5712d15a8af795341bd2545694d49bd3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Introduction to Computers & Networking n Introduction to Computers – History – Organization – Operating System n Introduction to Network – – – n n LAN, MAN and WAN Transmission Media, Network Topologies Protocols & Internet How to login on server and Unix commands PINE software – Email , file attachment n Servers at http: //www. imtech. res. in/raghava/
Introduction to Computers & Networking n Introduction to Computers – History – Organization – Operating System n Introduction to Network – – – n n LAN, MAN and WAN Transmission Media, Network Topologies Protocols & Internet How to login on server and Unix commands PINE software – Email , file attachment n Servers at http: //www. imtech. res. in/raghava/
 History of Computing - Early Computers n n n Abacus (ancient orient, still in use) Slide rule (17 C, John Napier) Adding machine with geared wheels (17 C, B. Pascal) Difference Engine (19 C, C. Babbage): First device using the principles of modern computer. ENIAC (1945, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, Jr. ) – Vacuum tube computer (18, 000 electron tubes) Three important inventions – Stored program concept (John von Neumann) – Transistor (J. Bardeen, W. H. Brattain, W. Shockley) – Magnetic core memory (J. W. Forrester and colleagues in MIT)
History of Computing - Early Computers n n n Abacus (ancient orient, still in use) Slide rule (17 C, John Napier) Adding machine with geared wheels (17 C, B. Pascal) Difference Engine (19 C, C. Babbage): First device using the principles of modern computer. ENIAC (1945, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, Jr. ) – Vacuum tube computer (18, 000 electron tubes) Three important inventions – Stored program concept (John von Neumann) – Transistor (J. Bardeen, W. H. Brattain, W. Shockley) – Magnetic core memory (J. W. Forrester and colleagues in MIT)
 IBM 701 (Defense Calculator) Addition time: 60 microseconds n Multiplication: 456 microseconds n Memory: 2048 (36 bit) words using Williams tubes n Secondary memory: n – Magnetic drum: 8192 words – Magnetic tape: plastic n Delivered: December 1952: IBM World Headquarters (total of 19 installed)
IBM 701 (Defense Calculator) Addition time: 60 microseconds n Multiplication: 456 microseconds n Memory: 2048 (36 bit) words using Williams tubes n Secondary memory: n – Magnetic drum: 8192 words – Magnetic tape: plastic n Delivered: December 1952: IBM World Headquarters (total of 19 installed)
 Second Generation (1958 -1964) n 1958 Philco introduces TRANSAC S-2000 – first transistorized commercial machine n n IBM 7070, 7074 (1960), 7072(1961) 1959 IBM 7090, 7040 (1961), 7094 (1962) 1959 IBM 1401, 1410 (1960), 1440 (1962) FORTRAN, ALGOL, and COBOL are first standardized programming languages
Second Generation (1958 -1964) n 1958 Philco introduces TRANSAC S-2000 – first transistorized commercial machine n n IBM 7070, 7074 (1960), 7072(1961) 1959 IBM 7090, 7040 (1961), 7094 (1962) 1959 IBM 1401, 1410 (1960), 1440 (1962) FORTRAN, ALGOL, and COBOL are first standardized programming languages
 Third Generation (1964 -1971) n April 1964 IBM announces the System/360 – solid logic technology (integrated circuits) – family of “compatible” computers n n 1964 Control Data delivers the CDC 6600 nanoseconds telecommunications BASIC, Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code
Third Generation (1964 -1971) n April 1964 IBM announces the System/360 – solid logic technology (integrated circuits) – family of “compatible” computers n n 1964 Control Data delivers the CDC 6600 nanoseconds telecommunications BASIC, Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code
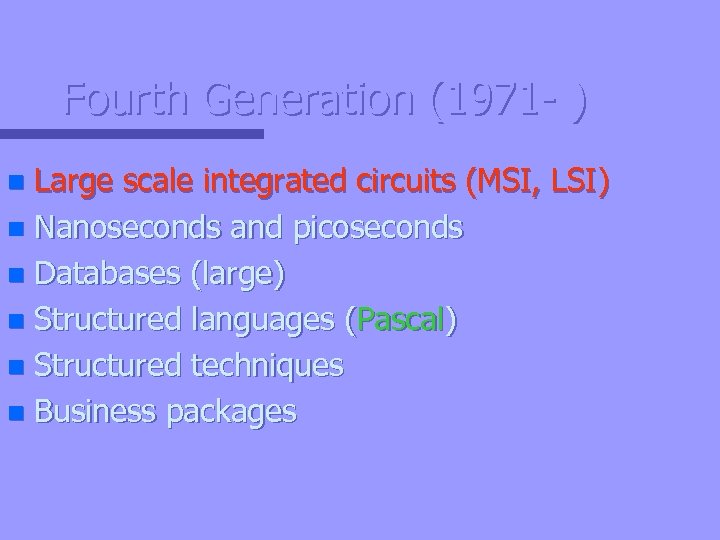 Fourth Generation (1971 - ) Large scale integrated circuits (MSI, LSI) n Nanoseconds and picoseconds n Databases (large) n Structured languages (Pascal) n Structured techniques n Business packages n
Fourth Generation (1971 - ) Large scale integrated circuits (MSI, LSI) n Nanoseconds and picoseconds n Databases (large) n Structured languages (Pascal) n Structured techniques n Business packages n
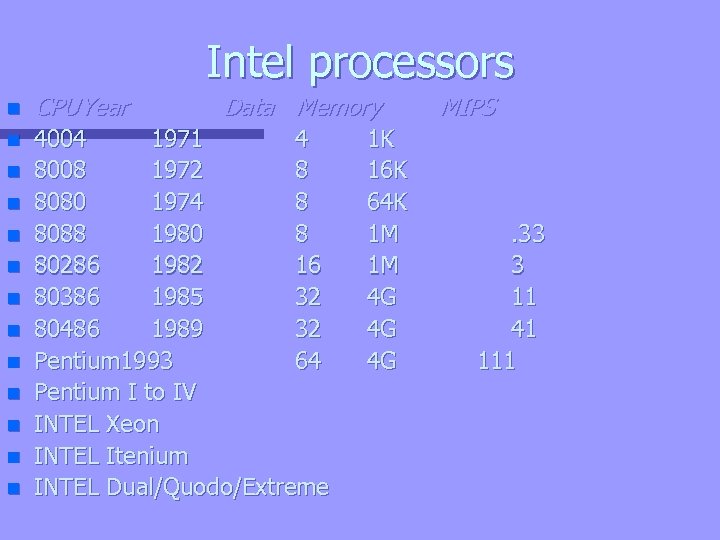 Intel processors n CPU Year n 4004 1971 4 8008 1972 8 8080 1974 8 8088 1980 8 80286 1982 16 80386 1985 32 80486 1989 32 Pentium 1993 64 Pentium I to IV INTEL Xeon INTEL Itenium INTEL Dual/Quodo/Extreme n n n Data Memory 1 K 16 K 64 K 1 M 1 M 4 G 4 G 4 G MIPS . 33 3 11 41 111
Intel processors n CPU Year n 4004 1971 4 8008 1972 8 8080 1974 8 8088 1980 8 80286 1982 16 80386 1985 32 80486 1989 32 Pentium 1993 64 Pentium I to IV INTEL Xeon INTEL Itenium INTEL Dual/Quodo/Extreme n n n Data Memory 1 K 16 K 64 K 1 M 1 M 4 G 4 G 4 G MIPS . 33 3 11 41 111
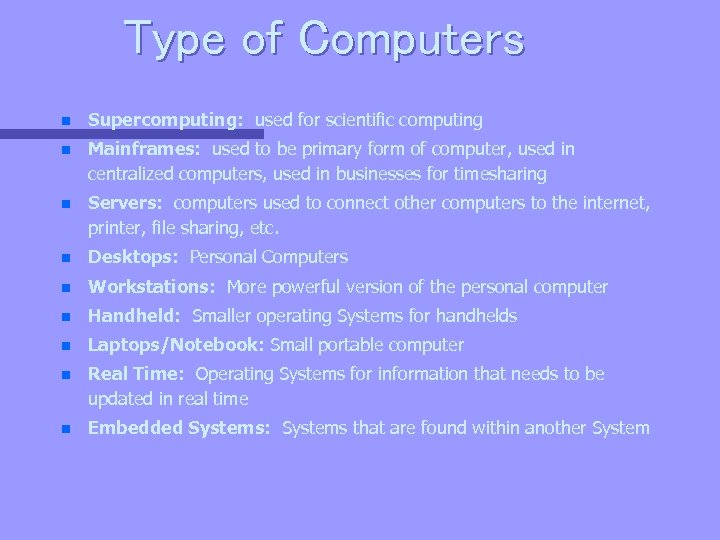 Type of Computers n Supercomputing: used for scientific computing n Mainframes: used to be primary form of computer, used in centralized computers, used in businesses for timesharing n Servers: computers used to connect other computers to the internet, printer, file sharing, etc. n Desktops: Personal Computers n Workstations: More powerful version of the personal computer n Handheld: Smaller operating Systems for handhelds n Laptops/Notebook: Small portable computer n Real Time: Operating Systems for information that needs to be updated in real time n Embedded Systems: Systems that are found within another System
Type of Computers n Supercomputing: used for scientific computing n Mainframes: used to be primary form of computer, used in centralized computers, used in businesses for timesharing n Servers: computers used to connect other computers to the internet, printer, file sharing, etc. n Desktops: Personal Computers n Workstations: More powerful version of the personal computer n Handheld: Smaller operating Systems for handhelds n Laptops/Notebook: Small portable computer n Real Time: Operating Systems for information that needs to be updated in real time n Embedded Systems: Systems that are found within another System
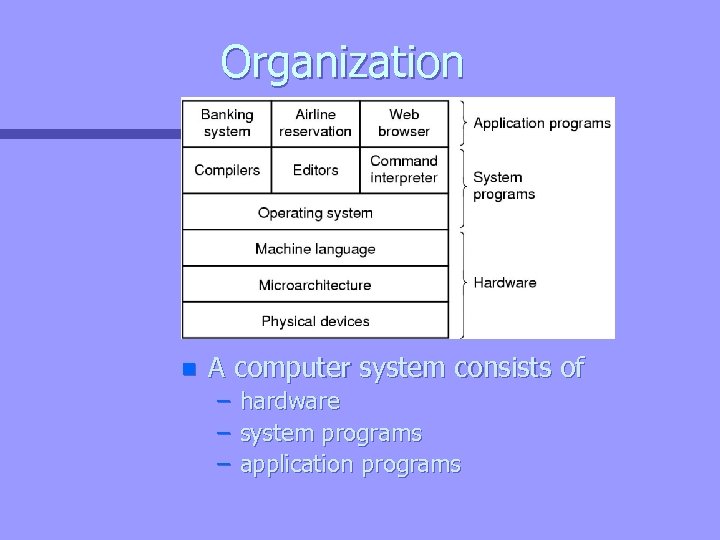 Organization n A computer system consists of – hardware – system programs – application programs
Organization n A computer system consists of – hardware – system programs – application programs
 Organization of Computer n Input Devices – Keyboard; Mouse; Digitiger; Joystick; Punch card etc. n Output Devices – Monitors/Screens (MDA, MGA; CGA; EGA; VGA & SVGA) ; Printers; Plotters; LCD; LED etc. n Data Storage – Primary Storage (RAM) – Secondary Storage (floppy disk & hard disk) n n Central Processing Unit Microprocessors (INTEL 8080, 8086, 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium I, III, IV)
Organization of Computer n Input Devices – Keyboard; Mouse; Digitiger; Joystick; Punch card etc. n Output Devices – Monitors/Screens (MDA, MGA; CGA; EGA; VGA & SVGA) ; Printers; Plotters; LCD; LED etc. n Data Storage – Primary Storage (RAM) – Secondary Storage (floppy disk & hard disk) n n Central Processing Unit Microprocessors (INTEL 8080, 8086, 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium I, III, IV)
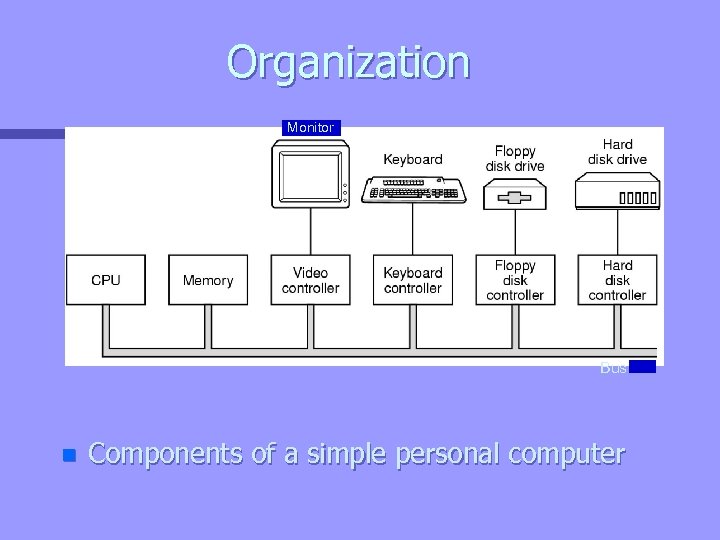 Organization Monitor Bus n Components of a simple personal computer
Organization Monitor Bus n Components of a simple personal computer
 Concept and Implementation of Network n n Transmission Media & Techniques Ethernet – UTP (10 base 2) – Thick ethernet (10 base 5) – Thin Ethernet (10 base 2) n n Optical Fiber Network Topologies – – Star (Easy services, One Device, Centralize cont. ) BUS (Short cable; Expandable; simplicity) RING (Short cable; suitable for optical Fibers) Hybrid (Tree topology; ring-star)
Concept and Implementation of Network n n Transmission Media & Techniques Ethernet – UTP (10 base 2) – Thick ethernet (10 base 5) – Thin Ethernet (10 base 2) n n Optical Fiber Network Topologies – – Star (Easy services, One Device, Centralize cont. ) BUS (Short cable; Expandable; simplicity) RING (Short cable; suitable for optical Fibers) Hybrid (Tree topology; ring-star)
 Network Topologies n n Physical and Logical Topologies – – – Bus Ring Star Extended Star Mesh Hybrid
Network Topologies n n Physical and Logical Topologies – – – Bus Ring Star Extended Star Mesh Hybrid
 Bus Topology
Bus Topology
 Bus Topology
Bus Topology
 Ring Topology
Ring Topology
 Star Topology
Star Topology
 Extended Star Topology A Star Network which has been expanded to include an additional hub or hubs.
Extended Star Topology A Star Network which has been expanded to include an additional hub or hubs.
 Hybrid Topology
Hybrid Topology
 Communication Protocols TCP/IP n Novel Net n Netbui (Windows Network) n Digital Network n Internet n
Communication Protocols TCP/IP n Novel Net n Netbui (Windows Network) n Digital Network n Internet n
 Concept of Proxy Server & Firewalls Internet Service Providers n Telephone Line n – Modem ISDN Line n Lease Line n Proxy server IP Address n – Port number
Concept of Proxy Server & Firewalls Internet Service Providers n Telephone Line n – Modem ISDN Line n Lease Line n Proxy server IP Address n – Port number
 What Is the Internet? n n A network of networks, joining many government, university and private computers together and providing an infrastructure for the use of E-mail, bulletin boards, file archives, hypertext documents, databases and other computational resources The vast collection of computer networks which form and act as a single huge network for transport of data and messages across distances which can be anywhere from the same office to anywhere in the world. Written by William F. Slater, III 1996 President of the Chicago Chapter of the Internet Society Copyright 2002, William F. Slater, III, Chicago, IL, USA
What Is the Internet? n n A network of networks, joining many government, university and private computers together and providing an infrastructure for the use of E-mail, bulletin boards, file archives, hypertext documents, databases and other computational resources The vast collection of computer networks which form and act as a single huge network for transport of data and messages across distances which can be anywhere from the same office to anywhere in the world. Written by William F. Slater, III 1996 President of the Chicago Chapter of the Internet Society Copyright 2002, William F. Slater, III, Chicago, IL, USA
 Brief History of the Internet n n 1968 - DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) contracts with BBN (Bolt, Beranek & Newman) to create ARPAnet 1970 - First five nodes: – – – UCLA Stanford UC Santa Barbara U of Utah, and BBN 1974 - TCP specification by Vint Cerf 1984 – On January 1, the Internet with its 1000 hosts converts en masse to using TCP/IP for its messaging
Brief History of the Internet n n 1968 - DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) contracts with BBN (Bolt, Beranek & Newman) to create ARPAnet 1970 - First five nodes: – – – UCLA Stanford UC Santa Barbara U of Utah, and BBN 1974 - TCP specification by Vint Cerf 1984 – On January 1, the Internet with its 1000 hosts converts en masse to using TCP/IP for its messaging
 Internet Growth Trends n n n 1977: 111 hosts on Internet 1981: 213 hosts 1983: 562 hosts 1984: 1, 000 hosts 1986: 5, 000 hosts 1987: 10, 000 hosts 1989: 100, 000 hosts 1992: 1, 000 hosts 2001: 150 – 175 million hosts 2002: over 200 million hosts By 2010, about 80% of the planet will be on the Internet
Internet Growth Trends n n n 1977: 111 hosts on Internet 1981: 213 hosts 1983: 562 hosts 1984: 1, 000 hosts 1986: 5, 000 hosts 1987: 10, 000 hosts 1989: 100, 000 hosts 1992: 1, 000 hosts 2001: 150 – 175 million hosts 2002: over 200 million hosts By 2010, about 80% of the planet will be on the Internet
 TCP/IP Addresses n n n Every host on the Internet must have a unique IP address The IP address is a 32 -bit number which we write in dotted decimal notation The first part of the IP address is the network address – the remainder is the host ID A subnet mask is used to determine the network address from a IP host address All hosts on the same network are configured with the same subnet mask
TCP/IP Addresses n n n Every host on the Internet must have a unique IP address The IP address is a 32 -bit number which we write in dotted decimal notation The first part of the IP address is the network address – the remainder is the host ID A subnet mask is used to determine the network address from a IP host address All hosts on the same network are configured with the same subnet mask
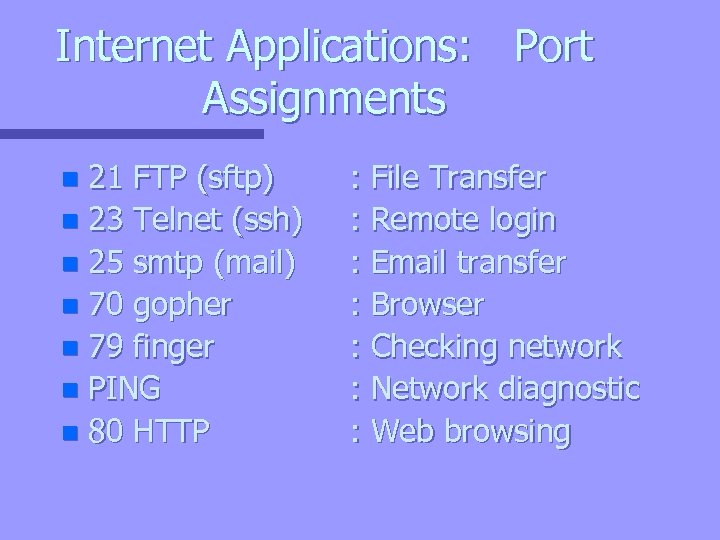 Internet Applications: Port Assignments 21 FTP (sftp) n 23 Telnet (ssh) n 25 smtp (mail) n 70 gopher n 79 finger n PING n 80 HTTP n : File Transfer : Remote login : Email transfer : Browser : Checking network : Network diagnostic : Web browsing
Internet Applications: Port Assignments 21 FTP (sftp) n 23 Telnet (ssh) n 25 smtp (mail) n 70 gopher n 79 finger n PING n 80 HTTP n : File Transfer : Remote login : Email transfer : Browser : Checking network : Network diagnostic : Web browsing
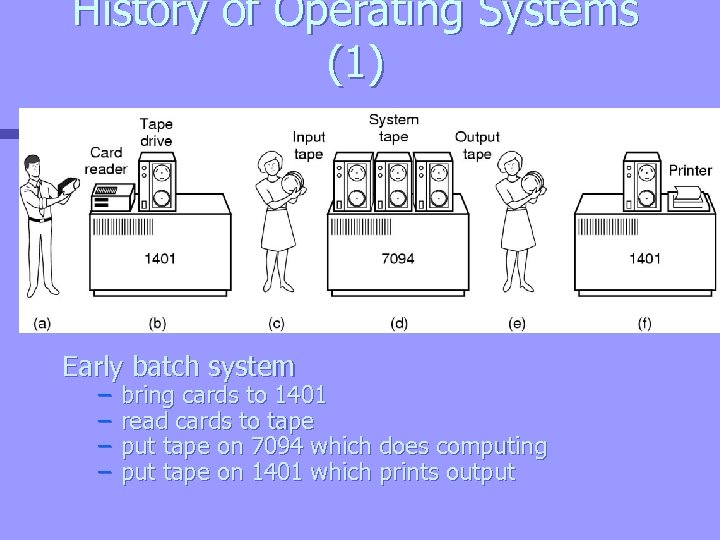 History of Operating Systems (1) Early batch system – – bring cards to 1401 read cards to tape put tape on 7094 which does computing put tape on 1401 which prints output
History of Operating Systems (1) Early batch system – – bring cards to 1401 read cards to tape put tape on 7094 which does computing put tape on 1401 which prints output
 Operating Systems n Single User – – n a) CP/M ; b) MS-DOS; c) Macintosh; d) Windows Multiple User – – – UNIX (1969 by Ken Thompson; C; Bell) Linux Solaris IRIX VMS (Digital)
Operating Systems n Single User – – n a) CP/M ; b) MS-DOS; c) Macintosh; d) Windows Multiple User – – – UNIX (1969 by Ken Thompson; C; Bell) Linux Solaris IRIX VMS (Digital)
 What is Unix? A fully featured modern operating system It is available in a variety of “flavors. ” It’s comprised of simple tools that perform a single function well. These tools can be used together to perform complex tasks.
What is Unix? A fully featured modern operating system It is available in a variety of “flavors. ” It’s comprised of simple tools that perform a single function well. These tools can be used together to perform complex tasks.
 Using Other Commands Syntax: command file cat n grep n Echos file contents to the screen Searches a file for a string n more Echos a file a line at a time n less Same as more but more features n wc Counts the words in a file and more n sort Sorts the contents of a file
Using Other Commands Syntax: command file cat n grep n Echos file contents to the screen Searches a file for a string n more Echos a file a line at a time n less Same as more but more features n wc Counts the words in a file and more n sort Sorts the contents of a file
 Other File System Utilities n ls Lists all files in a directory n cp Copies files n mv Moves files n rm Deletes files n mkdir Makes directories n rmdir Removes directories
Other File System Utilities n ls Lists all files in a directory n cp Copies files n mv Moves files n rm Deletes files n mkdir Makes directories n rmdir Removes directories


