e8a09effadaeca0cc777e1e20484e756.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Introduction to M&E 28 February, 2011 University of Pretoria

Session Objectives § Describe Health Information/M&E Systems § Define Monitoring § Define Evaluation § Purposes of M&E § Describe the relationship between monitoring and evaluation § Define Program Components § Identify the different types of M&E Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will be able to: § Define key M&E terms § Identify components of programs to evaluate § Describe different purposes for M&E § State why Monitoring & Evaluation are important in programming § Describe characteristics of good M&E system 3 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
Session Overview § Key M&E terms § “M” vs. “E” § The purpose of M&E § Types of evaluation 4 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Defining Programs, Projects & Interventions § Program: organized effort to respond to a broad social problem (typically organized at national level) § Project: specific set of activities with linked objectives, that contribute to the overall objective of a program (typically organized at sub-national level) § Intervention: often used in same was as “project”, sometimes a specific sub-set of program or project activities 5 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Program Planning Involves Setting… § Goals & Objectives based on intended Impact § Intended Outcomes § Intended Outputs or Deliverables § Planned Activities (Processes) § Inputs or Resources 6 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Inputs What you need to implement the program e. g. the financial , human and material resources used to implement an HIV counseling and testing program § Trained personnel § C&T protocols and guidelines § Training materials § HIV test kits and other supplies § Money 7 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Activities What the program provides to accomplish its objectives (micro level) § Training workshops on C&T for personnel and site managers § Providing pre-test and post-test counseling to clients § Curriculum development § Recording & reporting § Dissemination of IEC materials § Supervision 8 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Outputs What the program delivers § Condoms distributed § Clients receiving pre-test counseling, HIV tests, post-test counseling § Materials distributed § People reached § Intervention sessions completed 9 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Outcomes The results of the program or changes that occur both immediately or some time after activities are completed § Changes in knowledge, behavior, attitudes and skills § Quality of C&T improved § Clients develop and adhere to personalized risk-reduction and treatment strategy 10 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Impact The wider effect of the program on longterm results § HIV transmission rates decrease § HIV incidence decreases § Changes in HIV mortality and morbidity § Decrease in deaths due to HIV-related TB 11 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
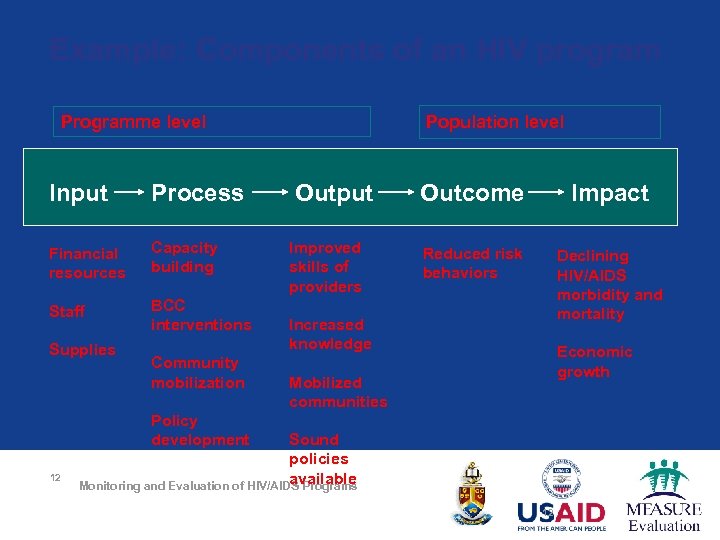
Example: Components of an HIV program Programme level Input Process Financial resources Capacity building Staff BCC interventions Supplies Community mobilization Population level Output Improved skills of providers Outcome Impact Reduced risk behaviors Declining HIV/AIDS morbidity and mortality Increased knowledge Economic growth Mobilized communities Policy development 12 Sound policies available Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs 12

So how does this relate to M&E? Back to our definitions… 13 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What Do We Mean by M&E? § Set of procedures & analytical tools to examine • how programs are conducted (inputs & activities) • their level of performance (outputs) • whether they achieved what they were intended to achieve (outcomes & impact) § Types of evaluation • monitoring (including process evaluation) • evaluation (outcome and impact evaluation) [+ surveillance] 14 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Monitoring vs Evaluation Monitoring: What are we doing? Tracking inputs and outputs to assess whether programs are performing according to plans (e. g. , people trained, condoms distributed) Evaluation: What have we achieved? Assessment of impact of the programme on behaviour or health outcome (e. g. , condom use at last risky sex, HIV prevalence) 15 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What is Monitoring? § Is a a continuous systematic process of collecting, analyzing and using information to track the efficiency of achieving program goals and objectives § Provides regular feedback that measures change over time in any of the program components such as costs, personnel and program implementation § An unexpected change in monitoring data may trigger the need for a more formal evaluation of activities 16 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
Illustration of Program Monitoring Program indicator 17 Program TIME Monitoring andstart Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs Program end
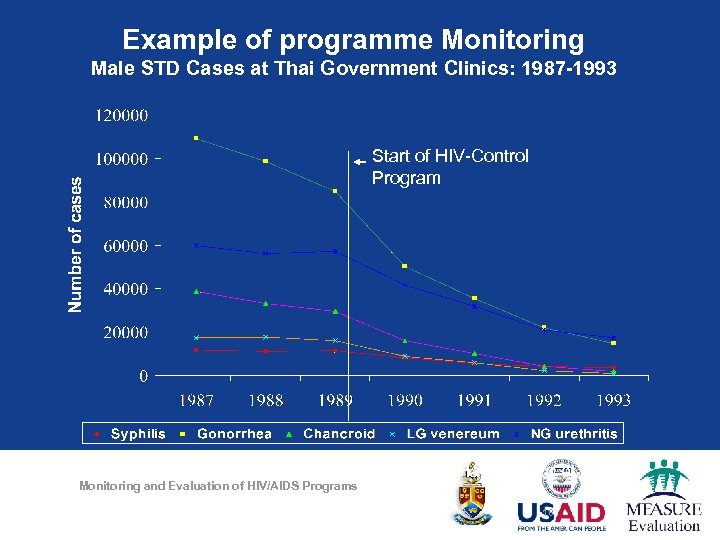
Example of programme Monitoring Male STD Cases at Thai Government Clinics: 1987 -1993 Start of HIV-Control Program Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs Source: Hannenberg et al. 1994 18

Key M&E Questions § Is the program being implemented as planned? § Are things moving in the right direction? § Did the program achieve its objectives? § Can results be attributed to program efforts? § Which program activities were more (or less) important/effective? § Did the target population benefit from the program? § At what cost? Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What is Evaluation? § Is a systematic process limited in time of collecting, analyzing and using information to assess the effectiveness, relevance and impact of achieving your program’s goals. § Requires study design; sometimes a control or comparison group; often measurement over time. § Often involves measuring changes in knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, skills, community norms, utilization of health services, & health status at population level § Provides regular feedback that helps programs analyze the consequences, outcomes and results of its actions 20 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What is Evaluation? (con’t) Rigorous research design need for: § Establishing a causal link between program effort and desired outcomes § Isolating program effect from other, nonprogram influences on the outcome of interest § Not undertaken routinely; usually reserved for specific situations, such as determining the success of a project for scale-up or replication 21 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
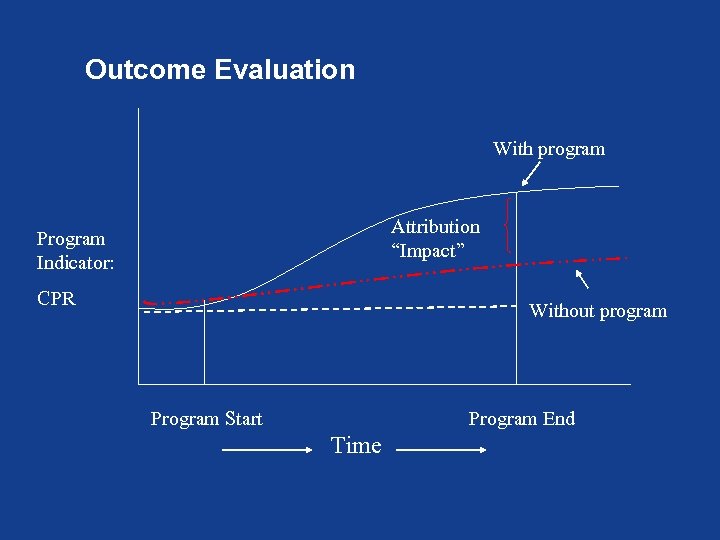
Outcome Evaluation With program Attribution “Impact” Program Indicator: CPR Without program Program Start Program End Time
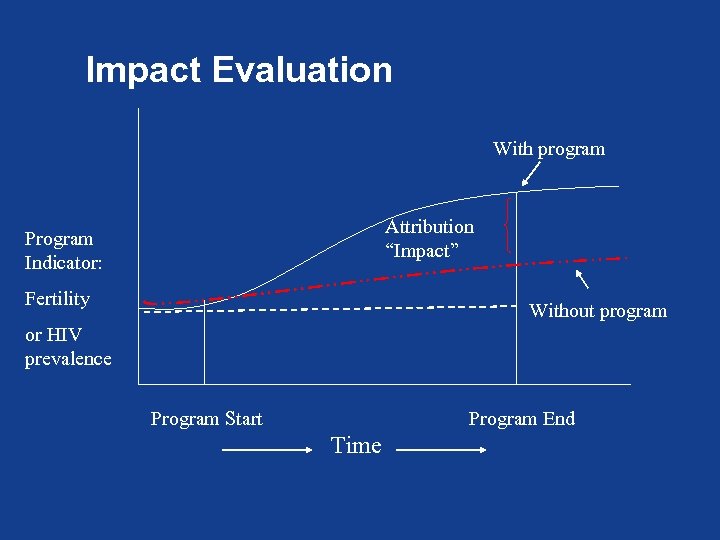
Impact Evaluation With program Attribution “Impact” Program Indicator: Fertility Without program or HIV prevalence Program Start Program End Time
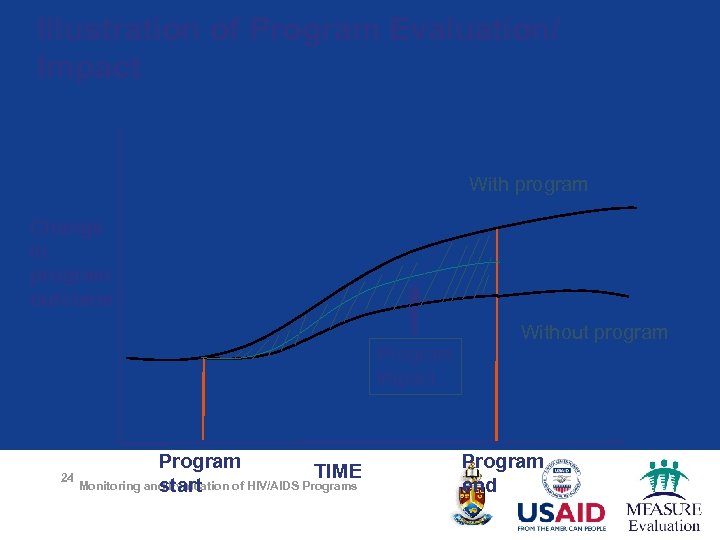
Illustration of Program Evaluation/ Impact With program Change in program outcome Program impact Program TIME 24 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs start Without program Program end
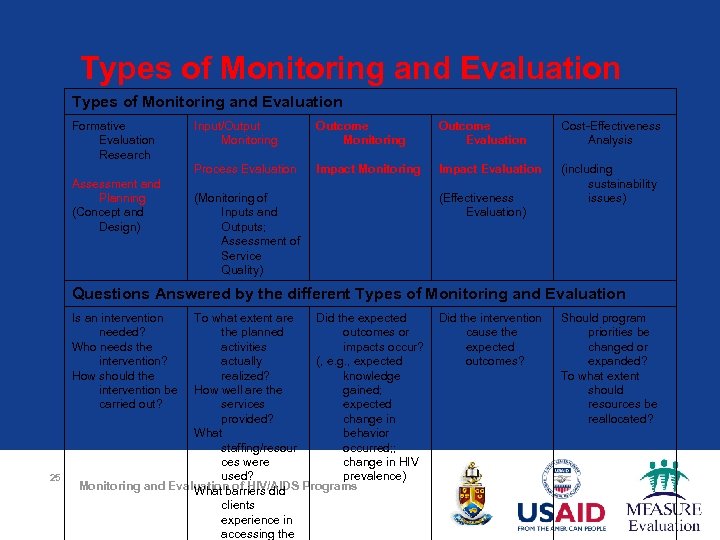
Types of Monitoring and Evaluation Formative Evaluation Research Outcome Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Process Evaluation Assessment and Planning (Concept and Design) Input/Output Monitoring Impact Evaluation (including sustainability issues) (Monitoring of Inputs and Outputs; Assessment of Service Quality) (Effectiveness Evaluation) Questions Answered by the different Types of Monitoring and Evaluation Is an intervention needed? Who needs the intervention? How should the intervention be carried out? 25 To what extent are Did the expected the planned outcomes or activities impacts occur? actually (, e. g. , expected realized? knowledge How well are the gained; services expected provided? change in What behavior staffing/resour occurred; ; ces were change in HIV used? prevalence) Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs What barriers did clients experience in accessing the Did the intervention cause the expected outcomes? Should program priorities be changed or expanded? To what extent should resources be reallocated?
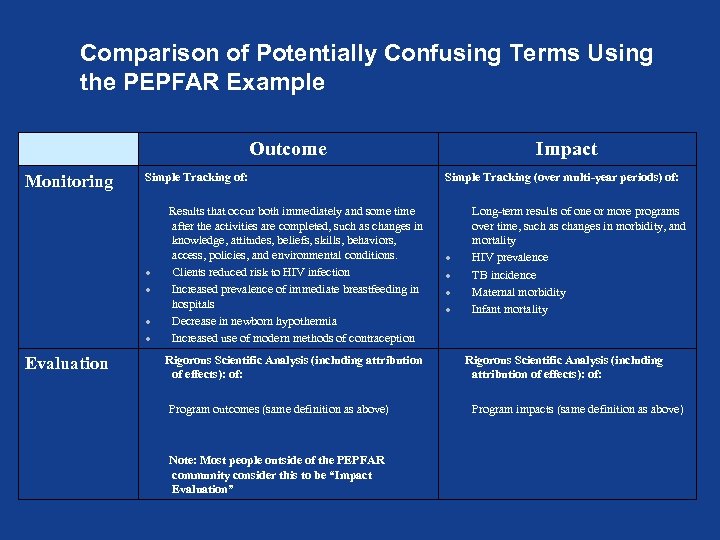
Comparison of Potentially Confusing Terms Using the PEPFAR Example Outcome Monitoring Simple Tracking of: Evaluation Results that occur both immediately and some time after the activities are completed, such as changes in knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, skills, behaviors, access, policies, and environmental conditions. Clients reduced risk to HIV infection Increased prevalence of immediate breastfeeding in hospitals Decrease in newborn hypothermia Increased use of modern methods of contraception Rigorous Scientific Analysis (including attribution of effects): of: Program outcomes (same definition as above) Note: Most people outside of the PEPFAR community consider this to be “Impact Evaluation” Impact Simple Tracking (over multi-year periods) of: Long-term results of one or more programs over time, such as changes in morbidity, and mortality HIV prevalence TB incidence Maternal morbidity Infant mortality Rigorous Scientific Analysis (including attribution of effects): of: Program impacts (same definition as above)

Key M&E Questions § § Did the program achieve its objectives? Did the target population benefit from the program? At what cost? Can improved health outcomes be attributed to program efforts? § Which program activities were more (or less) important/effective? § What would have happened in the absence of the program? § How can we know or measure this (the counterfactual)? 27 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Why Monitor & Evaluate? § To make decisions about project management and service delivery § To ensure effective and efficient use of resources and provide accountability to donors § To assess whether the project has achieved its objectives - has the desired effects § To learn from our activities, and provide information to design future projects Program Improvement Share with Partners Reporting/ Accountability

Purposes of Monitoring and Evaluation § Determine whether a plan or program is on schedule with planned activities § Assess whether a policy, plan or program has produced desired impacts § Generate knowledge: • Identify factors (individual, community, programmatic) that influence health outcomes § Help inform policy, planning or program decisions: new services, resource allocation, corrections, etc. 29 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Reasons to Monitor & Evaluate - Different Needs for Different Stakeholders: Funding Agencies & Policy Makers § § What M&E Measures § Evidence of achievement of program objective § Program outcome and impact § Program cost-efficiency § Data about the target population What M&E Results Identify § Priorities for strategic planning § Programs that qualify for donor assistance § Best practices § Impact of donor assistance 30 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs § What Decisions are Guided by M&E Results q How much funding should be allocated to a program q What types of programs should be funded q Which programs approaches should be presented as models q New strategic objectives, activities or results packages q Replication and scaling up of successful programs

Reasons to Monitor & Evaluate - Different Needs for Different Stakeholders: Communities & Youth § What M&E Measures § Youth behavior related to reproductive health § Young peoples’ needs § How program funs are being spent § The process and impact of community participation § What M&E Results Identify § Actual and potential benefits of youth programs § Need for new and better youth services § Community resources that can be used to support ARH programs § Need for local support for ARH issues and actions 31 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs § What Decisions are Guided by M&E Results q Degree to which community members and youth should participate in and support the program q How to better coordinate community actions to address ARH q How many and what type of local resources should be allocated to ARH

Reasons to Monitor & Evaluate - Different Needs for Different Stakeholders: Program Managers & Staff § § What M&E Measures § Quality of activities and/or services § Why some sites are more successful § Program coverage What M&E Results Identify § Priorities for strategic planning § Training and supervision needs § How to improve reporting to funding agency § Feedback from clients § Why program is not accomplishing what it set out to do 32 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs § What Decisions are Guided by M&E Results q Resource allocation q Replication and scaling up of intervention q Fund-raising q Motivating staff q Policy advocacy

Fundamental Steps to Carry out M&E § Agreement on the scope and objectives of M&E plan with stakeholders § Selection of Indicators § Systematic and consistent collection of information on the selected indicators § Analyze the information gathered § Compare results with program initial goals and objectives § Share results with stakeholders 33 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Defining the Scope of M&E Effort § Scope refers to the extent of the activity you will undertake in a M&E effort. Scope is determined by several factors (questions) § What should be monitored and evaluated? § When should health programs be monitored and evaluated? § How much will M&E cost? § Who should be involved in M&E? § Who should carry out the evaluation? § Where should M&E take place? 34 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What Should be Monitored & Evaluated? § M&E can be measure each stage of your program development: design, system development and functioning, and implementation. § After goals, objectives and activities are developed, decision on about M&E at each stage is needed. § M&E effort can measure each stage to determine how the program is working and its impact on the target population. 35 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

What Should be Monitored & Evaluated? § Program Design is measured by process evaluation: § Assessing how well the program has designed § Documenting the success/challenges with program design § System development and functioning is measured by monitoring and process evaluation: § Document the development of support systems and determine if they are actually § § § operating once program implementation begins Assess the performance of support systems Measure how effective the preparatory activities are in readying program personal for program implementation Implementation is measured by monitoring, process evaluation, and outcome/impact evaluation: § Reveal how program implementation is occurring § Determine whether program is achieving its objectives by measuring the changes in outcomes in your target population 36 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

When Should Health Programs be Monitored & Evaluated? § Monitoring and process evaluation should occur throughout the life of a program § Outcome and impact evaluations are usually done near the end of a program (baseline gathered to measure change) § Starting M&E at the beginning of a program is ideal § Some activities can still be measured if M&E is started in the middle of a program § Even Fewer activities can be measured if M&E is started towards the end of the program 37 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

When Should Health Programs be Monitored & Evaluated? Stage of Program Monitoring Process Outcome/Impact Early - Set up monitoring system; identify indicators and tools, plan for tracking program, data analysis, and reporting. - Assess systems development and functioning. Provide early feedback. Assess if program is responsive to target. - Identify objectives and indicators. Take baseline measurements. Crate an outcome or impact evaluation plan. Middle - Assess MIS and data. Modify original system is inadequate. If program is not performing, launch process evaluation. - Conduct more formal midterm process evaluation to assess quality of program performance. Determine coverage, or whether program is reaching target. - Take mid-term measurements. Analyze short term outcome measures, such as changes in knowledge, increase in use of programs and changes in contextual factors. Provide feedback to program. Late - Analyze data from tracking system to conclude if you conducted the program as planned. Prepare and submit reports. - Analyze end of program measurements. Determine what was done to improve quality of program implementation. Make recommendations for program replication or expansion. - Take end of program measurements. Examine evidence of changes in outcomes. Depending on study design conduct impact analysis to conclude whether outcomes are attributable to program activities. Report to donor and other stakeholders. 38 Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs 38

Where are the levers in a working health systems § 6 building blocks of health systems strengthening § Service delivery § Health workforce § INFORMATION § Medical products , Vaccines and technologies § Financing § Leadership and governance § WHO: Nellie Bristol www. globalhealthmagazine. com Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Input-Output Exercise Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
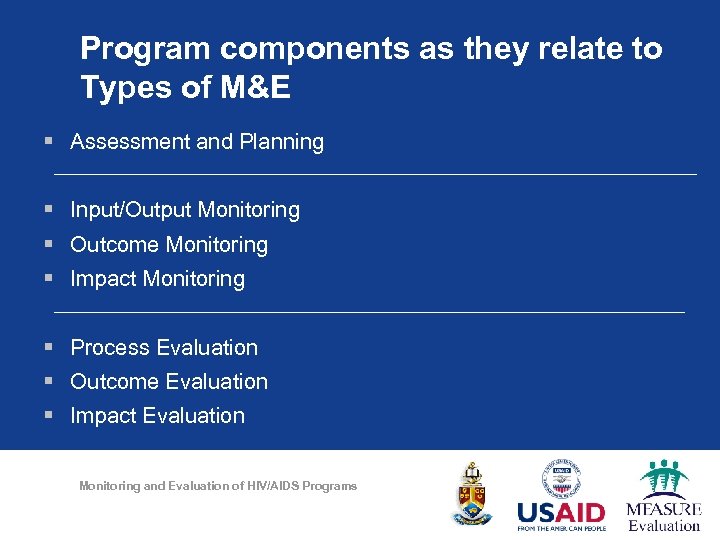
Program components as they relate to Types of M&E § Assessment and Planning § Input/Output Monitoring § Outcome Monitoring § Impact Monitoring § Process Evaluation § Outcome Evaluation § Impact Evaluation Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
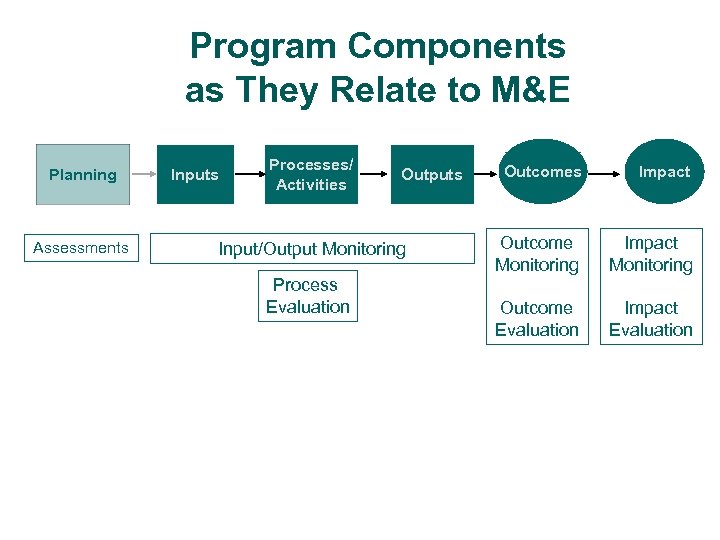
Program Components as They Relate to M&E Planning Assessments Inputs Processes/ Activities Outputs Input/Output Monitoring Process Evaluation Outcomes Impact Outcome Monitoring Impact Monitoring Outcome Evaluation Impact Evaluation
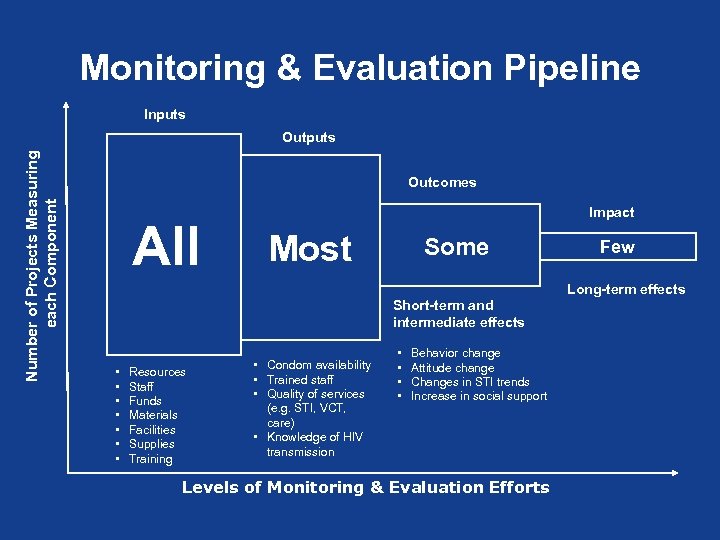
Monitoring & Evaluation Pipeline Inputs Number of Projects Measuring each Component Outputs Outcomes All Impact Most Some Few Long-term effects Short-term and intermediate effects • • Resources Staff Funds Materials Facilities Supplies Training • Condom availability • Trained staff • Quality of services (e. g. STI, VCT, care) • Knowledge of HIV transmission • • Behavior change Attitude change Changes in STI trends Increase in social support Levels of Monitoring & Evaluation Efforts

M&E Terminology Quiz Work in pairs/group and determine which type of M&E each example is describing. Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

Additional M&E Websites § MEASURE Evaluation: www. cpc. unc. edu/measure § Health Metrics Network: www. who. int/healthmetrics § John Snow Inc. : www. jsi. com § HIV Global Partners: www. globalhivmeinform. org Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs

MEASURE Evaluation is funded by the U. S. Agency for International Development (USAID) through Cooperative Agreement GHA-A-00 -08 -00003 -00 and is implemented by the Carolina Population Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, in partnership With Futures Group International, John Snow, Inc. , Macro International Inc. , Management Sciences for Health, and Tulane University. The views expressed in this presentation do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the United States government. Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS Programs
e8a09effadaeca0cc777e1e20484e756.ppt