fa7ee6a39a57d9d98c205eb5d3686395.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Introduction to Judaism

Judaism began almost 4000 years ago, in a region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, where human civilization first began.

In this region, called Mesopotamia, people practiced polytheism, which means they worshiped many gods, such as: Utu and Ishtar

A man named Abram and his wife Sarai lived in Mesopotamia, in a city called Ur. God appeared to Abram and made a covenant with him. A covenant is a sacred promise.

The Abrahamic Covenant God told Abram that he was the ONLY God, and if Abram would serve only him, God would give him a land that his children would number more than the stars. The belief in only one god is called monotheism.

Abram and Sarai accepted God’s covenant and made the long journey from their home in Ur to the land of Canaan, which God had given them. They changed their names to Abraham and Sarah, and kept their promise to serve only one God. Their name for God was Yahweh. Their descendents were called the Hebrews.
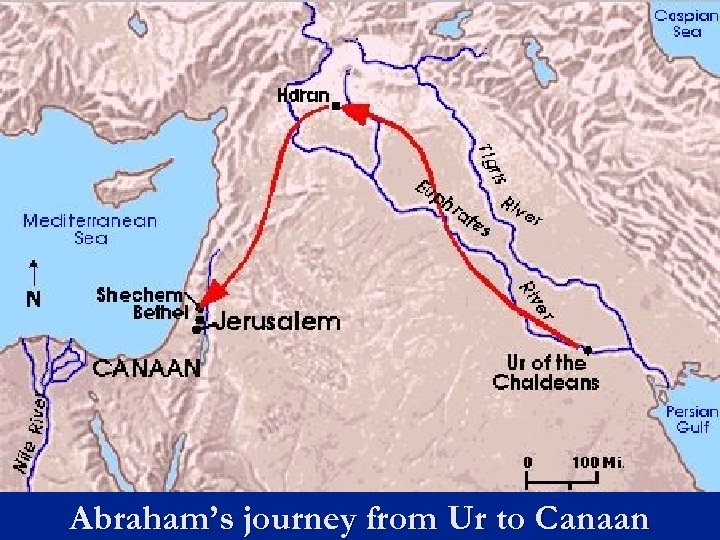
Abraham’s journey from Ur to Canaan
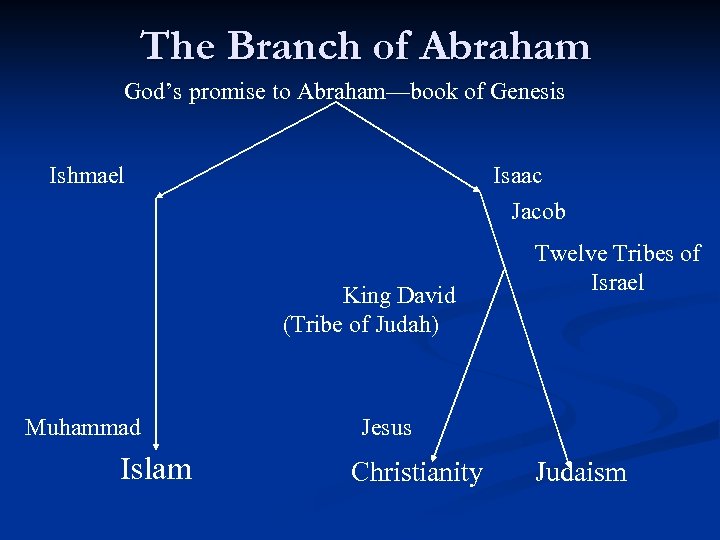
The Branch of Abraham God’s promise to Abraham—book of Genesis Ishmael Isaac Jacob King David (Tribe of Judah) Muhammad Islam Twelve Tribes of Israel Jesus Christianity Judaism

The Hebrew people lived well in Canaan for hundreds of years. Around 1500 BC however, their was a famine in the region, and many of the Hebrew people moved to Egypt. As their numbers grew, the Egyptian pharaoh grew afraid they would take over, so he turned them into slaves.

Around 1200 BC, God raised up a leader named MOSES to rescue his people from slavery in Egypt. When the pharaoh refused to set the Hebrew slaves free, God sent several plagues. Finally Moses was able to lead his people out of Egypt, through the Red Sea. Their journey back to freedom was called the EXODUS.

The journey back to Canaan took the Hebrews forty years. While they were crossing the desert they came to Mt. Sinai. The bible says that while Moses was on the mountain God gave him two stone tablets with laws on them. These laws were the Ten Commandments. Ever since then these laws have governed Hebrew life.

Ten Commandments 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Have no other gods before Me Do not worship a graven image Do not take the Lord’s name in vain Keep the Sabbath holy Honor your mother and father Do not murder Do not steal Do not commit adultery Do not give false testimony Do not covet

Mosaic Covenant Jewish people believe that when God gave Moses the Ten Commandments he made a new covenant with them. He promised that if they would follow his laws he would return the land of Canaan which he had given to Abraham to them. This “promised land” is what is now the land of Israel, and why Jews believe they have a God-given right to that land.

When the Hebrews finally got back to Canaan Many invaders tried to take their lands. Strong kings such as David, who became King around 1000 BC defeated the invaders and kept the land safe. He made Jerusalem its capital. David wrote many poems and songs praising God, which today are called the Psalms.

After King David died, in 965 BC, his son Solomon became the next king of Israel, as their land was now known. King Solomon was the known as the wisest and wealthiest of all of Israel’s rulers. Among his accomplishments was the building of the great Temple in Jerusalem.

After Solomon died the country eventually split into two kingdoms: Israel and Judah. The people of Judah became known as Jews, and their religion was called Judaism.
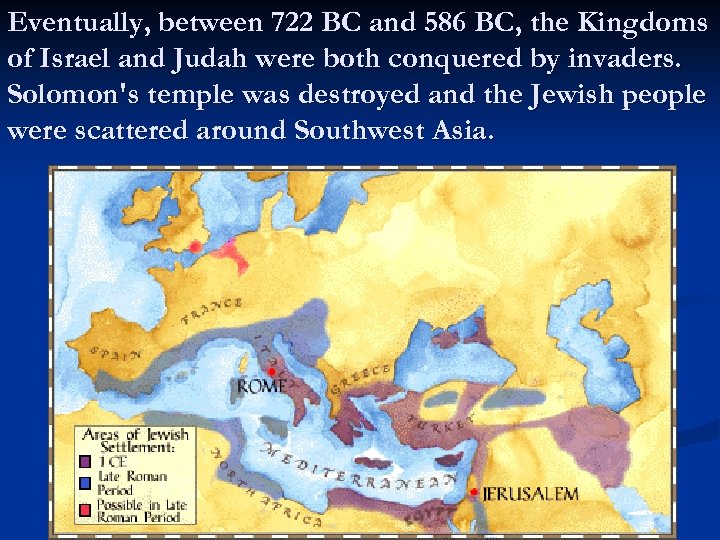
Eventually, between 722 BC and 586 BC, the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah were both conquered by invaders. Solomon's temple was destroyed and the Jewish people were scattered around Southwest Asia.

Some Jews returned to the area around Jerusalem, and rebuilt the temple, but then they were once again conquered by the Romans, who destroyed the 2 nd temple in AD 70, and once again scattered the Jews around Asia and Europe. The scattering of the Jews outside of Israel and Judah is known as the Diaspora.

The central beliefs of Judaism are: • One God (monotheism) • Justice & Righteousness • Importance of Law

The early Jews recorded the laws God had given them through Abraham and Moses in five books called the Torah. The Torah is the most important scripture in Judaism. The Jewish Bible is called the Tanach, and has three parts: the Torah, eight books of prophets, and a collection of songs, poetry, proverbs and psalms.

The Talmud is another sacred Jewish writing. It was written between AD 200 and 600, and is a collection of explanations and reflections on the Jewish Bible by wise Rabbis who have studied the Torah. Jews consider the name of the supreme being to be so holy that they do not write it out. Instead, they write it G-d.

Beliefs about G-d n n n n G-d is Omniscient G-d is Omni-present G-d is Omnipotent G-d is Eternal G-d is neither male nor female G-d is both just and merciful G-d is holy and perfect G-d is the father and King

Messianic Covenant Jews also believe that the according to the prophets in their scriptures and history, God has promised them a “messiah” – a savior. They believe this savior will: n n n Establish a government in Israel that will be the center of all world government, both for Jews and gentiles Rebuild the Temple and re-establish its worship Restore the religious court system of Israel and establish Jewish law as the law of the land

The Jewish day of rest and prayer is called the Sabbath. It begins at sundown on Friday and lasts until sundown on Saturday. The Jewish place of worship is called a Synagogue or a temple.
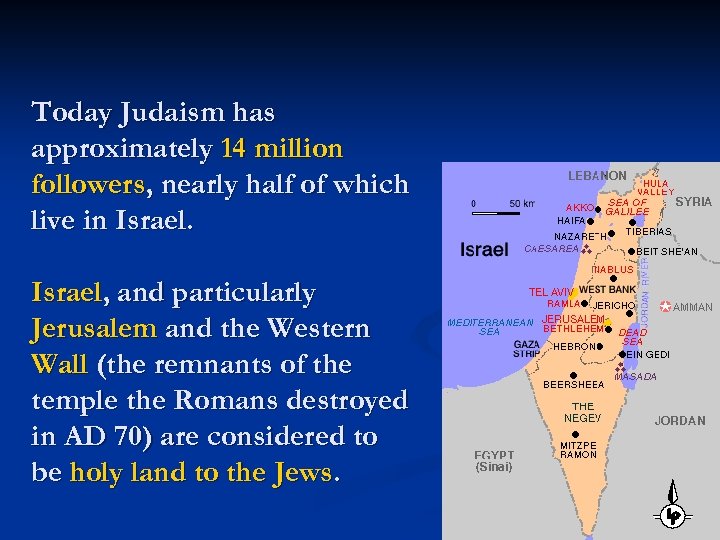
Today Judaism has approximately 14 million followers, nearly half of which live in Israel, and particularly Jerusalem and the Western Wall (the remnants of the temple the Romans destroyed in AD 70) are considered to be holy land to the Jews.

Western Wall

Dietary Laws (Kosher Laws) 1. 2. 3. Certain animals may not be eaten at all (chews cud, split hoof, sea creatures without fins/scales, certain birds, certain insects) Lev. 11: 9 -46 Of the animals that may be eaten, the birds and mammals must be killed in accordance with Jewish law. All blood must be drained from the meat (under Rabbinical supervision) or broiled out of it before it is eaten.

4. Certain parts of permitted animals may not be eaten. 5. Meat cannot be eaten with dairy. 6. Eggs, fruits, vegetables and grains can be eaten with either meat or dairy. Kosher Symbols on Food Packages

Kosher for Passover

Rituals and Celebrations

Rosh Hashanah n n Jewish New Year (Sep or Oct) Celebration of the Creation of the Earth No work is performed Considered a “High Holy Day”

Yom Kippur Day of Atonement n Holiest day in entire Jewish calendar n No work; must fast n Considered a “High Holy Day” n

Passover Honors the deliverance of Jews from Egyptian slavery n Major Holiday (seven days long) n

Chanukah (Hanukkah) Festival of Lights (8 days long) n Celebrates victory of the Maccabees over the Syrians n Minor holiday n

Rituals Bar Mitzvah (son of the commandment) n Bat Mitzvah (daughter of the commandment) n Marriage n
fa7ee6a39a57d9d98c205eb5d3686395.ppt