c4f7adba472016a4c6cf09a8e76f6c37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Introduction to Nursing Pamela M. Llana, MSN, RN
Introduction to Nursing Pamela M. Llana, MSN, RN
 Definition
Definition
 Nursing • “the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, communities, and populations” (ANA, 2010, p. 10) • Requires: – Creativity – Sensitivity – Applications based on scientific rationale
Nursing • “the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, communities, and populations” (ANA, 2010, p. 10) • Requires: – Creativity – Sensitivity – Applications based on scientific rationale
 Nursing History • 1836 -Florence Nightingale “founder of modern nursing” • Defined nursing as “the act of utilizing the environment of the client to assist him in his recovery” (1859) • Hygiene and comfort • Developed nursing schools • Changed society’s view of nursing -from the “dregs of society” to dignity and value, worthy of respect
Nursing History • 1836 -Florence Nightingale “founder of modern nursing” • Defined nursing as “the act of utilizing the environment of the client to assist him in his recovery” (1859) • Hygiene and comfort • Developed nursing schools • Changed society’s view of nursing -from the “dregs of society” to dignity and value, worthy of respect
 • 1872 Linda Richards “America’s first trained nurse” • 1882 Clara Barton forms American Red Cross • Historical timeline pp. 3 -4 (not responsible to know!)
• 1872 Linda Richards “America’s first trained nurse” • 1882 Clara Barton forms American Red Cross • Historical timeline pp. 3 -4 (not responsible to know!)
 Nursing Theory • Theories provide different explanations of the nursing discipline but share four central concepts that are defined, related and emphasized differently – – Person Environment Health Nursing • Nightingale – first theorist • 16 additional theorists through the 1980’s
Nursing Theory • Theories provide different explanations of the nursing discipline but share four central concepts that are defined, related and emphasized differently – – Person Environment Health Nursing • Nightingale – first theorist • 16 additional theorists through the 1980’s
 Image of Nursing • Not physician’s “handmaiden” • Professional • High-tech • Respected/trusted • Changing faces of nursing
Image of Nursing • Not physician’s “handmaiden” • Professional • High-tech • Respected/trusted • Changing faces of nursing
 Nursing Roles & Responsibilities • Caregiver • Decision-maker • Patient (client) advocate • Manager • Coordinator • Communicator • Educator
Nursing Roles & Responsibilities • Caregiver • Decision-maker • Patient (client) advocate • Manager • Coordinator • Communicator • Educator
 Professional Nursing Education • Registered Nurse (RN) – Associate Degree (ADN) • 2 years – Diploma • 3 years (phasing out) – Baccalaureate (BSN) • 4 years
Professional Nursing Education • Registered Nurse (RN) – Associate Degree (ADN) • 2 years – Diploma • 3 years (phasing out) – Baccalaureate (BSN) • 4 years
 Professional Nursing Education • Advanced Education – Master’s (MSN) • Family Nurse Practitioner • Acute Care Nurse Practitioner • Pediatric Nurse Practitioner • CRNA-Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist • Nurse Educator – Doctorate (Ph. D. – research; DNP – clinical) – Certification
Professional Nursing Education • Advanced Education – Master’s (MSN) • Family Nurse Practitioner • Acute Care Nurse Practitioner • Pediatric Nurse Practitioner • CRNA-Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist • Nurse Educator – Doctorate (Ph. D. – research; DNP – clinical) – Certification
 Nursing Organizations • ANA – American Nurses Assn. • MNA – MS Nurses Assn. • MASN – MS Assn. of Student Nurses • NOADN – National Org. for Associate Degree Nursing • MOADN – MS Org. for ADN • MOSA – MS Org. Student Assn. • SNA – MOSA Chapter at NWCC
Nursing Organizations • ANA – American Nurses Assn. • MNA – MS Nurses Assn. • MASN – MS Assn. of Student Nurses • NOADN – National Org. for Associate Degree Nursing • MOADN – MS Org. for ADN • MOSA – MS Org. Student Assn. • SNA – MOSA Chapter at NWCC
 Nursing Organizations • Special Interest organizations – Surgical nurses, Men, Critical Care, Emergency, Pediatric, Oncology, Nurse Executives • ACEN – accreditation; ensures public need of nursing is met; formerly called NLNAC • Alpha Delta Nu – Honor Society of Nursing (ADN) • Sigma Theta Tau – Honor Society of Nursing (BSN, MSN) • International Council of Nurses – develops nursing throughout the world
Nursing Organizations • Special Interest organizations – Surgical nurses, Men, Critical Care, Emergency, Pediatric, Oncology, Nurse Executives • ACEN – accreditation; ensures public need of nursing is met; formerly called NLNAC • Alpha Delta Nu – Honor Society of Nursing (ADN) • Sigma Theta Tau – Honor Society of Nursing (BSN, MSN) • International Council of Nurses – develops nursing throughout the world
 Nursing Research • National Center for Nursing Research in the National Institutes of Health • Findings used in clinical practice
Nursing Research • National Center for Nursing Research in the National Institutes of Health • Findings used in clinical practice
 “Evidence-based Practice” • Problem-solving approach to clinical practice • Integrates use of: Best evidence with Clinician’s expertise and Client’s preferences and values • Research-based articles • Evidence-based care – 28% better outcomes
“Evidence-based Practice” • Problem-solving approach to clinical practice • Integrates use of: Best evidence with Clinician’s expertise and Client’s preferences and values • Research-based articles • Evidence-based care – 28% better outcomes
 “Evidence-based Practice” • EBP-references on class guides • Textbooks – may be outdated • EBP Sources: – Articles-library search engines – AHRQ-Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – Cochrane Database – National Guidelines Clearinghouse – Joanna Briggs Institute
“Evidence-based Practice” • EBP-references on class guides • Textbooks – may be outdated • EBP Sources: – Articles-library search engines – AHRQ-Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – Cochrane Database – National Guidelines Clearinghouse – Joanna Briggs Institute
 Health and Wellness • Health – “state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” (WHO, 1947) • Difficult to define – individual concept • It is MORE than absence of disease.
Health and Wellness • Health – “state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” (WHO, 1947) • Difficult to define – individual concept • It is MORE than absence of disease.
 Health Promotion and Disease Prevention • Health promotion – exercise/nutrition • Wellness education – stress management • Illness prevention – screening guidelines
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention • Health promotion – exercise/nutrition • Wellness education – stress management • Illness prevention – screening guidelines
 3 Levels of Prevention • Primary Prevention (true prevention) – Health Promotion (nutrition, sex education) – Specific Protection (immunizations) • Secondary Prevention – Early Diagnosis & Prompt Treatment (screening) – Disability Limitations (tx to prevent complications) • Tertiary Prevention – Restoration & Rehab
3 Levels of Prevention • Primary Prevention (true prevention) – Health Promotion (nutrition, sex education) – Specific Protection (immunizations) • Secondary Prevention – Early Diagnosis & Prompt Treatment (screening) – Disability Limitations (tx to prevent complications) • Tertiary Prevention – Restoration & Rehab
 ILLNESS Health beliefs – a person’s ideas, convictions and attitudes about health and illness – can be positive (+) or negative (-) • “state in which physical, emotional, intellectual, social, developmental, or spiritual functioning is diminished or impaired compared with previous experience • Acute – short term and severe • Chronic – persists, usually longer than 6 months, affects functioning • Impact-illness behavior – how people monitor their bodies, take action and use the health care system
ILLNESS Health beliefs – a person’s ideas, convictions and attitudes about health and illness – can be positive (+) or negative (-) • “state in which physical, emotional, intellectual, social, developmental, or spiritual functioning is diminished or impaired compared with previous experience • Acute – short term and severe • Chronic – persists, usually longer than 6 months, affects functioning • Impact-illness behavior – how people monitor their bodies, take action and use the health care system
 Risk Factors for Illness or Injury • Definition: any situation, habit, environmental condition, physiological condition that increases likelihood of illness or accident • Genetics (including Race) • Gender • Physical (weight, pregnancy) • Age • Environment (toxins, chemicals) • Lifestyle (alcohol/drugs/sexual behavior)
Risk Factors for Illness or Injury • Definition: any situation, habit, environmental condition, physiological condition that increases likelihood of illness or accident • Genetics (including Race) • Gender • Physical (weight, pregnancy) • Age • Environment (toxins, chemicals) • Lifestyle (alcohol/drugs/sexual behavior)
 Vulnerable Populations • High risk for health problems • Due to excess risk; limited health care • Dependent on others for care • Includes: homeless, poverty, older adults, immigrants, abusive relationships, substance abusers, severely mentally ill
Vulnerable Populations • High risk for health problems • Due to excess risk; limited health care • Dependent on others for care • Includes: homeless, poverty, older adults, immigrants, abusive relationships, substance abusers, severely mentally ill
 Holistic Health – Complementary or Alternative Medicine Person as bio-psycho-social and spiritual being; Interventions focus on interrelated needs of body, mind, emotions, and spirit
Holistic Health – Complementary or Alternative Medicine Person as bio-psycho-social and spiritual being; Interventions focus on interrelated needs of body, mind, emotions, and spirit
 Holistic Health includes: • • • Vitamins/herbals Chiropractic care Biofeedback Meditation Therapeutic touch Art/music therapy Humor Prayer Guided imagery • Nurse’s Role – Assess client’s need and use of CAM – Provide CAM within scope of practice when appropriate – Inform/refer – Evaluate outcomes of CAM
Holistic Health includes: • • • Vitamins/herbals Chiropractic care Biofeedback Meditation Therapeutic touch Art/music therapy Humor Prayer Guided imagery • Nurse’s Role – Assess client’s need and use of CAM – Provide CAM within scope of practice when appropriate – Inform/refer – Evaluate outcomes of CAM
 Nursing Care of Individual, Family and Community
Nursing Care of Individual, Family and Community
 Community Nursing • Our clients include the family and the community • Goal: promote, maintain and restore health • Examples of nursing care for: – Family: Therapy to deal with acute or chronic illness of family member – Community: TB screening of employees, replacing soda machines with water/juice in schools
Community Nursing • Our clients include the family and the community • Goal: promote, maintain and restore health • Examples of nursing care for: – Family: Therapy to deal with acute or chronic illness of family member – Community: TB screening of employees, replacing soda machines with water/juice in schools
 Nurse Roles in the Community • Community-based Nursing – provides acute and chronic care services to individual within community • Community Health Nursing - provides services to individuals, families, and groups identified by risk factors of community • Public Health Nursing – provides focus of practice on primary prevention with the community as client
Nurse Roles in the Community • Community-based Nursing – provides acute and chronic care services to individual within community • Community Health Nursing - provides services to individuals, families, and groups identified by risk factors of community • Public Health Nursing – provides focus of practice on primary prevention with the community as client
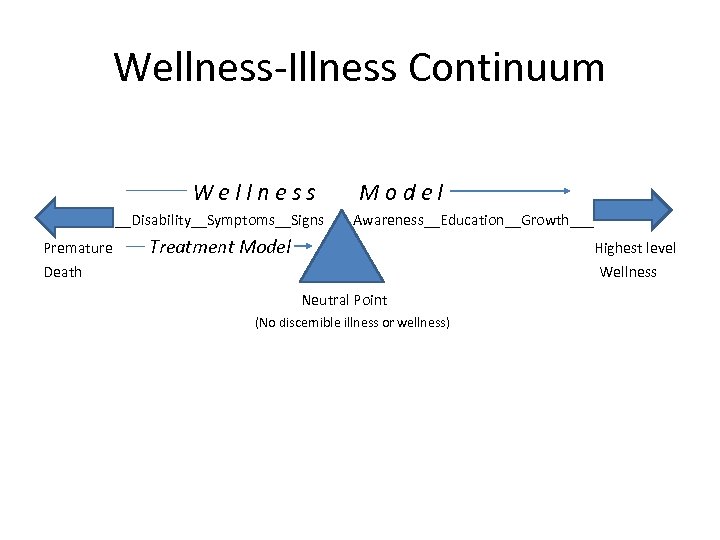 Wellness-Illness Continuum Wellness __Disability__Symptoms__Signs Premature Model Awareness__Education__Growth___ Treatment Model Highest level Death Wellness Neutral Point (No discernible illness or wellness)
Wellness-Illness Continuum Wellness __Disability__Symptoms__Signs Premature Model Awareness__Education__Growth___ Treatment Model Highest level Death Wellness Neutral Point (No discernible illness or wellness)
 Health Care Delivery Systems • Participants – Consumers (patient/client and community) – Providers (licensed and unlicensed) • Settings – Hospitals – Home, Schools – Skilled-nursing, Assisted-living, Extended care, Rehab units, Hospice – Health Departments – Adult Daycare centers
Health Care Delivery Systems • Participants – Consumers (patient/client and community) – Providers (licensed and unlicensed) • Settings – Hospitals – Home, Schools – Skilled-nursing, Assisted-living, Extended care, Rehab units, Hospice – Health Departments – Adult Daycare centers
 Delivery Systems – cont. • Regulatory agencies – FDA – State/local health agencies – State licensing – The Joint Commission • Financing mechanisms – Private plans – Insurance – Public funding • Medicare – over 65 • Medicaid – low income – state determined
Delivery Systems – cont. • Regulatory agencies – FDA – State/local health agencies – State licensing – The Joint Commission • Financing mechanisms – Private plans – Insurance – Public funding • Medicare – over 65 • Medicaid – low income – state determined
 Interdisciplinary Team • Collaborates to provide holistic care • Nursing personnel – RN/LPN – Advanced Practice: NP, CRNA, Educator, Administrator – CNA, PCA, Nurse intern/extern • Non-nursing (Dietician, lab tech, pharmacist, PT, MD, radiology, respiratory therapy, social worker, speech therapy, clerical)
Interdisciplinary Team • Collaborates to provide holistic care • Nursing personnel – RN/LPN – Advanced Practice: NP, CRNA, Educator, Administrator – CNA, PCA, Nurse intern/extern • Non-nursing (Dietician, lab tech, pharmacist, PT, MD, radiology, respiratory therapy, social worker, speech therapy, clerical)
 Discharge Planning • Starts AT ADMISSION! • Provides continuity of care: – From health care facility to the home – From one level of care to another • Goals: – Reduce readmission – Improve patient outcomes • Collaboration required: – With patient AND family – With other members of the healthcare team
Discharge Planning • Starts AT ADMISSION! • Provides continuity of care: – From health care facility to the home – From one level of care to another • Goals: – Reduce readmission – Improve patient outcomes • Collaboration required: – With patient AND family – With other members of the healthcare team
 Delegation of Nurse-related Tasks • RN – responsible & accountable for care • Use professional judgment & critical thinking skills to implement 5 rights of delegation: – Right task – Right circumstances – Right person – Right direction/communication – Right supervision
Delegation of Nurse-related Tasks • RN – responsible & accountable for care • Use professional judgment & critical thinking skills to implement 5 rights of delegation: – Right task – Right circumstances – Right person – Right direction/communication – Right supervision
 Delegation • To LPN – Licensed Practical Nurse – Patient Assessment (not all assessments) • RN must do initial assessment, post-surgical assessment, unstable patient assessments – Care must be coordinated/supervised by RN – Certain areas restricted to RN • To PCA – Patient Care Assistant/Nurse’s Aide – Can feed, bathe, turn pt. , vital signs unless unstable or facility policy (i. e. BP) – NO medications – NO sterile procedures
Delegation • To LPN – Licensed Practical Nurse – Patient Assessment (not all assessments) • RN must do initial assessment, post-surgical assessment, unstable patient assessments – Care must be coordinated/supervised by RN – Certain areas restricted to RN • To PCA – Patient Care Assistant/Nurse’s Aide – Can feed, bathe, turn pt. , vital signs unless unstable or facility policy (i. e. BP) – NO medications – NO sterile procedures
 Thinking Strategies for Nursing • Nursing Process A D P I E • Critical Thinking
Thinking Strategies for Nursing • Nursing Process A D P I E • Critical Thinking
 What Critical Thinking Is • Purposeful thinking that aims to make judgments based on evidence (Alfaro -Le. Fevre, 2003) • Reasonable, reflective thinking focused on what to believe or do (Ennis & Milman, 1985)
What Critical Thinking Is • Purposeful thinking that aims to make judgments based on evidence (Alfaro -Le. Fevre, 2003) • Reasonable, reflective thinking focused on what to believe or do (Ennis & Milman, 1985)
 What it is NOT • Common sense • Working in isolation • Spontaneous responses • Being competitive • Regular or “normal” thinking • Being critical or judgmental • Inability to communicate with others • Disorganized • Lack of concern with motives, facts, underlying reasons • Task-oriented • Emotion-driven
What it is NOT • Common sense • Working in isolation • Spontaneous responses • Being competitive • Regular or “normal” thinking • Being critical or judgmental • Inability to communicate with others • Disorganized • Lack of concern with motives, facts, underlying reasons • Task-oriented • Emotion-driven
 How does this translate to nursing? • Reflective, reasonable thinking about nursing problems with more than one solution • Clinical decision-making, diagnostic reasoning, and professional judgment
How does this translate to nursing? • Reflective, reasonable thinking about nursing problems with more than one solution • Clinical decision-making, diagnostic reasoning, and professional judgment
 Components of Critical Thinking • Knowledge Education – basic, continuing, and advanced • Experience Success with other patients • Competence Evidence-based practice
Components of Critical Thinking • Knowledge Education – basic, continuing, and advanced • Experience Success with other patients • Competence Evidence-based practice
 DSM - 5 • Standard classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals in United States • Contains listing of diagnostic criteria for every psychiatric disorder recognized by U. S. healthcare
DSM - 5 • Standard classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals in United States • Contains listing of diagnostic criteria for every psychiatric disorder recognized by U. S. healthcare



