ec4968abfadc81aeaf65689906c23c2b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) Abstract: What is AI? What happened within AI, history? Going deeper: What really is AI? Where AI happens? What will you learn? How will this course go? Prerequisites 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: What is AI? AI <is> Computer Science! Whatever is at the FRONTIER of computer science is AI! It is really about NEW challenges that is CURRENTLY beyond computing Chasing elusive goals! 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

As soon as “it” is achieved – “it” is no longer AI! AI is really a perception! However, a pattern of topics, problems and algorithmtypes emerge as we pursue a “dream” List of AI problems in text on slide 25: http: //cs. fit. edu/~dmitra/Art. Int/Text. Slides/chapter 01. pdf 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Historical Journey Early Computers = Calculator plus stored program • The Dream: Neuron model 1943, Turing test, 1950 • Look Ma, No Hands! 1952 -69 – Samuel’s checkers program: game playing – Newell-Simon’s Logic Theorist: proving math theorems – Geltner’s Geometry Engine: geometry theorems • “AI” 1956 Dartmouth meeting • Knowledge is power: Knowledge-based Systems, 1960 -80 – – – 3/17/2018 Mycin, Dendral, and other expert systems Expert systems industry boom, 1980 -90 Fifth generation computing system (Japan), MCC (US) “Smart-X” 2000 -10 Deep-learning resurgence, 2010 -present (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Historical Journey • Challenge catches up, 1980 -2000 – Smaller niche areas flourish – Integrate: Agent view (text) • Large knowledge bases, 1990 -present – – – MCC Cyc project / IBM Watson DARPA / SRI International /Apple Iphone Siri Big data to Intelligence • Machine learning – Handwriting recognition, Speech recognition, by HMM 2000 -10 – Big data, by Convolutional Neural Net, 2010+ 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: What really is it? • Computers manipulate numbers (hardware) • Computers can map symbols internally to numbers (Unicode) • First AI question: Can programs manipulate symbols? – Symbolic AI: Expert systems • Second AI question: Is symbol manipulation enough? – No! Human intelligence is not just symbol manipulation – And it is not efficient either as was thought of initially • Third AI question: Should we go back to number manipulations – Optimization: Machine learning – … • Future of AI: Numbers + Symbols! – Data types: Real Ordinal Partial order Categorical 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Course content • <<It is only algorithms, dummy!>> No “Intelligence” – Because, there is no definition of intelligence 1. Search Algorithms 2. Constraint Reasoning 3. Automated Reasoning Exam 1: 20% 4. Probabilistic Reasoning 5. Machine Learning Exam 3: 20% Project: 30 -20% Final: 20 -30% 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
Introduction to AI: Course content: Samples 1. Search Algorithms 1. 2. 3. Blind search Guided search Optimization 2. Constraint Reasoning 1. 2. 3. Consistency levels Back-jumping Randomized algorithms 3. Automated Reasoning 1. 2. 3. 3/17/2018 Logic First order logic Knowledge-base (C) Debasis Mitra
Introduction to AI: Course content: Samples 4. Probabilistic Reasoning 4. 5. 6. Bayesian network Dynamic network Fuzzy logic 5. Machine Learning 5. 6. 7. 8. Decision tree Training with samples Neural networks Clustering 6. Advanced topics – – 3/17/2018 Planning Computer Vision Robotics Natural Language Processing (C) Debasis Mitra Three levels of learning in our course : • Tourist-level: definition-concepts • Deeper level: Solving exercises • Expert level: Coding

• Industry! Frontiers Introduction to AI: Where AI Happens – Google, Amazon, Facebook, … start-ups, … • Academic AI is away from real life, but – – Challenges are addressed by new algorithms here “Industry is 10 years behind academics, ” a past Ph. D, at Amazon now AIMA: our Text by Russell-Norvig My own humble interest: AI in Science and Engineering • Conferences – – – AAAI: Association for Advancement (used to be American ) of AI IJCAI: International Joint Conference on AI ISAIM: International Symposium on AI and Math IEA/AIE: Applied AI FLAIRS: Used to be Florida AI Research Symposium • Journals – – 3/17/2018 AI journal Journal of AI Research, online Applied AI AI and Math (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: What can you do with this course? • Some companies prefer students with AI background • Current boom in Data Science (a new name for Data Mining) • Helps in other advanced courses – – – Machine learning Computer Vision Scientific computing Computational Molecular Biology Complex network • Research in/out our department • AI algorithms / concepts are good to know as a CS-IT person 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Pre-Quiz (One sentence each, total 7 min) • Name: • Level (UG/Grad): • Major, if non-CS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What did you know about AI (i. e. your current perception)? If you were to develop an AI program, what would that be on? Name 3 topics that will be covered in this course. Name one of the popular AI software or application. Why are you taking this course (honest answer please)? 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Required Background • • List-Queue-Stack. Tree-Graph-Spanning tree. Djikstra. Recursion-Convert to Iteration Combinatorics Big. O-Loop Complexity-NPProgramming skill in any high level language: – 3/17/2018 I encourage you to learn Python, it is “hot” now (C) Debasis Mitra
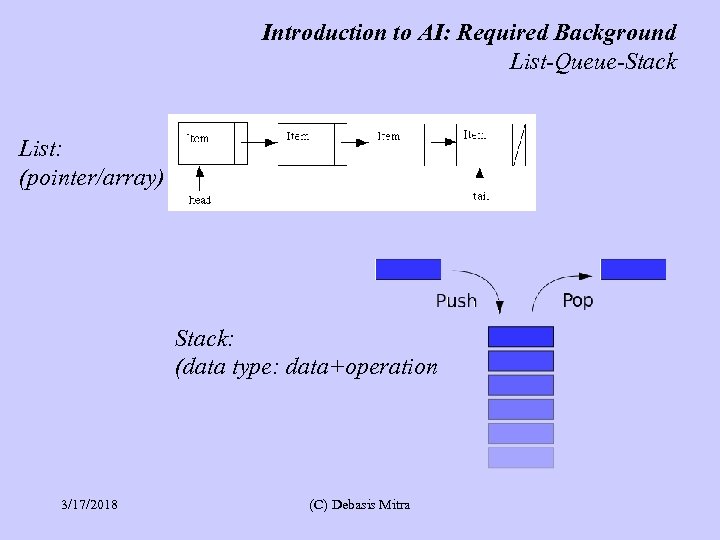
Introduction to AI: Required Background List-Queue-Stack List: (pointer/array) Stack: (data type: data+operation 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
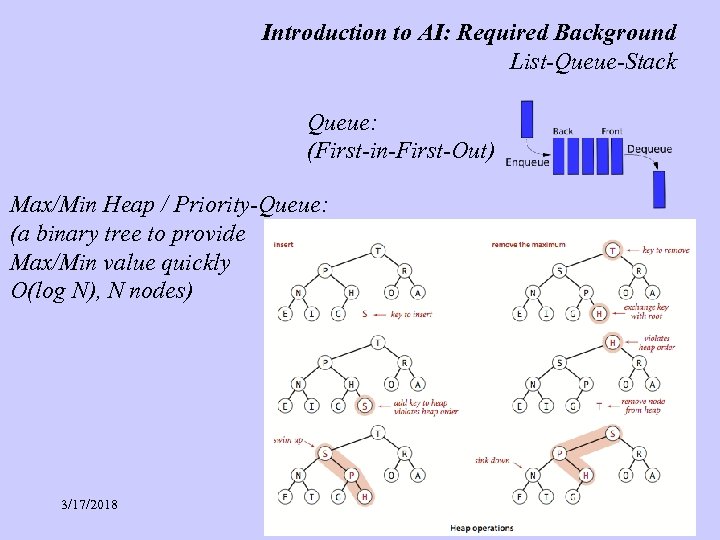
Introduction to AI: Required Background List-Queue-Stack Queue: (First-in-First-Out) Max/Min Heap / Priority-Queue: (a binary tree to provide Max/Min value quickly O(log N), N nodes) 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
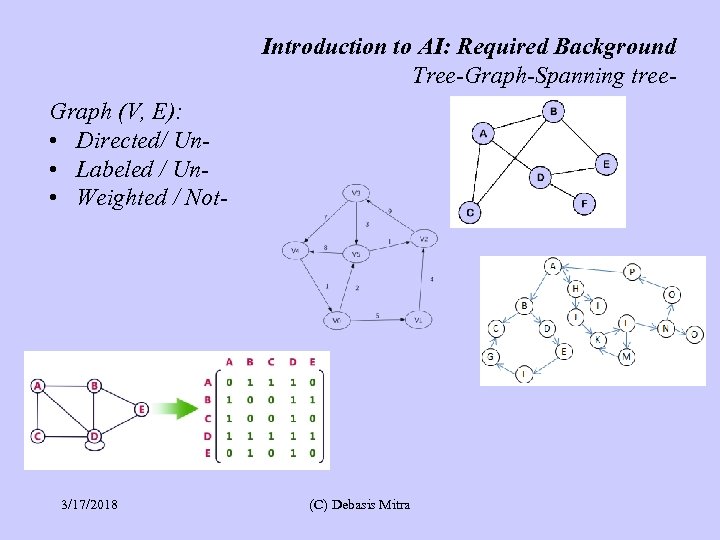
Introduction to AI: Required Background Tree-Graph-Spanning tree. Graph (V, E): • Directed/ Un • Labeled / Un • Weighted / Not- 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
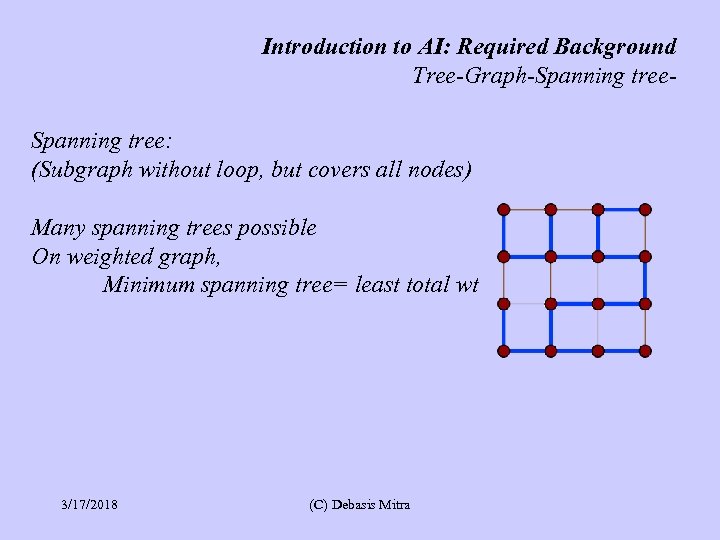
Introduction to AI: Required Background Tree-Graph-Spanning tree: (Subgraph without loop, but covers all nodes) Many spanning trees possible On weighted graph, Minimum spanning tree= least total wt 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
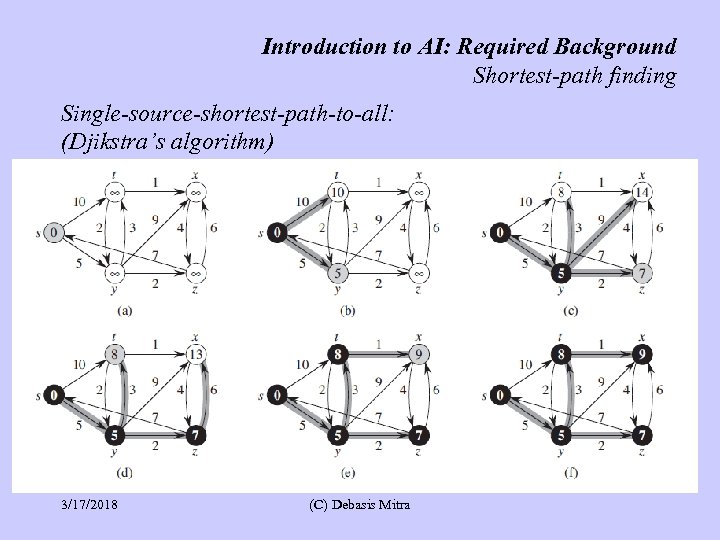
Introduction to AI: Required Background Shortest-path finding Single-source-shortest-path-to-all: (Djikstra’s algorithm) 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
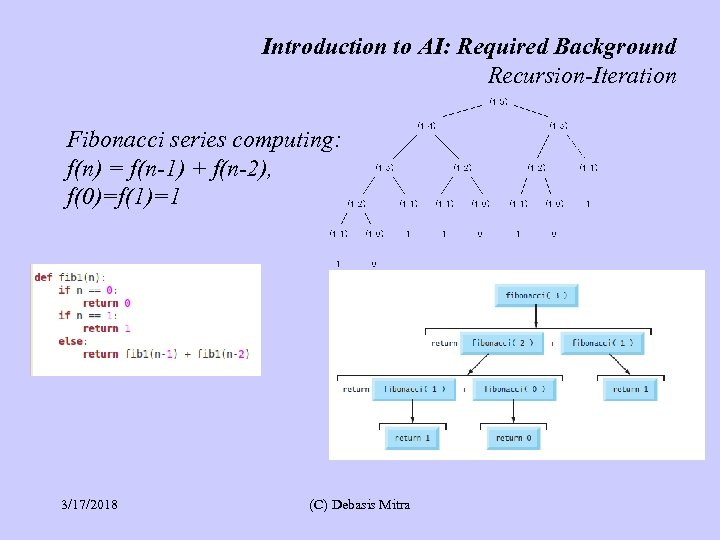
Introduction to AI: Required Background Recursion-Iteration Fibonacci series computing: f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2), f(0)=f(1)=1 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
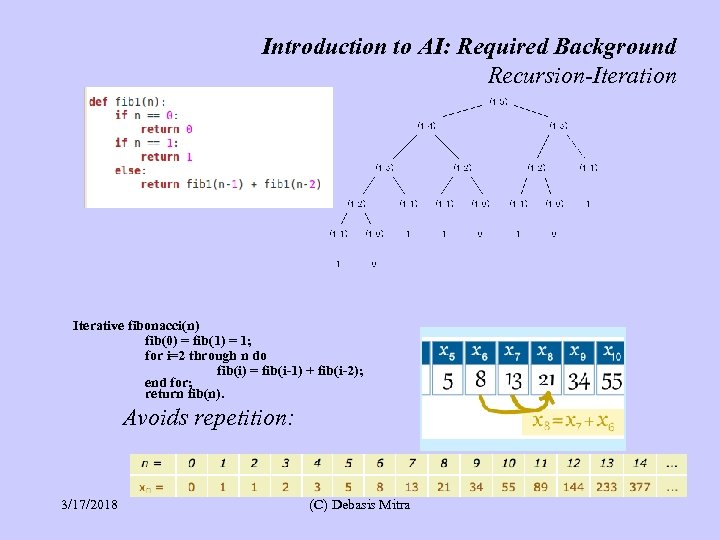
Introduction to AI: Required Background Recursion-Iteration Iterative fibonacci(n) fib(0) = fib(1) = 1; for i=2 through n do fib(i) = fib(i-1) + fib(i-2); end for; return fib(n). Avoids repetition: 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra

Introduction to AI: Required Background Combinatorics Permutation-Combination-Factorial-Power. Set Quiz Questions (do later): 1. 20 nodes, how many pair of nodes? 2. 20 nodes, how many triangles possible? 3. 20 nodes, how many subsets of nodes? 4. 20 letters, how many unique words of length 20 possible? 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
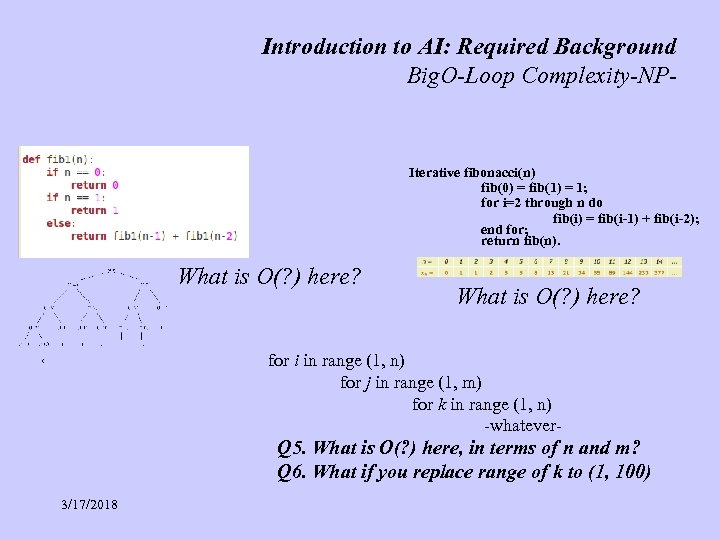
Introduction to AI: Required Background Big. O-Loop Complexity-NP- Iterative fibonacci(n) fib(0) = fib(1) = 1; for i=2 through n do fib(i) = fib(i-1) + fib(i-2); end for; return fib(n). What is O(? ) here? for i in range (1, n) for j in range (1, m) for k in range (1, n) -whatever- Q 5. What is O(? ) here, in terms of n and m? Q 6. What if you replace range of k to (1, 100) 3/17/2018

Introduction to AI: Required Background QUIZ Quiz Questions: KEY 20 nodes, how many pair of nodes, excluding self loops? 20 choose 2, def of ‘choose’, = 20! / ((20 -2)! * 2!) if you include self-loops: above+20 20 nodes, how many triangles possible, excluding repeat nodes, or straight-line triangles? 20 choose 3, = 20! / ((20 -3)! * 3!) 20 nodes, how subsets of nodes? 2^20, each element absent/present in the subset, true/false bit-string is often used for subsets of fixed sized sets 20 letters, how many unique words possible for word of length 20? unique lettering: 20!, first position 20 possibilities * next position 19 possibilities * … not unique lettering: 2 0^20, each position 20 possibilities, 20*20* … 20 -times max size of word up to 20: 20 + 20^2 + 20^3 + …+20^20 if no max size is specified: infinity for i in range (1, n) for j in range (1, m) for k in range (1, n) -whatever 5. What is O(? ) here, in terms of n and m? : O(n 2 m) 6. What if you replace range of k to (1, 100): O(nm) 3/17/2018 (C) Debasis Mitra
ec4968abfadc81aeaf65689906c23c2b.ppt