139dd4c7ca01e13e3eb3075bcdd3d52f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Introduction to Computing CSCI 101 Marguerite Doman, Ph. D v r
Introduction to Computing CSCI 101 Marguerite Doman, Ph. D v r
 Communications n Syllabus n Blackboard - online. winthrop. edu n Homework to be turned in through Blackboard Quizzes will be done through Blackboard n
Communications n Syllabus n Blackboard - online. winthrop. edu n Homework to be turned in through Blackboard Quizzes will be done through Blackboard n
 Grading n n n Practical Exercises and Homework: 40% Online Quizzes 10% Exam 1 : 15% Exam 2 : 15% Cumulative Final Exam: 20%
Grading n n n Practical Exercises and Homework: 40% Online Quizzes 10% Exam 1 : 15% Exam 2 : 15% Cumulative Final Exam: 20%
 Practical Assignments n Hardware Software Assignment n Cyber. Protect n Hour of Code n Ear. Sketch q Music technology and Python
Practical Assignments n Hardware Software Assignment n Cyber. Protect n Hour of Code n Ear. Sketch q Music technology and Python
 Late Homework Policy n Online quizzes must be completed on time. The quizzes will be closed at the end of day of the lecture. n 3 slip days q n Gain additional days by short in-class activities Extra Credit q q Remaining slip days (. 5%) Extra credit assignment: . . %
Late Homework Policy n Online quizzes must be completed on time. The quizzes will be closed at the end of day of the lecture. n 3 slip days q n Gain additional days by short in-class activities Extra Credit q q Remaining slip days (. 5%) Extra credit assignment: . . %
 Exercise : Who are your classmates n n n Name Major Hometown One thing he/she did over the summer One more question… you come up with this one.
Exercise : Who are your classmates n n n Name Major Hometown One thing he/she did over the summer One more question… you come up with this one.
 History of Computing … Very Short Marguerite Doman, Ph. D
History of Computing … Very Short Marguerite Doman, Ph. D
 What is a Computer? n Perform the repetitive calculations for – q q q q Sheep Grain Astronomy Census information Navigational tides Finance ----- Anything we want
What is a Computer? n Perform the repetitive calculations for – q q q q Sheep Grain Astronomy Census information Navigational tides Finance ----- Anything we want
 In the beginning… Calculating Machines photos from en. wikipedia. org
In the beginning… Calculating Machines photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Counting Tables Ø Ø A stone with grooves on one side used as place values. Small stones were used within the lines for calculating n Thought to be the precursors of the Abacus. n Medieval device with 2000 years of documented use Store ‘counter’ derived from counting tables n Pullan, J. M, The History of the abacus. Lunodon: Books that Matter, 1986; Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
Counting Tables Ø Ø A stone with grooves on one side used as place values. Small stones were used within the lines for calculating n Thought to be the precursors of the Abacus. n Medieval device with 2000 years of documented use Store ‘counter’ derived from counting tables n Pullan, J. M, The History of the abacus. Lunodon: Books that Matter, 1986; Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
 The Salamis Tablet n n The oldest surviving counting board used by the Babylonians circa 300 B. C. Gaming board “The gaming boards used by ancient cultures such as the Babylonians and the Romans are thought to be the precursors of the Abacus. n The Salamis tablet is approximately 150 x 75 x 4. 5 cm and is made of marble. Pullan, J. M, The History of the abacus. Lunodon: Books that Matter, 1986; Salamis Tablet; Jacksonville University http: //users. ju. edu/ssundbe/salamis. html Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
The Salamis Tablet n n The oldest surviving counting board used by the Babylonians circa 300 B. C. Gaming board “The gaming boards used by ancient cultures such as the Babylonians and the Romans are thought to be the precursors of the Abacus. n The Salamis tablet is approximately 150 x 75 x 4. 5 cm and is made of marble. Pullan, J. M, The History of the abacus. Lunodon: Books that Matter, 1986; Salamis Tablet; Jacksonville University http: //users. ju. edu/ssundbe/salamis. html Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
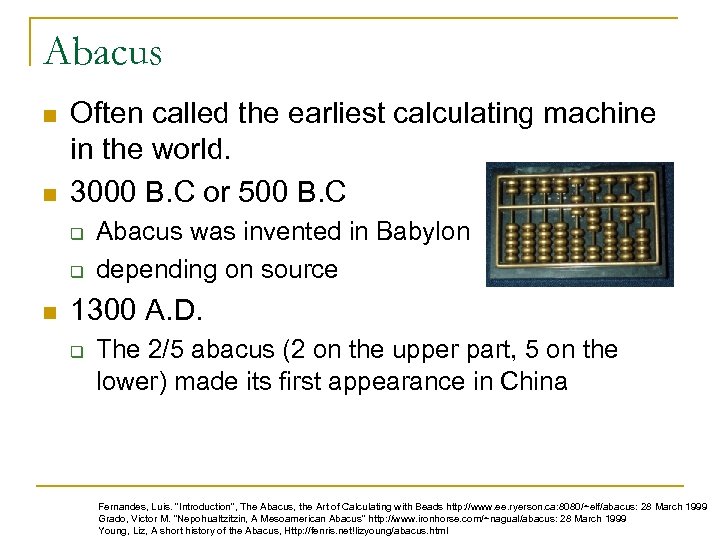 Abacus n n Often called the earliest calculating machine in the world. 3000 B. C or 500 B. C q q n Abacus was invented in Babylon depending on source 1300 A. D. q The 2/5 abacus (2 on the upper part, 5 on the lower) made its first appearance in China Fernandes, Luis. "Introduction", The Abacus, the Art of Calculating with Beads http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca: 8080/~elf/abacus: 28 March 1999 Grado, Victor M. "Nepohualtzitzin, A Mesoamerican Abacus" http: //www. ironhorse. com/~nagual/abacus: 28 March 1999 Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
Abacus n n Often called the earliest calculating machine in the world. 3000 B. C or 500 B. C q q n Abacus was invented in Babylon depending on source 1300 A. D. q The 2/5 abacus (2 on the upper part, 5 on the lower) made its first appearance in China Fernandes, Luis. "Introduction", The Abacus, the Art of Calculating with Beads http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca: 8080/~elf/abacus: 28 March 1999 Grado, Victor M. "Nepohualtzitzin, A Mesoamerican Abacus" http: //www. ironhorse. com/~nagual/abacus: 28 March 1999 Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
 Abacus An form of the abacus was found during archeological excavations in Central America. q q q dates to around 900 AD and is constructed from maize kernels threaded on a string, all contained within a wooden frame 7 beads by 13 columns. Fernandes, Luis. "Introduction", The Abacus, the Art of Calculating with Beads http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca: 8080/~elf/abacus: 28 March 1999 Grado, Victor M. "Nepohualtzitzin, A Mesoamerican Abacus" http: //www. ironhorse. com/~nagual/abacus: 28 March 1999 Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
Abacus An form of the abacus was found during archeological excavations in Central America. q q q dates to around 900 AD and is constructed from maize kernels threaded on a string, all contained within a wooden frame 7 beads by 13 columns. Fernandes, Luis. "Introduction", The Abacus, the Art of Calculating with Beads http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca: 8080/~elf/abacus: 28 March 1999 Grado, Victor M. "Nepohualtzitzin, A Mesoamerican Abacus" http: //www. ironhorse. com/~nagual/abacus: 28 March 1999 Young, Liz, A short history of the Abacus, Http: //fenris. net!lizyoung/abacus. html
 Antikythera mechanism n n n 80 A. D. Bronze mechanical calculator for lunar calendar The mechanism is the oldest known complex scientific calculator. Antikythera video
Antikythera mechanism n n n 80 A. D. Bronze mechanical calculator for lunar calendar The mechanism is the oldest known complex scientific calculator. Antikythera video
 Napier’s Bones 1600 n n 1600 A. D. John Napier invented strips to help with mulitiplication Napier’s bones demonstration
Napier’s Bones 1600 n n 1600 A. D. John Napier invented strips to help with mulitiplication Napier’s bones demonstration
 Slide Rule 1622 n n Invented by William Oughtred Mechanical analog computer Used primarily for multiplication and division, and also for "scientific" functions such as roots, logarithms and trigonometry. Still in use in the 1960's by the NASA programs which landed men on the moon.
Slide Rule 1622 n n Invented by William Oughtred Mechanical analog computer Used primarily for multiplication and division, and also for "scientific" functions such as roots, logarithms and trigonometry. Still in use in the 1960's by the NASA programs which landed men on the moon.
 Calculating Machines … with Logic photos from en. wikipedia. org
Calculating Machines … with Logic photos from en. wikipedia. org
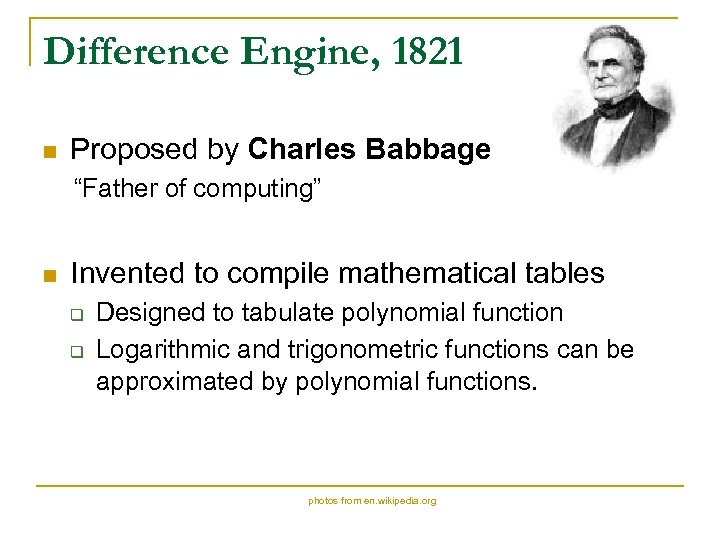 Difference Engine, 1821 n Proposed by Charles Babbage “Father of computing” n Invented to compile mathematical tables q q Designed to tabulate polynomial function Logarithmic and trigonometric functions can be approximated by polynomial functions. photos from en. wikipedia. org
Difference Engine, 1821 n Proposed by Charles Babbage “Father of computing” n Invented to compile mathematical tables q q Designed to tabulate polynomial function Logarithmic and trigonometric functions can be approximated by polynomial functions. photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Close up of a reconstruction of Babbage’s Difference Engine photos from en. wikipedia. org
Close up of a reconstruction of Babbage’s Difference Engine photos from en. wikipedia. org
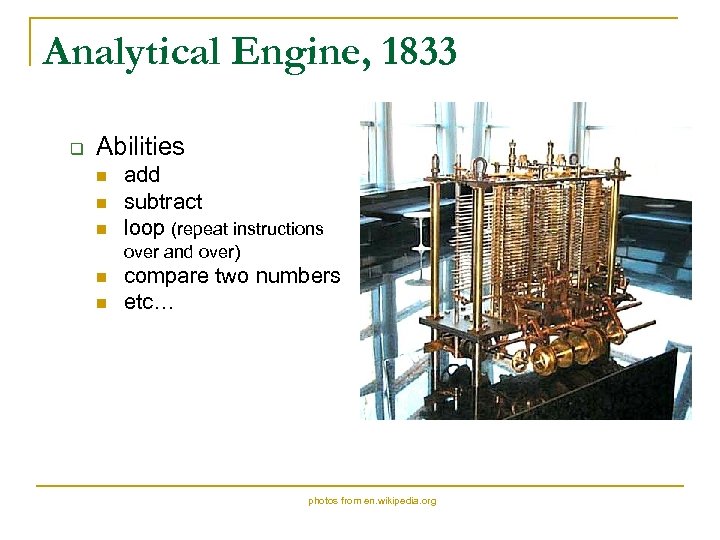 Analytical Engine, 1833 q Abilities n n n add subtract loop (repeat instructions over and over) n n compare two numbers etc… photos from en. wikipedia. org
Analytical Engine, 1833 q Abilities n n n add subtract loop (repeat instructions over and over) n n compare two numbers etc… photos from en. wikipedia. org
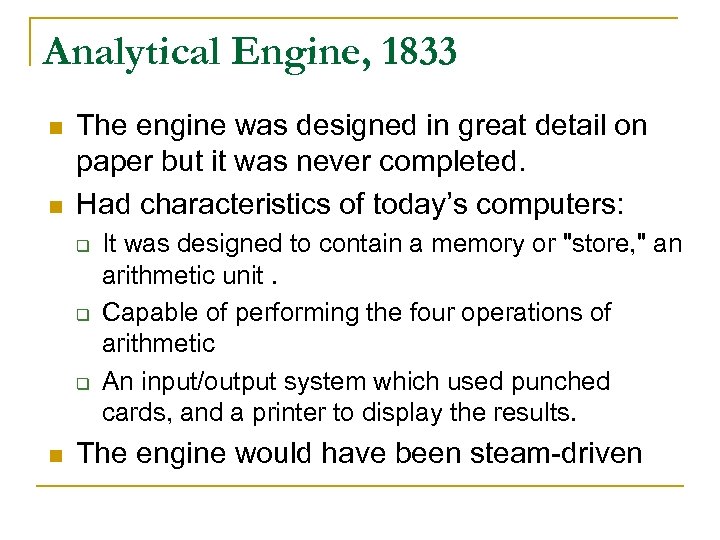 Analytical Engine, 1833 n n The engine was designed in great detail on paper but it was never completed. Had characteristics of today’s computers: q q q n It was designed to contain a memory or "store, " an arithmetic unit. Capable of performing the four operations of arithmetic An input/output system which used punched cards, and a printer to display the results. The engine would have been steam-driven
Analytical Engine, 1833 n n The engine was designed in great detail on paper but it was never completed. Had characteristics of today’s computers: q q q n It was designed to contain a memory or "store, " an arithmetic unit. Capable of performing the four operations of arithmetic An input/output system which used punched cards, and a printer to display the results. The engine would have been steam-driven
 Ada Byron, Countess of Lovelace n n n Daughter of Lord Byron Suggests to Babbage that he use the binary system. She writes programs for his analytical engine, becoming the world's first programmer photos from en. wikipedia. org
Ada Byron, Countess of Lovelace n n n Daughter of Lord Byron Suggests to Babbage that he use the binary system. She writes programs for his analytical engine, becoming the world's first programmer photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Internet Related Developments n n 1844 – Samuel Morse sends the first telegraphic message from Washing ton to Baltimore. 1856 -1866 Europe and all of America is connected by telegraph 1876 - Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone. 1901 Marconi sends the first transatlantic wireless message.
Internet Related Developments n n 1844 – Samuel Morse sends the first telegraphic message from Washing ton to Baltimore. 1856 -1866 Europe and all of America is connected by telegraph 1876 - Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone. 1901 Marconi sends the first transatlantic wireless message.
 Modern Computers 1 st Generation - Vacuum Tubes 1946 -1958
Modern Computers 1 st Generation - Vacuum Tubes 1946 -1958
 Vacuum Tube, 1906 n n A glass tube surrounding a vacuum. When electrical contacts are put on the ends, a current flows though that vacuum. In electronics, a vacuum tube, is used to amplify, switch, otherwise modify, or create an electrical signal by controlling the movement of electrons in a lowpressure space. Inventor: Lee De. Forest From www. pbs. org/transitor/science/events/vacuumt. html
Vacuum Tube, 1906 n n A glass tube surrounding a vacuum. When electrical contacts are put on the ends, a current flows though that vacuum. In electronics, a vacuum tube, is used to amplify, switch, otherwise modify, or create an electrical signal by controlling the movement of electrons in a lowpressure space. Inventor: Lee De. Forest From www. pbs. org/transitor/science/events/vacuumt. html
 Atanasoff-Berry Computer, 1930 n n n Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry The first electrically powered digital computer Used vacuum tubes to store data n First computer to use the binary system photos from en. wikipedia. org
Atanasoff-Berry Computer, 1930 n n n Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry The first electrically powered digital computer Used vacuum tubes to store data n First computer to use the binary system photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Colossus 1944 n n Developed in UK during WWII Used by British codebreakers to help read encrypted German messages in World War II. photos from en. wikipedia. org
Colossus 1944 n n Developed in UK during WWII Used by British codebreakers to help read encrypted German messages in World War II. photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Harvard Mark 1, 1944 n n n Created by Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper Electro-mechanical mechanism used to compute artillery tables Handled 4 arithmetic functions, with special programs for logs and trig. storage = 72 numbers photos from en. wikipedia. org
Harvard Mark 1, 1944 n n n Created by Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper Electro-mechanical mechanism used to compute artillery tables Handled 4 arithmetic functions, with special programs for logs and trig. storage = 72 numbers photos from en. wikipedia. org
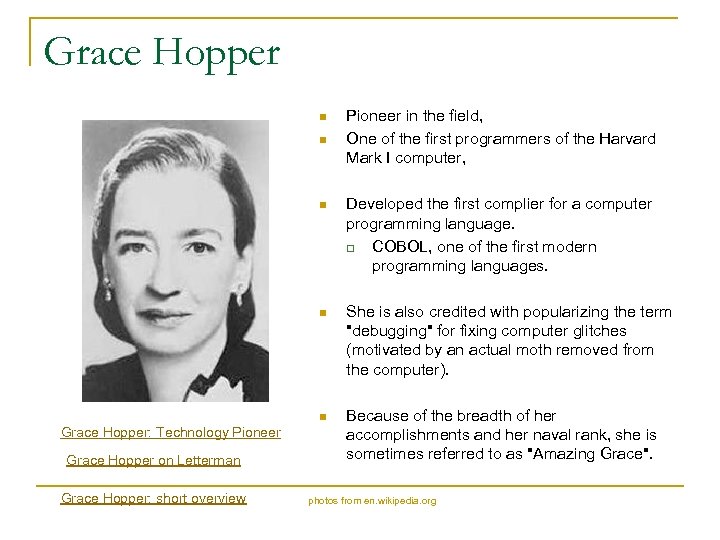 Grace Hopper n n Pioneer in the field, One of the first programmers of the Harvard Mark I computer, n n Grace Hopper on Letterman Grace Hopper: short overview She is also credited with popularizing the term "debugging" for fixing computer glitches (motivated by an actual moth removed from the computer). n Grace Hopper: Technology Pioneer Developed the first complier for a computer programming language. q COBOL, one of the first modern programming languages. Because of the breadth of her accomplishments and her naval rank, she is sometimes referred to as "Amazing Grace". photos from en. wikipedia. org
Grace Hopper n n Pioneer in the field, One of the first programmers of the Harvard Mark I computer, n n Grace Hopper on Letterman Grace Hopper: short overview She is also credited with popularizing the term "debugging" for fixing computer glitches (motivated by an actual moth removed from the computer). n Grace Hopper: Technology Pioneer Developed the first complier for a computer programming language. q COBOL, one of the first modern programming languages. Because of the breadth of her accomplishments and her naval rank, she is sometimes referred to as "Amazing Grace". photos from en. wikipedia. org
 Grace Hopper “ If it’s a good idea, you should do it. ” Grace Hopper: Technology Pioneer Grace Hopper on Letterman Grace Hopper: short overview photos from en. wikipedia. org
Grace Hopper “ If it’s a good idea, you should do it. ” Grace Hopper: Technology Pioneer Grace Hopper on Letterman Grace Hopper: short overview photos from en. wikipedia. org
 ENIAC 1946 n First General Purpose Computer n -Turing complete machine n ENIAC q q n EDVAC q q n 1946 - Univ of Pennsylvania programmed via wires based on ENIAC program stored memory UNIVAC q q 1951 first commercial machine photos from en. wikipedia. org in
ENIAC 1946 n First General Purpose Computer n -Turing complete machine n ENIAC q q n EDVAC q q n 1946 - Univ of Pennsylvania programmed via wires based on ENIAC program stored memory UNIVAC q q 1951 first commercial machine photos from en. wikipedia. org in
 Modern Computers 2 nd Generation - Transistors 1959 -1964
Modern Computers 2 nd Generation - Transistors 1959 -1964
 Transistors n Invented at Bell Laboratories The Bell Labs team of John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley won the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work in developing transistors. Vacuum tubes were far from ideal. They had to warm up before they worked (and sometimes overheated when they did), they were unreliable and bulky and they used too much energy. In the years after World War II, scientists were looking for alternatives to vacuum tubes. Transistors, made from silicon, have 2 different states. They are either on or off based on the current photos from http: //electronics. howstuffworks. com/transistor. htm
Transistors n Invented at Bell Laboratories The Bell Labs team of John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley won the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work in developing transistors. Vacuum tubes were far from ideal. They had to warm up before they worked (and sometimes overheated when they did), they were unreliable and bulky and they used too much energy. In the years after World War II, scientists were looking for alternatives to vacuum tubes. Transistors, made from silicon, have 2 different states. They are either on or off based on the current photos from http: //electronics. howstuffworks. com/transistor. htm
 Successful nd 2 Generation Computers n Time of big computers in big companies Proprietary and basically free software n Successful companies: n q q IBM Burroughs Control Data Honeywell
Successful nd 2 Generation Computers n Time of big computers in big companies Proprietary and basically free software n Successful companies: n q q IBM Burroughs Control Data Honeywell
 Example: IBM 1400 n n A general purpose system Used in conjunction with IBM punched card equipment.
Example: IBM 1400 n n A general purpose system Used in conjunction with IBM punched card equipment.
 Modern Computers 3 rd Generation Integrated Circuit 1965 -1970
Modern Computers 3 rd Generation Integrated Circuit 1965 -1970
 Integrated Circuits n Small chip containing thousands of transistors n Inventor: Jack Kilby, Nobel Laureate of Physics
Integrated Circuits n Small chip containing thousands of transistors n Inventor: Jack Kilby, Nobel Laureate of Physics
 System Examples: Burroughs B 5000 • First offered in 1960 • Consider the first of the 3 rd generation computers photo from http: //jack. hoaroots. org/Burr 104. html http: //www. vikingwaters. com/htmlpages/MFHistory. htm
System Examples: Burroughs B 5000 • First offered in 1960 • Consider the first of the 3 rd generation computers photo from http: //jack. hoaroots. org/Burr 104. html http: //www. vikingwaters. com/htmlpages/MFHistory. htm
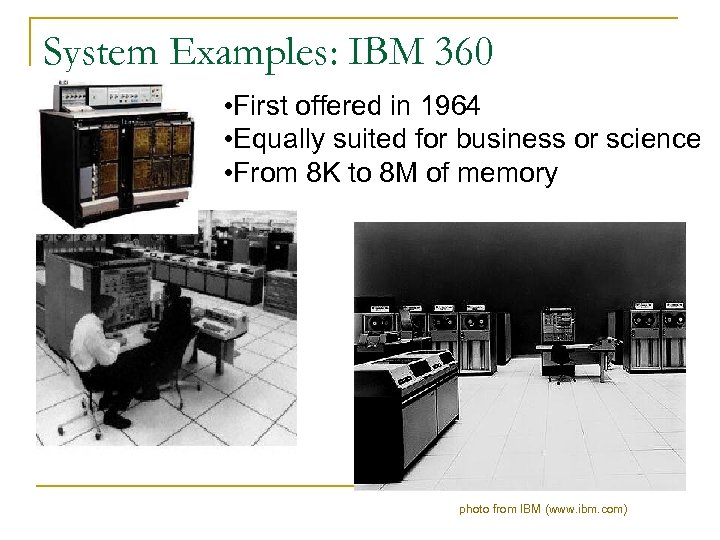 System Examples: IBM 360 • First offered in 1964 • Equally suited for business or science • From 8 K to 8 M of memory photo from IBM (www. ibm. com)
System Examples: IBM 360 • First offered in 1964 • Equally suited for business or science • From 8 K to 8 M of memory photo from IBM (www. ibm. com)
 Other advances of the n Generation Evolution of operating systems q n rd 3 Becoming more general purpose Separate pricing for hardware and software.
Other advances of the n Generation Evolution of operating systems q n rd 3 Becoming more general purpose Separate pricing for hardware and software.
 Internet Related Developments n n n 1962 – The Telstar communications satellite is launched and relays the first transatlantic television broadcast 1968 – Intel formed 1969 - ARPA-Net, the forerunner of the Internet, is established by the US Department of Defense.
Internet Related Developments n n n 1962 – The Telstar communications satellite is launched and relays the first transatlantic television broadcast 1968 – Intel formed 1969 - ARPA-Net, the forerunner of the Internet, is established by the US Department of Defense.
 Modern Computers 4 th Generation Computers The Microprocessor 1971 - Today
Modern Computers 4 th Generation Computers The Microprocessor 1971 - Today
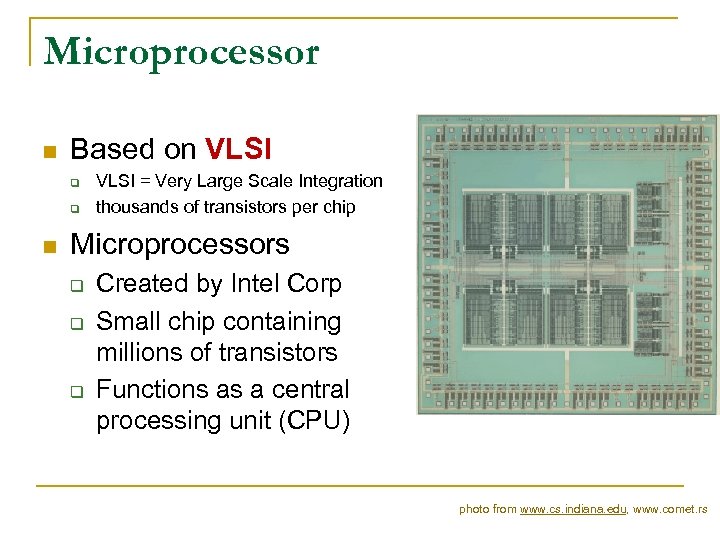 Microprocessor n Based on VLSI q q n VLSI = Very Large Scale Integration thousands of transistors per chip Microprocessors q q q Created by Intel Corp Small chip containing millions of transistors Functions as a central processing unit (CPU) photo from www. cs. indiana. edu, www. comet. rs
Microprocessor n Based on VLSI q q n VLSI = Very Large Scale Integration thousands of transistors per chip Microprocessors q q q Created by Intel Corp Small chip containing millions of transistors Functions as a central processing unit (CPU) photo from www. cs. indiana. edu, www. comet. rs
 Computers are getting faster, more powerful, smaller and cheaper
Computers are getting faster, more powerful, smaller and cheaper
 Altair 8800 n n n The first microcomputer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output The first PC, the Altair 8800, was introduced in kit form and was featured in an article in Popular Electronics magazine. The response for orders was unexpectedly overwhelming.
Altair 8800 n n n The first microcomputer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output The first PC, the Altair 8800, was introduced in kit form and was featured in an article in Popular Electronics magazine. The response for orders was unexpectedly overwhelming.
 Apple Computer n 1976 - Two other young hacker geeks, Steven Jobs and Stephen Wozniac build a computer in Steve's parents garage. They call it the Apple. From Computer Hope: www. compyterhope. com/history Photo from Http: //inventors. about. com
Apple Computer n 1976 - Two other young hacker geeks, Steven Jobs and Stephen Wozniac build a computer in Steve's parents garage. They call it the Apple. From Computer Hope: www. compyterhope. com/history Photo from Http: //inventors. about. com
 Microsoft n n n 1980 IBM hires Paul Allen and Bill Gates to create an operating system for a new PC. The pair buy the rights to a simple operating system manufactured by Seattle Computer Products and use it as a template. IBM allows the two to keep the marketing rights to the operating system, called DOS. From Computer Hope: www. compyterhope. com/history
Microsoft n n n 1980 IBM hires Paul Allen and Bill Gates to create an operating system for a new PC. The pair buy the rights to a simple operating system manufactured by Seattle Computer Products and use it as a template. IBM allows the two to keep the marketing rights to the operating system, called DOS. From Computer Hope: www. compyterhope. com/history
 Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) n Revolutionized software industry n Easy to learn n Lead to the creation of Microsoft Made programming easier for the masses n
Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) n Revolutionized software industry n Easy to learn n Lead to the creation of Microsoft Made programming easier for the masses n
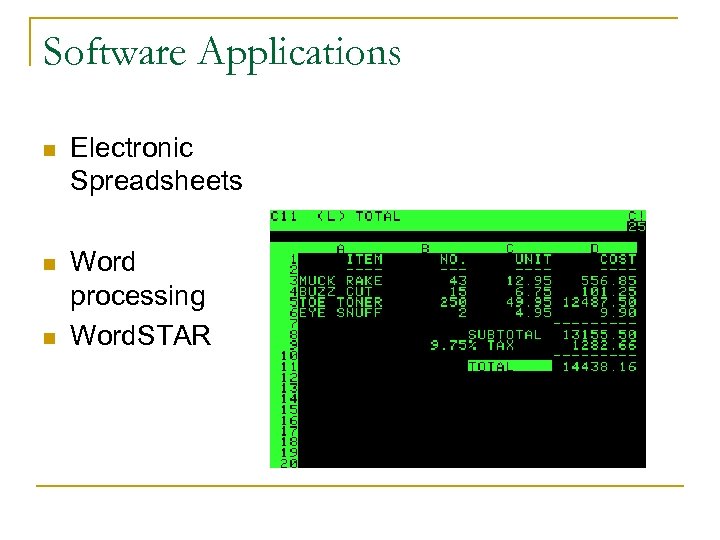 Software Applications n Electronic Spreadsheets n Word processing Word. STAR n
Software Applications n Electronic Spreadsheets n Word processing Word. STAR n
 Other advancements: User Interface n n n Switches/Cards/tape Previously: Command line interface WYSIWYG: What you see is what you get
Other advancements: User Interface n n n Switches/Cards/tape Previously: Command line interface WYSIWYG: What you see is what you get
 Ubiquitous Computing n Computing that is inseparable from our everyday lifestyle n Internet of Things (Io. T) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 59
Ubiquitous Computing n Computing that is inseparable from our everyday lifestyle n Internet of Things (Io. T) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 59
 Other technologies n Augmented Reality a live direct or indirect view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are augmented (or supplemented) by computer-generated sensory input such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data (Wikipedia) n Virtual Reality - computer-simulated reality, replicates an environment that simulates a physical presence in places in the real world or an imagined world, allowing the user to interact in that world. (Wikipedia) n n Cloud Computing 3 D Printing Robotics IEEE 2016 Top Tech to Watch
Other technologies n Augmented Reality a live direct or indirect view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are augmented (or supplemented) by computer-generated sensory input such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data (Wikipedia) n Virtual Reality - computer-simulated reality, replicates an environment that simulates a physical presence in places in the real world or an imagined world, allowing the user to interact in that world. (Wikipedia) n n Cloud Computing 3 D Printing Robotics IEEE 2016 Top Tech to Watch
 Fifth Generation n Based on ? ? ? technology
Fifth Generation n Based on ? ? ? technology
 Software Industry in the U. S. Current Job Market? v v "software engineer" tops the Money Magazine Best Jobs list software development in U. S. is a $150 Billion business Who hires CS graduates? v Any company that owns a computer. How much do CS graduates make? v v starting salary = $43 K to $55 K average software engineer = $80 K to $150 K
Software Industry in the U. S. Current Job Market? v v "software engineer" tops the Money Magazine Best Jobs list software development in U. S. is a $150 Billion business Who hires CS graduates? v Any company that owns a computer. How much do CS graduates make? v v starting salary = $43 K to $55 K average software engineer = $80 K to $150 K
 Specialties within Computer Science Web Application Design Networking and Computer Security Graphics Artificial Intelligence Database Analysis
Specialties within Computer Science Web Application Design Networking and Computer Security Graphics Artificial Intelligence Database Analysis
 Future Software Trends n Continued Movement to the Web v v Delivering Home and Mobile Entertainment New Services v e. g. Google Medical n Handheld Devices v multi-media / intelligent / interconnected n Unknown v integration of devices
Future Software Trends n Continued Movement to the Web v v Delivering Home and Mobile Entertainment New Services v e. g. Google Medical n Handheld Devices v multi-media / intelligent / interconnected n Unknown v integration of devices
 Next Class… n Computer Guts q q n Components of a modern computer What to look for when buying a computer Operating Systems q Differences in Windows and Linux
Next Class… n Computer Guts q q n Components of a modern computer What to look for when buying a computer Operating Systems q Differences in Windows and Linux


