Introduction_Statistics.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

Introduction to Business Management: Statistics Instructor: Iya Y. Churakova, Ph. D Senior Lecturer, GSOM e-mail churakova@gsom. pu. ru 2014

Course Information Study language: English Course type: elective Forms of academic studies : § § § 14 hours of lectures (including two in-class assignments, 1 academic hour each) 1 hour of classroom interim assessment 10 hours of students self-work (including two home assignments)

Annotation This introductory course in data analysis and statistical inference requires no background in statistics. It is designed to introduce students to modern methods of processing and analyzing statistical information and the possibility of their use in decision-making on management of economic and social processes.

Reasons to study Statistics l l l To be informed: numerical information is everywhere. To be professional: statistical techniques are used to make decisions. To be intellectual: basic statistics is an intellectual challenge, new area for your talent application.
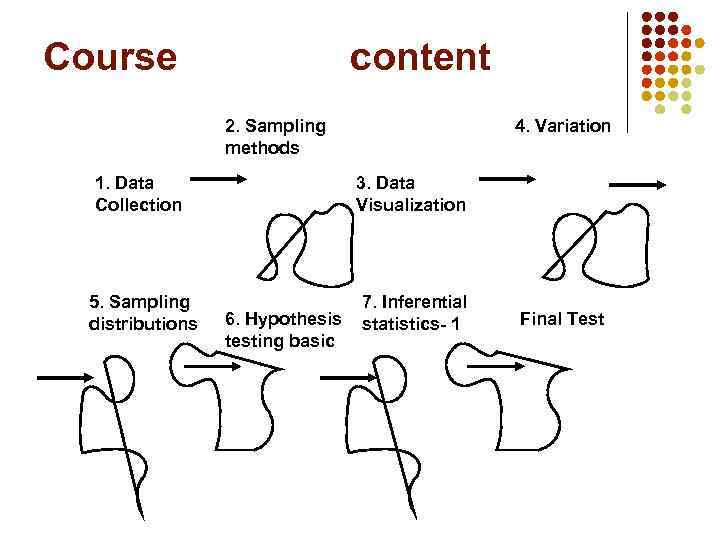
Course content 2. Sampling methods 4. Variation 1. Data Collection 3. Data Visualization 5. Sampling distributions 7. Inferential statistics- 1 6. Hypothesis testing basic Final Test
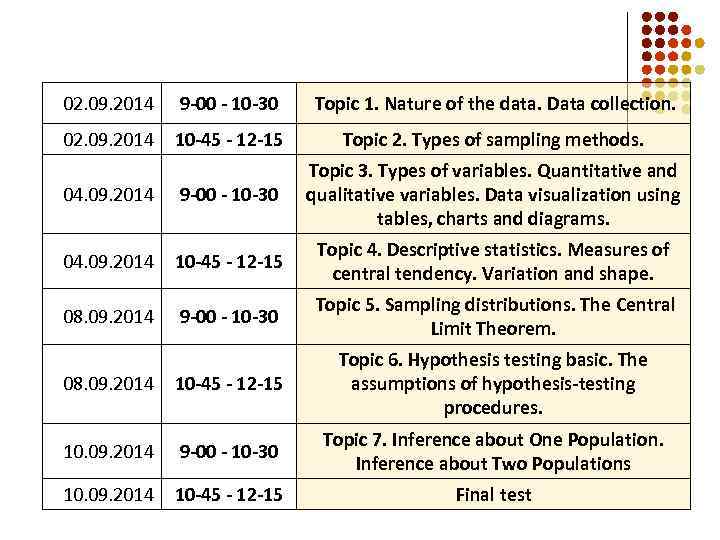
02. 09. 2014 9 -00 - 10 -30 Topic 1. Nature of the data. Data collection. 02. 09. 2014 10 -45 - 12 -15 Topic 2. Types of sampling methods. 04. 09. 2014 9 -00 - 10 -30 Topic 3. Types of variables. Quantitative and qualitative variables. Data visualization using tables, charts and diagrams. 04. 09. 2014 10 -45 - 12 -15 Topic 4. Descriptive statistics. Measures of central tendency. Variation and shape. 08. 09. 2014 9 -00 - 10 -30 Topic 5. Sampling distributions. The Central Limit Theorem. 08. 09. 2014 10 -45 - 12 -15 Topic 6. Hypothesis testing basic. The assumptions of hypothesis-testing procedures. 10. 09. 2014 9 -00 - 10 -30 Topic 7. Inference about One Population. Inference about Two Populations 10. 09. 2014 10 -45 - 12 -15 Final test

Basic learning principles l l l Attend each lesson, work on everyday basis. Ask questions if you do not understand the material. Form a study group, study with friends, discuss all the topics for better understanding. Look for applications to make statistics more real. Practice, practice…

Course books l Levine, David M. , David F. Stephan, Timothy C. Krehbiel, and Mark L. Berenson (2011) Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel. Sixth Edition. Pearson Education, Inc. ISBN: 0136113494 l Field, Andy (2013). Discovering Statistics using IBM SPSS Statistics 4 th edition. SAGE Publications Ltd. , ISBN 9781446249179

Evaluation system Homework assignments (2 tasks, estimated at 10% of the total grade each) 20% of the total grade; In-class assignment (2 works, estimated at 10% of the total grade each), 20% of the total grade; Interim attestation as a classroom test, duration 45 minutes, open-book. Test will contain six questions (essays or problems) 10% each question, attestation will accumulate 60% of the total grade.
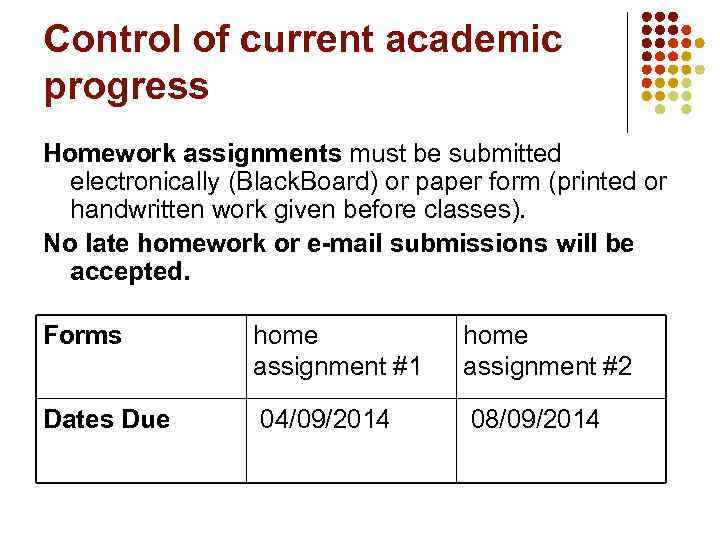
Control of current academic progress Homework assignments must be submitted electronically (Black. Board) or paper form (printed or handwritten work given before classes). No late homework or e-mail submissions will be accepted. Forms home assignment #1 home assignment #2 Dates Due 04/09/2014 08/09/2014
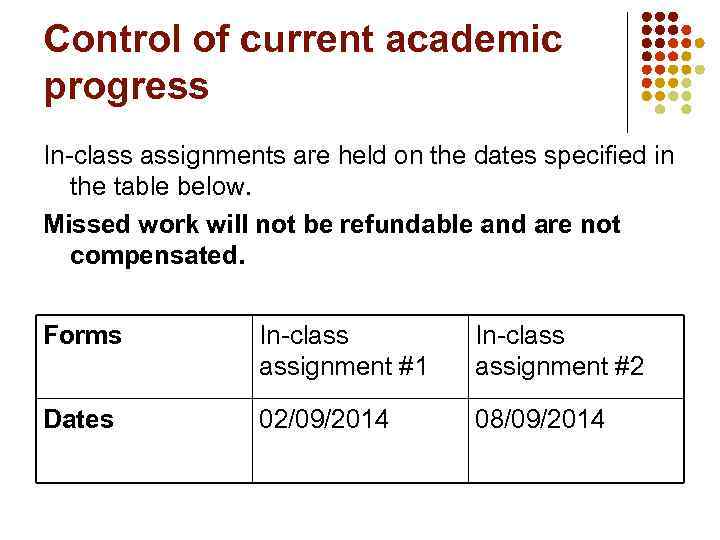
Control of current academic progress In-class assignments are held on the dates specified in the table below. Missed work will not be refundable and are not compensated. Forms In-class assignment #1 In-class assignment #2 Dates 02/09/2014 08/09/2014
Course results l l l Knowledge of basic statistical algorithms to analyze data; Practical experience in setting statistical process: main hypotheses modeling, data selection, analysis and visualization; Skills to use Excel add-in "Data Analysis" in the calculation of basic statistics and graphical representation of the results; Ability to use simple statistical procedures for research and management of business processes. Ability to study the QMBR course (basic) together with students with quantitative background.

Statistics is the grammar of science Karl Pearson

Questions?
Introduction_Statistics.ppt