29dbdae72cf89582357989ec4e6149a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Introduction to Computer Hardware
Introduction to Computer Hardware
 Hardware vs Software • Hardware is anything you can physically touch. • The Encyclopedia on the CD-ROM is software. The encyclopedia doesn’t actually exist. It is a set of instructions for the computer to follow, called a program, which is software.
Hardware vs Software • Hardware is anything you can physically touch. • The Encyclopedia on the CD-ROM is software. The encyclopedia doesn’t actually exist. It is a set of instructions for the computer to follow, called a program, which is software.
 Computer Hardware • Input device (used to put information into a computer, like a keyboard or mouse) • Output device (used to get information from a computer, like a monitor or printer) • Storage device (used to store data or programs) Can be permanent (like a CD or hard drive) or temporary (like RAM) • Process device (used to process or direct information, like the microprocessor or motherboard)
Computer Hardware • Input device (used to put information into a computer, like a keyboard or mouse) • Output device (used to get information from a computer, like a monitor or printer) • Storage device (used to store data or programs) Can be permanent (like a CD or hard drive) or temporary (like RAM) • Process device (used to process or direct information, like the microprocessor or motherboard)
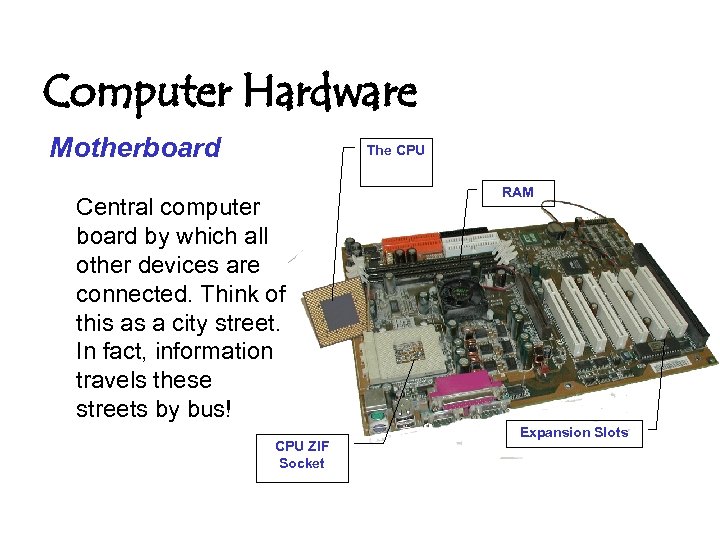 Computer Hardware Motherboard The CPU Central computer board by which all other devices are connected. Think of this as a city street. In fact, information travels these streets by bus! CPU ZIF Socket RAM Expansion Slots
Computer Hardware Motherboard The CPU Central computer board by which all other devices are connected. Think of this as a city street. In fact, information travels these streets by bus! CPU ZIF Socket RAM Expansion Slots
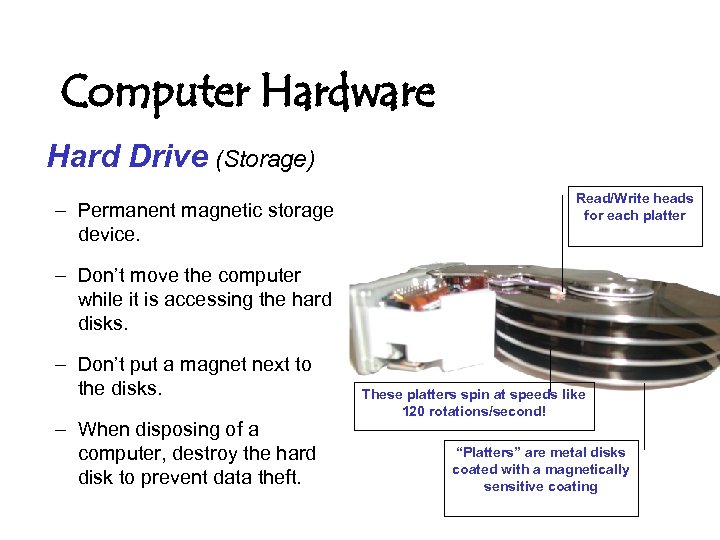 Computer Hardware Hard Drive (Storage) – Permanent magnetic storage device. Read/Write heads for each platter – Don’t move the computer while it is accessing the hard disks. – Don’t put a magnet next to the disks. – When disposing of a computer, destroy the hard disk to prevent data theft. These platters spin at speeds like 120 rotations/second! “Platters” are metal disks coated with a magnetically sensitive coating
Computer Hardware Hard Drive (Storage) – Permanent magnetic storage device. Read/Write heads for each platter – Don’t move the computer while it is accessing the hard disks. – Don’t put a magnet next to the disks. – When disposing of a computer, destroy the hard disk to prevent data theft. These platters spin at speeds like 120 rotations/second! “Platters” are metal disks coated with a magnetically sensitive coating
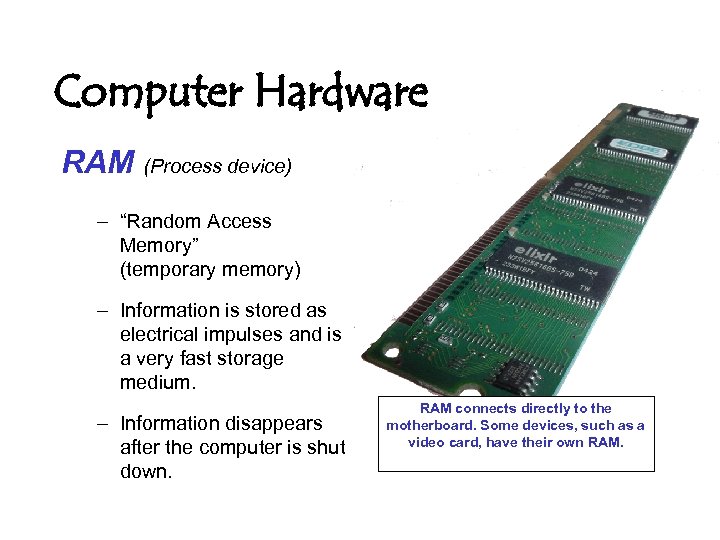 Computer Hardware RAM (Process device) – “Random Access Memory” (temporary memory) – Information is stored as electrical impulses and is a very fast storage medium. – Information disappears after the computer is shut down. RAM connects directly to the motherboard. Some devices, such as a video card, have their own RAM.
Computer Hardware RAM (Process device) – “Random Access Memory” (temporary memory) – Information is stored as electrical impulses and is a very fast storage medium. – Information disappears after the computer is shut down. RAM connects directly to the motherboard. Some devices, such as a video card, have their own RAM.
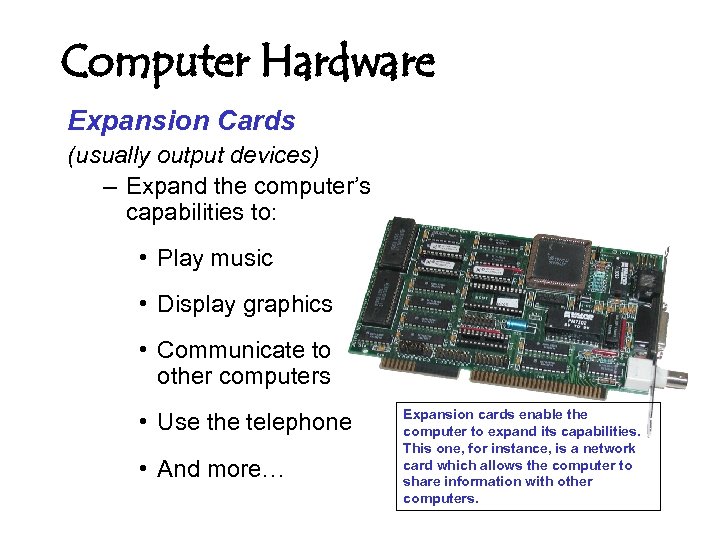 Computer Hardware Expansion Cards (usually output devices) – Expand the computer’s capabilities to: • Play music • Display graphics • Communicate to other computers • Use the telephone • And more… Expansion cards enable the computer to expand its capabilities. This one, for instance, is a network card which allows the computer to share information with other computers.
Computer Hardware Expansion Cards (usually output devices) – Expand the computer’s capabilities to: • Play music • Display graphics • Communicate to other computers • Use the telephone • And more… Expansion cards enable the computer to expand its capabilities. This one, for instance, is a network card which allows the computer to share information with other computers.
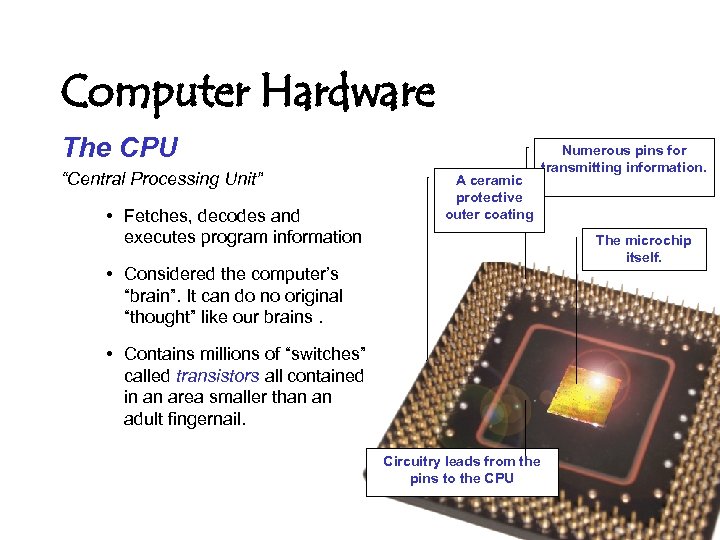 Computer Hardware The CPU “Central Processing Unit” • Fetches, decodes and executes program information A ceramic protective outer coating Numerous pins for transmitting information. The microchip itself. • Considered the computer’s “brain”. It can do no original “thought” like our brains. • Contains millions of “switches” called transistors all contained in an area smaller than an adult fingernail. Circuitry leads from the pins to the CPU
Computer Hardware The CPU “Central Processing Unit” • Fetches, decodes and executes program information A ceramic protective outer coating Numerous pins for transmitting information. The microchip itself. • Considered the computer’s “brain”. It can do no original “thought” like our brains. • Contains millions of “switches” called transistors all contained in an area smaller than an adult fingernail. Circuitry leads from the pins to the CPU
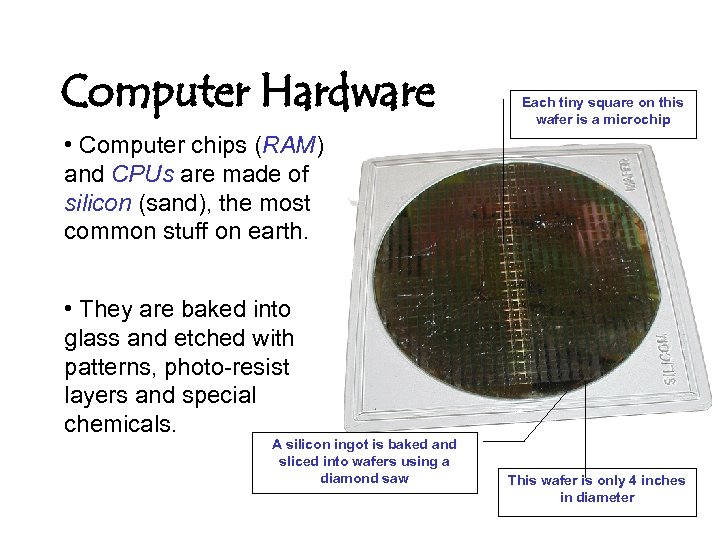 Computer Hardware Each tiny square on this wafer is a microchip • Computer chips (RAM) and CPUs are made of silicon (sand), the most common stuff on earth. • They are baked into glass and etched with patterns, photo-resist layers and special chemicals. A silicon ingot is baked and sliced into wafers using a diamond saw This wafer is only 4 inches in diameter
Computer Hardware Each tiny square on this wafer is a microchip • Computer chips (RAM) and CPUs are made of silicon (sand), the most common stuff on earth. • They are baked into glass and etched with patterns, photo-resist layers and special chemicals. A silicon ingot is baked and sliced into wafers using a diamond saw This wafer is only 4 inches in diameter
 Peripherals • The monitor, (also known as a CRT, after the Cathode Ray Tube inside that displays the picture), is measured in size with a ruler, diagonally across the screen. • Monitor quality is measured in terms of how many pixels, (“picture elements”) can be displayed per square inch. This is the monitor’s resolution. Most monitors are wider than taller.
Peripherals • The monitor, (also known as a CRT, after the Cathode Ray Tube inside that displays the picture), is measured in size with a ruler, diagonally across the screen. • Monitor quality is measured in terms of how many pixels, (“picture elements”) can be displayed per square inch. This is the monitor’s resolution. Most monitors are wider than taller.
 Computer Hardware • I/O ports - Connections on the back of a computer used to plug in peripherals. • Common peripherals are printers, scanners, digital cameras, keyboards and mice.
Computer Hardware • I/O ports - Connections on the back of a computer used to plug in peripherals. • Common peripherals are printers, scanners, digital cameras, keyboards and mice.
 Software • Software refers to a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do. These instructions are also called Operating Systems or Programs • Operating Systems – examples are Windows XP, Windows Vista. • Programs – there are thousands of examples of programs. Games, office systems like Microsoft Office and Power. Point, anti-virus software.
Software • Software refers to a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do. These instructions are also called Operating Systems or Programs • Operating Systems – examples are Windows XP, Windows Vista. • Programs – there are thousands of examples of programs. Games, office systems like Microsoft Office and Power. Point, anti-virus software.
 Bits and Bytes http: //webdeveloper. earthweb. com/repository/javascripts/2001/04/41291/byteconverter. htm • The computer really doesn’t understand any programming language. It is simply a machine. It is like asking if a hammer knows that it is building a house. The tool simply does what it is told to do. • Computers “understand” the presence or absence of electricity. This is represented by binary numbers. Binary is a kind of mathematical system that uses only 1’s and 0’s. • 0100 1011 0110 0101 0110 1100 0111 1001 http: //www. tutorials 4 u. com/c/ascii. htm#ASCIICodes
Bits and Bytes http: //webdeveloper. earthweb. com/repository/javascripts/2001/04/41291/byteconverter. htm • The computer really doesn’t understand any programming language. It is simply a machine. It is like asking if a hammer knows that it is building a house. The tool simply does what it is told to do. • Computers “understand” the presence or absence of electricity. This is represented by binary numbers. Binary is a kind of mathematical system that uses only 1’s and 0’s. • 0100 1011 0110 0101 0110 1100 0111 1001 http: //www. tutorials 4 u. com/c/ascii. htm#ASCIICodes


