be6ff5f161b9b94ecb20907066e10155.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Introduction to Mobile IPv 6 IIS 5711: Mobile Computing and Broadband Networking Laboratory CIS, NCTU 1

Outline n n n n n Introduction Relevant Features of IPv 6 Major Differences between MIPv 4 and MIPv 6 Mobile IPv 6 Operation Home Agent Discovery Mechanism Handover Quality of Service Conclusions References 2

Introduction n n Mobile IPv 6 is intended to enable IPv 6 nodes to move from one IP subnet to another While a mobile node is away from home n n It sends information about its current location to a home agent The home agent intercepts packets addressed to the mobile node and tunnels them to the mobile node’s present location 3
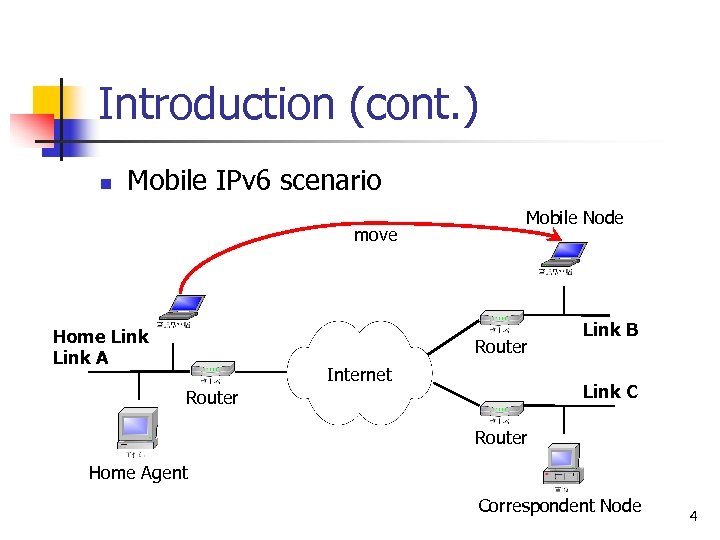
Introduction (cont. ) n Mobile IPv 6 scenario move Home Link A Mobile Node Router Internet Link B Link C Router Home Agent Correspondent Node 4

Relevant Features of IPv 6 n Address Autoconfiguration n Stateless autoconfiguratoin n n Stateful autoconfiguration n n Network Prefix + Interface ID DHCPv 6 Neighbor Discovery n n n Discover each other’s presence and find routers Determine each other’s link-layer addresses Maintain reachability information 5
Relevant Features of IPv 6 (cont. ) n Extension Headers n Routing header n n For route optimization Destination Options header n For mobile node originated datagrams 6
Major Differences between MIPv 4 and MIPv 6 n No FA in Mobile IPv 6 requires every mobile node to support n n n IPv 6 Decapsulation Address Autoconfiguration Neighbor Discovery 7
Major Differences between MIPv 4 and MIPv 6 (cont. ) n Packets delivery n MIPv 6 mobile node uses care-of address as source address in foreign links n n No ingress filtering problem Correspondence Node uses IPv 6 routing header rather than IP encapsulation n Supports “Route Optimization” naturally 8
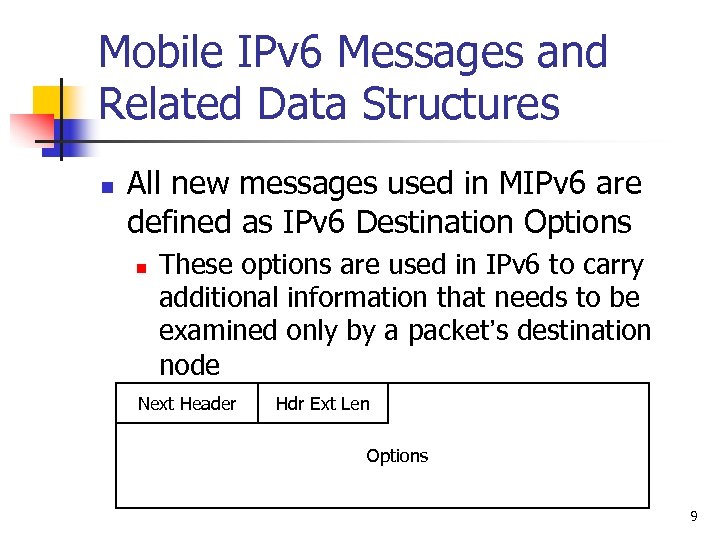
Mobile IPv 6 Messages and Related Data Structures n All new messages used in MIPv 6 are defined as IPv 6 Destination Options n These options are used in IPv 6 to carry additional information that needs to be examined only by a packet’s destination node Next Header Hdr Ext Len Options 9

Mobile IPv 6 Messages and Related Data Structures (cont. ) n Four new Destination Options n Binding Update n n Used by an MN to inform its HA or any other CN about its current care-of address Binding Acknowledgement n Used to acknowledge the receipt of a Binding Update 10

Mobile IPv 6 Messages and Related Data Structures (cont. ) n Binding Request n n Used by any node to request an MN to send a Binding Update with the current care-of address Home Address n Used in a packet sent by a mobile node to inform the receiver of this packet about the mobile node’s home address 11

Mobile IPv 6 Messages and Related Data Structures (cont. ) n Data Structures n n n Binding Cache Binding Update List Home Agent List 12

Mobile IPv 6 Operation n Home Agent Registration n n An MN performs address autoconfiguration (stateful or stateless) to get its care-of address The MN registers its care-of address with its home agent on the home link n n Use “Binding Update” Destination Option The HA uses proxy Neighbor Discovery and also replies to Neighbor Solicitations on behalf of the MN 13
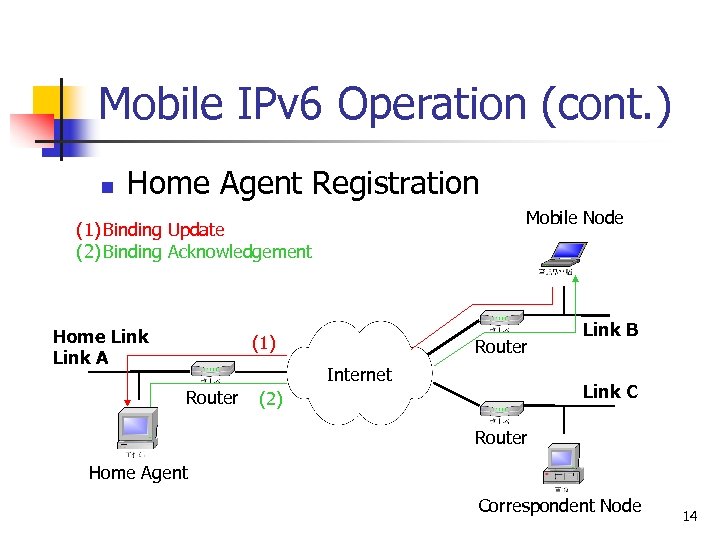
Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n Home Agent Registration Mobile Node (1) Binding Update (2) Binding Acknowledgement Home Link A (1) Router Internet Router Link B Link C (2) Router Home Agent Correspondent Node 14

Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n Route Optimization n To avoid triangle routing Mobile Node (1) Packet (2) Tunneled Packet (3) Packet Home Link A (2) Router Internet Router (1) (3) Link B Link C Router Home Agent Correspondent Node 15
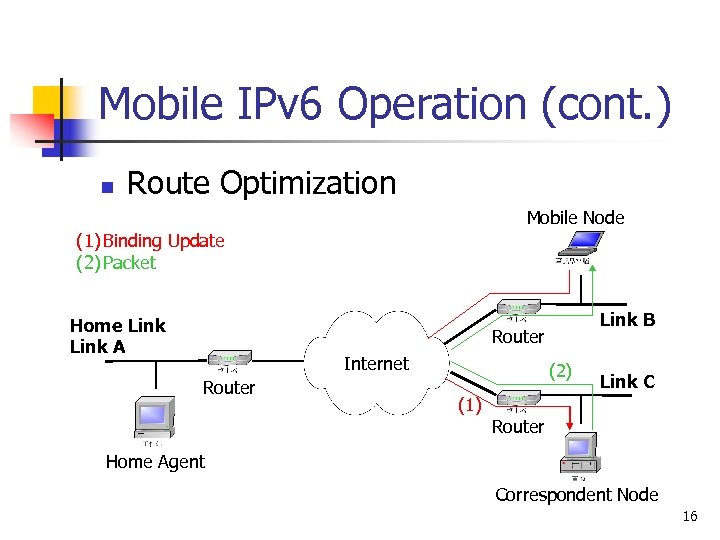
Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n Route Optimization Mobile Node (1) Binding Update (2) Packet Home Link A Link B Router Internet Router (2) Link C (1) Router Home Agent Correspondent Node 16
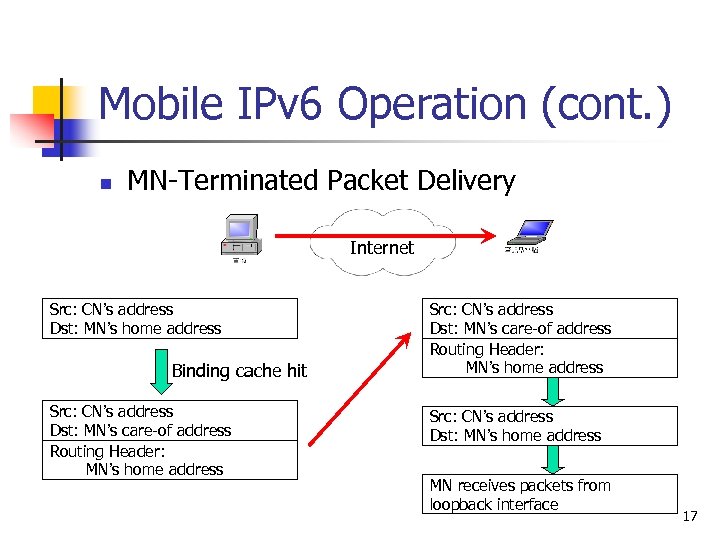
Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n MN-Terminated Packet Delivery Internet Src: CN’s address Dst: MN’s home address Binding cache hit Src: CN’s address Dst: MN’s care-of address Routing Header: MN’s home address Src: CN’s address Dst: MN’s home address MN receives packets from loopback interface 17

Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n MN-Originated Packet Delivery Internet Src: MN’s care-of address Dst: CN’s address Destination Optoins header – Home Address Option: MN’s home address Move MN’s home address to Source Address Src: MN’s home address Dst: CN’s address MN at home: Src: MN’s home address Dst: CN’s address MN at visited network: Src: MN’s care-of address Dst: CN’s address Destination Optoins header – Home Address Option: MN’s home address 18

Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n Movement Detection n n While away from home, an MN selects one router and one subnet prefix advertised by that router to use as the subnet prefix in its primary care-of address To wait for the periodically sent Router Advertisements 19

Mobile IPv 6 Operation (cont. ) n Binding Management n To trigger Binding Acknowledgement, the MN sets the Acknowledge bit in the Binding Update n n n Retransmitting the Biding Update periodically until receipt of the acknowledgement An MN MUST set the Acknowledge bit in Binding Updates addressed to an HA The MN MAY also set the Acknowledge bit in Binding Updates sent to a CN 20
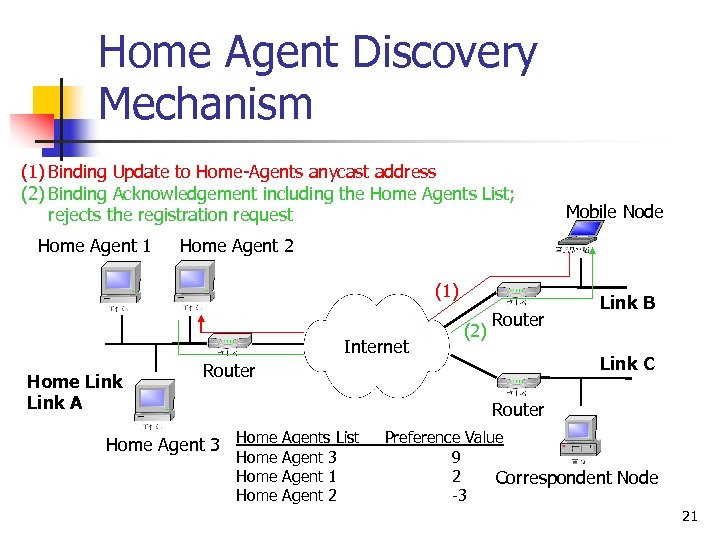
Home Agent Discovery Mechanism (1) Binding Update to Home-Agents anycast address (2) Binding Acknowledgement including the Home Agents List; rejects the registration request Home Agent 1 Home Agent 2 (1) Internet Home Link A Mobile Node (2) Router Link B Link C Router Home Agent 3 Home Agents List Home Agent 3 Home Agent 1 Home Agent 2 Preference Value 9 2 Correspondent Node -3 21

Home Agent Discovery Mechanism (cont. ) (1) Binding Update to Home Agents 3 (2) Binding Acknowledgement, registration OK Home Agent 1 Mobile Node Home Agent 2 (1) Internet Home Link A Router (2) Link B Link C Router Home Agent 3 Home Agents List Home Agent 3 Home Agent 1 Home Agent 2 Preference Value 9 2 Correspondent Node -3 22
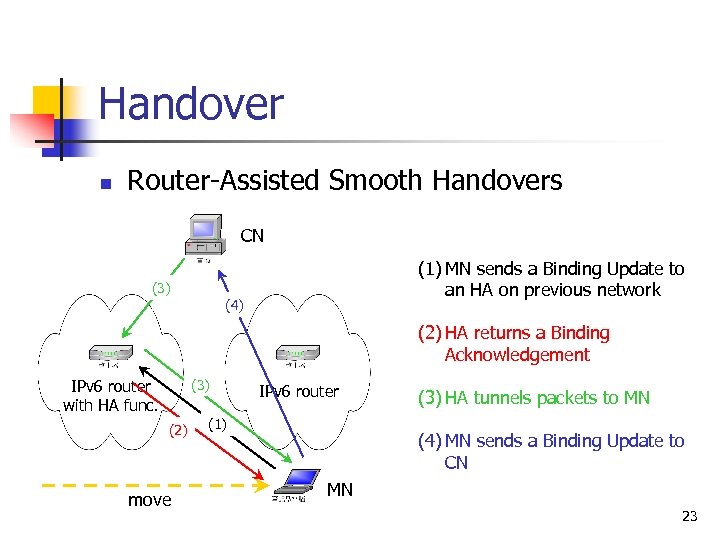
Handover n Router-Assisted Smooth Handovers CN (1) MN sends a Binding Update to an HA on previous network (3) (4) (2) HA returns a Binding Acknowledgement IPv 6 router with HA func. (3) (2) move IPv 6 router (1) (3) HA tunnels packets to MN (4) MN sends a Binding Update to CN MN 23

Handover (cont. ) n Three kinds of handover operations n Smooth Handover n n Fast Handover n n Minimizes data loss during the time that the MN is establishing its link to the new access point Minimizes or eliminates latency for establishing new communication paths to the MN at the new access router Seamless Handover n Both Smooth and Fast Handover 24

Quality of Service n IPv 6 header has two Qo. S-related fields n 20 -bit Flow Label n n n Used by a source to label sequences of packets for which it requests special handling by the IPv 6 routers Geared to Int. Serv and RSVP 8 -bit Traffic Class Indicator n n Used by originating nodes and/or forwarding routers to identify and distinguish between different classes or priorities of IPv 6 packets Geared to Diff. Serv 25

Quality of Service (cont. ) n New IPv 6 option – Qo. S Object n n Qo. S Object describes Qo. S requirement, traffic volume and packet classification parameters for MN's packet stream Included as a Destination Option in IPv 6 packets carrying Binding Update and Biding Acknowledgment messages 26

Conclusions n Mobile IPv 6 is n n n An efficient and deployable protocol for handling mobility with IPv 6 Lightweight protocol To minimize the control traffic needed to effect mobility 27

References n n C. Perkins, “Mobility for IPv 6, ” Internet Draft, June 2002. K. Zhigang et al. , “Qo. S in Mobile IPv 6, ” in Proc. of International Conferences on Info-tech and Info-net 2001, vol. 2, pp. 492 -497. n N. Montavont and T. Noel, “Handover Management for Mobile Nodes in IPv 6 Networks, ” IEEE Communication Magazine, pp. 38 -43, Aug. 2002. 28
be6ff5f161b9b94ecb20907066e10155.ppt