d06c62dd820cd78ca24defcba50cc80f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Introduction to Image Processing
Introduction to Image Processing
 What is Image Processing? • Manipulation of digital images by computer. • Image processing focuses on two major tasks: – Improvement of pictorial information for human interpretation and high level processing. – Processing of image data for storage and transmission.
What is Image Processing? • Manipulation of digital images by computer. • Image processing focuses on two major tasks: – Improvement of pictorial information for human interpretation and high level processing. – Processing of image data for storage and transmission.
 Related Areas • Image Processing • Computer Vision • Computer Graphics
Related Areas • Image Processing • Computer Vision • Computer Graphics
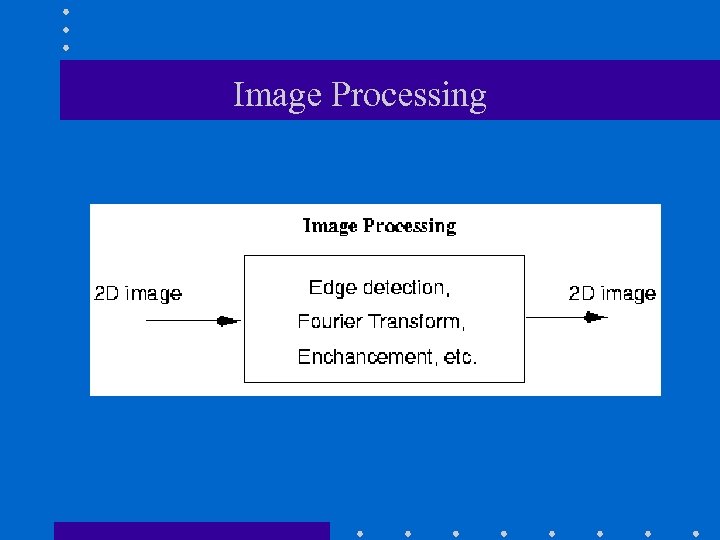 Image Processing
Image Processing
 Image Processing • Image Enhancement
Image Processing • Image Enhancement
 Image Processing (cont’d) • Image Restoration
Image Processing (cont’d) • Image Restoration
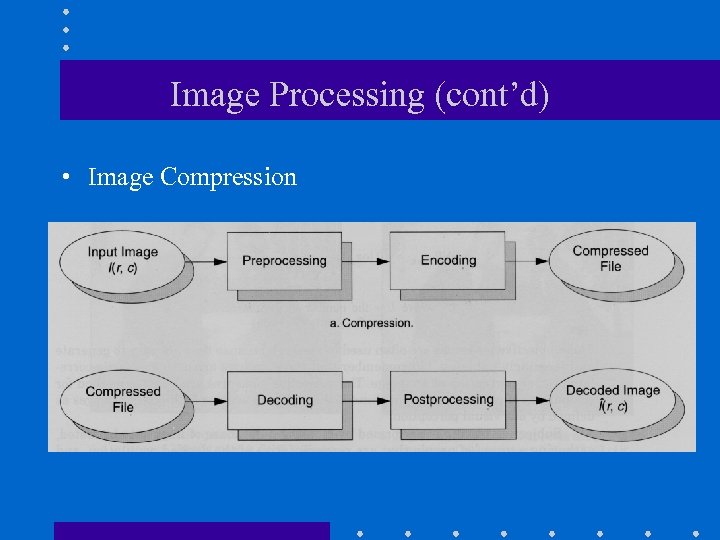 Image Processing (cont’d) • Image Compression
Image Processing (cont’d) • Image Compression
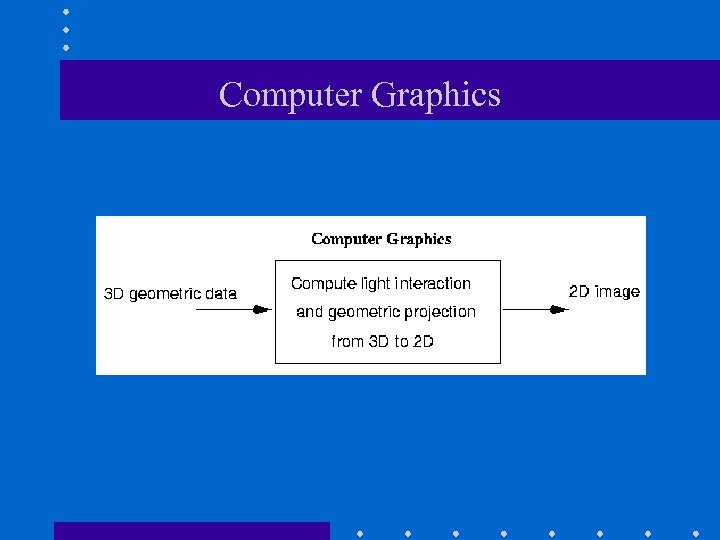 Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics
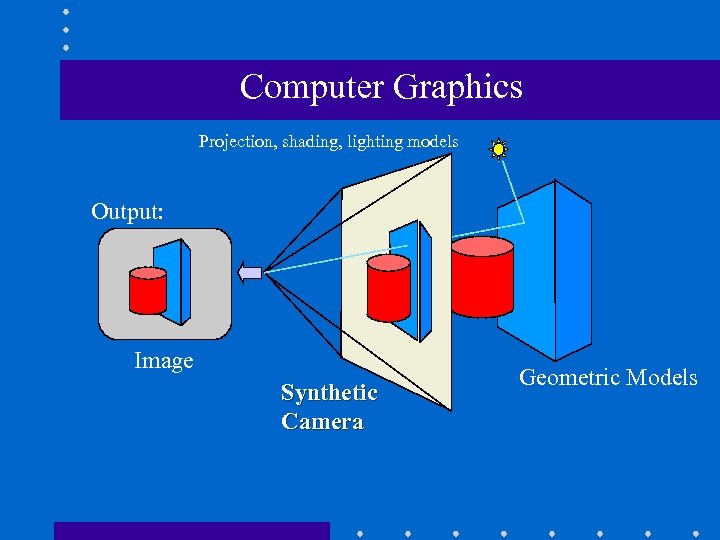 Computer Graphics Projection, shading, lighting models Output: Image Synthetic Camera Geometric Models
Computer Graphics Projection, shading, lighting models Output: Image Synthetic Camera Geometric Models
 Computer Vision
Computer Vision
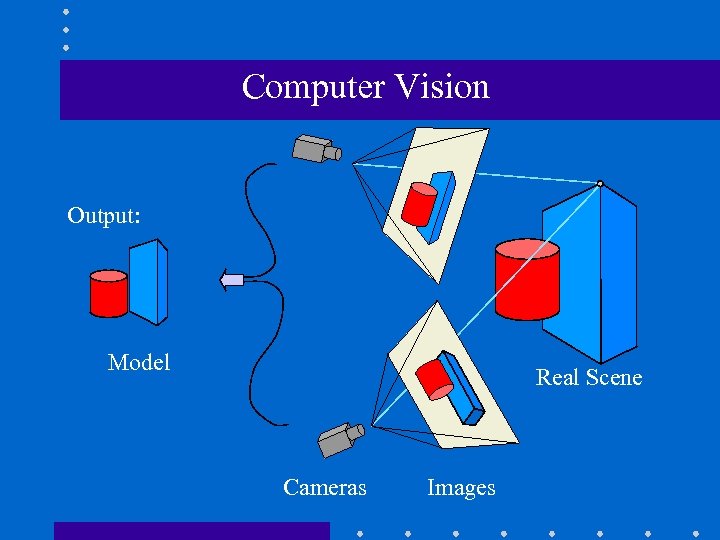 Computer Vision Output: Model Real Scene Cameras Images
Computer Vision Output: Model Real Scene Cameras Images
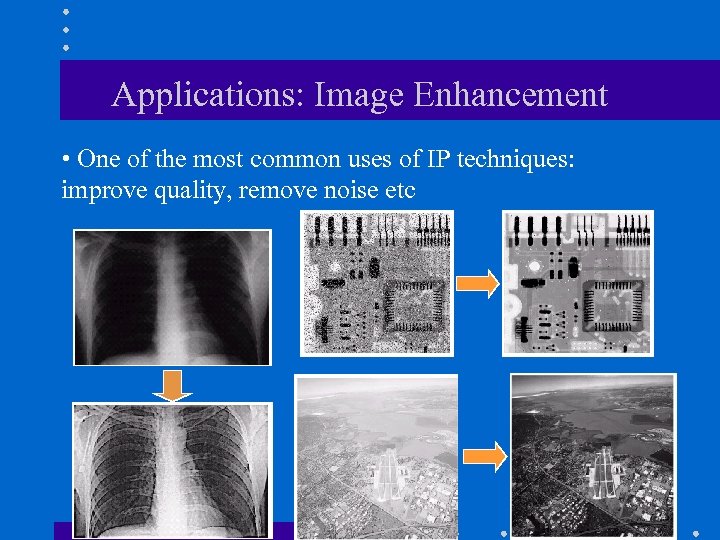 Applications: Image Enhancement • One of the most common uses of IP techniques: improve quality, remove noise etc
Applications: Image Enhancement • One of the most common uses of IP techniques: improve quality, remove noise etc
 Applications: Space • Launched in 1990 the Hubble telescope can take images of very distant objects • An incorrect mirror made many of Hubble’s images useless • Image processing techniques were used to fix this!
Applications: Space • Launched in 1990 the Hubble telescope can take images of very distant objects • An incorrect mirror made many of Hubble’s images useless • Image processing techniques were used to fix this!
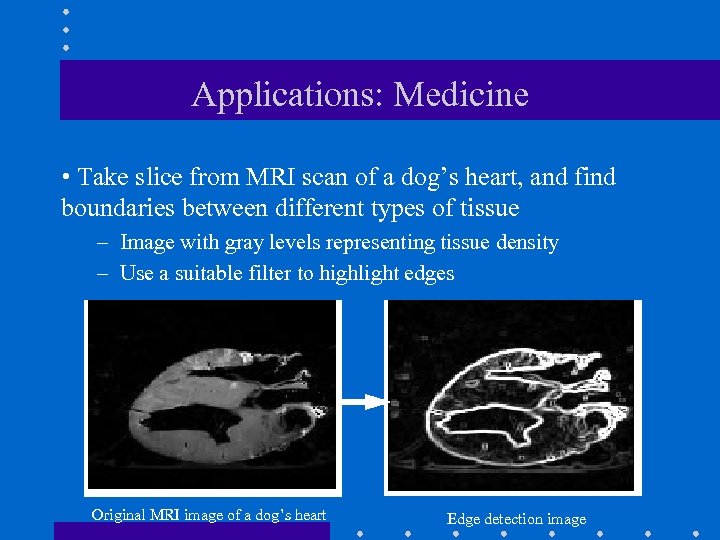 Applications: Medicine • Take slice from MRI scan of a dog’s heart, and find boundaries between different types of tissue – Image with gray levels representing tissue density – Use a suitable filter to highlight edges Original MRI image of a dog’s heart Edge detection image
Applications: Medicine • Take slice from MRI scan of a dog’s heart, and find boundaries between different types of tissue – Image with gray levels representing tissue density – Use a suitable filter to highlight edges Original MRI image of a dog’s heart Edge detection image
 Applications: GIS • Geographic Information Systems – Digital image processing techniques are used extensively to manipulate satellite imagery. terrain classification meteorology
Applications: GIS • Geographic Information Systems – Digital image processing techniques are used extensively to manipulate satellite imagery. terrain classification meteorology
 Applications: Industrial Inspection • Human operators are expensive, slow and unreliable • Make machines do the job instead! • Industrial vision systems are used in all kinds of industries
Applications: Industrial Inspection • Human operators are expensive, slow and unreliable • Make machines do the job instead! • Industrial vision systems are used in all kinds of industries
 Applications: Law Enforcement • Image processing techniques are used extensively by law enforcers Fingerprint recognition Number plate recognition for speed cameras or automated toll systems
Applications: Law Enforcement • Image processing techniques are used extensively by law enforcers Fingerprint recognition Number plate recognition for speed cameras or automated toll systems
 Examples: HCI • Make Human Computer Interaction (HCI) more natural – Face recognition – Gesture recognition
Examples: HCI • Make Human Computer Interaction (HCI) more natural – Face recognition – Gesture recognition
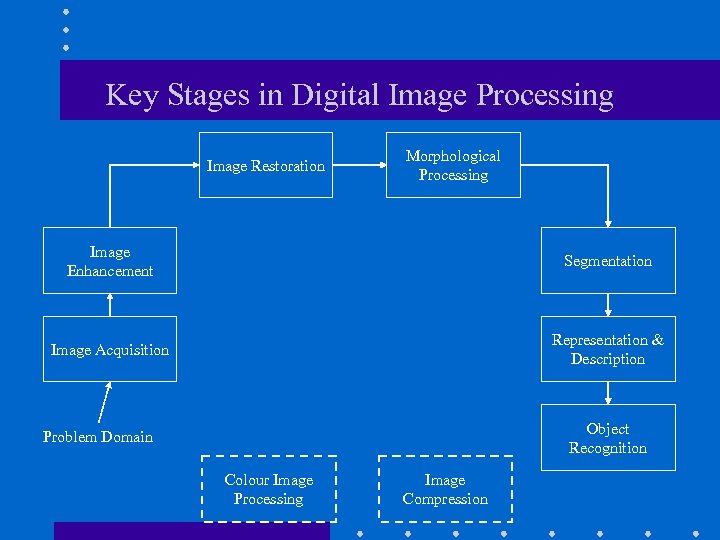 Key Stages in Digital Image Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Key Stages in Digital Image Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
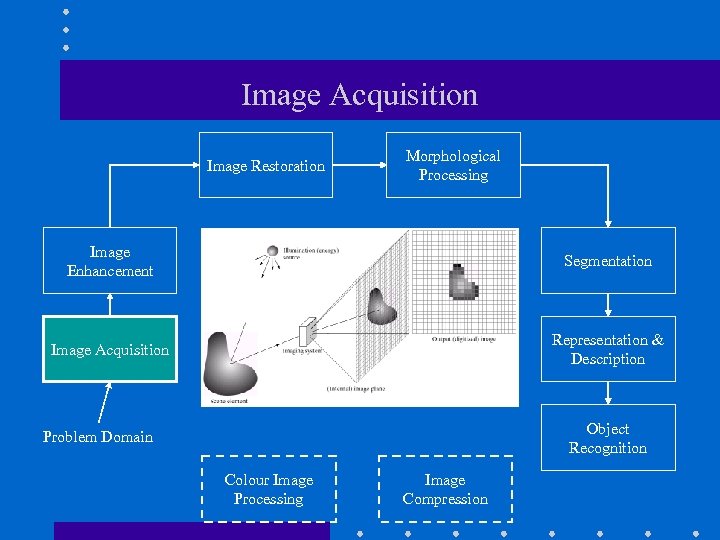 Image Acquisition Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Image Acquisition Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
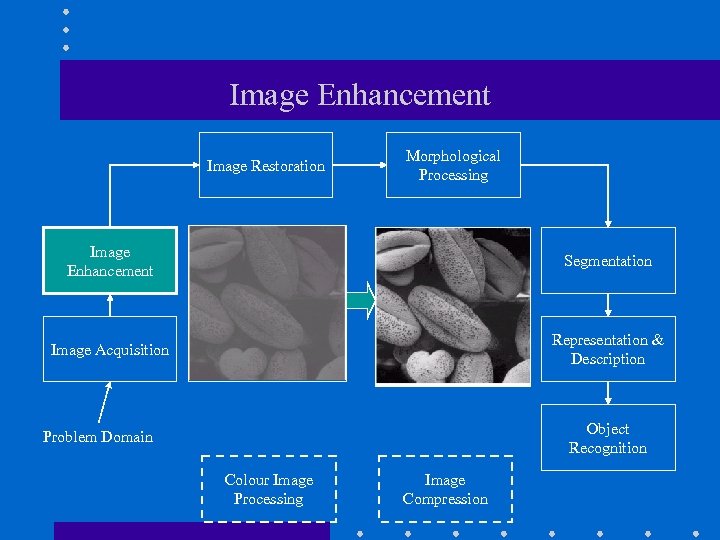 Image Enhancement Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Image Enhancement Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
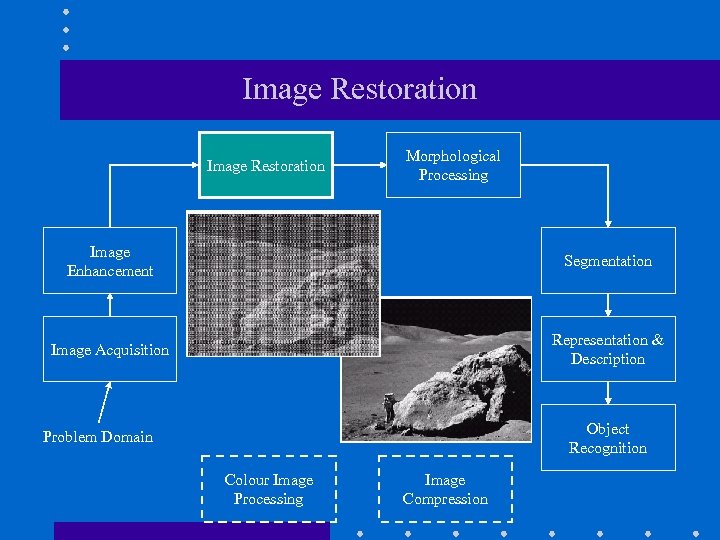 Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
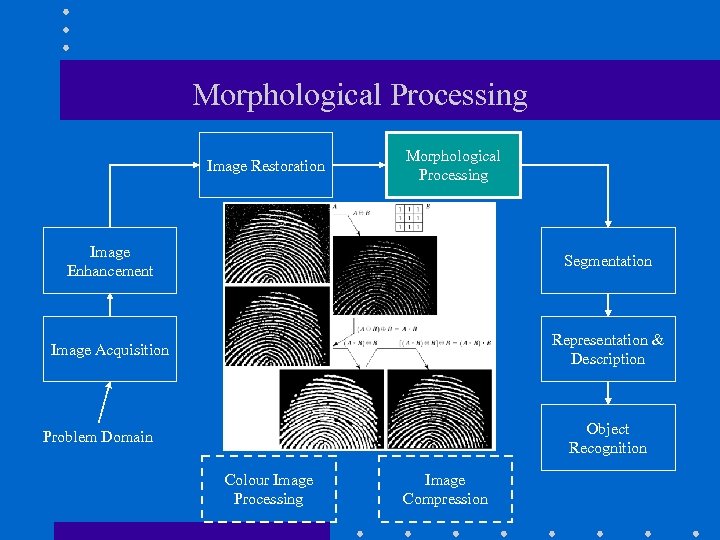 Morphological Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Morphological Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
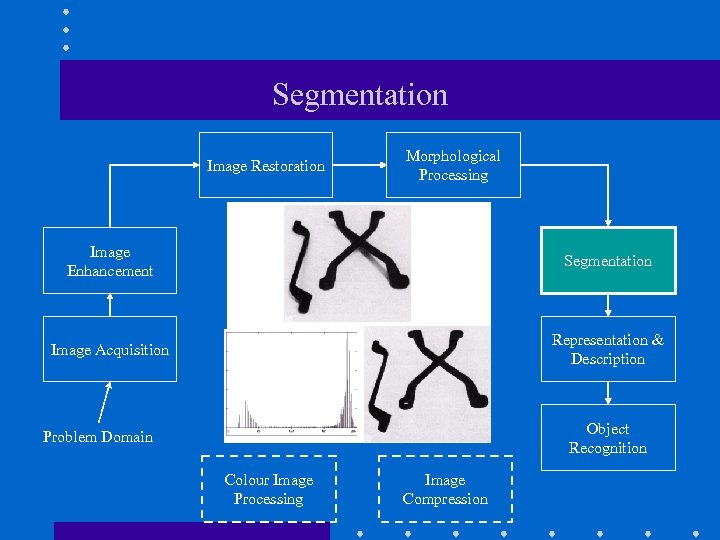 Segmentation Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Segmentation Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
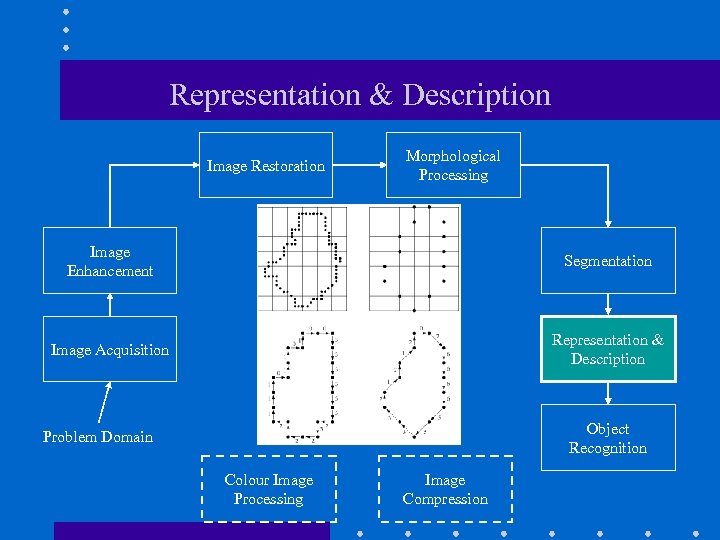 Representation & Description Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Representation & Description Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
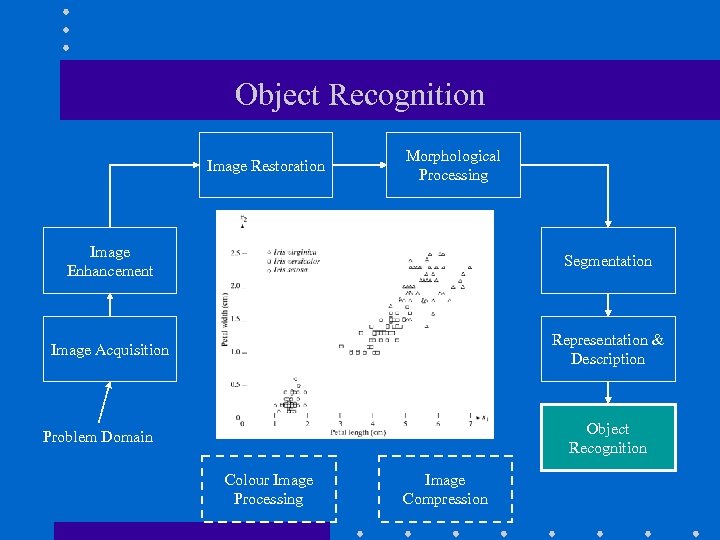 Object Recognition Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Object Recognition Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Representation & Description Object Recognition Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
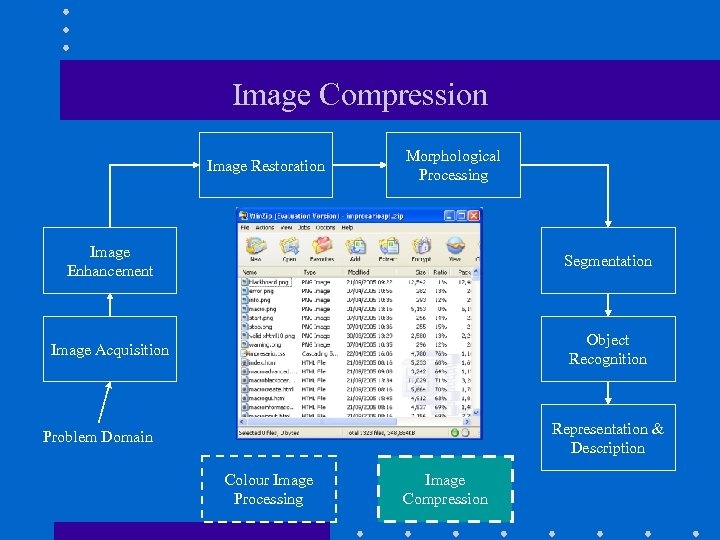 Image Compression Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Object Recognition Representation & Description Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
Image Compression Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Object Recognition Representation & Description Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression
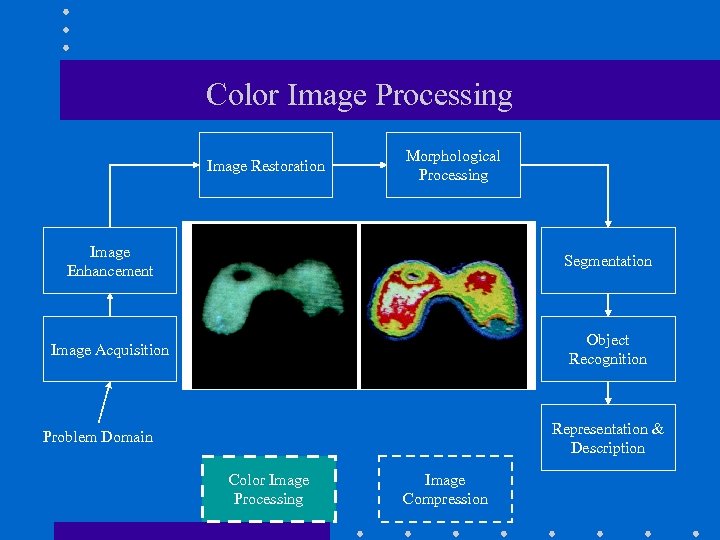 Color Image Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Object Recognition Representation & Description Problem Domain Color Image Processing Image Compression
Color Image Processing Image Restoration Morphological Processing Image Enhancement Segmentation Image Acquisition Object Recognition Representation & Description Problem Domain Color Image Processing Image Compression
 How are images represented in the computer?
How are images represented in the computer?
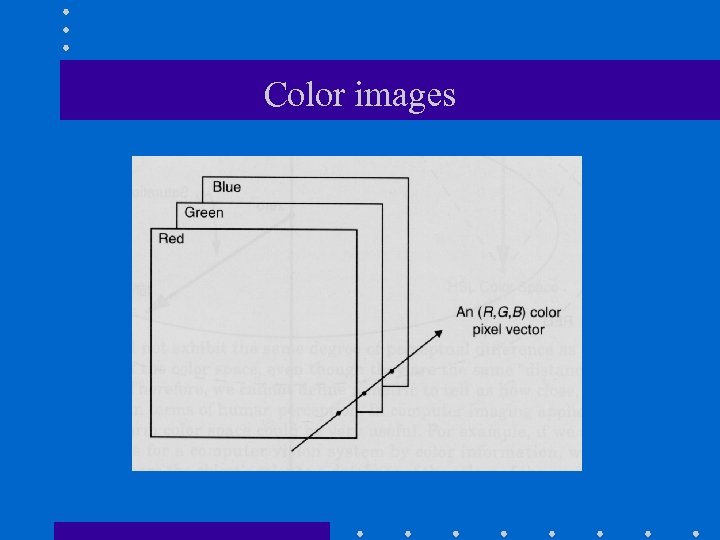 Color images
Color images
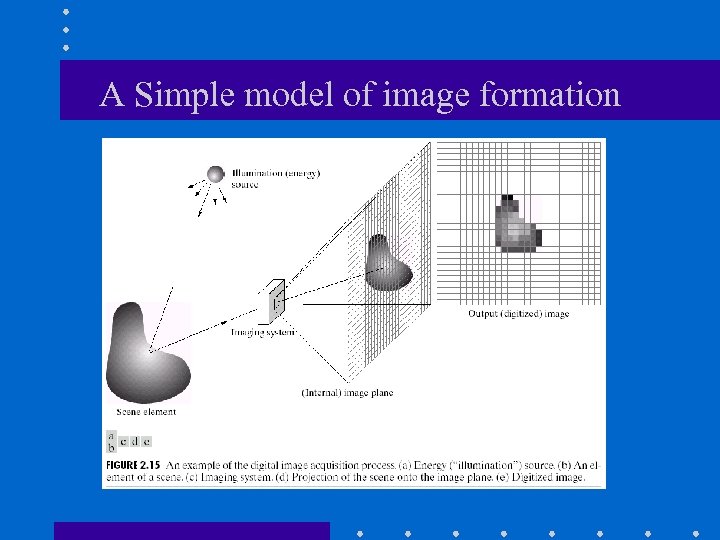 A Simple model of image formation
A Simple model of image formation
 What is (visible) light? • The visible portion of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. – Approximately between 400 and 700 nanometers.
What is (visible) light? • The visible portion of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. – Approximately between 400 and 700 nanometers.
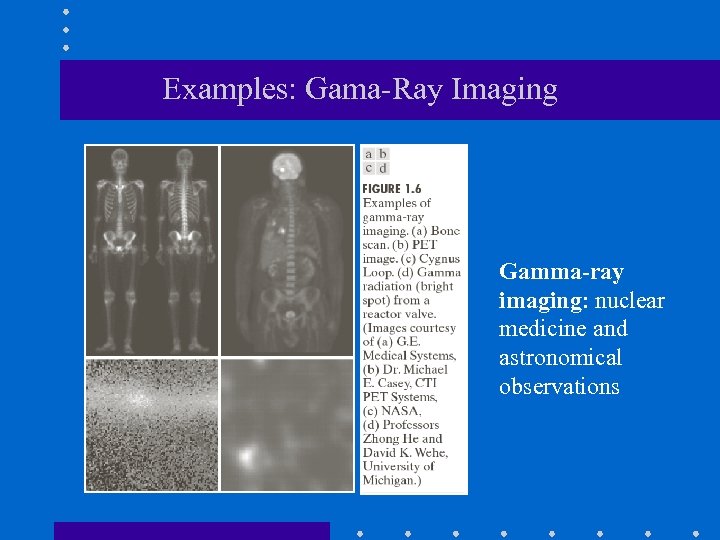 Examples: Gama-Ray Imaging Gamma-ray imaging: nuclear medicine and astronomical observations
Examples: Gama-Ray Imaging Gamma-ray imaging: nuclear medicine and astronomical observations
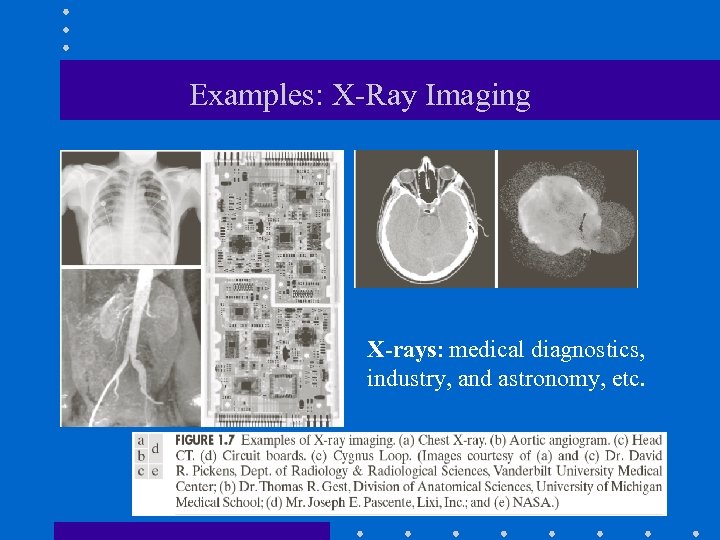 Examples: X-Ray Imaging X-rays: medical diagnostics, industry, and astronomy, etc.
Examples: X-Ray Imaging X-rays: medical diagnostics, industry, and astronomy, etc.
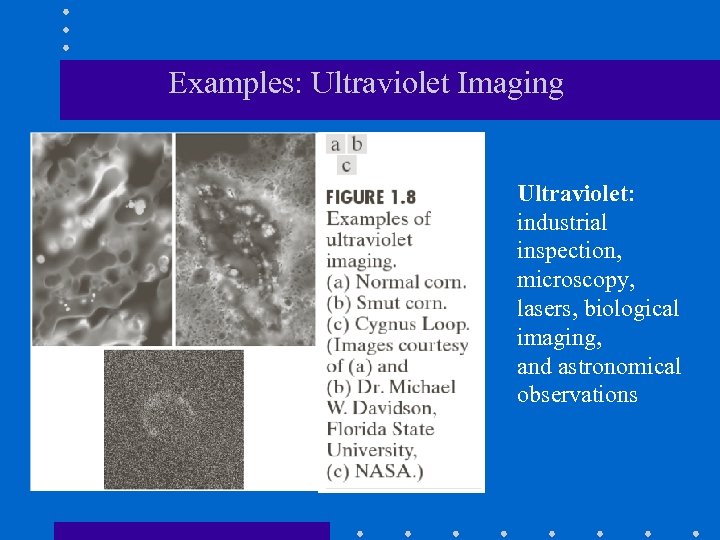 Examples: Ultraviolet Imaging Ultraviolet: industrial inspection, microscopy, lasers, biological imaging, and astronomical observations
Examples: Ultraviolet Imaging Ultraviolet: industrial inspection, microscopy, lasers, biological imaging, and astronomical observations
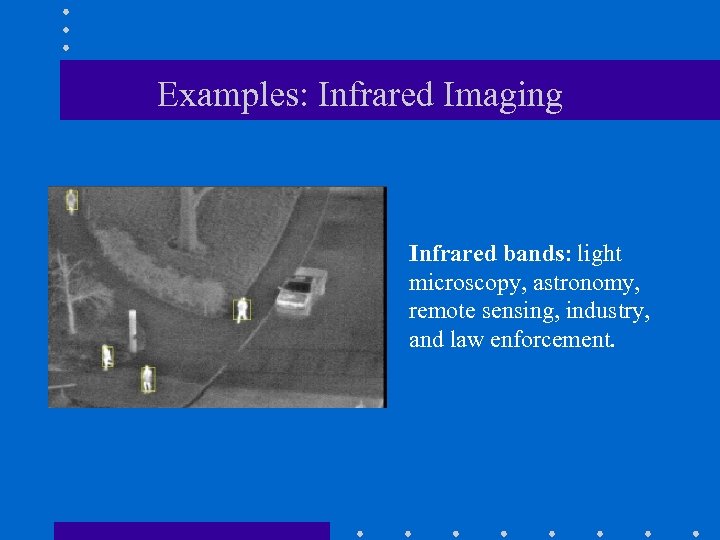 Examples: Infrared Imaging Infrared bands: light microscopy, astronomy, remote sensing, industry, and law enforcement.
Examples: Infrared Imaging Infrared bands: light microscopy, astronomy, remote sensing, industry, and law enforcement.
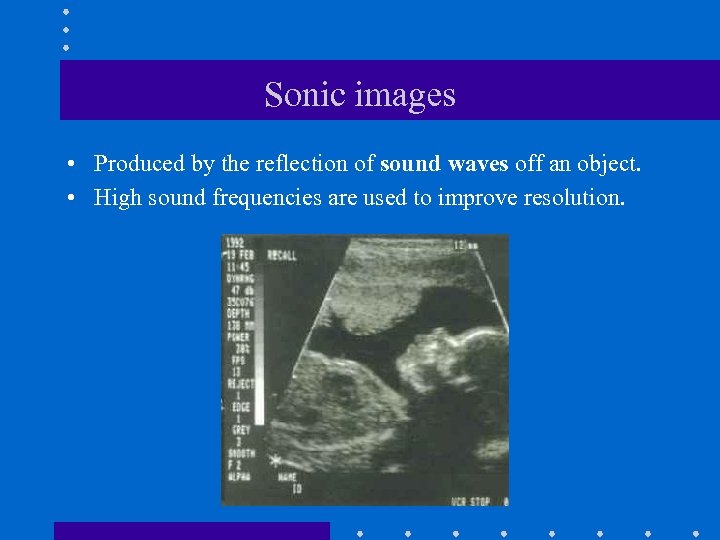 Sonic images • Produced by the reflection of sound waves off an object. • High sound frequencies are used to improve resolution.
Sonic images • Produced by the reflection of sound waves off an object. • High sound frequencies are used to improve resolution.
 Range images • Can be produced by using laser range-finders. • An array of distances to the objects in the scene.
Range images • Can be produced by using laser range-finders. • An array of distances to the objects in the scene.
 Image formation • There are two parts to the image formation process: – The geometry of image formation, which determines where in the image plane the projection of a point in the scene will be located. – The physics of light, which determines the brightness of a point in the image plane as a function of illumination and surface properties.
Image formation • There are two parts to the image formation process: – The geometry of image formation, which determines where in the image plane the projection of a point in the scene will be located. – The physics of light, which determines the brightness of a point in the image plane as a function of illumination and surface properties.
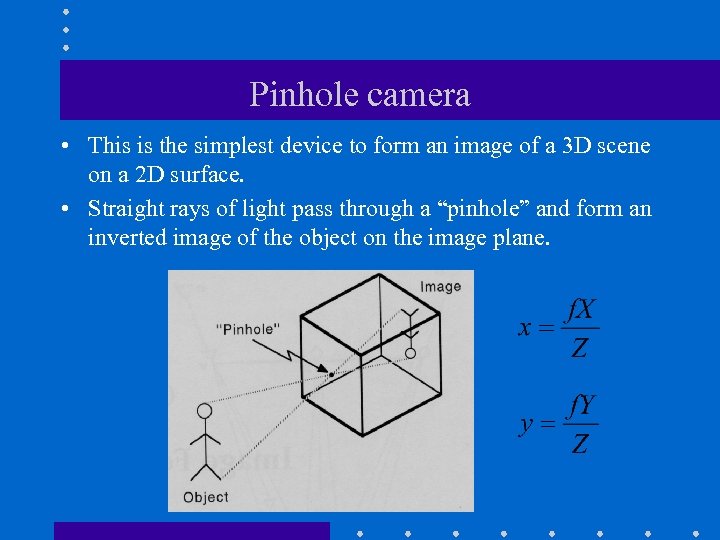 Pinhole camera • This is the simplest device to form an image of a 3 D scene on a 2 D surface. • Straight rays of light pass through a “pinhole” and form an inverted image of the object on the image plane.
Pinhole camera • This is the simplest device to form an image of a 3 D scene on a 2 D surface. • Straight rays of light pass through a “pinhole” and form an inverted image of the object on the image plane.
 Camera optics • In practice, the aperture must be larger to admit more light. • Lenses are placed in the aperture to focus the bundle of rays from each scene point onto the corresponding point in the image plane
Camera optics • In practice, the aperture must be larger to admit more light. • Lenses are placed in the aperture to focus the bundle of rays from each scene point onto the corresponding point in the image plane
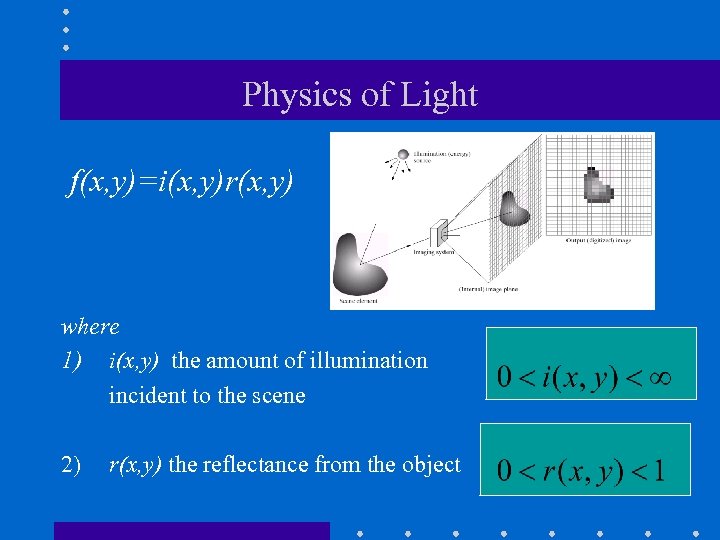 Physics of Light f(x, y)=i(x, y)r(x, y) where 1) i(x, y) the amount of illumination incident to the scene 2) r(x, y) the reflectance from the object
Physics of Light f(x, y)=i(x, y)r(x, y) where 1) i(x, y) the amount of illumination incident to the scene 2) r(x, y) the reflectance from the object
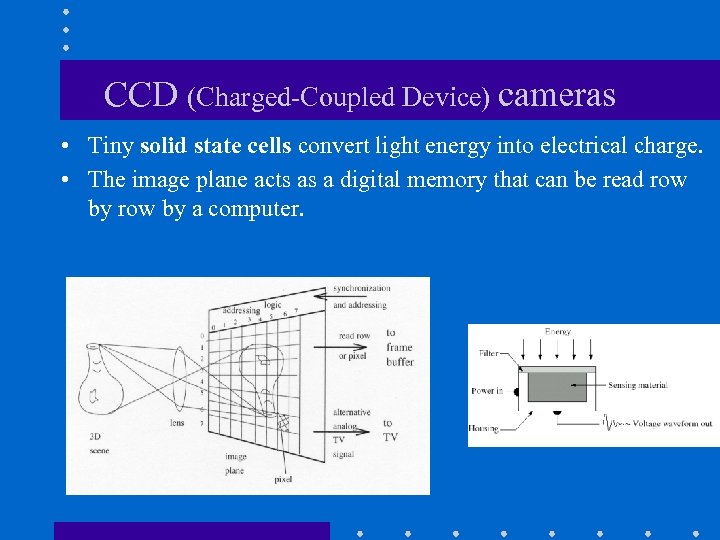 CCD (Charged-Coupled Device) cameras • Tiny solid state cells convert light energy into electrical charge. • The image plane acts as a digital memory that can be read row by a computer.
CCD (Charged-Coupled Device) cameras • Tiny solid state cells convert light energy into electrical charge. • The image plane acts as a digital memory that can be read row by a computer.
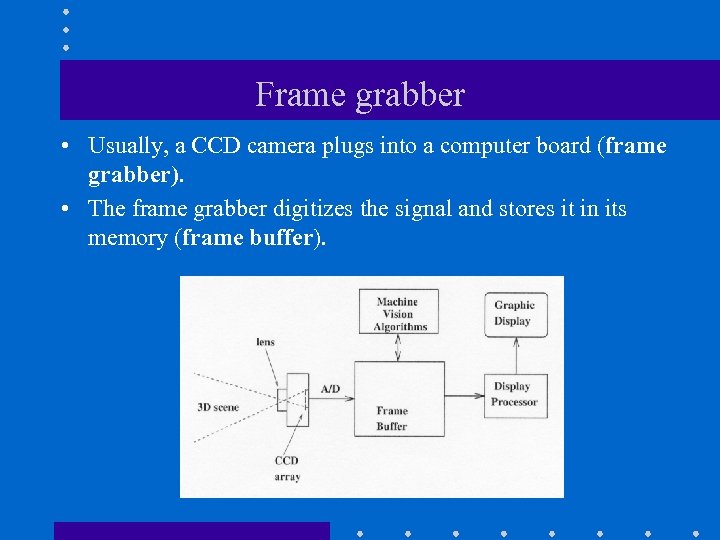 Frame grabber • Usually, a CCD camera plugs into a computer board (frame grabber). • The frame grabber digitizes the signal and stores it in its memory (frame buffer).
Frame grabber • Usually, a CCD camera plugs into a computer board (frame grabber). • The frame grabber digitizes the signal and stores it in its memory (frame buffer).
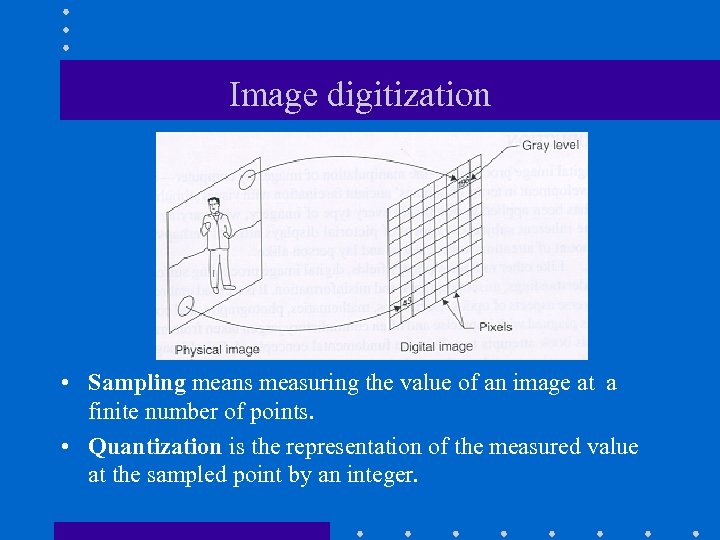 Image digitization • Sampling means measuring the value of an image at a finite number of points. • Quantization is the representation of the measured value at the sampled point by an integer.
Image digitization • Sampling means measuring the value of an image at a finite number of points. • Quantization is the representation of the measured value at the sampled point by an integer.
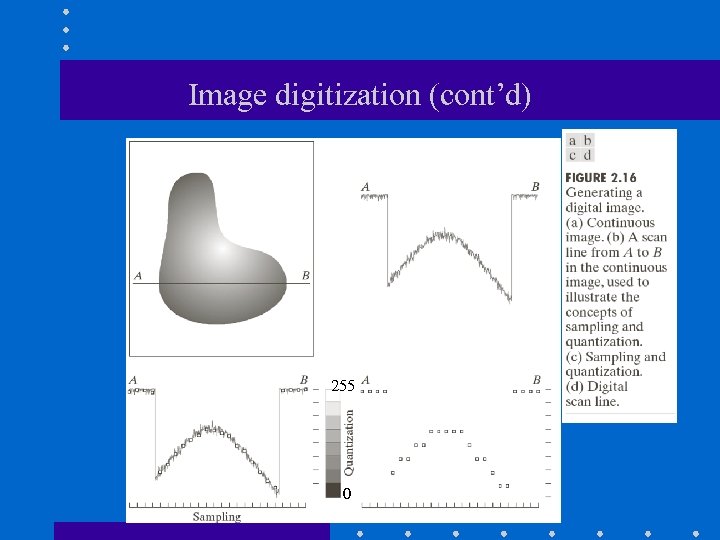 Image digitization (cont’d) 255 0
Image digitization (cont’d) 255 0
 Image digitization (cont’d) 2 D example
Image digitization (cont’d) 2 D example
 Effect of Image Sampling original image sampled by a factor of 4 sampled by a factor of 2 sampled by a factor of 8
Effect of Image Sampling original image sampled by a factor of 4 sampled by a factor of 2 sampled by a factor of 8
 Effect of Image Quantization 256 gray levels (8 bits/pixel) 32 gray levels (5 bits/pixel) 8 gray levels (3 bits/pixel) 4 gray levels (2 bits/pixel) 16 gray levels (4 bits/pixel) 2 gray levels (1 bit/pixel)
Effect of Image Quantization 256 gray levels (8 bits/pixel) 32 gray levels (5 bits/pixel) 8 gray levels (3 bits/pixel) 4 gray levels (2 bits/pixel) 16 gray levels (4 bits/pixel) 2 gray levels (1 bit/pixel)
 Representing Digital Images The result of sampling and quantization is a matrix of integer numbers. Here we have an image f(x, y) that was sampled to produce M rows and N columns.
Representing Digital Images The result of sampling and quantization is a matrix of integer numbers. Here we have an image f(x, y) that was sampled to produce M rows and N columns.
 Representing Digital Images (cont’d) • There is no requirements about M and N • Usually L= 2 k • Dynamic Range : [0, L-1] The number of bits b required to store an image: b=Mx. Nxk where k is the number of bits/pixel
Representing Digital Images (cont’d) • There is no requirements about M and N • Usually L= 2 k • Dynamic Range : [0, L-1] The number of bits b required to store an image: b=Mx. Nxk where k is the number of bits/pixel
 Image file formats • Many image formats adhere to the following simple model: – Header – Data (line by line, no breaks between lines).
Image file formats • Many image formats adhere to the following simple model: – Header – Data (line by line, no breaks between lines).
 Image file formats (cont. ) • Header contains at least: – A signature or “magic number” (i. e. , a short sequence of bytes for identifying the file format). – The width and height of the image.
Image file formats (cont. ) • Header contains at least: – A signature or “magic number” (i. e. , a short sequence of bytes for identifying the file format). – The width and height of the image.
 Common image file formats • • • PGM (Portable Gray Map) PNG (Portable Network Graphics) GIF (Graphic Interchange Format) – JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) FITS (Flexible Image Transport System)
Common image file formats • • • PGM (Portable Gray Map) PNG (Portable Network Graphics) GIF (Graphic Interchange Format) – JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) FITS (Flexible Image Transport System)


