4d786cd771a3ae5297f3987a1ab08ca0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance---NMR Principle of NMR
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance---NMR Principle of NMR
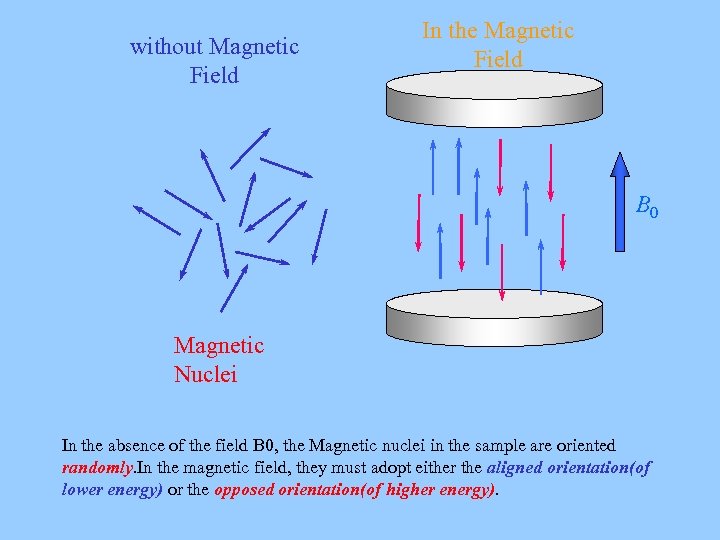 without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei In the absence of the field B 0, the Magnetic nuclei in the sample are oriented randomly. In the magnetic field, they must adopt either the aligned orientation(of lower energy) or the opposed orientation(of higher energy).
without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei In the absence of the field B 0, the Magnetic nuclei in the sample are oriented randomly. In the magnetic field, they must adopt either the aligned orientation(of lower energy) or the opposed orientation(of higher energy).
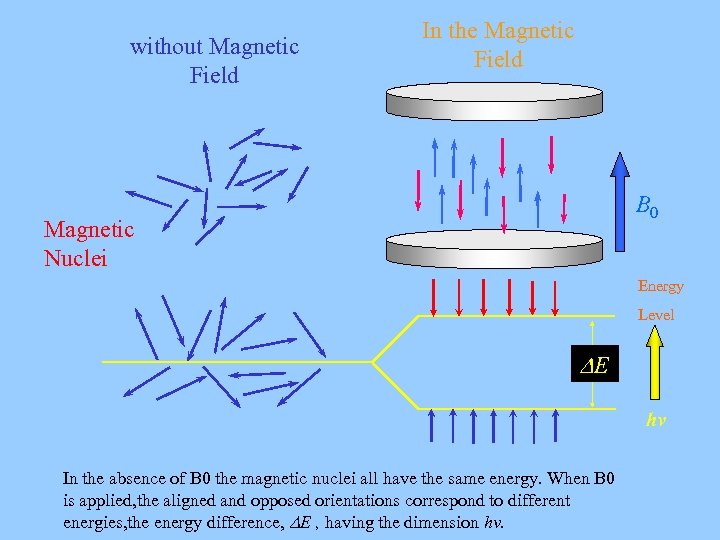 without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei Energy Level E hv In the absence of B 0 the magnetic nuclei all have the same energy. When B 0 is applied, the aligned and opposed orientations correspond to different energies, the energy difference, E , having the dimension hv.
without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei Energy Level E hv In the absence of B 0 the magnetic nuclei all have the same energy. When B 0 is applied, the aligned and opposed orientations correspond to different energies, the energy difference, E , having the dimension hv.
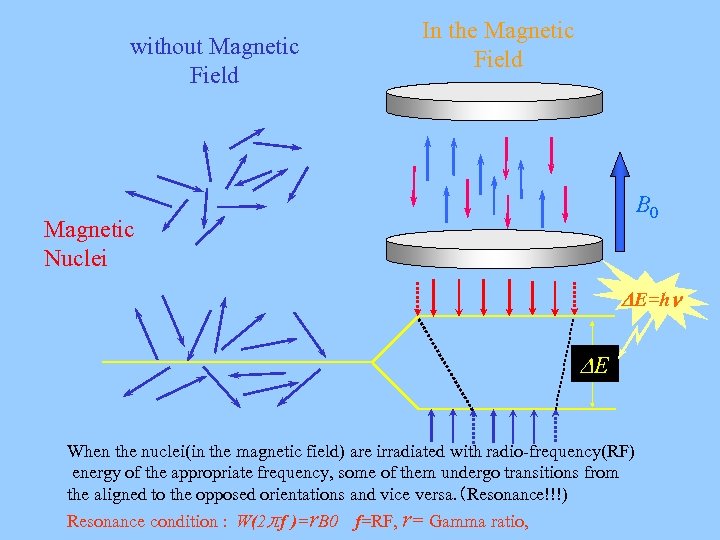 without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei E=h E When the nuclei(in the magnetic field) are irradiated with radio-frequency(RF) energy of the appropriate frequency, some of them undergo transitions from the aligned to the opposed orientations and vice versa. (Resonance!!!) Resonance condition : W(2兀f )=r. B 0 f=RF, r= Gamma ratio,
without Magnetic Field In the Magnetic Field B 0 Magnetic Nuclei E=h E When the nuclei(in the magnetic field) are irradiated with radio-frequency(RF) energy of the appropriate frequency, some of them undergo transitions from the aligned to the opposed orientations and vice versa. (Resonance!!!) Resonance condition : W(2兀f )=r. B 0 f=RF, r= Gamma ratio,
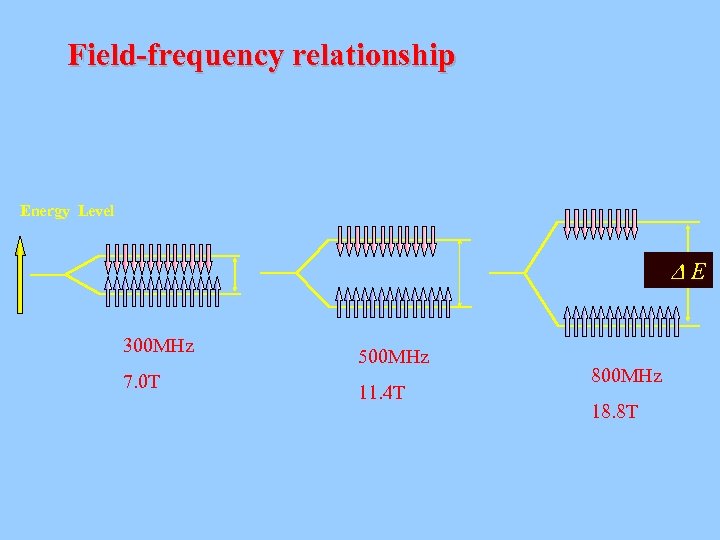 Field-frequency relationship Energy Level E 300 MHz 7. 0 T 500 MHz 11. 4 T 800 MHz 18. 8 T
Field-frequency relationship Energy Level E 300 MHz 7. 0 T 500 MHz 11. 4 T 800 MHz 18. 8 T
 Magnetic moment(1) 1 If both the mass number(A) and the atomic number(Z) are even, I = 0 (No NMR signal) 12 C, 16 O 2 If (A) is odd and (Z) is odd or even, I will have halfintegral values. I =1/2, 3/2, 5/2 etc 1 H, 19 F, 29 Si, 11 B(3/2), 17 O(5/2) 3 If (A) is even and (Z) is odd, I will have integral value 1, 2, 3 etc. 14 N, 6 Li,
Magnetic moment(1) 1 If both the mass number(A) and the atomic number(Z) are even, I = 0 (No NMR signal) 12 C, 16 O 2 If (A) is odd and (Z) is odd or even, I will have halfintegral values. I =1/2, 3/2, 5/2 etc 1 H, 19 F, 29 Si, 11 B(3/2), 17 O(5/2) 3 If (A) is even and (Z) is odd, I will have integral value 1, 2, 3 etc. 14 N, 6 Li,
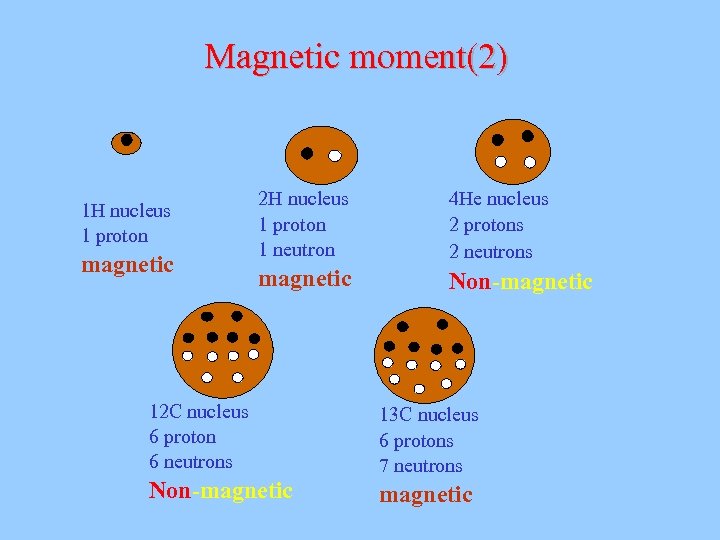 Magnetic moment(2) 1 H nucleus 1 proton magnetic 2 H nucleus 1 proton 1 neutron 4 He nucleus 2 protons 2 neutrons magnetic Non-magnetic 12 C nucleus 6 proton 6 neutrons 13 C nucleus 6 protons 7 neutrons Non-magnetic
Magnetic moment(2) 1 H nucleus 1 proton magnetic 2 H nucleus 1 proton 1 neutron 4 He nucleus 2 protons 2 neutrons magnetic Non-magnetic 12 C nucleus 6 proton 6 neutrons 13 C nucleus 6 protons 7 neutrons Non-magnetic
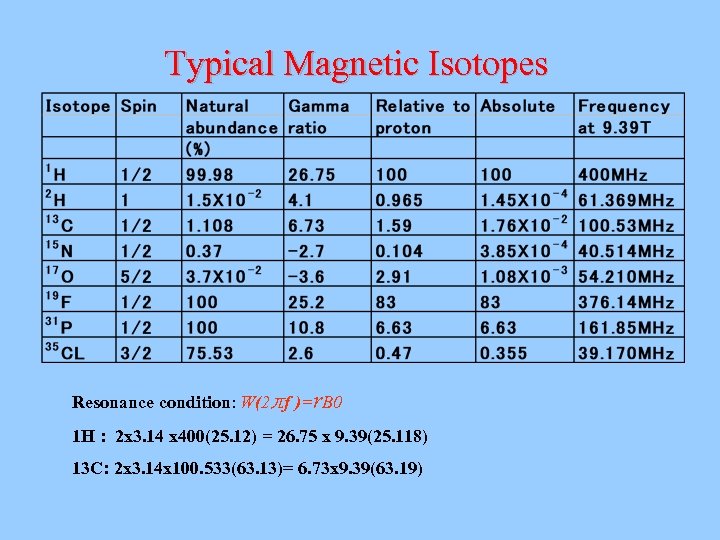 Typical Magnetic Isotopes Resonance condition: W(2兀f )=r. B 0 1 H : 2 x 3. 14 x 400(25. 12) = 26. 75 x 9. 39(25. 118) 13 C: 2 x 3. 14 x 100. 533(63. 13)= 6. 73 x 9. 39(63. 19)
Typical Magnetic Isotopes Resonance condition: W(2兀f )=r. B 0 1 H : 2 x 3. 14 x 400(25. 12) = 26. 75 x 9. 39(25. 118) 13 C: 2 x 3. 14 x 100. 533(63. 13)= 6. 73 x 9. 39(63. 19)
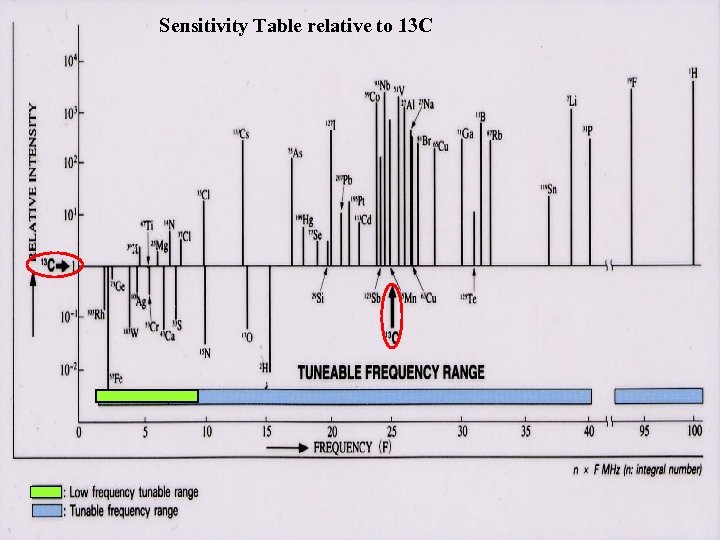 Sensitivity Table relative to 13 C
Sensitivity Table relative to 13 C
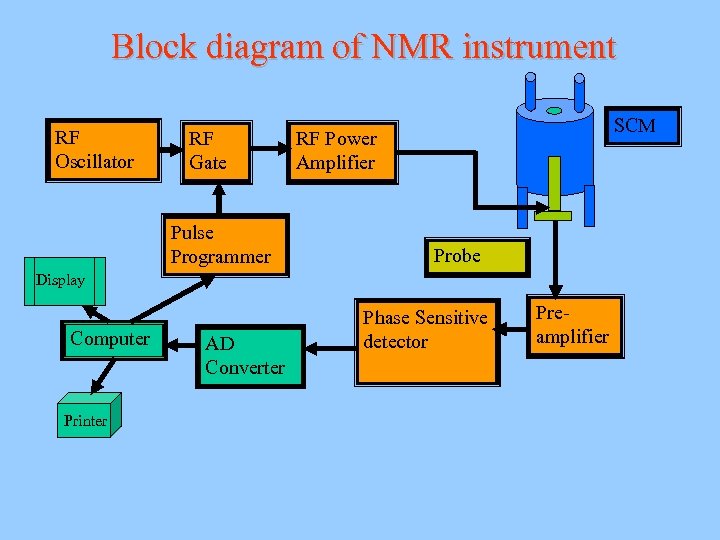 Block diagram of NMR instrument RF Oscillator RF Gate Pulse Programmer SCM RF Power Amplifier Probe Display Computer Printer AD Converter Phase Sensitive detector Preamplifier
Block diagram of NMR instrument RF Oscillator RF Gate Pulse Programmer SCM RF Power Amplifier Probe Display Computer Printer AD Converter Phase Sensitive detector Preamplifier
 Composition of NMR instrument ECA 500 NMR JEOL LTD
Composition of NMR instrument ECA 500 NMR JEOL LTD
 The NMR information 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Chemical Shift Spin-Spin Coupling Intensity(Area) of Signal Relaxation(T 1, T 2) NOE
The NMR information 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Chemical Shift Spin-Spin Coupling Intensity(Area) of Signal Relaxation(T 1, T 2) NOE
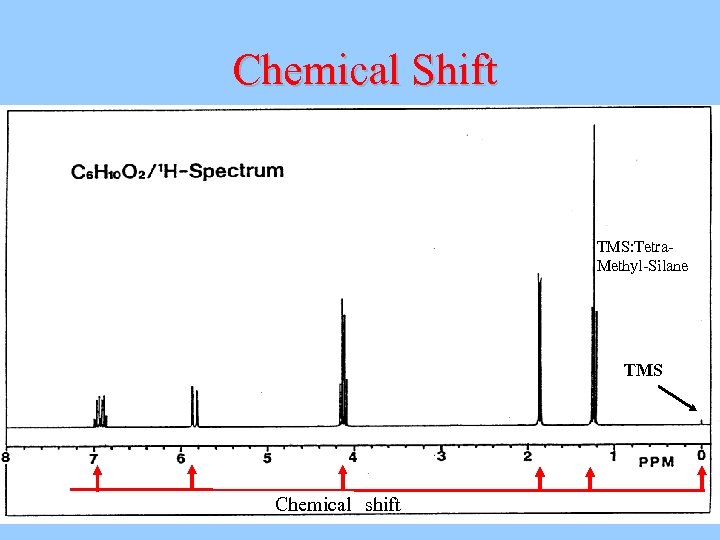 Chemical Shift TMS: Tetra- Methyl-Silane TMS Chemical shift
Chemical Shift TMS: Tetra- Methyl-Silane TMS Chemical shift
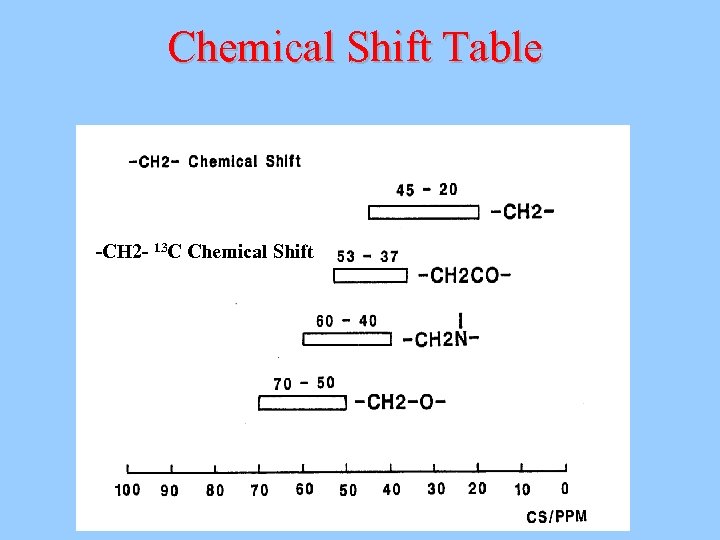 Chemical Shift Table -CH 2 - 13 C Chemical Shift
Chemical Shift Table -CH 2 - 13 C Chemical Shift
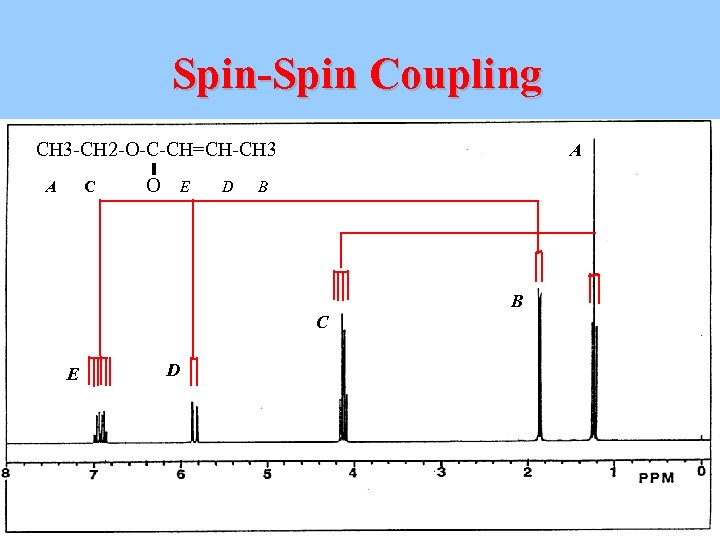 Spin-Spin Coupling CH 3 -CH 2 -O-C-CH=CH-CH 3 A C O E D A B B C E D
Spin-Spin Coupling CH 3 -CH 2 -O-C-CH=CH-CH 3 A C O E D A B B C E D
 Intensity(Area) Information
Intensity(Area) Information
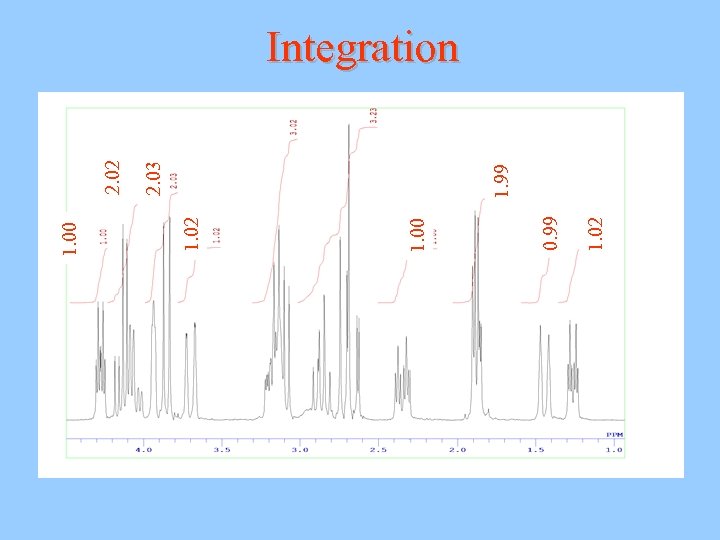 1. 02 0. 99 1. 00 1. 02 1. 00 1. 99 2. 03 2. 02 Integration
1. 02 0. 99 1. 00 1. 02 1. 00 1. 99 2. 03 2. 02 Integration
 Various measurement methods 1 dimension (1 H, 13 C, DEPT, ……. ) 2 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …) 3 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …) 4 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …)
Various measurement methods 1 dimension (1 H, 13 C, DEPT, ……. ) 2 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …) 3 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …) 4 dimension (COSY, NOESY, TOCSY, HMBC, HMQC, …)
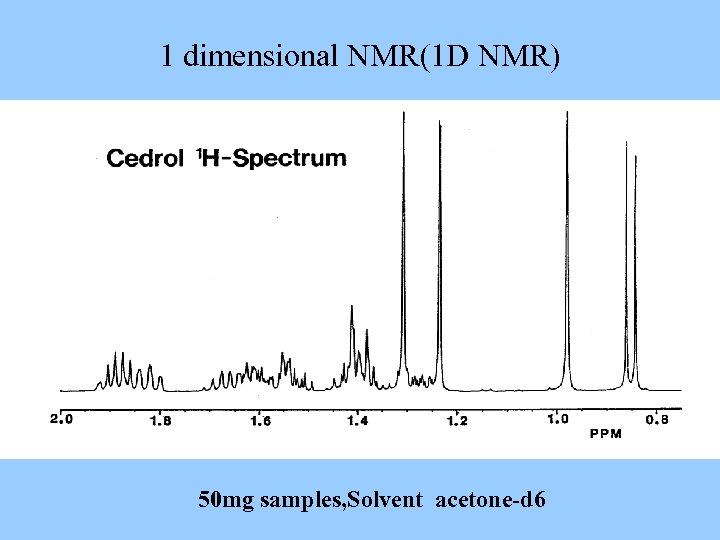 1 dimensional NMR(1 D NMR) 50 mg samples, Solvent acetone-d 6
1 dimensional NMR(1 D NMR) 50 mg samples, Solvent acetone-d 6
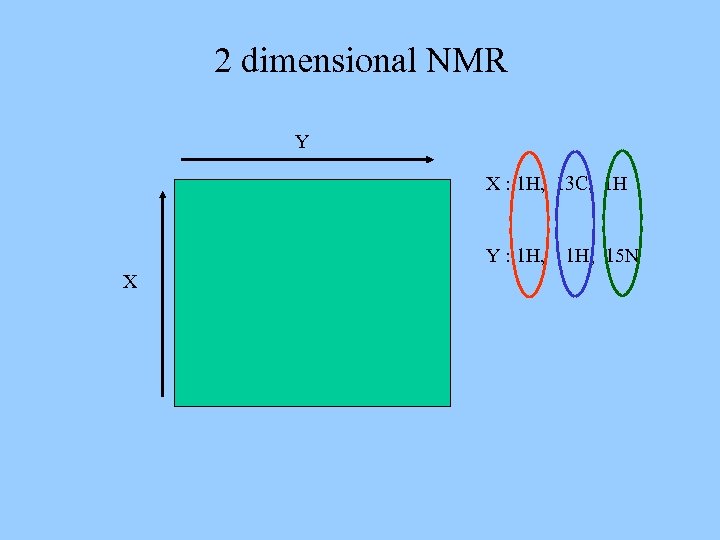 2 dimensional NMR Y X : 1 H, 13 C, 1 H Y : 1 H, X 1 H, 15 N
2 dimensional NMR Y X : 1 H, 13 C, 1 H Y : 1 H, X 1 H, 15 N
 2 dimensional NMR
2 dimensional NMR
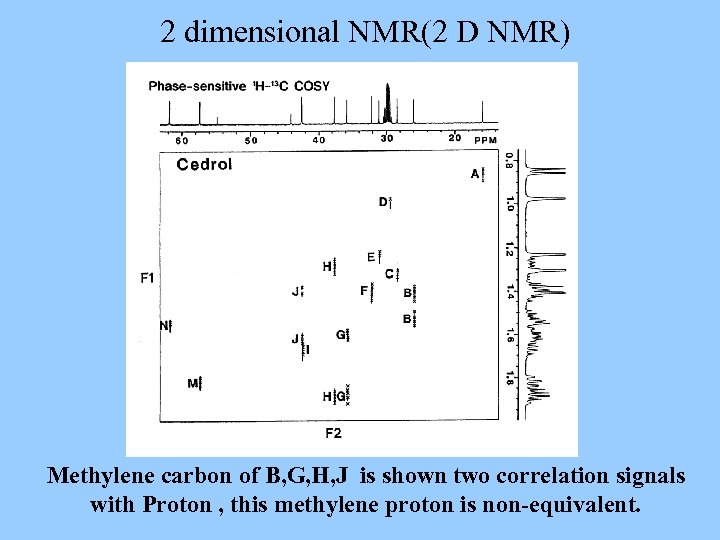 2 dimensional NMR(2 D NMR) Methylene carbon of B, G, H, J is shown two correlation signals with Proton , this methylene proton is non-equivalent.
2 dimensional NMR(2 D NMR) Methylene carbon of B, G, H, J is shown two correlation signals with Proton , this methylene proton is non-equivalent.
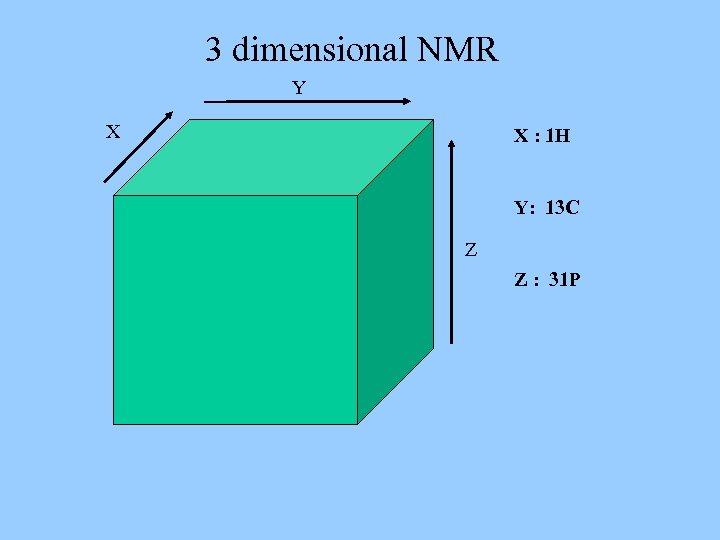 3 dimensional NMR Y X X : 1 H Y: 13 C Z Z : 31 P
3 dimensional NMR Y X X : 1 H Y: 13 C Z Z : 31 P
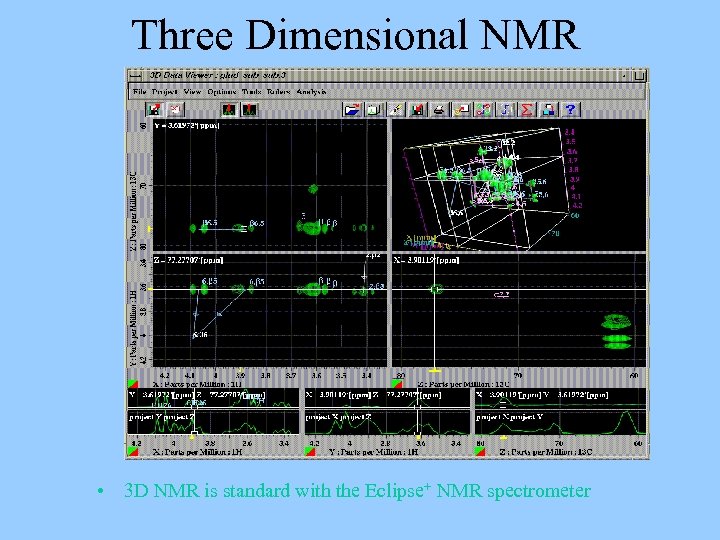 Three Dimensional NMR • 3 D NMR is standard with the Eclipse+ NMR spectrometer
Three Dimensional NMR • 3 D NMR is standard with the Eclipse+ NMR spectrometer
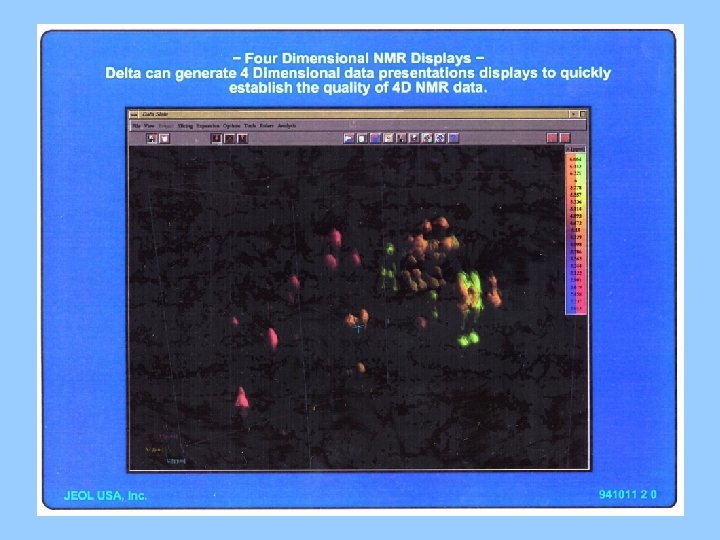
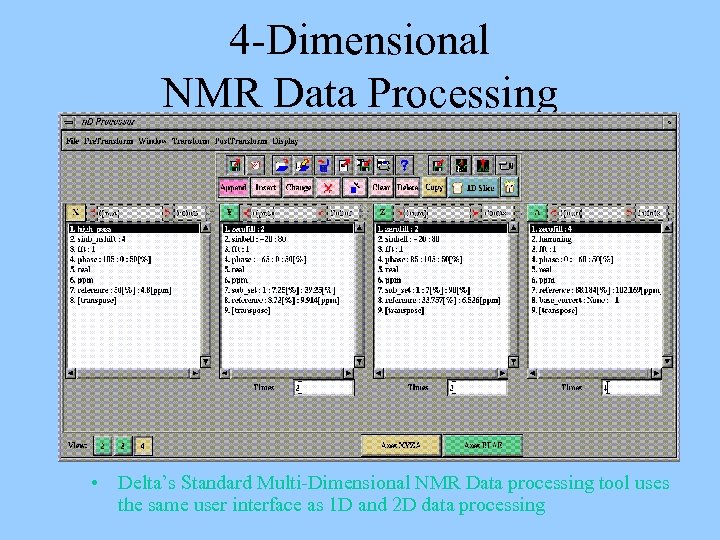 4 -Dimensional NMR Data Processing • Delta’s Standard Multi-Dimensional NMR Data processing tool uses the same user interface as 1 D and 2 D data processing
4 -Dimensional NMR Data Processing • Delta’s Standard Multi-Dimensional NMR Data processing tool uses the same user interface as 1 D and 2 D data processing
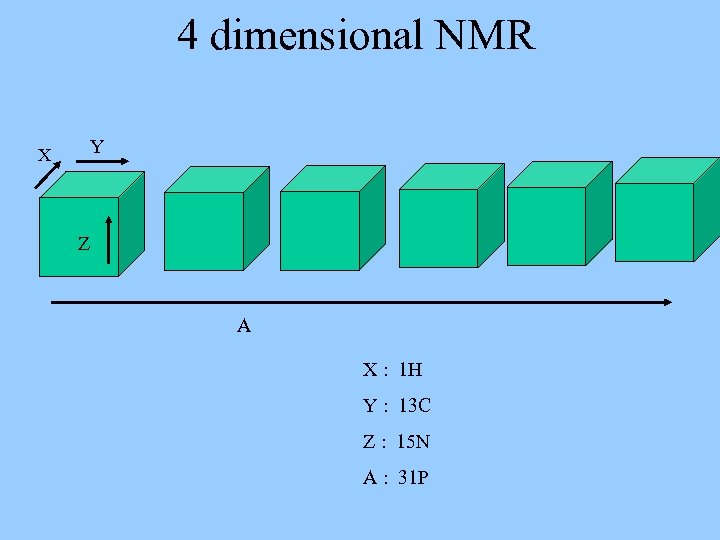 4 dimensional NMR X Y Z A X : 1 H Y : 13 C Z : 15 N A : 31 P
4 dimensional NMR X Y Z A X : 1 H Y : 13 C Z : 15 N A : 31 P
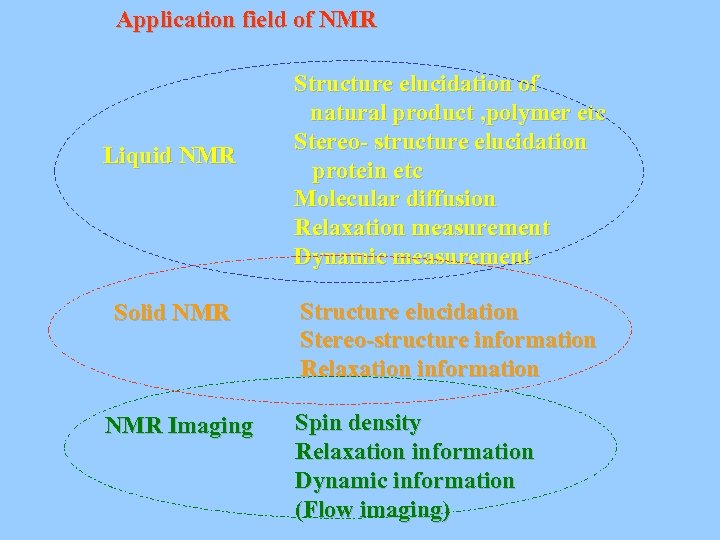 Application field of NMR Liquid NMR Solid NMR Imaging Structure elucidation of natural product , polymer etc Stereo- structure elucidation protein etc Molecular diffusion Relaxation measurement Dynamic measurement Structure elucidation Stereo-structure information Relaxation information Spin density Relaxation information Dynamic information (Flow imaging)
Application field of NMR Liquid NMR Solid NMR Imaging Structure elucidation of natural product , polymer etc Stereo- structure elucidation protein etc Molecular diffusion Relaxation measurement Dynamic measurement Structure elucidation Stereo-structure information Relaxation information Spin density Relaxation information Dynamic information (Flow imaging)


