a54822ac90d5ad4fd6f29cf2a3633842.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Introduction to Oracle e. AM (Enterprise Asset Management) and our implementation experiences Jeremy Carson Applications Manager
Introduction to Oracle e. AM (Enterprise Asset Management) and our implementation experiences Jeremy Carson Applications Manager
 CMMS - Computerised Maintenance Management System Point Solution e. g. Maximo, Mexx or ERP Integrated Solution e. g Oracle E-Business Suite, JDE, Peoplesoft or Other e. g. Excel
CMMS - Computerised Maintenance Management System Point Solution e. g. Maximo, Mexx or ERP Integrated Solution e. g Oracle E-Business Suite, JDE, Peoplesoft or Other e. g. Excel
 What do you have ? ?
What do you have ? ?
 Agenda · Solid Energy Overview · Key Configuration Steps · Asset Model · Maintenance Tasks · Work Management · Preventative Maintenance · Cost Management · Key experiences · Questions ?
Agenda · Solid Energy Overview · Key Configuration Steps · Asset Model · Maintenance Tasks · Work Management · Preventative Maintenance · Cost Management · Key experiences · Questions ?
 Solid Energy Overview
Solid Energy Overview
 Solid Energy Overview – Energy Business · Coal - Steel Production (Export / NZ Steel) Electricity Generation (Genesis) - Domestic Industries (Fonterra / Holcim / Alliance / Silver Fern) · Renewables – Wood pellets / Biodiesel / Solar · New Energy – Coal Seam Gas, Coal to Fertiliser
Solid Energy Overview – Energy Business · Coal - Steel Production (Export / NZ Steel) Electricity Generation (Genesis) - Domestic Industries (Fonterra / Holcim / Alliance / Silver Fern) · Renewables – Wood pellets / Biodiesel / Solar · New Energy – Coal Seam Gas, Coal to Fertiliser
 Solid Energy Overview - People · Approx 1200 employees nationwide, predominately in the Waikato, South Island West Coast and Southland · Approx 600 directly employed contractors
Solid Energy Overview - People · Approx 1200 employees nationwide, predominately in the Waikato, South Island West Coast and Southland · Approx 600 directly employed contractors
 Solid Energy Overview - Assets · An asset intensive business · High focus on Health and Safety · High focus on availability and utilisation of assets · Predominately Mobile and Fixed Plant assets
Solid Energy Overview - Assets · An asset intensive business · High focus on Health and Safety · High focus on availability and utilisation of assets · Predominately Mobile and Fixed Plant assets
 Solid Energy Assets - Trucks
Solid Energy Assets - Trucks
 Solid Energy Assets - Excavators
Solid Energy Assets - Excavators
 Solid Energy Assets – Conveyors
Solid Energy Assets – Conveyors
 Solid Energy Assets – Underground Miners
Solid Energy Assets – Underground Miners
 Solid Energy Assets – Water Treatment Plants
Solid Energy Assets – Water Treatment Plants
 Solid Energy Assets – Train Loadouts
Solid Energy Assets – Train Loadouts
 Solid Energy Overview – Our e. AM Install · Have used Oracle e. AM since 2003 as an early adopter on Oracle EBusiness Suite 11. 5. 7 · Now using Oracle E-Business Suite 12. 0. 6 · Currently have 6 live Oracle e. AM sites/organisations · System Statistics - 15, 000+ work orders per annum 2000+ maintained assets 4000+ preventative maintenance activities 5000+ maintenance purchase requisitions per annum 10000+ maintenance inventory issues per annum
Solid Energy Overview – Our e. AM Install · Have used Oracle e. AM since 2003 as an early adopter on Oracle EBusiness Suite 11. 5. 7 · Now using Oracle E-Business Suite 12. 0. 6 · Currently have 6 live Oracle e. AM sites/organisations · System Statistics - 15, 000+ work orders per annum 2000+ maintained assets 4000+ preventative maintenance activities 5000+ maintenance purchase requisitions per annum 10000+ maintenance inventory issues per annum
 Key Configuration Steps
Key Configuration Steps
 Configuration Steps – Taxonomy document · As part of solution design create a Taxonomy document, which defines; · e. AM organization parameters e. g. default WIP Accounting Class · Key lookups e. g. Areas, Departments, Categories · Define standards and naming conventions for key setup areas - Asset Model e. g. Asset Number/Groups/Hierarchy/Categories - Maintenance Tasks e. g. Activities, Activity Type/Source/Cause - Work Management e. g. Work Order Type/Status/Priority - Preventative Maintenance e. g. Meters, Schedules · Taxonomy must understand system limitations e. g. Asset Number must be unique · Taxonomy is a living document…refine with subsequent implementations · Successful taxonomy makes system intuitive for users
Configuration Steps – Taxonomy document · As part of solution design create a Taxonomy document, which defines; · e. AM organization parameters e. g. default WIP Accounting Class · Key lookups e. g. Areas, Departments, Categories · Define standards and naming conventions for key setup areas - Asset Model e. g. Asset Number/Groups/Hierarchy/Categories - Maintenance Tasks e. g. Activities, Activity Type/Source/Cause - Work Management e. g. Work Order Type/Status/Priority - Preventative Maintenance e. g. Meters, Schedules · Taxonomy must understand system limitations e. g. Asset Number must be unique · Taxonomy is a living document…refine with subsequent implementations · Successful taxonomy makes system intuitive for users
 Configuration Steps – Solution Design document · Document how Oracle e. AM will deliver each business process e. g. Asset Breakdown to Work Order creation · Swim lane the business process across business roles e. g. maintenance, procurement, stores · Detailed application mapping to requirements for each process step · Review regularly and iteratively with key maintenance personnel · Develop Proof of Concepts to assist with design validation and acceptance
Configuration Steps – Solution Design document · Document how Oracle e. AM will deliver each business process e. g. Asset Breakdown to Work Order creation · Swim lane the business process across business roles e. g. maintenance, procurement, stores · Detailed application mapping to requirements for each process step · Review regularly and iteratively with key maintenance personnel · Develop Proof of Concepts to assist with design validation and acceptance
 Asset Model
Asset Model
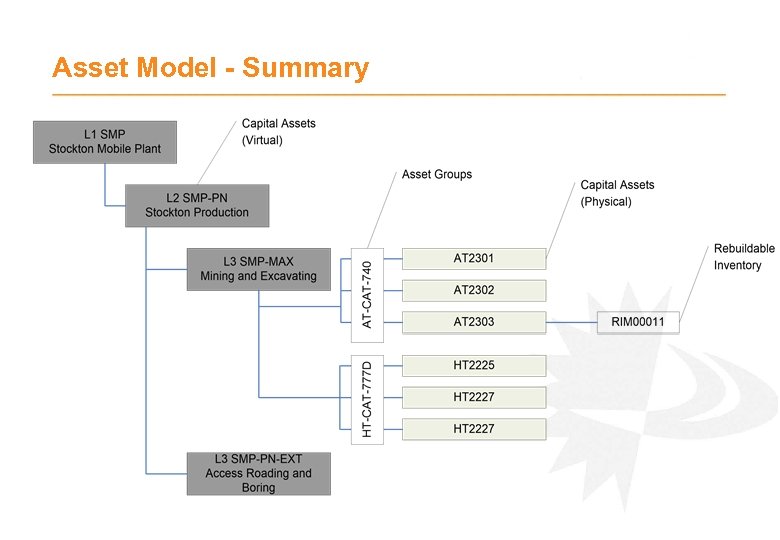
 Asset Model - Asset Numbers · · Asset Numbers are the key entity in e. AM Mostly represent physical assets Can be virtual assets in asset hierarchy for roll-up/grouping Assets are setup either as a; - Capital Asset or - Rebuildable Inventory Components which rotate on/off Capital Assets and are repaired/refurbished in between. · Asset Numbers exist in separate register (using Oracle Install Base) than the Fixed Asset register · Asset Numbers can be linked to a single Fixed Asset Number TIP: Asset Numbers must be unique through the system Consider physical asset naming and common sites names
Asset Model - Asset Numbers · · Asset Numbers are the key entity in e. AM Mostly represent physical assets Can be virtual assets in asset hierarchy for roll-up/grouping Assets are setup either as a; - Capital Asset or - Rebuildable Inventory Components which rotate on/off Capital Assets and are repaired/refurbished in between. · Asset Numbers exist in separate register (using Oracle Install Base) than the Fixed Asset register · Asset Numbers can be linked to a single Fixed Asset Number TIP: Asset Numbers must be unique through the system Consider physical asset naming and common sites names
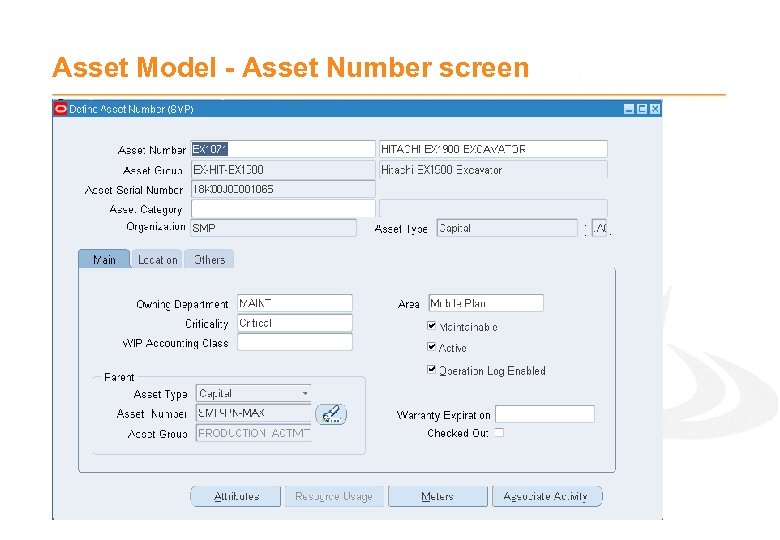 Asset Model - Asset Number screen
Asset Model - Asset Number screen
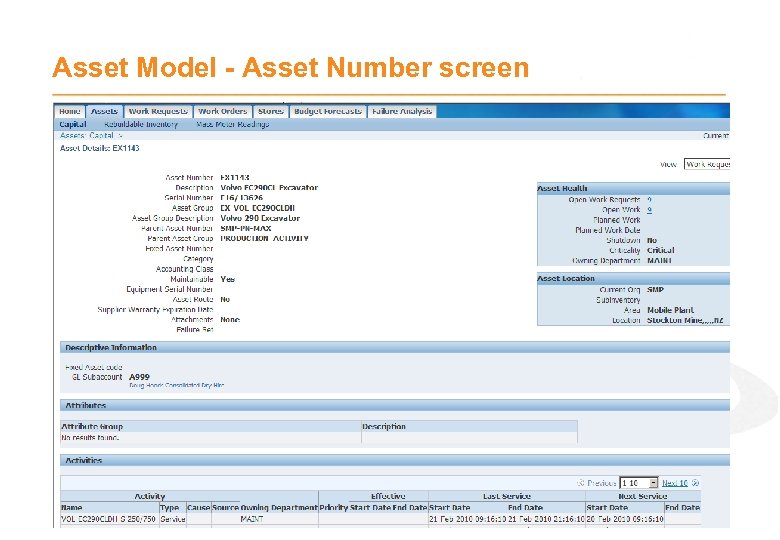 Asset Model - Asset Number screen
Asset Model - Asset Number screen
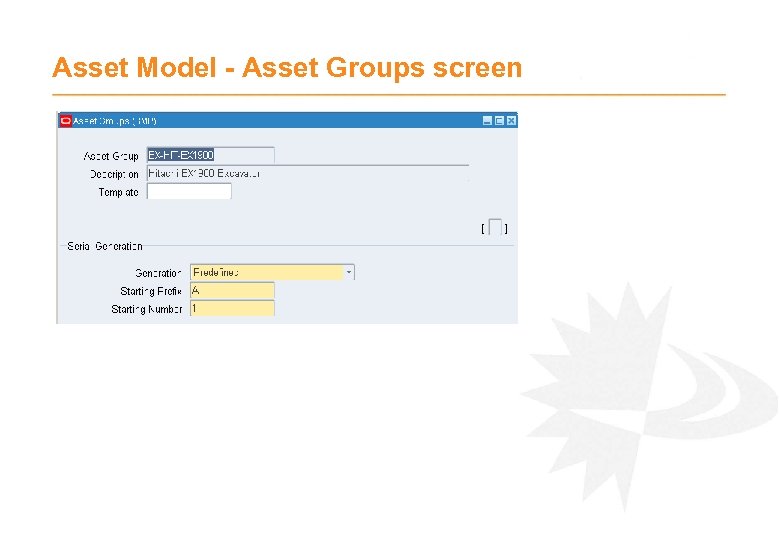
 Asset Model - Asset Groups · Each Asset belongs to an Asset Group · Many key configurations driven by Asset Group - Asset Bills of Materials – Typical materials used for maintenance - Templates – Provides automatic creation of Preventative Maintenance configuration e. g. Activities, Meters, Schedules - Asset Attributes – Storage of additional asset information - Failure Analysis – Failure, Cause and Resolution · Define groups to represent virtually identical assets, in terms of materials and preventative maintenance e. g. Make and Model combination. TIP: Asset Groups must be unique through the system
Asset Model - Asset Groups · Each Asset belongs to an Asset Group · Many key configurations driven by Asset Group - Asset Bills of Materials – Typical materials used for maintenance - Templates – Provides automatic creation of Preventative Maintenance configuration e. g. Activities, Meters, Schedules - Asset Attributes – Storage of additional asset information - Failure Analysis – Failure, Cause and Resolution · Define groups to represent virtually identical assets, in terms of materials and preventative maintenance e. g. Make and Model combination. TIP: Asset Groups must be unique through the system
 Asset Model - Asset Groups screen
Asset Model - Asset Groups screen
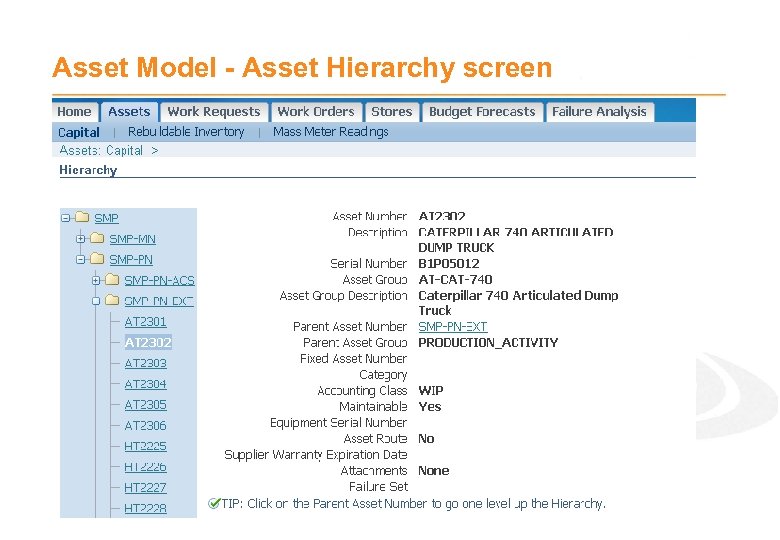
 Asset Model - Asset Hierarchy · Assets belong in a hierarchy · Each Asset has a Parent Asset · Establishes a roll-up mechanism for; - Cost reporting Preventative Maintenance forecasting Searches Maintenance and failure history · Virtual assets at top of hierarchy to deliver meaningful rollups; - Production or process affinity - Geographical or physical location
Asset Model - Asset Hierarchy · Assets belong in a hierarchy · Each Asset has a Parent Asset · Establishes a roll-up mechanism for; - Cost reporting Preventative Maintenance forecasting Searches Maintenance and failure history · Virtual assets at top of hierarchy to deliver meaningful rollups; - Production or process affinity - Geographical or physical location
 Asset Model - Asset Hierarchy screen
Asset Model - Asset Hierarchy screen
 Asset Model - Summary
Asset Model - Summary
 Maintenance Tasks
Maintenance Tasks
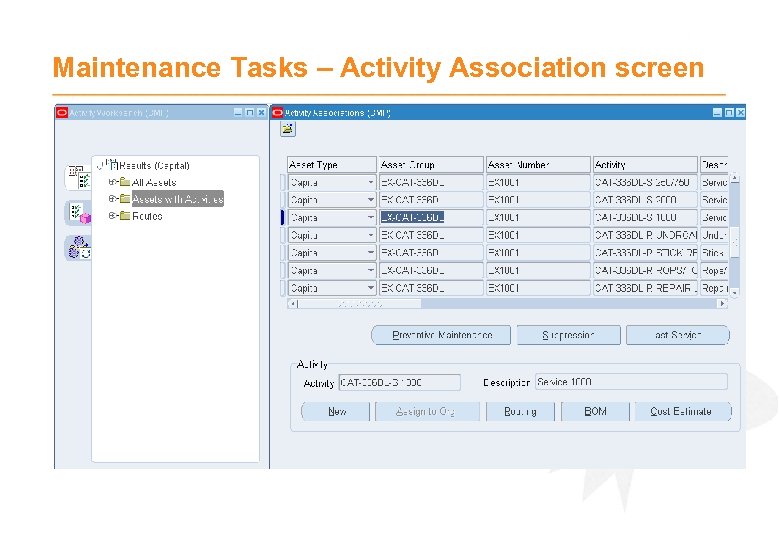
 Maintenance Tasks - Activities · Activities are predefined Maintenance work to be completed · Generally routine work e. g. exchange pump, replace tyres or preventative maintenance work e. g. services / inspections · Activities define the following - Tasks – More detailed tasks of the predefined work - Bills of Materials – Required materials - Routings – Required labour or equipment - File attachments – Such as service sheet, diagrams, safety procedures · Create Activity Association Template to associate to an Asset Group or associate to an individual Asset
Maintenance Tasks - Activities · Activities are predefined Maintenance work to be completed · Generally routine work e. g. exchange pump, replace tyres or preventative maintenance work e. g. services / inspections · Activities define the following - Tasks – More detailed tasks of the predefined work - Bills of Materials – Required materials - Routings – Required labour or equipment - File attachments – Such as service sheet, diagrams, safety procedures · Create Activity Association Template to associate to an Asset Group or associate to an individual Asset
 Maintenance Tasks – Activity Association screen
Maintenance Tasks – Activity Association screen
 Work Management
Work Management
 Work Management – Work Requests · Simple interface to capture reactive Maintenance work · Can go through approval process, then be assigned to Work Orders
Work Management – Work Requests · Simple interface to capture reactive Maintenance work · Can go through approval process, then be assigned to Work Orders
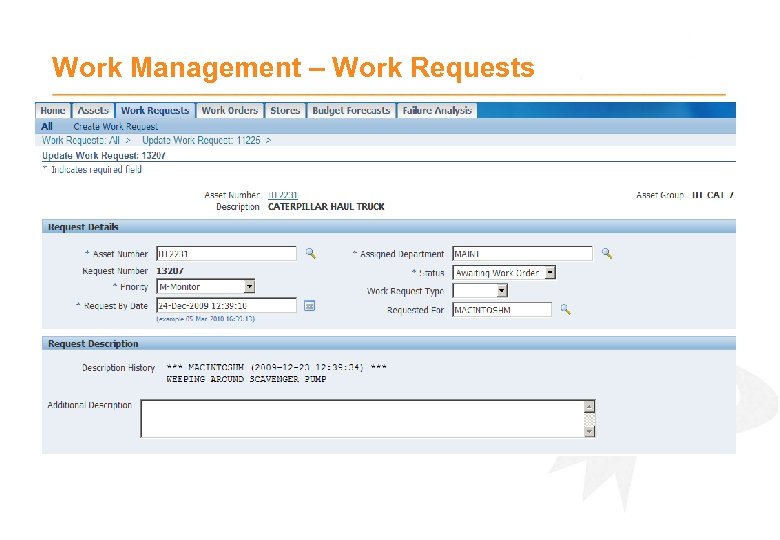 Work Management – Work Requests
Work Management – Work Requests
 Work Management – Work Orders · Work Orders represent specific instances of Maintenance work for an asset · Created in the following ways; - Manually i. e. unplanned / corrective work - Automatically by Preventative Maintenance forecast - Automatically from Condition Based monitoring (via Oracle Quality) · Work Orders record maintenance history and planned and actual costs · Work Orders must have; - Asset associated - One or more Tasks i. e. Operations - Scheduled Start / End Time · Work Orders can have; - Predefined Work assigned i. e. Activity - Material requirements i. e. Stock, Non Stock, Requisitions - Labour requirements i. e. Trade resource
Work Management – Work Orders · Work Orders represent specific instances of Maintenance work for an asset · Created in the following ways; - Manually i. e. unplanned / corrective work - Automatically by Preventative Maintenance forecast - Automatically from Condition Based monitoring (via Oracle Quality) · Work Orders record maintenance history and planned and actual costs · Work Orders must have; - Asset associated - One or more Tasks i. e. Operations - Scheduled Start / End Time · Work Orders can have; - Predefined Work assigned i. e. Activity - Material requirements i. e. Stock, Non Stock, Requisitions - Labour requirements i. e. Trade resource
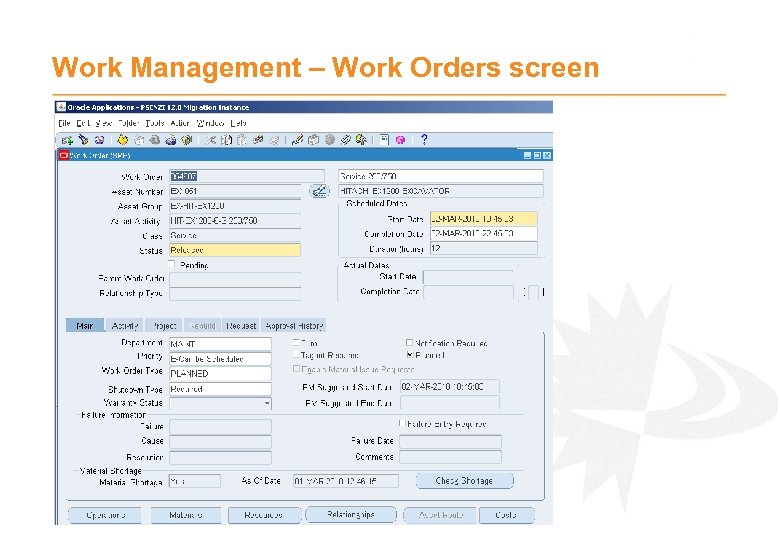 Work Management – Work Orders screen
Work Management – Work Orders screen
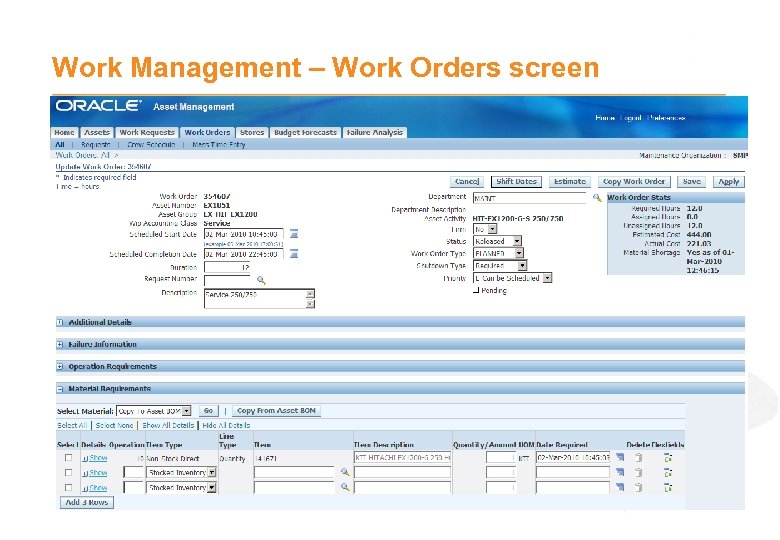 Work Management – Work Orders screen
Work Management – Work Orders screen
 Work Management – Completion · Completion updates Last Service information e. g. 250 hr service completed at 12, 500 hrs on 01 -Feb-2010 · Prevents further costs being coded to the Work Order · Captures the following information; - Actual Start and End time - Job Notes - Failure Analysis
Work Management – Completion · Completion updates Last Service information e. g. 250 hr service completed at 12, 500 hrs on 01 -Feb-2010 · Prevents further costs being coded to the Work Order · Captures the following information; - Actual Start and End time - Job Notes - Failure Analysis
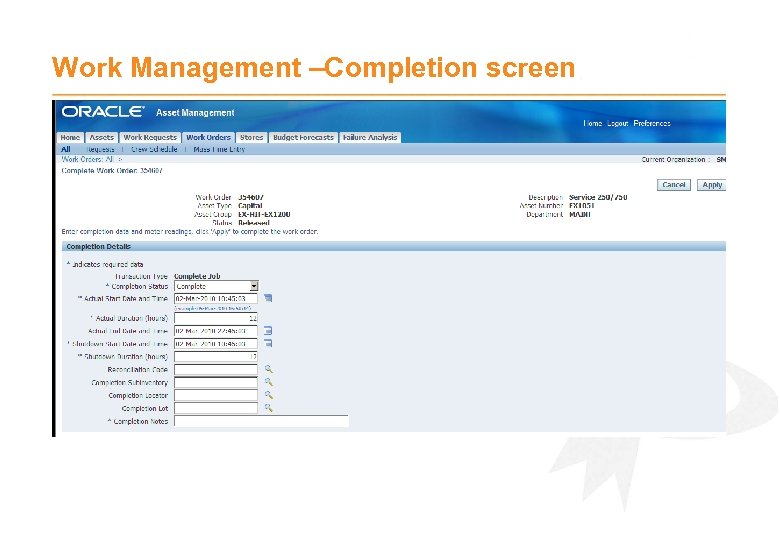 Work Management –Completion screen
Work Management –Completion screen
 Preventative Maintenance
Preventative Maintenance
 Preventative Maintenance - Schedules · Define when activities should occur for an Asset or Asset Group · Defined to occur by; - Date Rules – every 7 days - Meter Rules – every 50 hours, 10000 km’s - List Dates – on 01 -Jan-2011 · Work forecasts from Last Service Information i. e. when activity was last completed for the asset - Date Rules – on 01 -Jan-2010 - Meter Rules – at 2000 hours - Combinations of the above · Single definition can schedule multiple activities which share a common base interval · Schedules can include suppression e. g. 250 hr service suppresses 50 hr service if its forecast within 20 hours of it
Preventative Maintenance - Schedules · Define when activities should occur for an Asset or Asset Group · Defined to occur by; - Date Rules – every 7 days - Meter Rules – every 50 hours, 10000 km’s - List Dates – on 01 -Jan-2011 · Work forecasts from Last Service Information i. e. when activity was last completed for the asset - Date Rules – on 01 -Jan-2010 - Meter Rules – at 2000 hours - Combinations of the above · Single definition can schedule multiple activities which share a common base interval · Schedules can include suppression e. g. 250 hr service suppresses 50 hr service if its forecast within 20 hours of it
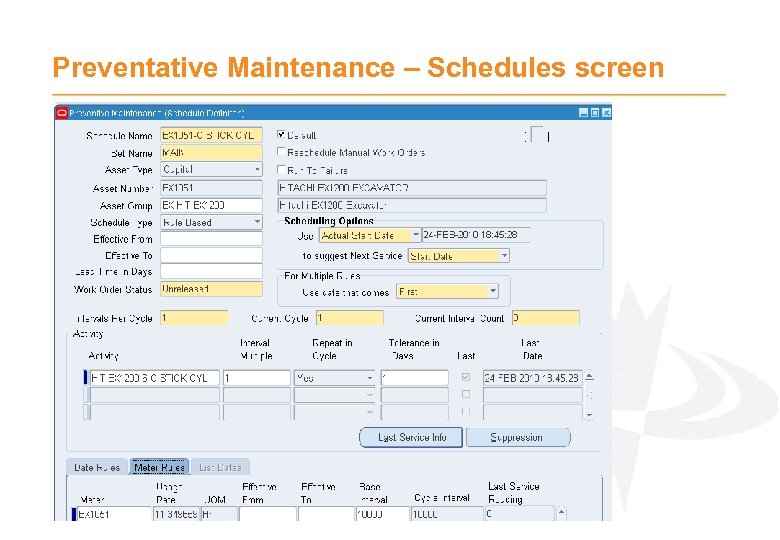 Preventative Maintenance – Schedules screen
Preventative Maintenance – Schedules screen
 Preventative Maintenance - Meters · Meters used to schedule activities · Ascending meters e. g. kilometres, hours · Fluctuating meters e. g. temperature, pressure, vibration · Meter hierarchies allowing parent meter to increment children e. g. truck hours increments rim hours
Preventative Maintenance - Meters · Meters used to schedule activities · Ascending meters e. g. kilometres, hours · Fluctuating meters e. g. temperature, pressure, vibration · Meter hierarchies allowing parent meter to increment children e. g. truck hours increments rim hours
 Preventative Maintenance – Meters screen
Preventative Maintenance – Meters screen
 Preventative Maintenance - Forecasting · Forecasting generates Work Orders as per schedules · Forecasts for a specified maintenance window e. g. next 14 days · Can perform online or as a concurrent program · Can selectively forecasts groups of assets
Preventative Maintenance - Forecasting · Forecasting generates Work Orders as per schedules · Forecasts for a specified maintenance window e. g. next 14 days · Can perform online or as a concurrent program · Can selectively forecasts groups of assets
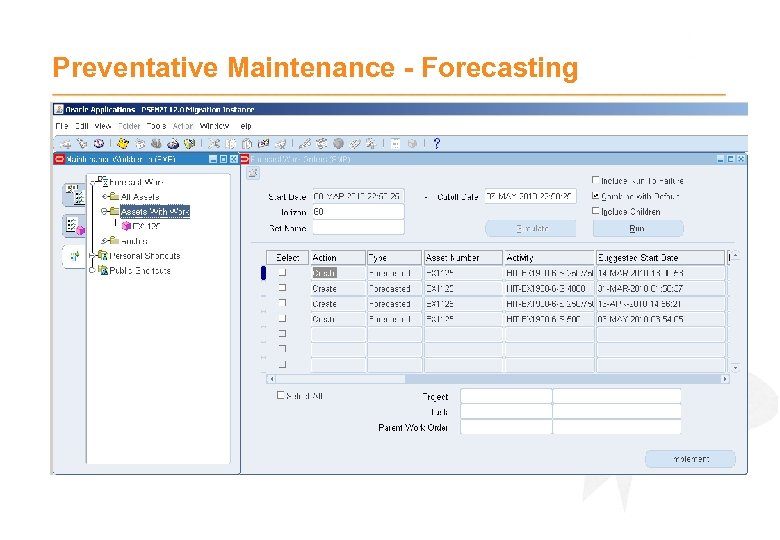 Preventative Maintenance - Forecasting
Preventative Maintenance - Forecasting
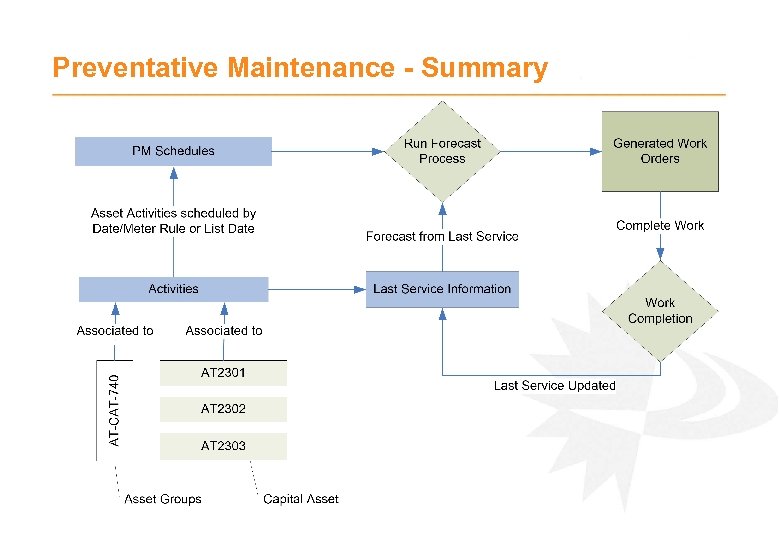 Preventative Maintenance - Summary
Preventative Maintenance - Summary
 Cost Management
Cost Management
 Cost Management – WIP Accounting Class (WAC) · WIP Accounting Classes (WAC) define accounting rules · Single GL accounts defined for Material and Resource transactions · Limited capability for complex accounting requirements · Default WAC for Organisation · Can be superseded by WAC configured against the at Asset, Activity or Work Order
Cost Management – WIP Accounting Class (WAC) · WIP Accounting Classes (WAC) define accounting rules · Single GL accounts defined for Material and Resource transactions · Limited capability for complex accounting requirements · Default WAC for Organisation · Can be superseded by WAC configured against the at Asset, Activity or Work Order
 Cost Management – Actual to Planned Costs · Planned Costs built up on Work Order using - Materials – Defaulted from Activity BOM or manually requested - Labour – Defaulted from Activity Routing or manually requested · Actual Costs accumulate on Work Order from - Stores inventory issues to Work Order - Purchase requisition (Direct Item) receipts - Maintenance Resource transactions - Invoice Price Variances (PO Matching) · Cost Analysis can then be performed in multiple ways, such as; - Asset using Hierarchy - Work Order - By Activity
Cost Management – Actual to Planned Costs · Planned Costs built up on Work Order using - Materials – Defaulted from Activity BOM or manually requested - Labour – Defaulted from Activity Routing or manually requested · Actual Costs accumulate on Work Order from - Stores inventory issues to Work Order - Purchase requisition (Direct Item) receipts - Maintenance Resource transactions - Invoice Price Variances (PO Matching) · Cost Analysis can then be performed in multiple ways, such as; - Asset using Hierarchy - Work Order - By Activity
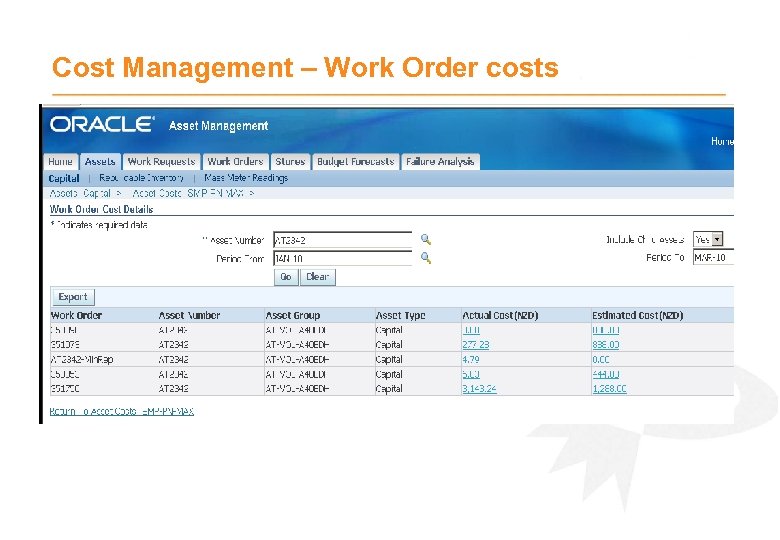 Cost Management – Work Order costs
Cost Management – Work Order costs
 Key experiences
Key experiences
 Key Experiences – What we have achieved · A single maintenance system throughout the organization · Better integration between stores and maintenance · Comprehensive asset and component history · Focus on preventative maintenance, driving better asset reliability · Better management of maintenance workload · Standardised asset information and maintenance procedures · Ability to analyse asset and maintenance department performance
Key Experiences – What we have achieved · A single maintenance system throughout the organization · Better integration between stores and maintenance · Comprehensive asset and component history · Focus on preventative maintenance, driving better asset reliability · Better management of maintenance workload · Standardised asset information and maintenance procedures · Ability to analyse asset and maintenance department performance
 Key experiences – Maintenance Staff Involvement · Maintenance staff involvement essential throughout implementation lifecycle · Creates required buy-in for successful business transition and adoption · Select “right” person carefully - Positive / Seeks improvement i. e. this is something new, but we should use - Resilient / Can do attitude i. e. that not ideal but we can make it work - Well Respected i. e. will lead others to accept solution and advocate it · Ensure the maintenance team is well trained and supported once live
Key experiences – Maintenance Staff Involvement · Maintenance staff involvement essential throughout implementation lifecycle · Creates required buy-in for successful business transition and adoption · Select “right” person carefully - Positive / Seeks improvement i. e. this is something new, but we should use - Resilient / Can do attitude i. e. that not ideal but we can make it work - Well Respected i. e. will lead others to accept solution and advocate it · Ensure the maintenance team is well trained and supported once live
 Key experiences – Data load · Data load is manual, complicated and time consuming · Limited open interfaces - Items (Asset Group, Activities) / Asset Number / Meter Reading · Now several more APIs in R 12 - Maintenance Object (Asset Number) / Activity / Preventative Maintenance · We have built custom Excel templates and used Data. Load utility · Have final dataset loaded for UAT, you will get many useful “corrections”
Key experiences – Data load · Data load is manual, complicated and time consuming · Limited open interfaces - Items (Asset Group, Activities) / Asset Number / Meter Reading · Now several more APIs in R 12 - Maintenance Object (Asset Number) / Activity / Preventative Maintenance · We have built custom Excel templates and used Data. Load utility · Have final dataset loaded for UAT, you will get many useful “corrections”
 Key experiences – Reporting · Standard reports are “limited” · Develop a custom Work Order, probably in BI Publisher now · Develop suite of reports to meet user requirements · We developed Discoverer reports, some examples; - Asset Hierarchy / History / Availability Asset / Work Order costing – by Hierarchy Asset / Work Order Material Requirements Asset Failure Analysis Key Performance e. g. Planned Versus Unplanned, Maintenance backlog Configuration reports e. g. BOMS, Activities, Schedules · Other off the shelf options worth investigating - Oracle e. AM Daily Business Intelligence - Vizaya Work. Align® Analytics - Signum EAM Analytics™
Key experiences – Reporting · Standard reports are “limited” · Develop a custom Work Order, probably in BI Publisher now · Develop suite of reports to meet user requirements · We developed Discoverer reports, some examples; - Asset Hierarchy / History / Availability Asset / Work Order costing – by Hierarchy Asset / Work Order Material Requirements Asset Failure Analysis Key Performance e. g. Planned Versus Unplanned, Maintenance backlog Configuration reports e. g. BOMS, Activities, Schedules · Other off the shelf options worth investigating - Oracle e. AM Daily Business Intelligence - Vizaya Work. Align® Analytics - Signum EAM Analytics™
 Key experiences – Reporting
Key experiences – Reporting
 Key experiences – Subledger Accounting · “Get around” limitation of single material and labour GL accounts · We use Subledger Accounting to re-code; - Expense Account – Based on Item/PO Category - Asset Account – Based on Flexfield held against Asset Number · Not too complicated once you have a working prototype · Use some consulting initially to get initial setup working
Key experiences – Subledger Accounting · “Get around” limitation of single material and labour GL accounts · We use Subledger Accounting to re-code; - Expense Account – Based on Item/PO Category - Asset Account – Based on Flexfield held against Asset Number · Not too complicated once you have a working prototype · Use some consulting initially to get initial setup working
 Key experiences – Usability · Release 12 Self Service is a dramatic improvement · Maintenance Supervisors can work solely in Self Service · Personalisation can de-clutter Self Service · Consider customisation for “pain points”
Key experiences – Usability · Release 12 Self Service is a dramatic improvement · Maintenance Supervisors can work solely in Self Service · Personalisation can de-clutter Self Service · Consider customisation for “pain points”
 Questions ? · Ask now if we have time · Come see me afterwards · Email me after the conference jeremy. carson@solidenergy. co. nz
Questions ? · Ask now if we have time · Come see me afterwards · Email me after the conference jeremy. carson@solidenergy. co. nz


