eeddc576c5c447340733b996f966f24d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Introduction to Human Resource Management 1
Introduction to Human Resource Management 1
 After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Give at least eight examples of how all managers can use human resource management concepts and techniques. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. Provide a good example that illustrates HR’s role in formulating and executing company strategy. Write a short essay that addresses the topic: Why metrics and measurement are crucial to today’s HR managers. Outline the plan of this book. 3. 4. 5. 2 6.
After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Give at least eight examples of how all managers can use human resource management concepts and techniques. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. Provide a good example that illustrates HR’s role in formulating and executing company strategy. Write a short essay that addresses the topic: Why metrics and measurement are crucial to today’s HR managers. Outline the plan of this book. 3. 4. 5. 2 6.
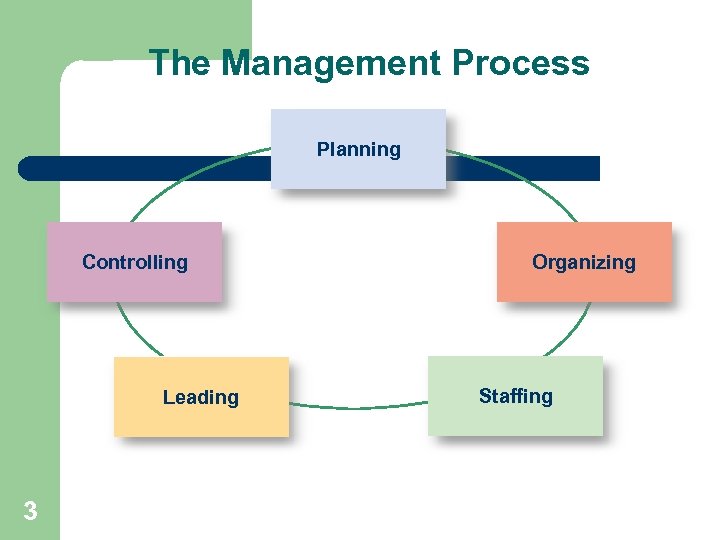 The Management Process Planning Controlling Leading 3 Organizing Staffing
The Management Process Planning Controlling Leading 3 Organizing Staffing
 Human Resource Management at Work l What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)? – 4 The policies and practices involved in carrying out the “people” or human resource aspects of a management position, including recruiting, screening, training, rewarding, and appraising.
Human Resource Management at Work l What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)? – 4 The policies and practices involved in carrying out the “people” or human resource aspects of a management position, including recruiting, screening, training, rewarding, and appraising.
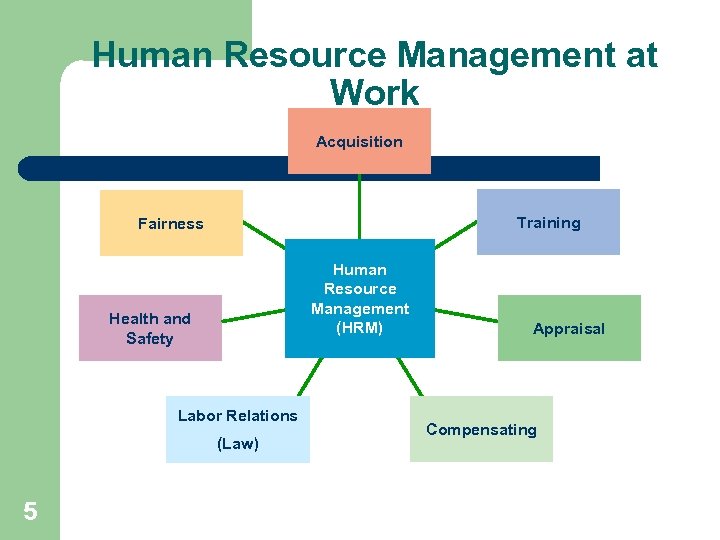 Human Resource Management at Work Acquisition Training Fairness Human Resource Management (HRM) Health and Safety Labor Relations (Law) 5 Appraisal Compensating
Human Resource Management at Work Acquisition Training Fairness Human Resource Management (HRM) Health and Safety Labor Relations (Law) 5 Appraisal Compensating
 Personnel Aspects of a Manager’s Job l l Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates l Selecting job candidates l Orienting and training new employees l Managing wages and salaries l Providing incentives and benefits l Appraising performance l 6 Conducting job analyses Communicating l Training and developing managers l Building employee commitment
Personnel Aspects of a Manager’s Job l l Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates l Selecting job candidates l Orienting and training new employees l Managing wages and salaries l Providing incentives and benefits l Appraising performance l 6 Conducting job analyses Communicating l Training and developing managers l Building employee commitment
 Personnel Mistakes l l Experience high turnover l Have your people not doing their best l Waste time with useless interviews l Have your company in court because of discriminatory actions l Have your company cited by OSHA for unsafe practices l Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and inequitable relative to others in the organization l 7 Hire the wrong person for the job Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s effectiveness l Commit any unfair labor practices
Personnel Mistakes l l Experience high turnover l Have your people not doing their best l Waste time with useless interviews l Have your company in court because of discriminatory actions l Have your company cited by OSHA for unsafe practices l Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and inequitable relative to others in the organization l 7 Hire the wrong person for the job Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s effectiveness l Commit any unfair labor practices
 Basic HR Concepts l l 8 The bottom line of managing: Getting results HR creates value by engaging in activities that produce the employee behaviors that the company needs to achieve its strategic goals.
Basic HR Concepts l l 8 The bottom line of managing: Getting results HR creates value by engaging in activities that produce the employee behaviors that the company needs to achieve its strategic goals.
 Line and Staff Aspects of HRM l Line manager – l Staff manager – 9 A manager who is authorized to direct the work of subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the organization’s tasks. A manager who assists and advises line managers.
Line and Staff Aspects of HRM l Line manager – l Staff manager – 9 A manager who is authorized to direct the work of subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the organization’s tasks. A manager who assists and advises line managers.
 Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities 1. 2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation) 3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them 4. Improving the job performance of each person 5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth working relationships 6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures 7. Controlling labor costs 8. Developing the abilities of each person 9. 10 Placing the right person on the right job Creating and maintaining department morale 10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition
Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities 1. 2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation) 3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them 4. Improving the job performance of each person 5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth working relationships 6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures 7. Controlling labor costs 8. Developing the abilities of each person 9. 10 Placing the right person on the right job Creating and maintaining department morale 10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition
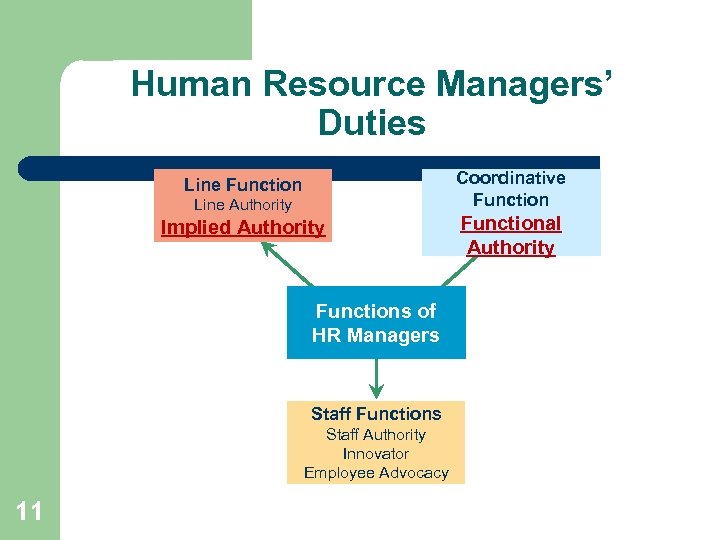 Human Resource Managers’ Duties Coordinative Function Line Authority Implied Authority Functions of HR Managers Staff Functions Staff Authority Innovator Employee Advocacy 11 Functional Authority
Human Resource Managers’ Duties Coordinative Function Line Authority Implied Authority Functions of HR Managers Staff Functions Staff Authority Innovator Employee Advocacy 11 Functional Authority
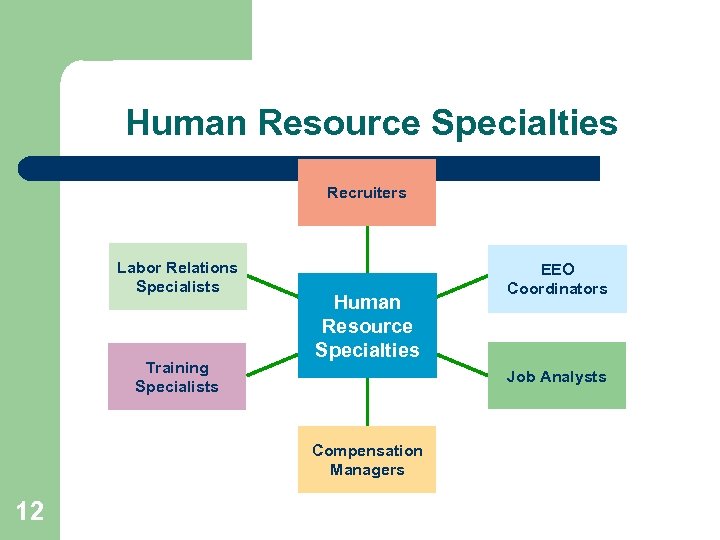 Human Resource Specialties Recruiters Labor Relations Specialists Training Specialists Human Resource Specialties Job Analysts Compensation Managers 12 EEO Coordinators
Human Resource Specialties Recruiters Labor Relations Specialists Training Specialists Human Resource Specialties Job Analysts Compensation Managers 12 EEO Coordinators
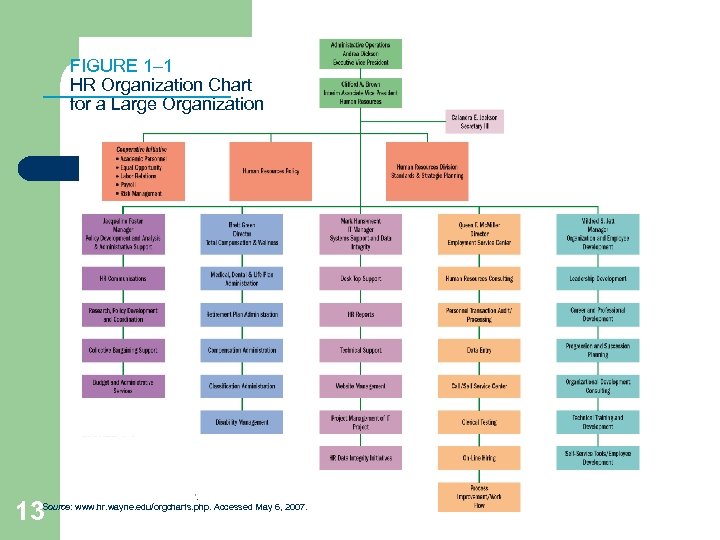 FIGURE 1– 1 HR Organization Chart for a Large Organization 13 Source: www. hr. wayne. edu/orgcharts. php. Accessed May 6, 2007.
FIGURE 1– 1 HR Organization Chart for a Large Organization 13 Source: www. hr. wayne. edu/orgcharts. php. Accessed May 6, 2007.
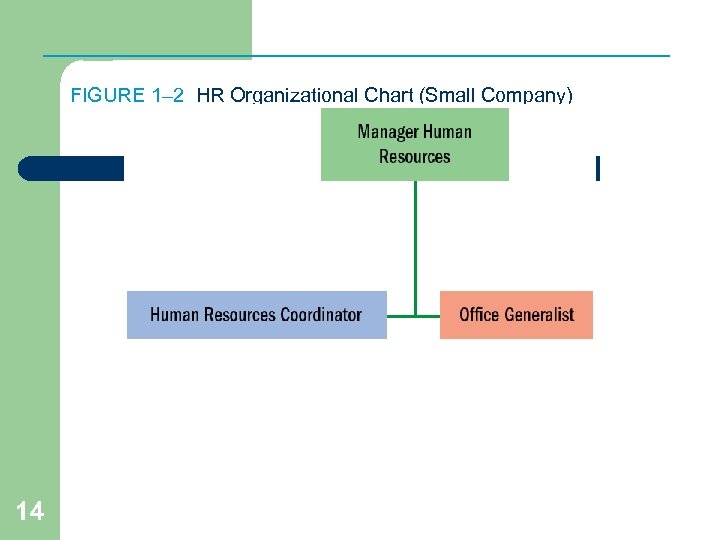 FIGURE 1– 2 HR Organizational Chart (Small Company) 14
FIGURE 1– 2 HR Organizational Chart (Small Company) 14
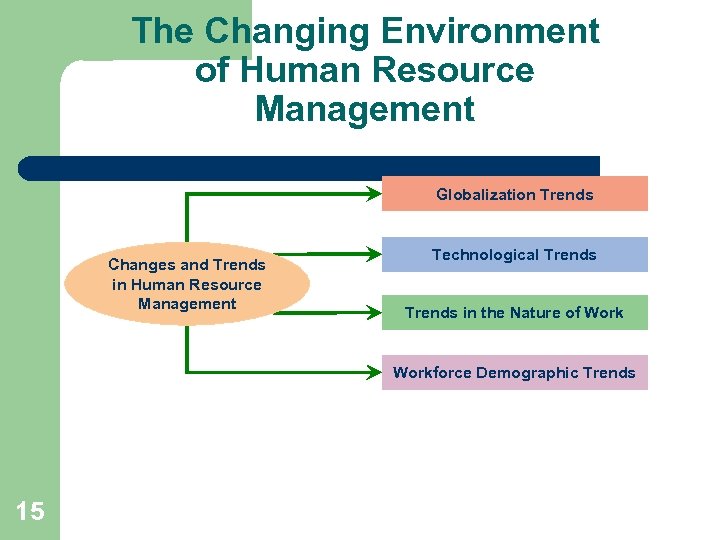 The Changing Environment of Human Resource Management Globalization Trends Changes and Trends in Human Resource Management Technological Trends in the Nature of Workforce Demographic Trends 15
The Changing Environment of Human Resource Management Globalization Trends Changes and Trends in Human Resource Management Technological Trends in the Nature of Workforce Demographic Trends 15
 16
16
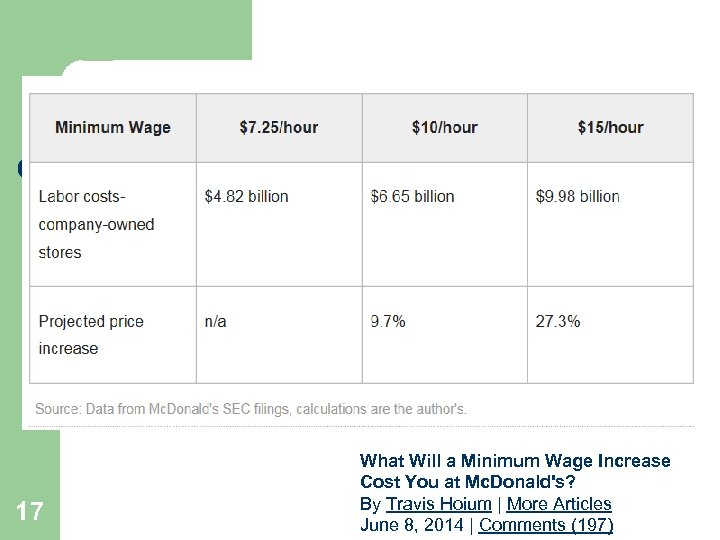 17 What Will a Minimum Wage Increase Cost You at Mc. Donald's? By Travis Hoium | More Articles June 8, 2014 | Comments (197)
17 What Will a Minimum Wage Increase Cost You at Mc. Donald's? By Travis Hoium | More Articles June 8, 2014 | Comments (197)
 18 What Will a Minimum Wage Increase Cost You at Mc. Donald's? By Travis Hoium | More Articles June 8, 2014 | Comments (197)
18 What Will a Minimum Wage Increase Cost You at Mc. Donald's? By Travis Hoium | More Articles June 8, 2014 | Comments (197)
 19 CEO Letter to terminated Hostess Brands employees - Emporia Gazette: Business
19 CEO Letter to terminated Hostess Brands employees - Emporia Gazette: Business
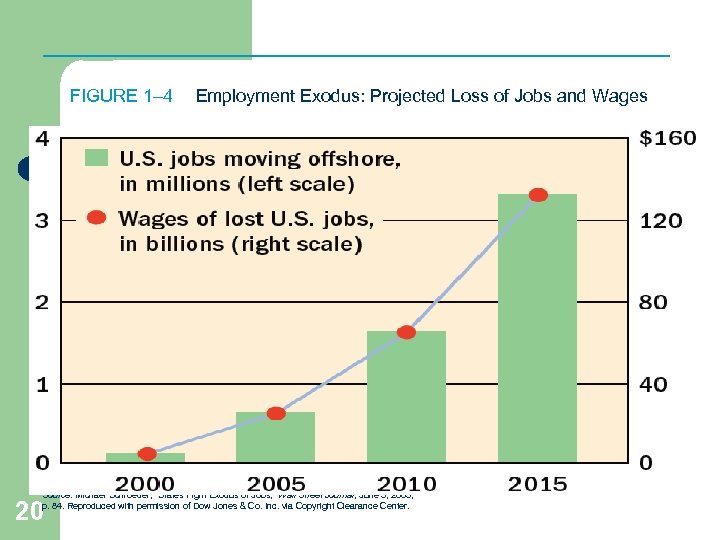 FIGURE 1– 4 Employment Exodus: Projected Loss of Jobs and Wages Source: Michael Schroeder, “States Fight Exodus of Jobs, ” Wall Street Journal, June 3, 2003, p. 84. Reproduced with permission of Dow Jones & Co. Inc. via Copyright Clearance Center. 20
FIGURE 1– 4 Employment Exodus: Projected Loss of Jobs and Wages Source: Michael Schroeder, “States Fight Exodus of Jobs, ” Wall Street Journal, June 3, 2003, p. 84. Reproduced with permission of Dow Jones & Co. Inc. via Copyright Clearance Center. 20
 Something’s Got to Give! 21 Humans or Machines?
Something’s Got to Give! 21 Humans or Machines?
 22
22
 Understanding Labor Issues
Understanding Labor Issues
 Herzberg’s Theory Figure 10. 5 Comparison of Maslow and Herzberg
Herzberg’s Theory Figure 10. 5 Comparison of Maslow and Herzberg
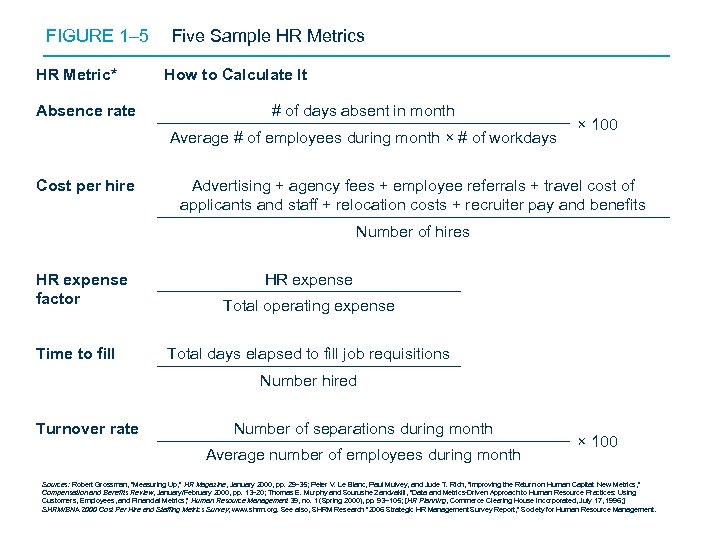 FIGURE 1– 5 HR Metric* Absence rate Five Sample HR Metrics How to Calculate It # of days absent in month Average # of employees during month × # of workdays Cost per hire × 100 Advertising + agency fees + employee referrals + travel cost of applicants and staff + relocation costs + recruiter pay and benefits Number of hires HR expense factor Time to fill HR expense Total operating expense Total days elapsed to fill job requisitions Number hired Turnover rate Number of separations during month Average number of employees during month × 100 Sources: Robert Grossman, “Measuring Up, ” HR Magazine, January 2000, pp. 29– 35; Peter V. Le Blanc, Paul Mulvey, and Jude T. Rich, “Improving the Return on Human Capital: New Metrics, ” Compensation and Benefits Review, January/February 2000, pp. 13– 20; Thomas E. Murphy and Sourushe Zandvakili, “Data and Metrics-Driven Approach to Human Resource Practices: Using Customers, Employees, and Financial Metrics, ” Human Resource Management 39, no. 1 (Spring 2000), pp. 93– 105; [HR Planning, Commerce Clearing House Incorporated, July 17, 1996; ] SHRM/BNA 2000 Cost Per Hire and Staffing Metrics Survey; www. shrm. org. See also, SHRM Research “ 2006 Strategic HR Management Survey Report, ” Society for Human Resource Management. . 25
FIGURE 1– 5 HR Metric* Absence rate Five Sample HR Metrics How to Calculate It # of days absent in month Average # of employees during month × # of workdays Cost per hire × 100 Advertising + agency fees + employee referrals + travel cost of applicants and staff + relocation costs + recruiter pay and benefits Number of hires HR expense factor Time to fill HR expense Total operating expense Total days elapsed to fill job requisitions Number hired Turnover rate Number of separations during month Average number of employees during month × 100 Sources: Robert Grossman, “Measuring Up, ” HR Magazine, January 2000, pp. 29– 35; Peter V. Le Blanc, Paul Mulvey, and Jude T. Rich, “Improving the Return on Human Capital: New Metrics, ” Compensation and Benefits Review, January/February 2000, pp. 13– 20; Thomas E. Murphy and Sourushe Zandvakili, “Data and Metrics-Driven Approach to Human Resource Practices: Using Customers, Employees, and Financial Metrics, ” Human Resource Management 39, no. 1 (Spring 2000), pp. 93– 105; [HR Planning, Commerce Clearing House Incorporated, July 17, 1996; ] SHRM/BNA 2000 Cost Per Hire and Staffing Metrics Survey; www. shrm. org. See also, SHRM Research “ 2006 Strategic HR Management Survey Report, ” Society for Human Resource Management. . 25
 Academic Absence Form
Academic Absence Form
 Classified Absence Form
Classified Absence Form
 The Changing Role of Human Resource Management Strategic Human Resource Management Managing with the HR Scorecard Process New Responsibilities for HR Managers Measuring the HRM Team’s Performance 28 Creating High. Performance Work Systems
The Changing Role of Human Resource Management Strategic Human Resource Management Managing with the HR Scorecard Process New Responsibilities for HR Managers Measuring the HRM Team’s Performance 28 Creating High. Performance Work Systems
 High-Performance Work System Practices l l l l l 29 l Employment security Selective hiring Extensive training Self-managed teams/decentralized decision making Reduced status distinctions Information sharing Contingent (pay-for-performance) rewards Transformational leadership Measurement of management practices Emphasis on high-quality work
High-Performance Work System Practices l l l l l 29 l Employment security Selective hiring Extensive training Self-managed teams/decentralized decision making Reduced status distinctions Information sharing Contingent (pay-for-performance) rewards Transformational leadership Measurement of management practices Emphasis on high-quality work
 Benefits of a High-Performance Work System (HPWS) l l Screen candidates more effectively l Provide more and better training l Link pay more explicitly to performance l Provide a safer work environment l Produce more qualified applicants per position l 30 Generate more job applicants Hiring based on validated selection tests l Provide more hours of training for new employees
Benefits of a High-Performance Work System (HPWS) l l Screen candidates more effectively l Provide more and better training l Link pay more explicitly to performance l Provide a safer work environment l Produce more qualified applicants per position l 30 Generate more job applicants Hiring based on validated selection tests l Provide more hours of training for new employees
 Measuring HR’s Contribution l The HR Scorecard – – Measures the employee behaviors resulting from these activities. – 31 Shows the quantitative standards, or “metrics” the firm uses to measure HR activities. Measures the strategically relevant organizational outcomes of those employee behaviors.
Measuring HR’s Contribution l The HR Scorecard – – Measures the employee behaviors resulting from these activities. – 31 Shows the quantitative standards, or “metrics” the firm uses to measure HR activities. Measures the strategically relevant organizational outcomes of those employee behaviors.
 The Human Resource Manager’s Proficiencies l New Proficiencies – – Business proficiencies – Leadership proficiencies – 32 HR proficiencies Learning proficiencies
The Human Resource Manager’s Proficiencies l New Proficiencies – – Business proficiencies – Leadership proficiencies – 32 HR proficiencies Learning proficiencies
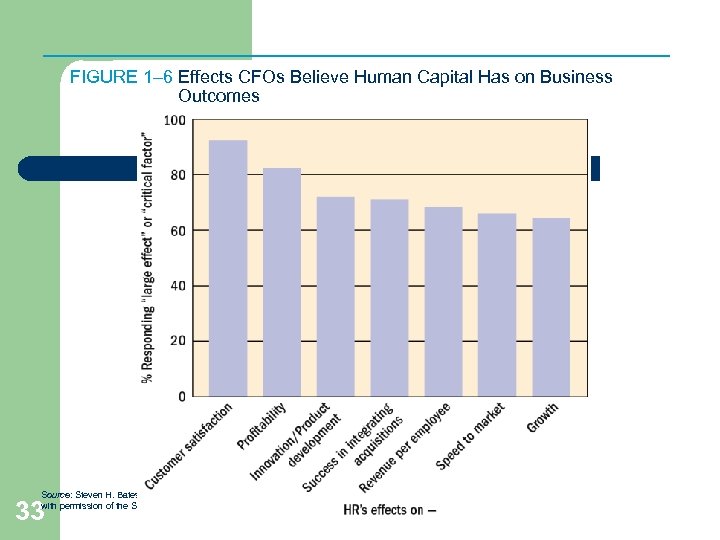 FIGURE 1– 6 Effects CFOs Believe Human Capital Has on Business Outcomes Source: Steven H. Bates, “Business Partners, ” HR Magazine, September 2003, p. 49. Reproduced with permission of the Society for Human Resource Management via Copyright Clearance Center. 33
FIGURE 1– 6 Effects CFOs Believe Human Capital Has on Business Outcomes Source: Steven H. Bates, “Business Partners, ” HR Magazine, September 2003, p. 49. Reproduced with permission of the Society for Human Resource Management via Copyright Clearance Center. 33
 The Human Resource Manager’s Proficiencies (cont’d) l Managing within the Law – – Occupational safety and health laws – l Equal employment laws Labor laws Managing Ethics – 34 Ethical lapses – Sarbanes-Oxley in 2003
The Human Resource Manager’s Proficiencies (cont’d) l Managing within the Law – – Occupational safety and health laws – l Equal employment laws Labor laws Managing Ethics – 34 Ethical lapses – Sarbanes-Oxley in 2003
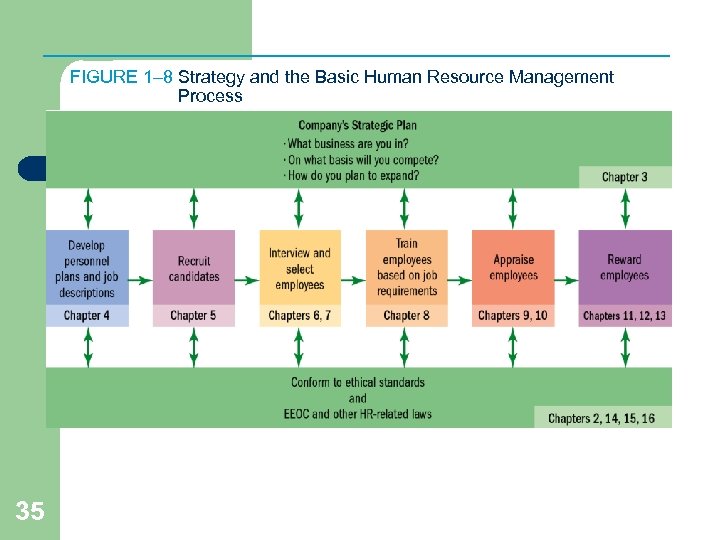 FIGURE 1– 8 Strategy and the Basic Human Resource Management Process 35
FIGURE 1– 8 Strategy and the Basic Human Resource Management Process 35
 http: //www. shrm. org/Pages/default. aspx 36
http: //www. shrm. org/Pages/default. aspx 36
 BECOME A STUDENT MEMBER OF SHRM 37 BECOME A STUDENT MEMBER OF SHRM
BECOME A STUDENT MEMBER OF SHRM 37 BECOME A STUDENT MEMBER OF SHRM
 38
38
 HR Certification l HR is becoming more professionalized. l Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) – SHRM’s Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI) l l 39 SPHR (senior professional in HR) certificate PHR (professional in HR) certificate
HR Certification l HR is becoming more professionalized. l Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) – SHRM’s Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI) l l 39 SPHR (senior professional in HR) certificate PHR (professional in HR) certificate


