9ad0f4b8af90742477b44ede3095dea9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Introduction to ERP Dr Celeste Ng 吳思佩 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Outline • • • ERP Evolution ERP Definition ERP Vendors SCM CRM E-Business 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU
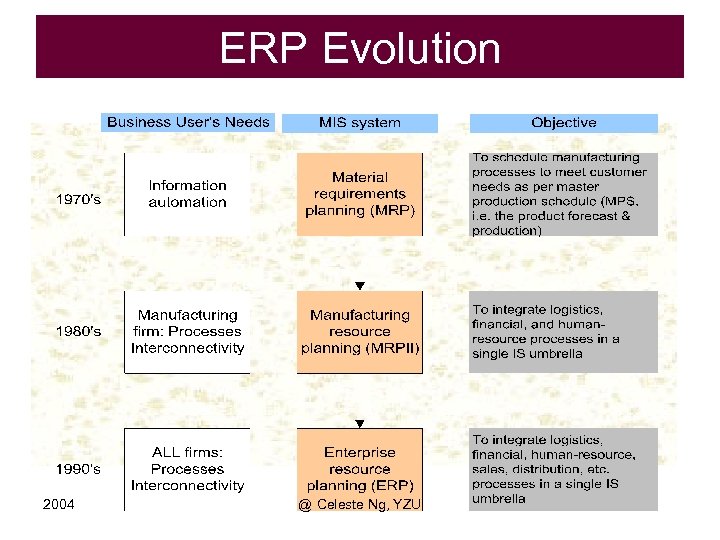
ERP Evolution 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU
ERP definition (1) • Enterprise resource planning (ERP), also known as enterprise systems • It is configurable, cross-functional, and integrated standard software packages • A set of integrated software modules that make up the core engine of internal transaction processing • Implementing ERP requires major changes to organizational, cultural and business processes 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

ERP definition (2) • ERP is an – IT backbone – Enabling technology, but not intrinsically strategic • ERP provides – A standard user interface, – Single database, – Real-time information system, and – Corporate infrastructures for the prevalent ebusiness technologies. 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

ERP definition (3) • It is a new type of information system for enterprise integration that integrates application programs for various business functions and processes for example, – – – 2004 Finance, Human resources management, Sales and distribution, Manufacturing and logistics, Supply chain management, Customer relationship management. @ Celeste Ng, YZU

ERP definition (4) • It also provides industry solutions for – banking, – healthcare, – insurance, etc. 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

What ERP does? • Organize, codify, and standardize an enterprise’s business processes and data • Transform transaction data into useful information and collate the data so that – It can be analyzed, and therefore – Can be used to support business decision • Optimize company’s internal value chain 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

ERP Vendors • International – SAP AG (Germany) – Oracle (USA) – People. Soft (USA) • Local (Taiwan) – Data Systems Consulting Co. , Ltd. (鼎新電腦), – Wellan System Co. , Ltd. (偉盟系統股份有限公 司), – Datawin (鉅茂科技股份有限公司). 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Supply Chain Management (1) • Supply chain – The sequence of business processes and information that provides a product or service from suppliers thru manufacturing and distribution to the ultimate customer (Schroeder, 2000) – ‘process umbrella’ under which products are created and delivered to customers (Sheikh, 2003) – The cycle of buy-make-move-store-sell (Sheikh, 2003) 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Supply Chain Management (2) • SCM is defined as – The planning, design, and control of the flow of information, materials, and money along the supply chain in order to meet customer requirements in an efficient manner, now and in the future – The function of coordinating the material, information, and financial flows between and among all participating enterprises 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Supply Chain Management (3) • Material flows – Physical product flow from suppliers to customers thru the chain, including reverse flow, i. e. product returns, servicing, recycling, and disposal • Information flows – Involve demand forecasts, order transmission, and delivery status reports • Financial flows – Involve credit card information, credit terms, payment schedules, and consignment and title ownership arrangement (Kalakota and Robinson, 2000) 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Customer Relationship Management (1) • Term for methodologies, software, and Internet capabilities that help an enterprise manage customer relationships in an organized way 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Customer Relationship Management (2) • E. g. build a database about its customers that describes relationships in sufficient detail so that mm, salesperson, and customer – Can directly access information – Match customer needs with product plans and offerings – Remind customers of service requirements – Know what other products a customer had purchased 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

Customer Relationship Management (3) • Enables the creation of long term, profitable relationships with customer thru – Increased customer intimacy, and improved business process effectiveness • Links back-office and front-office functions with all of a company’s touch points (e. g. call centers, Web site) with the customer • Covers all customer touch points e. g. face-toface, Internet, phone – allowing all individuals (employees, business partners or consumers) to collaborate 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU

E-Business • Use electronic information technologies and open standards to connect suppliers and customers along the value chain • Improves business performance 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU
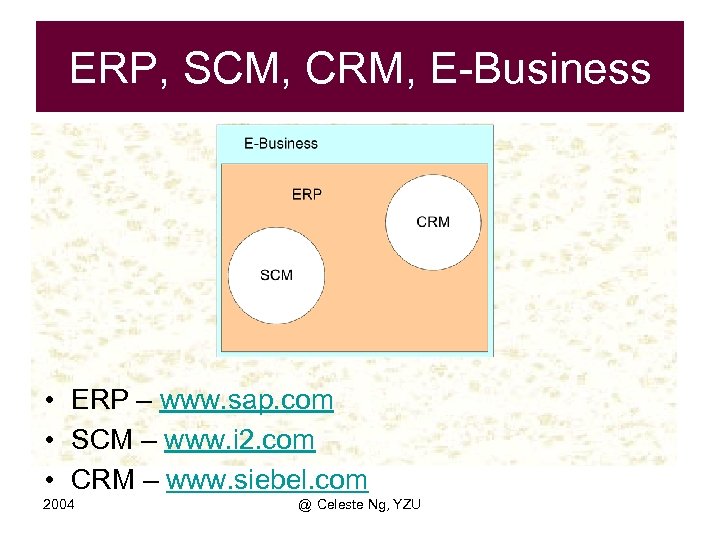
ERP, SCM, CRM, E-Business • ERP – www. sap. com • SCM – www. i 2. com • CRM – www. siebel. com 2004 @ Celeste Ng, YZU
9ad0f4b8af90742477b44ede3095dea9.ppt