db0f12a610054b3ada254de43773c865.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Kurt Akeley CS 248 Lecture 1 25 September 2007 http: //graphics. stanford. edu/courses/cs 248 -07/
Introduction to Computer Graphics Kurt Akeley CS 248 Lecture 1 25 September 2007 http: //graphics. stanford. edu/courses/cs 248 -07/
 Instructor information Education and employment n BEE University of Delaware, 1976 -1980 n MSEE Stanford, 1980 -1982 n SGI co-founder, chief engineer, CTO, 1982– 2000 n Ph. D (EE) Stanford, 2001 -2004 n NVIDIA graphics architect (part-time) 2001 -2004 n Microsoft Research Asia asst. director, 2005 -2007 n Principal Researcher, MSR Silicon Valley CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Instructor information Education and employment n BEE University of Delaware, 1976 -1980 n MSEE Stanford, 1980 -1982 n SGI co-founder, chief engineer, CTO, 1982– 2000 n Ph. D (EE) Stanford, 2001 -2004 n NVIDIA graphics architect (part-time) 2001 -2004 n Microsoft Research Asia asst. director, 2005 -2007 n Principal Researcher, MSR Silicon Valley CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Instructor information Professional experience n Graphics systems: GT, GTX, VGX, Reality. Engine, … n Open. GL: specification, early extensions, ARB, … n SIGGRAPH: attend 1984 -2007, papers chair 2000, … n SIGGRAPH Asia 2008: papers chair Teaching experience n Co-taught CS 448, Real-time Graphics Architecture , with Pat Hanrahan fall 2001 and spring 2007 n Lectured in several SIGGRAPH courses n Have given lots of talks CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Instructor information Professional experience n Graphics systems: GT, GTX, VGX, Reality. Engine, … n Open. GL: specification, early extensions, ARB, … n SIGGRAPH: attend 1984 -2007, papers chair 2000, … n SIGGRAPH Asia 2008: papers chair Teaching experience n Co-taught CS 448, Real-time Graphics Architecture , with Pat Hanrahan fall 2001 and spring 2007 n Lectured in several SIGGRAPH courses n Have given lots of talks CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
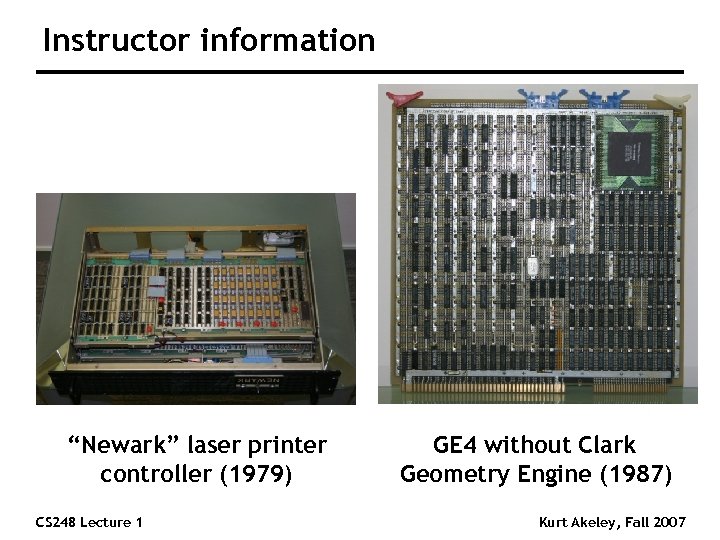 Instructor information “Newark” laser printer controller (1979) CS 248 Lecture 1 GE 4 without Clark Geometry Engine (1987) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Instructor information “Newark” laser printer controller (1979) CS 248 Lecture 1 GE 4 without Clark Geometry Engine (1987) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Instructor information Fixed-viewpoint volumetric display (2004) CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Instructor information Fixed-viewpoint volumetric display (2004) CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Instructor information This is my first n Stanford course on my own n time teaching an introductory graphics course n detailed exposure to some concepts I’m learning too! n Let’s interact n I’ll try not to cram too much into the lectures CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Instructor information This is my first n Stanford course on my own n time teaching an introductory graphics course n detailed exposure to some concepts I’m learning too! n Let’s interact n I’ll try not to cram too much into the lectures CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Teaching assistants Andrew Adams Justin Talbot Won game competition in ’ 04 TA’d course in ’ 05 and ’ 06 Second-year Ph. D student BYU MS global illumination CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Teaching assistants Andrew Adams Justin Talbot Won game competition in ’ 04 TA’d course in ’ 05 and ’ 06 Second-year Ph. D student BYU MS global illumination CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Course content Based on the course as taught by Marc Levoy last year n http: //graphics. stanford. edu/courses/cs 248 -06/ More emphasis on Open. GL and applied graphics n Z-buffer, tuning, hardware, details & depth (why) Less emphasis on history and alternate approaches n Perspective in art, visibility algorithms, volume rendering Projects n First is new (still under construction) n Second is the same (for now) n Third (game competition) remains n But we may de-emphasize game play requirement n This course really isn’t about game play CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Course content Based on the course as taught by Marc Levoy last year n http: //graphics. stanford. edu/courses/cs 248 -06/ More emphasis on Open. GL and applied graphics n Z-buffer, tuning, hardware, details & depth (why) Less emphasis on history and alternate approaches n Perspective in art, visibility algorithms, volume rendering Projects n First is new (still under construction) n Second is the same (for now) n Third (game competition) remains n But we may de-emphasize game play requirement n This course really isn’t about game play CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Human perception Interactive graphics is (typically) for human viewers n Guided-missile design is a counterexample n Human will be presumed in this course Good designers know their customers’ needs and problems n Have basic understanding of visual perception n NTSC is a great engineering design example The evolution of computer graphics has been directed by the quirks of human perception, e. g. , n Tri-color stimulus n Sensitivity to change in light reaching the eye CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Human perception Interactive graphics is (typically) for human viewers n Guided-missile design is a counterexample n Human will be presumed in this course Good designers know their customers’ needs and problems n Have basic understanding of visual perception n NTSC is a great engineering design example The evolution of computer graphics has been directed by the quirks of human perception, e. g. , n Tri-color stimulus n Sensitivity to change in light reaching the eye CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Purpose of computer graphics? Communication is the purpose Human perception is the context n Techniques leverage visual perception abilities Fidelity is a tool, not (necessarily) the goal n Virtual reality is great, but n Don’t want to be limited to reality n Want to do super reality n Non-photorealistic rendering (NPR) is valuable – n Bill Buxton, Sketching User Experiences, 2006 No apology is required for “approximations” n CS 248 Lecture 1 Especially for interactive graphics Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Purpose of computer graphics? Communication is the purpose Human perception is the context n Techniques leverage visual perception abilities Fidelity is a tool, not (necessarily) the goal n Virtual reality is great, but n Don’t want to be limited to reality n Want to do super reality n Non-photorealistic rendering (NPR) is valuable – n Bill Buxton, Sketching User Experiences, 2006 No apology is required for “approximations” n CS 248 Lecture 1 Especially for interactive graphics Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
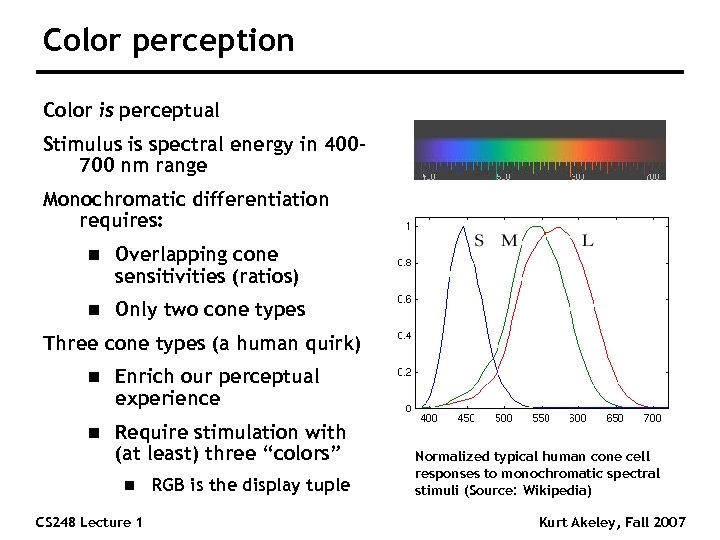 Color perception Color is perceptual Stimulus is spectral energy in 400700 nm range Monochromatic differentiation requires: n Overlapping cone sensitivities (ratios) n Only two cone types Three cone types (a human quirk) n Enrich our perceptual experience n Require stimulation with (at least) three “colors” n CS 248 Lecture 1 RGB is the display tuple Normalized typical human cone cell responses to monochromatic spectral stimuli (Source: Wikipedia) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Color perception Color is perceptual Stimulus is spectral energy in 400700 nm range Monochromatic differentiation requires: n Overlapping cone sensitivities (ratios) n Only two cone types Three cone types (a human quirk) n Enrich our perceptual experience n Require stimulation with (at least) three “colors” n CS 248 Lecture 1 RGB is the display tuple Normalized typical human cone cell responses to monochromatic spectral stimuli (Source: Wikipedia) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
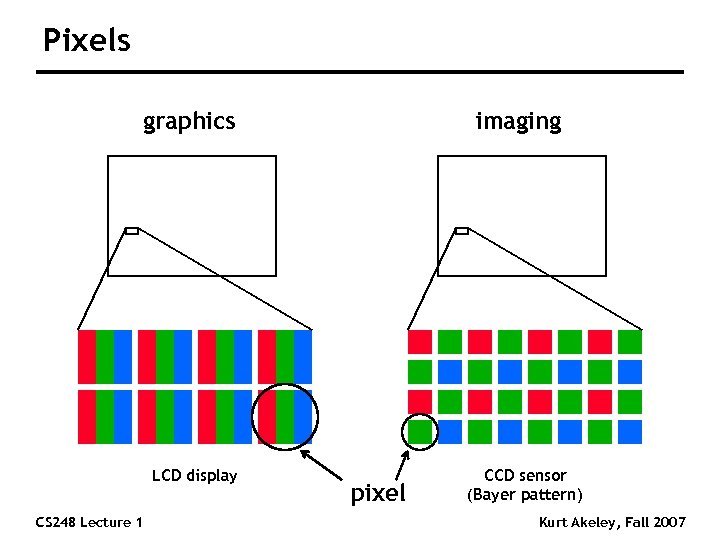 Pixels graphics LCD display CS 248 Lecture 1 imaging pixel CCD sensor (Bayer pattern) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Pixels graphics LCD display CS 248 Lecture 1 imaging pixel CCD sensor (Bayer pattern) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Pixels Why do CCDs use the Bayer pattern? Why don’t LCD monitors use the Bayer pattern? What is graphics missing? n Microsoft Clear. Type n Claude Betrisey, Jim Blinn, Bodin Dresevic, Bill Hill, Greg Hitchcock, Bert Kely, Don Mitchell, John Platt, Turner Whitted, 20. 4: Displaced Filtering for Patterned Displays, Society for Information Display, 2000. CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Pixels Why do CCDs use the Bayer pattern? Why don’t LCD monitors use the Bayer pattern? What is graphics missing? n Microsoft Clear. Type n Claude Betrisey, Jim Blinn, Bodin Dresevic, Bill Hill, Greg Hitchcock, Bert Kely, Don Mitchell, John Platt, Turner Whitted, 20. 4: Displaced Filtering for Patterned Displays, Society for Information Display, 2000. CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
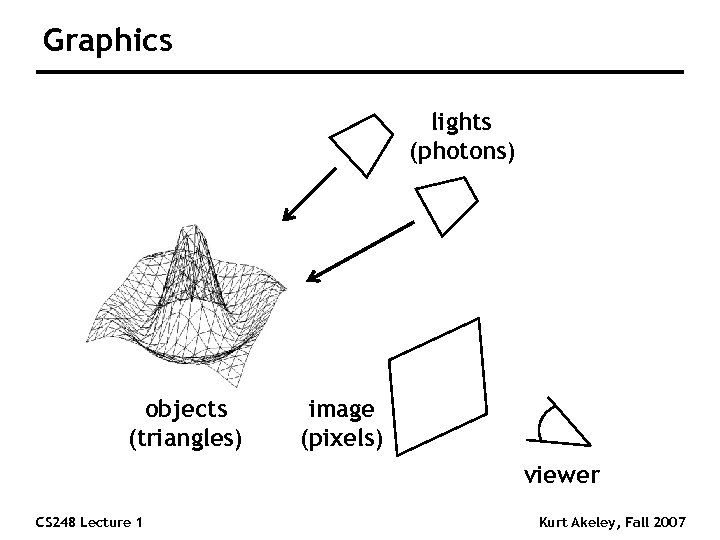 Graphics lights (photons) objects (triangles) image (pixels) viewer CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Graphics lights (photons) objects (triangles) image (pixels) viewer CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
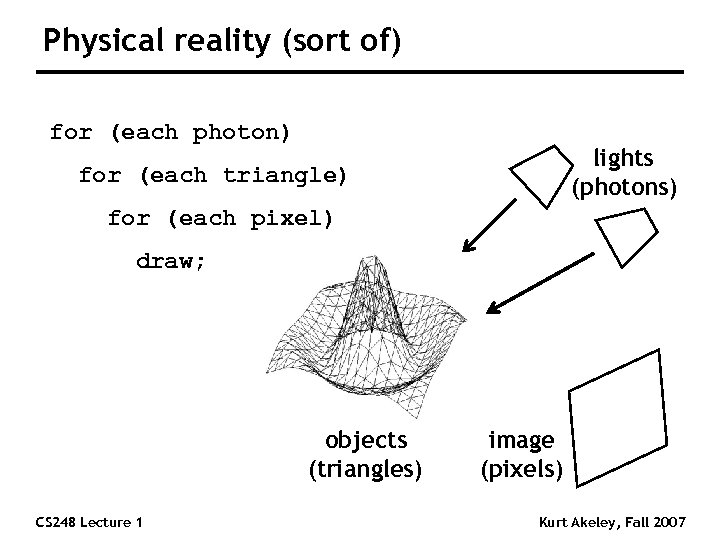 Physical reality (sort of) for (each photon) lights (photons) for (each triangle) for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Physical reality (sort of) for (each photon) lights (photons) for (each triangle) for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
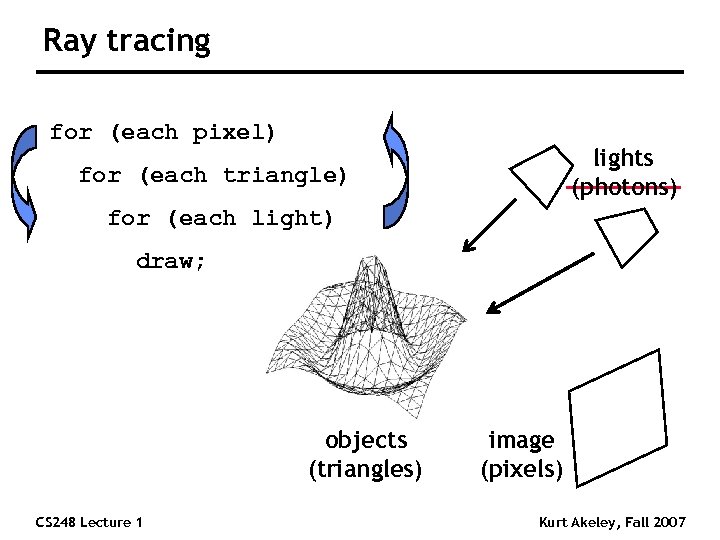 Ray tracing for (each pixel) lights (photons) for (each triangle) for (each light) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Ray tracing for (each pixel) lights (photons) for (each triangle) for (each light) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
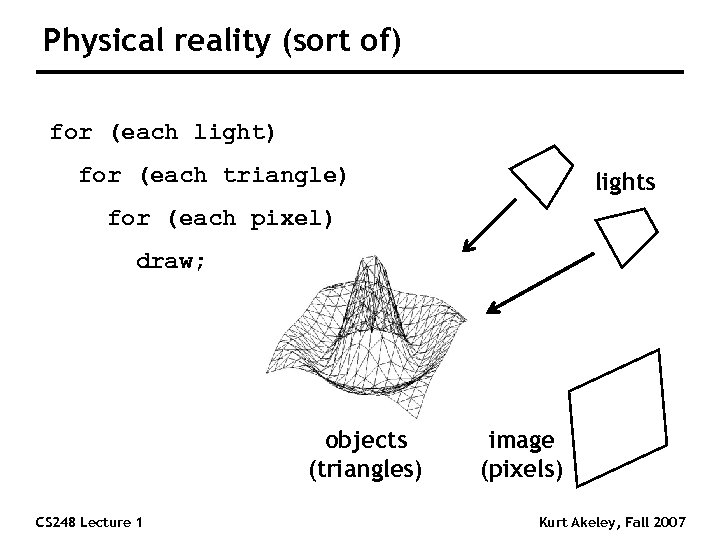 Physical reality (sort of) for (each light) for (each triangle) lights for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Physical reality (sort of) for (each light) for (each triangle) lights for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
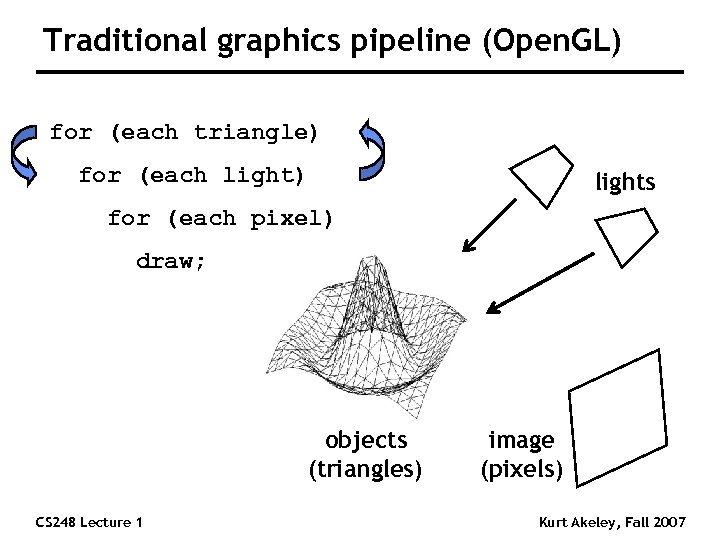 Traditional graphics pipeline (Open. GL) for (each triangle) for (each light) lights for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Traditional graphics pipeline (Open. GL) for (each triangle) for (each light) lights for (each pixel) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
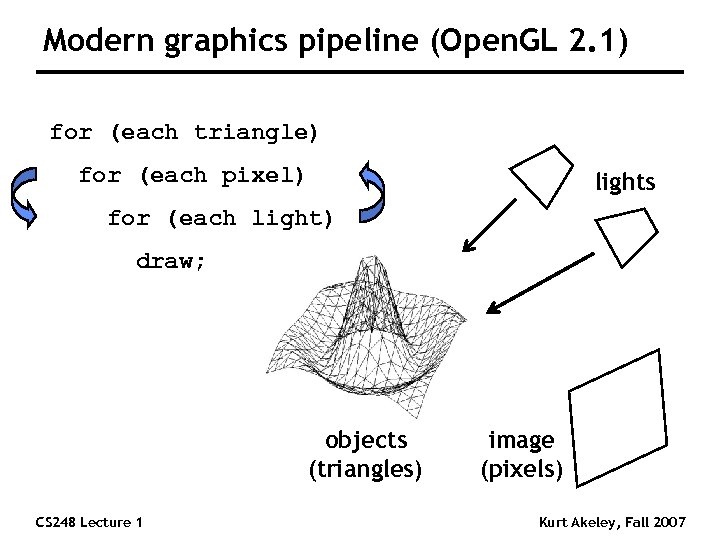 Modern graphics pipeline (Open. GL 2. 1) for (each triangle) for (each pixel) lights for (each light) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Modern graphics pipeline (Open. GL 2. 1) for (each triangle) for (each pixel) lights for (each light) draw; objects (triangles) CS 248 Lecture 1 image (pixels) Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
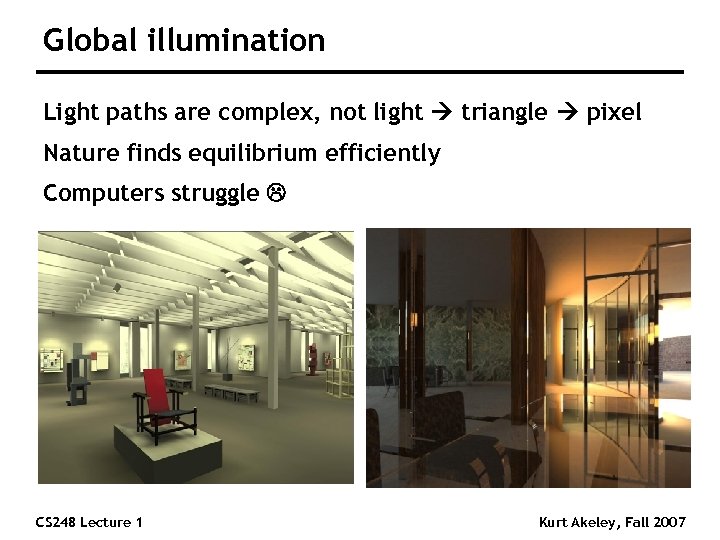 Global illumination Light paths are complex, not light triangle pixel Nature finds equilibrium efficiently Computers struggle CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Global illumination Light paths are complex, not light triangle pixel Nature finds equilibrium efficiently Computers struggle CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Animation Sequence of still frames n Update rate: minimum of 24 hz or so n Flicker rate: minimum of 50 hz or so “Rule 1”: All discontinuous frame-to-frame changes correspond to discontinuous scene or visibility changes CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Animation Sequence of still frames n Update rate: minimum of 24 hz or so n Flicker rate: minimum of 50 hz or so “Rule 1”: All discontinuous frame-to-frame changes correspond to discontinuous scene or visibility changes CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
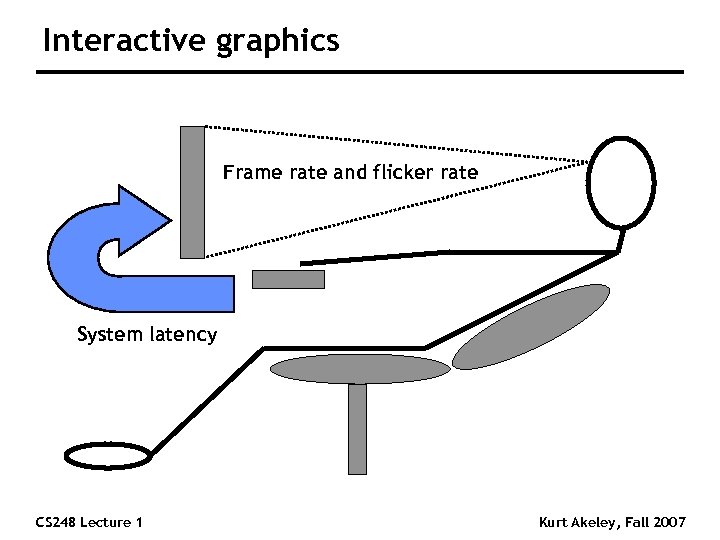 Interactive graphics Frame rate and flicker rate System latency CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Interactive graphics Frame rate and flicker rate System latency CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
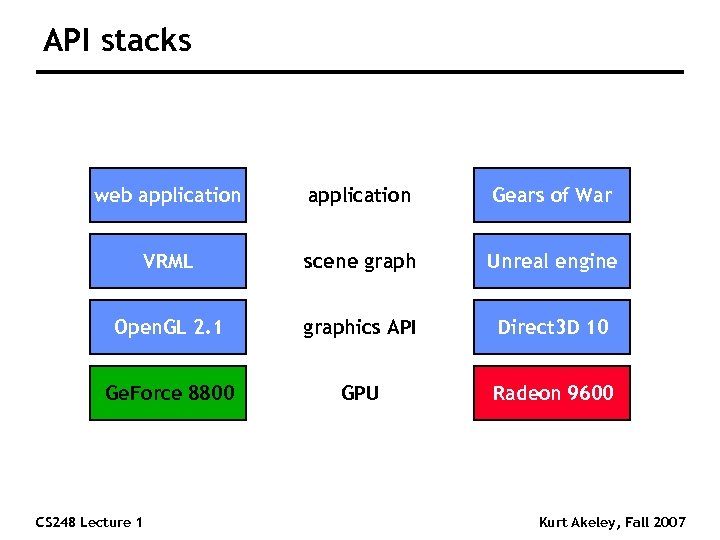 API stacks web application Gears of War VRML scene graph Unreal engine Open. GL 2. 1 graphics API Direct 3 D 10 Ge. Force 8800 GPU Radeon 9600 CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
API stacks web application Gears of War VRML scene graph Unreal engine Open. GL 2. 1 graphics API Direct 3 D 10 Ge. Force 8800 GPU Radeon 9600 CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
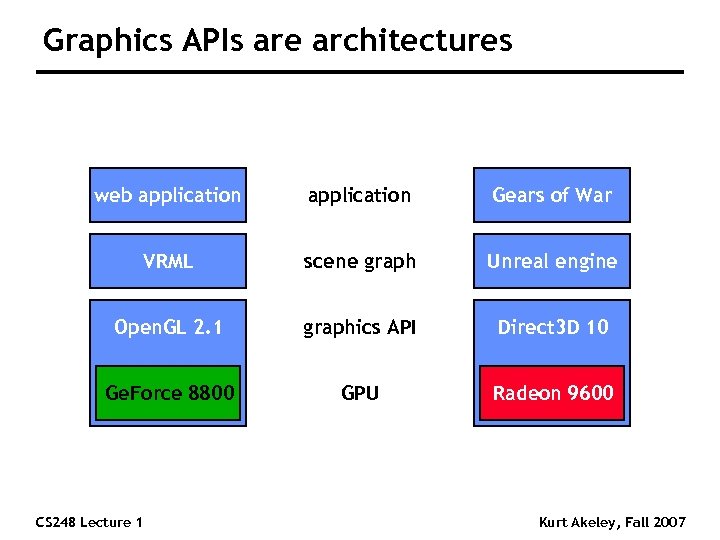 Graphics APIs are architectures web application Gears of War VRML scene graph Unreal engine Open. GL 2. 1 graphics API Direct 3 D 10 Ge. Force 8800 GPU Radeon 9600 CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Graphics APIs are architectures web application Gears of War VRML scene graph Unreal engine Open. GL 2. 1 graphics API Direct 3 D 10 Ge. Force 8800 GPU Radeon 9600 CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Summary Communication is the purpose of computer graphics n Human perception is the context n Fidelity is a tool, not (necessarily) a goal Our focus will be interactive graphics n Instructor’s bias n Emphasis on Open. GL Your instructor is learning too n Your opinions, corrections, and concerns are appreciated! CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Summary Communication is the purpose of computer graphics n Human perception is the context n Fidelity is a tool, not (necessarily) a goal Our focus will be interactive graphics n Instructor’s bias n Emphasis on Open. GL Your instructor is learning too n Your opinions, corrections, and concerns are appreciated! CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 Reading assignment Before Thursday’s class, read n Mark Segal and Kurt Akeley, The Design of the Open. GL Graphics Interface, unpublished n Open. GL Programming Guide n Chapter 1 - Introduction to Open. GL n Appendix D - Basics of GLUT: the Open. GL Utility Tool Also become familiar with www. opengl. org: n Open. GL, GLU, and GLUT Specifications n Extension specifications n … Optional: n David Blythe, The Direct 3 D 10 System SIGGRAPH 2006 , n Set up your Open. GL/GLUT programming environment CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
Reading assignment Before Thursday’s class, read n Mark Segal and Kurt Akeley, The Design of the Open. GL Graphics Interface, unpublished n Open. GL Programming Guide n Chapter 1 - Introduction to Open. GL n Appendix D - Basics of GLUT: the Open. GL Utility Tool Also become familiar with www. opengl. org: n Open. GL, GLU, and GLUT Specifications n Extension specifications n … Optional: n David Blythe, The Direct 3 D 10 System SIGGRAPH 2006 , n Set up your Open. GL/GLUT programming environment CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
 End CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007
End CS 248 Lecture 1 Kurt Akeley, Fall 2007


