1c76ede22bfa2f74649ece5a6c38268d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

INTRODUCTION TO INTERTEMPORAL ANALYSIS Friday, October 20
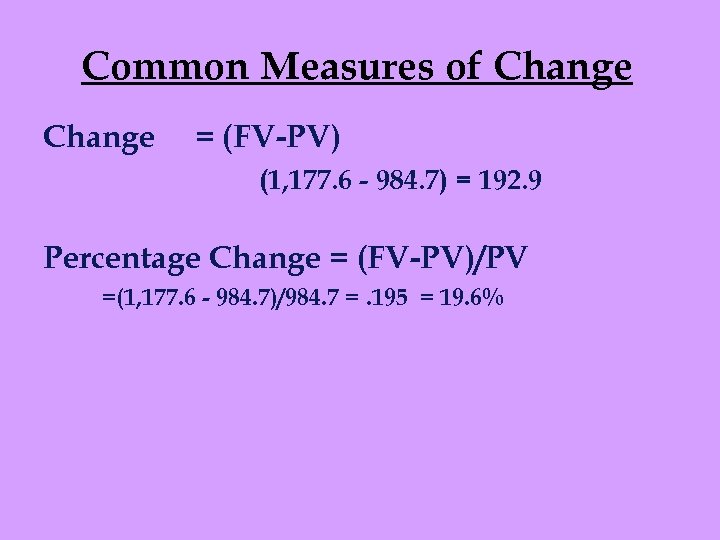
Common Measures of Change = (FV-PV) (1, 177. 6 - 984. 7) = 192. 9 Percentage Change = (FV-PV)/PV =(1, 177. 6 - 984. 7)/984. 7 =. 195 = 19. 6%
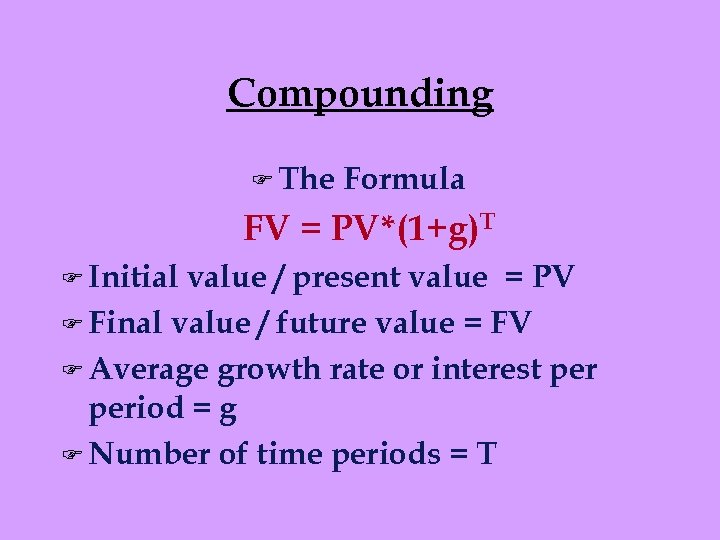
Compounding F The Formula FV = PV*(1+g)T F Initial value / present value = PV F Final value / future value = FV F Average growth rate or interest period = g F Number of time periods = T

Future Value Example u Q. What will the population of India be in the year 2020 if the population in 1985 was 751 million and the growth rate is 2. 5% a year? u A. The initial value is 751, the growth rate is 2. 5% (. 0251), and the time horizon is 35 years.

Average Growth Rate Example u Q. What was average yearly rate of wage growth if wages grew from $102 in 1970 to $389 in 1989? u A. The present value is 102, the future value is 389, and the time period is 19.

Present Value Example u Q. How much will I need to save today to have $1, 000 in 3 years if the interest rate is 8%. ? u A. The end value is $1, 000, the time horizon is 3 years, and the growth rate is 8%. .

An Introduction to the Mathematics of Finance u Q: What is a Bond? u A: A promise to pay in the future u Q: What is the price of a Bond? u A: How much you need to pay today to ‘buy’ the future payment(s)? u Q: What does the bond’s price depend on? u A: How fast money grows

Determining the Price of a Bond The Deal: u On January 1 you are offered the following deal: $100 on January 1 for the next three years The Starting Point: u A dollar a year from now is not worth a dollar today so we must convert the ‘future’ dollars to ‘‘present’ dollars.
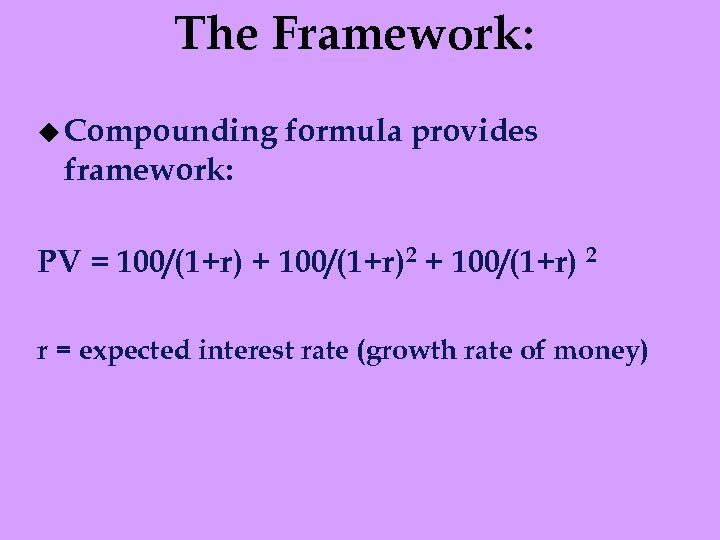
The Framework: u Compounding formula provides framework: PV = 100/(1+r) + 100/(1+r)2 + 100/(1+r) 2 r = expected interest rate (growth rate of money)

The Key to Intertemporal Analysis The Compounding Formula FV = PV*(1+g)T
1c76ede22bfa2f74649ece5a6c38268d.ppt