fef364ec47fecca430ca89b55541306c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Introduction to Computer and Programming Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University, Bangkok, THAILAND 1 st Semester 2006 1
Introduction to Computer and Programming Computer Engineering Department Kasetsart University, Bangkok, THAILAND 1 st Semester 2006 1
 Instructor Information Instructor: สทธชย ศรออน (Sitichai Srioon( n Email Address: fengsis@ku. ac. th n Website: http: //www. cpe. ku. ac. th/~scs n Office: Building 15 (Computer Engineering Building) Room 414 n TA (Teaching Assistant): Will be announced n 1 st Semester 2006 2
Instructor Information Instructor: สทธชย ศรออน (Sitichai Srioon( n Email Address: fengsis@ku. ac. th n Website: http: //www. cpe. ku. ac. th/~scs n Office: Building 15 (Computer Engineering Building) Room 414 n TA (Teaching Assistant): Will be announced n 1 st Semester 2006 2
 Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 3
Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 3
 Computer Categories n Personal Computer (PC) Desktop Computer n Notebook (Laptop) n PDA – Personal Digital Assistant (Palmtop) n n High Computation Power Computer Workstation n Supercomputer Mainframe n 1 st Semester 2006 4
Computer Categories n Personal Computer (PC) Desktop Computer n Notebook (Laptop) n PDA – Personal Digital Assistant (Palmtop) n n High Computation Power Computer Workstation n Supercomputer Mainframe n 1 st Semester 2006 4
 What is a Computer ? n Computer is a device with sophisticated electronic parts that operates under the control of instructions (software) that is stored in its own memory, n accepts data (input), n manipulates data (process), n and then produces information (output) from the processing unit n 1 st Semester 2006 5
What is a Computer ? n Computer is a device with sophisticated electronic parts that operates under the control of instructions (software) that is stored in its own memory, n accepts data (input), n manipulates data (process), n and then produces information (output) from the processing unit n 1 st Semester 2006 5
 Computer Components Input Devices n Output Devices n Computing & Processing Unit n Storage Devices n 1 st Semester 2006 6
Computer Components Input Devices n Output Devices n Computing & Processing Unit n Storage Devices n 1 st Semester 2006 6
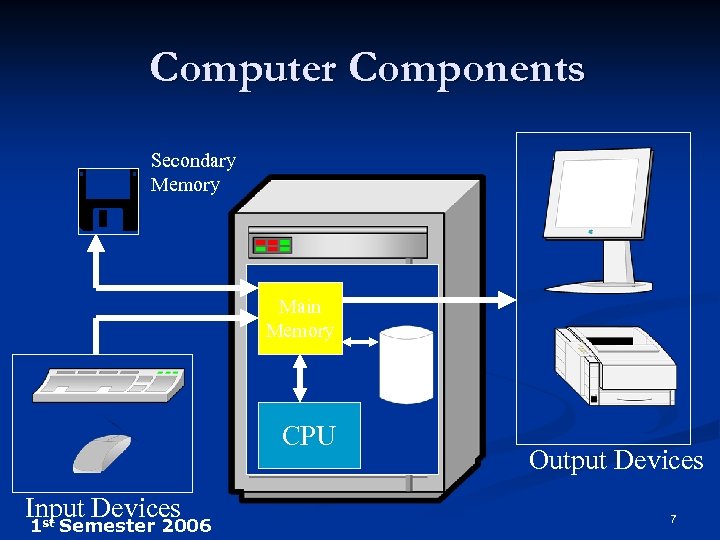 Computer Components Secondary Memory Main Memory HD CPU Input Devices st 1 Semester 2006 Output Devices 7
Computer Components Secondary Memory Main Memory HD CPU Input Devices st 1 Semester 2006 Output Devices 7
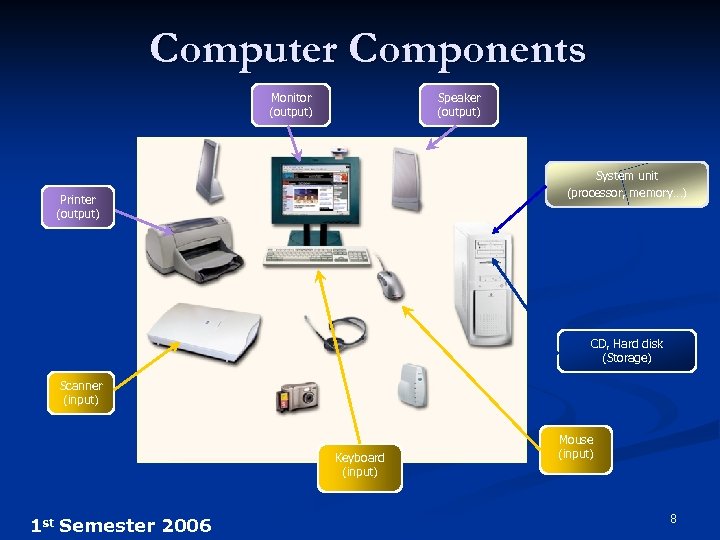 Computer Components Monitor (output) Speaker (output) System unit (processor, memory…) Printer (output) CD, Hard disk (Storage) Scanner (input) Keyboard (input) 1 st Semester 2006 Mouse (input) 8
Computer Components Monitor (output) Speaker (output) System unit (processor, memory…) Printer (output) CD, Hard disk (Storage) Scanner (input) Keyboard (input) 1 st Semester 2006 Mouse (input) 8
 Application Software Consists of programs that tell a computer how to produce information n Some examples: n Word processing n Electronic spreadsheet n Database n Presentation graphics n 1 st Semester 2006 9
Application Software Consists of programs that tell a computer how to produce information n Some examples: n Word processing n Electronic spreadsheet n Database n Presentation graphics n 1 st Semester 2006 9
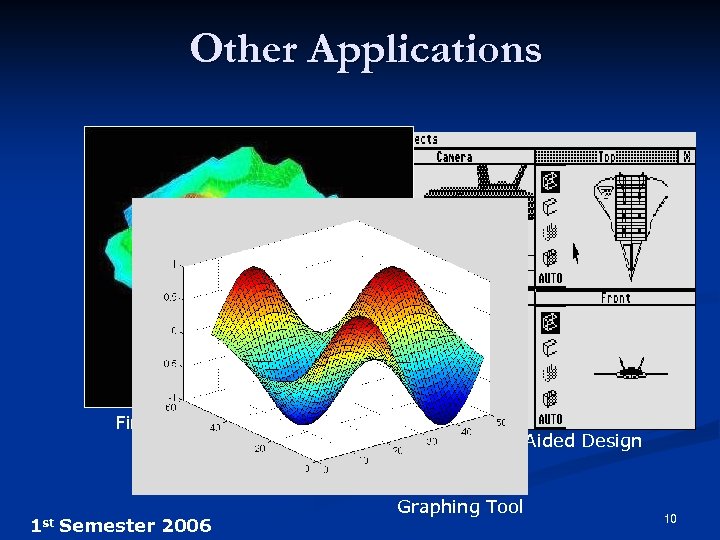 Other Applications Finite Element Analysis 1 st Semester 2006 Computer-Aided Design Graphing Tool 10
Other Applications Finite Element Analysis 1 st Semester 2006 Computer-Aided Design Graphing Tool 10
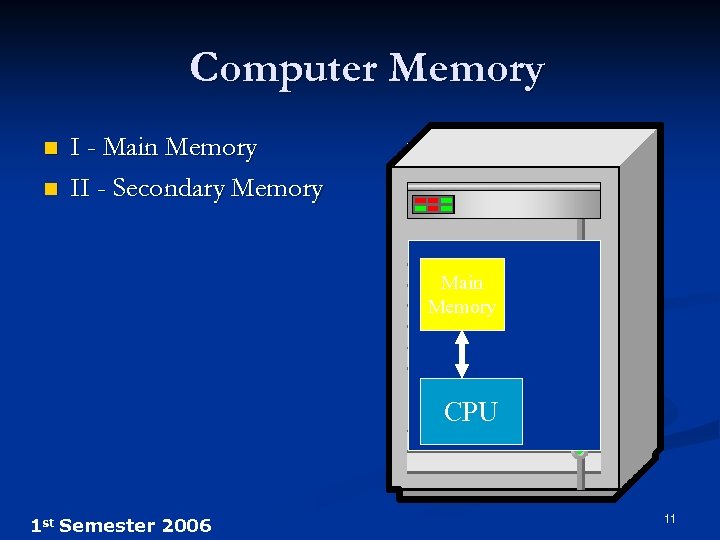 Computer Memory n n I - Main Memory II - Secondary Memory Main Memory CPU 1 st Semester 2006 11
Computer Memory n n I - Main Memory II - Secondary Memory Main Memory CPU 1 st Semester 2006 11
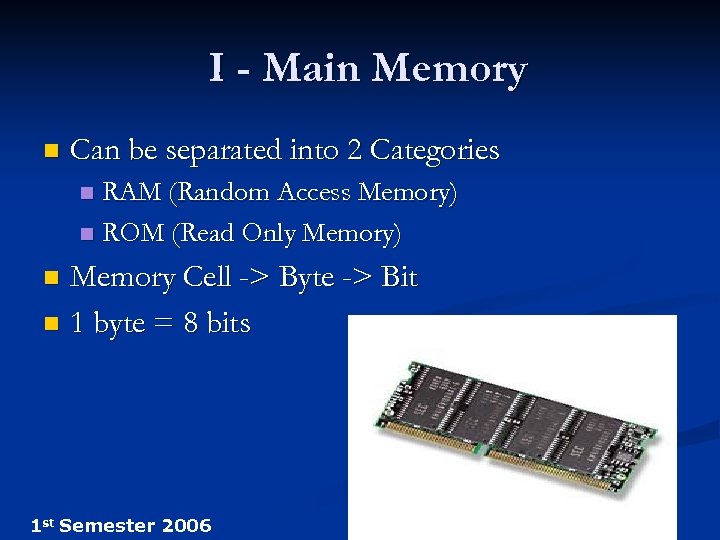 I - Main Memory n Can be separated into 2 Categories RAM (Random Access Memory) n ROM (Read Only Memory) n Memory Cell -> Byte -> Bit n 1 byte = 8 bits n 1 st Semester 2006 12
I - Main Memory n Can be separated into 2 Categories RAM (Random Access Memory) n ROM (Read Only Memory) n Memory Cell -> Byte -> Bit n 1 byte = 8 bits n 1 st Semester 2006 12
 II - Secondary Memory Floppy disk (1. 44 MB) n Hard disk (80 GB, 100 GB) n CD-ROM (700 MB)/DVD-ROM (4. 7/8. 5 GB) n Flash Memory (Compact Flash, MMC, SD) Etc… 1 KB (Kilo. Bytes) = 210 = 1024 bytes 1 MB (Mega. Bytes) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes 1 GB (Giga. Bytes) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes n 1 st Semester 2006 13
II - Secondary Memory Floppy disk (1. 44 MB) n Hard disk (80 GB, 100 GB) n CD-ROM (700 MB)/DVD-ROM (4. 7/8. 5 GB) n Flash Memory (Compact Flash, MMC, SD) Etc… 1 KB (Kilo. Bytes) = 210 = 1024 bytes 1 MB (Mega. Bytes) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes 1 GB (Giga. Bytes) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes n 1 st Semester 2006 13
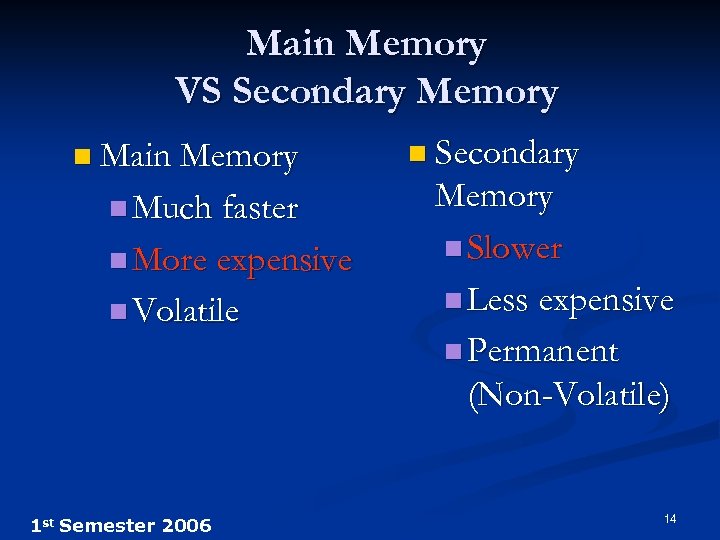 Main Memory VS Secondary Memory n Main Memory n Much faster n More expensive n Volatile 1 st Semester 2006 n Secondary Memory n Slower n Less expensive n Permanent (Non-Volatile) 14
Main Memory VS Secondary Memory n Main Memory n Much faster n More expensive n Volatile 1 st Semester 2006 n Secondary Memory n Slower n Less expensive n Permanent (Non-Volatile) 14
 Computer Components (Revisit ( n Computer Specification Intel® Pentium® D Processors 820 Dual Core (2 x 1 MB L 2 cache, 800 MHz FSB) n Genuine Windows® XP Professional n Up to 4 GB of 533 MHz Dual Channel Shared 2 DDR 2 SDRAM n Intel® Graphics Media Accelerator 950 (GMA 950) n Integrated Broadcom® Gigabit 4 LOM (LAN on Motherboard) n 1 st Semester 2006 15
Computer Components (Revisit ( n Computer Specification Intel® Pentium® D Processors 820 Dual Core (2 x 1 MB L 2 cache, 800 MHz FSB) n Genuine Windows® XP Professional n Up to 4 GB of 533 MHz Dual Channel Shared 2 DDR 2 SDRAM n Intel® Graphics Media Accelerator 950 (GMA 950) n Integrated Broadcom® Gigabit 4 LOM (LAN on Motherboard) n 1 st Semester 2006 15
 Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 16
Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 16
 Programming Languages Machine Language n Assembly Language n High-Level Language n 1 st Semester 2006 17
Programming Languages Machine Language n Assembly Language n High-Level Language n 1 st Semester 2006 17
 High-levelvs Assembly vs Machine Language n High-level Language SUM = A * 2 + ALPHA/3; n Assembly Language MULL 3 DIVL 3 ADDL 3 n A, #2, AX #3, ALPHA, BX AX, BX, SUM Machine Language 0001100001111 10011000111 1 st Semester 2006 18
High-levelvs Assembly vs Machine Language n High-level Language SUM = A * 2 + ALPHA/3; n Assembly Language MULL 3 DIVL 3 ADDL 3 n A, #2, AX #3, ALPHA, BX AX, BX, SUM Machine Language 0001100001111 10011000111 1 st Semester 2006 18
 High-Level Languages n Procedural Language n n n Object-Oriented Language n n C++ Java C# Functional Language n n Fortran Cobol Basic C Pascal Lisp Logic Language n Prolog 1 st Semester 2006 19
High-Level Languages n Procedural Language n n n Object-Oriented Language n n C++ Java C# Functional Language n n Fortran Cobol Basic C Pascal Lisp Logic Language n Prolog 1 st Semester 2006 19
 Translators Language Translator Assembly Assembler High-Level Languages Compilers 1 st Semester 2006 20
Translators Language Translator Assembly Assembler High-Level Languages Compilers 1 st Semester 2006 20
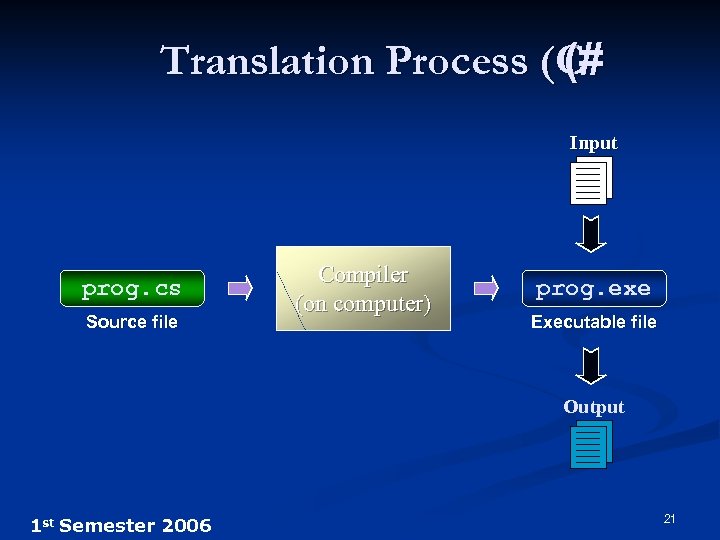 Translation Process (C (# Input prog. cs Source file Compiler (on computer) prog. exe Executable file Output 1 st Semester 2006 21
Translation Process (C (# Input prog. cs Source file Compiler (on computer) prog. exe Executable file Output 1 st Semester 2006 21
 Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 22
Outline Introduction to Computer n Programming Languages n How to Run a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 22
 How to run program ? n After boot Process n n May be Windows XP (Operating System) has been loaded into Main Memory User tell OS to load program prog OS Load program prog from the hard disk into the memory n OS run program from the memory n 1 st Semester 2006 23
How to run program ? n After boot Process n n May be Windows XP (Operating System) has been loaded into Main Memory User tell OS to load program prog OS Load program prog from the hard disk into the memory n OS run program from the memory n 1 st Semester 2006 23
 Summary Computer Basic n Programming Language n Running a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 24
Summary Computer Basic n Programming Language n Running a Program n 1 st Semester 2006 24
 To Do n Add yourself on M@x. Learn Go to http: //course. ku. ac. th n Section 5 n Instructor: Sitichai Srioon n n Upload your picture 1 st Semester 2006 25
To Do n Add yourself on M@x. Learn Go to http: //course. ku. ac. th n Section 5 n Instructor: Sitichai Srioon n n Upload your picture 1 st Semester 2006 25
 Questions? 1 st Semester 2006 26
Questions? 1 st Semester 2006 26


