28f1dd9e1b8f97c01e61deb30839b02c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 11: A World of States Victoria Alapo, Instructor Geog 1010
Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 11: A World of States Victoria Alapo, Instructor Geog 1010
 Nations & States n What is the difference btw a Nation & a State? ¡ ¡ States are political boundaries i. e. countries Nations are just the people themselves not the boundaries. n See “stateless nations” (textbook, pg 448). Any Examples? n Nation-States ¡ ¡ Many European countries are Nation-States (e. g. ? ) These are a single set of people who share the same ideals/culture within the state.
Nations & States n What is the difference btw a Nation & a State? ¡ ¡ States are political boundaries i. e. countries Nations are just the people themselves not the boundaries. n See “stateless nations” (textbook, pg 448). Any Examples? n Nation-States ¡ ¡ Many European countries are Nation-States (e. g. ? ) These are a single set of people who share the same ideals/culture within the state.
 Formation Outside Europe n Superimposed boundaries ¡ European colonial rule. See next slide. Many African countries are NOT nationstates. This is because of the various cultures within each country.
Formation Outside Europe n Superimposed boundaries ¡ European colonial rule. See next slide. Many African countries are NOT nationstates. This is because of the various cultures within each country.

 The Shapes of States n n Compact shape is closest to the “circular ideal”. Prorupted ¡ n n Sometimes formed because of corridors to the sea/ navigable waterways e. g. Dem. Rep. of Congo; Namibia. Elongated e. g. Chile Archipelago – these are islands. Usually called “fragmented states”. E. g. Japan, Philippines, Indonesia. Perforated – e. g. S/Africa; Italy (perforated by the Vatican and San Marino). What Shape is the U. S. ?
The Shapes of States n n Compact shape is closest to the “circular ideal”. Prorupted ¡ n n Sometimes formed because of corridors to the sea/ navigable waterways e. g. Dem. Rep. of Congo; Namibia. Elongated e. g. Chile Archipelago – these are islands. Usually called “fragmented states”. E. g. Japan, Philippines, Indonesia. Perforated – e. g. S/Africa; Italy (perforated by the Vatican and San Marino). What Shape is the U. S. ?

 Subdivision & Representation n Defining the balance of power between local and national government n Unitary ¡ n Power lies at the center (that is, central govt/capital) Federal ¡ ¡ ¡ Power lies with the subunits (local states) In Canada, provinces have more power than in U. S. local states However, Ontario and Quebec dominate national government in Canada
Subdivision & Representation n Defining the balance of power between local and national government n Unitary ¡ n Power lies at the center (that is, central govt/capital) Federal ¡ ¡ ¡ Power lies with the subunits (local states) In Canada, provinces have more power than in U. S. local states However, Ontario and Quebec dominate national government in Canada

 Representative Districts n Electoral Geography ¡ ¡ n Sub-field of political geography Voting districts and boundaries Gerrymandering ¡ ¡ Manipulating boundaries so that one group gains unfair advantage Here, district lines can be drawn in such a way to include/exclude specific groups of voters. See cartoon (textbook, pg 472).
Representative Districts n Electoral Geography ¡ ¡ n Sub-field of political geography Voting districts and boundaries Gerrymandering ¡ ¡ Manipulating boundaries so that one group gains unfair advantage Here, district lines can be drawn in such a way to include/exclude specific groups of voters. See cartoon (textbook, pg 472).
 Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 12: National Paths to Economic Growth Victoria Alapo, Instructor Geog 1010
Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 12: National Paths to Economic Growth Victoria Alapo, Instructor Geog 1010
 Measures of Gross Product n Gross domestic product (GDP) ¡ Total value of all goods and services produced within a country, and it’s measured per capita (per person) Measurement Limitations: n Undercounting of subsistence peoples and areas. Govts only count activities can be taxed. n Exaggerating the impact of cities n Underground, informal (or even Illegal) economies. See points made above. n Varying exchange rates; always converting things in other countries to “dollars”.
Measures of Gross Product n Gross domestic product (GDP) ¡ Total value of all goods and services produced within a country, and it’s measured per capita (per person) Measurement Limitations: n Undercounting of subsistence peoples and areas. Govts only count activities can be taxed. n Exaggerating the impact of cities n Underground, informal (or even Illegal) economies. See points made above. n Varying exchange rates; always converting things in other countries to “dollars”.


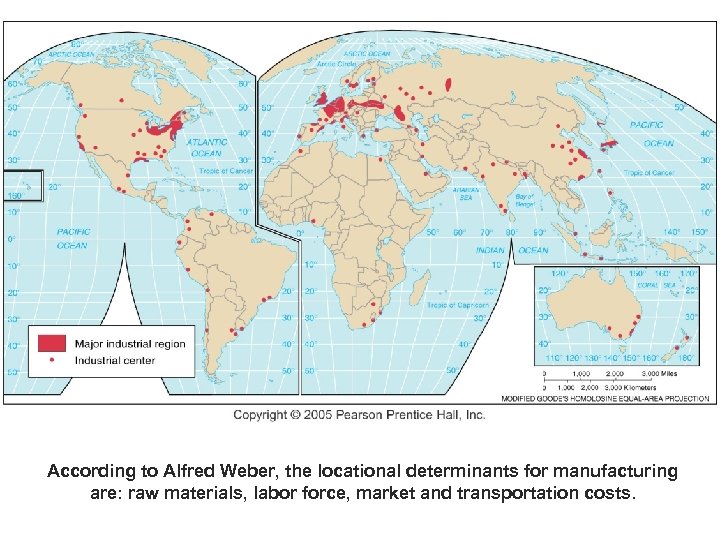 According to Alfred Weber, the locational determinants for manufacturing are: raw materials, labor force, market and transportation costs.
According to Alfred Weber, the locational determinants for manufacturing are: raw materials, labor force, market and transportation costs.
 Types of Political Economies n Communism – direct govt. involvement; everything is nationalized. n Capitalism – private enterprise and stock market are determinants ¡ n However, government still has a role e. g. regulations (EPA, etc), types of production during war, etc Mixed economies – most countries are in this “in -between”.
Types of Political Economies n Communism – direct govt. involvement; everything is nationalized. n Capitalism – private enterprise and stock market are determinants ¡ n However, government still has a role e. g. regulations (EPA, etc), types of production during war, etc Mixed economies – most countries are in this “in -between”.
 Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 13: Political Regionalization and Globalization Victoria Alapo Geog 1010
Introduction to Geography People, Places, and Environment, 4 e Edward F. Bergman William H. Renwick Chapter 13: Political Regionalization and Globalization Victoria Alapo Geog 1010
 Multiple Nation Organizations n Supranational organizations: when 3 or more countries come together for economic/ political/ cultural reasons e. g. n EU (European Union); see next slide AU (African Union); NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement); CARICOM (English speaking countries of the Caribbean); MERCOSUR (Latin American countries); ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations); ECOWAS – Econ. Community of West African States; Arab League, etc n n n n
Multiple Nation Organizations n Supranational organizations: when 3 or more countries come together for economic/ political/ cultural reasons e. g. n EU (European Union); see next slide AU (African Union); NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement); CARICOM (English speaking countries of the Caribbean); MERCOSUR (Latin American countries); ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations); ECOWAS – Econ. Community of West African States; Arab League, etc n n n n
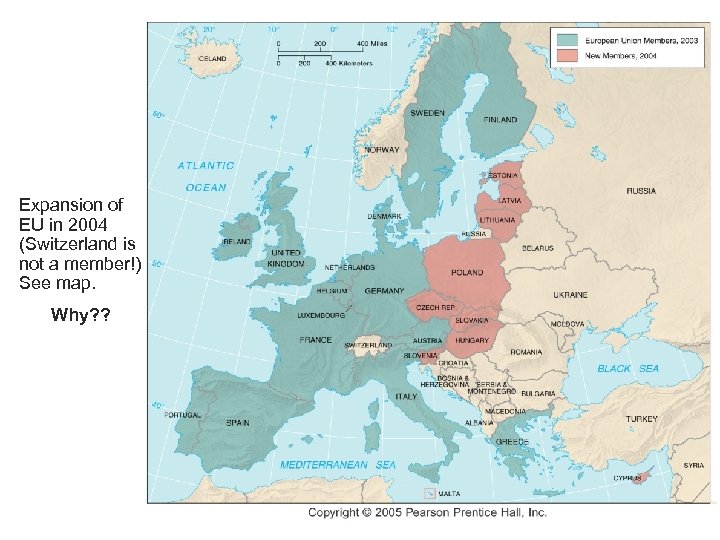 Expansion of EU in 2004 (Switzerland is not a member!) See map. Why? ?
Expansion of EU in 2004 (Switzerland is not a member!) See map. Why? ?

 NAFTA n North American Free Trade Agreement ¡ 1994, between Canada, U. S. and Mexico. ¡ As of 2004, the EU was larger in total members, population, income. ¡ Promotes free trade, easier investment flows. And because of cheaper labor, also led to the increase in Maquiladoras (foreign-owned factories), esp. in Mexico.
NAFTA n North American Free Trade Agreement ¡ 1994, between Canada, U. S. and Mexico. ¡ As of 2004, the EU was larger in total members, population, income. ¡ Promotes free trade, easier investment flows. And because of cheaper labor, also led to the increase in Maquiladoras (foreign-owned factories), esp. in Mexico.
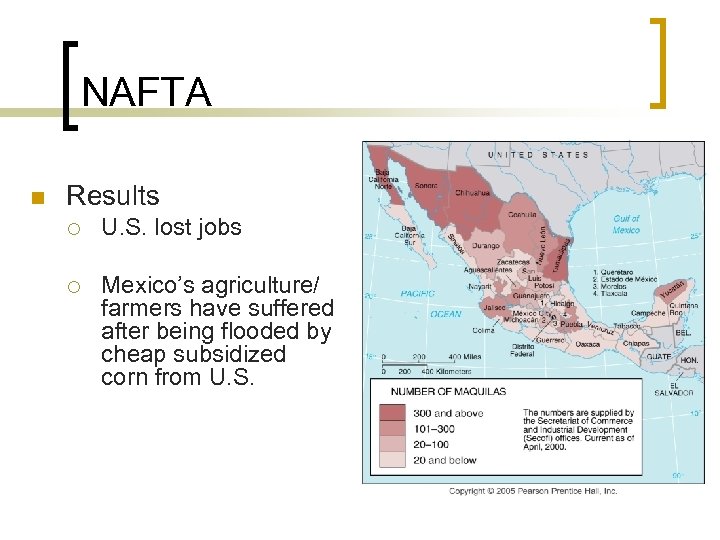 NAFTA n Results ¡ U. S. lost jobs ¡ Mexico’s agriculture/ farmers have suffered after being flooded by cheap subsidized corn from U. S.
NAFTA n Results ¡ U. S. lost jobs ¡ Mexico’s agriculture/ farmers have suffered after being flooded by cheap subsidized corn from U. S.
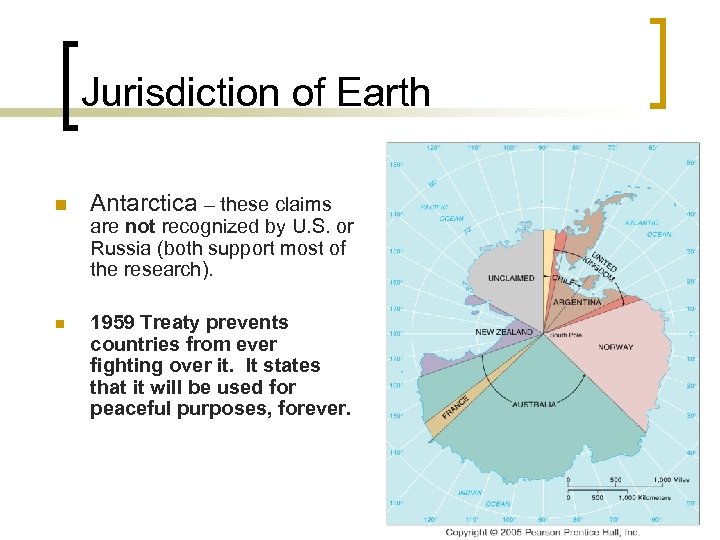 Jurisdiction of Earth n Antarctica – these claims are not recognized by U. S. or Russia (both support most of the research). n 1959 Treaty prevents countries from ever fighting over it. It states that it will be used for peaceful purposes, forever.
Jurisdiction of Earth n Antarctica – these claims are not recognized by U. S. or Russia (both support most of the research). n 1959 Treaty prevents countries from ever fighting over it. It states that it will be used for peaceful purposes, forever.
 British Empire n n 1900 peak (¼ of Earth’s land surface) Vestiges of British culture remain in: ¡ ¡ Legal system (see pg 457), Anglican churches, language, education Queen Elizabeth still head of state in 16 countries in addition to UK n ¡ Canada, New Zealand, Jamaica Northern Ireland n n 26 of 32 counties independent from UK in 1921 Ulster province (6 counties) chose to remain with UK – (Protestants – majority; Catholics – minority).
British Empire n n 1900 peak (¼ of Earth’s land surface) Vestiges of British culture remain in: ¡ ¡ Legal system (see pg 457), Anglican churches, language, education Queen Elizabeth still head of state in 16 countries in addition to UK n ¡ Canada, New Zealand, Jamaica Northern Ireland n n 26 of 32 counties independent from UK in 1921 Ulster province (6 counties) chose to remain with UK – (Protestants – majority; Catholics – minority).
 French Empire n French Republic today: ¡ ¡ ¡ France Overseas departments and territorial collectives (e. g. French Guiana). A LOT of islands
French Empire n French Republic today: ¡ ¡ ¡ France Overseas departments and territorial collectives (e. g. French Guiana). A LOT of islands
 Ottoman Empire n n Turkey emerged in 1920 s with collapse of Ottoman Empire Middle East divided between France and Britain after Ottoman Empire collapsed. ¡ Arabs loyal to clans, families, ethnic groups, than to countries. ¡ Israel – Jewish homeland
Ottoman Empire n n Turkey emerged in 1920 s with collapse of Ottoman Empire Middle East divided between France and Britain after Ottoman Empire collapsed. ¡ Arabs loyal to clans, families, ethnic groups, than to countries. ¡ Israel – Jewish homeland
 United States Empire n Cuba – taken from Spain in 1898 and colonized by the U. S. Granted independence in 1934; naval base maintained in Guantanamo Bay. n Philippines – colonized by the U. S. from 1898 -1946, after Spain was defeated. n Panama ¡ U. S. provoked uprising for independence (1903), then leased canal from new govt. , completing the work started by the French. Canal surrendered in 1999. ¡ 1989 invasion – to bring dictator, Manuel Noriega to U. S. for trial; occupied Panama until late 1999; drug trafficking did NOT go down, despite invasion.
United States Empire n Cuba – taken from Spain in 1898 and colonized by the U. S. Granted independence in 1934; naval base maintained in Guantanamo Bay. n Philippines – colonized by the U. S. from 1898 -1946, after Spain was defeated. n Panama ¡ U. S. provoked uprising for independence (1903), then leased canal from new govt. , completing the work started by the French. Canal surrendered in 1999. ¡ 1989 invasion – to bring dictator, Manuel Noriega to U. S. for trial; occupied Panama until late 1999; drug trafficking did NOT go down, despite invasion.
 United States Empire n Liberia Ethnic conflict – U. S. involvement due to historical reasons (freed U. S. slaves settled there). n Islands – large number still under U. S. control ¡ n Puerto Rico ¡ ¡ 1952 free commonwealth; not a 51 st state. U. S. citizens who cannot vote; use dollar bill, pay no income taxes, but under jurisdiction of Fed. Govt. Resource poor, densely populated, low per capita income. Poorer than the U. S. ’ poorest State (Mississippi).
United States Empire n Liberia Ethnic conflict – U. S. involvement due to historical reasons (freed U. S. slaves settled there). n Islands – large number still under U. S. control ¡ n Puerto Rico ¡ ¡ 1952 free commonwealth; not a 51 st state. U. S. citizens who cannot vote; use dollar bill, pay no income taxes, but under jurisdiction of Fed. Govt. Resource poor, densely populated, low per capita income. Poorer than the U. S. ’ poorest State (Mississippi).
 Russian Empire n Vladimir Lenin (1870 -1924) ¡ ¡ n Communist leader, control in 1917 Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (1922) 1990 ¡ ¡ USSR consisted of 15 union republics 17% of Earth’s land area (excluding Antarctica) Russia was the largest republic in USSR (76%) Russian acculturation, influence & infiltration over centuries (see next slide)
Russian Empire n Vladimir Lenin (1870 -1924) ¡ ¡ n Communist leader, control in 1917 Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (1922) 1990 ¡ ¡ USSR consisted of 15 union republics 17% of Earth’s land area (excluding Antarctica) Russia was the largest republic in USSR (76%) Russian acculturation, influence & infiltration over centuries (see next slide)
 Break-up of Soviet Union n Gorbachev ¡ n Glasnost ¡ n n n Freedom of speech and press Perestroika ¡ n Became leader in 1985, and introduced: Restructuring of economy and politics Led to events and policies could not be controlled 15 new countries Economic struggles with Capitalism (see Russia video).
Break-up of Soviet Union n Gorbachev ¡ n Glasnost ¡ n n n Freedom of speech and press Perestroika ¡ n Became leader in 1985, and introduced: Restructuring of economy and politics Led to events and policies could not be controlled 15 new countries Economic struggles with Capitalism (see Russia video).
 Developments in Russia n n n Economic challenges Privatization of state-owned economy & “grabbing”. Slow progress Chechnya fighting for independence Advantages Russia has: ¡ ¡ ¡ Educated workforce Natural resources Scientific institutes
Developments in Russia n n n Economic challenges Privatization of state-owned economy & “grabbing”. Slow progress Chechnya fighting for independence Advantages Russia has: ¡ ¡ ¡ Educated workforce Natural resources Scientific institutes


