b299f960defe0343db49a2085247b988.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Introduction to Management Information Systems Chapter 6 System Development HTM 304 Spring 06
Introduction to Management Information Systems Chapter 6 System Development HTM 304 Spring 06
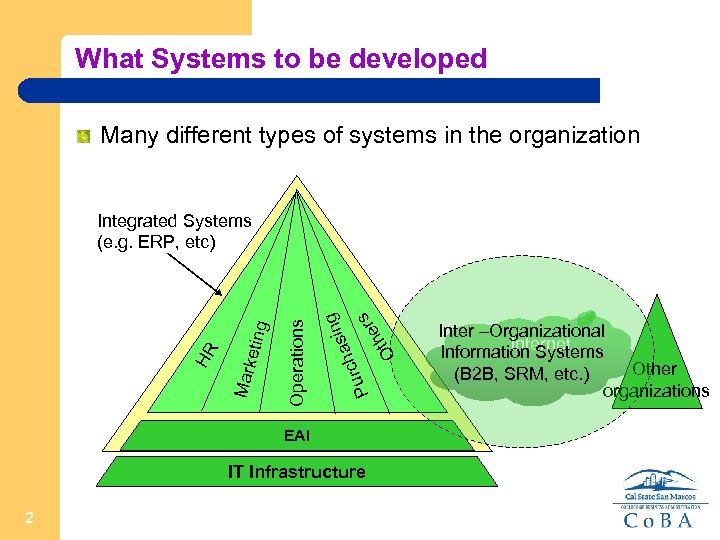 What Systems to be developed Many different types of systems in the organization g asin h urc P s er h Ot Operations Mark eting HR Integrated Systems (e. g. ERP, etc) EAI IT Infrastructure 2 Inter –Organizational Internet Information Systems Other (B 2 B, SRM, etc. ) organizations
What Systems to be developed Many different types of systems in the organization g asin h urc P s er h Ot Operations Mark eting HR Integrated Systems (e. g. ERP, etc) EAI IT Infrastructure 2 Inter –Organizational Internet Information Systems Other (B 2 B, SRM, etc. ) organizations
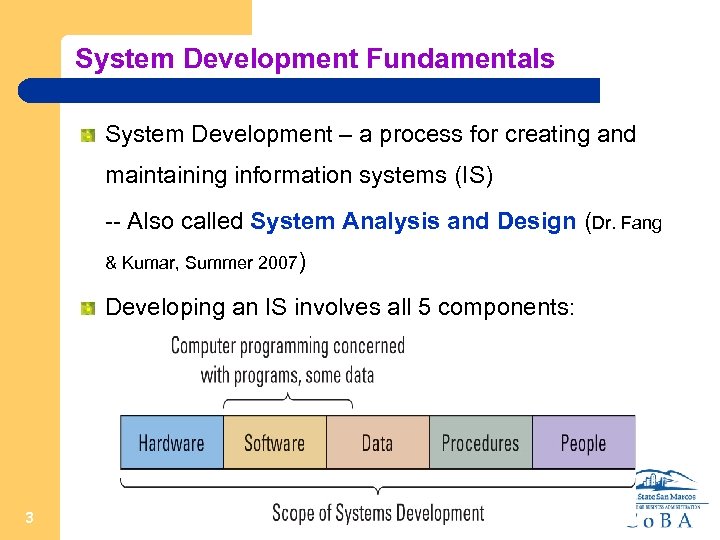 System Development Fundamentals System Development – a process for creating and maintaining information systems (IS) -- Also called System Analysis and Design (Dr. Fang & Kumar, Summer 2007) Developing an IS involves all 5 components: 3
System Development Fundamentals System Development – a process for creating and maintaining information systems (IS) -- Also called System Analysis and Design (Dr. Fang & Kumar, Summer 2007) Developing an IS involves all 5 components: 3
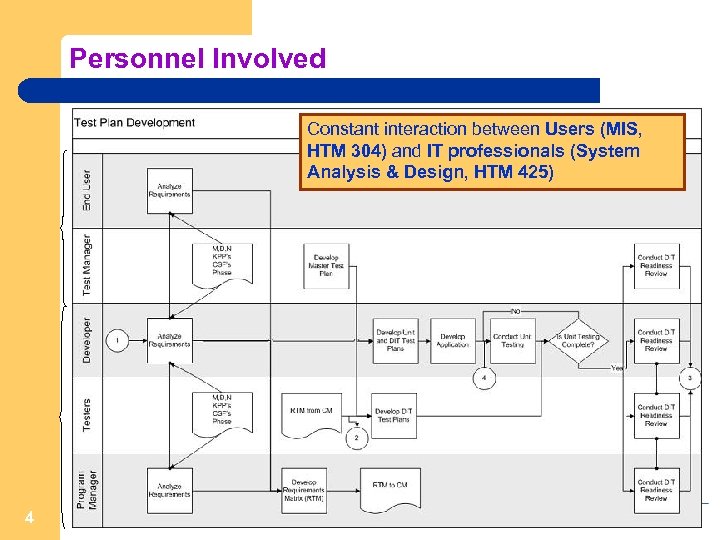 Personnel Involved Constant interaction between Users (MIS, HTM 304) and IT professionals (System Analysis & Design, HTM 425) 4
Personnel Involved Constant interaction between Users (MIS, HTM 304) and IT professionals (System Analysis & Design, HTM 425) 4
 Video – System Development 5
Video – System Development 5
 Think Big About System Development Many students are new to the systems development process due to working with personal computer tools. The scope of work is large with largescale corporate information systems and may be global with different languages and cultures. Management of resources is a critical success factor. Comprehensive processes are required for project staff to follow and adhere to in order to successfully meet project and systems objectives. 6
Think Big About System Development Many students are new to the systems development process due to working with personal computer tools. The scope of work is large with largescale corporate information systems and may be global with different languages and cultures. Management of resources is a critical success factor. Comprehensive processes are required for project staff to follow and adhere to in order to successfully meet project and systems objectives. 6
 Think Big (cont) Three software sources Off-the-shelf Off-the shelf-with adaptation Tailor-made Major IS rarely off-the-shelf due to involvement of company people and resources 7
Think Big (cont) Three software sources Off-the-shelf Off-the shelf-with adaptation Tailor-made Major IS rarely off-the-shelf due to involvement of company people and resources 7
 System Development Is Challenging Systems development difficult and risky Many projects never finished Some projects finish 200 -300% over budget Some projects finish on schedule and within budget but don’t meet the goals 8
System Development Is Challenging Systems development difficult and risky Many projects never finished Some projects finish 200 -300% over budget Some projects finish on schedule and within budget but don’t meet the goals 8
 System Development Challenges Difficulties in determining requirements Changes in requirements Scheduling and budgeting difficulties Changing technology Diseconomies of scale 9
System Development Challenges Difficulties in determining requirements Changes in requirements Scheduling and budgeting difficulties Changing technology Diseconomies of scale 9
 Systems Development Methodologies There are many different system development processes System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Rapid Application Development (RAD) Object-oriented System Development (OOD) Extreme Programming (XP) Information Systems Differ No single process works for all situations 10
Systems Development Methodologies There are many different system development processes System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Rapid Application Development (RAD) Object-oriented System Development (OOD) Extreme Programming (XP) Information Systems Differ No single process works for all situations 10
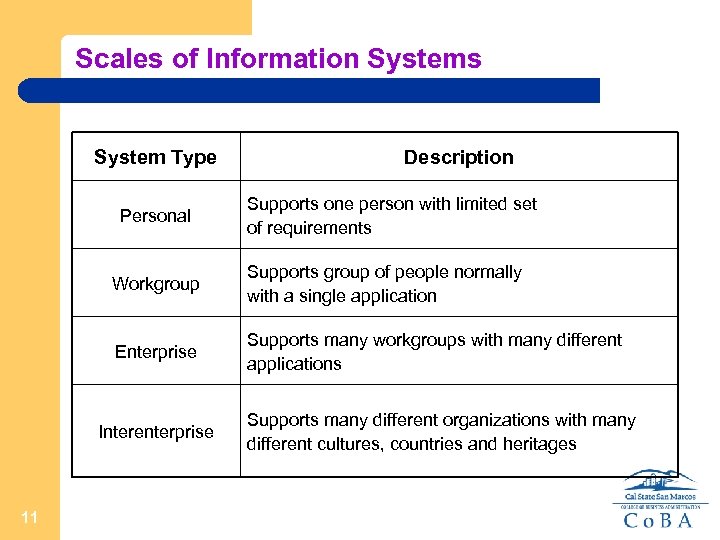 Scales of Information Systems System Type Personal Description Supports one person with limited set of requirements Workgroup Supports group of people normally with a single application Enterprise Supports many workgroups with many different applications Interenterprise 11 Supports many different organizations with many different cultures, countries and heritages
Scales of Information Systems System Type Personal Description Supports one person with limited set of requirements Workgroup Supports group of people normally with a single application Enterprise Supports many workgroups with many different applications Interenterprise 11 Supports many different organizations with many different cultures, countries and heritages
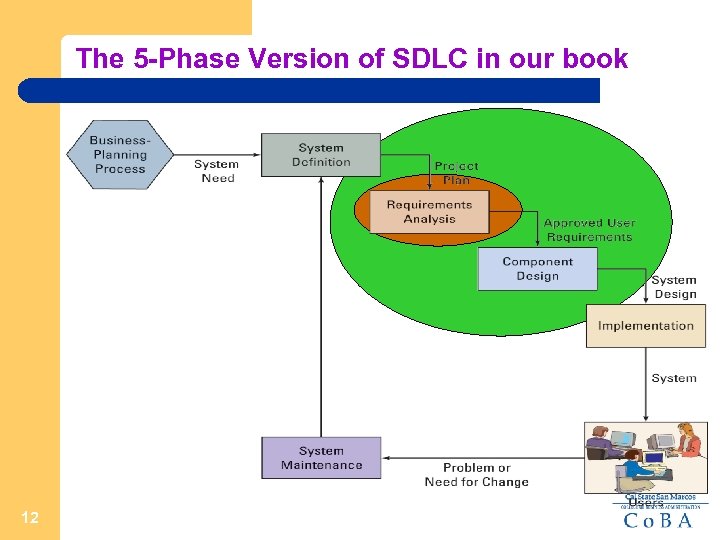 The 5 -Phase Version of SDLC in our book 12
The 5 -Phase Version of SDLC in our book 12
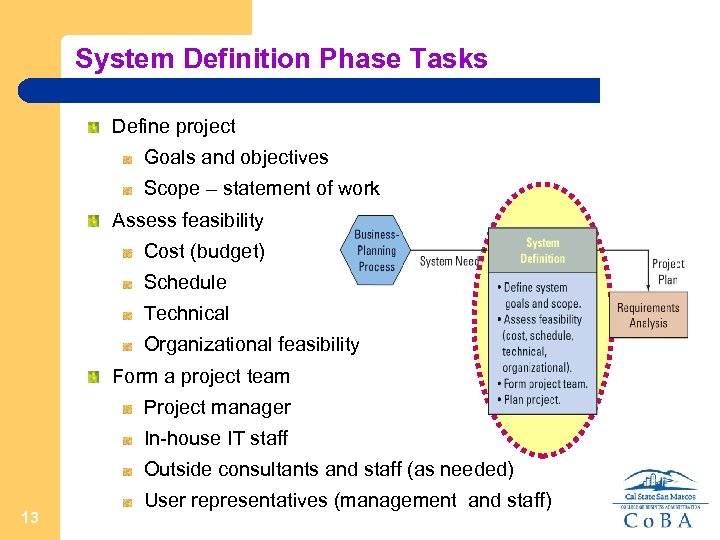 System Definition Phase Tasks Define project Goals and objectives Scope – statement of work Assess feasibility Cost (budget) Schedule Technical Organizational feasibility Form a project team Project manager In-house IT staff Outside consultants and staff (as needed) 13 User representatives (management and staff)
System Definition Phase Tasks Define project Goals and objectives Scope – statement of work Assess feasibility Cost (budget) Schedule Technical Organizational feasibility Form a project team Project manager In-house IT staff Outside consultants and staff (as needed) 13 User representatives (management and staff)
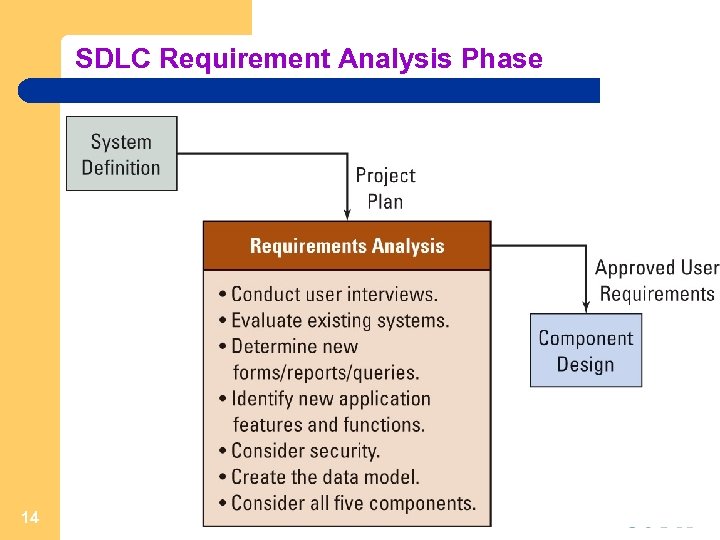 SDLC Requirement Analysis Phase 14
SDLC Requirement Analysis Phase 14
 Requirement Analysis Phase Tasks The most important phase in the system development process is determining system requirements. If the requirements are wrong, the system will be wrong. If the requirements are determined completely and correctly, then the design and implementation will be easier and more likely to result in success. Seasoned and experienced system analysts know how to conduct interviews to bring such requirements to light. 15
Requirement Analysis Phase Tasks The most important phase in the system development process is determining system requirements. If the requirements are wrong, the system will be wrong. If the requirements are determined completely and correctly, then the design and implementation will be easier and more likely to result in success. Seasoned and experienced system analysts know how to conduct interviews to bring such requirements to light. 15
 Obtain User Approval Before You Move-on Once the requirements have been specified, the users must review and approve them before the project continues. The easiest and cheapest time to alter the information system is in the requirements phase. Changing a requirement in the implementation phase may require weeks of reworking applications components and the database. 16
Obtain User Approval Before You Move-on Once the requirements have been specified, the users must review and approve them before the project continues. The easiest and cheapest time to alter the information system is in the requirements phase. Changing a requirement in the implementation phase may require weeks of reworking applications components and the database. 16
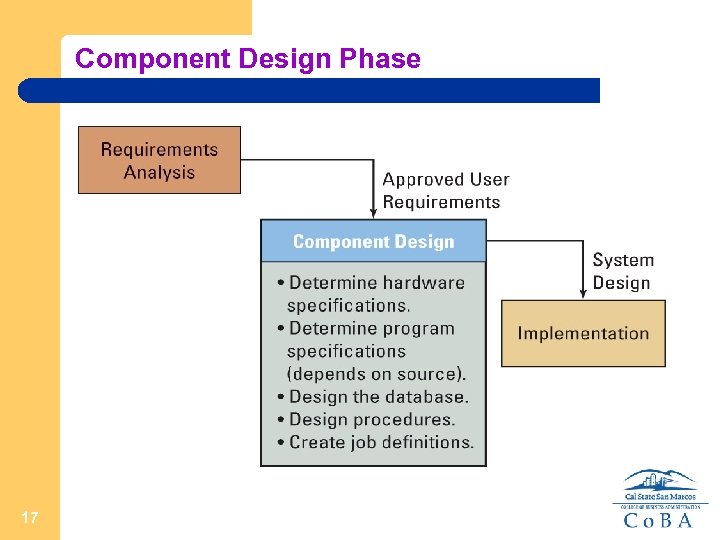 Component Design Phase 17
Component Design Phase 17
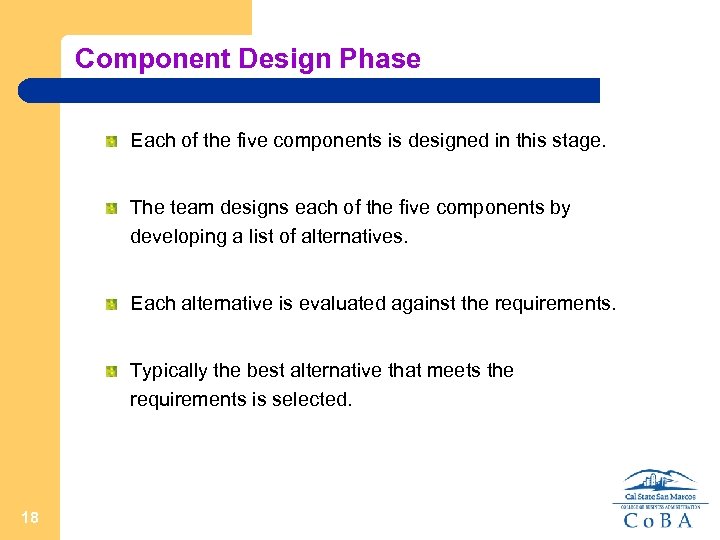 Component Design Phase Each of the five components is designed in this stage. The team designs each of the five components by developing a list of alternatives. Each alternative is evaluated against the requirements. Typically the best alternative that meets the requirements is selected. 18
Component Design Phase Each of the five components is designed in this stage. The team designs each of the five components by developing a list of alternatives. Each alternative is evaluated against the requirements. Typically the best alternative that meets the requirements is selected. 18
 Hardware Design Team determines specifications for hardware they want to acquire Team NOT designing hardware Typically, large company has some type of computer network infrastructure 19
Hardware Design Team determines specifications for hardware they want to acquire Team NOT designing hardware Typically, large company has some type of computer network infrastructure 19
 Hardware Networking Alternatives PC or LANs over public Internet Point-to-point leased lines Lease time on some type of PSDN Create Virtual Private Network (VPN) over Internet 20
Hardware Networking Alternatives PC or LANs over public Internet Point-to-point leased lines Lease time on some type of PSDN Create Virtual Private Network (VPN) over Internet 20
 Program Design Depends on program source Off-the-shelf – team must assess products and evaluate them against requirements Off-the-shelf with alteration - team IDs products and assesses alterations Custom-design programs – team write specifications (documentation) for program code 21
Program Design Depends on program source Off-the-shelf – team must assess products and evaluate them against requirements Off-the-shelf with alteration - team IDs products and assesses alterations Custom-design programs – team write specifications (documentation) for program code 21
 Database and Procedure Design Database design Convert database design to data model If off-the-shelf DB, little design needed Procedure design Procedures must be developed for system users and operations personnel to follow Procedures typically address Normal processing: procedures for using the system to accomplish business tasks Backup: user procedures for backing up data and other resources Failure recovery: Procedure to continue operation when system fails 22 and procedures to convert back to the system after recovery
Database and Procedure Design Database design Convert database design to data model If off-the-shelf DB, little design needed Procedure design Procedures must be developed for system users and operations personnel to follow Procedures typically address Normal processing: procedures for using the system to accomplish business tasks Backup: user procedures for backing up data and other resources Failure recovery: Procedure to continue operation when system fails 22 and procedures to convert back to the system after recovery
 People Component -- Design of Job Descriptions Job descriptions needed for both users and operations personnel New IS may require new jobs Organizations may have to add new duties and responsibilities due to information systems changes and enhancements 23
People Component -- Design of Job Descriptions Job descriptions needed for both users and operations personnel New IS may require new jobs Organizations may have to add new duties and responsibilities due to information systems changes and enhancements 23
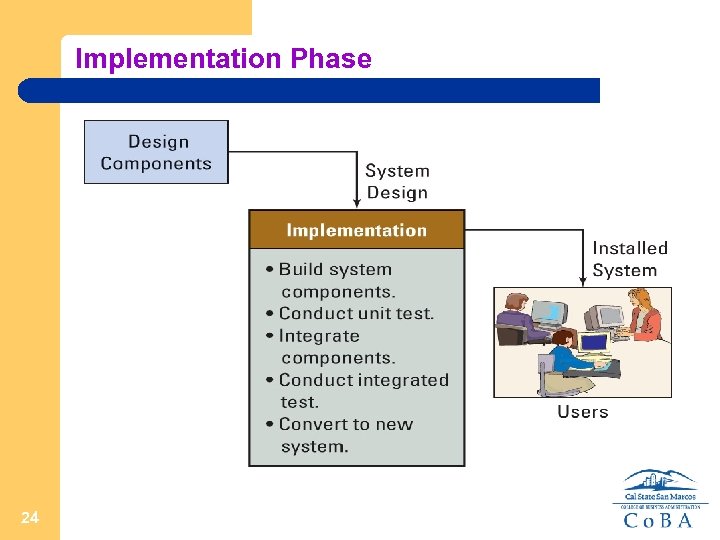 Implementation Phase 24
Implementation Phase 24
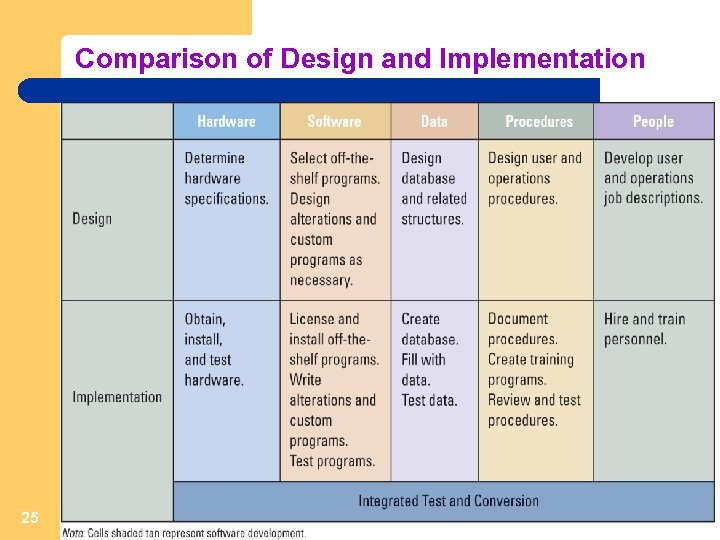 Comparison of Design and Implementation 25
Comparison of Design and Implementation 25
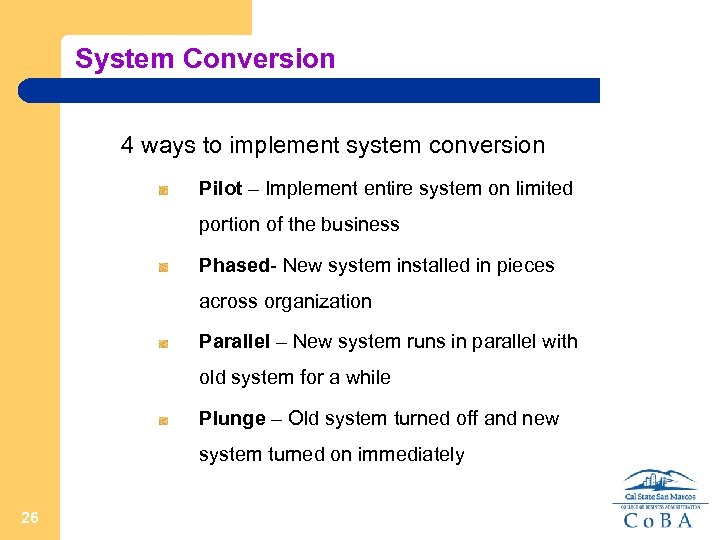 System Conversion 4 ways to implement system conversion Pilot – Implement entire system on limited portion of the business Phased- New system installed in pieces across organization Parallel – New system runs in parallel with old system for a while Plunge – Old system turned off and new system turned on immediately 26
System Conversion 4 ways to implement system conversion Pilot – Implement entire system on limited portion of the business Phased- New system installed in pieces across organization Parallel – New system runs in parallel with old system for a while Plunge – Old system turned off and new system turned on immediately 26
 Maintenance Phase New needs 27
Maintenance Phase New needs 27
 Information System Maintenance Either fixing system to make it do what is expected Or adapting system to changing requirement 28
Information System Maintenance Either fixing system to make it do what is expected Or adapting system to changing requirement 28
 Problems with SDLC The most formal procedure to develop large IS project Systems development seldom smooth Sometimes need to crawl back up waterfall Difficulty documenting requirements in usable way Scheduling and budgeting difficult, especially for large projects with large SDLC phases 29
Problems with SDLC The most formal procedure to develop large IS project Systems development seldom smooth Sometimes need to crawl back up waterfall Difficulty documenting requirements in usable way Scheduling and budgeting difficult, especially for large projects with large SDLC phases 29
 Review of SDLC What are the five phases? Which phase is the most important? Briefly describe the five phases. 30
Review of SDLC What are the five phases? Which phase is the most important? Briefly describe the five phases. 30
 Other Developing Methods Rapid application development (RAD) Object-oriented systems development (OOD) Extreme programming (XP) 31
Other Developing Methods Rapid application development (RAD) Object-oriented systems development (OOD) Extreme programming (XP) 31
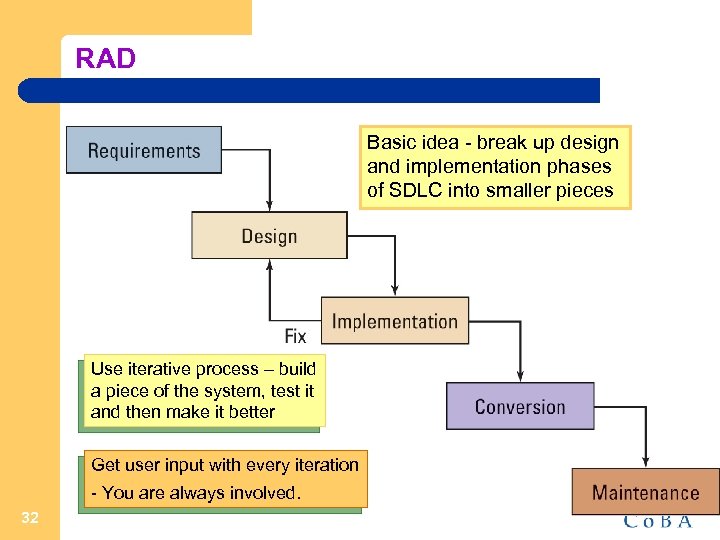 RAD Basic idea - break up design and implementation phases of SDLC into smaller pieces Use iterative process – build a piece of the system, test it and then make it better Get user input with every iteration - You are always involved. 32
RAD Basic idea - break up design and implementation phases of SDLC into smaller pieces Use iterative process – build a piece of the system, test it and then make it better Get user input with every iteration - You are always involved. 32
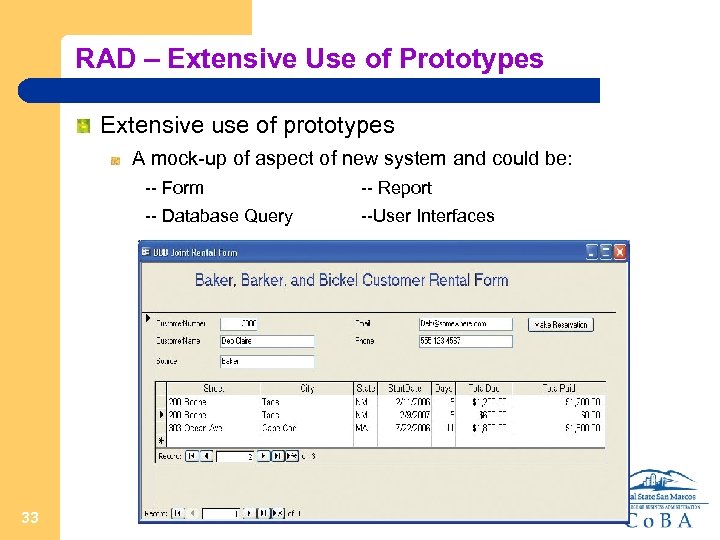 RAD – Extensive Use of Prototypes Extensive use of prototypes A mock-up of aspect of new system and could be: -- Form -- Database Query 33 -- Report --User Interfaces
RAD – Extensive Use of Prototypes Extensive use of prototypes A mock-up of aspect of new system and could be: -- Form -- Database Query 33 -- Report --User Interfaces
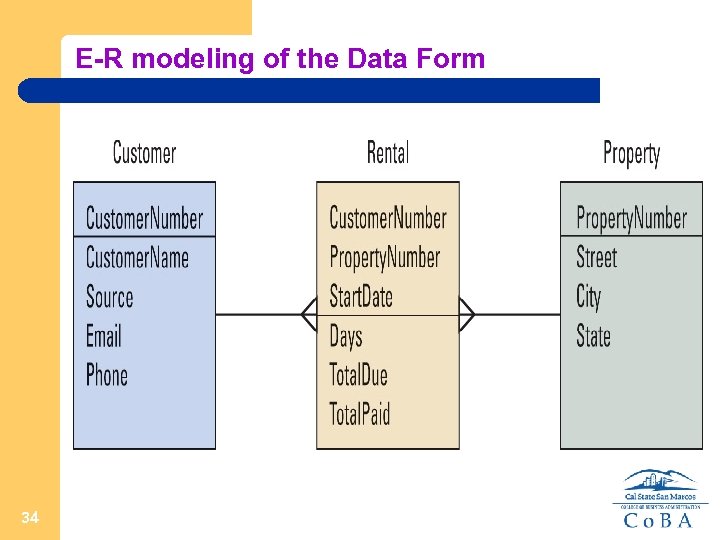 E-R modeling of the Data Form 34
E-R modeling of the Data Form 34
 CASE Tools CASE: Computer-assisted systems engineering 35
CASE Tools CASE: Computer-assisted systems engineering 35
 Summary of RAD Characteristics Design / implement / fix development process Continuous user involvement throughout Extensive use of prototypes Joint Application Design (JAD) Use of CASE Tools 36
Summary of RAD Characteristics Design / implement / fix development process Continuous user involvement throughout Extensive use of prototypes Joint Application Design (JAD) Use of CASE Tools 36
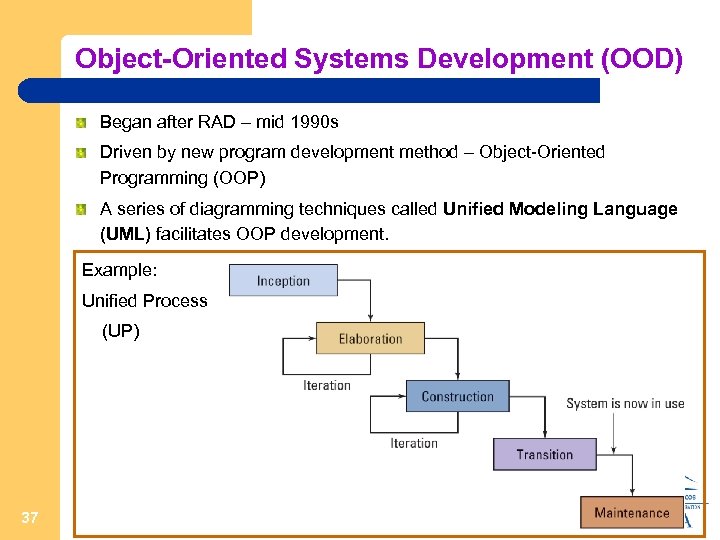 Object-Oriented Systems Development (OOD) Began after RAD – mid 1990 s Driven by new program development method – Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) A series of diagramming techniques called Unified Modeling Language (UML) facilitates OOP development. Example: Unified Process (UP) 37
Object-Oriented Systems Development (OOD) Began after RAD – mid 1990 s Driven by new program development method – Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) A series of diagramming techniques called Unified Modeling Language (UML) facilitates OOP development. Example: Unified Process (UP) 37
 Extreme Programming Emerging Technique Developing Computer Programs Not useful for large scale development system requiring business processes & procedures (or at least not yet realized) There are cases where organizations have used it successfully in developing application programs. Three main characteristics 1) 2) Just-In-Time (JIT) Design 3) 38 Customer-Centric Paired Programming
Extreme Programming Emerging Technique Developing Computer Programs Not useful for large scale development system requiring business processes & procedures (or at least not yet realized) There are cases where organizations have used it successfully in developing application programs. Three main characteristics 1) 2) Just-In-Time (JIT) Design 3) 38 Customer-Centric Paired Programming
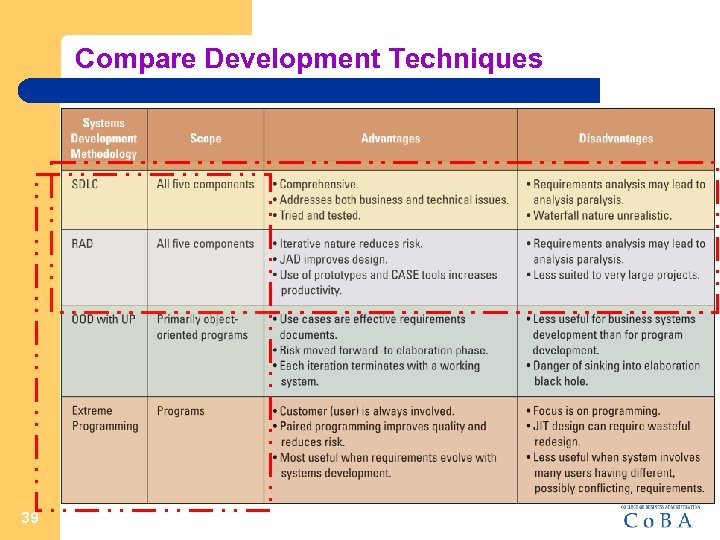 Compare Development Techniques 39
Compare Development Techniques 39


