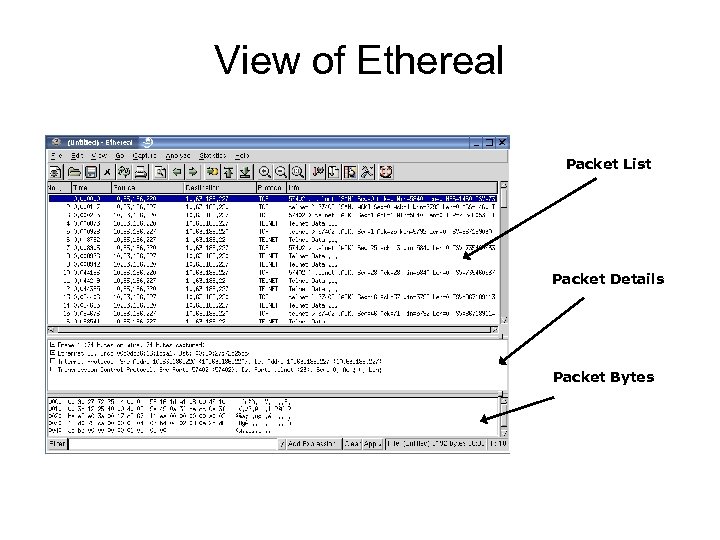 View of Ethereal Packet List Packet Details Packet Bytes
View of Ethereal Packet List Packet Details Packet Bytes
 Packet List Packet Order Time Order Source IP Destination IP Protocol Information
Packet List Packet Order Time Order Source IP Destination IP Protocol Information
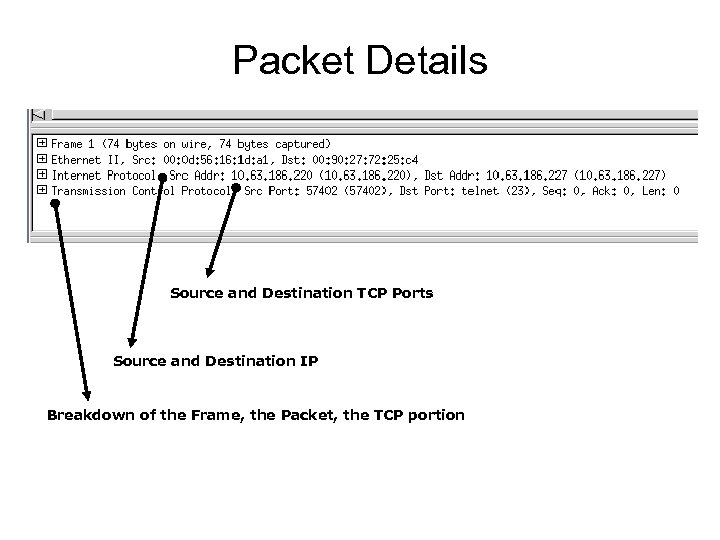 Packet Details Source and Destination TCP Ports Source and Destination IP Breakdown of the Frame, the Packet, the TCP portion
Packet Details Source and Destination TCP Ports Source and Destination IP Breakdown of the Frame, the Packet, the TCP portion
 Packet Bytes View of the data – Hexidecimal and Raw Data
Packet Bytes View of the data – Hexidecimal and Raw Data
 Ethereal Capture
Ethereal Capture
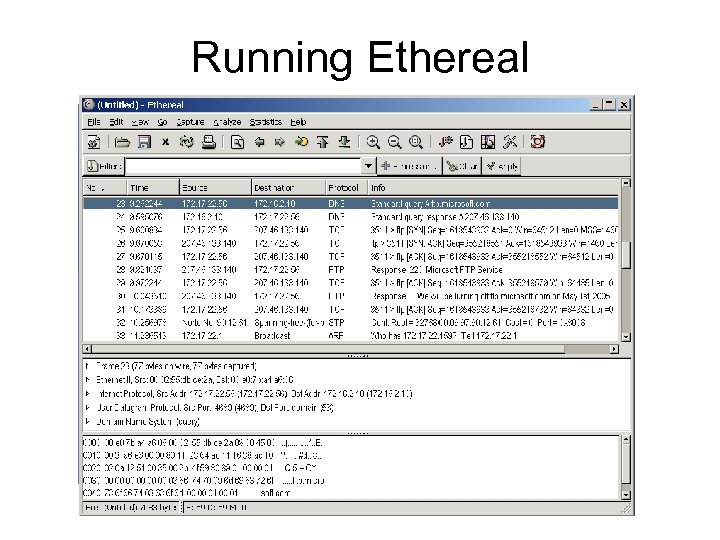 Running Ethereal
Running Ethereal
 Ethereal Analysis
Ethereal Analysis
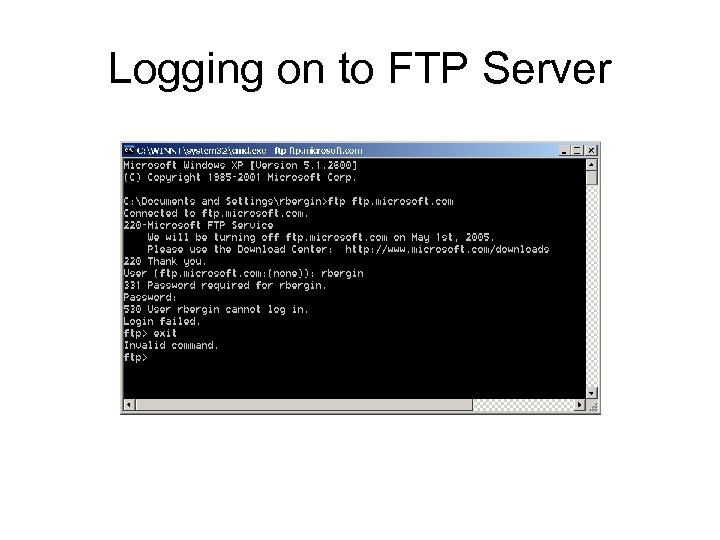 Logging on to FTP Server
Logging on to FTP Server
 What Ethereal saw
What Ethereal saw
 What Ethereal saw
What Ethereal saw
 What Ethereal saw
What Ethereal saw
 What Ethereal saw
What Ethereal saw
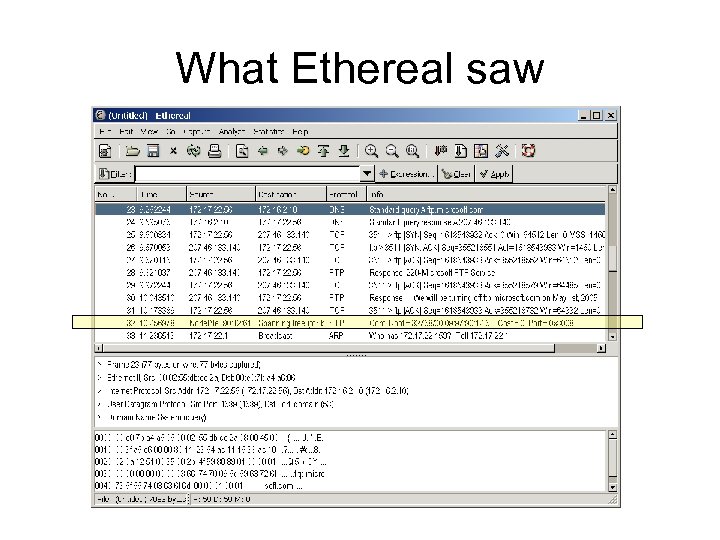 What Ethereal saw
What Ethereal saw
 Ethereal Filtering.
Ethereal Filtering.
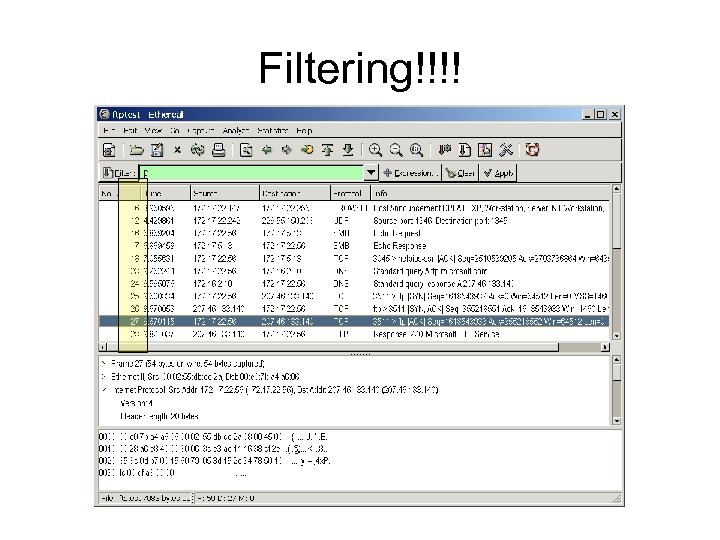 Filtering!!!!
Filtering!!!!
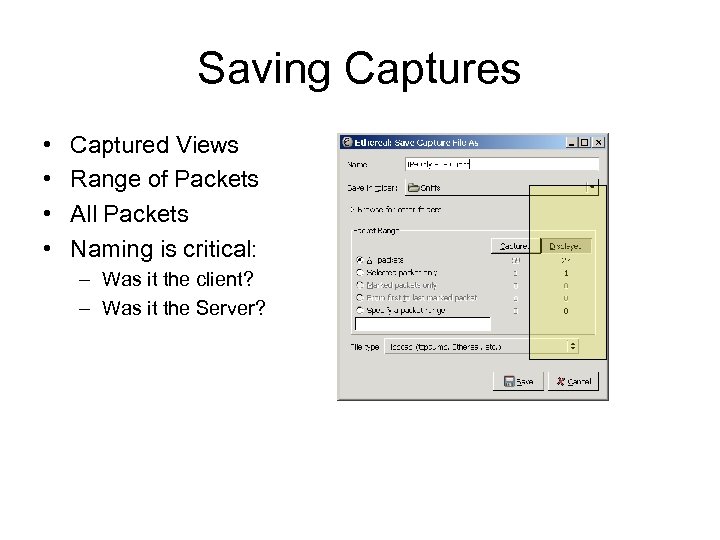 Saving Captures • • Captured Views Range of Packets All Packets Naming is critical: – Was it the client? – Was it the Server?
Saving Captures • • Captured Views Range of Packets All Packets Naming is critical: – Was it the client? – Was it the Server?
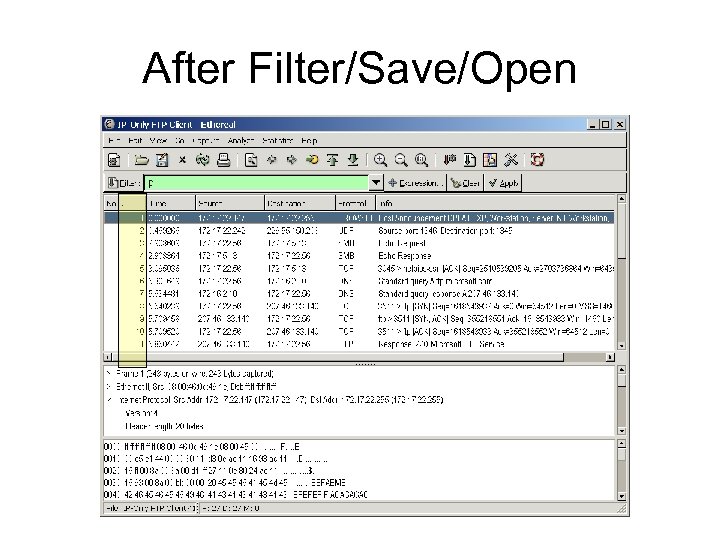 After Filter/Save/Open
After Filter/Save/Open
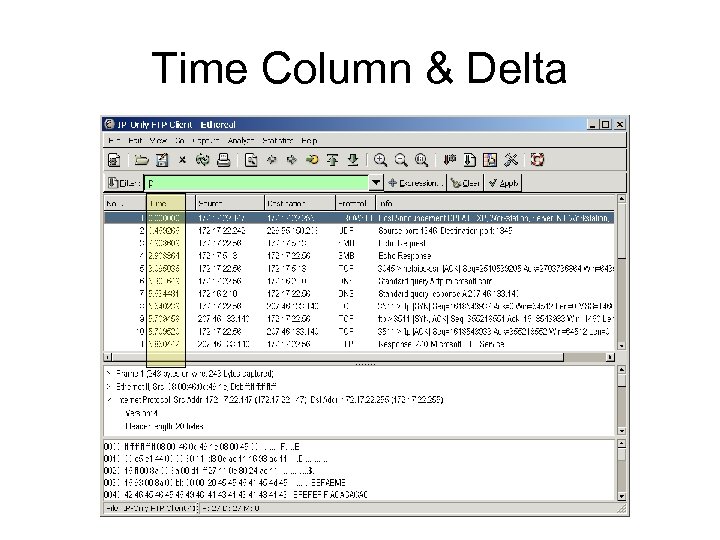 Time Column & Delta
Time Column & Delta
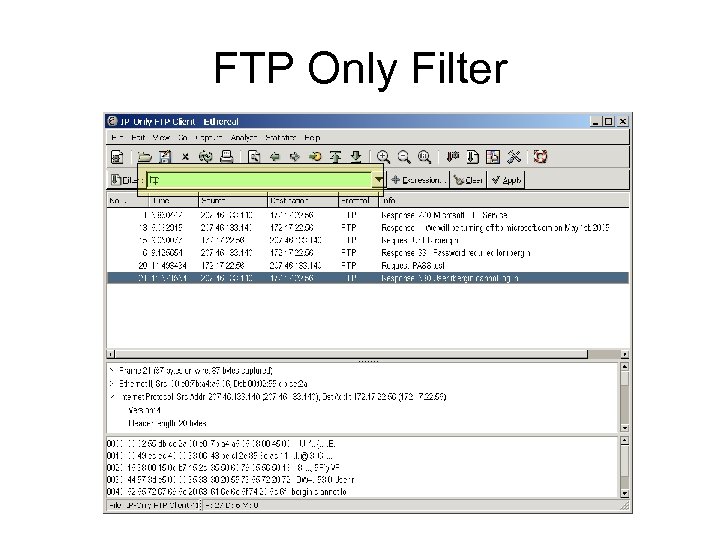 FTP Only Filter
FTP Only Filter
 Ethereal Packet Analysis
Ethereal Packet Analysis
 What Username?
What Username?
 Is Password Required?
Is Password Required?
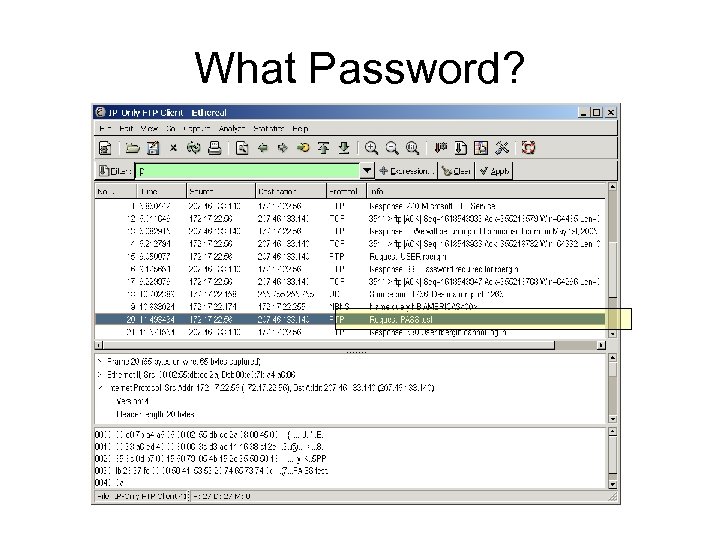 What Password?
What Password?
 Why can’t I log in?
Why can’t I log in?
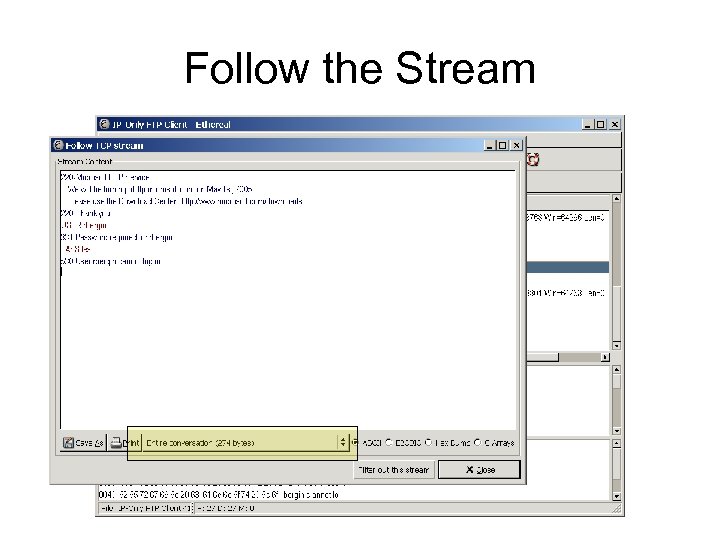 Follow the Stream
Follow the Stream
 Advanced Filtering Filter for just that stream (ip. addr eq 207. 46. 133. 140 and ip. addr eq 172. 17. 22. 56) and (tcp. port eq 21 and tcp. port eq 3511) Filter for traffic between two hosts ip. addr == 207. 46. 133. 140 and ip. addr == 172. 17. 22. 56 Filter for IP Traffic and removal of other traffic ip and !(nbns) and !(msnms) and !(browser) and !(rip)
Advanced Filtering Filter for just that stream (ip. addr eq 207. 46. 133. 140 and ip. addr eq 172. 17. 22. 56) and (tcp. port eq 21 and tcp. port eq 3511) Filter for traffic between two hosts ip. addr == 207. 46. 133. 140 and ip. addr == 172. 17. 22. 56 Filter for IP Traffic and removal of other traffic ip and !(nbns) and !(msnms) and !(browser) and !(rip)
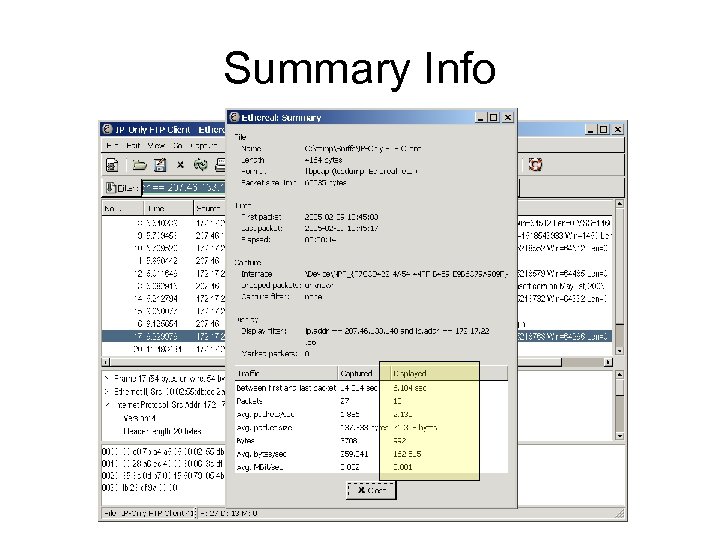 Summary Info
Summary Info
 Ethereal: Encryption
Ethereal: Encryption
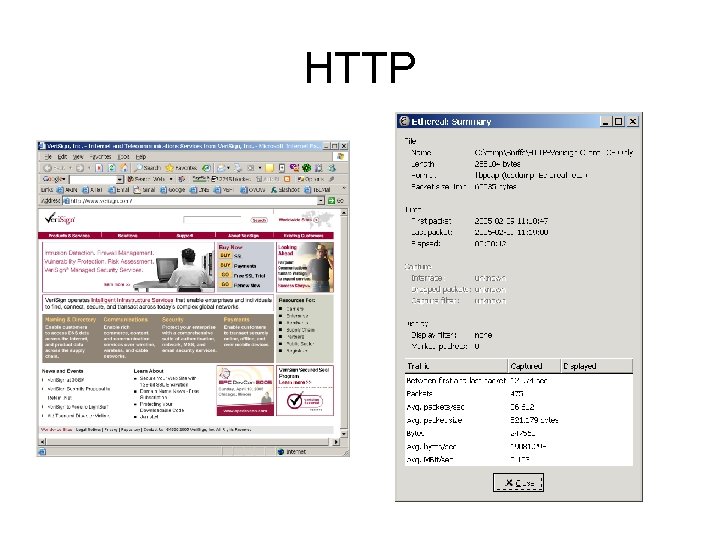 HTTP
HTTP
 HTTPS
HTTPS
 HTTP vs. HTTPS
HTTP vs. HTTPS
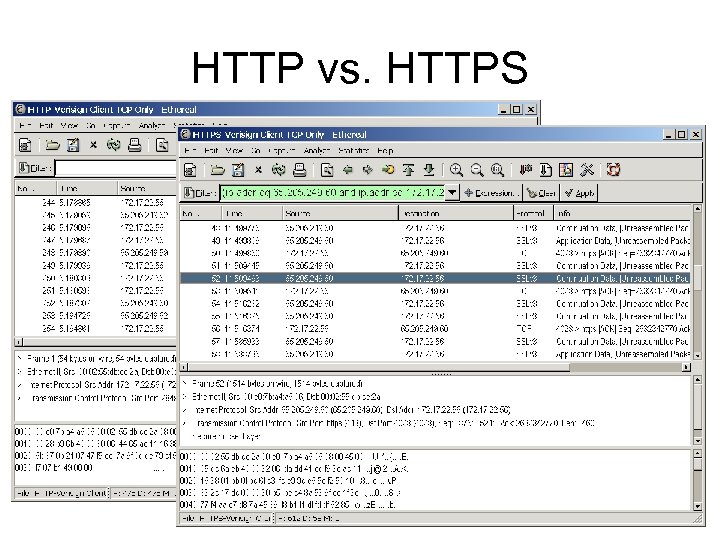 HTTP vs. HTTPS
HTTP vs. HTTPS
 HTTP vs. HTTPS
HTTP vs. HTTPS
 TCP Stream vs. HTML Source
TCP Stream vs. HTML Source
 Ethereal: Miscellaneous
Ethereal: Miscellaneous
 Protocol Hierarchy
Protocol Hierarchy
 I/O Graphing
I/O Graphing
 HTTP Breakdown
HTTP Breakdown
 Coloring Packets
Coloring Packets
 Commercial Sniffers • Sniffer Pro • Omni. Peek • Observer • IT Guru and ACE
Commercial Sniffers • Sniffer Pro • Omni. Peek • Observer • IT Guru and ACE

 Final Words “If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it” - Peter Drucker
Final Words “If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it” - Peter Drucker


