 Introduction to Economics Microeconomics - Supply
Introduction to Economics Microeconomics - Supply
 Supply and Price ¡ ¡ ¡ Sellers create supply – they must have the desire and ability to sell When the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise (POSITIVE relationship) Why? l l l Higher prices make higher costs (as productions rises) worth incurring (short run) Higher prices mean production is more profitable (short run) Over time, new producers will enter the market (long run)
Supply and Price ¡ ¡ ¡ Sellers create supply – they must have the desire and ability to sell When the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise (POSITIVE relationship) Why? l l l Higher prices make higher costs (as productions rises) worth incurring (short run) Higher prices mean production is more profitable (short run) Over time, new producers will enter the market (long run)
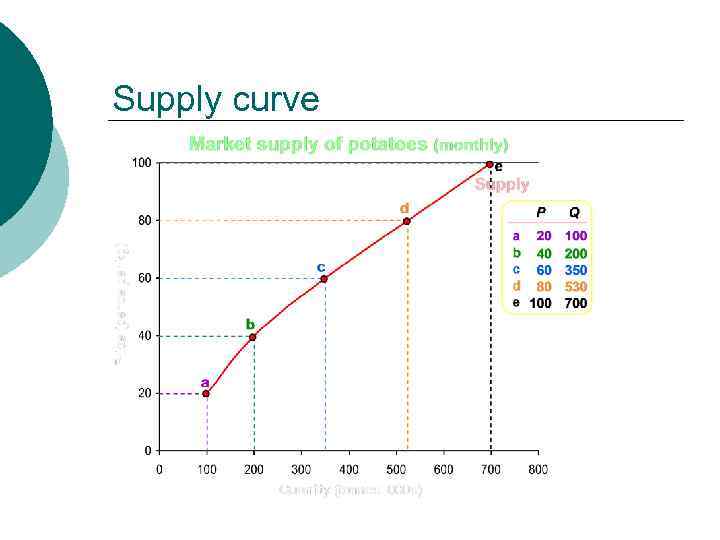 Supply curve
Supply curve
 Key terms ¡ Supply Positive relationship l Change in quantity supplied (movement along) l Non-price determinants of supply (shift of curve) l ¡ ¡ costs of production, technology, organisational changes, government policy, profitability of alternative products, profitability of goods in joint supply, nature and other random shocks, expectations of producers Change in supply (shift of curve)
Key terms ¡ Supply Positive relationship l Change in quantity supplied (movement along) l Non-price determinants of supply (shift of curve) l ¡ ¡ costs of production, technology, organisational changes, government policy, profitability of alternative products, profitability of goods in joint supply, nature and other random shocks, expectations of producers Change in supply (shift of curve)
 Nature of supply curves Most supply curves will rise from left to right ¡ Supply curves may be horizontal, vertical, or even downward ¡ Dependent on: ¡ l l Time Elasticity
Nature of supply curves Most supply curves will rise from left to right ¡ Supply curves may be horizontal, vertical, or even downward ¡ Dependent on: ¡ l l Time Elasticity
 Other (non-price) determinants of supply (1) ¡ Costs of production l l Change in input costs Change in technology Organisational changes Government policy (taxation/subsidy) Profitability of substitutes ¡ Profitability of goods in joint supply ¡ Unpredictable events –”random shock” ¡
Other (non-price) determinants of supply (1) ¡ Costs of production l l Change in input costs Change in technology Organisational changes Government policy (taxation/subsidy) Profitability of substitutes ¡ Profitability of goods in joint supply ¡ Unpredictable events –”random shock” ¡
 Non-price determinants of supply (2) ¡ Aims of producers l ¡ Profit or sales maximisation Expectations of future price changes l Expected rise = Reduced supply ¡ Build up of stocks ¡ Plan for increased production ¡ ¡ Number of suppliers l New firms – supply likely to rise
Non-price determinants of supply (2) ¡ Aims of producers l ¡ Profit or sales maximisation Expectations of future price changes l Expected rise = Reduced supply ¡ Build up of stocks ¡ Plan for increased production ¡ ¡ Number of suppliers l New firms – supply likely to rise
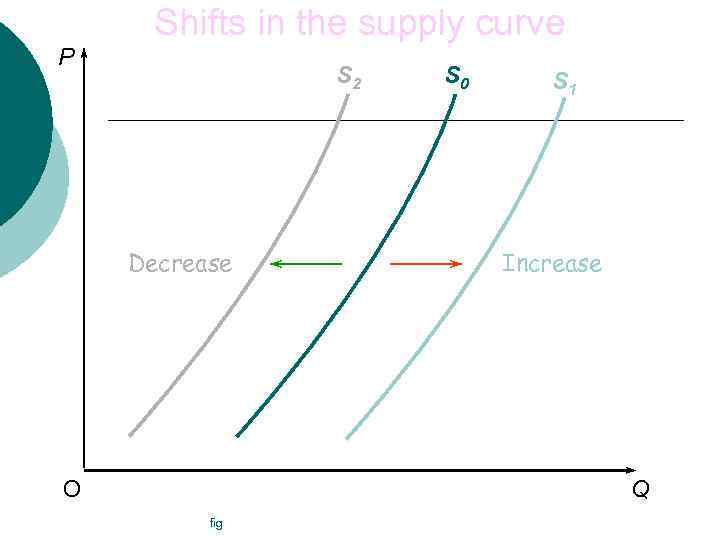 Shifts in the supply curve P S 2 Decrease O S 0 S 1 Increase Q fig
Shifts in the supply curve P S 2 Decrease O S 0 S 1 Increase Q fig
 Movements along and shifts in Supply Curve ¡ ¡ Movement along = change in quantity supplied Shift = change in supply l l Shift right – increased supply Shift left – reduced supply
Movements along and shifts in Supply Curve ¡ ¡ Movement along = change in quantity supplied Shift = change in supply l l Shift right – increased supply Shift left – reduced supply
 Discussion ¡ Thinking about all the factors that determine supply, identify what would cause : l (a) the supply of potatoes to fall and l (b) the supply of leather to rise
Discussion ¡ Thinking about all the factors that determine supply, identify what would cause : l (a) the supply of potatoes to fall and l (b) the supply of leather to rise
 Summary ¡ ¡ As the price of a good rises, quantity supplied over a period of time will rise Short run supply rises due to: l l ¡ ¡ Willingness to incur higher costs Switch from less profitable products Long run – new producers attracted Non-price determinants – production costs, alternatives, complements, random shocks, future expectations Price change – movement along curve Other determinant – shift left or right
Summary ¡ ¡ As the price of a good rises, quantity supplied over a period of time will rise Short run supply rises due to: l l ¡ ¡ Willingness to incur higher costs Switch from less profitable products Long run – new producers attracted Non-price determinants – production costs, alternatives, complements, random shocks, future expectations Price change – movement along curve Other determinant – shift left or right