8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 160
 Introduction to GPRS
Introduction to GPRS
 Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 簡介 GPRS系統架構 GPRS介面 GPRS無線電介面協定 GPRS核心網路
Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 簡介 GPRS系統架構 GPRS介面 GPRS無線電介面協定 GPRS核心網路
 1. 簡介 o GPRS n General Packet Radio Service n 一般封包式無線電服務 o GPRS標準 n 制訂於 1994年 n 制訂單位ETSI/SMG (European Telecommunications Standards Institute / Special Mobile Group) n 主要內容於 1997年由SMG#25通過 n 完成於 1999年
1. 簡介 o GPRS n General Packet Radio Service n 一般封包式無線電服務 o GPRS標準 n 制訂於 1994年 n 制訂單位ETSI/SMG (European Telecommunications Standards Institute / Special Mobile Group) n 主要內容於 1997年由SMG#25通過 n 完成於 1999年
 o GPRS核心網路 n 可加入現有GSM系統 n 可做為IS-136的加強版 n 可直接演進為 3 G核心網路的一部份 o GPRS是一種分封數據交換(packet switch)協定 n 提供如WWW,需耗費許多時間閱讀,偶爾傳送大 量數據的應用
o GPRS核心網路 n 可加入現有GSM系統 n 可做為IS-136的加強版 n 可直接演進為 3 G核心網路的一部份 o GPRS是一種分封數據交換(packet switch)協定 n 提供如WWW,需耗費許多時間閱讀,偶爾傳送大 量數據的應用
 o GPRS提供數據傳輸服務 n 點對點(point-to-point)服務 n 單點對多點(point-to-multipoint)服務 o GPRS靠自有的傳輸網路(transport network)提 供封包傳送服務
o GPRS提供數據傳輸服務 n 點對點(point-to-point)服務 n 單點對多點(point-to-multipoint)服務 o GPRS靠自有的傳輸網路(transport network)提 供封包傳送服務
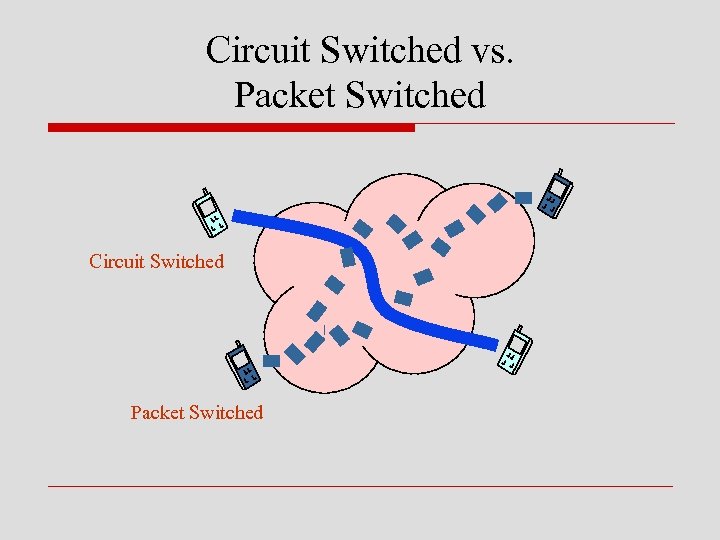 Circuit Switched vs. Packet Switched Circuit Switched Packet Switched
Circuit Switched vs. Packet Switched Circuit Switched Packet Switched
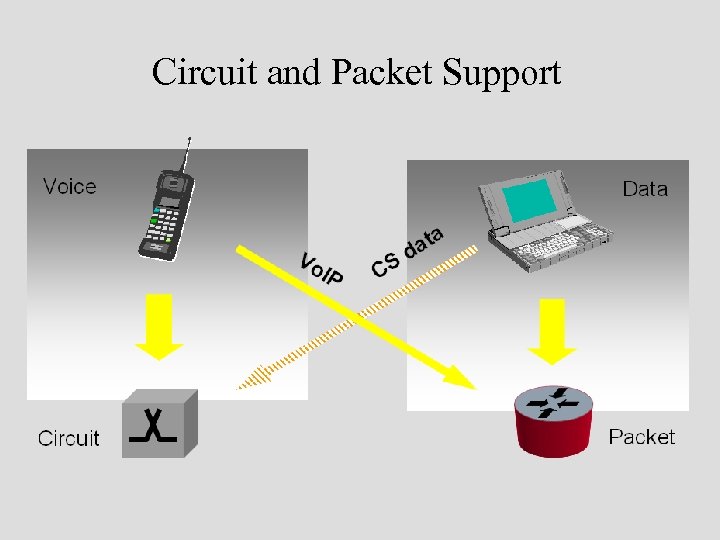 Circuit and Packet Support
Circuit and Packet Support
 1. 1 GSM→GPRS的演進 o GPRS使用現有的BS,做少數修改 o 無線電介面定義許多logic radio channel n 傳送packet n 控制訊號(signal)交換
1. 1 GSM→GPRS的演進 o GPRS使用現有的BS,做少數修改 o 無線電介面定義許多logic radio channel n 傳送packet n 控制訊號(signal)交換
 o 設計GPRS協定時,盡可能讓channel的配置 有彈性,以增加系統容量 n 以timeslot為基本傳送packet的單位,最多可將同 一carrier的8個timeslots都分配給同一個MS n 手機傳送封包的channel o 以符合像web、file transfer之asymmetric flow 的特性,分別分配uplink與downlink的channel n 提供fast reservation,可在 0. 5到 1 sec啟動資料傳 輸
o 設計GPRS協定時,盡可能讓channel的配置 有彈性,以增加系統容量 n 以timeslot為基本傳送packet的單位,最多可將同 一carrier的8個timeslots都分配給同一個MS n 手機傳送封包的channel o 以符合像web、file transfer之asymmetric flow 的特性,分別分配uplink與downlink的channel n 提供fast reservation,可在 0. 5到 1 sec啟動資料傳 輸
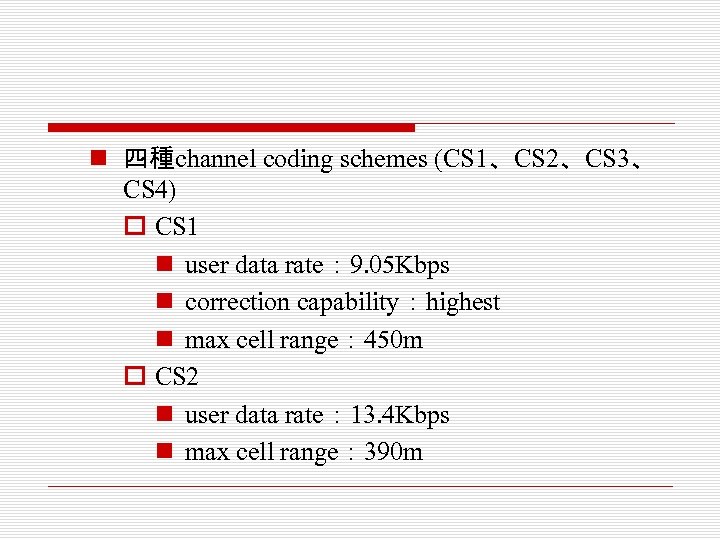 n 四種channel coding schemes (CS 1、CS 2、CS 3、 CS 4) o CS 1 n user data rate: 9. 05 Kbps n correction capability:highest n max cell range: 450 m o CS 2 n user data rate: 13. 4 Kbps n max cell range: 390 m
n 四種channel coding schemes (CS 1、CS 2、CS 3、 CS 4) o CS 1 n user data rate: 9. 05 Kbps n correction capability:highest n max cell range: 450 m o CS 2 n user data rate: 13. 4 Kbps n max cell range: 390 m
 o CS 3 n user data rate: 15. 6 Kbps n max cell range: 350 m o CS 4 n user data rate: 21. 4 Kbps n max cell range: 290 m n correction capability:none
o CS 3 n user data rate: 15. 6 Kbps n max cell range: 350 m o CS 4 n user data rate: 21. 4 Kbps n max cell range: 290 m n correction capability:none
 o 安全機制:GPRS與GSM相同 o 編碼演算法:GPRS調整GSM編碼演算法以 適合packet data的傳輸 o GPRS系統方面 n GPRS元件中由舊的GSM元件加以修改(software upgrade)而得 o MS、BSS、MSC/VLR、HLR o 例如:HLR會加上GPRS subscriber information
o 安全機制:GPRS與GSM相同 o 編碼演算法:GPRS調整GSM編碼演算法以 適合packet data的傳輸 o GPRS系統方面 n GPRS元件中由舊的GSM元件加以修改(software upgrade)而得 o MS、BSS、MSC/VLR、HLR o 例如:HLR會加上GPRS subscriber information
 n 軟體部分 o 由遠端遙控方式下載到BTSs n 硬體部分 o 在BSC加上PCU (Packet Control Unit) o 增加GGSN和SGSN用以傳送封包資料
n 軟體部分 o 由遠端遙控方式下載到BTSs n 硬體部分 o 在BSC加上PCU (Packet Control Unit) o 增加GGSN和SGSN用以傳送封包資料
 o 手機方面 n 主要挑戰:解決省電問題 n GPRS手機為支援與資料相關的特性(e. g. multiple time-slot transmission),比GSM手機耗電
o 手機方面 n 主要挑戰:解決省電問題 n GPRS手機為支援與資料相關的特性(e. g. multiple time-slot transmission),比GSM手機耗電
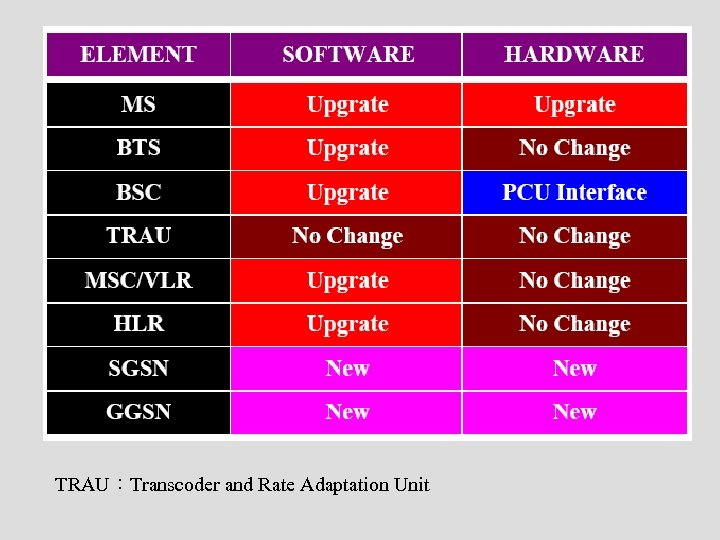 TRAU:Transcoder and Rate Adaptation Unit
TRAU:Transcoder and Rate Adaptation Unit
 1. 2 GPRS Implementation o GPRS phase 1 implementation n 標準封包傳送服務(point to point packet bearer service) n 達成CS-1及CS-2通道編碼技術 n 建置下列介面 o Gn (SGSN ↔ SGSN) o Gb (SGSN ↔ BSS) o Gp (SGSN ↔ GGSN (other PLMN)) o Gs (SGSN ↔ MSC/VLR)
1. 2 GPRS Implementation o GPRS phase 1 implementation n 標準封包傳送服務(point to point packet bearer service) n 達成CS-1及CS-2通道編碼技術 n 建置下列介面 o Gn (SGSN ↔ SGSN) o Gb (SGSN ↔ BSS) o Gp (SGSN ↔ GGSN (other PLMN)) o Gs (SGSN ↔ MSC/VLR)
 n 彈性的無線電資源配置 n Class B與Class C手機的規範 o Class A:上網時可同時接聽電話 n can be connected to GPRS service and GSM service (voice, SMS), using both at the same time n such devices are known to be available today o Class B:上網時不可同時接聽電話 n can be connected to GPRS service and GSM service (voice, SMS), but using only one or the other at a given time n during GSM service (voice call or SMS), GPRS service is suspended, and then resumed automatically after the GSM service (voice call or SMS) has concluded n most GPRS mobile devices are Class B
n 彈性的無線電資源配置 n Class B與Class C手機的規範 o Class A:上網時可同時接聽電話 n can be connected to GPRS service and GSM service (voice, SMS), using both at the same time n such devices are known to be available today o Class B:上網時不可同時接聽電話 n can be connected to GPRS service and GSM service (voice, SMS), but using only one or the other at a given time n during GSM service (voice call or SMS), GPRS service is suspended, and then resumed automatically after the GSM service (voice call or SMS) has concluded n most GPRS mobile devices are Class B
 o Class C:只可上網不可接聽電話 n are connected to either GPRS service or GSM service (voice, SMS) n must be switched manually between one or the other service n n GPRS計費,如以封包計費及Qo. S計費 提供靜態及動態IP address配置 匿名存取(anonymous access) 安全性(security)
o Class C:只可上網不可接聽電話 n are connected to either GPRS service or GSM service (voice, SMS) n must be switched manually between one or the other service n n GPRS計費,如以封包計費及Qo. S計費 提供靜態及動態IP address配置 匿名存取(anonymous access) 安全性(security)
 n 建立與外界封包資料網路的IP,X. 25的介面 o 註:X. 25從 1970年開始發展,由國際電話暨 電報諮詢委員會(CCITT)制訂,是發展最早也 是最純熟的網路封包交換(packet switching)標 準,是一種點對點通訊協定(Point-to-Point Protocol,PPP),傳送資料前須先建立傳送路 徑(path),定義終端機使用者和數位通訊設備 的交換通訊程序
n 建立與外界封包資料網路的IP,X. 25的介面 o 註:X. 25從 1970年開始發展,由國際電話暨 電報諮詢委員會(CCITT)制訂,是發展最早也 是最純熟的網路封包交換(packet switching)標 準,是一種點對點通訊協定(Point-to-Point Protocol,PPP),傳送資料前須先建立傳送路 徑(path),定義終端機使用者和數位通訊設備 的交換通訊程序
![o GPRS phase 2 implementation n 加強GPRS的Qo. S支援 n 無格式化位元組資料流(unstructured octet [八位 元組] stream)的GPRS o GPRS phase 2 implementation n 加強GPRS的Qo. S支援 n 無格式化位元組資料流(unstructured octet [八位 元組] stream)的GPRS](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-20.jpg) o GPRS phase 2 implementation n 加強GPRS的Qo. S支援 n 無格式化位元組資料流(unstructured octet [八位 元組] stream)的GPRS PDP (Packet Data Protocol) type n 對ISP及Intranet的接取 n GPRS預付機制(prepaid)
o GPRS phase 2 implementation n 加強GPRS的Qo. S支援 n 無格式化位元組資料流(unstructured octet [八位 元組] stream)的GPRS PDP (Packet Data Protocol) type n 對ISP及Intranet的接取 n GPRS預付機制(prepaid)
 n GPRS收費建議(Advice of Charge,Ao. C)機制 o Ao. C service provides the mobile subscriber with an estimate of the call charges o two types of Ao. C information n provides the subscriber with an estimate of the bill n used for immediate charging purposes (hot billing) n 群體通話(point-to-multipoint services) n 點對多點的multicast服務
n GPRS收費建議(Advice of Charge,Ao. C)機制 o Ao. C service provides the mobile subscriber with an estimate of the call charges o two types of Ao. C information n provides the subscriber with an estimate of the bill n used for immediate charging purposes (hot billing) n 群體通話(point-to-multipoint services) n 點對多點的multicast服務
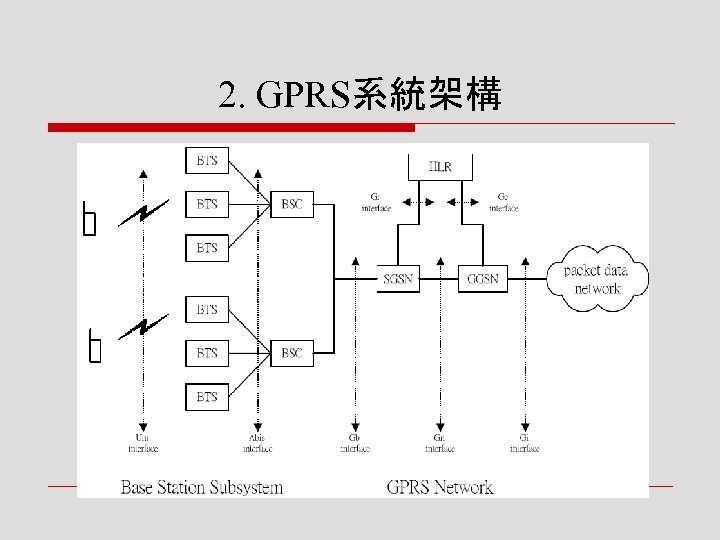 2. GPRS系統架構
2. GPRS系統架構
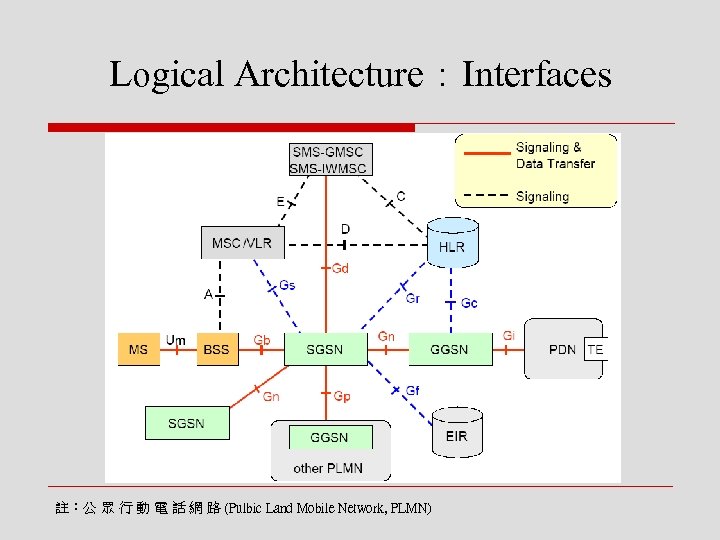 Logical Architecture:Interfaces 註:公 眾 行 動 電 話 網 路 (Pulbic Land Mobile Network, PLMN)
Logical Architecture:Interfaces 註:公 眾 行 動 電 話 網 路 (Pulbic Land Mobile Network, PLMN)
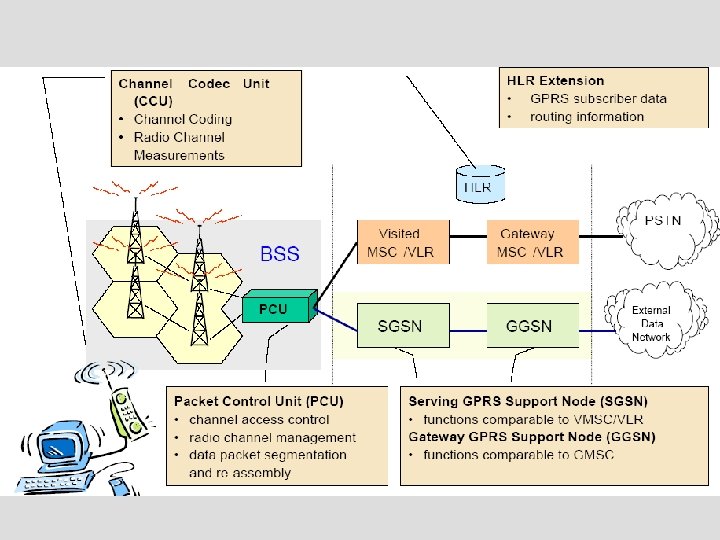
 o 在此GPRS網路內,GSM定義一種新的邏輯 網路節點 n GPRS支援節點(GPRS Support Node,GSN) o GSN依其負責的功能劃分 n GPRS服務支援節點(Serving GPRS Support Node, SGSN) n GSN閘道(Gateway GPRS Support Node,GGSN)
o 在此GPRS網路內,GSM定義一種新的邏輯 網路節點 n GPRS支援節點(GPRS Support Node,GSN) o GSN依其負責的功能劃分 n GPRS服務支援節點(Serving GPRS Support Node, SGSN) n GSN閘道(Gateway GPRS Support Node,GGSN)
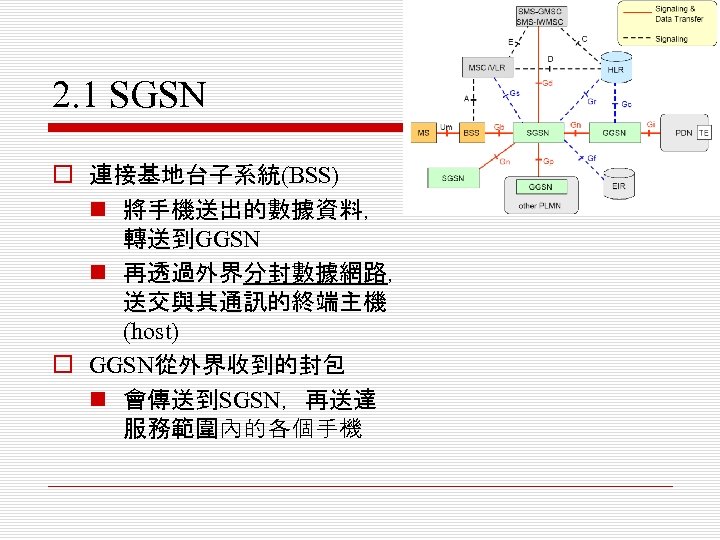 2. 1 SGSN o 連接基地台子系統(BSS) n 將手機送出的數據資料, 轉送到GGSN n 再透過外界分封數據網路, 送交與其通訊的終端主機 (host) o GGSN從外界收到的封包 n 會傳送到SGSN,再送達 服務範圍內的各個手機
2. 1 SGSN o 連接基地台子系統(BSS) n 將手機送出的數據資料, 轉送到GGSN n 再透過外界分封數據網路, 送交與其通訊的終端主機 (host) o GGSN從外界收到的封包 n 會傳送到SGSN,再送達 服務範圍內的各個手機
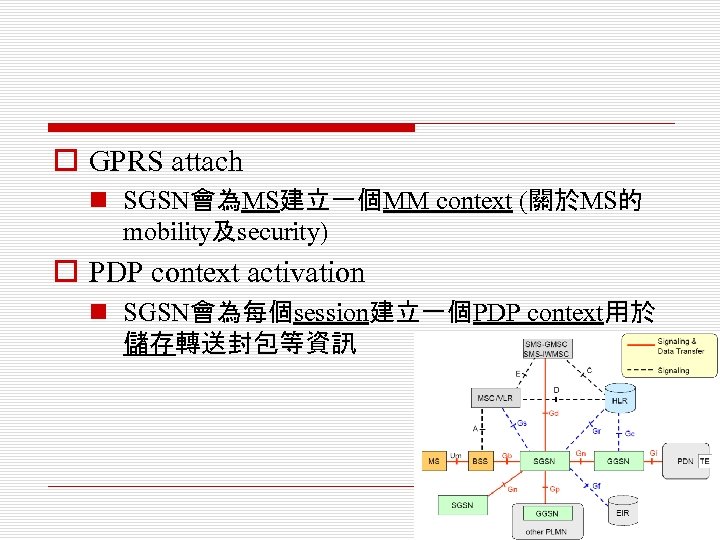 o GPRS attach n SGSN會為MS建立一個MM context (關於MS的 mobility及security) o PDP context activation n SGSN會為每個session建立一個PDP context用於 儲存轉送封包等資訊
o GPRS attach n SGSN會為MS建立一個MM context (關於MS的 mobility及security) o PDP context activation n SGSN會為每個session建立一個PDP context用於 儲存轉送封包等資訊
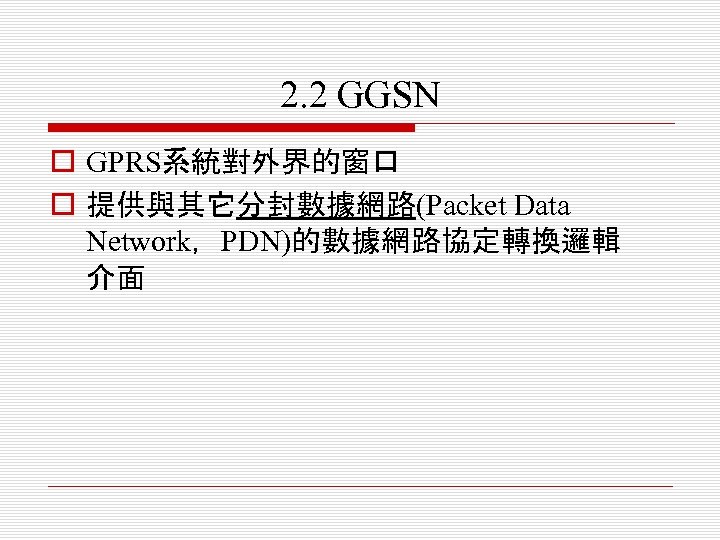 2. 2 GGSN o GPRS系統對外界的窗口 o 提供與其它分封數據網路(Packet Data Network,PDN)的數據網路協定轉換邏輯 介面
2. 2 GGSN o GPRS系統對外界的窗口 o 提供與其它分封數據網路(Packet Data Network,PDN)的數據網路協定轉換邏輯 介面
 2. 3 GPRS Backbone Network o GGSN與SGSN形成GPRS backbone network n 用來傳送資料的GPRS網路本身就是一個以IP為 基礎的網路,作為傳送封包的骨幹網路
2. 3 GPRS Backbone Network o GGSN與SGSN形成GPRS backbone network n 用來傳送資料的GPRS網路本身就是一個以IP為 基礎的網路,作為傳送封包的骨幹網路
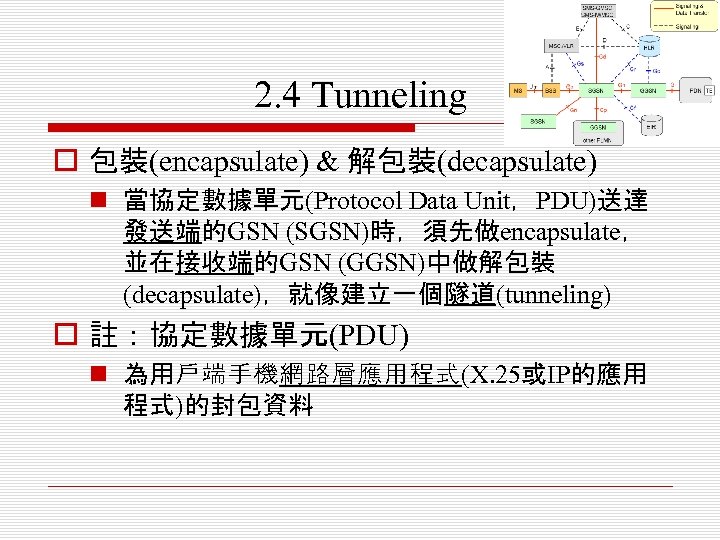 2. 4 Tunneling o 包裝(encapsulate) & 解包裝(decapsulate) n 當協定數據單元(Protocol Data Unit,PDU)送達 發送端的GSN (SGSN)時,須先做encapsulate, 並在接收端的GSN (GGSN)中做解包裝 (decapsulate),就像建立一個隧道(tunneling) o 註:協定數據單元(PDU) n 為用戶端手機網路層應用程式(X. 25或IP的應用 程式)的封包資料
2. 4 Tunneling o 包裝(encapsulate) & 解包裝(decapsulate) n 當協定數據單元(Protocol Data Unit,PDU)送達 發送端的GSN (SGSN)時,須先做encapsulate, 並在接收端的GSN (GGSN)中做解包裝 (decapsulate),就像建立一個隧道(tunneling) o 註:協定數據單元(PDU) n 為用戶端手機網路層應用程式(X. 25或IP的應用 程式)的封包資料
 o PDU的路由相關資訊儲存在GGSN中 o GPRS用於傳送資料與路由方式的用戶資訊, 存在HLR中
o PDU的路由相關資訊儲存在GGSN中 o GPRS用於傳送資料與路由方式的用戶資訊, 存在HLR中
 2. 5 兩手機間通訊的路由範例 o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的手機 o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網路的手機 o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN (Packet Data Network)上的PC
2. 5 兩手機間通訊的路由範例 o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的手機 o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網路的手機 o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN (Packet Data Network)上的PC
![o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的 手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機(MS 1)的 SGSN 1,先將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,根據HLR中的 資訊,找到目前負責MS 2的 o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的 手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機(MS 1)的 SGSN 1,先將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,根據HLR中的 資訊,找到目前負責MS 2的](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-33.jpg) o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的 手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機(MS 1)的 SGSN 1,先將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,根據HLR中的 資訊,找到目前負責MS 2的 SGSN 2的位置 n [步驟 2] 建立隧道的流程,PDU 在SGSN 1包裝,傳送到SGSN 2, 進行解包裝的 作 n [步驟 3] 透過無線電傳輸,最後 資料將到達MS 2 而完成整個傳 遞的過程
o Case 1:二個位在相同GPRS網路的 手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機(MS 1)的 SGSN 1,先將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,根據HLR中的 資訊,找到目前負責MS 2的 SGSN 2的位置 n [步驟 2] 建立隧道的流程,PDU 在SGSN 1包裝,傳送到SGSN 2, 進行解包裝的 作 n [步驟 3] 透過無線電傳輸,最後 資料將到達MS 2 而完成整個傳 遞的過程
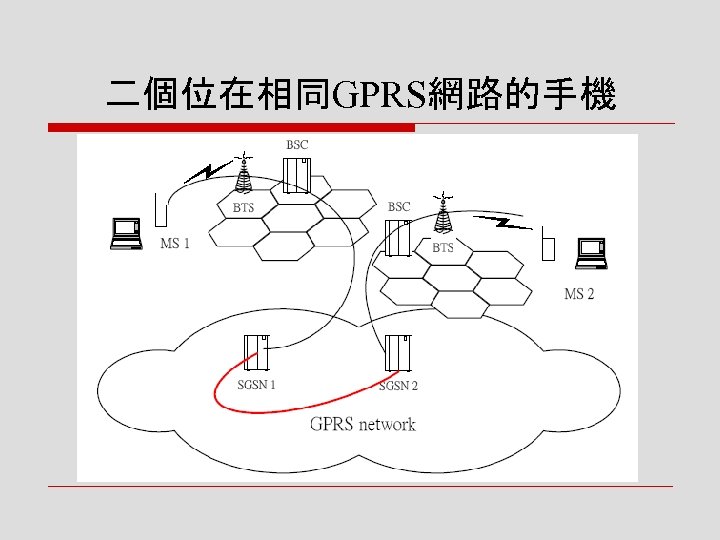 二個位在相同GPRS網路的手機
二個位在相同GPRS網路的手機
![o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網 路的手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機MS 1 的GPRS服務支援節點 SGSN 1將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,送到適當的 GPRS支援節點閘道GGSN o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網 路的手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機MS 1 的GPRS服務支援節點 SGSN 1將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,送到適當的 GPRS支援節點閘道GGSN](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-35.jpg) o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網 路的手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機MS 1 的GPRS服務支援節點 SGSN 1將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,送到適當的 GPRS支援節點閘道GGSN 1 n [步驟 2] 在GGSN 1解包裝後, 根據封包的目的位置,透過 一般的分封數據網路或網際 網路(Internet),轉送給接收 端手機MS 2所在的網路 GPRS network 2
o Case 2:二個位在不同GPRS網 路的手機 n [步驟 1] 在發送端手機MS 1 的GPRS服務支援節點 SGSN 1將手機所要傳送的 PDU加以包裝,送到適當的 GPRS支援節點閘道GGSN 1 n [步驟 2] 在GGSN 1解包裝後, 根據封包的目的位置,透過 一般的分封數據網路或網際 網路(Internet),轉送給接收 端手機MS 2所在的網路 GPRS network 2
![n [步驟 3] 當經過網路的入 口GPRS支援節點閘道 GGSN 2時,GGSN 2可根 據本身資料庫中的資訊, 找到MS 2所在的GPRS服 務支援節點SGSN 2的位置 n n [步驟 3] 當經過網路的入 口GPRS支援節點閘道 GGSN 2時,GGSN 2可根 據本身資料庫中的資訊, 找到MS 2所在的GPRS服 務支援節點SGSN 2的位置 n](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-36.jpg) n [步驟 3] 當經過網路的入 口GPRS支援節點閘道 GGSN 2時,GGSN 2可根 據本身資料庫中的資訊, 找到MS 2所在的GPRS服 務支援節點SGSN 2的位置 n [步驟 4] 再經過一次建立 隧道的流程,PDU在 GGSN 2包裝,傳送到 SGSN 2,進行解包裝的 作,透過無線電傳輸,最 後資料將到達MS 2而完成 整個傳遞的過程
n [步驟 3] 當經過網路的入 口GPRS支援節點閘道 GGSN 2時,GGSN 2可根 據本身資料庫中的資訊, 找到MS 2所在的GPRS服 務支援節點SGSN 2的位置 n [步驟 4] 再經過一次建立 隧道的流程,PDU在 GGSN 2包裝,傳送到 SGSN 2,進行解包裝的 作,透過無線電傳輸,最 後資料將到達MS 2而完成 整個傳遞的過程
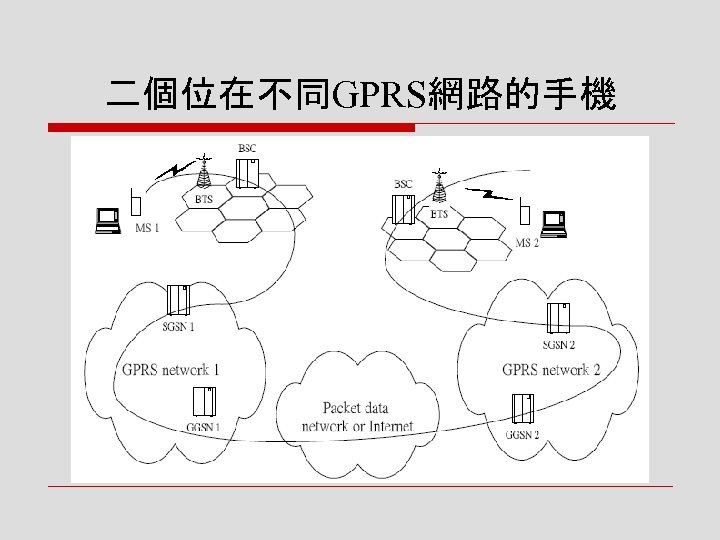 二個位在不同GPRS網路的手機
二個位在不同GPRS網路的手機
![o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN上的PC n [步驟 1] MS首先會做GPRS-attached,以開始啟 動GPRS的服務,此後MS與SGSN建立起一個 session o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN上的PC n [步驟 1] MS首先會做GPRS-attached,以開始啟 動GPRS的服務,此後MS與SGSN建立起一個 session](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-38.jpg) o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN上的PC n [步驟 1] MS首先會做GPRS-attached,以開始啟 動GPRS的服務,此後MS與SGSN建立起一個 session
o Case 3:GPRS手機與PDN上的PC n [步驟 1] MS首先會做GPRS-attached,以開始啟 動GPRS的服務,此後MS與SGSN建立起一個 session
![n [步驟 2] 此時若MS想要傳資料 給某一external network的PC, 或網路有資料要傳給手機,就 須建立傳送資料的連結(PDP context activation) o PDP:類似於啟動 modem 與dial n [步驟 2] 此時若MS想要傳資料 給某一external network的PC, 或網路有資料要傳給手機,就 須建立傳送資料的連結(PDP context activation) o PDP:類似於啟動 modem 與dial](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-39.jpg) n [步驟 2] 此時若MS想要傳資料 給某一external network的PC, 或網路有資料要傳給手機,就 須建立傳送資料的連結(PDP context activation) o PDP:類似於啟動 modem 與dial up到ISP的動作 o 每個連結(PDP context)須一 個IP address,MS可同時連 到不同的網路 n GPRS最多允許一個 mobile device有14個PDP contexts同時存在
n [步驟 2] 此時若MS想要傳資料 給某一external network的PC, 或網路有資料要傳給手機,就 須建立傳送資料的連結(PDP context activation) o PDP:類似於啟動 modem 與dial up到ISP的動作 o 每個連結(PDP context)須一 個IP address,MS可同時連 到不同的網路 n GPRS最多允許一個 mobile device有14個PDP contexts同時存在
![n [步驟 3] GGSN 1向DHCP server要到一個IP address,透過SGSN 1送給MS,建立起PDP context o 註:DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration n [步驟 3] GGSN 1向DHCP server要到一個IP address,透過SGSN 1送給MS,建立起PDP context o 註:DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-40.jpg) n [步驟 3] GGSN 1向DHCP server要到一個IP address,透過SGSN 1送給MS,建立起PDP context o 註:DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
n [步驟 3] GGSN 1向DHCP server要到一個IP address,透過SGSN 1送給MS,建立起PDP context o 註:DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
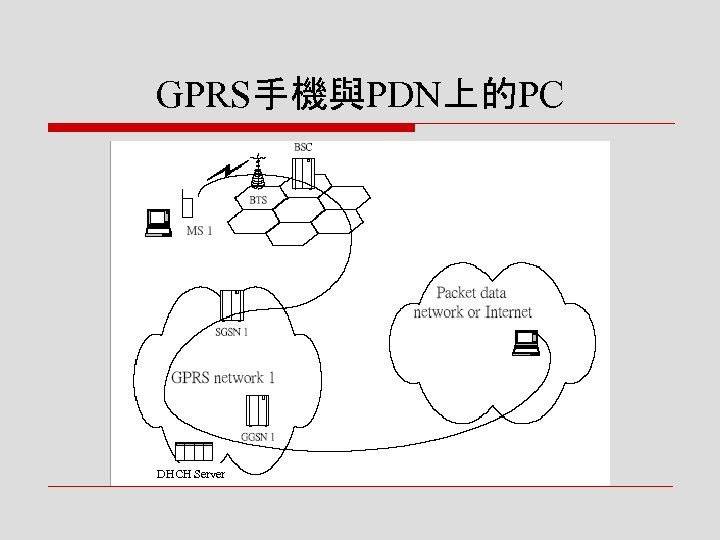 GPRS手機與PDN上的PC DHCH Server
GPRS手機與PDN上的PC DHCH Server
 2. 6 APN (Access Point Name) o APN可在GPRS網路上,用以描述MS要連上 的外部網路 o APN可將一個GPRS service,用簡單的name 表示出來 o APN是個label,根據DNS命名原則,用於描 述對外部資料網路的存取點(GGSN) n 例如:電信業者會提供其GPRS使用者預設的 APN,供使用者能順利連接上外部網路
2. 6 APN (Access Point Name) o APN可在GPRS網路上,用以描述MS要連上 的外部網路 o APN可將一個GPRS service,用簡單的name 表示出來 o APN是個label,根據DNS命名原則,用於描 述對外部資料網路的存取點(GGSN) n 例如:電信業者會提供其GPRS使用者預設的 APN,供使用者能順利連接上外部網路
 o 在Internet上,DNS server會把domain name轉 成IP address,在GPRS network上的DNS server,會將此APN轉成GGSN的IP address
o 在Internet上,DNS server會把domain name轉 成IP address,在GPRS network上的DNS server,會將此APN轉成GGSN的IP address
 o 在HLR和MS會儲存APN,HLR會檢查 MS是 否可以存取此APN n HLR中可能會有APN*代表 o default的APN或 o user可存取任何的APN
o 在HLR和MS會儲存APN,HLR會檢查 MS是 否可以存取此APN n HLR中可能會有APN*代表 o default的APN或 o user可存取任何的APN
![透過APN存取GPRS Service的步驟 o [步驟一] 使用者啟動一個 service,MS會送 request給SGSN o [步驟二] SGSN比較HLR中的用戶資料,檢 查此 service是否有授權給該user o [步驟三] 透過APN存取GPRS Service的步驟 o [步驟一] 使用者啟動一個 service,MS會送 request給SGSN o [步驟二] SGSN比較HLR中的用戶資料,檢 查此 service是否有授權給該user o [步驟三]](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-45.jpg) 透過APN存取GPRS Service的步驟 o [步驟一] 使用者啟動一個 service,MS會送 request給SGSN o [步驟二] SGSN比較HLR中的用戶資料,檢 查此 service是否有授權給該user o [步驟三] SGSN向local GPRS DNS server查詢 負責此APN的GGSN的IP address
透過APN存取GPRS Service的步驟 o [步驟一] 使用者啟動一個 service,MS會送 request給SGSN o [步驟二] SGSN比較HLR中的用戶資料,檢 查此 service是否有授權給該user o [步驟三] SGSN向local GPRS DNS server查詢 負責此APN的GGSN的IP address
![o [步驟四] 如果在local DNS找不到APN相對應 的IP address n case 1:user在自己的home network,此request會 被拒絕 n case 2:user在foreign o [步驟四] 如果在local DNS找不到APN相對應 的IP address n case 1:user在自己的home network,此request會 被拒絕 n case 2:user在foreign](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-46.jpg) o [步驟四] 如果在local DNS找不到APN相對應 的IP address n case 1:user在自己的home network,此request會 被拒絕 n case 2:user在foreign network,SGSN會向MS的 home network的DNS查詢 o [步驟五] 當找到GGSN的IP address n SGSN會藉助GTP (GPRS Tunneling Protocol)建立 起與GGSN間的tunnel
o [步驟四] 如果在local DNS找不到APN相對應 的IP address n case 1:user在自己的home network,此request會 被拒絕 n case 2:user在foreign network,SGSN會向MS的 home network的DNS查詢 o [步驟五] 當找到GGSN的IP address n SGSN會藉助GTP (GPRS Tunneling Protocol)建立 起與GGSN間的tunnel
 2. 7 MS IP Address Allocation o 要建立起MS與external network間的連結(PDP context),MS必須要有IP address o GPRS有兩種分配MS IP address的方式 n fixed addressing n dynamic addressing
2. 7 MS IP Address Allocation o 要建立起MS與external network間的連結(PDP context),MS必須要有IP address o GPRS有兩種分配MS IP address的方式 n fixed addressing n dynamic addressing
 o Fixed addressing n 永遠分配給MS相同的IP address,此IP address存 在HLR中 n 當MS想要開啟一個 PDP context到某一個APN, HLR將IP address送到SGSN再送到MS n 此種方式是搶迫MS一定要使用network分配的IP address
o Fixed addressing n 永遠分配給MS相同的IP address,此IP address存 在HLR中 n 當MS想要開啟一個 PDP context到某一個APN, HLR將IP address送到SGSN再送到MS n 此種方式是搶迫MS一定要使用network分配的IP address
 o Dynamic addressing n 當MS開啟 PDP context時,GGSN會分配一個IP address,並透過SGSN傳送給MS n 當關閉PDP context時,SGSN收回此IP address
o Dynamic addressing n 當MS開啟 PDP context時,GGSN會分配一個IP address,並透過SGSN傳送給MS n 當關閉PDP context時,SGSN收回此IP address
 2. 8 GGSN取得IP Address的四種方 式 o 四種方式 n n from a local address pool on the GGSN via RADIUS form an external RADIUS server via DHCP from the customer network via an L 2 TP tunnel from the GGSN
2. 8 GGSN取得IP Address的四種方 式 o 四種方式 n n from a local address pool on the GGSN via RADIUS form an external RADIUS server via DHCP from the customer network via an L 2 TP tunnel from the GGSN
 o From a local address pool on the GGSN n 運作方式類似PSTN dialup server o GGSN有一個IP address pool o 當有MS需要IP,GGSN從pool分配一個IP給 MS n 如客戶端選擇由operator分配IP,這是所有方式 中最簡單的方式
o From a local address pool on the GGSN n 運作方式類似PSTN dialup server o GGSN有一個IP address pool o 當有MS需要IP,GGSN從pool分配一個IP給 MS n 如客戶端選擇由operator分配IP,這是所有方式 中最簡單的方式
 o Via RADIUS form an external RADIUS server n 通常RADIUS server會在customer network n RADIUS server認證user terminal,給予一個fixed IP address o 註:RADIUS (Remote Access Dial In User Service) Protocol n 提供authentication機制,用來辨認使用者的身份與密碼 n 確認通過後,經由authorization授權使用者登入網域使用 相關資源 n 提供accounting機制,保存使用者的網路使用記錄,以提 供系統服務業者完整認證收費機制的一個基礎
o Via RADIUS form an external RADIUS server n 通常RADIUS server會在customer network n RADIUS server認證user terminal,給予一個fixed IP address o 註:RADIUS (Remote Access Dial In User Service) Protocol n 提供authentication機制,用來辨認使用者的身份與密碼 n 確認通過後,經由authorization授權使用者登入網域使用 相關資源 n 提供accounting機制,保存使用者的網路使用記錄,以提 供系統服務業者完整認證收費機制的一個基礎
 o Via DHCP n GGSN向DHCP server要一個IP address n 可把DHCP server設定成fixed IP address,則MS 每次都會取得相同的IP address
o Via DHCP n GGSN向DHCP server要一個IP address n 可把DHCP server設定成fixed IP address,則MS 每次都會取得相同的IP address
 o From the customer network via an L 2 TP tunnel from the GGSN n L 2 TP是Layer 2的tunneling protocol o 通常用於PSTN dial-up到一個Remote Access Server n 對GPRS而言,L 2 TP在GGSN與customer network 的router間建立一個安全的連結
o From the customer network via an L 2 TP tunnel from the GGSN n L 2 TP是Layer 2的tunneling protocol o 通常用於PSTN dial-up到一個Remote Access Server n 對GPRS而言,L 2 TP在GGSN與customer network 的router間建立一個安全的連結
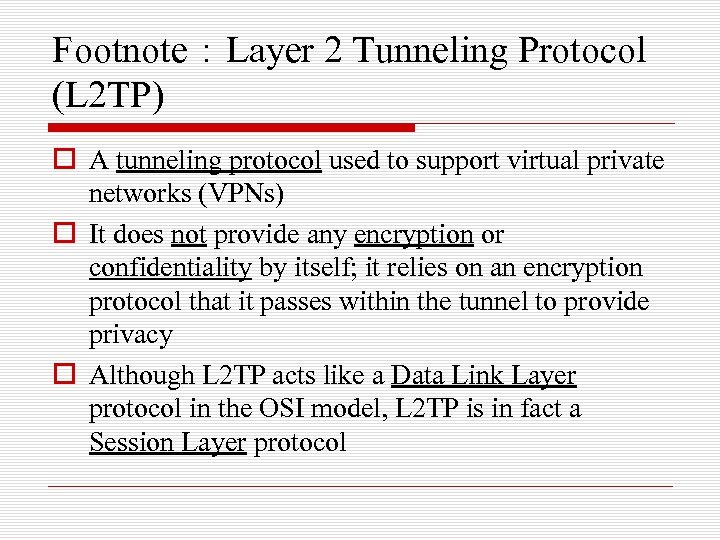 Footnote:Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L 2 TP) o A tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) o It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself; it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy o Although L 2 TP acts like a Data Link Layer protocol in the OSI model, L 2 TP is in fact a Session Layer protocol
Footnote:Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L 2 TP) o A tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) o It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself; it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy o Although L 2 TP acts like a Data Link Layer protocol in the OSI model, L 2 TP is in fact a Session Layer protocol
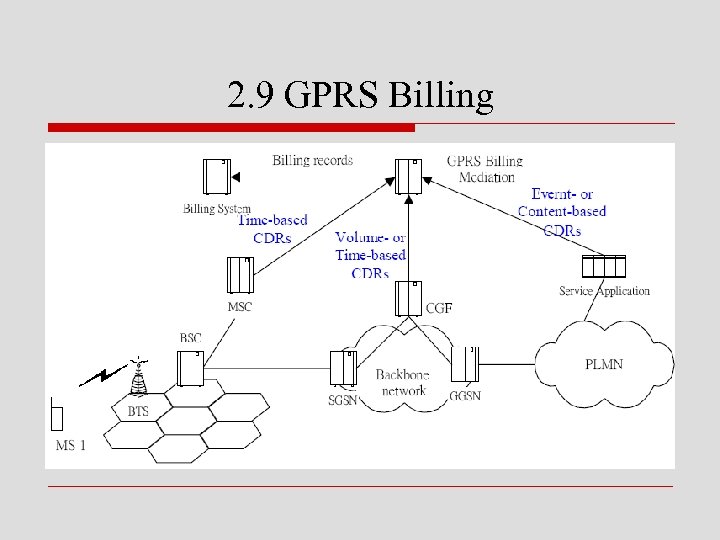 2. 9 GPRS Billing
2. 9 GPRS Billing
 o GPRS的計費資訊是由SGSN及GGSN收集 n SGSN收集MS的radio resource usage n GGSN收集MS的network usage n 如MS到其它GPRS network使用資源 o 若到訪的GPRS network使用dynamic address 連到MS,則計費資料會送到home GPRS network
o GPRS的計費資訊是由SGSN及GGSN收集 n SGSN收集MS的radio resource usage n GGSN收集MS的network usage n 如MS到其它GPRS network使用資源 o 若到訪的GPRS network使用dynamic address 連到MS,則計費資料會送到home GPRS network
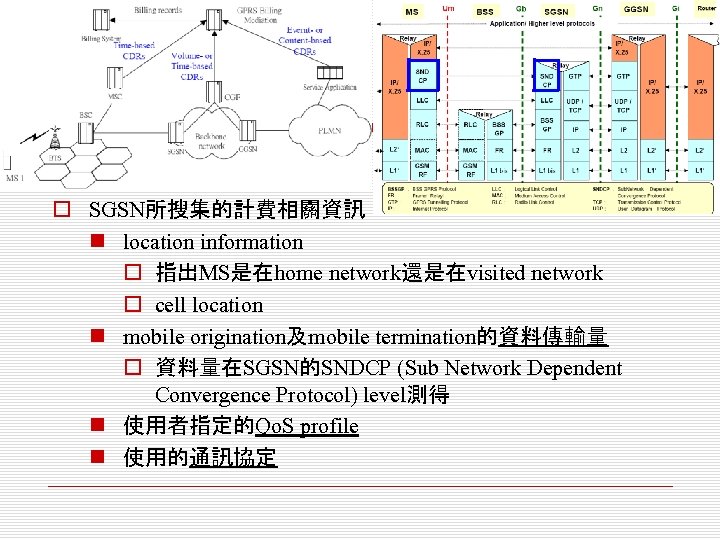 o SGSN所搜集的計費相關資訊 n location information o 指出MS是在home network還是在visited network o cell location n mobile origination及mobile termination的資料傳輸量 o 資料量在SGSN的SNDCP (Sub Network Dependent Convergence Protocol) level測得 n 使用者指定的Qo. S profile n 使用的通訊協定
o SGSN所搜集的計費相關資訊 n location information o 指出MS是在home network還是在visited network o cell location n mobile origination及mobile termination的資料傳輸量 o 資料量在SGSN的SNDCP (Sub Network Dependent Convergence Protocol) level測得 n 使用者指定的Qo. S profile n 使用的通訊協定
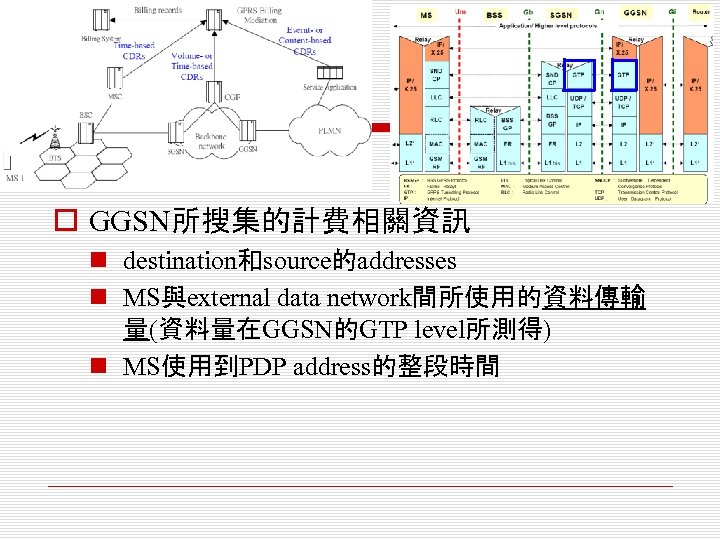 o GGSN所搜集的計費相關資訊 n destination和source的addresses n MS與external data network間所使用的資料傳輸 量(資料量在GGSN的GTP level所測得) n MS使用到PDP address的整段時間
o GGSN所搜集的計費相關資訊 n destination和source的addresses n MS與external data network間所使用的資料傳輸 量(資料量在GGSN的GTP level所測得) n MS使用到PDP address的整段時間
 Call Detailed Records (CDRs) o SGSN與GGSN收集到的計費資料會轉成call detailed records (CDR) o Call detailed record分成 n S-CDR (SGSN PDP context generated-CDR) o 由SGSN產生,記錄MS無線電資源的使用量 n G-CDR (GGSN generated-CDR) o 由GGSN產生,記錄MS所使用GGSN的外部網路 n M-CDR (Mobility Management generated-CDR) o 由SGSN產生,記錄MS行動管理的相關資料
Call Detailed Records (CDRs) o SGSN與GGSN收集到的計費資料會轉成call detailed records (CDR) o Call detailed record分成 n S-CDR (SGSN PDP context generated-CDR) o 由SGSN產生,記錄MS無線電資源的使用量 n G-CDR (GGSN generated-CDR) o 由GGSN產生,記錄MS所使用GGSN的外部網路 n M-CDR (Mobility Management generated-CDR) o 由SGSN產生,記錄MS行動管理的相關資料
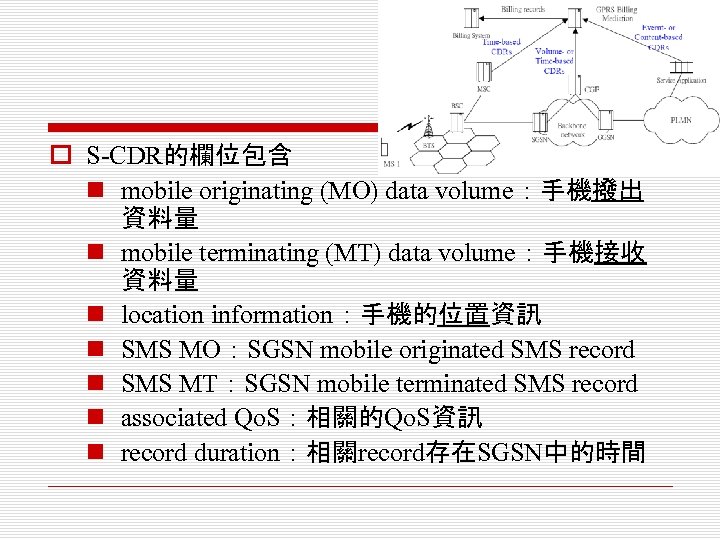 o S-CDR的欄位包含 n mobile originating (MO) data volume:手機撥出 資料量 n mobile terminating (MT) data volume:手機接收 資料量 n location information:手機的位置資訊 n SMS MO:SGSN mobile originated SMS record n SMS MT:SGSN mobile terminated SMS record n associated Qo. S:相關的Qo. S資訊 n record duration:相關record存在SGSN中的時間
o S-CDR的欄位包含 n mobile originating (MO) data volume:手機撥出 資料量 n mobile terminating (MT) data volume:手機接收 資料量 n location information:手機的位置資訊 n SMS MO:SGSN mobile originated SMS record n SMS MT:SGSN mobile terminated SMS record n associated Qo. S:相關的Qo. S資訊 n record duration:相關record存在SGSN中的時間
 o G-CDR的欄位包含 n n n source address destination address 收到外部網路的資料量 送到外部網路的資料量 相關的Qo. S資訊 record duration:record存在GGSN中的時間
o G-CDR的欄位包含 n n n source address destination address 收到外部網路的資料量 送到外部網路的資料量 相關的Qo. S資訊 record duration:record存在GGSN中的時間
 o 每位使用者的PDP context,會產生一個CDR n 啟動 (activate) PDP context時,會開始產生相對 應的CDR n 每個PDP context可能產生數筆S-CDRs及G-CDRs
o 每位使用者的PDP context,會產生一個CDR n 啟動 (activate) PDP context時,會開始產生相對 應的CDR n 每個PDP context可能產生數筆S-CDRs及G-CDRs
 o CDR可依下列三種方式產生 n end-of-call accounting schedule:通話結束時產生 n time-of-day accounting schedule:一天中的某時 刻產生 n inter-SGSN routing area update:跨SGSN RA (Routing Area)移動時產生 o 當手機在通訊狀態下移動到不同GSN,數個 CDRs可由不同的GSNs及外部資料網路產生
o CDR可依下列三種方式產生 n end-of-call accounting schedule:通話結束時產生 n time-of-day accounting schedule:一天中的某時 刻產生 n inter-SGSN routing area update:跨SGSN RA (Routing Area)移動時產生 o 當手機在通訊狀態下移動到不同GSN,數個 CDRs可由不同的GSNs及外部資料網路產生
 o 計算封包數(packet-switched)計費遠較circuitswitched困難 n 量測封包數量所花的成本,可能比因傳送封包 賺取的金額還高 n 原有GSM計費系統無法處理GPRS即時CDR資訊 n 系統中通常會有所謂的charging gateway,根據 SGSNs/GGSNs所提供的資訊來執行帳務調整
o 計算封包數(packet-switched)計費遠較circuitswitched困難 n 量測封包數量所花的成本,可能比因傳送封包 賺取的金額還高 n 原有GSM計費系統無法處理GPRS即時CDR資訊 n 系統中通常會有所謂的charging gateway,根據 SGSNs/GGSNs所提供的資訊來執行帳務調整
 o Charging gateway function (CGF) n 控制charging data record (CDR)的收集 o CDR被送到GPRS Billing Mediation (調停) n 組成billing record,再送到billing system,做為 計費的依據
o Charging gateway function (CGF) n 控制charging data record (CDR)的收集 o CDR被送到GPRS Billing Mediation (調停) n 組成billing record,再送到billing system,做為 計費的依據
 o GPRS的幾種billing方式 n flat-rate billing (ex:月租費 800元) n per-packet billing (ex: 0. 2元/128 kbytes) n volume-based billing (PDP activate到deactivate的 時間) n value-based billing (加值服務, depend on context)
o GPRS的幾種billing方式 n flat-rate billing (ex:月租費 800元) n per-packet billing (ex: 0. 2元/128 kbytes) n volume-based billing (PDP activate到deactivate的 時間) n value-based billing (加值服務, depend on context)
 o 影響上述rate的因素 n Quality of Service n time of day (如減價時段,off-peak time/peak time) n day of week (如weekend,weekday,holiday) n content, call type, services used (ex: 0204、圖形 下載) n source or destination (如國外電話,用戶是員 、 員警等屬性)
o 影響上述rate的因素 n Quality of Service n time of day (如減價時段,off-peak time/peak time) n day of week (如weekend,weekday,holiday) n content, call type, services used (ex: 0204、圖形 下載) n source or destination (如國外電話,用戶是員 、 員警等屬性)
 Billing by Quality of Service o Service precedence class o Reliability class n n n loss ratio (for each layer) out of order (失序率) corrupted ratio (誤碼率) duplicate ratio (重覆率) reliability (1 -5 levels) o Peak throughput class (吞吐量) o Mean throughput class o Delay class (傳輸延遲)
Billing by Quality of Service o Service precedence class o Reliability class n n n loss ratio (for each layer) out of order (失序率) corrupted ratio (誤碼率) duplicate ratio (重覆率) reliability (1 -5 levels) o Peak throughput class (吞吐量) o Mean throughput class o Delay class (傳輸延遲)
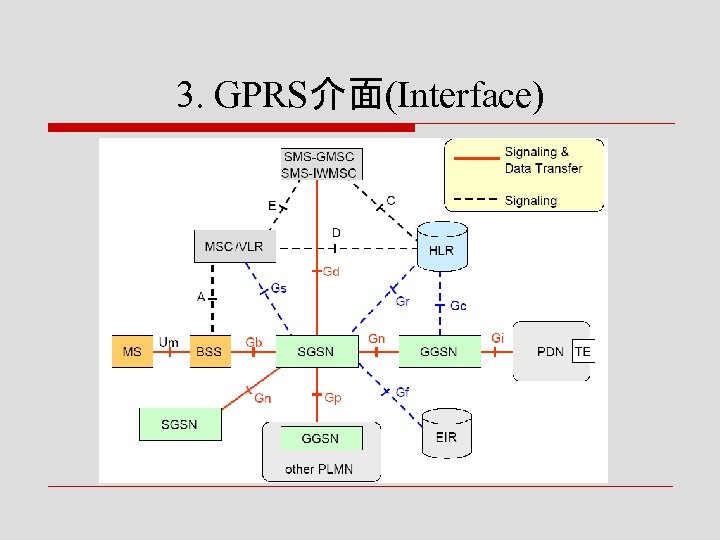 3. GPRS介面(Interface)
3. GPRS介面(Interface)
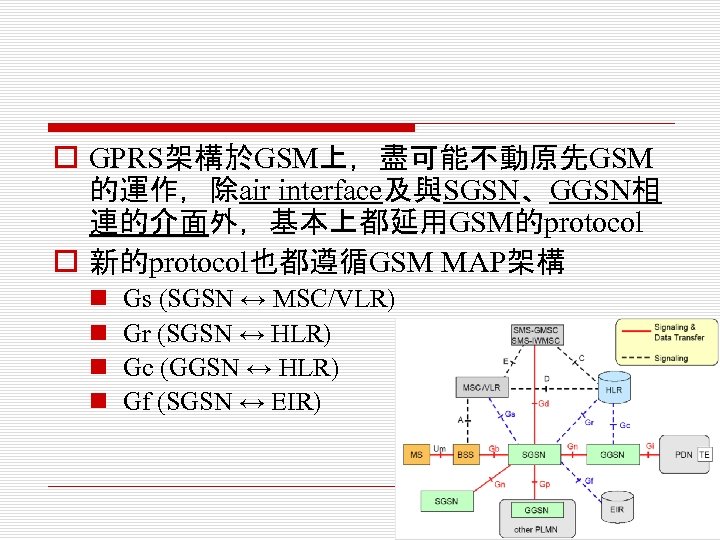 o GPRS架構於GSM上,盡可能不動原先GSM 的運作,除air interface及與SGSN、GGSN相 連的介面外,基本上都延用GSM的protocol o 新的protocol也都遵循GSM MAP架構 n n Gs (SGSN ↔ MSC/VLR) Gr (SGSN ↔ HLR) Gc (GGSN ↔ HLR) Gf (SGSN ↔ EIR)
o GPRS架構於GSM上,盡可能不動原先GSM 的運作,除air interface及與SGSN、GGSN相 連的介面外,基本上都延用GSM的protocol o 新的protocol也都遵循GSM MAP架構 n n Gs (SGSN ↔ MSC/VLR) Gr (SGSN ↔ HLR) Gc (GGSN ↔ HLR) Gf (SGSN ↔ EIR)
 3. 1 GPRS Transmission & Signaling Planes o GPRS延用OSI 7 -layer概念,每個interface定義的協定都 具layered structure o 使用的protocol stack分為 n transmission plane o 傳送使用者資料及與此資訊傳送相關的控制程序 o 例如:流量控制、錯誤偵測、更正與回覆 n signaling plane o 其它用於控制transmission plane functions所用到 的控制訊號
3. 1 GPRS Transmission & Signaling Planes o GPRS延用OSI 7 -layer概念,每個interface定義的協定都 具layered structure o 使用的protocol stack分為 n transmission plane o 傳送使用者資料及與此資訊傳送相關的控制程序 o 例如:流量控制、錯誤偵測、更正與回覆 n signaling plane o 其它用於控制transmission plane functions所用到 的控制訊號
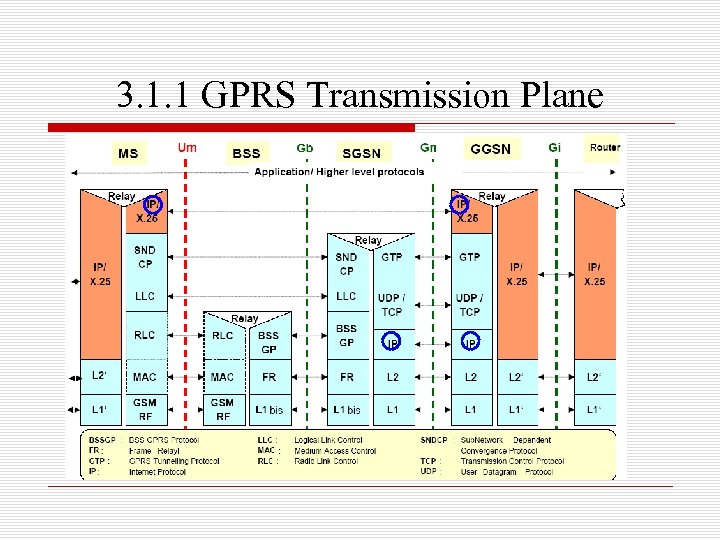 3. 1. 1 GPRS Transmission Plane
3. 1. 1 GPRS Transmission Plane
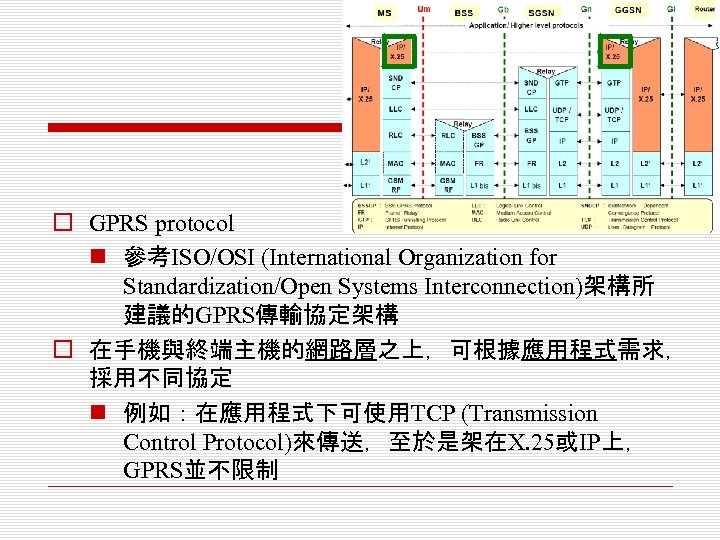 o GPRS protocol n 參考ISO/OSI (International Organization for Standardization/Open Systems Interconnection)架構所 建議的GPRS傳輸協定架構 o 在手機與終端主機的網路層之上,可根據應用程式需求, 採用不同協定 n 例如:在應用程式下可使用TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)來傳送,至於是架在X. 25或IP上, GPRS並不限制
o GPRS protocol n 參考ISO/OSI (International Organization for Standardization/Open Systems Interconnection)架構所 建議的GPRS傳輸協定架構 o 在手機與終端主機的網路層之上,可根據應用程式需求, 採用不同協定 n 例如:在應用程式下可使用TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)來傳送,至於是架在X. 25或IP上, GPRS並不限制
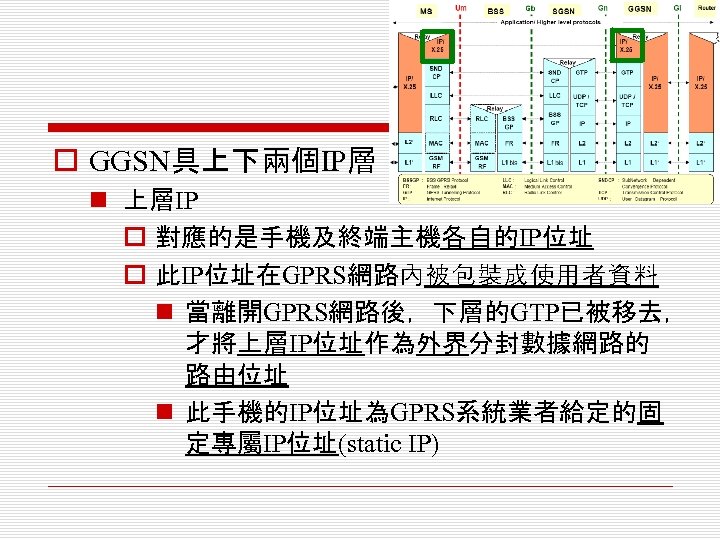 o GGSN具上下兩個IP層 n 上層IP o 對應的是手機及終端主機各自的IP位址 o 此IP位址在GPRS網路內被包裝成使用者資料 n 當離開GPRS網路後,下層的GTP已被移去, 才將上層IP位址作為外界分封數據網路的 路由位址 n 此手機的IP位址為GPRS系統業者給定的固 定專屬IP位址(static IP)
o GGSN具上下兩個IP層 n 上層IP o 對應的是手機及終端主機各自的IP位址 o 此IP位址在GPRS網路內被包裝成使用者資料 n 當離開GPRS網路後,下層的GTP已被移去, 才將上層IP位址作為外界分封數據網路的 路由位址 n 此手機的IP位址為GPRS系統業者給定的固 定專屬IP位址(static IP)
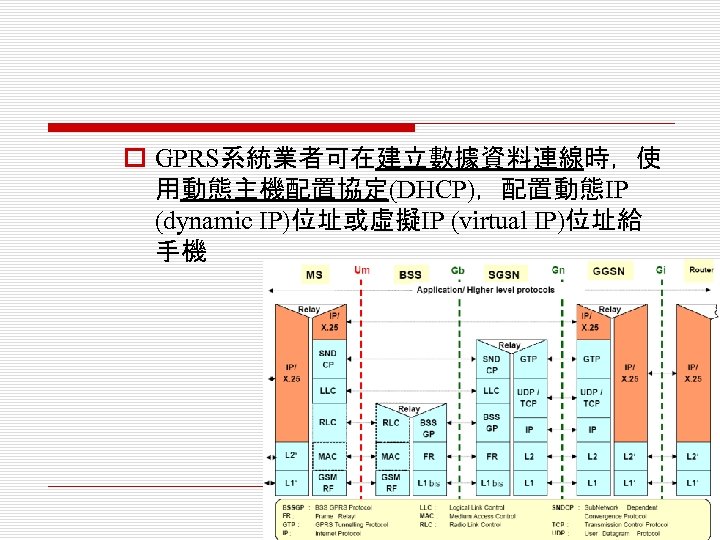 o GPRS系統業者可在建立數據資料連線時,使 用動態主機配置協定(DHCP),配置動態IP (dynamic IP)位址或虛擬IP (virtual IP)位址給 手機
o GPRS系統業者可在建立數據資料連線時,使 用動態主機配置協定(DHCP),配置動態IP (dynamic IP)位址或虛擬IP (virtual IP)位址給 手機
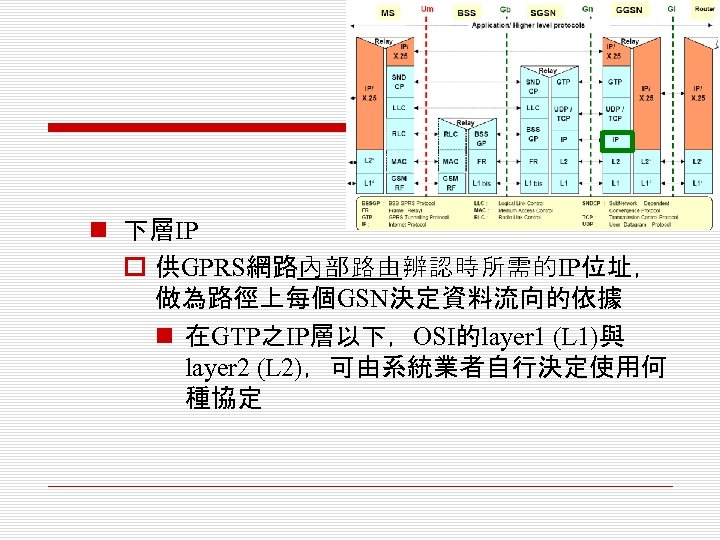 n 下層IP o 供GPRS網路內部路由辨認時所需的IP位址, 做為路徑上每個GSN決定資料流向的依據 n 在GTP之IP層以下,OSI的layer 1 (L 1)與 layer 2 (L 2),可由系統業者自行決定使用何 種協定
n 下層IP o 供GPRS網路內部路由辨認時所需的IP位址, 做為路徑上每個GSN決定資料流向的依據 n 在GTP之IP層以下,OSI的layer 1 (L 1)與 layer 2 (L 2),可由系統業者自行決定使用何 種協定
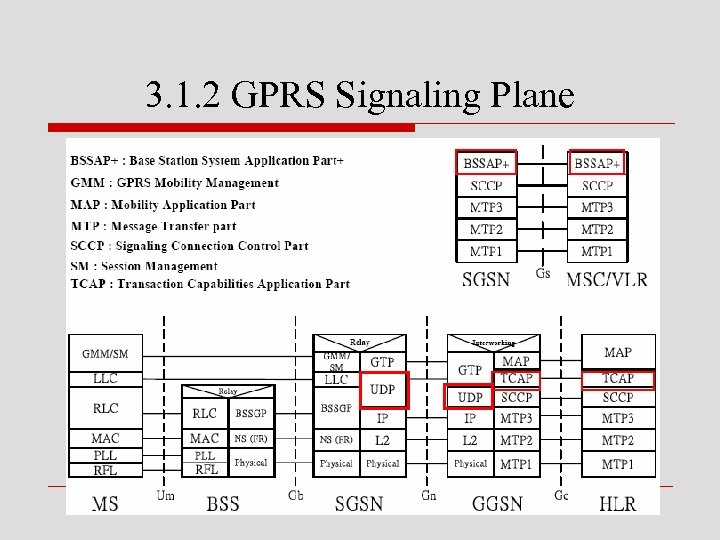 3. 1. 2 GPRS Signaling Plane
3. 1. 2 GPRS Signaling Plane
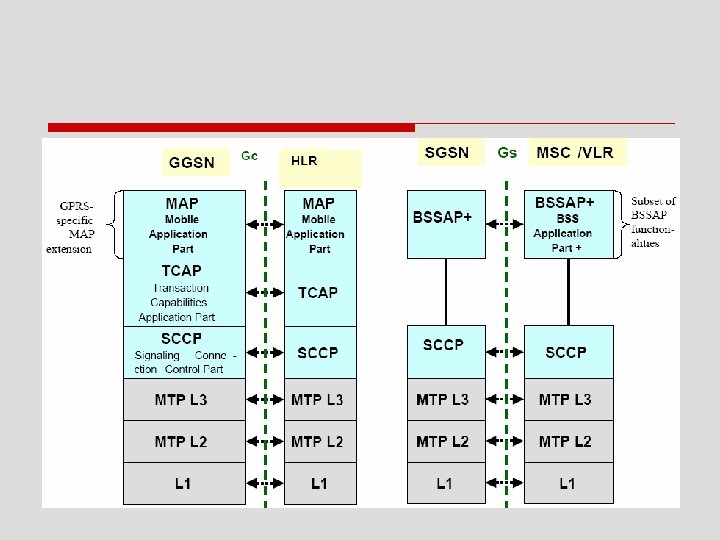
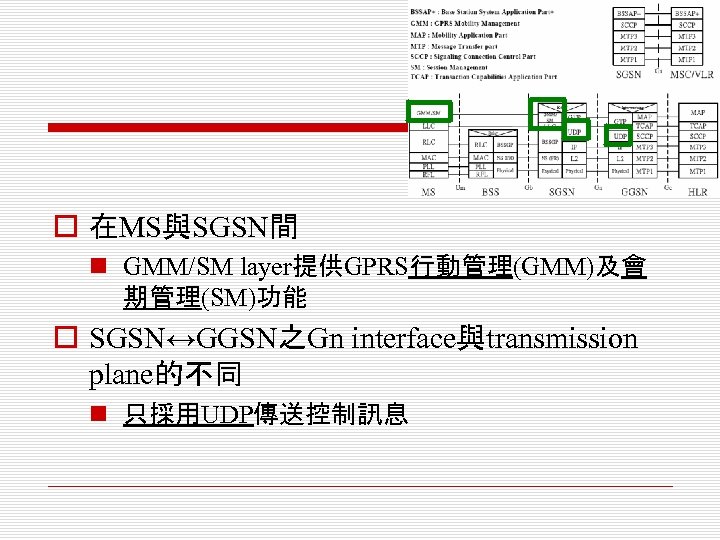 o 在MS與SGSN間 n GMM/SM layer提供GPRS行動管理(GMM)及會 期管理(SM)功能 o SGSN↔GGSN之Gn interface與transmission plane的不同 n 只採用UDP傳送控制訊息
o 在MS與SGSN間 n GMM/SM layer提供GPRS行動管理(GMM)及會 期管理(SM)功能 o SGSN↔GGSN之Gn interface與transmission plane的不同 n 只採用UDP傳送控制訊息
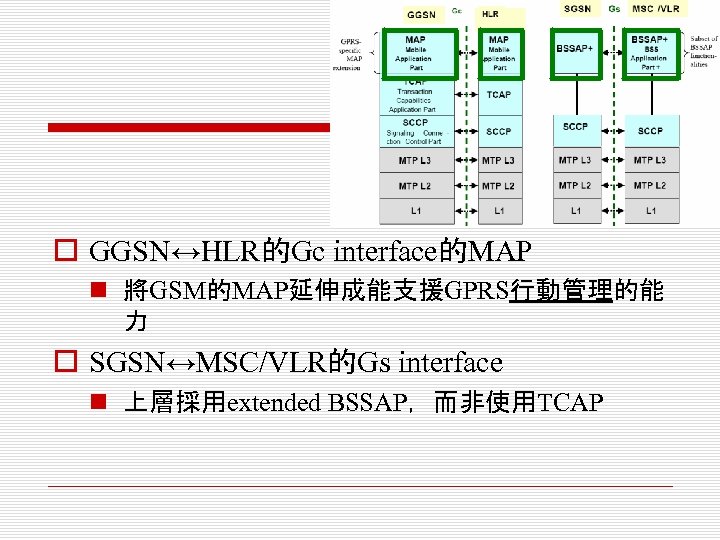 o GGSN↔HLR的Gc interface的MAP n 將GSM的MAP延伸成能支援GPRS行動管理的能 力 o SGSN↔MSC/VLR的Gs interface n 上層採用extended BSSAP,而非使用TCAP
o GGSN↔HLR的Gc interface的MAP n 將GSM的MAP延伸成能支援GPRS行動管理的能 力 o SGSN↔MSC/VLR的Gs interface n 上層採用extended BSSAP,而非使用TCAP
 3. 1. 2. 1 MS ↔ BSS o MS與BSS間實體層(physical layer) n 實體無線電子層(physical RF sub. Layer,RFL) o 負責GSM無線電相關規範,執行 modulation/demodulation n 實體連結子層(Physical Link sub. Layer,PLL) o 負責在實際連結上資訊的傳輸
3. 1. 2. 1 MS ↔ BSS o MS與BSS間實體層(physical layer) n 實體無線電子層(physical RF sub. Layer,RFL) o 負責GSM無線電相關規範,執行 modulation/demodulation n 實體連結子層(Physical Link sub. Layer,PLL) o 負責在實際連結上資訊的傳輸
 o MS與BSS間MAC層/RLC層 n 無線電連結控制層(Radio Link Control,RLC) 和媒介擷取控制層(Medium Access Control, MAC)的功用 o 讓上層服務能順利經由GPRS無線電介面的 實體層傳送(RLC) o 定義讓數個手機能同時共享相同傳輸介質的 傳送方式(MAC)
o MS與BSS間MAC層/RLC層 n 無線電連結控制層(Radio Link Control,RLC) 和媒介擷取控制層(Medium Access Control, MAC)的功用 o 讓上層服務能順利經由GPRS無線電介面的 實體層傳送(RLC) o 定義讓數個手機能同時共享相同傳輸介質的 傳送方式(MAC)
 n MAC層 o 採用Slotted Aloha型保留協定(Slotted Aloha based reservation protocol),負責管理無線電 資源分配 o 因存取通道有限,當眾多手機同時送出無線 電通道存取要求時,可能會發生碰撞 o 主要 作是解決碰撞後重送的問題 o 負責在眾多手機提出服務要求時,在網路端 根據用戶需求,決定無線電資源分配的方式
n MAC層 o 採用Slotted Aloha型保留協定(Slotted Aloha based reservation protocol),負責管理無線電 資源分配 o 因存取通道有限,當眾多手機同時送出無線 電通道存取要求時,可能會發生碰撞 o 主要 作是解決碰撞後重送的問題 o 負責在眾多手機提出服務要求時,在網路端 根據用戶需求,決定無線電資源分配的方式
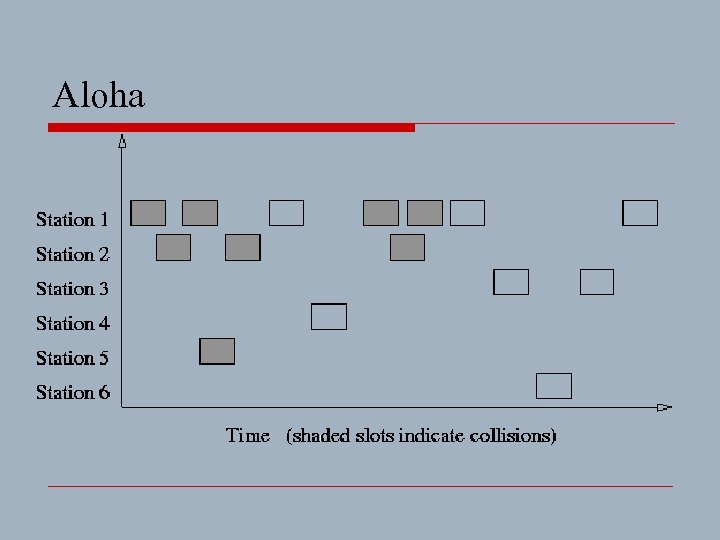
 Note:Aloha o A system for coordinating and arbitrating access to some shared communication channel o A medium access method is supposed to prevent two or more systems from transmitting at the time on a shared medium
Note:Aloha o A system for coordinating and arbitrating access to some shared communication channel o A medium access method is supposed to prevent two or more systems from transmitting at the time on a shared medium
 o In the Aloha system n a station transmits whenever data is available to send n if another station transmits at the same time, a collision occurs and the frames that were transmitted are lost n however, a station can listen to broadcasts on the medium, even its own, and determine if the frames were transmitted
o In the Aloha system n a station transmits whenever data is available to send n if another station transmits at the same time, a collision occurs and the frames that were transmitted are lost n however, a station can listen to broadcasts on the medium, even its own, and determine if the frames were transmitted
 Aloha
Aloha
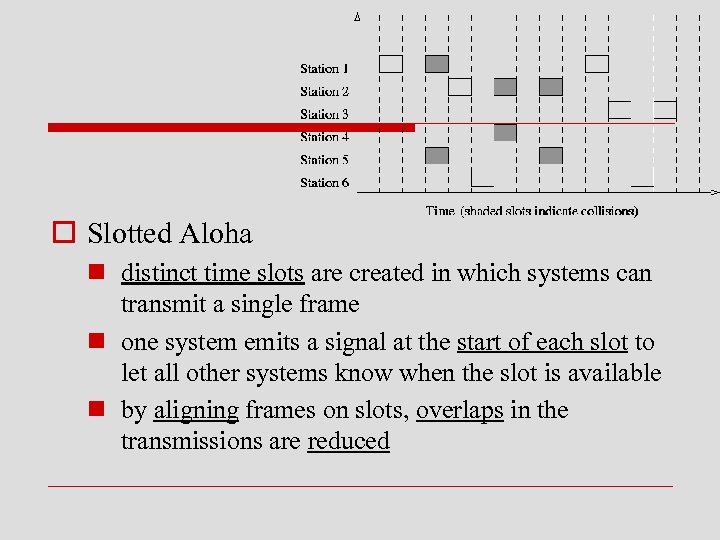 o Slotted Aloha n distinct time slots are created in which systems can transmit a single frame n one system emits a signal at the start of each slot to let all other systems know when the slot is available n by aligning frames on slots, overlaps in the transmissions are reduced
o Slotted Aloha n distinct time slots are created in which systems can transmit a single frame n one system emits a signal at the start of each slot to let all other systems know when the slot is available n by aligning frames on slots, overlaps in the transmissions are reduced
 n however, systems must wait a fraction of a second for the beginning of a time slot before they can transmit n also, data may be lost if stations contend for the same slot n tests have shown that slotted Aloha has a performance advantage
n however, systems must wait a fraction of a second for the beginning of a time slot before they can transmit n also, data may be lost if stations contend for the same slot n tests have shown that slotted Aloha has a performance advantage
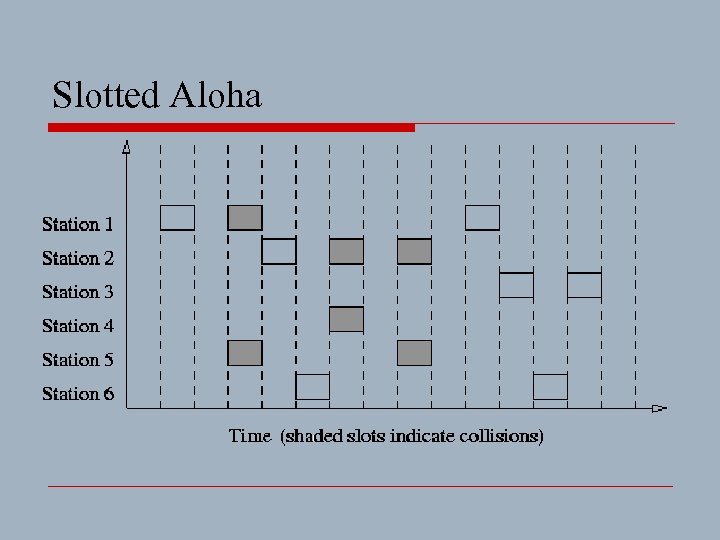 Slotted Aloha
Slotted Aloha
 n RLC層 o 負責將資料透過無線電介面傳送的過程,使 用選擇性重送(selective ARQ)的錯誤更正程序, 提供可靠的邏輯無線電連結傳輸
n RLC層 o 負責將資料透過無線電介面傳送的過程,使 用選擇性重送(selective ARQ)的錯誤更正程序, 提供可靠的邏輯無線電連結傳輸
 Note:Selective ARQ o Automatic Repeat-re. Quest (ARQ) n an error control method for data transmission which uses acknowledgments and timeouts to achieve reliable data transmission o an acknowledgment is a message sent by the receiver to the transmitter to indicate that it has correctly received a data frame o a timeout is a reasonable point in time after the sender sends the data frame; if the sender does not receive an acknowledgment before the timeout, it usually re-transmits the frame until it receives an acknowledgment or exceeds a predefined number of re-transmissions
Note:Selective ARQ o Automatic Repeat-re. Quest (ARQ) n an error control method for data transmission which uses acknowledgments and timeouts to achieve reliable data transmission o an acknowledgment is a message sent by the receiver to the transmitter to indicate that it has correctly received a data frame o a timeout is a reasonable point in time after the sender sends the data frame; if the sender does not receive an acknowledgment before the timeout, it usually re-transmits the frame until it receives an acknowledgment or exceeds a predefined number of re-transmissions
 o Selective (Repeat) ARQ n a specific instance of the Automatic Repeat-re. Quest (ARQ) Protocol n it may be utilized as a protocol for the delivery and acknowledge of message units, or it may be utilized as a protocol for the delivery of subdivided message sub-units n the sending process continues to send a number of frames specified by a window size even after a frame loss n the receiving process will continue to accept and acknowledge frames sent after an initial error
o Selective (Repeat) ARQ n a specific instance of the Automatic Repeat-re. Quest (ARQ) Protocol n it may be utilized as a protocol for the delivery and acknowledge of message units, or it may be utilized as a protocol for the delivery of subdivided message sub-units n the sending process continues to send a number of frames specified by a window size even after a frame loss n the receiving process will continue to accept and acknowledge frames sent after an initial error
 n the receiver process keeps track of the sequence number of the earliest frame it has not received, and sends that number with every ACK it sends n if a frame from the sender does not reach the receiver, the sender continues to send subsequent frames until it has emptied its window n the receiver continues to fill its receiving window with the subsequent frames, replying each time with an ACK containing the sequence number of the earliest missing frame n once the sender has sent all the frames in its window, it resends the frame number given by the ACKs, and then continues where it left off
n the receiver process keeps track of the sequence number of the earliest frame it has not received, and sends that number with every ACK it sends n if a frame from the sender does not reach the receiver, the sender continues to send subsequent frames until it has emptied its window n the receiver continues to fill its receiving window with the subsequent frames, replying each time with an ACK containing the sequence number of the earliest missing frame n once the sender has sent all the frames in its window, it resends the frame number given by the ACKs, and then continues where it left off
 3. 1. 2. 2 BSS ↔ SGSN o NS (Network Service) n 利用下層frame relay建立起BSS與SGSN間的 virtual connection (NS-VC) n NS是在管理NS-VC以提供上層BSSGP傳送 BSSGP PDU
3. 1. 2. 2 BSS ↔ SGSN o NS (Network Service) n 利用下層frame relay建立起BSS與SGSN間的 virtual connection (NS-VC) n NS是在管理NS-VC以提供上層BSSGP傳送 BSSGP PDU
 o 基地台GPRS協定(BSS GPRS Protocol, BSSGP) n 負責在BSS與SGSN間傳送路由與Qo. S資訊的 作, 並提供上層LLC傳遞的服務 n 在BSS上,BSSGP的relay function須提供RLC/MAC (MS↔BSS)與BSSGP (BSS↔SGSN)間buffering及 parameter mapping功能,以轉送MS 與SGSN間的 packet
o 基地台GPRS協定(BSS GPRS Protocol, BSSGP) n 負責在BSS與SGSN間傳送路由與Qo. S資訊的 作, 並提供上層LLC傳遞的服務 n 在BSS上,BSSGP的relay function須提供RLC/MAC (MS↔BSS)與BSSGP (BSS↔SGSN)間buffering及 parameter mapping功能,以轉送MS 與SGSN間的 packet
 n BSSGP也要執行 o mobility management (MM) n 通知cell去page MS n 指示MS更新Routing Area o network management (NM) n 管理BSS與SGSN n downlink flow control n Qo. S link的相關 作
n BSSGP也要執行 o mobility management (MM) n 通知cell去page MS n 指示MS更新Routing Area o network management (NM) n 管理BSS與SGSN n downlink flow control n Qo. S link的相關 作
 3. 1. 2. 3 MS ↔ SGSN o 在Layer 2的LLC要提供服務,使MS與SGSN間能有可靠 的第三層連結 n flow control n sequence control n error detection and recovery n ciphered data link n Qo. S delay class n ack/unack mode
3. 1. 2. 3 MS ↔ SGSN o 在Layer 2的LLC要提供服務,使MS與SGSN間能有可靠 的第三層連結 n flow control n sequence control n error detection and recovery n ciphered data link n Qo. S delay class n ack/unack mode
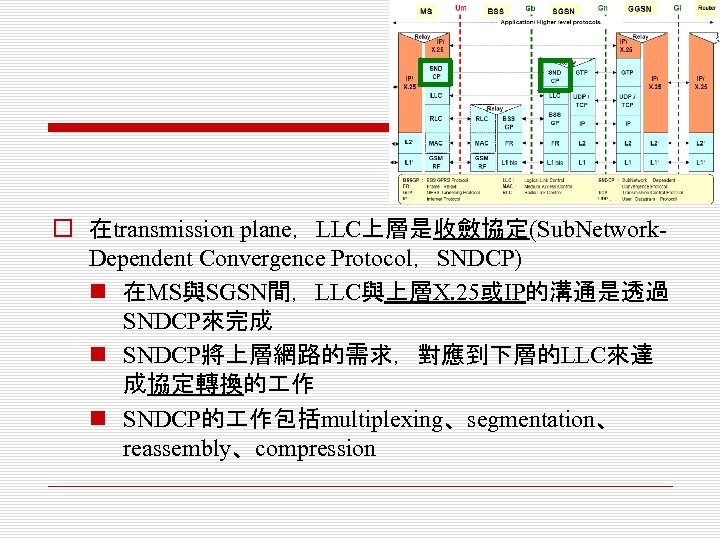 o 在transmission plane,LLC上層是收斂協定(Sub. Network. Dependent Convergence Protocol,SNDCP) n 在MS與SGSN間,LLC與上層X. 25或IP的溝通是透過 SNDCP來完成 n SNDCP將上層網路的需求,對應到下層的LLC來達 成協定轉換的 作 n SNDCP的 作包括multiplexing、segmentation、 reassembly、compression
o 在transmission plane,LLC上層是收斂協定(Sub. Network. Dependent Convergence Protocol,SNDCP) n 在MS與SGSN間,LLC與上層X. 25或IP的溝通是透過 SNDCP來完成 n SNDCP將上層網路的需求,對應到下層的LLC來達 成協定轉換的 作 n SNDCP的 作包括multiplexing、segmentation、 reassembly、compression
 3. 1. 2. 4 SGSN ↔ GGSN o 在GTP之下採用TCP或UDP (User Datagram Protocol)及 IP路由的方式,作為傳輸的骨幹 o 在GPRS網路上,封包的發送端與接收端兩個GPRS支援 節點間,使用GPRS隧道協定(GPRS Tunnel Protocol, GTP) n 透過附加路由資訊(包裝)的方式,將上層X. 25或IP應 用程式的協定數據單元(PDU)包裝起來,經由GPRS 骨幹網路傳送 n 依據應用程式需求,提供不同服務品質(Qo. S)
3. 1. 2. 4 SGSN ↔ GGSN o 在GTP之下採用TCP或UDP (User Datagram Protocol)及 IP路由的方式,作為傳輸的骨幹 o 在GPRS網路上,封包的發送端與接收端兩個GPRS支援 節點間,使用GPRS隧道協定(GPRS Tunnel Protocol, GTP) n 透過附加路由資訊(包裝)的方式,將上層X. 25或IP應 用程式的協定數據單元(PDU)包裝起來,經由GPRS 骨幹網路傳送 n 依據應用程式需求,提供不同服務品質(Qo. S)
 4. GPRS無線電介面協定 o 規定MS與BSS間,實體層、RLC層及MAC層彼此 間在相互通訊時,須遵守的協定 o RLC/MAC層是要讓許多用戶共享這些數據通道, 透過無線電介面的實體層來傳送資料 o 對分封數據服務而言,最大特色是單向、短暫的傳 輸,而非語音般雙向、對稱、固定資料量大小的傳 輸 n 為提供非對稱性(asymmetric)、高速率的數據傳 輸服務,GPRS的上行、下行通道基本上是獨立 運作,並依據用戶實際需求,動態配置頻道, 確保無線電資源有效利用
4. GPRS無線電介面協定 o 規定MS與BSS間,實體層、RLC層及MAC層彼此 間在相互通訊時,須遵守的協定 o RLC/MAC層是要讓許多用戶共享這些數據通道, 透過無線電介面的實體層來傳送資料 o 對分封數據服務而言,最大特色是單向、短暫的傳 輸,而非語音般雙向、對稱、固定資料量大小的傳 輸 n 為提供非對稱性(asymmetric)、高速率的數據傳 輸服務,GPRS的上行、下行通道基本上是獨立 運作,並依據用戶實際需求,動態配置頻道, 確保無線電資源有效利用
 o GPRS分封數據邏輯通道(packet data logic channel)所提供的功能與現有GSM所提供的 相同 n 為區別分封數據服務與現有GSM線路交換服務, 特別使用不同邏輯通道名稱來定義其功能 o 專門用於packet data的實體層通道統稱為 PDCH (Packet Data CHannel) n PDCH再分別為各邏輯通道所使用
o GPRS分封數據邏輯通道(packet data logic channel)所提供的功能與現有GSM所提供的 相同 n 為區別分封數據服務與現有GSM線路交換服務, 特別使用不同邏輯通道名稱來定義其功能 o 專門用於packet data的實體層通道統稱為 PDCH (Packet Data CHannel) n PDCH再分別為各邏輯通道所使用
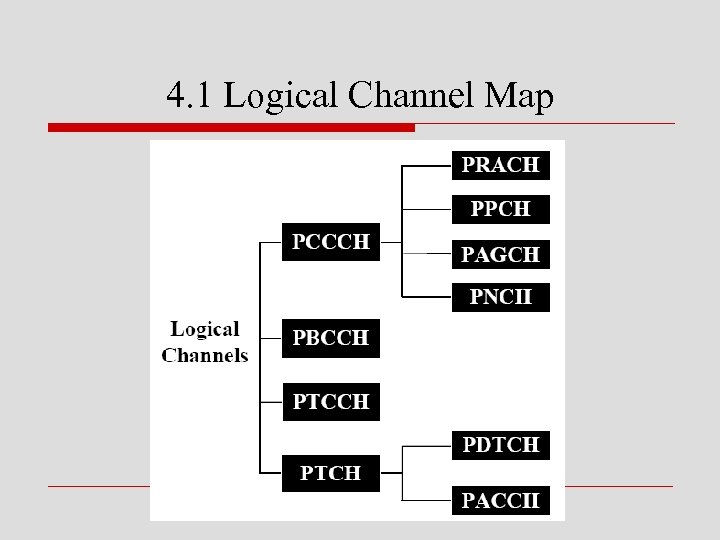 4. 1 Logical Channel Map
4. 1 Logical Channel Map
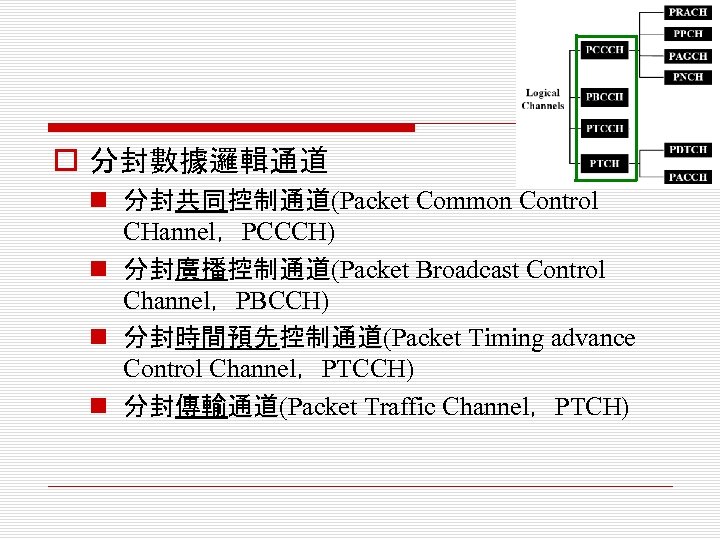 o 分封數據邏輯通道 n 分封共同控制通道(Packet Common Control CHannel,PCCCH) n 分封廣播控制通道(Packet Broadcast Control Channel,PBCCH) n 分封時間預先控制通道(Packet Timing advance Control Channel,PTCCH) n 分封傳輸通道(Packet Traffic Channel,PTCH)
o 分封數據邏輯通道 n 分封共同控制通道(Packet Common Control CHannel,PCCCH) n 分封廣播控制通道(Packet Broadcast Control Channel,PBCCH) n 分封時間預先控制通道(Packet Timing advance Control Channel,PTCCH) n 分封傳輸通道(Packet Traffic Channel,PTCH)
 4. 1. 1 分封共同控制通道(PCCCH) o 分封共同控制通道(Packet Common Control CHannel,PCCCH) n 所有手機間共享的通訊通道,做為建立GPRS數 據通訊服務之用
4. 1. 1 分封共同控制通道(PCCCH) o 分封共同控制通道(Packet Common Control CHannel,PCCCH) n 所有手機間共享的通訊通道,做為建立GPRS數 據通訊服務之用
 n PCCCH細分為 o 分封隨機擷取通道(Packet Random Access CHannel,PRACH) n 每位用戶都能透過該上行通道,以隨機存取 程序自由傳送各自的數據通道要求 o 分封傳呼通道(Packet Paging Channel, PPCH) n 用於網路端下行呼叫手機
n PCCCH細分為 o 分封隨機擷取通道(Packet Random Access CHannel,PRACH) n 每位用戶都能透過該上行通道,以隨機存取 程序自由傳送各自的數據通道要求 o 分封傳呼通道(Packet Paging Channel, PPCH) n 用於網路端下行呼叫手機
 o 分封擷取允諾通道(Packet Access Grant CHannel,PAGCH) n 用於網路下行通知手機所分配到的資源 o 分封通知通道(Packet Notification CHannel, PNCH) n 用於網路下行通知一群手機(即單點對多點 的服務)所分配到的資源
o 分封擷取允諾通道(Packet Access Grant CHannel,PAGCH) n 用於網路下行通知手機所分配到的資源 o 分封通知通道(Packet Notification CHannel, PNCH) n 用於網路下行通知一群手機(即單點對多點 的服務)所分配到的資源
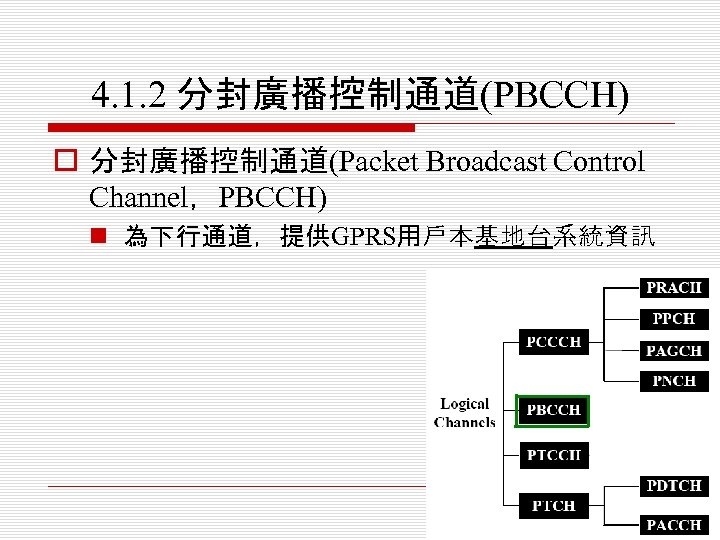 4. 1. 2 分封廣播控制通道(PBCCH) o 分封廣播控制通道(Packet Broadcast Control Channel,PBCCH) n 為下行通道,提供GPRS用戶本基地台系統資訊
4. 1. 2 分封廣播控制通道(PBCCH) o 分封廣播控制通道(Packet Broadcast Control Channel,PBCCH) n 為下行通道,提供GPRS用戶本基地台系統資訊
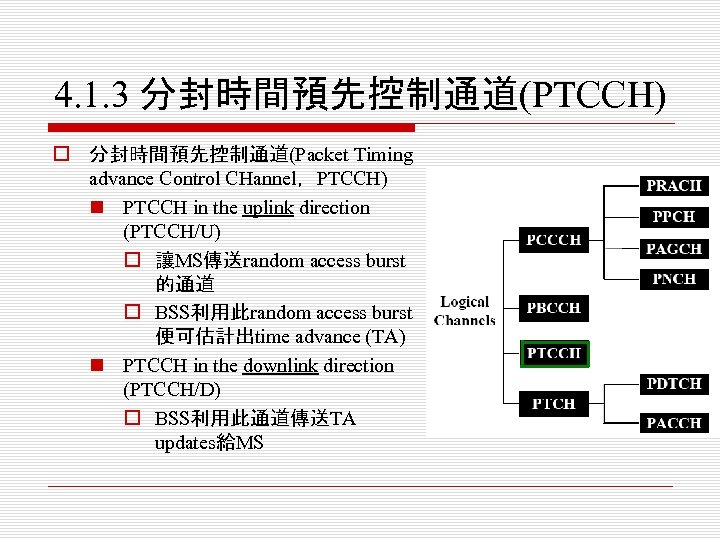 4. 1. 3 分封時間預先控制通道(PTCCH) o 分封時間預先控制通道(Packet Timing advance Control CHannel,PTCCH) n PTCCH in the uplink direction (PTCCH/U) o 讓MS傳送random access burst 的通道 o BSS利用此random access burst 便可估計出time advance (TA) n PTCCH in the downlink direction (PTCCH/D) o BSS利用此通道傳送TA updates給MS
4. 1. 3 分封時間預先控制通道(PTCCH) o 分封時間預先控制通道(Packet Timing advance Control CHannel,PTCCH) n PTCCH in the uplink direction (PTCCH/U) o 讓MS傳送random access burst 的通道 o BSS利用此random access burst 便可估計出time advance (TA) n PTCCH in the downlink direction (PTCCH/D) o BSS利用此通道傳送TA updates給MS
 4. 1. 4 分封傳輸通道(PTCH) o 分封傳輸通道(Packet Traffic Channel,PTCH) n 可上行與下行 n 分成兩類 o 分封數據傳輸通道(Packet Data Traffic Channel, PDTCH) o 分封相關控制通道(Packet Associated Control CHannel,PACCH)
4. 1. 4 分封傳輸通道(PTCH) o 分封傳輸通道(Packet Traffic Channel,PTCH) n 可上行與下行 n 分成兩類 o 分封數據傳輸通道(Packet Data Traffic Channel, PDTCH) o 分封相關控制通道(Packet Associated Control CHannel,PACCH)
 n 分封數據傳輸通道(Packet Data Traffic Channel, PDTCH) o 傳送資料的通道 o 一個PDTCH對應到一個實體通道 n 分封相關控制通道(Packet Associated Control CHannel,PACCH) o 當數據通道建立後,此通道負責傳送分封數 據建立與傳送過程所須的控制訊息
n 分封數據傳輸通道(Packet Data Traffic Channel, PDTCH) o 傳送資料的通道 o 一個PDTCH對應到一個實體通道 n 分封相關控制通道(Packet Associated Control CHannel,PACCH) o 當數據通道建立後,此通道負責傳送分封數 據建立與傳送過程所須的控制訊息
 4. 2 上行分封數據通道取得流程
4. 2 上行分封數據通道取得流程
![o 程序 n [步驟一] 當手機想利用GPRS傳送數據時,須透 過PRACH送出分封通道要求(packet channel request)爭取通道使用權 n [步驟二] 網路端將分配給此手機的分封數據通道, 透過分封即刻分配(packet immediate assignment) o 程序 n [步驟一] 當手機想利用GPRS傳送數據時,須透 過PRACH送出分封通道要求(packet channel request)爭取通道使用權 n [步驟二] 網路端將分配給此手機的分封數據通道, 透過分封即刻分配(packet immediate assignment)](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-113.jpg) o 程序 n [步驟一] 當手機想利用GPRS傳送數據時,須透 過PRACH送出分封通道要求(packet channel request)爭取通道使用權 n [步驟二] 網路端將分配給此手機的分封數據通道, 透過分封即刻分配(packet immediate assignment) 訊息通知用戶,此時就可開始傳送資料
o 程序 n [步驟一] 當手機想利用GPRS傳送數據時,須透 過PRACH送出分封通道要求(packet channel request)爭取通道使用權 n [步驟二] 網路端將分配給此手機的分封數據通道, 透過分封即刻分配(packet immediate assignment) 訊息通知用戶,此時就可開始傳送資料
![n [步驟三] 對需要較高速數據服務的用戶而言,其 用戶相關資訊與對頻寬的需求,可在PACCH通 道上送出分封資源要求(packet resource request) 告知網路,網路會衡量當時網路狀況,以分封 資源分配(packet resource assignment)訊息,分配 較多的PDCH(分封數據通道)給手機 n [步驟四] n [步驟三] 對需要較高速數據服務的用戶而言,其 用戶相關資訊與對頻寬的需求,可在PACCH通 道上送出分封資源要求(packet resource request) 告知網路,網路會衡量當時網路狀況,以分封 資源分配(packet resource assignment)訊息,分配 較多的PDCH(分封數據通道)給手機 n [步驟四]](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-114.jpg) n [步驟三] 對需要較高速數據服務的用戶而言,其 用戶相關資訊與對頻寬的需求,可在PACCH通 道上送出分封資源要求(packet resource request) 告知網路,網路會衡量當時網路狀況,以分封 資源分配(packet resource assignment)訊息,分配 較多的PDCH(分封數據通道)給手機 n [步驟四] 該預留的PACCH通道,使用戶不需再 透過PRACH的隨機存取競爭過程,就可直接將 分封資源要求送給網路
n [步驟三] 對需要較高速數據服務的用戶而言,其 用戶相關資訊與對頻寬的需求,可在PACCH通 道上送出分封資源要求(packet resource request) 告知網路,網路會衡量當時網路狀況,以分封 資源分配(packet resource assignment)訊息,分配 較多的PDCH(分封數據通道)給手機 n [步驟四] 該預留的PACCH通道,使用戶不需再 透過PRACH的隨機存取競爭過程,就可直接將 分封資源要求送給網路
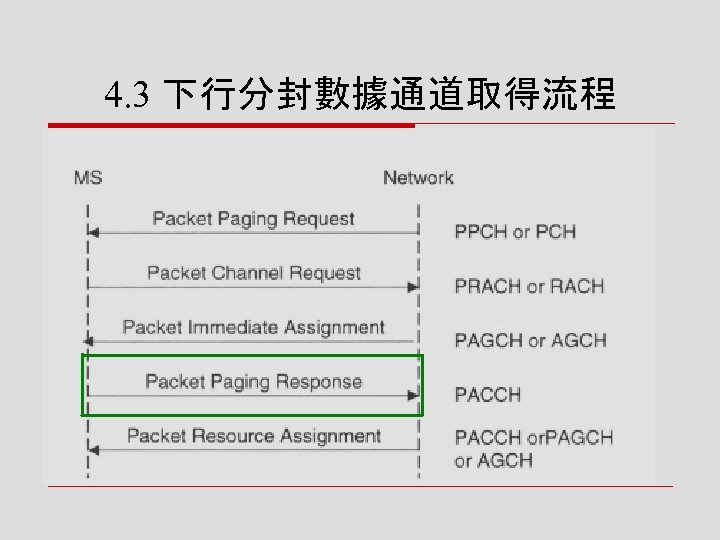 4. 3 下行分封數據通道取得流程
4. 3 下行分封數據通道取得流程
![o 程序 n [步驟一] 網路端首先須在 PPCH上呼叫手機,稱為分 封傳呼要求(packet paging request) n [步驟二] 手機需取得上行 的PRACH,回覆網路並送 出分封通道要求(packet o 程序 n [步驟一] 網路端首先須在 PPCH上呼叫手機,稱為分 封傳呼要求(packet paging request) n [步驟二] 手機需取得上行 的PRACH,回覆網路並送 出分封通道要求(packet](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-116.jpg) o 程序 n [步驟一] 網路端首先須在 PPCH上呼叫手機,稱為分 封傳呼要求(packet paging request) n [步驟二] 手機需取得上行 的PRACH,回覆網路並送 出分封通道要求(packet channel request) n [步驟三] 網路透過PAGCH 的分封即刻分配訊息,保 留一個PACCH通道給手機
o 程序 n [步驟一] 網路端首先須在 PPCH上呼叫手機,稱為分 封傳呼要求(packet paging request) n [步驟二] 手機需取得上行 的PRACH,回覆網路並送 出分封通道要求(packet channel request) n [步驟三] 網路透過PAGCH 的分封即刻分配訊息,保 留一個PACCH通道給手機
![n [步驟四] 手機將其分封傳呼 回應(packet paging response) 透過PACCH送回 n [步驟五] 當網路端確認無誤 後,以分封資源分配訊息通 知手機分封數據通道的資訊, 可開始傳送資料給用戶 n [步驟四] 手機將其分封傳呼 回應(packet paging response) 透過PACCH送回 n [步驟五] 當網路端確認無誤 後,以分封資源分配訊息通 知手機分封數據通道的資訊, 可開始傳送資料給用戶](https://present5.com/presentation/8fb5b5dd02da668298588da09021c519/image-117.jpg) n [步驟四] 手機將其分封傳呼 回應(packet paging response) 透過PACCH送回 n [步驟五] 當網路端確認無誤 後,以分封資源分配訊息通 知手機分封數據通道的資訊, 可開始傳送資料給用戶
n [步驟四] 手機將其分封傳呼 回應(packet paging response) 透過PACCH送回 n [步驟五] 當網路端確認無誤 後,以分封資源分配訊息通 知手機分封數據通道的資訊, 可開始傳送資料給用戶
 5. GPRS核心網路 o GPRS核心網路的服務區(service domains) n Circuit-switched service (CS) domain n Packet-switched service (PS) domain o 建立連線傳送packet時須先建立的內容 n Mobility Management (MM) context n Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context n Quality-of-Service (Qo. S) profile
5. GPRS核心網路 o GPRS核心網路的服務區(service domains) n Circuit-switched service (CS) domain n Packet-switched service (PS) domain o 建立連線傳送packet時須先建立的內容 n Mobility Management (MM) context n Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context n Quality-of-Service (Qo. S) profile
 5. 1 Location Tracking o MS可能同時在CS domain與PS domain上運作, 因此會分別有不同的location記錄,分開做 mobility management n 如MS與CS domain連上(i. e. 與GSM MS同),稱為 IMSI-attached o 此時以LA (Location Area)做為記錄MS位置的 基本單位,記錄於VLR上
5. 1 Location Tracking o MS可能同時在CS domain與PS domain上運作, 因此會分別有不同的location記錄,分開做 mobility management n 如MS與CS domain連上(i. e. 與GSM MS同),稱為 IMSI-attached o 此時以LA (Location Area)做為記錄MS位置的 基本單位,記錄於VLR上
 n 如MS與PS domain連上,稱為GPRS-attached o 此時以RA (Routing Area)做為記錄MS位置的 單位 o MS與SGSN都會有MS狀態的記錄 o 如果MS正在傳送數據,SGSN會以cell為單位 追蹤MS
n 如MS與PS domain連上,稱為GPRS-attached o 此時以RA (Routing Area)做為記錄MS位置的 單位 o MS與SGSN都會有MS狀態的記錄 o 如果MS正在傳送數據,SGSN會以cell為單位 追蹤MS
 5. 2 Mobility Management o 追蹤MS的位置,以傳送data給MS n GPRS自行定義所謂的Routing Area (RA),是數 個cell所組成的區域,當做是MS location的基本 單位 n 基本上Routing Area是GSM的Location Area的 subarea
5. 2 Mobility Management o 追蹤MS的位置,以傳送data給MS n GPRS自行定義所謂的Routing Area (RA),是數 個cell所組成的區域,當做是MS location的基本 單位 n 基本上Routing Area是GSM的Location Area的 subarea
 o 當MS跨越一個cell時,不一定會跨越routing area,當然也不見得會跨越location area,會 有下列三種狀況 n 一定要做cell update n 可能要做RA update及LA update
o 當MS跨越一個cell時,不一定會跨越routing area,當然也不見得會跨越location area,會 有下列三種狀況 n 一定要做cell update n 可能要做RA update及LA update
 o MS要執行GPRS的功能,須支援GPRS MM 功能,儲存 n MM (Mobility Management) context n PDP (Packet Data Protocol) context
o MS要執行GPRS的功能,須支援GPRS MM 功能,儲存 n MM (Mobility Management) context n PDP (Packet Data Protocol) context
 o MS存取GPRS服務 n 若MS使用具GPRS功能(GPRS-aware)的SIM card o 所有與GPRS相關的參數都會存在SIM中,並 在各個程序中取出使用 n 若MS使用沒有GPRS功能的SIM card o 這些特殊參數會存在ME (Mobile Equipment) 中,稱為IMSI image
o MS存取GPRS服務 n 若MS使用具GPRS功能(GPRS-aware)的SIM card o 所有與GPRS相關的參數都會存在SIM中,並 在各個程序中取出使用 n 若MS使用沒有GPRS功能的SIM card o 這些特殊參數會存在ME (Mobile Equipment) 中,稱為IMSI image
 o 其他GPRS使用到的參數,但與SIM無關,也 會存在ME中,包括 n n n MM state cell ID ciphering algorithm radio access classmark SGSN classmark PDP type. . .
o 其他GPRS使用到的參數,但與SIM無關,也 會存在ME中,包括 n n n MM state cell ID ciphering algorithm radio access classmark SGSN classmark PDP type. . .
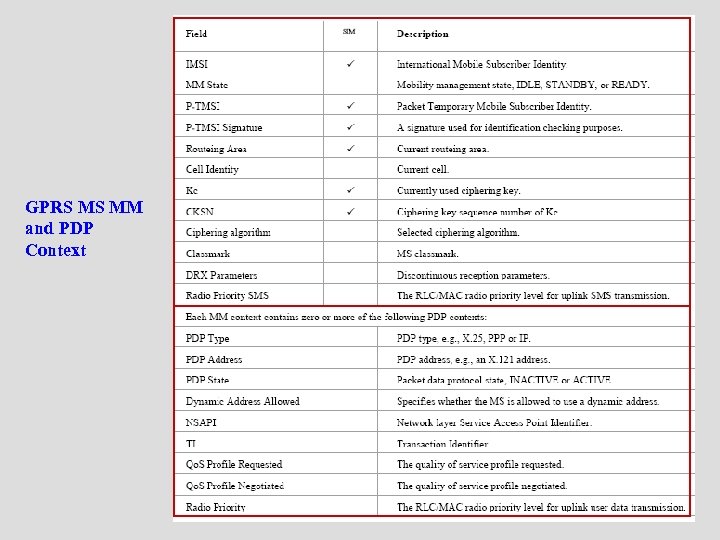 GPRS MS MM and PDP Context
GPRS MS MM and PDP Context
 o 與SIM相關的參數(在上圖SIM欄中標示為∨ 者) n IMSI (International mobile subscriber identity) o 用於存取VLR、HLR與SGSN、GGSN的資料 庫 n P-TMSI (Packet-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) o 是GPRS中與GSM TMSI功能相同的ID
o 與SIM相關的參數(在上圖SIM欄中標示為∨ 者) n IMSI (International mobile subscriber identity) o 用於存取VLR、HLR與SGSN、GGSN的資料 庫 n P-TMSI (Packet-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) o 是GPRS中與GSM TMSI功能相同的ID
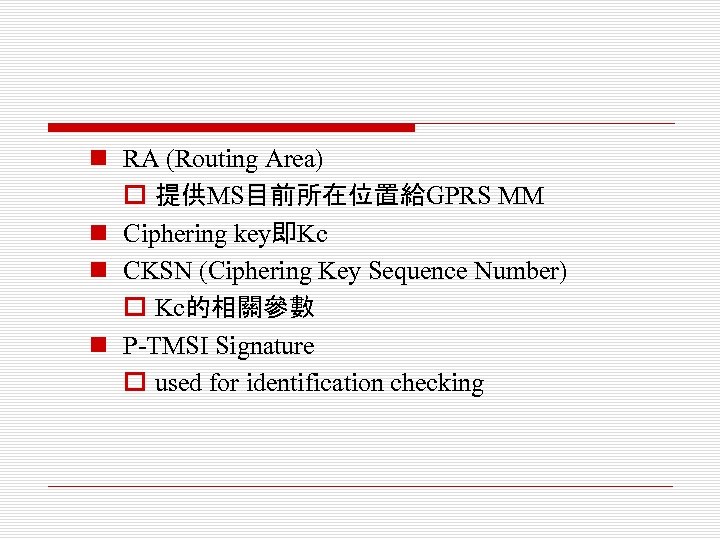 n RA (Routing Area) o 提供MS目前所在位置給GPRS MM n Ciphering key即Kc n CKSN (Ciphering Key Sequence Number) o Kc的相關參數 n P-TMSI Signature o used for identification checking
n RA (Routing Area) o 提供MS目前所在位置給GPRS MM n Ciphering key即Kc n CKSN (Ciphering Key Sequence Number) o Kc的相關參數 n P-TMSI Signature o used for identification checking
 o 與MM相關參數 n n MM state cell identity ciphering algorithm radio access classmark o 決定radio capabilities n 如multiple time slot capability、power class n SGSN classmark o 決定network-related capability n 如ciphering capability
o 與MM相關參數 n n MM state cell identity ciphering algorithm radio access classmark o 決定radio capabilities n 如multiple time slot capability、power class n SGSN classmark o 決定network-related capability n 如ciphering capability
 o 與PDP context相關參數 n n PDP type PDP address PDP state dynamic-address-allowed o 決定MS是否可使用dynamic address n requested and negotiated Qo. S profile
o 與PDP context相關參數 n n PDP type PDP address PDP state dynamic-address-allowed o 決定MS是否可使用dynamic address n requested and negotiated Qo. S profile
 5. 3 MM State o MM state用於描述MS在GPRS網路上目前 mobility的三種狀態(states) n IDLE state:MS尚未與GPRS MM建立起連繫(not GPRS-attached) n STANDBY state:MS已與GPRS MM連繫,但只 保留部份的location資訊(GPRS-attached) n READY state:MS已與GPRS連繫,且有詳細記 錄到MS cell位置的資訊(GPRS-attached)
5. 3 MM State o MM state用於描述MS在GPRS網路上目前 mobility的三種狀態(states) n IDLE state:MS尚未與GPRS MM建立起連繫(not GPRS-attached) n STANDBY state:MS已與GPRS MM連繫,但只 保留部份的location資訊(GPRS-attached) n READY state:MS已與GPRS連繫,且有詳細記 錄到MS cell位置的資訊(GPRS-attached)
 o 當MS想要傳送data時,就要進行GPRSattached procedure n MS與SGSN會記錄MS進入READY state,分別建 立一份MM context,之後可做authentication/ ciphering n 在GPRS-attached狀況下,MS與SGSN間會存在 邏輯上的連結(data link)
o 當MS想要傳送data時,就要進行GPRSattached procedure n MS與SGSN會記錄MS進入READY state,分別建 立一份MM context,之後可做authentication/ ciphering n 在GPRS-attached狀況下,MS與SGSN間會存在 邏輯上的連結(data link)
 o GPRS的兩種location tracking n READY state o SGSN知道MS所在的cell,當有packet要傳給 MS,paging cost低但location update cost高 o MS每跨一個cell都要做location update
o GPRS的兩種location tracking n READY state o SGSN知道MS所在的cell,當有packet要傳給 MS,paging cost低但location update cost高 o MS每跨一個cell都要做location update
 n STANDBY state o SGSN知道MS所在的RA,當有packet要傳給 MS,paging cost高但location update cost低 o MS跨RA時才要做location update
n STANDBY state o SGSN知道MS所在的RA,當有packet要傳給 MS,paging cost高但location update cost低 o MS跨RA時才要做location update
 5. 4 Mobility Management (MM) Context o MS及SGSN存放的MM context內含 n MM state n MM-related information o GPRS MS n 只連繫GSM網路(IMSI-attached) n 只連繫GPRS網路(GPRS-attached) n 可同時連繫GSM網路及GPRS網路(IMSI-attached 及GPRS-attached)
5. 4 Mobility Management (MM) Context o MS及SGSN存放的MM context內含 n MM state n MM-related information o GPRS MS n 只連繫GSM網路(IMSI-attached) n 只連繫GPRS網路(GPRS-attached) n 可同時連繫GSM網路及GPRS網路(IMSI-attached 及GPRS-attached)
 o MS在IDLE state時 n 不允許執行任何關於MM的procedure o 當啟動 GPRS-attach n 會由IDLE state變成READY state n 此時建立起MM context,分別在MS與SGSN各有 一MM context n 接下來進行authentication及ciphering n MS與SGSN建立起logic link,從MS做GPRS attach (READY,STANDBY),到GPRS detach ( 進入IDLE),期間稱為一個session
o MS在IDLE state時 n 不允許執行任何關於MM的procedure o 當啟動 GPRS-attach n 會由IDLE state變成READY state n 此時建立起MM context,分別在MS與SGSN各有 一MM context n 接下來進行authentication及ciphering n MS與SGSN建立起logic link,從MS做GPRS attach (READY,STANDBY),到GPRS detach ( 進入IDLE),期間稱為一個session
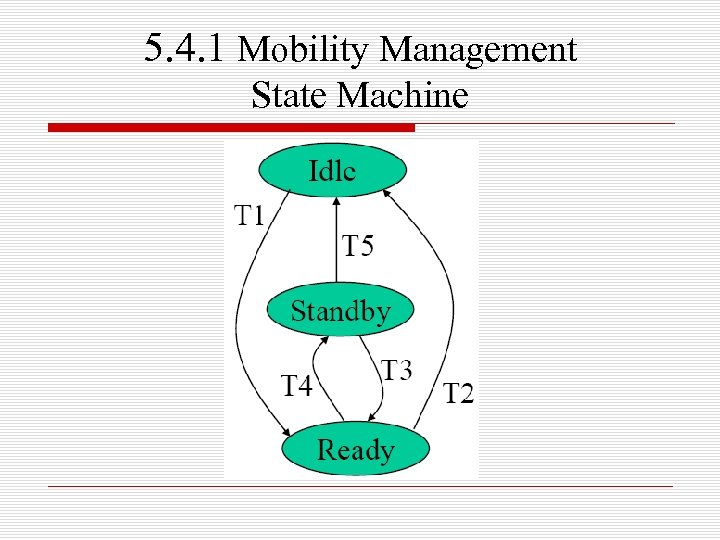 5. 4. 1 Mobility Management State Machine
5. 4. 1 Mobility Management State Machine
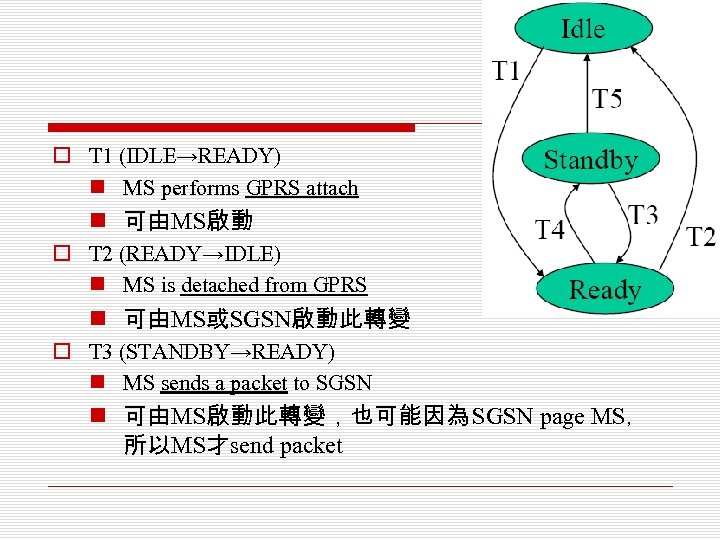 o T 1 (IDLE→READY) n MS performs GPRS attach n 可由MS啟動 o T 2 (READY→IDLE) n MS is detached from GPRS n 可由MS或SGSN啟動此轉變 o T 3 (STANDBY→READY) n MS sends a packet to SGSN n 可由MS啟動此轉變,也可能因為 SGSN page MS, 所以MS才send packet
o T 1 (IDLE→READY) n MS performs GPRS attach n 可由MS啟動 o T 2 (READY→IDLE) n MS is detached from GPRS n 可由MS或SGSN啟動此轉變 o T 3 (STANDBY→READY) n MS sends a packet to SGSN n 可由MS啟動此轉變,也可能因為 SGSN page MS, 所以MS才send packet
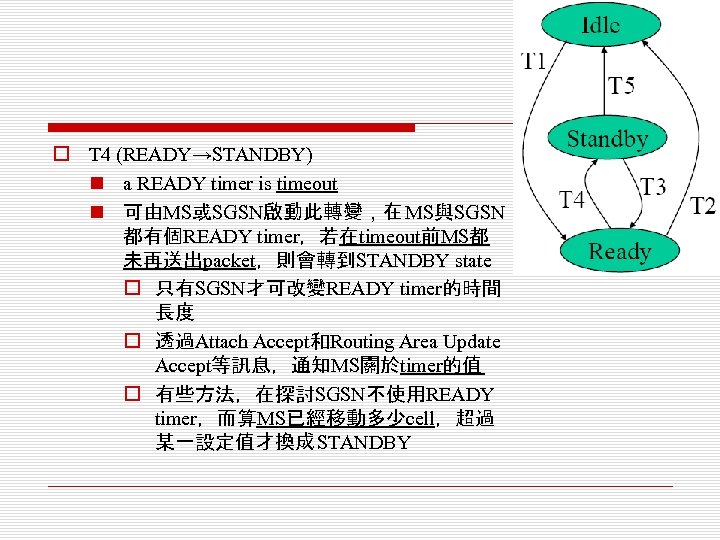 o T 4 (READY→STANDBY) n a READY timer is timeout n 可由MS或SGSN啟動此轉變,在 MS與SGSN 都有個READY timer,若在timeout前MS都 未再送出packet,則會轉到STANDBY state o 只有SGSN才可改變READY timer的時間 長度 o 透過Attach Accept和Routing Area Update Accept等訊息,通知MS關於timer的值 o 有些方法,在探討SGSN不使用READY timer,而算MS已經移動多少cell,超過 某一設定值才換成 STANDBY
o T 4 (READY→STANDBY) n a READY timer is timeout n 可由MS或SGSN啟動此轉變,在 MS與SGSN 都有個READY timer,若在timeout前MS都 未再送出packet,則會轉到STANDBY state o 只有SGSN才可改變READY timer的時間 長度 o 透過Attach Accept和Routing Area Update Accept等訊息,通知MS關於timer的值 o 有些方法,在探討SGSN不使用READY timer,而算MS已經移動多少cell,超過 某一設定值才換成 STANDBY
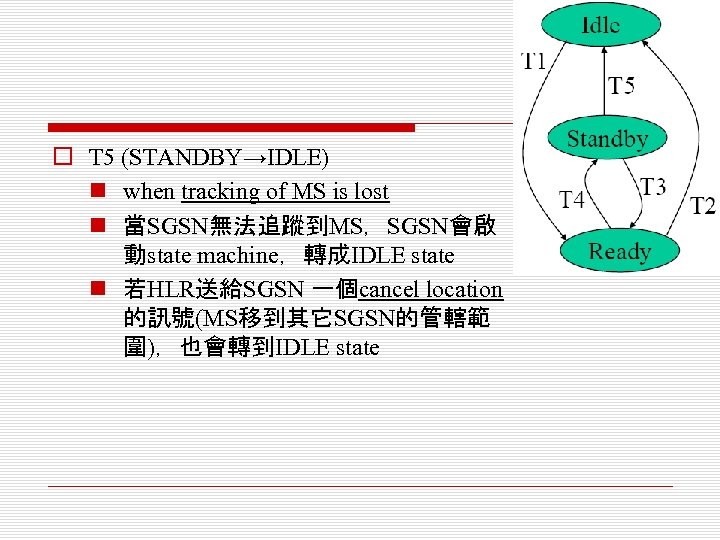 o T 5 (STANDBY→IDLE) n when tracking of MS is lost n 當SGSN無法追蹤到MS,SGSN會啟 動state machine,轉成IDLE state n 若HLR送給SGSN 一個cancel location 的訊號(MS移到其它SGSN的管轄範 圍),也會轉到IDLE state
o T 5 (STANDBY→IDLE) n when tracking of MS is lost n 當SGSN無法追蹤到MS,SGSN會啟 動state machine,轉成IDLE state n 若HLR送給SGSN 一個cancel location 的訊號(MS移到其它SGSN的管轄範 圍),也會轉到IDLE state
 5. 4. 1. 1 STANDBY State o MS執行GPRS-attached,MS進入STANDBY 狀態 n MS開始偵測是否有被呼叫要傳送資料或訊號 n 此時仍不可進行資料傳輸(只有在READY才能傳 送資料) n 若要傳送資料,可進行PDP context activation (ACTIVE) n 也可讓已經進入ACTIVE的PDP context回到 INACTIVE
5. 4. 1. 1 STANDBY State o MS執行GPRS-attached,MS進入STANDBY 狀態 n MS開始偵測是否有被呼叫要傳送資料或訊號 n 此時仍不可進行資料傳輸(只有在READY才能傳 送資料) n 若要傳送資料,可進行PDP context activation (ACTIVE) n 也可讓已經進入ACTIVE的PDP context回到 INACTIVE
 n 一旦MS要傳送data (PDP context進入ACTIVE), 或MS被呼叫,就會自動進入READY狀態 n 如果執行GPRS-detach,就會結束MM連接,回 到IDLE狀態 n 對於追蹤MM的位置,SGSN只記錄到MS所在 RA的位置 n 當MS跨越RA時,會執行GMM RA update procedure (GPRS Mobility Management Routing Area update procedure)
n 一旦MS要傳送data (PDP context進入ACTIVE), 或MS被呼叫,就會自動進入READY狀態 n 如果執行GPRS-detach,就會結束MM連接,回 到IDLE狀態 n 對於追蹤MM的位置,SGSN只記錄到MS所在 RA的位置 n 當MS跨越RA時,會執行GMM RA update procedure (GPRS Mobility Management Routing Area update procedure)
 5. 4. 1. 2 READY State o MS做GPRS-attached動作,MS進入READY 狀態 n GPRS網路執行GPRS cell selection及re-selection n 當跨越cell時,會執行cell update;跨越RA時, 會執行RA update n 資料封包外層的BSSGP (Base Station System GPRS Protocol) header包含 o GCI (Global Cell Identity) o RAC (Routing Area Code) o LAC (Location Area Code)
5. 4. 1. 2 READY State o MS做GPRS-attached動作,MS進入READY 狀態 n GPRS網路執行GPRS cell selection及re-selection n 當跨越cell時,會執行cell update;跨越RA時, 會執行RA update n 資料封包外層的BSSGP (Base Station System GPRS Protocol) header包含 o GCI (Global Cell Identity) o RAC (Routing Area Code) o LAC (Location Area Code)
 n 可發送及接受PDP n 網路不再為處於READY state的手機起始GPRS 呼叫 n CS Page o SGSN可接受由MSC發來的calls或SM (Session Management)的連線要求,並經由GPRS channel呼 叫被呼的手機 o 手機隨後使用一般GSM channel回應呼叫
n 可發送及接受PDP n 網路不再為處於READY state的手機起始GPRS 呼叫 n CS Page o SGSN可接受由MSC發來的calls或SM (Session Management)的連線要求,並經由GPRS channel呼 叫被呼的手機 o 手機隨後使用一般GSM channel回應呼叫
 o Ready State的其它特性 n 若要傳送資料,可進行PDP context activation n 也可讓已經進入ACTIVE的PDP context回到 INACTIVE n 當READY State的timer結束時,MS會回到 STANDBY狀態
o Ready State的其它特性 n 若要傳送資料,可進行PDP context activation n 也可讓已經進入ACTIVE的PDP context回到 INACTIVE n 當READY State的timer結束時,MS會回到 STANDBY狀態
 5. 4. 2 SGSN MM Context o 對每個MS使用者,會有一相對應的SGSN MM Context, 包含下列資訊 n IMSI (the main reference key in SGSN) n P-TMSI (Packet-TMSI) n P-TMSI Signature (used for identification checking purposes) n MSISDN n IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity)
5. 4. 2 SGSN MM Context o 對每個MS使用者,會有一相對應的SGSN MM Context, 包含下列資訊 n IMSI (the main reference key in SGSN) n P-TMSI (Packet-TMSI) n P-TMSI Signature (used for identification checking purposes) n MSISDN n IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity)
 n MM state (Mobility Management state) o 可以是IDLE、STANDBY或 READY n Routing area o MS目前所在的routing area n Cell identity o 若MS是READY n cell identity是目前所在的cell ID o 若MS是STANDBY或IDLE n cell identity是最後一次READY得到的cell ID
n MM state (Mobility Management state) o 可以是IDLE、STANDBY或 READY n Routing area o MS目前所在的routing area n Cell identity o 若MS是READY n cell identity是目前所在的cell ID o 若MS是STANDBY或IDLE n cell identity是最後一次READY得到的cell ID
 n Cell identity age o 最後一個MS送LLC PDU到SGSN之已經過的時間 n VLR number o 正在負責該MS的VLR號碼 n New SGSN address o the IP address of the new SGSN where buffered and not sent should be forwarded to n Authentication, ciphering parameters, current ciphering key Kc, and the selected ciphering algorithm
n Cell identity age o 最後一個MS送LLC PDU到SGSN之已經過的時間 n VLR number o 正在負責該MS的VLR號碼 n New SGSN address o the IP address of the new SGSN where buffered and not sent should be forwarded to n Authentication, ciphering parameters, current ciphering key Kc, and the selected ciphering algorithm
 n Radio access classmark (MS radio access capabilities) n SGSN classmark (MS network capabilities) n Mobile station Not Reachable for GPRS flag (MNRG) o indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the HLR n Non-GPRS Alert Flag (NGAF) o indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the MSC/VLR n Paging Proceed Flag (PPF) o indicates whether paging for GPRS and non-GPRS services can be initiated
n Radio access classmark (MS radio access capabilities) n SGSN classmark (MS network capabilities) n Mobile station Not Reachable for GPRS flag (MNRG) o indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the HLR n Non-GPRS Alert Flag (NGAF) o indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the MSC/VLR n Paging Proceed Flag (PPF) o indicates whether paging for GPRS and non-GPRS services can be initiated
 5. 5 PDP (Packet Data Protocol) o 對於每條GGSN與MS間傳送封包的連結,都 會在各個節點建立起相對應的PDP context以 描述該session n MS、HLR、SGSN與GGSN都會有PDP context n 進行資料傳輸前,MS要先做PDP context activation procedure,最後做PDP context deactivation n PDP context有兩種狀態:ACTIVE與INACTIVE o 建立起PDP context,GGSN才會知道MS的存 在,也才能讓MS與外界網路通訊
5. 5 PDP (Packet Data Protocol) o 對於每條GGSN與MS間傳送封包的連結,都 會在各個節點建立起相對應的PDP context以 描述該session n MS、HLR、SGSN與GGSN都會有PDP context n 進行資料傳輸前,MS要先做PDP context activation procedure,最後做PDP context deactivation n PDP context有兩種狀態:ACTIVE與INACTIVE o 建立起PDP context,GGSN才會知道MS的存 在,也才能讓MS與外界網路通訊
 5. 5. 1 PDP Context o 當MS在STANDBY或READY的MM state時,可開啟 PDP context,而且令PDP context由INACTIVE改為 ACTIVE n 經過此程序後,GGSN才有MS的記錄,才可傳送資 料到外部網路 o 一個MS可有多個PDP context,分別是不同的session n 雖是同一個MS,但不同PDP context需使用不同IP address,所以terminal要有支援Multiple IP addresses 的功能
5. 5. 1 PDP Context o 當MS在STANDBY或READY的MM state時,可開啟 PDP context,而且令PDP context由INACTIVE改為 ACTIVE n 經過此程序後,GGSN才有MS的記錄,才可傳送資 料到外部網路 o 一個MS可有多個PDP context,分別是不同的session n 雖是同一個MS,但不同PDP context需使用不同IP address,所以terminal要有支援Multiple IP addresses 的功能
 o 對ACTIVE PDP context做deactivated時,會由ACTIVE state回到INACTIVE state o 如MS做GPRS-detached,所有PDP contexts都會作廢
o 對ACTIVE PDP context做deactivated時,會由ACTIVE state回到INACTIVE state o 如MS做GPRS-detached,所有PDP contexts都會作廢
 5. 5. 2 SGSN PDP Context o 對每個MM context (一個user),可能會有零或多個 PDP context o SGSN PDP context含有下列資訊 n PDP context identifier (index of PDP context), PDP type (e. g. , X. 25, PPP or IP), PDP address (e. g. , an X. 25 address), PDP state (Active, or Inactive) n Access Point Name (APN) to the external data network n Qo. S profile subscribed, Qo. S profile requested, Qo. S profile negotiated
5. 5. 2 SGSN PDP Context o 對每個MM context (一個user),可能會有零或多個 PDP context o SGSN PDP context含有下列資訊 n PDP context identifier (index of PDP context), PDP type (e. g. , X. 25, PPP or IP), PDP address (e. g. , an X. 25 address), PDP state (Active, or Inactive) n Access Point Name (APN) to the external data network n Qo. S profile subscribed, Qo. S profile requested, Qo. S profile negotiated
 n GGSN address in use o IP address of the GGSN currently used by the activated PDP context n Charging ID o charging identifier, identifies charging record generated by SGSN and GGSN
n GGSN address in use o IP address of the GGSN currently used by the activated PDP context n Charging ID o charging identifier, identifies charging record generated by SGSN and GGSN
 5. 6 Qo. S Profile o Qo. S profile中的attributes包括 n precedence class o 有三種傳送等級的優先權,如遇到congestion, 最低等級的封包將最先被丟棄
5. 6 Qo. S Profile o Qo. S profile中的attributes包括 n precedence class o 有三種傳送等級的優先權,如遇到congestion, 最低等級的封包將最先被丟棄
 n delay class o 傳送128位元組,所期望的傳輸速率有四種延 遲等級的優先權 n class 1:delay小於 0. 5 sec n class 2:delay小於 5 sec n class 3:delay小於 50 sec n class 4:best-effort (未指定任何傳輸速度的 限制)
n delay class o 傳送128位元組,所期望的傳輸速率有四種延 遲等級的優先權 n class 1:delay小於 0. 5 sec n class 2:delay小於 5 sec n class 3:delay小於 50 sec n class 4:best-effort (未指定任何傳輸速度的 限制)
 n peak throughput class o 設定期望的最大資料傳輸速率(maximum data transmission rate) 9種等級,從 8 Kbps到 2, 048 Kbps n mean throughput class o 指定平均的資料傳輸速率(average data transmission rate) 19種等級,從best-effort到 111 Kbps
n peak throughput class o 設定期望的最大資料傳輸速率(maximum data transmission rate) 9種等級,從 8 Kbps到 2, 048 Kbps n mean throughput class o 指定平均的資料傳輸速率(average data transmission rate) 19種等級,從best-effort到 111 Kbps
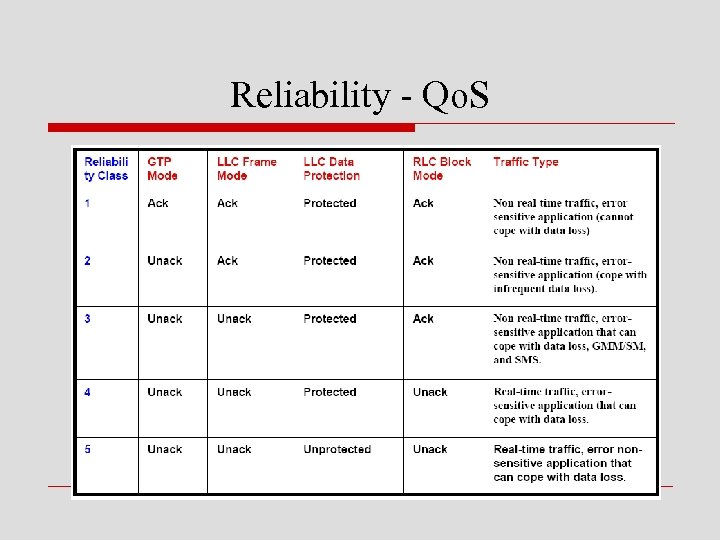
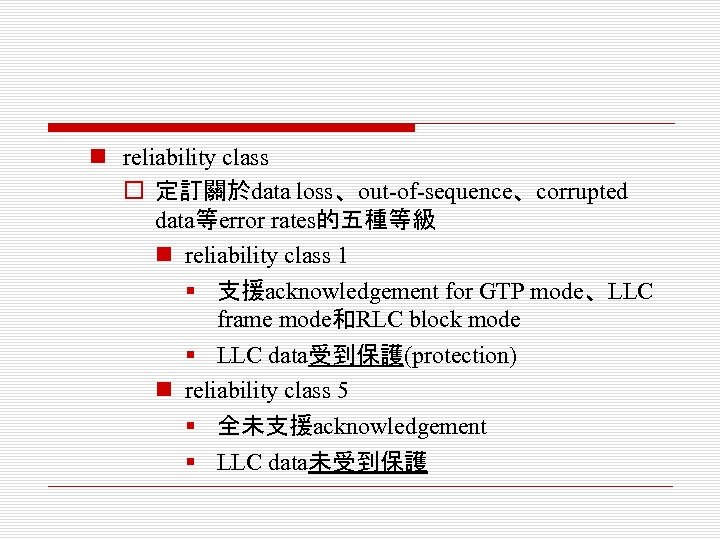 n reliability class o 定訂關於data loss、out-of-sequence、corrupted data等error rates的五種等級 n reliability class 1 § 支援acknowledgement for GTP mode、LLC frame mode和RLC block mode § LLC data受到保護(protection) n reliability class 5 § 全未支援acknowledgement § LLC data未受到保護
n reliability class o 定訂關於data loss、out-of-sequence、corrupted data等error rates的五種等級 n reliability class 1 § 支援acknowledgement for GTP mode、LLC frame mode和RLC block mode § LLC data受到保護(protection) n reliability class 5 § 全未支援acknowledgement § LLC data未受到保護
 Reliability - Qo. S
Reliability - Qo. S
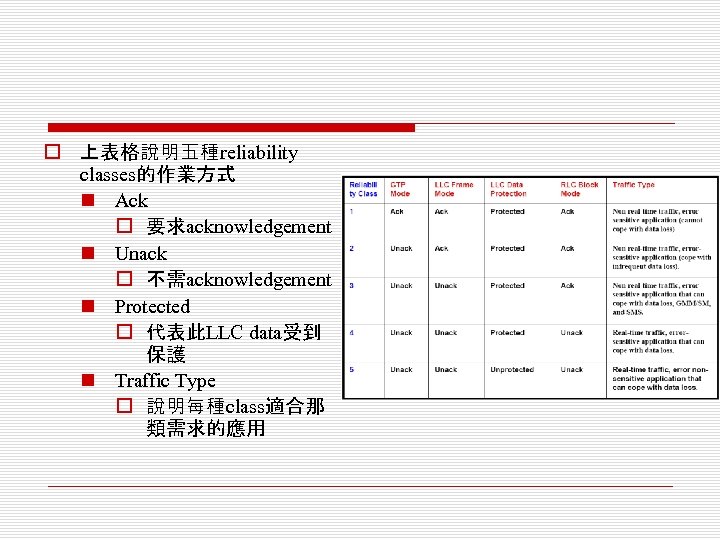 o 上表格說明五種reliability classes的作業方式 n Ack o 要求acknowledgement n Unack o 不需acknowledgement n Protected o 代表此LLC data受到 保護 n Traffic Type o 說明每種class適合那 類需求的應用
o 上表格說明五種reliability classes的作業方式 n Ack o 要求acknowledgement n Unack o 不需acknowledgement n Protected o 代表此LLC data受到 保護 n Traffic Type o 說明每種class適合那 類需求的應用


