7253f6f8ac8b33d2e4e9c52d4809c361.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81

Introduction to Alis Dr Robert Clark ALIS Project Manager

Ensuring Fairness

Principles of Fair Analysis : 1. Compare ‘Like’ with ‘Like’ 2. Appropriate Baseline 3. Reflect Statistical Uncertainty

The Analysis
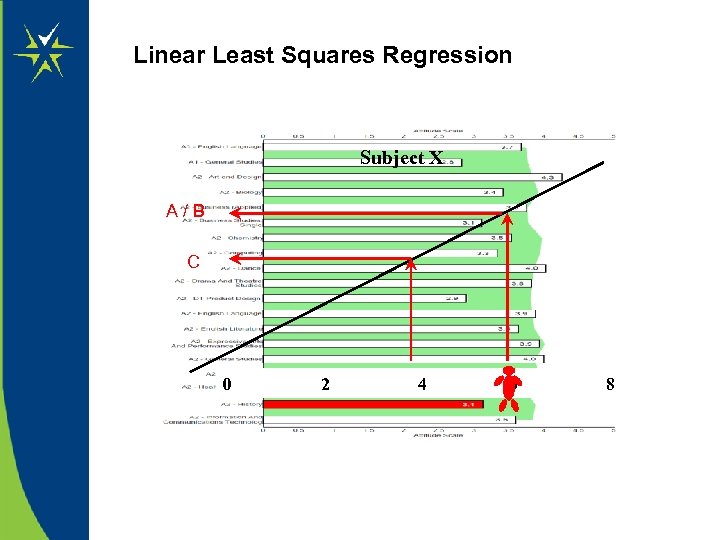
. Linear Least Squares Regression Subject X A/B C 0 2 4 6 8
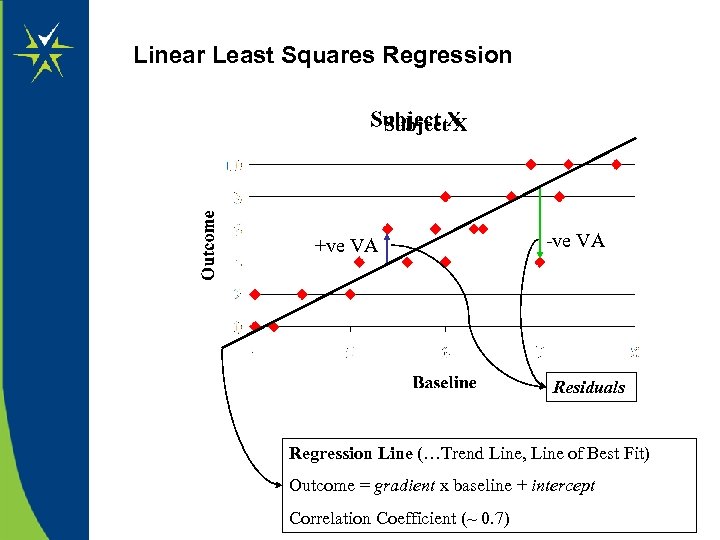
. Linear Least Squares Regression Subject X +ve VA -ve VA Residuals Regression Line (…Trend Line, Line of Best Fit) Outcome = gradient x baseline + intercept Correlation Coefficient (~ 0. 7)
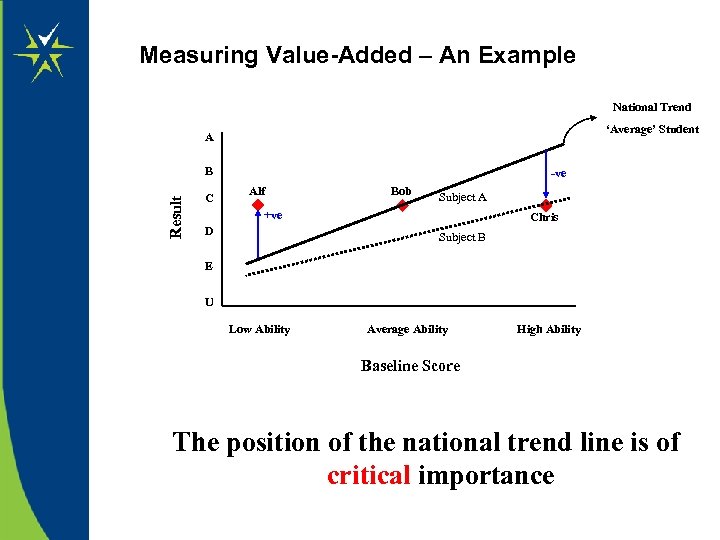
Measuring Value-Added – An Example National Trend ‘Average’ Student A Result B C -ve Alf Bob Subject A +ve D Chris Subject B E U Low Ability Average Ability High Ability Baseline Score The position of the national trend line is of critical importance
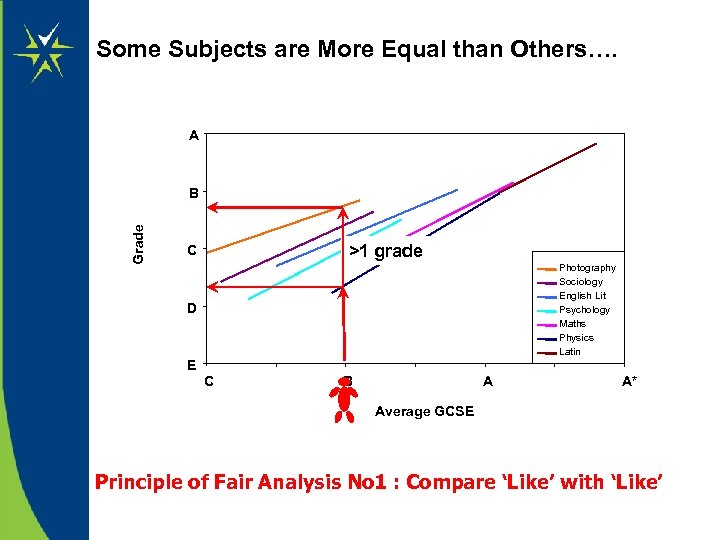
Some Subjects are More Equal than Others…. A Grade B >1 grade C Photography Sociology English Lit Psychology Maths Physics Latin D E C B A A* Average GCSE Principle of Fair Analysis No 1 : Compare ‘Like’ with ‘Like’

Some Subjects are More Equal than Others … Performance varies between subjects, thus analysing and predicting each subject individually is essential. e. g. Student with Average GCSE = 6. 0 Subject Choices Predicted Grades Maths, Physics, Chemistry, Economics C, C, C/D Sociology, Communication Studies, Drama, Media B, B/C, B/C
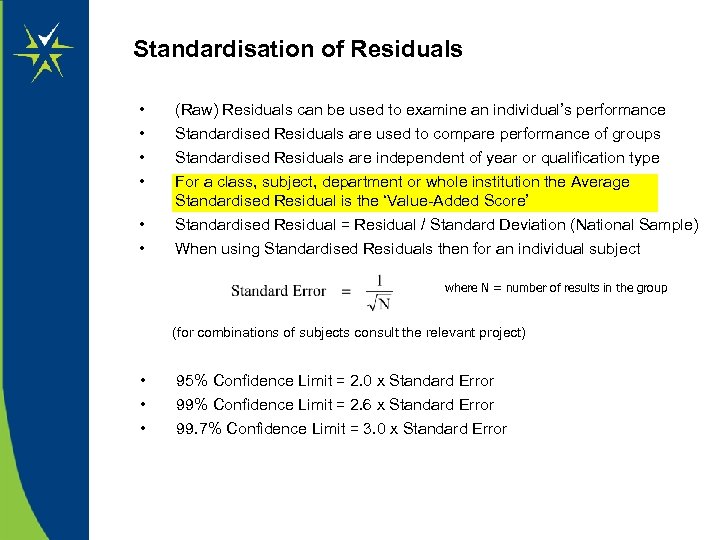
Standardisation of Residuals • • (Raw) Residuals can be used to examine an individual’s performance Standardised Residuals are used to compare performance of groups Standardised Residuals are independent of year or qualification type • • Standardised Residual = Residual / Standard Deviation (National Sample) When using Standardised Residuals then for an individual subject For a class, subject, department or whole institution the Average Standardised Residual is the ‘Value-Added Score’ where N = number of results in the group (for combinations of subjects consult the relevant project) • • • 95% Confidence Limit = 2. 0 x Standard Error 99% Confidence Limit = 2. 6 x Standard Error 99. 7% Confidence Limit = 3. 0 x Standard Error

Subjects Covered… • • A / AS Levels Applied A / AS levels (including dual award) International Baccalaureate BTec Nationals (Diploma, Certificate, Award) CACHE DCE OCR Nationals ifs Diploma / Certificate in Financial Studies Limited pool of level 2 (BTec First)

How to Administer the Project

1. Submit a registration form (Y 11 May onwards…. ) • • • 2. Submit student details – ‘Registration Spreadsheet’ (Y 12 Mid Sept onwards…. ) • • • 3. We need this before we can process any data We need this even if you are registering as part of a consortium Choose Basic / Full (Basic + Attitudinal surveys) and whether you wish to do baseline test This gives us student name details, GCSE scores and the subjects they are studying We always need this even if the students are sitting a baseline test Send spreadsheet once students are confirmed on courses (i. e. not first day of term…. ) Organise baseline testing – ‘Adaptive Test’ (End Y 11 June 15 th onwards…. ) • • This can happen before, at the same time as or after sending us the registration spreadsheet (2 above) Student details appear in ‘Check List’ on web site Early prediction are available for students with Adaptive Test scores as soon as they appear in the Check List. This function is removed one Alis has generated offical predictions (pdf reports). Don’t forget to click ‘Testing Complete’ once you have finished testing your students.
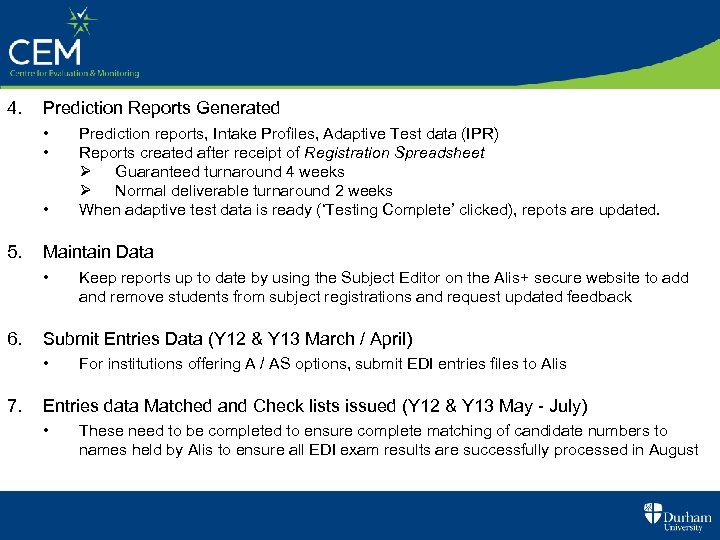
4. Prediction Reports Generated • • • 5. Maintain Data • 6. Keep reports up to date by using the Subject Editor on the Alis+ secure website to add and remove students from subject registrations and request updated feedback Submit Entries Data (Y 12 & Y 13 March / April) • 7. Prediction reports, Intake Profiles, Adaptive Test data (IPR) Reports created after receipt of Registration Spreadsheet Ø Guaranteed turnaround 4 weeks Ø Normal deliverable turnaround 2 weeks When adaptive test data is ready (‘Testing Complete’ clicked), repots are updated. For institutions offering A / AS options, submit EDI entries files to Alis Entries data Matched and Check lists issued (Y 12 & Y 13 May - July) • These need to be completed to ensure complete matching of candidate numbers to names held by Alis to ensure all EDI exam results are successfully processed in August

8. Results Collection (Y 12 & Y 13 August) • • • 9. Submit A / AS results to Alis via EDI Results Files Submit Other quals (IB, BTEc etc) to Alis using results spreadsheet (can opt to submit A / AS data in spreadsheet as well instead of EDI files) Submit results as soon after results day as possible Preliminary VA Feedback (Beginning of September) • • Preliminary feedback generated by 1 st Monday in September. Prompt return of results in August leads to early feedback Trend data not fixed, values may be subject to change 10. Definitive VA Feedback (End of September) • Trend data locked and feedback generated. Letter & CD sent to schools / colleges. 11. Maintain Data • Update results data (missing grades, withdrawals, remarks, appeals etc) using the Results Editor on the Alis+ secure website and request updated feedback.
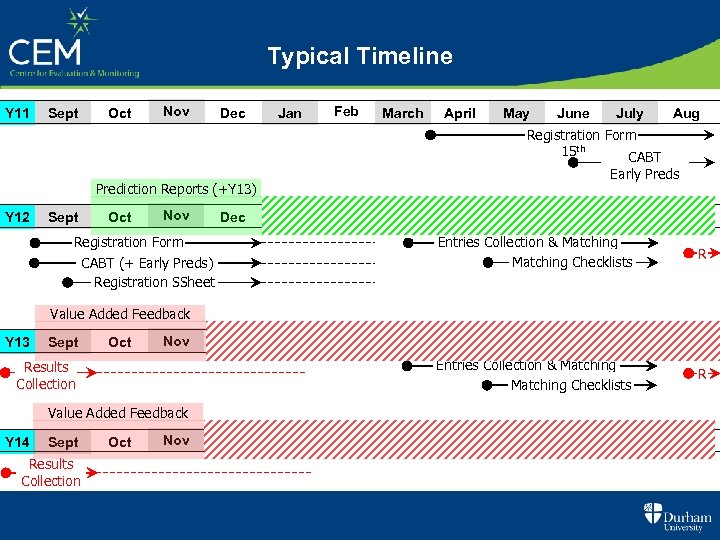
Typical Timeline Y 11 Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April Sept Oct Nov Dec June July Aug Registration Form 15 th CABT Early Preds Prediction Reports (+Y 13) Y 12 May Jan Feb March Registration Form April May June July Entries Collection & Matching Checklists CABT (+ Early Preds) Registration SSheet Aug R Value Added Feedback Y 13 Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April May June July Entries Collection & Matching Checklists Results Collection Aug R Value Added Feedback Y 14 Sept Results Collection Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April May June July Aug

Baseline Assessment
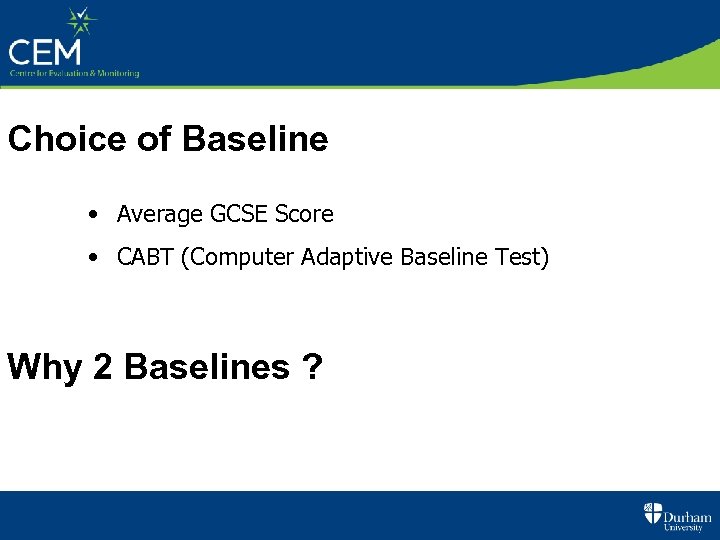
Choice of Baseline • Average GCSE Score • CABT (Computer Adaptive Baseline Test) Why 2 Baselines ?

Why 2 Baselines ? Average GCSE correlates very well to A-level / IB etc, but by itself is not sufficient…. • What is a GCSE ? • Students without GCSE ? • Years out between GCSE & A-level ? • Reliability of GCSE ? • Prior Value-Added ? Principle of Fair Analysis No 2 : Appropriate Baseline
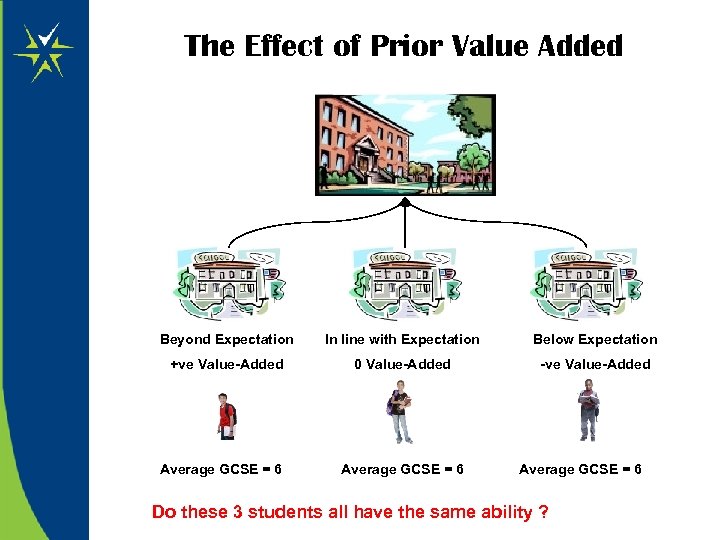
The Effect of Prior Value Added Beyond Expectation In line with Expectation Below Expectation +ve Value-Added 0 Value-Added -ve Value-Added Average GCSE = 6 Do these 3 students all have the same ability ?

Appropriate Baseline • Do students with the same GCSE score from feeder schools with differing value-added have the same ability ? • How can you tell if a student has underachieved at GCSE and thus can you maximise their potential ? • Has a student got v. good GCSE scores through the school effort rather than their ability alone ? • How will this affect expectation of attainment in the Sixth Form ? • Can you add value at every Key Stage ? Baseline testing provides a measure of ability that (to a large extent) is independent of the effect of prior treatment.
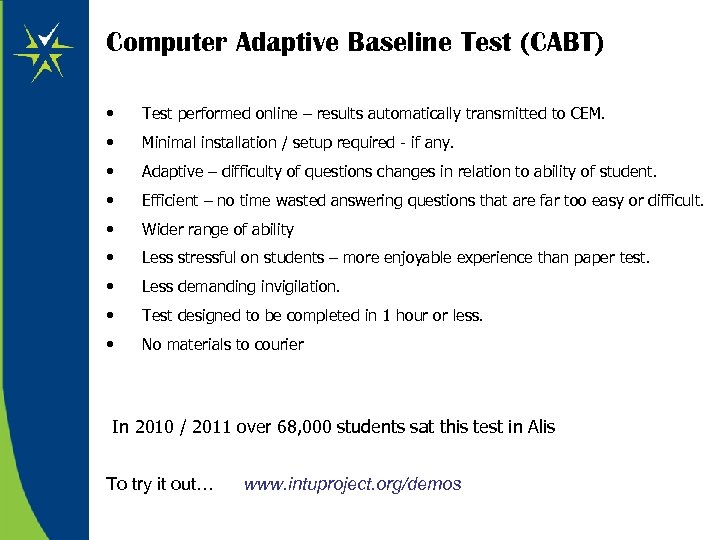
Computer Adaptive Baseline Test (CABT) • Test performed online – results automatically transmitted to CEM. • Minimal installation / setup required - if any. • Adaptive – difficulty of questions changes in relation to ability of student. • Efficient – no time wasted answering questions that are far too easy or difficult. • Wider range of ability • Less stressful on students – more enjoyable experience than paper test. • Less demanding invigilation. • Test designed to be completed in 1 hour or less. • No materials to courier In 2010 / 2011 over 68, 000 students sat this test in Alis To try it out… www. intuproject. org/demos

Understanding Your Students: Baseline & Predictive Feedback
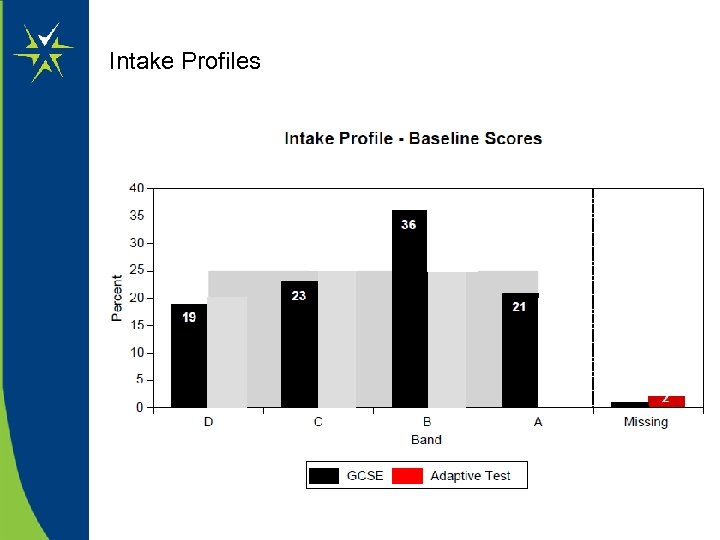
Intake Profiles
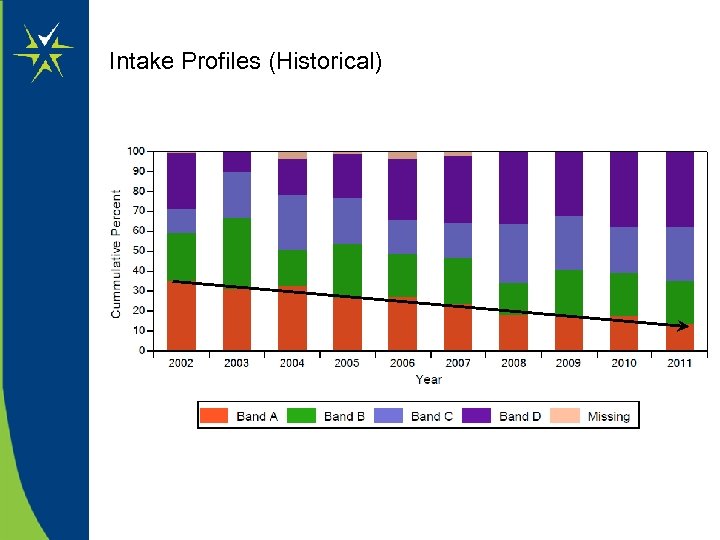
Intake Profiles (Historical)
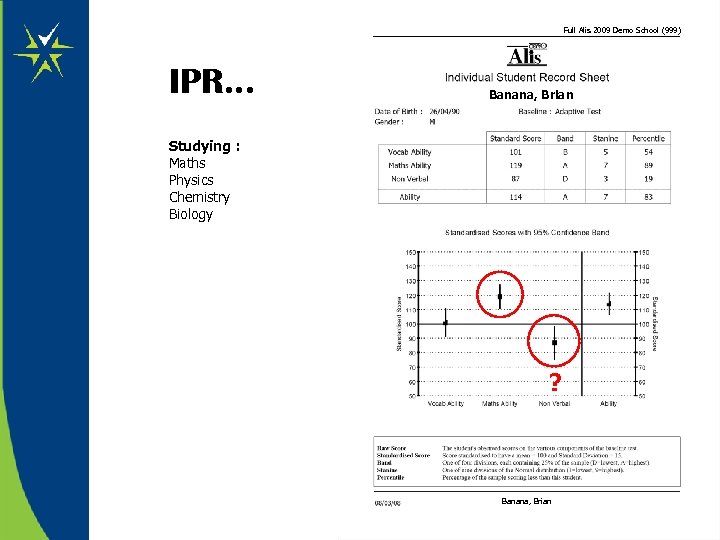
Full Alis 2009 Demo School (999) IPR. . . Banana, Brian Studying : Maths Physics Chemistry Biology ? Banana, Brian
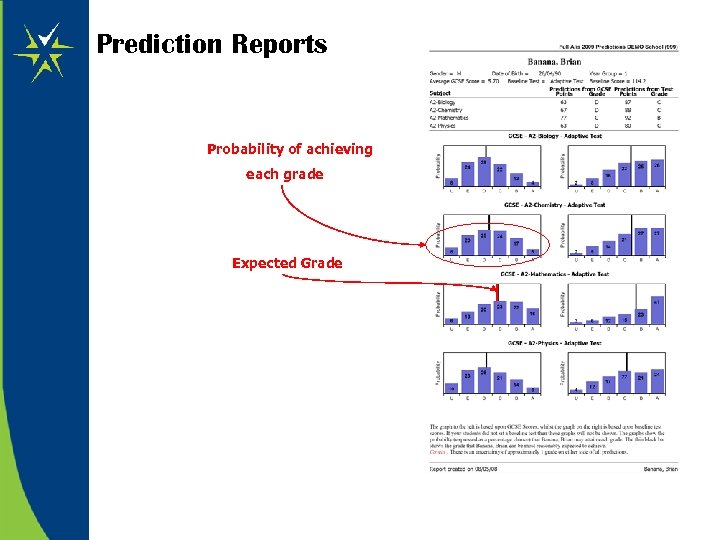
Prediction Reports Probability of achieving each grade Expected Grade
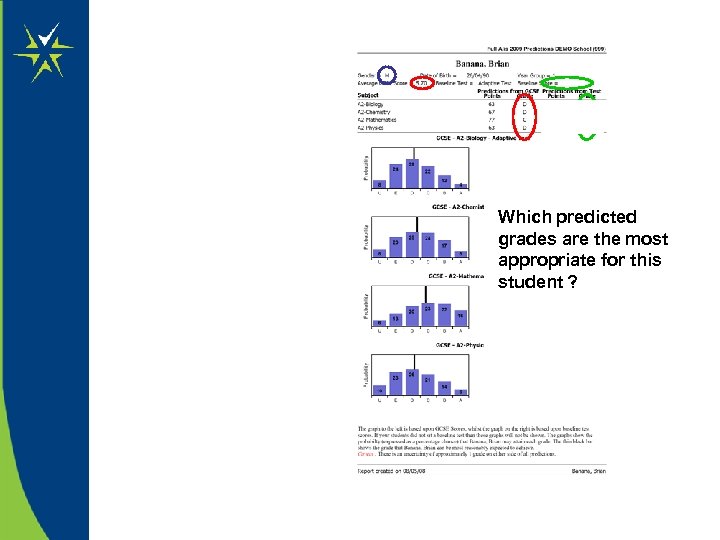
Which predicted grades are the most appropriate for this student ?
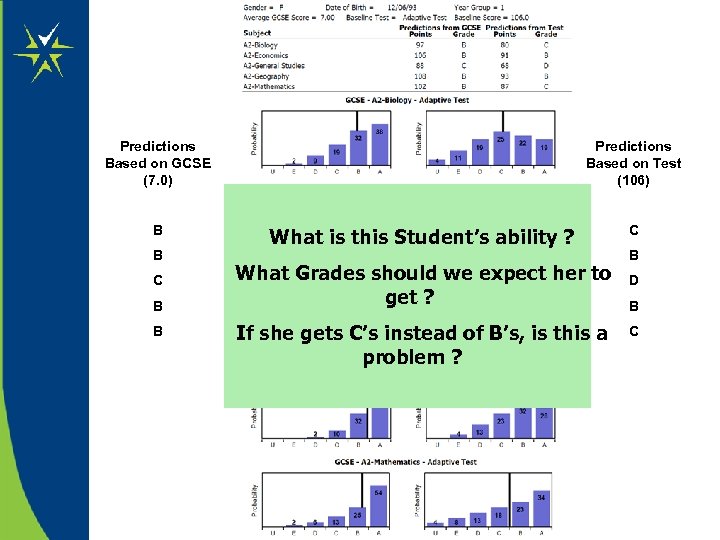
Predictions Based on GCSE (7. 0) B B C B B Predictions Based on Test (106) What is this Student’s ability ? C What Grades should we expect her to get ? D If she gets C’s instead of B’s, is this a problem ? B B C
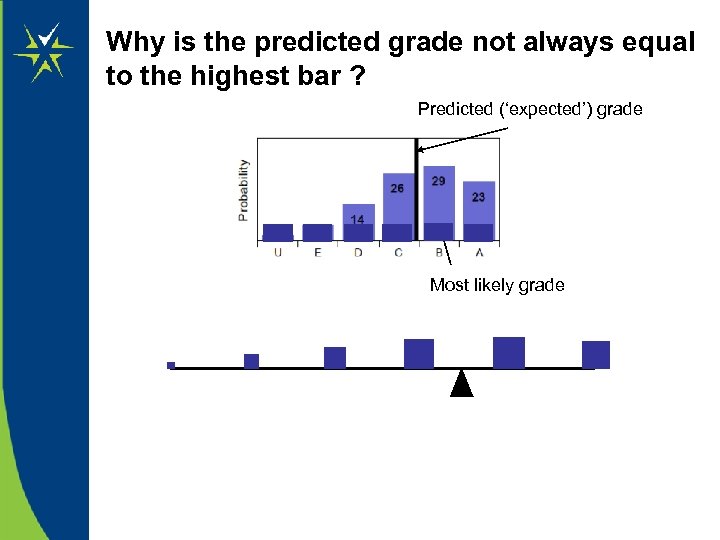
Why is the predicted grade not always equal to the highest bar ? Predicted (‘expected’) grade Most likely grade
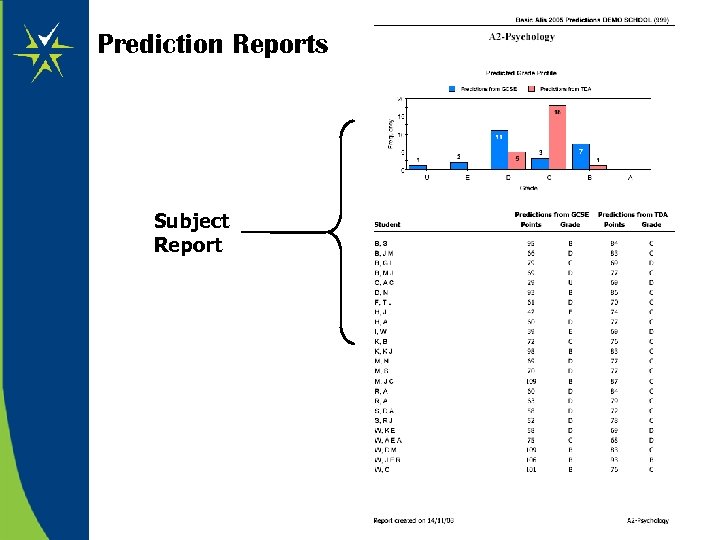
Prediction Reports Subject Report

A 2 vs AS predictions and the impact of the A* Grade
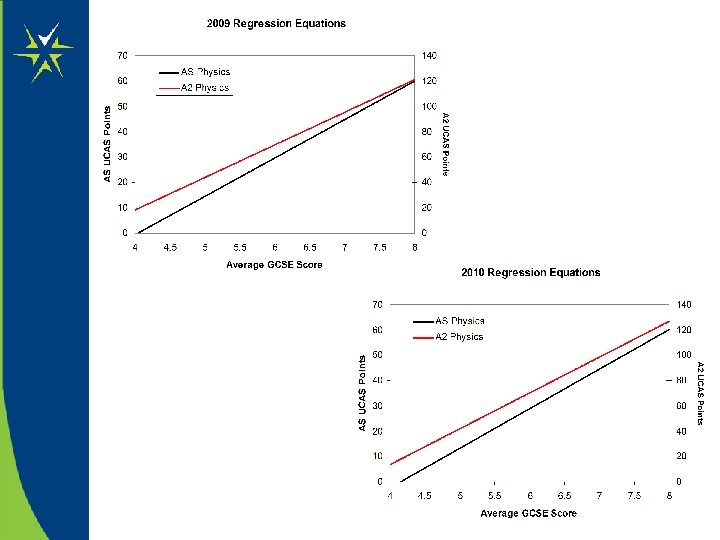
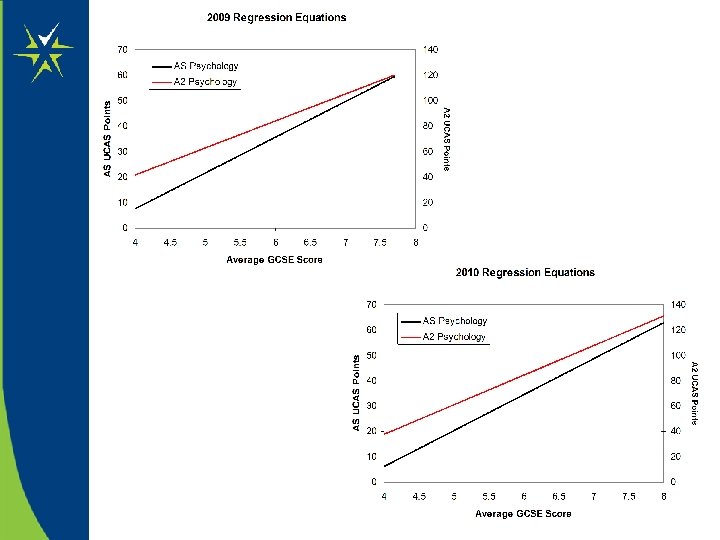

Worked Examples: Baseline Data & Predictions

Refer to the Intake Data on the next 2 slides • For each school what deductions might you make ? • What implications are there (if any) for teaching & learning ?
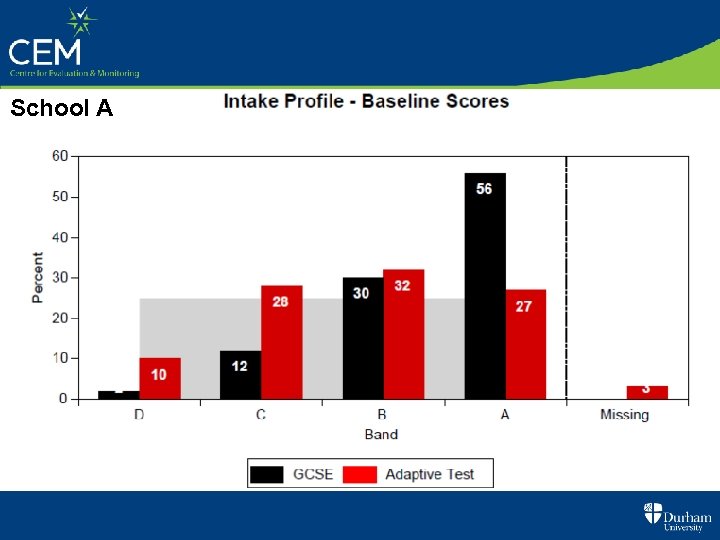
School A
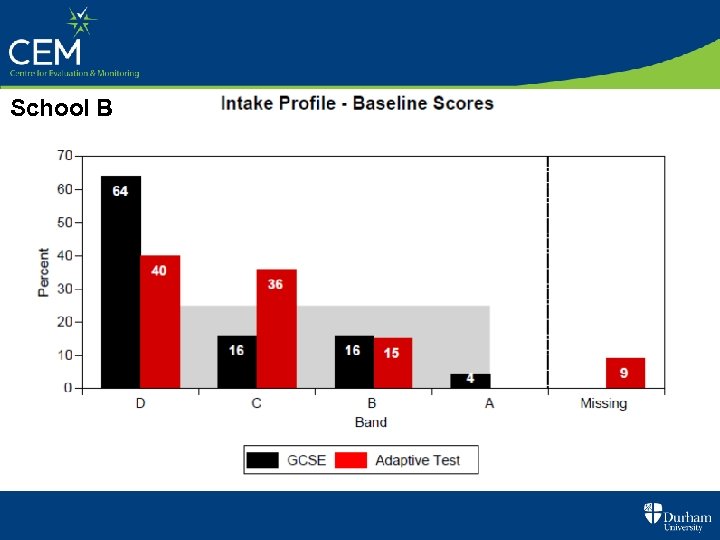
School B

Refer to the Y 12 data on the next 2 slides. • What impact might there be on the pupil’s learning ? • What subjects would you be worried about them studying ? Note : Non Verbal section includes Perceptual Speed and Accuracy, Pattern Matching, logical reasoning and dice folding
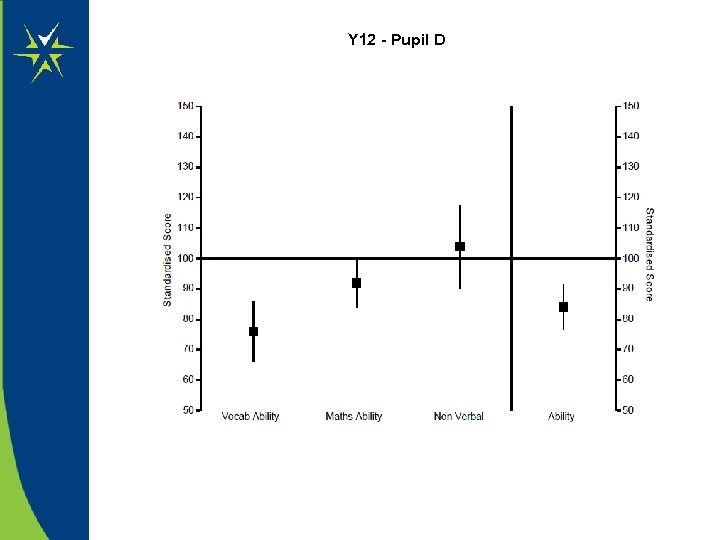
Y 12 - Pupil D
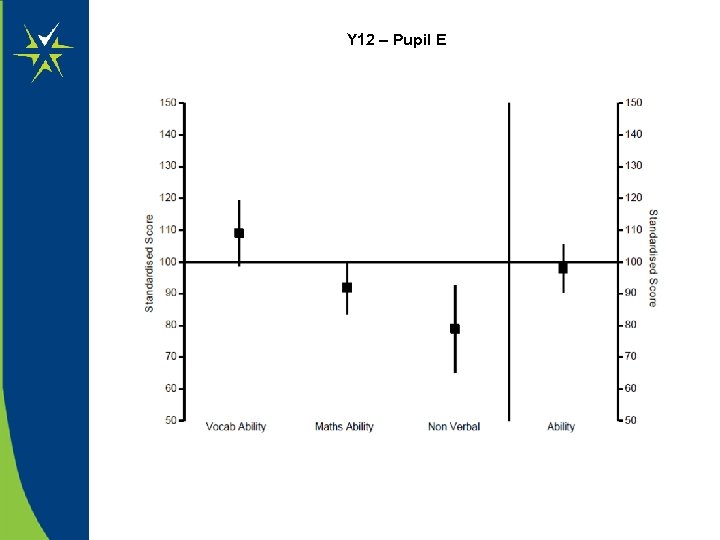
Y 12 – Pupil E

Refer to the data on the next 3 slides. • Does the data show any ‘warnings’ about future potential achievement? • Based only on the information provided, what would be realistic subject targets for the students, and why?
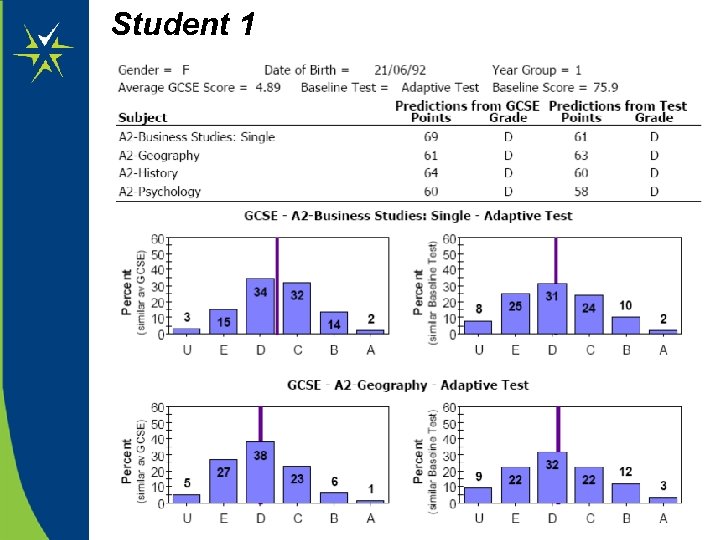
Student 1
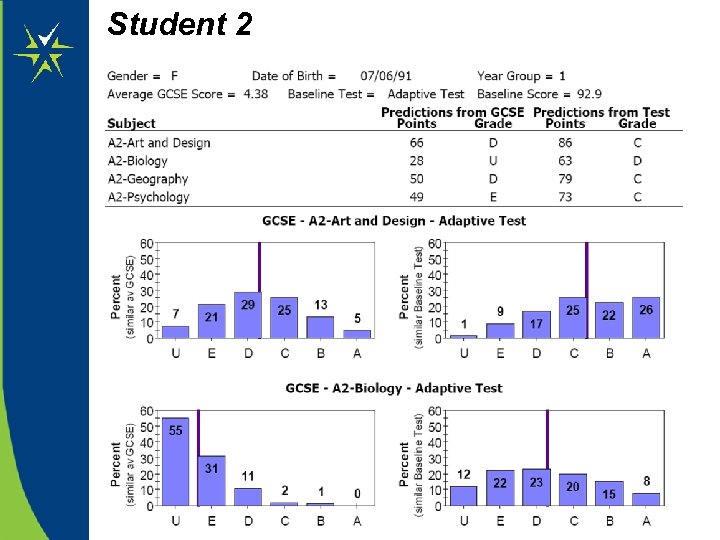
Student 2
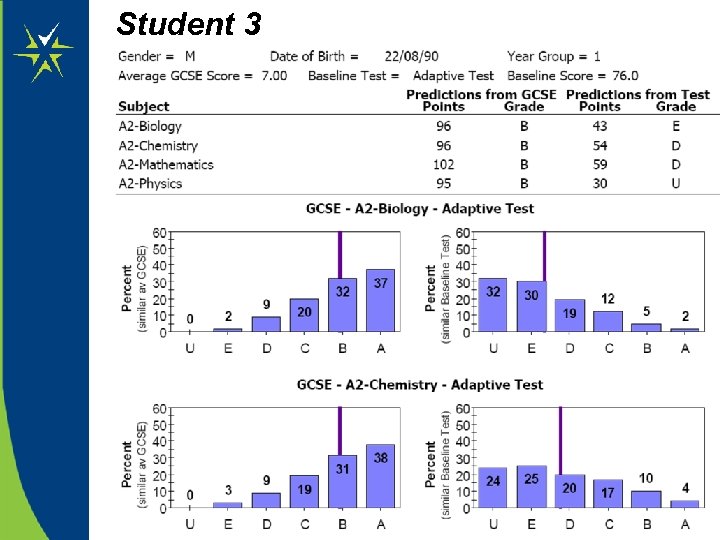
Student 3

Worked Examples: Target Setting

Basing Targets on Prior VA – One Methodology from an Alis School • Discuss previous value added data with each Ho. D • Start with an agreed REALISTIC representative figure based, if available on previous (3 years ideally) of value added data • add to each pupil prediction, and convert to grade (i. e. in-built value added) • Discuss with students, using professional judgment and the chances graphs, adjust target grade • calculate the department’s target grades from the addition of individual pupil’s targets
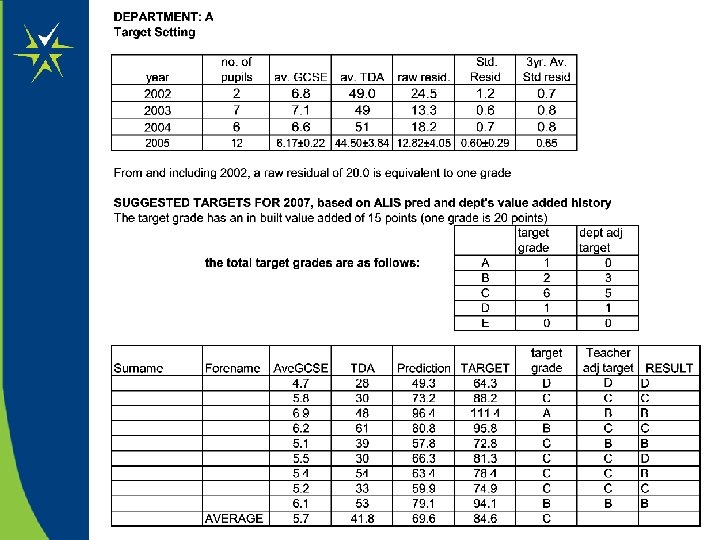
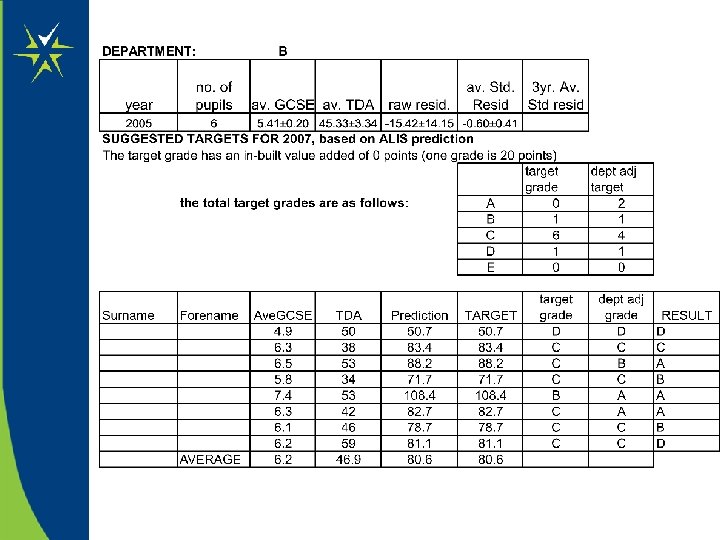

Discussion • Assess the merits and concerns you may have with this valueadded model of setting targets

Alis Value Added Feedback

Burning Question : What is my Value-Added Score ? Better Question : Is it Important ? Principle of Fair Analysis No 3 : Reflect Statistical Uncertainty
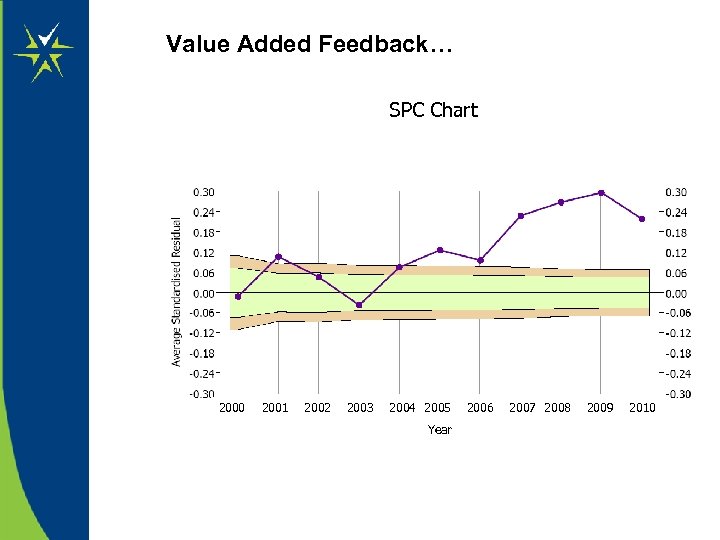
Value Added Feedback… SPC Chart 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Year 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
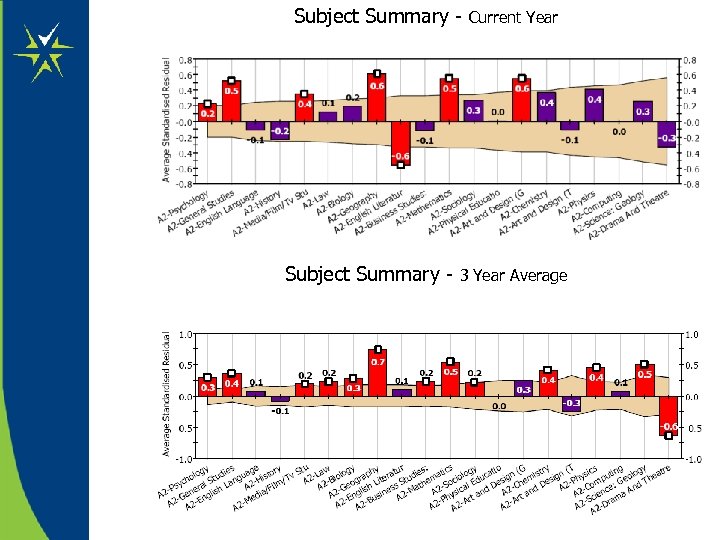
Subject Summary - Current Year 3 Year Average
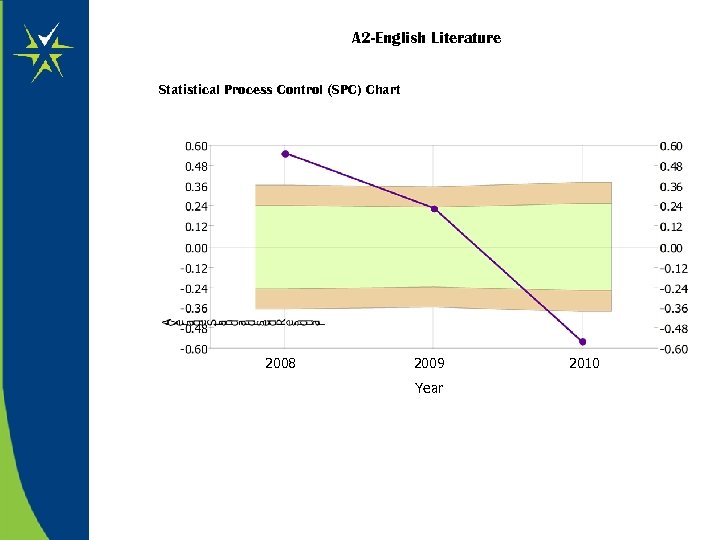
A 2 -English Literature Statistical Process Control (SPC) Chart 2008 2009 Year 2010
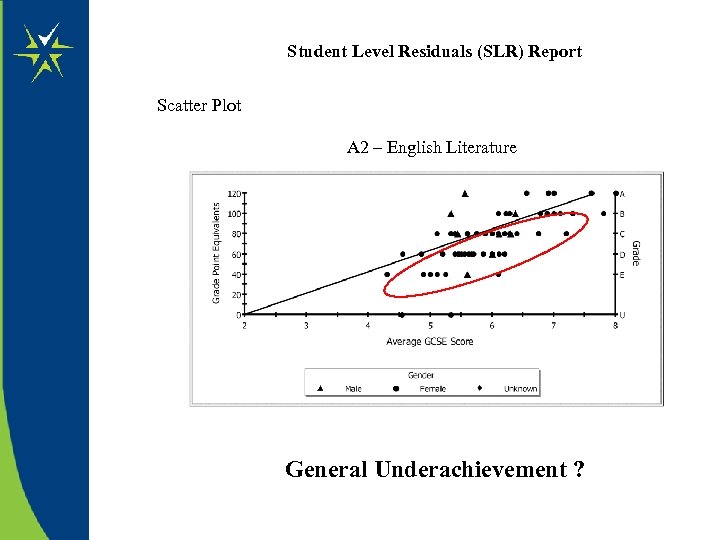
Student Level Residuals (SLR) Report Scatter Plot A 2 – English Literature General Underachievement ?
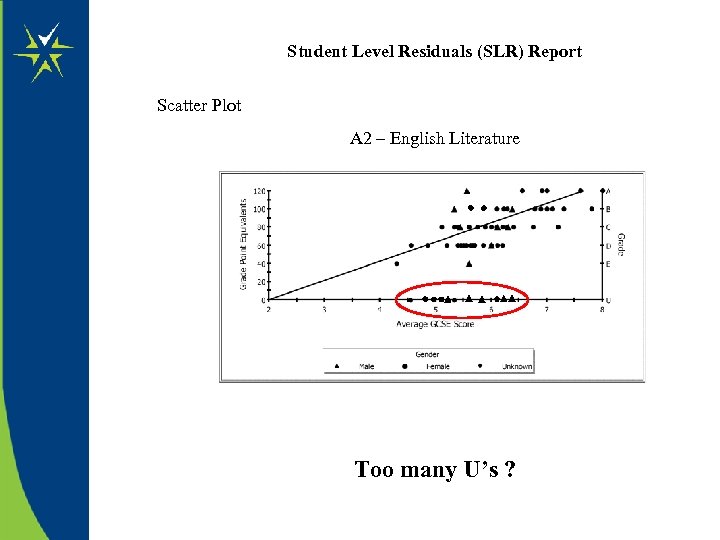
Student Level Residuals (SLR) Report Scatter Plot A 2 – English Literature Too many U’s ?
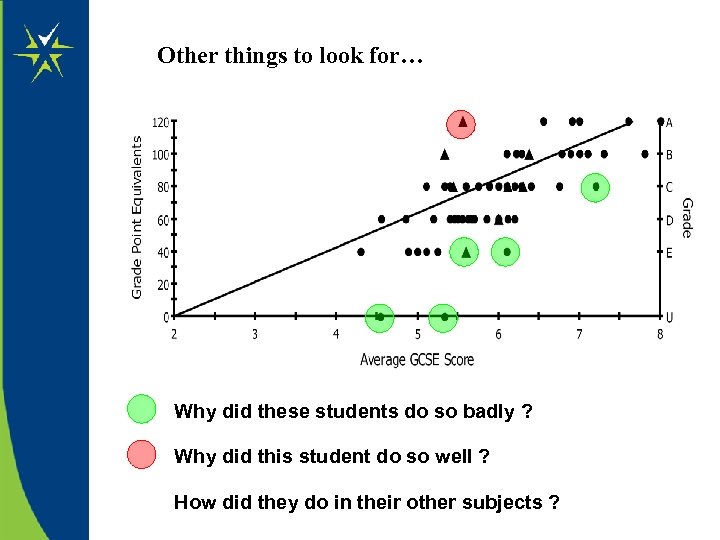
Other things to look for… Why did these students do so badly ? Why did this student do so well ? How did they do in their other subjects ?

Summary of Process • Examine Subject Summary • Determine ‘interesting’ (i. e. statistically significant) subjects • Look at 3 year average as well as single year • Look at trends in ‘Interesting Subjects’ • Examine student data – SLR Report, scatter graphs • Identify students over / under achieving (student list in SLR or Paris) • Any known issues ? • Don’t forget to look at over achieving subjects as well as under achieving • Phone / E-Mail ALIS when you need help understanding / interpreting the data / statistics !

Attitudinal Surveys

There is more to school / college than exams…. • • • Student attitudes Student Welfare & Safety Non-academic activities Support Social and personal development Self Evaluation (Every Child Matters) Full ALIS
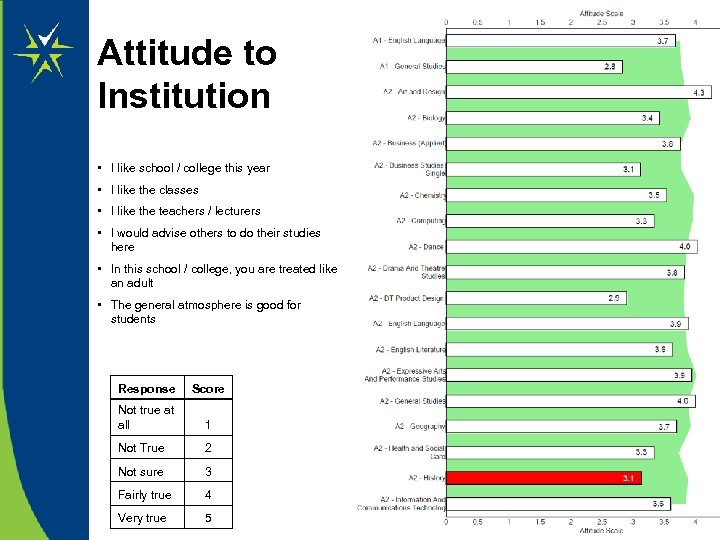
Attitude to Institution • I like school / college this year • I like the classes • I like the teachers / lecturers • I would advise others to do their studies here • In this school / college, you are treated like an adult • The general atmosphere is good for students Response Score Not true at all 1 Not True 2 Not sure 3 Fairly true 4 Very true 5

Attitude to Subject • I find it hard to get down to work in this subject • I find the work challenging • I like exams and tests in this subject • I look forward to lessons in this subject • I regret taking this subject • I think about this subject a lot, even in my spare time • I would advise others to take this subject here Response Score Not true of me at all 1 Not really true of me 2 Occaisionally true of me 3 This is fairly true of me 4 This is very true of
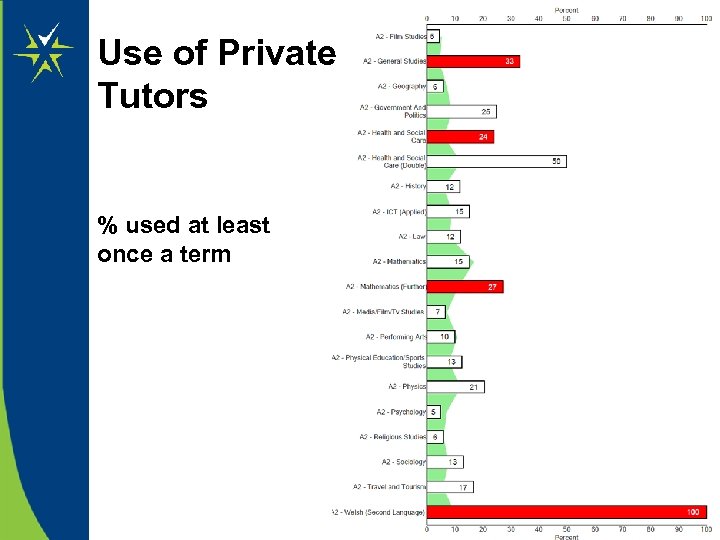
Use of Private Tutors % used at least once a term
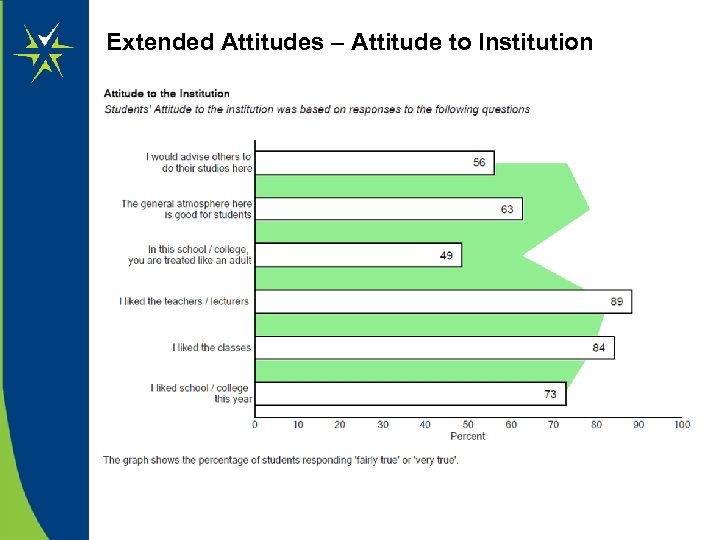
Extended Attitudes – Attitude to Institution
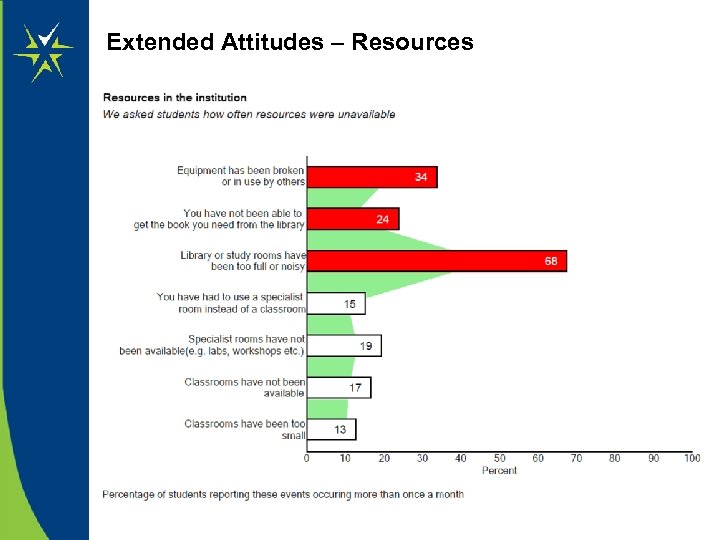
Extended Attitudes – Resources
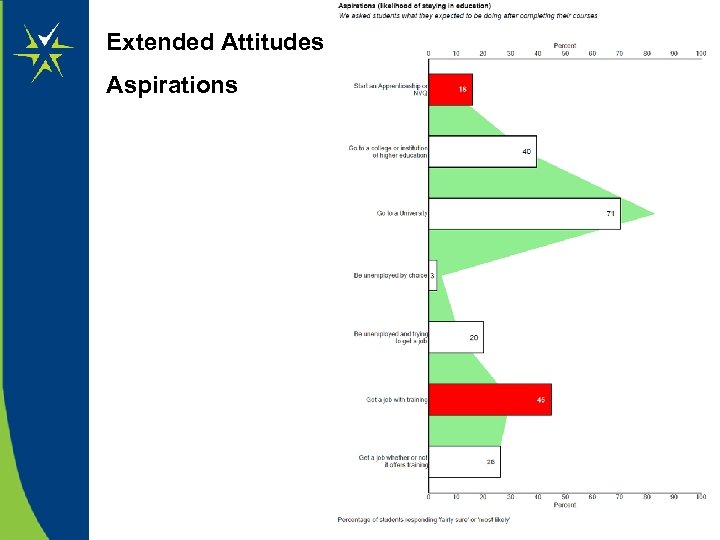
Extended Attitudes Aspirations
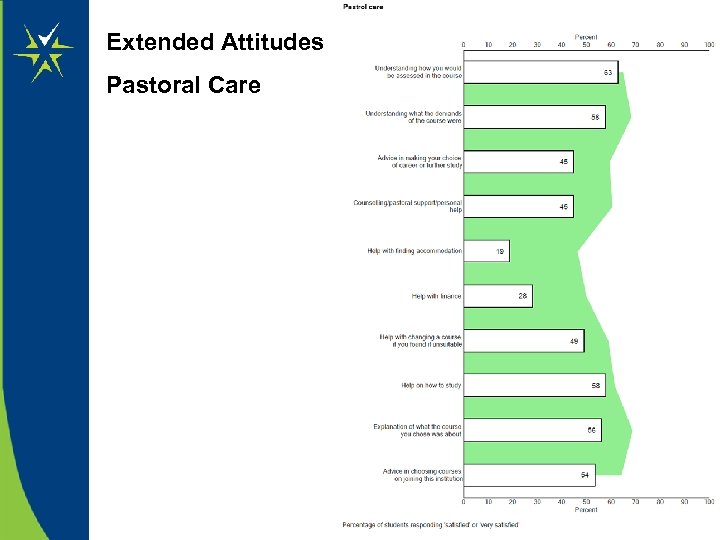
Extended Attitudes Pastoral Care
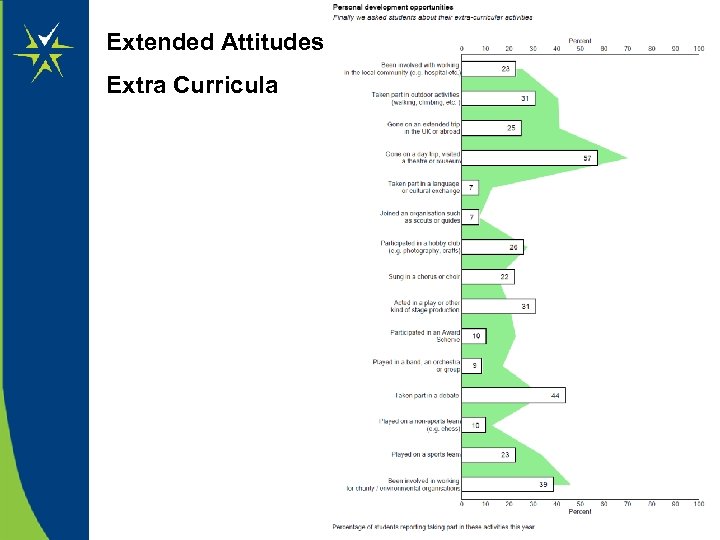
Extended Attitudes Extra Curricula
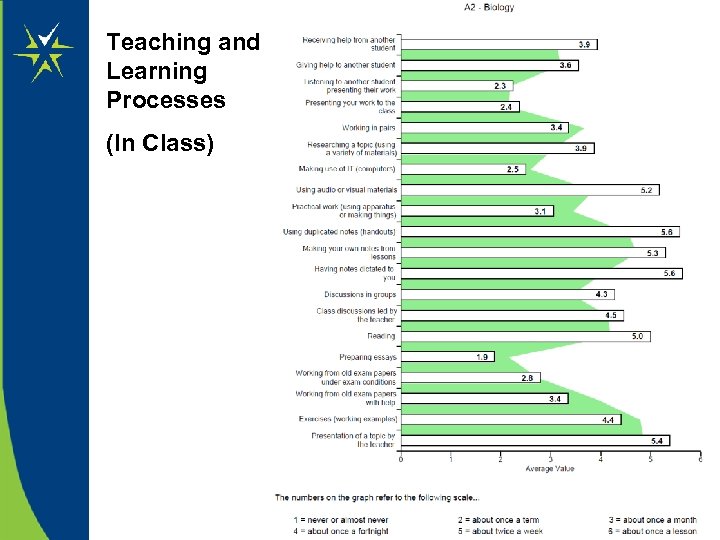
Teaching and Learning Processes (In Class)
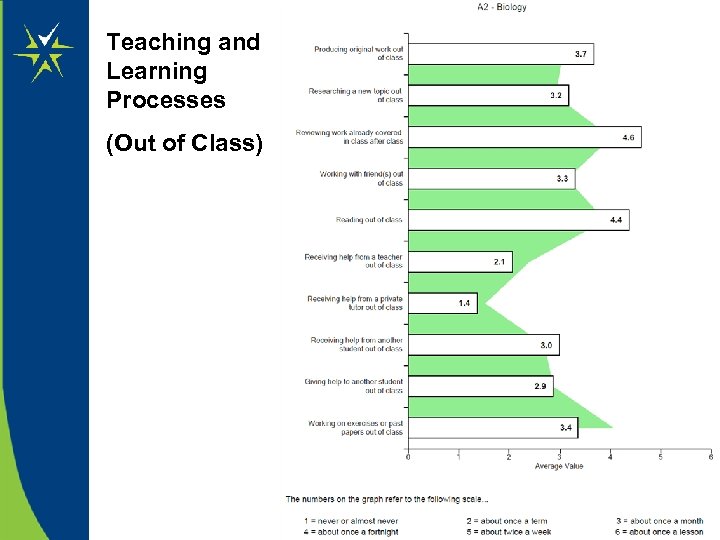
Teaching and Learning Processes (Out of Class)

SEF Survey • • • Extent of Bullying Extent of Racism Extent of Sectarianism Healthy Lifestyles How Well do Learner's Make a Positive Contribution to the Community How Well do Learner's Prepare for Their Future Economic Well Being Other Health and Safety Issues School's/College's Action on Bullying School's/College's Action on Racism School's/College's Action on Sectarianism School's/College's Action on Sexual Harassment Spiritual, Moral, Emotional and Cultural Development To try it out… www. intuproject. org/demos
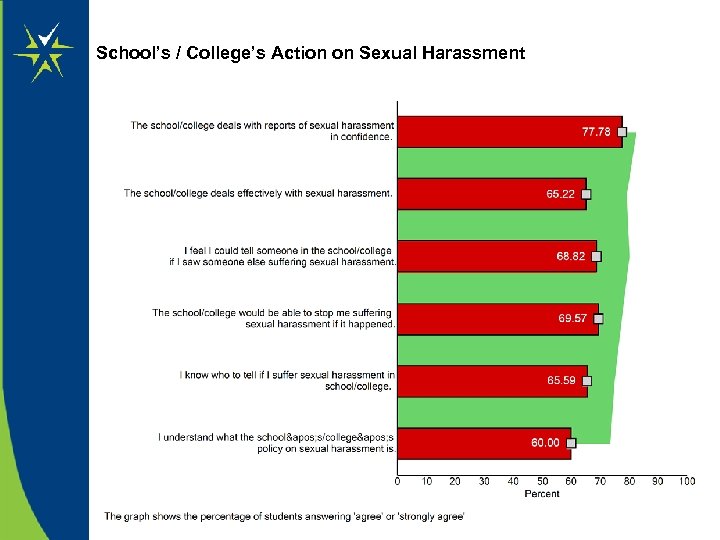
School’s / College’s Action on Sexual Harassment

Summary

Alis History : • Alis began in 2003 (started life called COMBSE) • Developed in partnership with schools by professional educational researchers • After spreading locally in the North East, Alis grew rapidly nationwide, largely through decisions by individual schools and colleges to subscribe • Alis is part of CEM which is affiliated to the School of Education at Durham University. • Research by CEM acknowledged by Durham in contributing significantly to the international research reputation of the School of Education. • Alis – developed in an educational context, by educational professionals for use by educational professionals.
Alis Coverage : • Approx 1700 school / colleges anually • > 50% UK A-levels anually • A/AS; IB; BTec National; OCR National; Cache DCE • Developing BTec First; GCSE Resit Alis Provides… Baseline Tests : • GCSE not always an appropriate or reliable measure of ability • GCSE Scores depend on KS 4 value-added performance • Alternative baseline test available • Provides predictions and value-added analysis independent of performance at prior key stage

Alis Provides… Predictions : • Predictions targeted at the individual subject (on average, students with similar GCSE scores get different grades in different A-level subjects) • Predictions from GCSE and Alis baseline test (how reliable is GCSE as a measure of ability ? Does the student have GCSE’s ? ) • Predictions at 50 th and 75 th percentile • Chances Data (what is the probability of achieving grades different to those predicted? ) • Standardised Scores from the baseline tests including section breakdown (IPR Report) – what are the student’s strengths & weaknesses ?

Alis Provides… Value Added : • All VA scores are specific to the student and each individual subject • Reports at school, subject and student level. • Current and historical trend data • Three sets of reports available: • • • Subject Level (Whole cohort) Syllabus Level (Whole Cohort) Subject Level (Specific to your school type) • VA available from GCSE and from the Alis baseline test • All data shown against appropriate confidence limits • Analysis available from beginning of September • Consortia / area / LA analysis available

Alis Provides… Attitudes : • In depth subject related attitudinal survey • In depth student welfare survey covering: • • • Extent of Bullying Extent of Racism Extent of Sectarianism Healthy Lifestyles How well do learners make a positive contribution to the community How well do learners prepare for their future economic well being School / College action on bullying School / College action on racism School / College action on sectarianism School / College action on sexual harassment Spiritual, moral, emotional and cultural development Can provide evidence to use in Self Evaluation To them out… www. intuproject. org/demos

Alis data can be used: • To support teaching and learning Ø Ø • School Band Profile Graphs IPR Data ‘Predictive’ data for target setting and monitoring Paris software for data analysis and on course monitoring To aid target setting and monitoring Ø Ø Use reliable predictive data (e. g. Alis data) Use professional judgment, including knowledge of the student Consider school/department expectations and ethos Give consideration to previous value added data where it is available (e. g. Alis data) • For Value Added analysis • For Self Evaluation Inset provision is available on any aspect of Alis to support any of the above issues.

Dr Robert Clark Alis Project Manager robert. clark@cem. dur. ac. uk 0191 33 44 193
7253f6f8ac8b33d2e4e9c52d4809c361.ppt