f72c3a0052ce33c7a2919fdd5156c5b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Introduction to Galileo Image: ESA
Introduction to Galileo Image: ESA
 Overview 4 4 4 4 Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation Technological Developments Experimental Satellites IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures Galileo Signals Galileo Services GPS & Galileo GNSS Market
Overview 4 4 4 4 Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation Technological Developments Experimental Satellites IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures Galileo Signals Galileo Services GPS & Galileo GNSS Market
 Galileo Programme Phases 4 4 4 Definition – Complete 2003 Development & In-Orbit Validation - Current Full Deployment and Operations 2003 2005 2008 2010 Images: ESA GPS Constellation GSTB V 1 Galileo Exp. SV (2) GSTB V 2 Galileo In Orbit Validation Const. (4) Galileo Full Operational Const. (30) IOV Phase FOC Phase Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
Galileo Programme Phases 4 4 4 Definition – Complete 2003 Development & In-Orbit Validation - Current Full Deployment and Operations 2003 2005 2008 2010 Images: ESA GPS Constellation GSTB V 1 Galileo Exp. SV (2) GSTB V 2 Galileo In Orbit Validation Const. (4) Galileo Full Operational Const. (30) IOV Phase FOC Phase Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
 Planning and Funding 48 Months 24 Months 20 Years Development and Validation Deployment 1. 2 Billion € 220 Million € per year Public 1/3 Public, 2/3 Private 1 -2 Test Satellite & 4 Operational Satellites 26 Satellites Ground Infrastructure EC/ESA Joint Undertaking Ground Infrastructure Operations and Maintenance Routine Operations and Replenishment GALILEO Concessionaire / Galileo Supervisory Authority Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
Planning and Funding 48 Months 24 Months 20 Years Development and Validation Deployment 1. 2 Billion € 220 Million € per year Public 1/3 Public, 2/3 Private 1 -2 Test Satellite & 4 Operational Satellites 26 Satellites Ground Infrastructure EC/ESA Joint Undertaking Ground Infrastructure Operations and Maintenance Routine Operations and Replenishment GALILEO Concessionaire / Galileo Supervisory Authority Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
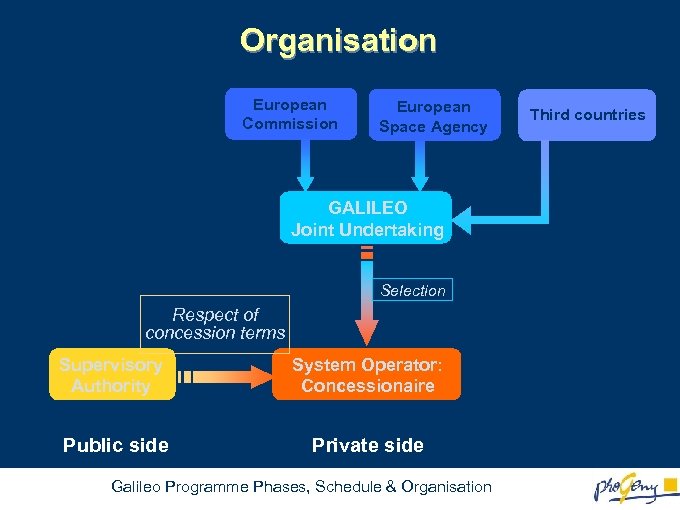 Organisation European Commission European Space Agency GALILEO Joint Undertaking Selection Respect of concession terms Supervisory Authority System Operator: Concessionaire Public side Private side Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation Third countries
Organisation European Commission European Space Agency GALILEO Joint Undertaking Selection Respect of concession terms Supervisory Authority System Operator: Concessionaire Public side Private side Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation Third countries
 Concession • Joining bidders • EURELY: Alcatel, Finmeccanica Aena, Hispasat • INAVSAT: Inmarsat, Eads, Thales • Confirm • services characteristics • financial robustness • commercial viability Reference Stations • Contract negotiation in 2005 • Contract Signing 2006 Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
Concession • Joining bidders • EURELY: Alcatel, Finmeccanica Aena, Hispasat • INAVSAT: Inmarsat, Eads, Thales • Confirm • services characteristics • financial robustness • commercial viability Reference Stations • Contract negotiation in 2005 • Contract Signing 2006 Galileo Programme Phases, Schedule & Organisation
 Key Technologies & Risk Management 4 GSTBv 1 – Experimental Ground Segment GPS Constellation – Galileo-like Ground Infrastructure Orbit Determination Algorithms, < 50 cm Integrity Monitoring Algorithms Experimental Galileo System Time 4 Clocks European Space Qualified Maser and Rubidium Clock Development. 4 GSTBv 2 Ensure Frequency Filings Orbit Environment Characterisation E 5 a E 5 b Technological Developments E 6 L 1
Key Technologies & Risk Management 4 GSTBv 1 – Experimental Ground Segment GPS Constellation – Galileo-like Ground Infrastructure Orbit Determination Algorithms, < 50 cm Integrity Monitoring Algorithms Experimental Galileo System Time 4 Clocks European Space Qualified Maser and Rubidium Clock Development. 4 GSTBv 2 Ensure Frequency Filings Orbit Environment Characterisation E 5 a E 5 b Technological Developments E 6 L 1
 Space Segment Atomic Clocks Source: ESA 4 Development of European Space. Qualified Atomic Clocks Passive Hydrogen Maser 18 kg, 45 litres Stability: 1 ns per Day, <1 ns per 100 minutes 4 Rubidium 3. 3 kg, 2. 4 litres 4 Images: ESA Technological Developments
Space Segment Atomic Clocks Source: ESA 4 Development of European Space. Qualified Atomic Clocks Passive Hydrogen Maser 18 kg, 45 litres Stability: 1 ns per Day, <1 ns per 100 minutes 4 Rubidium 3. 3 kg, 2. 4 litres 4 Images: ESA Technological Developments
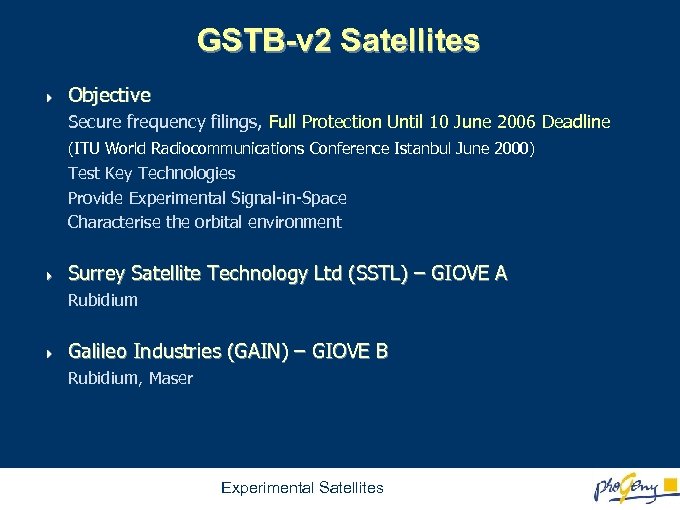 GSTB-v 2 Satellites 4 Objective Secure frequency filings, Full Protection Until 10 June 2006 Deadline (ITU World Radiocommunications Conference Istanbul June 2000) Test Key Technologies Provide Experimental Signal-in-Space Characterise the orbital environment 4 Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL) – GIOVE A Rubidium 4 Galileo Industries (GAIN) – GIOVE B Rubidium, Maser Experimental Satellites
GSTB-v 2 Satellites 4 Objective Secure frequency filings, Full Protection Until 10 June 2006 Deadline (ITU World Radiocommunications Conference Istanbul June 2000) Test Key Technologies Provide Experimental Signal-in-Space Characterise the orbital environment 4 Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL) – GIOVE A Rubidium 4 Galileo Industries (GAIN) – GIOVE B Rubidium, Maser Experimental Satellites
 GIOVE A Satellite Details 4 SSTL 28 M Euro 30 -month 4 Stowed Dimensions 1. 3 1. 74 1. 65 m 4 Lift-Off-Mass 450 kg 4 Power Demand 660 W Propulsion Bay 4 Timing Source 2 Rubidium Clocks 4 Broadcast 2 transmission channels in parallel Experimental Satellites
GIOVE A Satellite Details 4 SSTL 28 M Euro 30 -month 4 Stowed Dimensions 1. 3 1. 74 1. 65 m 4 Lift-Off-Mass 450 kg 4 Power Demand 660 W Propulsion Bay 4 Timing Source 2 Rubidium Clocks 4 Broadcast 2 transmission channels in parallel Experimental Satellites
 GIOVE A - First Galileo Launch 4 4 Successful Launch 28 th Dec 2005 Soyuz 4 -Stage Launch Vehicle 4 L 1, E 5 A & E 5 B Signals Transmitted & Received 12 th January 2006 4 E 6 Signal Transmitted & Received 14 th January 2006 4 Will lead to Frequency Filing Notification to the ITU Images: ESA Experimental Satellites
GIOVE A - First Galileo Launch 4 4 Successful Launch 28 th Dec 2005 Soyuz 4 -Stage Launch Vehicle 4 L 1, E 5 A & E 5 B Signals Transmitted & Received 12 th January 2006 4 E 6 Signal Transmitted & Received 14 th January 2006 4 Will lead to Frequency Filing Notification to the ITU Images: ESA Experimental Satellites
 GIOVE B Satellite Details 4 4 GAIN Stowed Dimensions 0. 955 2. 4 m 4 Lift-Off-Mass 4 523 kg Power Demand 943 W 4 Timing Source 2 Rubidium, 1 Passive Hydrogen Maser Clock 4 Broadcast 3 transmission channels in parallel Image: ESA Experimental Satellites
GIOVE B Satellite Details 4 4 GAIN Stowed Dimensions 0. 955 2. 4 m 4 Lift-Off-Mass 4 523 kg Power Demand 943 W 4 Timing Source 2 Rubidium, 1 Passive Hydrogen Maser Clock 4 Broadcast 3 transmission channels in parallel Image: ESA Experimental Satellites
 Galileo Industries Reference Stations Experimental Satellites
Galileo Industries Reference Stations Experimental Satellites
 IOV Satellites 4 4 4 4 Image: ESA 4 4 4 Satellites 4 Clocks – 2 Rubidium, 2 Maser Launcher Options: Ariane, Proton, Soyuz, Zenit C-Band, S-Band IR-Earth FSS sun Sensors SAR transponder: appr. 20 kg / 100 W 4 Navigation payload: 115 Kg / 780 W Laser Retro-Reflectors 10 Signal Transmission 19 th January - ESA and GAIN sign a € 950 million IOV contract - satellites and associated ground systems IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
IOV Satellites 4 4 4 4 Image: ESA 4 4 4 Satellites 4 Clocks – 2 Rubidium, 2 Maser Launcher Options: Ariane, Proton, Soyuz, Zenit C-Band, S-Band IR-Earth FSS sun Sensors SAR transponder: appr. 20 kg / 100 W 4 Navigation payload: 115 Kg / 780 W Laser Retro-Reflectors 10 Signal Transmission 19 th January - ESA and GAIN sign a € 950 million IOV contract - satellites and associated ground systems IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
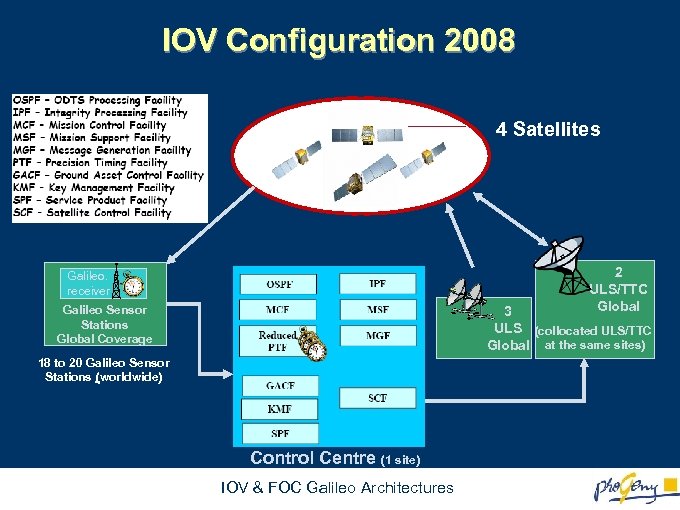 IOV Configuration 2008 4 Satellites 2 ULS/TTC Global Galileo. receiver Galileo Sensor Stations Global Coverage 3 ULS (collocated ULS/TTC Global at the same sites) 18 to 20 Galileo Sensor Stations (worldwide) Control Centre (1 site) IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
IOV Configuration 2008 4 Satellites 2 ULS/TTC Global Galileo. receiver Galileo Sensor Stations Global Coverage 3 ULS (collocated ULS/TTC Global at the same sites) 18 to 20 Galileo Sensor Stations (worldwide) Control Centre (1 site) IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
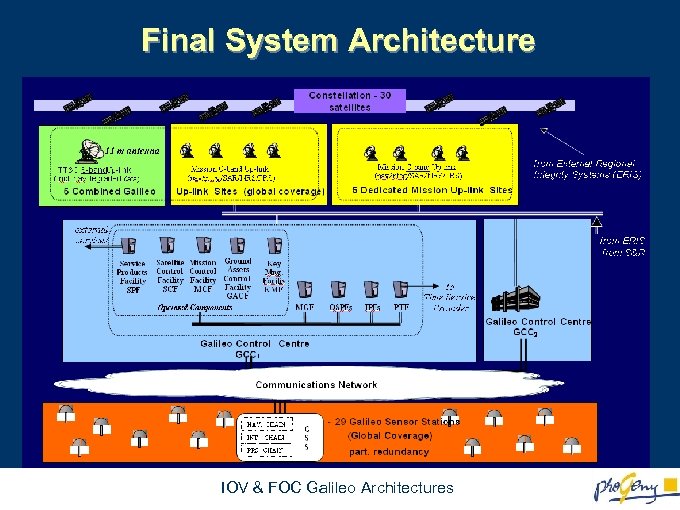 Final System Architecture Reference Stations IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
Final System Architecture Reference Stations IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
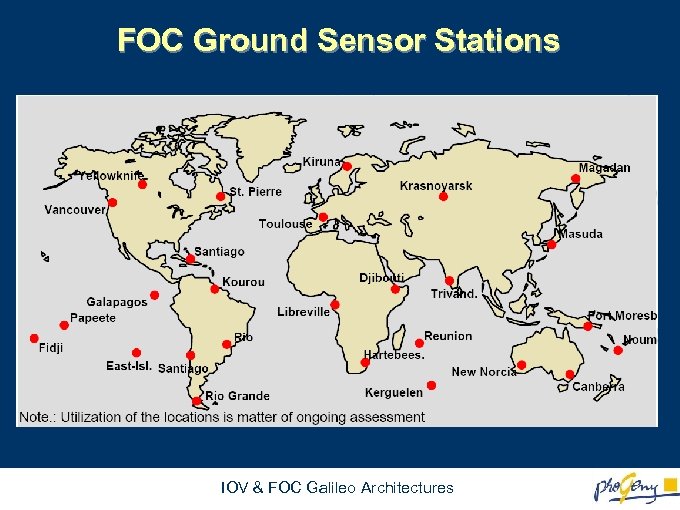 FOC Ground Sensor Stations IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
FOC Ground Sensor Stations IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
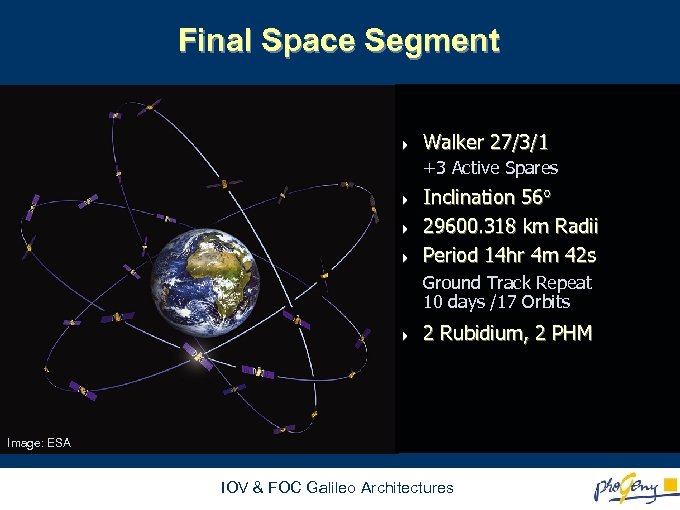 Final Space Segment 4 Walker 27/3/1 +3 Active Spares 4 4 4 Inclination 56 29600. 318 km Radii Period 14 hr 4 m 42 s Ground Track Repeat 10 days /17 Orbits 4 2 Rubidium, 2 PHM Image: ESA IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
Final Space Segment 4 Walker 27/3/1 +3 Active Spares 4 4 4 Inclination 56 29600. 318 km Radii Period 14 hr 4 m 42 s Ground Track Repeat 10 days /17 Orbits 4 2 Rubidium, 2 PHM Image: ESA IOV & FOC Galileo Architectures
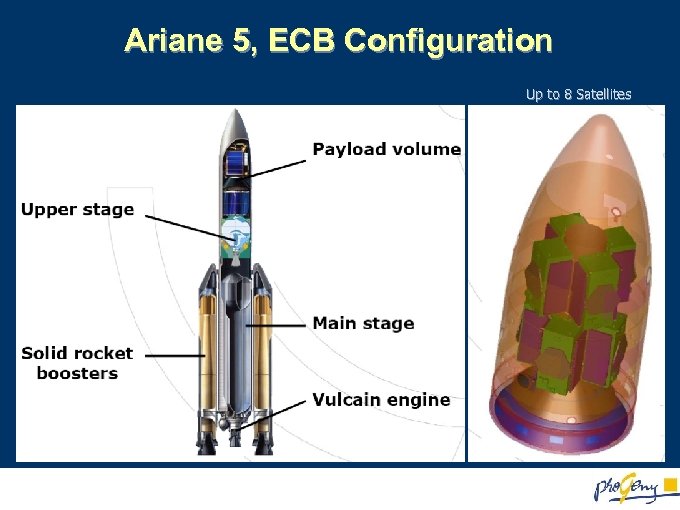 Ariane 5, ECB Configuration Up to 8 Satellites
Ariane 5, ECB Configuration Up to 8 Satellites
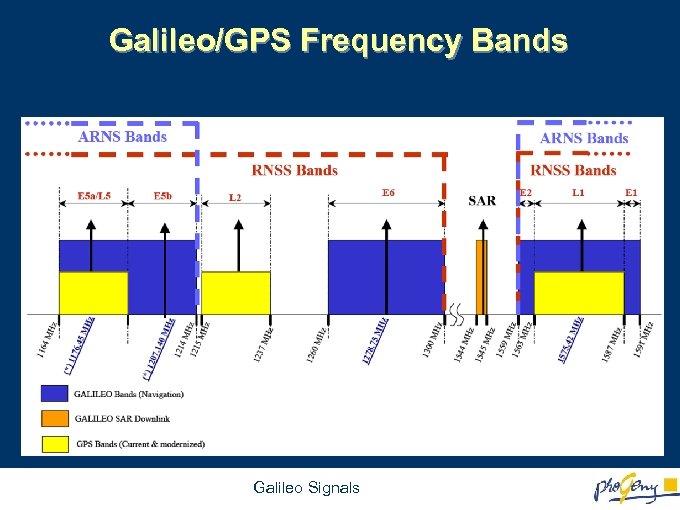 Galileo/GPS Frequency Bands Galileo Signals
Galileo/GPS Frequency Bands Galileo Signals
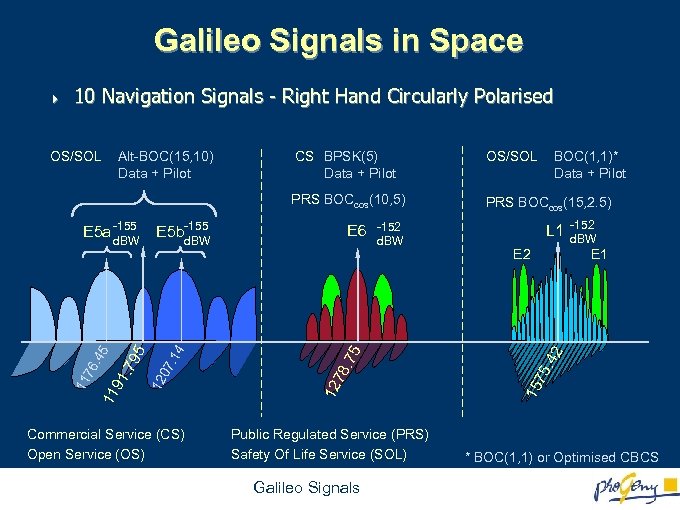 Galileo Signals in Space 4 10 Navigation Signals - Right Hand Circularly Polarised PRS BOCcos(15, 2. 5) Commercial Service (CS) Open Service (OS) 78 Public Regulated Service (PRS) Safety Of Life Service (SOL) Galileo Signals L 1 E 2 -152 d. BW E 1 . 42 -152 d. BW . 75 E 6 BOC(1, 1)* Data + Pilot 75 E 5 b-155 d. BW 12 5 91 . 79 11 76. 45 11 OS/SOL PRS BOCcos(10, 5) E 5 a -155 d. BW CS BPSK(5) Data + Pilot 15 Alt-BOC(15, 10) Data + Pilot 12 07. 14 OS/SOL * BOC(1, 1) or Optimised CBCS
Galileo Signals in Space 4 10 Navigation Signals - Right Hand Circularly Polarised PRS BOCcos(15, 2. 5) Commercial Service (CS) Open Service (OS) 78 Public Regulated Service (PRS) Safety Of Life Service (SOL) Galileo Signals L 1 E 2 -152 d. BW E 1 . 42 -152 d. BW . 75 E 6 BOC(1, 1)* Data + Pilot 75 E 5 b-155 d. BW 12 5 91 . 79 11 76. 45 11 OS/SOL PRS BOCcos(10, 5) E 5 a -155 d. BW CS BPSK(5) Data + Pilot 15 Alt-BOC(15, 10) Data + Pilot 12 07. 14 OS/SOL * BOC(1, 1) or Optimised CBCS
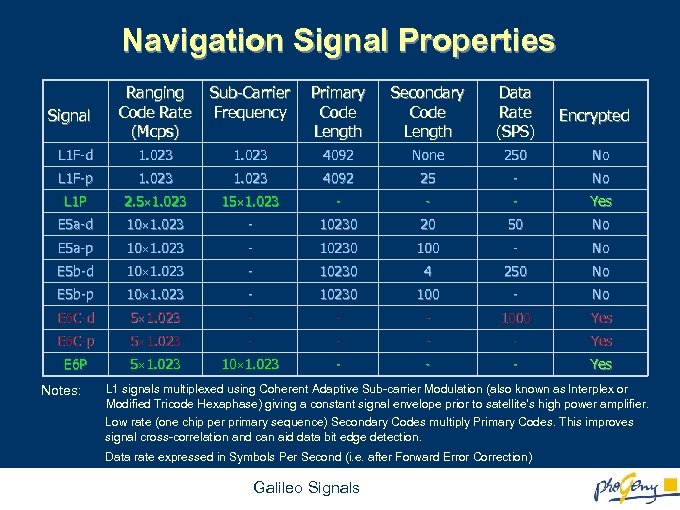 Navigation Signal Properties Ranging Code Rate (Mcps) Sub-Carrier Frequency Primary Code Length Secondary Code Length Data Rate (SPS) L 1 F-d 1. 023 4092 None 250 No L 1 F-p 1. 023 4092 25 - No L 1 P 2. 5 1. 023 15 1. 023 - - - Yes E 5 a-d 10 1. 023 - 10230 20 50 No E 5 a-p 10 1. 023 - 10230 100 - No E 5 b-d 10 1. 023 - 10230 4 250 No E 5 b-p 10 1. 023 - 10230 100 - No E 6 C-d 5 1. 023 - - - 1000 Yes E 6 C-p 5 1. 023 - - Yes E 6 P 5 1. 023 10 1. 023 - - - Yes Signal Notes: Encrypted L 1 signals multiplexed using Coherent Adaptive Sub-carrier Modulation (also known as Interplex or Modified Tricode Hexaphase) giving a constant signal envelope prior to satellite’s high power amplifier. Low rate (one chip per primary sequence) Secondary Codes multiply Primary Codes. This improves signal cross-correlation and can aid data bit edge detection. Data rate expressed in Symbols Per Second (i. e. after Forward Error Correction) Galileo Signals
Navigation Signal Properties Ranging Code Rate (Mcps) Sub-Carrier Frequency Primary Code Length Secondary Code Length Data Rate (SPS) L 1 F-d 1. 023 4092 None 250 No L 1 F-p 1. 023 4092 25 - No L 1 P 2. 5 1. 023 15 1. 023 - - - Yes E 5 a-d 10 1. 023 - 10230 20 50 No E 5 a-p 10 1. 023 - 10230 100 - No E 5 b-d 10 1. 023 - 10230 4 250 No E 5 b-p 10 1. 023 - 10230 100 - No E 6 C-d 5 1. 023 - - - 1000 Yes E 6 C-p 5 1. 023 - - Yes E 6 P 5 1. 023 10 1. 023 - - - Yes Signal Notes: Encrypted L 1 signals multiplexed using Coherent Adaptive Sub-carrier Modulation (also known as Interplex or Modified Tricode Hexaphase) giving a constant signal envelope prior to satellite’s high power amplifier. Low rate (one chip per primary sequence) Secondary Codes multiply Primary Codes. This improves signal cross-correlation and can aid data bit edge detection. Data rate expressed in Symbols Per Second (i. e. after Forward Error Correction) Galileo Signals
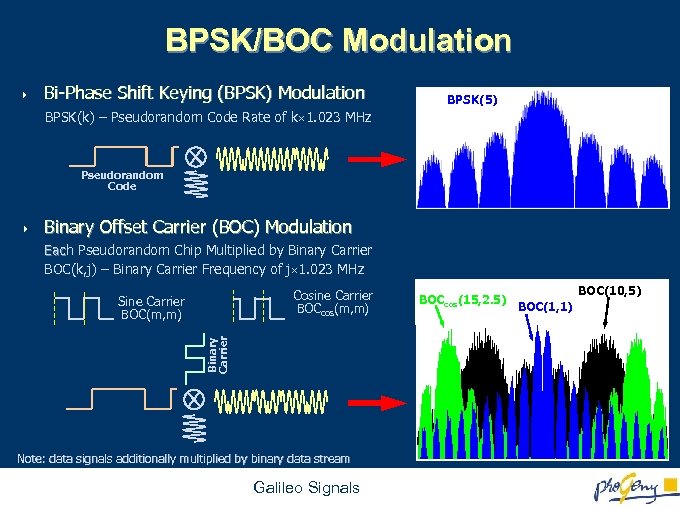 BPSK/BOC Modulation 4 Bi-Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) Modulation BPSK(5) BPSK(k) – Pseudorandom Code Rate of k 1. 023 MHz Pseudorandom Code 4 Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) Modulation Each Pseudorandom Chip Multiplied by Binary Carrier Eac BOC(k, j) – Binary Carrier Frequency of j 1. 023 MHz Cosine Carrier BOCcos(m, m) Binary Carrier Sine Carrier BOC(m, m) Note: data signals additionally multiplied by binary data stream Galileo Signals BOCcos(15, 2. 5) BOC(10, 5) BOC(1, 1)
BPSK/BOC Modulation 4 Bi-Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) Modulation BPSK(5) BPSK(k) – Pseudorandom Code Rate of k 1. 023 MHz Pseudorandom Code 4 Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) Modulation Each Pseudorandom Chip Multiplied by Binary Carrier Eac BOC(k, j) – Binary Carrier Frequency of j 1. 023 MHz Cosine Carrier BOCcos(m, m) Binary Carrier Sine Carrier BOC(m, m) Note: data signals additionally multiplied by binary data stream Galileo Signals BOCcos(15, 2. 5) BOC(10, 5) BOC(1, 1)
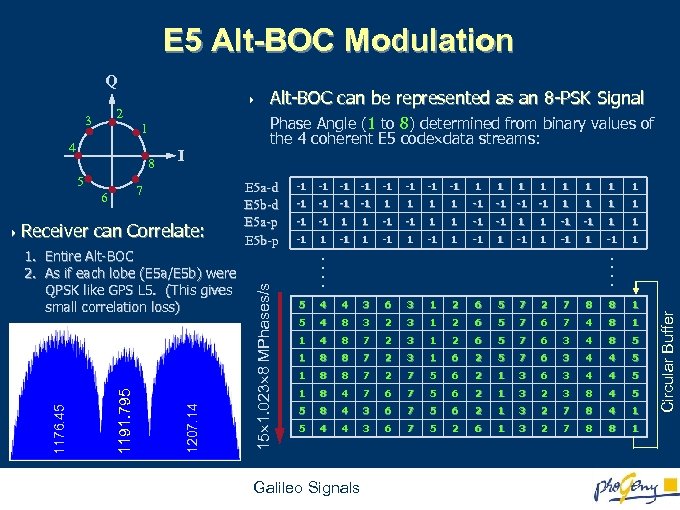 E 5 Alt-BOC Modulation Q 4 8 5 7 6 4 Receiver I can Correlate: 1207. 14 1191. 795 1176. 45 1. Entire Alt-BOC 2. As if each lobe (E 5 a/E 5 b) were QPSK like GPS L 5. (This gives small correlation loss) E 5 a-d E 5 b-d E 5 a-p E 5 b-p -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 1 -1 1 5 4 4 3 6 3 1 2 6 5 7 2 7 8 8 1 5 4 8 3 2 3 1 2 6 5 7 6 7 4 8 1 1 4 8 7 2 3 1 2 6 5 7 6 3 4 8 5 1 8 8 7 2 3 1 6 2 5 7 6 3 4 4 5 1 8 8 7 2 7 5 6 2 1 3 6 3 4 4 5 1 8 4 7 6 7 5 6 2 1 3 2 3 8 4 5 5 8 4 3 6 7 5 6 2 1 3 2 7 8 4 1 5 4 4 3 6 7 5 2 6 1 3 2 7 8 8 1 Galileo Signals Circular Buffer 4 Phase Angle (1 to 8) determined from binary values of the 4 coherent E 5 code data streams: . . 1 . . 3 Alt-BOC can be represented as an 8 -PSK Signal 15 1. 023 8 MPhases/s 2
E 5 Alt-BOC Modulation Q 4 8 5 7 6 4 Receiver I can Correlate: 1207. 14 1191. 795 1176. 45 1. Entire Alt-BOC 2. As if each lobe (E 5 a/E 5 b) were QPSK like GPS L 5. (This gives small correlation loss) E 5 a-d E 5 b-d E 5 a-p E 5 b-p -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 1 -1 1 5 4 4 3 6 3 1 2 6 5 7 2 7 8 8 1 5 4 8 3 2 3 1 2 6 5 7 6 7 4 8 1 1 4 8 7 2 3 1 2 6 5 7 6 3 4 8 5 1 8 8 7 2 3 1 6 2 5 7 6 3 4 4 5 1 8 8 7 2 7 5 6 2 1 3 6 3 4 4 5 1 8 4 7 6 7 5 6 2 1 3 2 3 8 4 5 5 8 4 3 6 7 5 6 2 1 3 2 7 8 4 1 5 4 4 3 6 7 5 2 6 1 3 2 7 8 8 1 Galileo Signals Circular Buffer 4 Phase Angle (1 to 8) determined from binary values of the 4 coherent E 5 code data streams: . . 1 . . 3 Alt-BOC can be represented as an 8 -PSK Signal 15 1. 023 8 MPhases/s 2
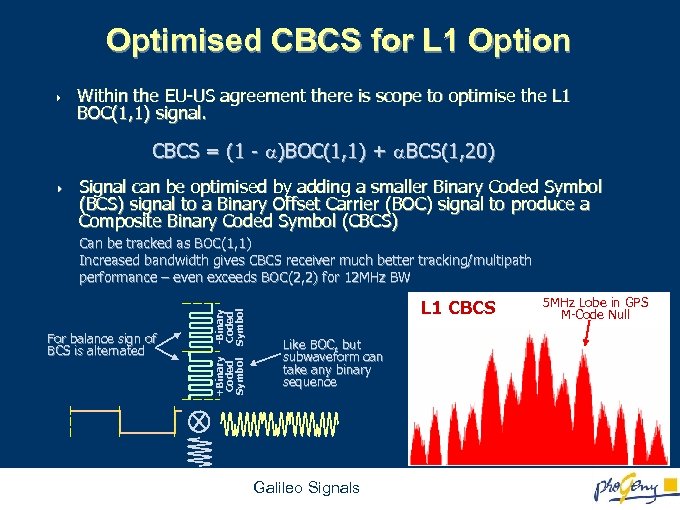 Optimised CBCS for L 1 Option 4 Within the EU-US agreement there is scope to optimise the L 1 BOC(1, 1) signal. CBCS = (1 - )BOC(1, 1) + BCS(1, 20) 4 Signal can be optimised by adding a smaller Binary Coded Symbol (BCS) signal to a Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) signal to produce a Composite Binary Coded Symbol (CBCS) +Binary Coded Symbol For balance sign of BCS is alternated -Binary Coded Symbol Can be tracked as BOC(1, 1) Increased bandwidth gives CBCS receiver much better tracking/multipath performance – even exceeds BOC(2, 2) for 12 MHz BW L 1 CBCS Like BOC, but subwaveform can take any binary sequence Galileo Signals 5 MHz Lobe in GPS M-Code Null
Optimised CBCS for L 1 Option 4 Within the EU-US agreement there is scope to optimise the L 1 BOC(1, 1) signal. CBCS = (1 - )BOC(1, 1) + BCS(1, 20) 4 Signal can be optimised by adding a smaller Binary Coded Symbol (BCS) signal to a Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) signal to produce a Composite Binary Coded Symbol (CBCS) +Binary Coded Symbol For balance sign of BCS is alternated -Binary Coded Symbol Can be tracked as BOC(1, 1) Increased bandwidth gives CBCS receiver much better tracking/multipath performance – even exceeds BOC(2, 2) for 12 MHz BW L 1 CBCS Like BOC, but subwaveform can take any binary sequence Galileo Signals 5 MHz Lobe in GPS M-Code Null
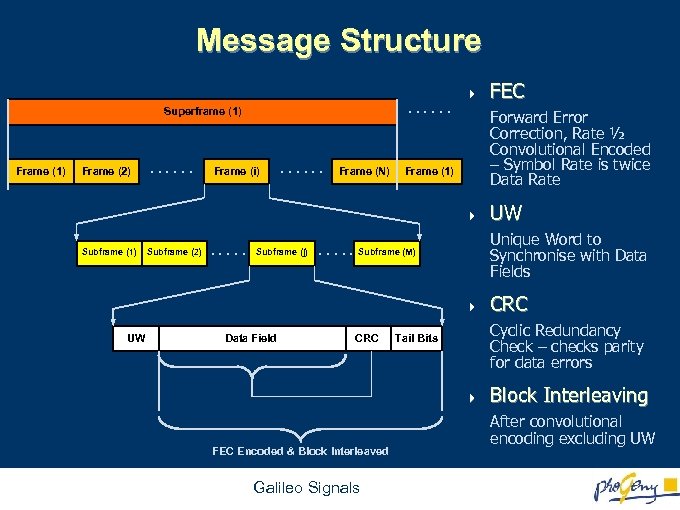 Message Structure. . . Superframe (1) Frame (2) . . . Frame (i) . . . Frame (N) 4 Forward Error Correction, Rate ½ Convolutional Encoded – Symbol Rate is twice Data Rate Frame (1) 4 Subframe (1) Subframe (2) . . . Subframe (j) . . . Data Field CRC Galileo Signals CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check – checks parity for data errors Tail Bits 4 FEC Encoded & Block Interleaved UW Unique Word to Synchronise with Data Fields Subframe (M) 4 UW FEC Block Interleaving After convolutional encoding excluding UW
Message Structure. . . Superframe (1) Frame (2) . . . Frame (i) . . . Frame (N) 4 Forward Error Correction, Rate ½ Convolutional Encoded – Symbol Rate is twice Data Rate Frame (1) 4 Subframe (1) Subframe (2) . . . Subframe (j) . . . Data Field CRC Galileo Signals CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check – checks parity for data errors Tail Bits 4 FEC Encoded & Block Interleaved UW Unique Word to Synchronise with Data Fields Subframe (M) 4 UW FEC Block Interleaving After convolutional encoding excluding UW
 Ephemeris Message Structure 4 Similar, but not identical, to GPS Galileo Signals
Ephemeris Message Structure 4 Similar, but not identical, to GPS Galileo Signals
 GNSS Signal Interoperability 4 GPS and Galileo Adoption of a common basis for Galileo L 1 and GPS III L 1 open signals: BOC(1, 1). Adoption of interoperable timing and geodesy standards to facilitate the joint use of Galileo and GPS. Broadcast of GPS/Galileo time offset. 4 GLONASS and Galileo Frequency sharing between Galileo E 5 B and GLONASS-L 3 gives prospect for interoperability of the two systems Joint broadcasting of GLONASS-K/Galileo time offset is envisaged 4 QZSS and Galileo: Agreement that same signal structure as Galileo E 6 Commercial Service is the best solution on compatibility and interoperability grounds Galileo Signals
GNSS Signal Interoperability 4 GPS and Galileo Adoption of a common basis for Galileo L 1 and GPS III L 1 open signals: BOC(1, 1). Adoption of interoperable timing and geodesy standards to facilitate the joint use of Galileo and GPS. Broadcast of GPS/Galileo time offset. 4 GLONASS and Galileo Frequency sharing between Galileo E 5 B and GLONASS-L 3 gives prospect for interoperability of the two systems Joint broadcasting of GLONASS-K/Galileo time offset is envisaged 4 QZSS and Galileo: Agreement that same signal structure as Galileo E 6 Commercial Service is the best solution on compatibility and interoperability grounds Galileo Signals
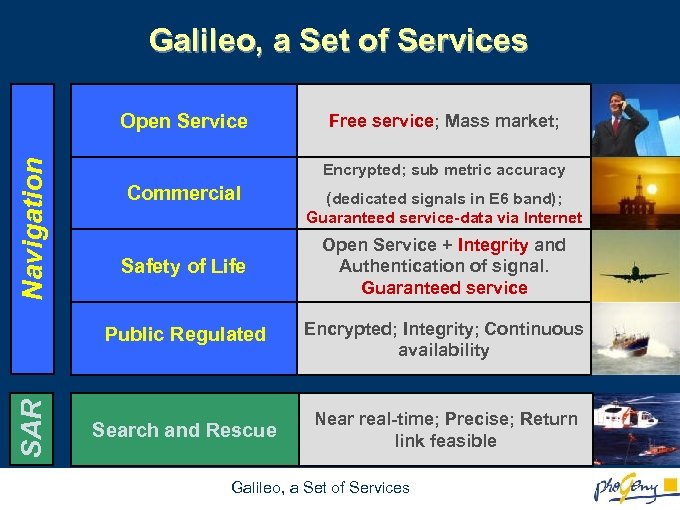 Galileo, a Set of Services Navigation Open Service Free service; Mass market; Encrypted; sub metric accuracy Commercial (dedicated signals in E 6 band); Guaranteed service-data via Internet Public Regulated SAR Safety of Life Open Service + Integrity and Authentication of signal. Guaranteed service Encrypted; Integrity; Continuous availability Search and Rescue Near real-time; Precise; Return link feasible Galileo, a Set of Services
Galileo, a Set of Services Navigation Open Service Free service; Mass market; Encrypted; sub metric accuracy Commercial (dedicated signals in E 6 band); Guaranteed service-data via Internet Public Regulated SAR Safety of Life Open Service + Integrity and Authentication of signal. Guaranteed service Encrypted; Integrity; Continuous availability Search and Rescue Near real-time; Precise; Return link feasible Galileo, a Set of Services
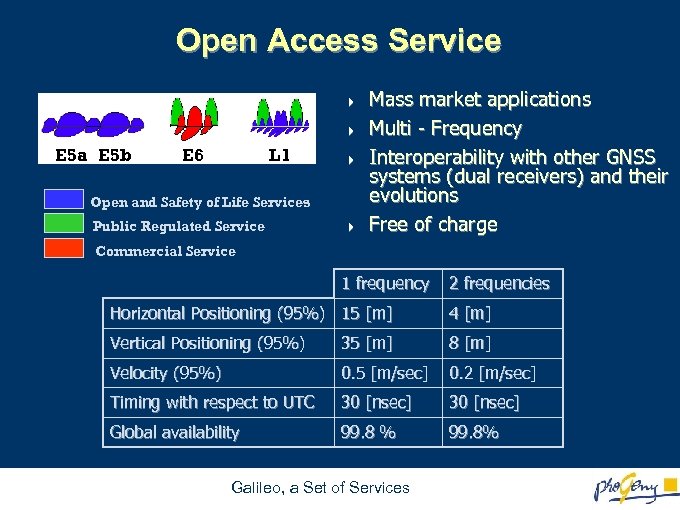 Open Access Service 4 4 E 5 a E 5 b E 6 L 1 4 Open and Safety of Life Services Public Regulated Service 4 Mass market applications Multi - Frequency Interoperability with other GNSS systems (dual receivers) and their evolutions Free of charge Commercial Service 1 frequency 2 frequencies Horizontal Positioning (95%) 15 [m] 4 [m] Vertical Positioning (95%) 35 [m] 8 [m] Velocity (95%) 0. 5 [m/sec] 0. 2 [m/sec] Timing with respect to UTC 30 [nsec] Global availability 99. 8 % 99. 8% Galileo, a Set of Services
Open Access Service 4 4 E 5 a E 5 b E 6 L 1 4 Open and Safety of Life Services Public Regulated Service 4 Mass market applications Multi - Frequency Interoperability with other GNSS systems (dual receivers) and their evolutions Free of charge Commercial Service 1 frequency 2 frequencies Horizontal Positioning (95%) 15 [m] 4 [m] Vertical Positioning (95%) 35 [m] 8 [m] Velocity (95%) 0. 5 [m/sec] 0. 2 [m/sec] Timing with respect to UTC 30 [nsec] Global availability 99. 8 % 99. 8% Galileo, a Set of Services
 Safety-of-Life Mission Level Requirements 4 Galileo supports operations employing Integrity Risk & Alert Limit Concepts (Designed with respect to ICAO & IMO Requirement) Level A: - aviation approach, rail and road applications. Level B: - aviation operations en-route to NPA Level C: - maritime operations. Galileo, a Set of Services
Safety-of-Life Mission Level Requirements 4 Galileo supports operations employing Integrity Risk & Alert Limit Concepts (Designed with respect to ICAO & IMO Requirement) Level A: - aviation approach, rail and road applications. Level B: - aviation operations en-route to NPA Level C: - maritime operations. Galileo, a Set of Services
 Safety of Life Service 4 4 Galileo to provide Global Real-Time Integrity Monitoring Safety-of-Life (So. L) - For transport applications where lives could be lost if the performance of the navigation system is degraded without real-time notification. 4 4 4 Service Will Increase Safety, especially in the absence of traditional ground infrastructure. Service Guarantee by Galileo Operating Company. Safety/Business Critical Applications Additional Regional Integrity Provision Signal Authentication Galileo, a Set of Services
Safety of Life Service 4 4 Galileo to provide Global Real-Time Integrity Monitoring Safety-of-Life (So. L) - For transport applications where lives could be lost if the performance of the navigation system is degraded without real-time notification. 4 4 4 Service Will Increase Safety, especially in the absence of traditional ground infrastructure. Service Guarantee by Galileo Operating Company. Safety/Business Critical Applications Additional Regional Integrity Provision Signal Authentication Galileo, a Set of Services
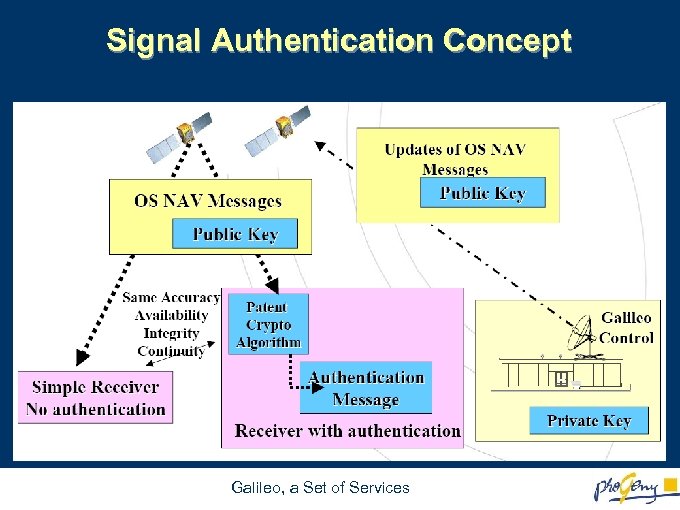 Signal Authentication Concept Galileo, a Set of Services
Signal Authentication Concept Galileo, a Set of Services
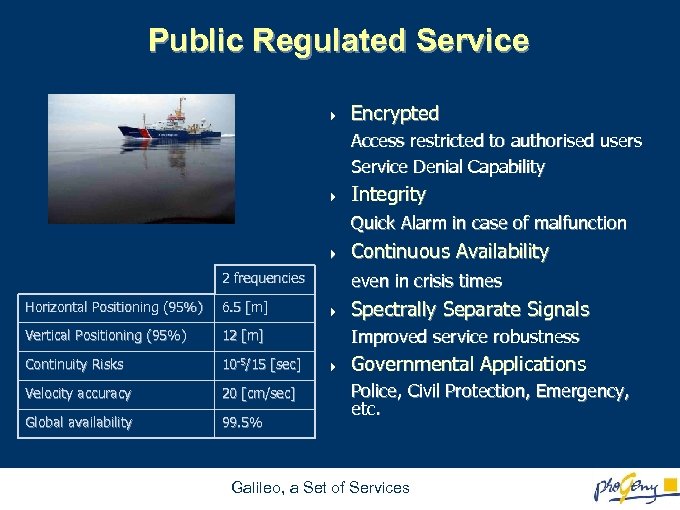 Public Regulated Service 4 Encrypted Access restricted to authorised users Service Denial Capability 4 Integrity Quick Alarm in case of malfunction 4 2 frequencies Horizontal Positioning (95%) 6. 5 [m] Vertical Positioning (95%) 10 -5/15 [sec] Velocity accuracy 20 [cm/sec] Global availability 99. 5% even in crisis times 12 [m] Continuity Risks Continuous Availability 4 Spectrally Separate Signals Improved service robustness 4 Governmental Applications Police, Civil Protection, Emergency, etc. Galileo, a Set of Services
Public Regulated Service 4 Encrypted Access restricted to authorised users Service Denial Capability 4 Integrity Quick Alarm in case of malfunction 4 2 frequencies Horizontal Positioning (95%) 6. 5 [m] Vertical Positioning (95%) 10 -5/15 [sec] Velocity accuracy 20 [cm/sec] Global availability 99. 5% even in crisis times 12 [m] Continuity Risks Continuous Availability 4 Spectrally Separate Signals Improved service robustness 4 Governmental Applications Police, Civil Protection, Emergency, etc. Galileo, a Set of Services
 Commercial Service 4 4 4 Based on the open service standard Provisions Additional commercial encrypted data Added value services (higher accuracy, data broadcast, authentication) with respect to the open service 4 Three-Carrier-Ambiguity Resolution 4 Service guarantees 4 Access through external Service Providers Galileo, a Set of Services
Commercial Service 4 4 4 Based on the open service standard Provisions Additional commercial encrypted data Added value services (higher accuracy, data broadcast, authentication) with respect to the open service 4 Three-Carrier-Ambiguity Resolution 4 Service guarantees 4 Access through external Service Providers Galileo, a Set of Services
 Galileo Search & Rescue 4 4 4 4 Galileo, a Set of Services COSPAS-SARSAT cooperative effort on Humanitarian Search and Rescue Activities Fulfil IMO & ICAO Requirements Backwards Compatible Global Near Real-Time Reception Multiple Satellite Detection + LEOSAR + GEOSAR 406 MHz New - Return Link 15441545 MHz
Galileo Search & Rescue 4 4 4 4 Galileo, a Set of Services COSPAS-SARSAT cooperative effort on Humanitarian Search and Rescue Activities Fulfil IMO & ICAO Requirements Backwards Compatible Global Near Real-Time Reception Multiple Satellite Detection + LEOSAR + GEOSAR 406 MHz New - Return Link 15441545 MHz
 GPS & Galileo
GPS & Galileo
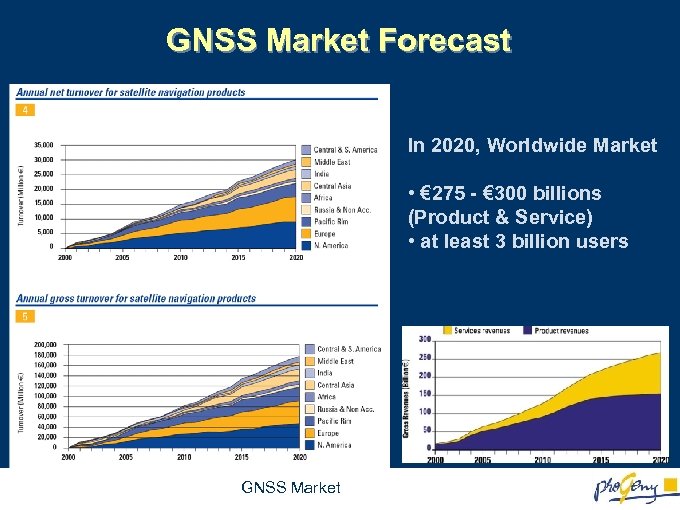 GNSS Market Forecast In 2020, Worldwide Market • € 275 - € 300 billions (Product & Service) • at least 3 billion users GNSS Market
GNSS Market Forecast In 2020, Worldwide Market • € 275 - € 300 billions (Product & Service) • at least 3 billion users GNSS Market
 Galileo Market Sectors 4 Location Based Services CPS: Global LBS Revenues of $35 Billion by 2008 4 Road Market By 2020 60% car 90% commercial 4 Road Tolling Legal Framework, Guarantee 4 Rail Sector Fleet Management, Guarantee 4 Agriculture Land Monitoring, Precision Farming 4 4 GNSS Market Justice Home Affairs Construction
Galileo Market Sectors 4 Location Based Services CPS: Global LBS Revenues of $35 Billion by 2008 4 Road Market By 2020 60% car 90% commercial 4 Road Tolling Legal Framework, Guarantee 4 Rail Sector Fleet Management, Guarantee 4 Agriculture Land Monitoring, Precision Farming 4 4 GNSS Market Justice Home Affairs Construction
 Revenue Mechanisms • Intellectual Property Rights • • Patents, Copyrights, Trademarks, Know-how, etc. • Activation fees • Licence in chipsets • Services authentication • Services (high accuracy) • Contractual Quality of Service • Legislation • Etc. GNSS Market
Revenue Mechanisms • Intellectual Property Rights • • Patents, Copyrights, Trademarks, Know-how, etc. • Activation fees • Licence in chipsets • Services authentication • Services (high accuracy) • Contractual Quality of Service • Legislation • Etc. GNSS Market
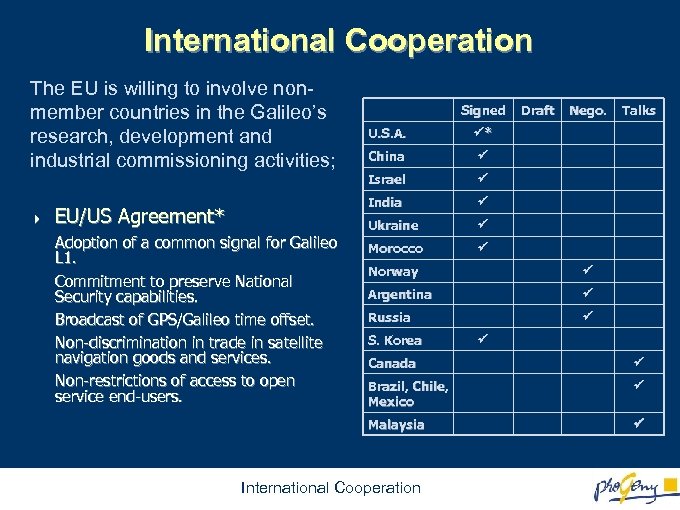 International Cooperation The EU is willing to involve nonmember countries in the Galileo’s research, development and industrial commissioning activities; 4 Signed Adoption of a common signal for Galileo L 1. Commitment to preserve National Security capabilities. Broadcast of GPS/Galileo time offset. Non-discrimination in trade in satellite navigation goods and services. Non-restrictions of access to open service end-users. China Ukraine Morocco Talks Israel Nego. * India EU/US Agreement* U. S. A. Draft Norway Argentina Russia S. Korea Canada Brazil, Chile, Mexico Malaysia International Cooperation
International Cooperation The EU is willing to involve nonmember countries in the Galileo’s research, development and industrial commissioning activities; 4 Signed Adoption of a common signal for Galileo L 1. Commitment to preserve National Security capabilities. Broadcast of GPS/Galileo time offset. Non-discrimination in trade in satellite navigation goods and services. Non-restrictions of access to open service end-users. China Ukraine Morocco Talks Israel Nego. * India EU/US Agreement* U. S. A. Draft Norway Argentina Russia S. Korea Canada Brazil, Chile, Mexico Malaysia International Cooperation
 Further Information 4 Further Galileo information is available on the following websites: europa. eu. int/comm/dgs/energy_transport/galileo/index_en. htm www. esa. int/esa. NA/galileo. html 4 Further information on the Joint Undertaking: www. galileoju. com
Further Information 4 Further Galileo information is available on the following websites: europa. eu. int/comm/dgs/energy_transport/galileo/index_en. htm www. esa. int/esa. NA/galileo. html 4 Further information on the Joint Undertaking: www. galileoju. com


