d4e5ca62c2d4d7ae1b5cd18be860cf2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

Introduction to DNS and its vulnerabilities Olaf M. Kolkman olaf@nlnetlabs. nl © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

and DNS C in a SSE DN tshell Nu 2 source: http: //upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/b/b 7/Korean. Pine. Seeds. jpg
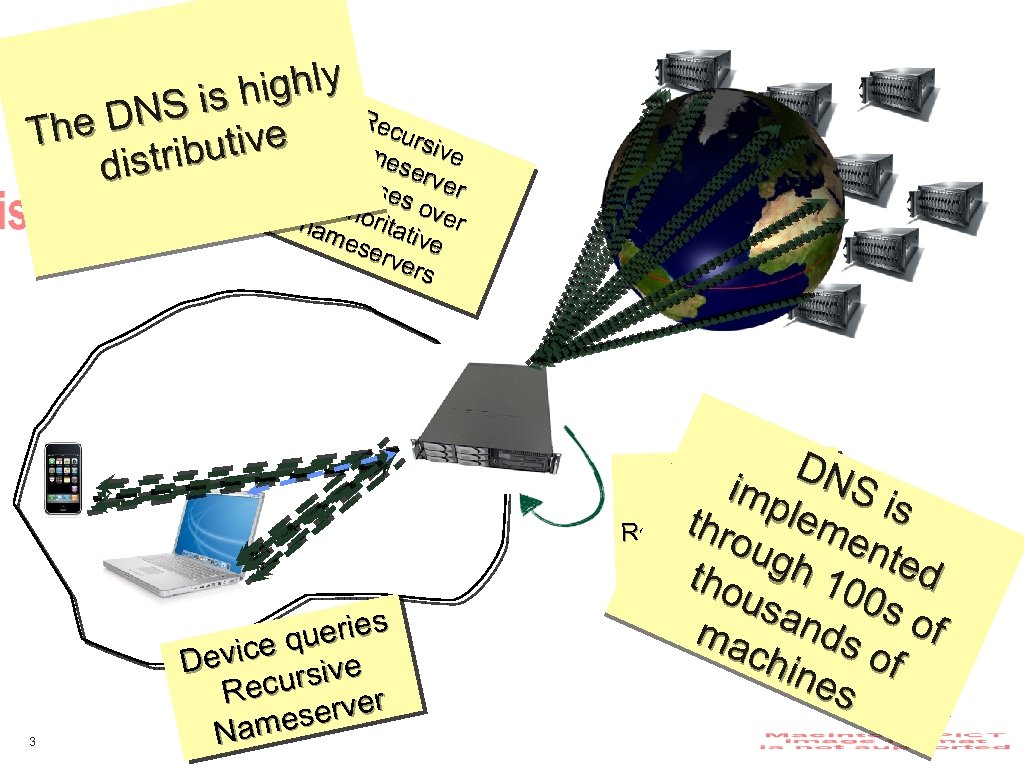
ighly S is h Rec e DN u Th ive R Names rsive tribut erv ecu dis er rse Aut hor s over nam itat ese ive rs 3 ueries ice q Dev ursive Rec erver ames N DN imp S is lem ts ro ulthare cached e Res ugh nte tho 100 d usa so f ma nds chi of nes
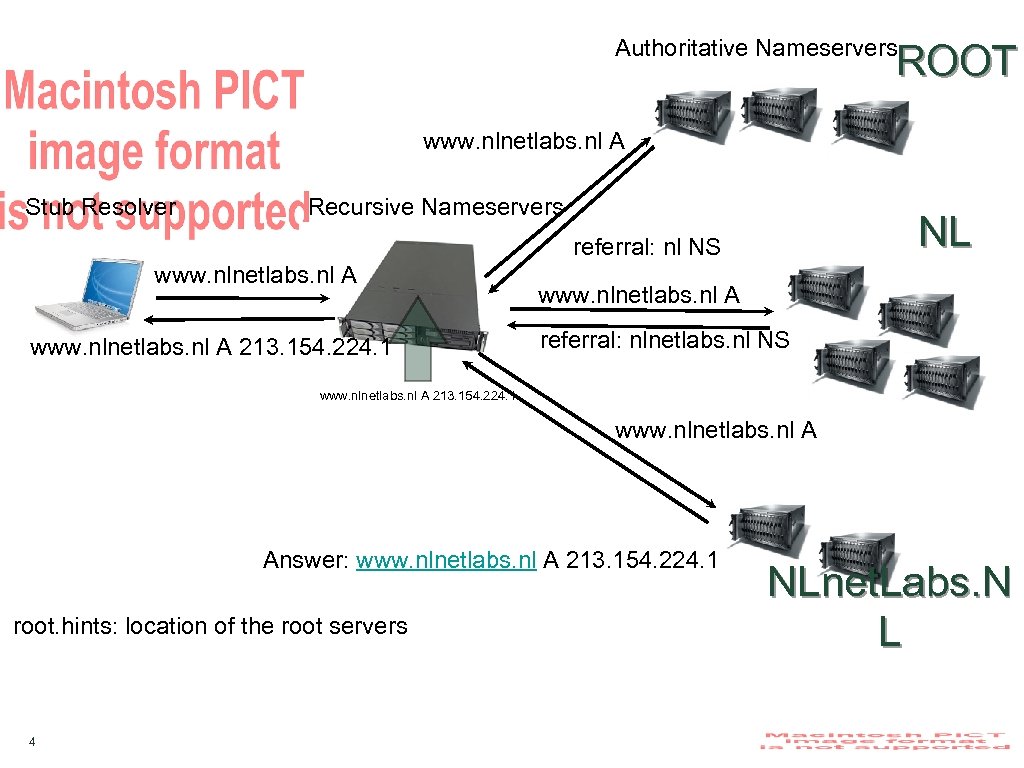
Authoritative Nameservers ROOT www. nlnetlabs. nl A Stub Resolver Recursive Nameservers NL referral: nl NS www. nlnetlabs. nl A 213. 154. 224. 1 www. nlnetlabs. nl A referral: nlnetlabs. nl NS www. nlnetlabs. nl A 213. 154. 224. 1 www. nlnetlabs. nl A Answer: www. nlnetlabs. nl A 213. 154. 224. 1 root. hints: location of the root servers 4 NLnet. Labs. N L
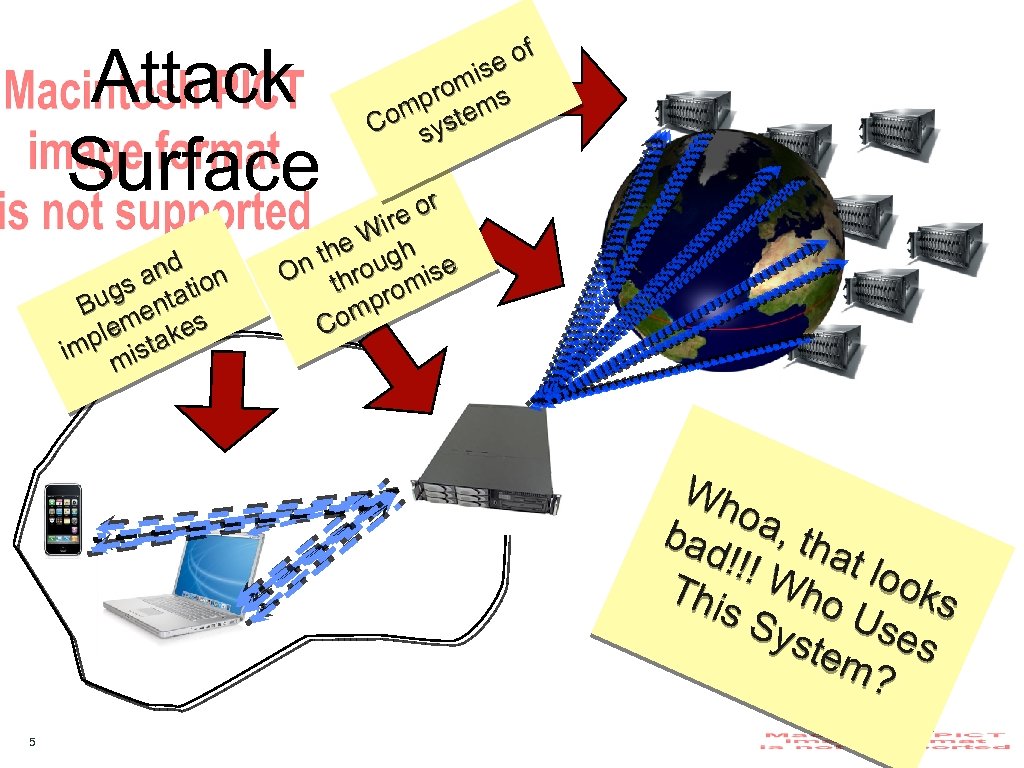
Attack Surface and tion gs ta Bu en lem takes mp is i m of ise rom s mp tem Co sys or ire e W gh n th rou ise O th rom mp Co Wh oa, bad tha !!! t loo Th Who ks is S Use yst em s ? 5
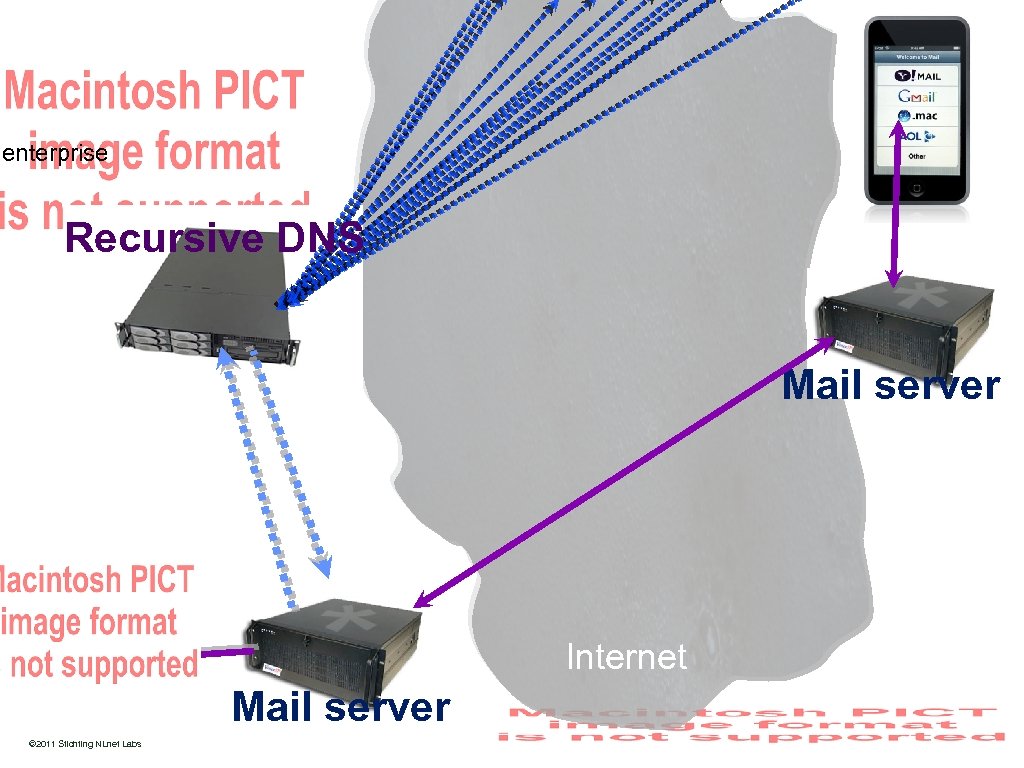
enterprise Recursive DNS Mail server Internet http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ © 2011 Stichting NLnet Labs Mail server
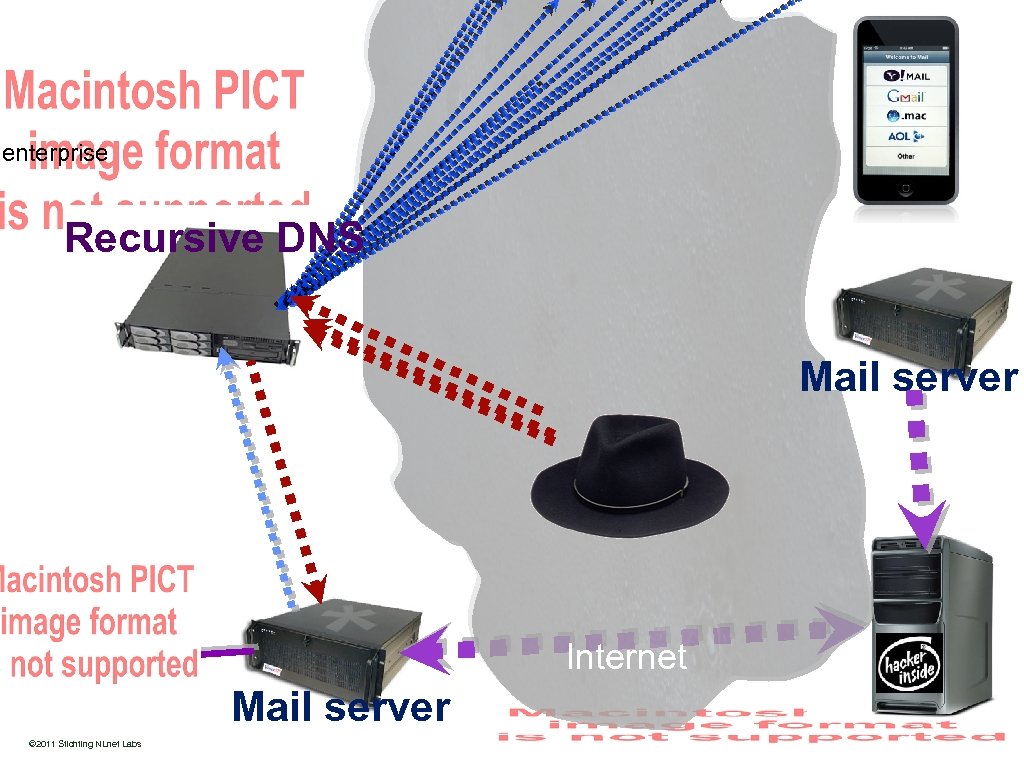
enterprise Recursive DNS Mail server Internet http: //www. nlnetlabs. nl/ © 2011 Stichting NLnet Labs Mail server
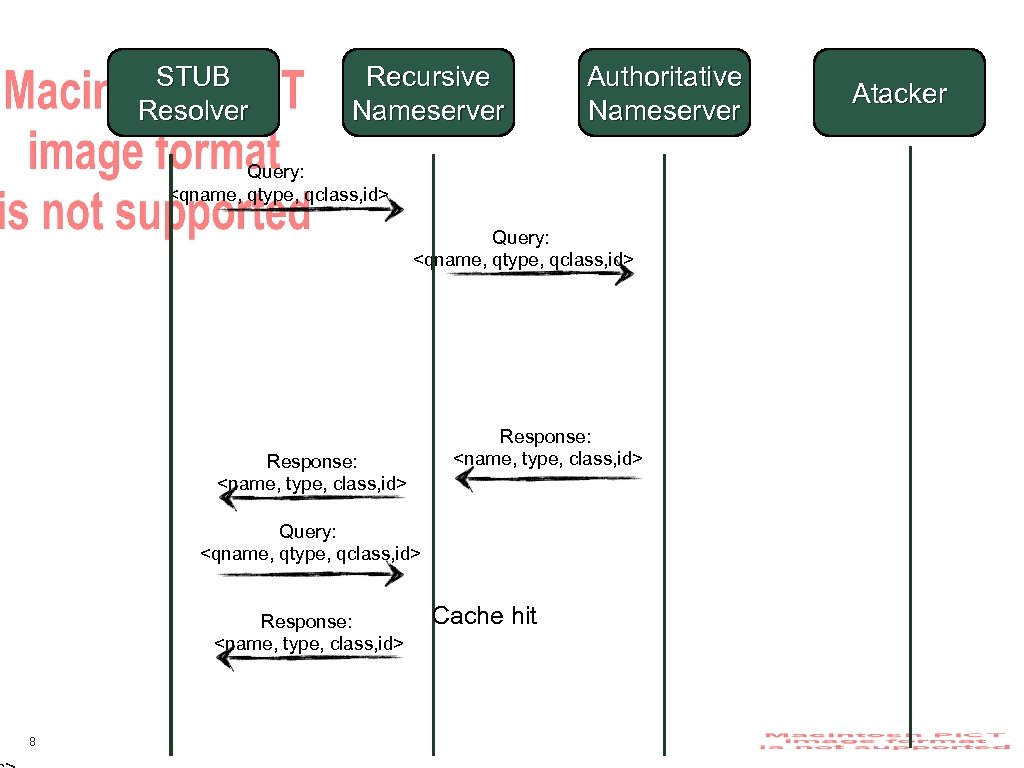
STUB Resolver Recursive Nameserver Authoritative Nameserver Query: <qname, qtype, qclass, id> Response: <name, type, class, id> 8 Cache hit Atacker
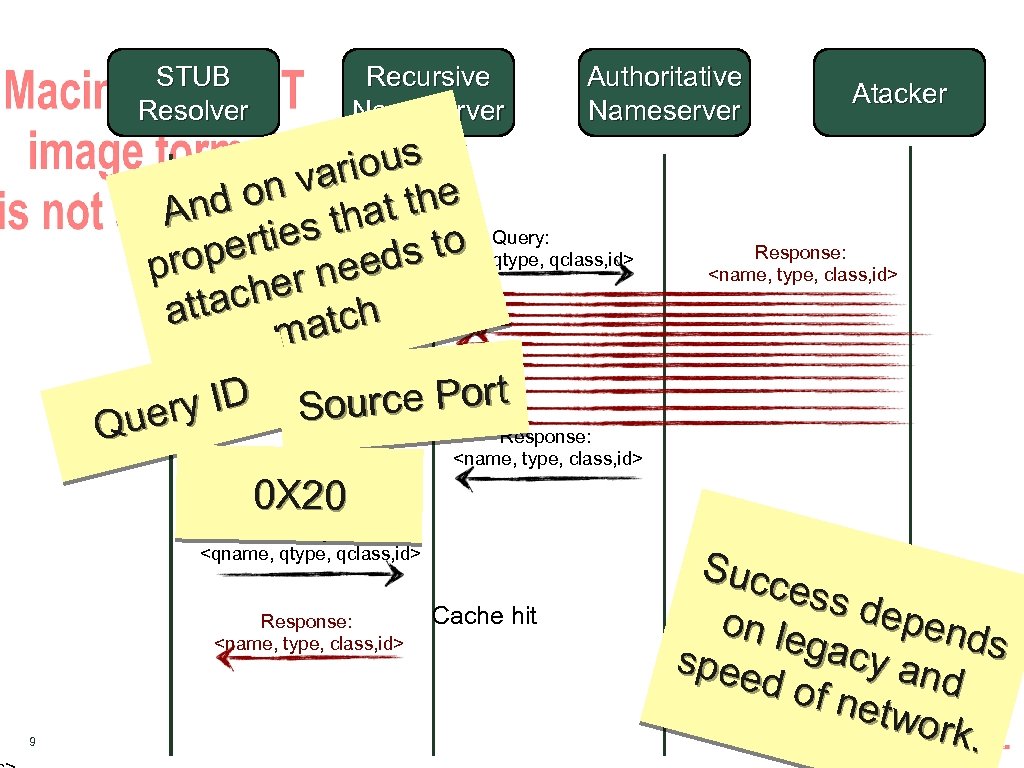
STUB Resolver Recursive Nameserver Authoritative Nameserver ious var d on that the An Query: rties o qtype, qclass, id> ds t ope e <qname, pr r ne che atta atch m Response: ID type, ource Port ery <name, S class, id> Qu Response: Atacker Query: <qname, qtype, qclass, id> Response: <name, type, class, id> 0 X 20 Query: <qname, qtype, qclass, id> Response: <name, type, class, id> 9 Cache hit Succ ess d epen on le ds gacy spee and d of netw ork.

TTL saves you? !? I don’t think so. . Dan Kaminsky’s image from zdnet. com 10 curity Se pstar Po
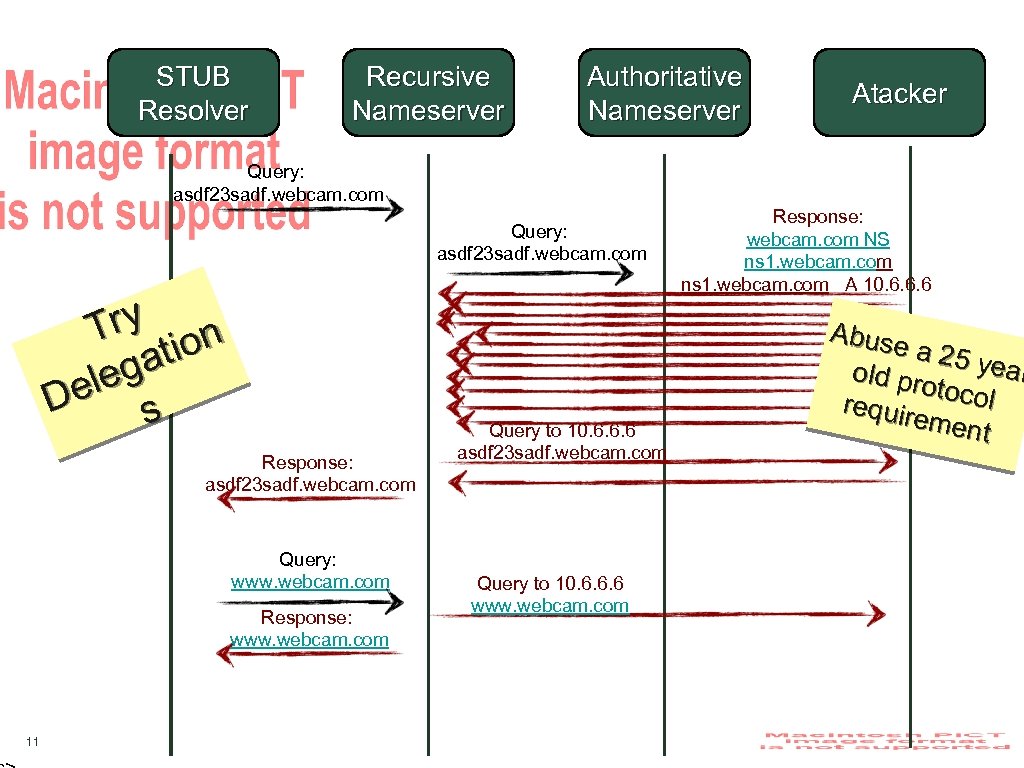
STUB Resolver Recursive Nameserver Authoritative Nameserver Atacker Query: asdf 23 sadf. webcam. com Try ion at leg De s Response: asdf 23 sadf. webcam. com Query: www. webcam. com Response: www. webcam. com 11 Query to 10. 6. 6. 6 asdf 23 sadf. webcam. com Query to 10. 6. 6. 6 www. webcam. com Response: webcam. com NS ns 1. webcam. com A 10. 6. 6. 6 Abuse a 25 y ear old pr otoco l requir emen t

Do a ttack happ s en in prac tice? notice? uld you Wo u d yo l Wou ll? te 12

Do a ttack happ s en in prac tice? one uld y wo DNS? Wh the tack at Wh ile one doi ng cou oth er t ld be hin gs 13

How to Prot ect? 14

one ould S? hy w W DN k the ttac a Sh ort yo -se ur llin sto g ck Mon€y Orga nizin g you r life 15 Follow the g ayin P r Tax you Your w eekly securit y update

Mon€y ese all th se on’t D ns u ctio nsa tra and SSL tes? ifica ert C 16
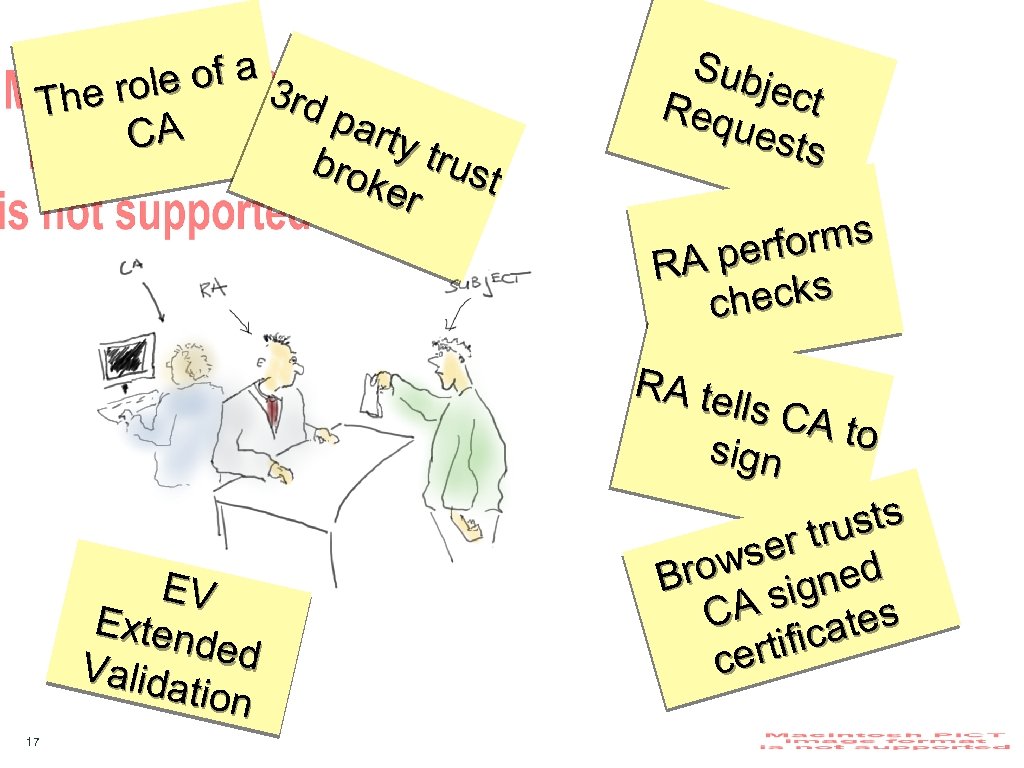
le of a 3 r he ro T dp arty CA bro trust ker Sub ject Req uest s forms A per R hecks c RA te lls CA to sign EV Exten ded Valida tion 17 sts r tru wse ed Bro sign CA ates rtific ce
Howe ver al little m l thes e en ar eaw bit ex ee pensi ve AUTOMATE THE LOT 18
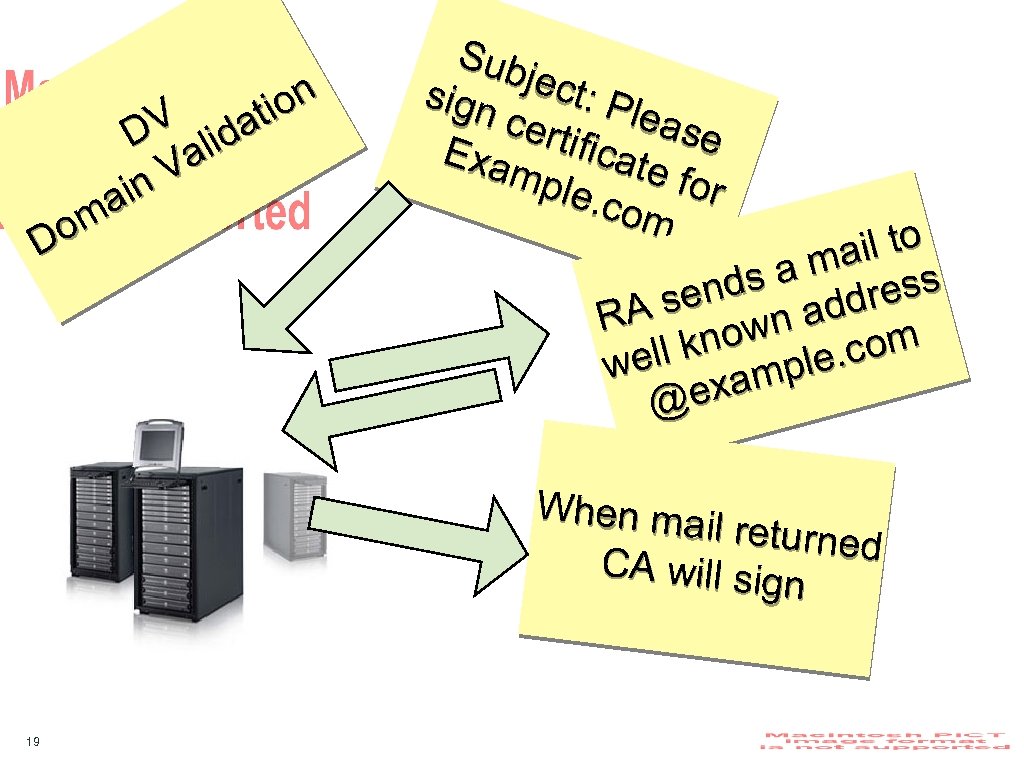
on V idati D l Va in a om D Sub ject sign : Ple certi ase fi ca Exa te fo mpl r e. co m il to ma s sa end addres As R own. com ll kn we ple xam @e When ma il returned CA will sig n 19
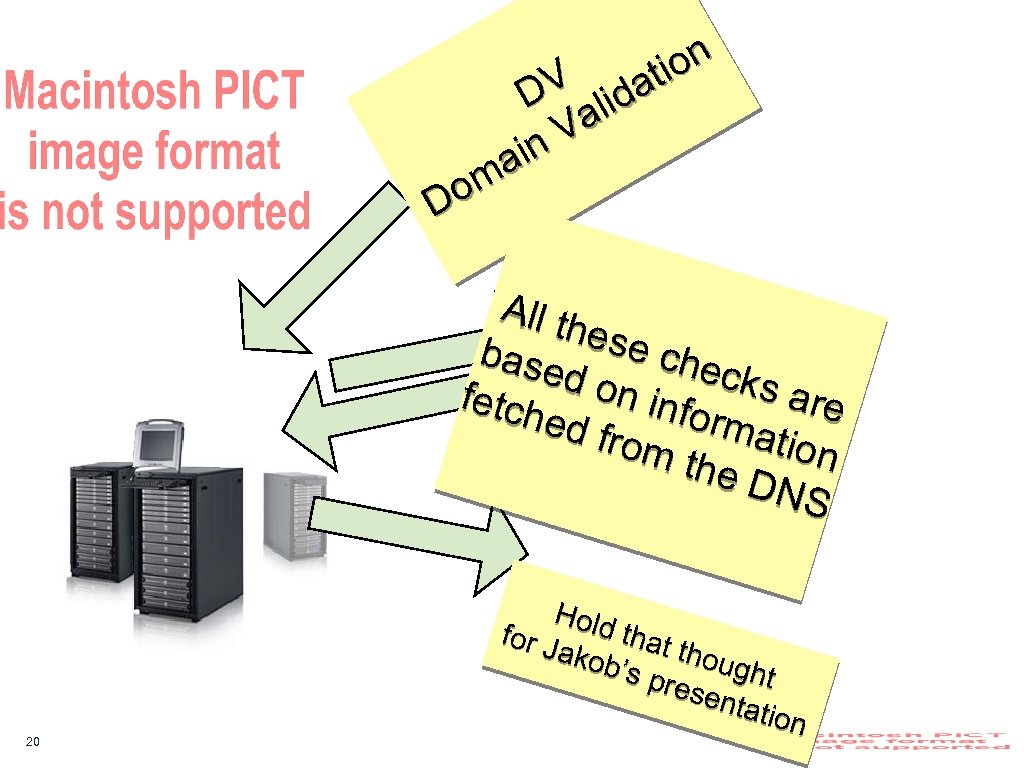
on V idati D l Va in a om D All th ese c base heck d on s ar fetch info e ed fr rma tion om t he D NS 20 Hold that for J thou akob ght ’s p rese ntatio n
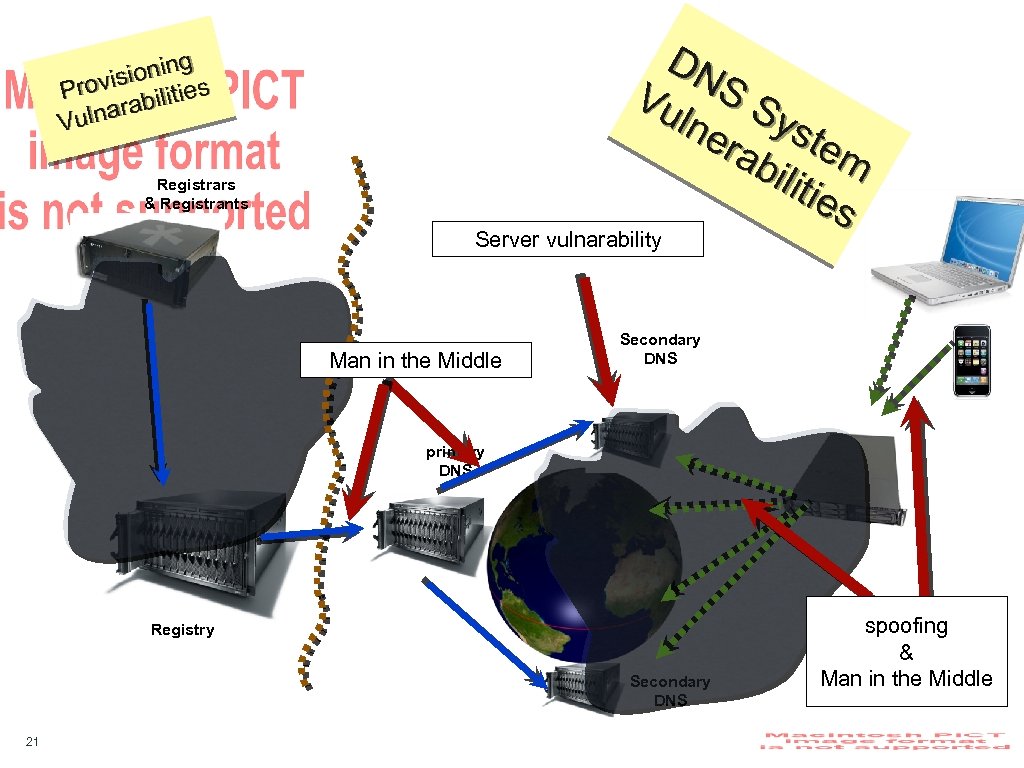
DN Vu S S lne ys rab tem iliti es g ionin rovis ilities P narab Vul Registrars & Registrants Server vulnarability Man in the Middle Secondary DNS primary DNS Registry Secondary DNS 21 spoofing & Man in the Middle

Wha t can one prot do to ect. . . (skip ping DNS SEC ) 22

Taking Unbound as example. Othe r ser mak vers e oth migh t but a er cho ices ny m reso , oder lver n take s sim appr oach ilar es © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
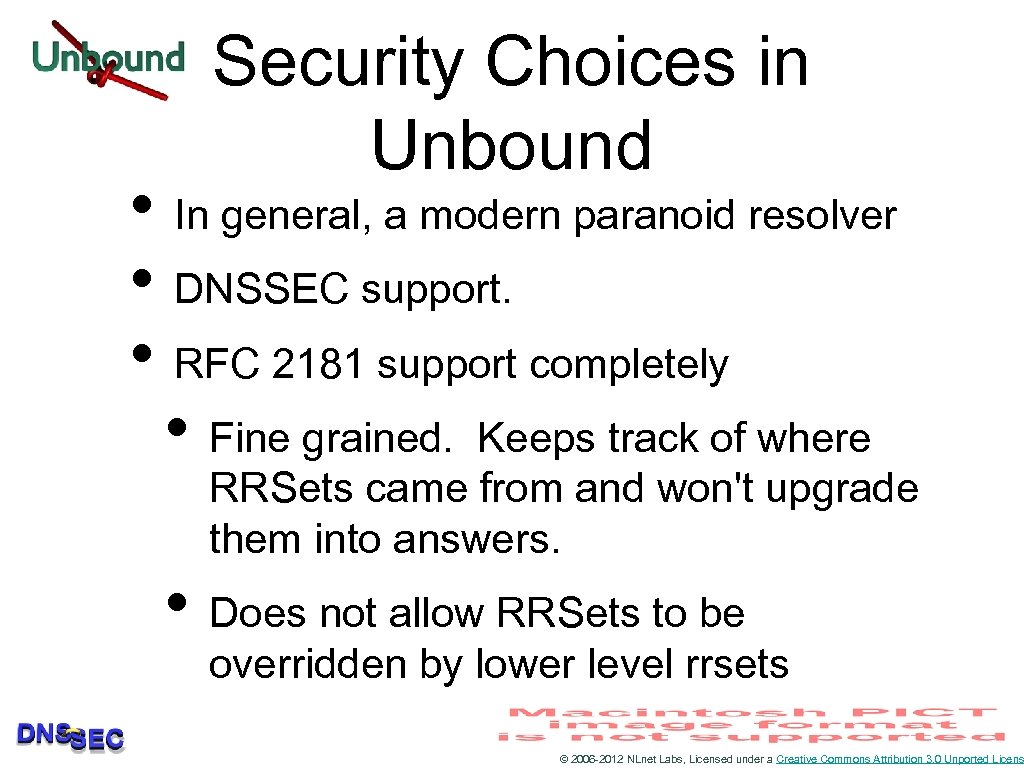
Security Choices in Unbound • In general, a modern paranoid resolver • DNSSEC support. • RFC 2181 support completely • Fine grained. Keeps track of where RRSets came from and won't upgrade them into answers. • Does not allow RRSets to be overridden by lower level rrsets © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
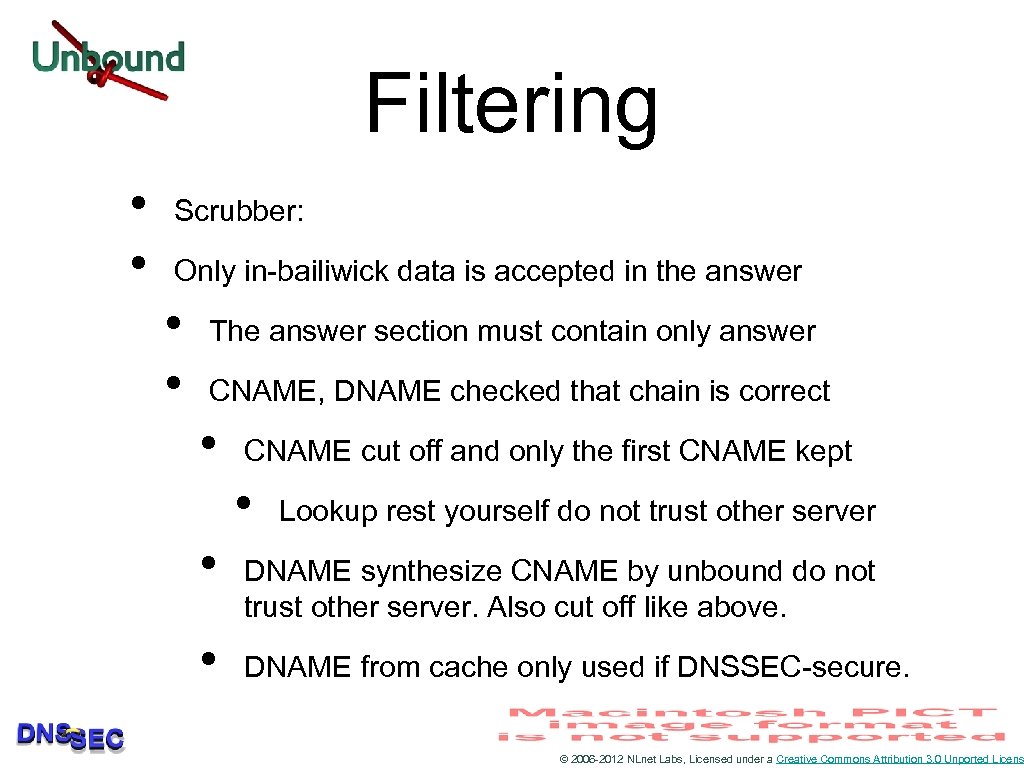
Filtering • • Scrubber: Only in-bailiwick data is accepted in the answer • • The answer section must contain only answer CNAME, DNAME checked that chain is correct • CNAME cut off and only the first CNAME kept • • • Lookup rest yourself do not trust other server DNAME synthesize CNAME by unbound do not trust other server. Also cut off like above. DNAME from cache only used if DNSSEC-secure. © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Filtering II • No address records in authority, additional section unless relevant – i. e. mentioned in a NS record in the authority section. • Irrelevant data is removed • When the message only had preliminary parsing and has not yet been copied to the working region of memory © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
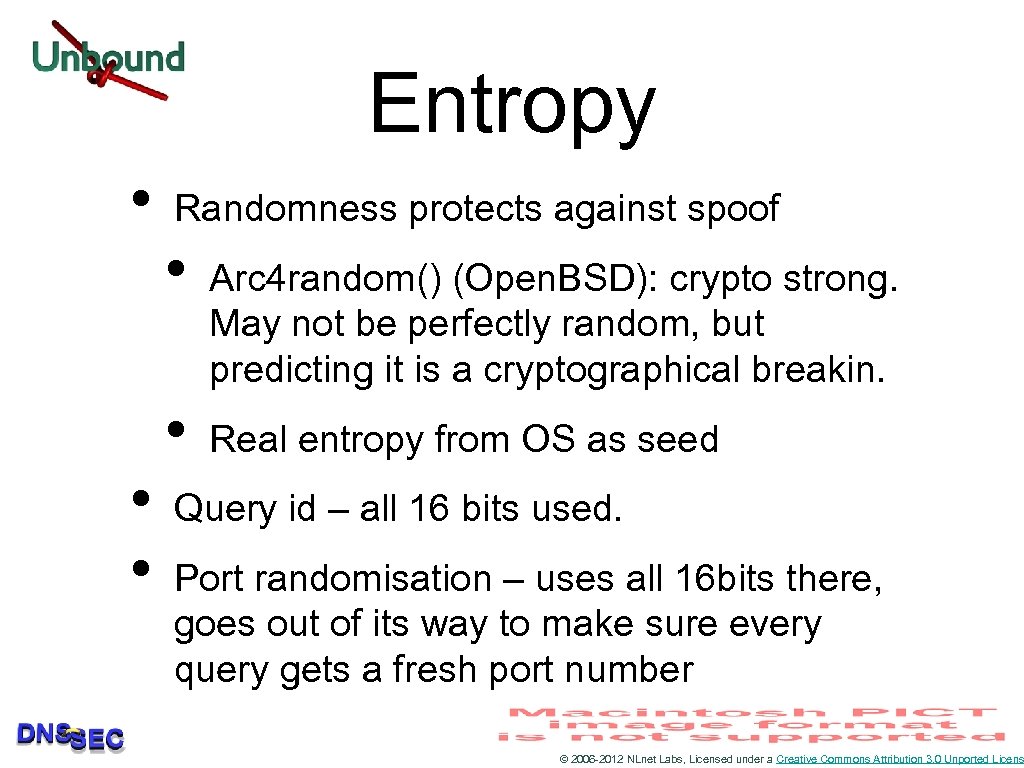
Entropy • • • Randomness protects against spoof • • Arc 4 random() (Open. BSD): crypto strong. May not be perfectly random, but predicting it is a cryptographical breakin. Real entropy from OS as seed Query id – all 16 bits used. Port randomisation – uses all 16 bits there, goes out of its way to make sure every query gets a fresh port number © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
Entropy II • Destination address, and ipv 4/ipv 6. RTT band of 400 msec (=everything). • • • Its not the timewindow but the randomness Query aggregation – same queries are not sent out – unless by different threads Qname strict match checked in reply 0 x 20 option Harden-referral-path (my draft) option Can use multiple source interfaces! • 4 outgoing IP address add +2 bits © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Other measures • Not for the wire itself • • Heap function pointer protection (whitelisted) Chroot() by default User privileges are dropped (lots of code!) ACL for recursion No detection of attacks – assume always under attack version. bind hostname. bind can be blocked or configured what to return (version hiding) Disprefer recursion lame servers – they have a cache that can be poisoned © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Arm s Ra ce. . . EC SS DN ing uc rod Int © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
Metaphor 31
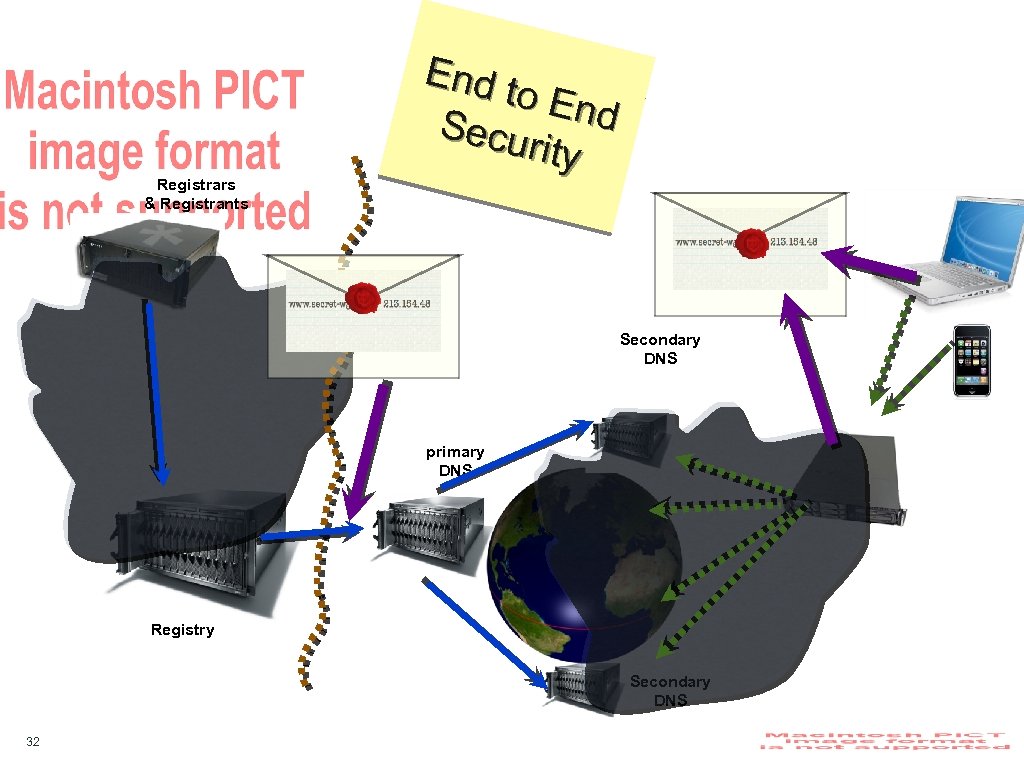
Registrars & Registrants End t o End Secu rity Secondary DNS primary DNS Registry Secondary DNS 32

All d one usin g Pu Key blic cryp to blic : pu KEY he NS D mt y fro ke pair key RR SIG ma : Si de gna with key ture from ap s the rivate key pair 33 EC 3 nd NS d EC a NS ulate e-calc or pr F ence Exist ial of Den DS ating leg de rity or cu F Se

But more on that later Let us h ano the ave a r cr DN ypto look a Sp t gra phic me rotec tion cha nism © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Securing Host Communication © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
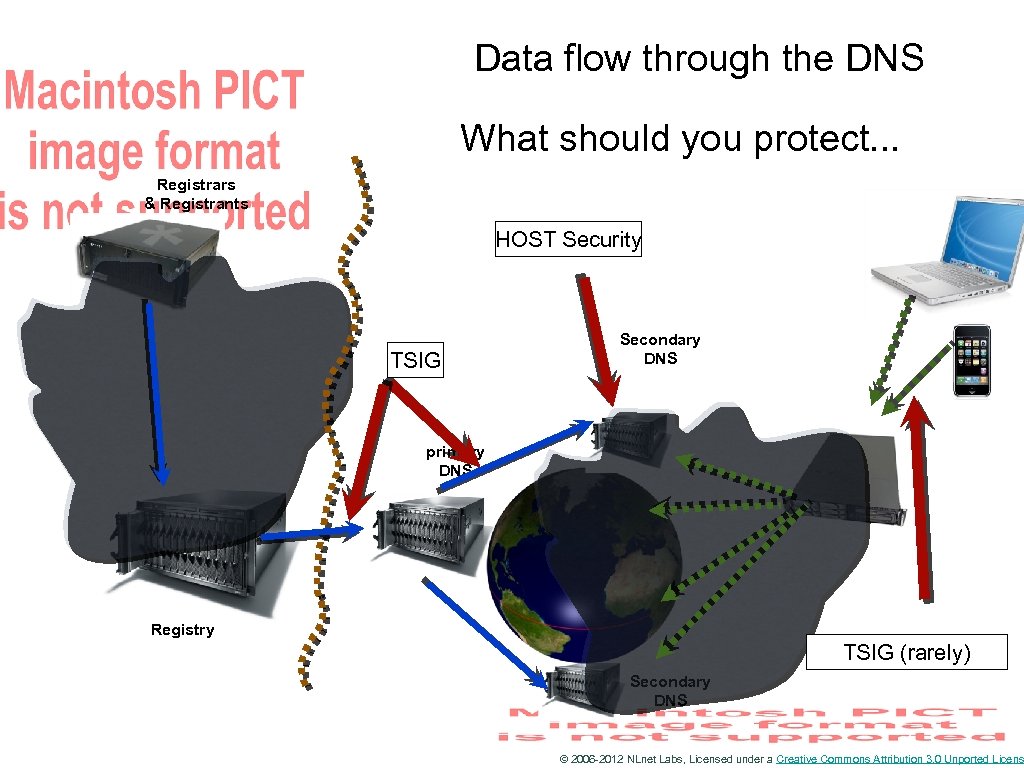
Data flow through the DNS What should you protect. . . Registrars & Registrants HOST Security TSIG Secondary DNS primary DNS Registry TSIG (rarely) Secondary DNS © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
Transaction Signature: TSIG • TSIG (RFC 2845) –Authorising dynamic updates and zone transfers –Authentication of caching forwarders –Independent from other features of DNSSEC • One-way hash function –DNS question or answer and timestamp • Traffic signed with “shared secret” key • Used in configuration, NOT in zone file © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
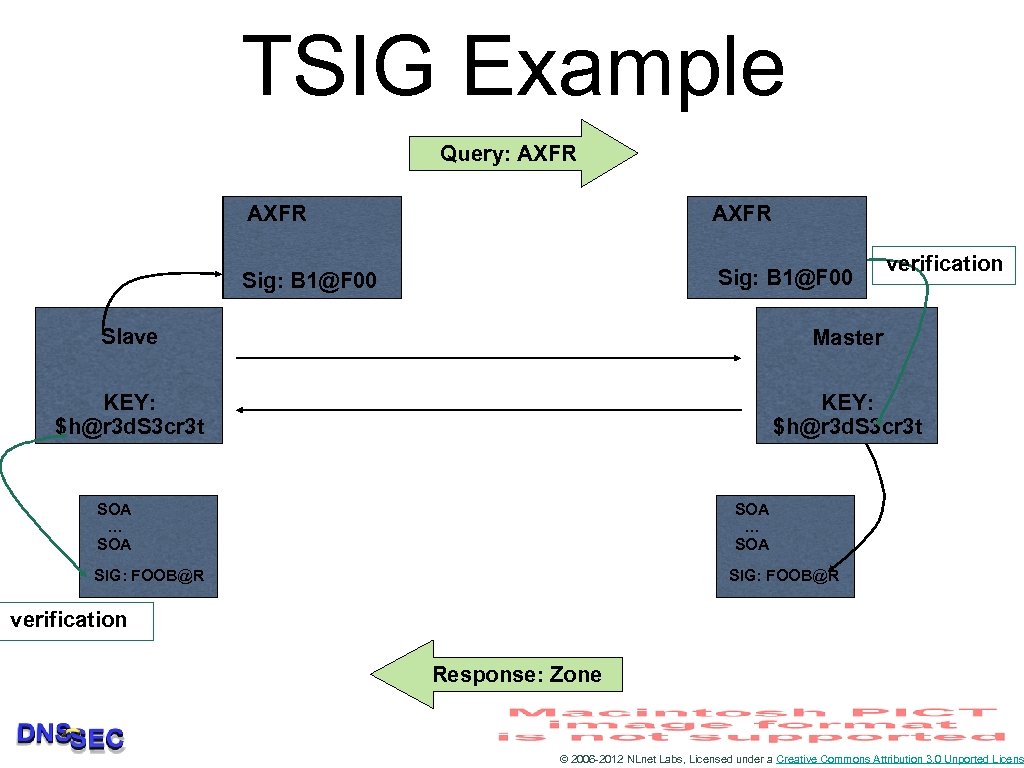
TSIG Example Query: AXFR Sig: B 1@F 00 verification Slave Master KEY: $h@r 3 d. S 3 cr 3 t SOA … SOA SIG: FOOB@R verification Response: Zone © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

TSIG for Zone Transfers 1. Generate secret 2. Communicate secret 3. Configure servers 4. Test © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Importance of the Time Stamp • TSIG/SIG(0) signs a complete DNS request / response with time stamp – To prevent replay attacks – Currently hardcoded at five minutes • Operational problems when comparing times – Make sure your local time zone is properly defined – date -u will give UTC time, easy to compare between the two systems – Use NTP synchronisation! © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

Authenticating Servers Using SIG(0) • Alternatively, it is possible to use SIG(0) –Not yet widely used –Works well in dynamic update environment • Public key algorithm –Authentication against a public key published in the DNS • SIG(0) specified in RFC 2931 © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
Cool Application • Use TSIG-ed dynamic updates to configure your laptops name • My laptop is know by the name of aagje. secret-wg. org – http: //ops. ietf. org/dns/dynupd/secure-ddnshowto. html –Mac OS users: there is a bonjour based tool. • www. dns-sd. org © 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens

© 2006 -2012 NLnet Labs, Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. 0 Unported Licens
d4e5ca62c2d4d7ae1b5cd18be860cf2d.ppt