 Introduction to International Law
Introduction to International Law
 Intro • • International Law versus Law International Law versus Political Science Basic Concepts Learning International Law
Intro • • International Law versus Law International Law versus Political Science Basic Concepts Learning International Law
 International Law versus Law • “Law” is a system of social rules usually enforced through a set of structured institutions.
International Law versus Law • “Law” is a system of social rules usually enforced through a set of structured institutions.
 International Law versus Law • “Public law" subjects, which relate closely to the state (including constitutional, administrative and criminal law) • “Private law" subjects (including contract, tort, property)
International Law versus Law • “Public law" subjects, which relate closely to the state (including constitutional, administrative and criminal law) • “Private law" subjects (including contract, tort, property)
 Example of Law • First Proposition: 10 Commandments by Moses: #6, Thou Shall Not Kill • Second Proposition: If you kill, you will be punished by…
Example of Law • First Proposition: 10 Commandments by Moses: #6, Thou Shall Not Kill • Second Proposition: If you kill, you will be punished by…
 International Law versus Law • But international law only refers to the first proposition
International Law versus Law • But international law only refers to the first proposition
 Example of International Law • Winners wrote the history. • Only the defeated will be labeled as “war criminal. ”
Example of International Law • Winners wrote the history. • Only the defeated will be labeled as “war criminal. ”
 International Law versus Law • International law (public), which involves for instance the United Nations, maritime law, international criminal law and the Geneva conventions. • International law (private) or conflict of laws, which addresses the question of which legal jurisdiction cases may be heard in.
International Law versus Law • International law (public), which involves for instance the United Nations, maritime law, international criminal law and the Geneva conventions. • International law (private) or conflict of laws, which addresses the question of which legal jurisdiction cases may be heard in.
 Subtle Difference • By definition, International private law is still the “law, ” since the domestic courts could generate the ruling toward the legal case and enforce it.
Subtle Difference • By definition, International private law is still the “law, ” since the domestic courts could generate the ruling toward the legal case and enforce it.
 Example of International Private Law • It is relatively easier for two locals to file divorce. If one of the couple were a foreigner, then the foreign law should be considered by local court. • However, it does not mean that foreign country has any say in the legal consideration. It is a private and foreign individual versus the state legal system. • And the true international law is one legal system versus another, or others.
Example of International Private Law • It is relatively easier for two locals to file divorce. If one of the couple were a foreigner, then the foreign law should be considered by local court. • However, it does not mean that foreign country has any say in the legal consideration. It is a private and foreign individual versus the state legal system. • And the true international law is one legal system versus another, or others.
 International Law versus Law • The key word is still “enforcement. ” • Although domestic enforcement did not get all the bad guys, (most of time, the function of domestic law is a lot worse than international law) at least bad guys would not claim themselves as just, like most of bad states in the history and now.
International Law versus Law • The key word is still “enforcement. ” • Although domestic enforcement did not get all the bad guys, (most of time, the function of domestic law is a lot worse than international law) at least bad guys would not claim themselves as just, like most of bad states in the history and now.
 Example • The Rape of Nanking • United States in Iraq
Example • The Rape of Nanking • United States in Iraq
 The Rape of Nanking
The Rape of Nanking
 United States in Iraq
United States in Iraq
 Intro • International Law versus Law • International Law versus Political Science • Basic Concepts
Intro • International Law versus Law • International Law versus Political Science • Basic Concepts
 International Law versus Political Science • Since there is no enforcement in international law, all the actions are determined by conflicts, struggles, possible consensus, conspiracies, or sophisticated calculations. • So, isn’t it the, simply put, POLITICS?
International Law versus Political Science • Since there is no enforcement in international law, all the actions are determined by conflicts, struggles, possible consensus, conspiracies, or sophisticated calculations. • So, isn’t it the, simply put, POLITICS?
 Basic Concepts • • Politics International Politics Anarchy State Realism vs. Liberalism International Organization and Institution International Law
Basic Concepts • • Politics International Politics Anarchy State Realism vs. Liberalism International Organization and Institution International Law
 Politics • Oxford Dictionary: “The art and science of government, ” “public life and affairs as involving authority and government, ” “activities concerned with the acquisition or exercise of authority or government, ” • Other occasions: office/family/couple • Harold Laswell: “Who gets what, when, how, ” “Authoritative allocation of values, ” • Mark Lai Definition: “Power and goods, their competition, compensation, implementation and continuation”
Politics • Oxford Dictionary: “The art and science of government, ” “public life and affairs as involving authority and government, ” “activities concerned with the acquisition or exercise of authority or government, ” • Other occasions: office/family/couple • Harold Laswell: “Who gets what, when, how, ” “Authoritative allocation of values, ” • Mark Lai Definition: “Power and goods, their competition, compensation, implementation and continuation”
 International Politics • Politics among states, level of analysis • Differences between International Politics and Taiwan Politics • Theoretical boundary between International Relations and Domestic Politics: Anarchy vs. Hierarchy
International Politics • Politics among states, level of analysis • Differences between International Politics and Taiwan Politics • Theoretical boundary between International Relations and Domestic Politics: Anarchy vs. Hierarchy
 Anarchy • Example: If you got a parking ticket just because of a broken meter, what would you do? • Example: If Cuba invaded Miami, what would the US do? • Example: If you had to go to a bad neighborhood with weak police enforcement, what would you prepare for this trip? • Definition: “No supreme power to govern, ” “no overarching power, ” “Self help system” • Anarchy vs. Chaos, Anarchic world still has order. • Value, legal and study system in an anarchic world
Anarchy • Example: If you got a parking ticket just because of a broken meter, what would you do? • Example: If Cuba invaded Miami, what would the US do? • Example: If you had to go to a bad neighborhood with weak police enforcement, what would you prepare for this trip? • Definition: “No supreme power to govern, ” “no overarching power, ” “Self help system” • Anarchy vs. Chaos, Anarchic world still has order. • Value, legal and study system in an anarchic world
 State • A corporate body exercising or claiming to exercise, sovereign political power over a particular geographic area. Sovereign power implies a monopoly on the legitimate use of violence and must be recognized by other sovereign states.
State • A corporate body exercising or claiming to exercise, sovereign political power over a particular geographic area. Sovereign power implies a monopoly on the legitimate use of violence and must be recognized by other sovereign states.
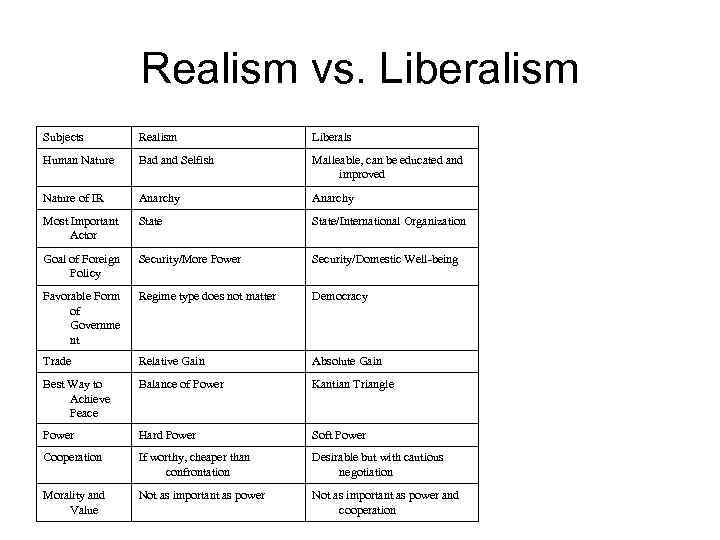 Realism vs. Liberalism Subjects Realism Liberals Human Nature Bad and Selfish Malleable, can be educated and improved Nature of IR Anarchy Most Important Actor State/International Organization Goal of Foreign Policy Security/More Power Security/Domestic Well-being Favorable Form of Governme nt Regime type does not matter Democracy Trade Relative Gain Absolute Gain Best Way to Achieve Peace Balance of Power Kantian Triangle Power Hard Power Soft Power Cooperation If worthy, cheaper than confrontation Desirable but with cautious negotiation Morality and Value Not as important as power and cooperation
Realism vs. Liberalism Subjects Realism Liberals Human Nature Bad and Selfish Malleable, can be educated and improved Nature of IR Anarchy Most Important Actor State/International Organization Goal of Foreign Policy Security/More Power Security/Domestic Well-being Favorable Form of Governme nt Regime type does not matter Democracy Trade Relative Gain Absolute Gain Best Way to Achieve Peace Balance of Power Kantian Triangle Power Hard Power Soft Power Cooperation If worthy, cheaper than confrontation Desirable but with cautious negotiation Morality and Value Not as important as power and cooperation
 International Organization and Institution • International organizations and institutions are the cooperative problem solving arrangements and activities that states and other actors have put into place to deal with various issues and problems. • They include international rules and laws, norms or soft law, and structures such as formal international intergovernmental organization as well as improvised arrangements that provide decision-making process, information gathering and analytical functions, dispute settlement procedures, and operational capabilities for managing technical and development assistance programs, relief aid, and force deployments.
International Organization and Institution • International organizations and institutions are the cooperative problem solving arrangements and activities that states and other actors have put into place to deal with various issues and problems. • They include international rules and laws, norms or soft law, and structures such as formal international intergovernmental organization as well as improvised arrangements that provide decision-making process, information gathering and analytical functions, dispute settlement procedures, and operational capabilities for managing technical and development assistance programs, relief aid, and force deployments.
 International Law • State as the Main Actor • The Rule of Game “Trying” to regulate relations among States • Original Function • Globalization • Expanded Function
International Law • State as the Main Actor • The Rule of Game “Trying” to regulate relations among States • Original Function • Globalization • Expanded Function
 State as the Main Actor • Public international law establishes the framework and the criteria for identifying states as the principal actors in the international legal system. • Why? Good or bad, Force is the final answer to conflict resolution and state is the actor with the strongest ability of using force.
State as the Main Actor • Public international law establishes the framework and the criteria for identifying states as the principal actors in the international legal system. • Why? Good or bad, Force is the final answer to conflict resolution and state is the actor with the strongest ability of using force.
 Original Function • International law deals with the acquisition of territory, state immunity and the legal responsibility of states in their conduct with each other.
Original Function • International law deals with the acquisition of territory, state immunity and the legal responsibility of states in their conduct with each other.
 Globalization • As the world gets smaller, the interaction among states dramatically became intense, frequent and sometimes complicated. • Globalization speeded up the growth, created the interdependence but also spurred the proliferation of negative transactions such as terrorism, drug trafficking, and financial speculation. • Most importantly, globalization hampered the function and influence of nation state governance. Traditional role nation states played could not deal with this world anymore.
Globalization • As the world gets smaller, the interaction among states dramatically became intense, frequent and sometimes complicated. • Globalization speeded up the growth, created the interdependence but also spurred the proliferation of negative transactions such as terrorism, drug trafficking, and financial speculation. • Most importantly, globalization hampered the function and influence of nation state governance. Traditional role nation states played could not deal with this world anymore.
 Expanded Function • “Legal responsibility of states in their conduct with each other. ” • War • Money • People • The Earth
Expanded Function • “Legal responsibility of states in their conduct with each other. ” • War • Money • People • The Earth
 Expanded Function • • • • Group rights The treatment of aliens The rights of refugees International crimes Nationality problems Human rights Maintenance of international peace and security Arms control The pacific settlement of disputes Regulation of the use of force Principles to govern the conduct of hostilities and the treatment of prisoners Global environment International waters Outer space Global communications World trade
Expanded Function • • • • Group rights The treatment of aliens The rights of refugees International crimes Nationality problems Human rights Maintenance of international peace and security Arms control The pacific settlement of disputes Regulation of the use of force Principles to govern the conduct of hostilities and the treatment of prisoners Global environment International waters Outer space Global communications World trade
 Learning International Law • Absent a world government, the environment of international politics is that of a loose anarchy. Observance of the law is voluntary, for no superior political authority exists to compel obedience.
Learning International Law • Absent a world government, the environment of international politics is that of a loose anarchy. Observance of the law is voluntary, for no superior political authority exists to compel obedience.
 Learning International Law • The truth that international law is not true law made the learning of the subject become hazy and sometimes cynical.
Learning International Law • The truth that international law is not true law made the learning of the subject become hazy and sometimes cynical.
 Learning International Law • Believers believed international law would and should be the solution for global problems and skeptics suspected that international law would do any good for currently chaotic nation-state world system. However, also this truth made the learning of the subject so challenging and rewarding.
Learning International Law • Believers believed international law would and should be the solution for global problems and skeptics suspected that international law would do any good for currently chaotic nation-state world system. However, also this truth made the learning of the subject so challenging and rewarding.
 Learning International Law • Through the understanding of international law, one could review theory of international relations, scrutinize the regional politics all over the world, as well as examine the conflict and cooperation between domestic law system and the international one.
Learning International Law • Through the understanding of international law, one could review theory of international relations, scrutinize the regional politics all over the world, as well as examine the conflict and cooperation between domestic law system and the international one.
 Learning International Law • Simply put, this course will lead students go through most of major issues touched in the four-years course load and prepare students to thesis writing and further graduate education.
Learning International Law • Simply put, this course will lead students go through most of major issues touched in the four-years course load and prepare students to thesis writing and further graduate education.


