717b3001ea3772fee56e5070241a4fac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 100

Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools INTRODUCTION TO PROBLEM SOLVING Simulation Practice Wrap-up Date Location Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 1
BALANCING NAILS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up In your teams: n Can you balance one nail on the head of the nail hammered into the wood? n Can you balance two nails on the head of the nail hammered into the wood? (at the same time etc - there is no trick in this!) n Make an estimate in your team as to how many nails you can balance at once n Demonstrate it n Problem Solving Can you balance 30 nails? ? ? © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 2

INTRODUCTION TO PROBLEM SOLVING Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Objectives: n To understand the need for a problem solving methodology and problem solving tools n To understand the steps of the PROBLEM approach and the tools and disciplines that support these n To be able to apply the approach to real problems n To be able to select and apply the appropriate problem solving tool for the task in hand n To know how we can develop our problem solving skills beyond this training session n To have fun Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 3
INTRODUCTION TO PROBLEM SOLVING Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Agenda: n Introduction n Problem solving approach (review of pre-reading) n Problem solving tools Practice n Process simulation n Wrap-up Working through the stages of improvement Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 4

SYNDICATE BRIEF Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up In your syndicates, consider the following questions: n What are the criteria for choosing to use a disciplined Problem Solving approach – what are the characteristics of the situations where it would be beneficial? n What would be the benefits of applying PS approach in these situations? Why would we bother? You have 30 minutes for the syndicate Be prepared to feed back your answers Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 5

WHY DO IMPROVEMENTS FAIL? Introduction PROBLEM Think back to improvement initiatives that you have been involved in or subject to in the past. PS Tools Simulation What examples have you seen of shortcomings? Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 6

WHY DO IMPROVEMENTS FAIL? Some examples from our experience: Introduction PROBLEM n n PS Tools Simulation n Practice Wrap-up n n Problem Solving Different departments saw the problem differently People leap to solutions rather than identify the real issue - symptoms instead of root cause Solutions are adopted before their implications are fully considered Once the ‘fire’ has stopped blazing people think that the problem is solved The solution implementation isn’t properly managed Nobody notices that the solution isn’t actually working properly When the focus shifts elsewhere, things drift back to how they were © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 7

A DISCIPLINED APPROACH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Wouldn’t it be nice if we could be sure that all of that could never happen We could then trust all sorts of people to solve their own problems! Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 8
A Clear Process to Address Common Examples of Why Improvements Fail Deficiencies - Step by Step Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Ensure everybody has a shared problem n Different departments saw the Profile view of the problem or issue differently Focus in identifying the real rather than identify n People leap to solutions Root Cause cause before leaping to solutions the real issue Ensure a range of possible n Solutions are adopted before their Options solutions is considered implications are fully Balance quick fixes with longerblazing people n Once the ‘fire’ has stopped Balance term improvement plans is solved think that the problem Ensure that the implementation isn’t properly n The solution implementation Launch is properly managed as a project managed Ensure the solution that the solution isn’t n Nobody notices is evaluated Evaluate andactually working properly its effectiveness monitored Bolt the solution into the day-ton When the focus shifts elsewhere, things drift Maintain dayback to how they were management routines © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 9
PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Profile Collect Data Root Cause Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Problem Not “idea” or “solution” Solving Not avoiding or quick-fix Process Not ad-hoc or as the wind blows © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 10
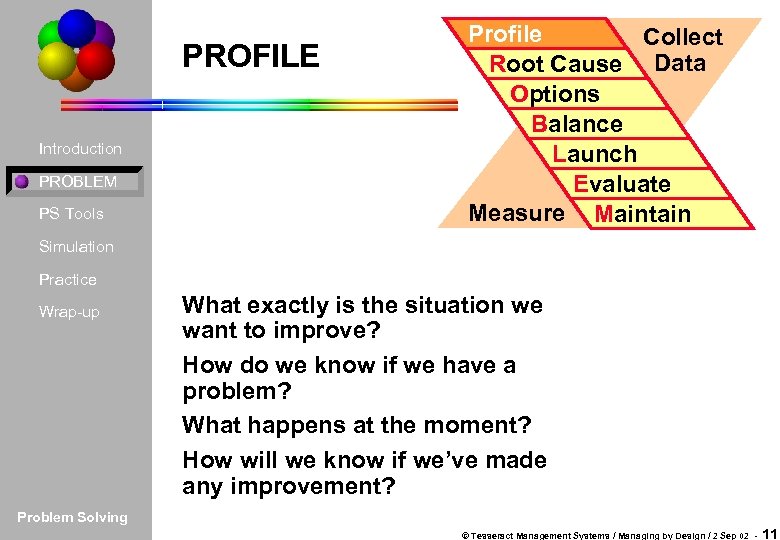
PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up What exactly is the situation we want to improve? How do we know if we have a problem? What happens at the moment? How will we know if we’ve made any improvement? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 11
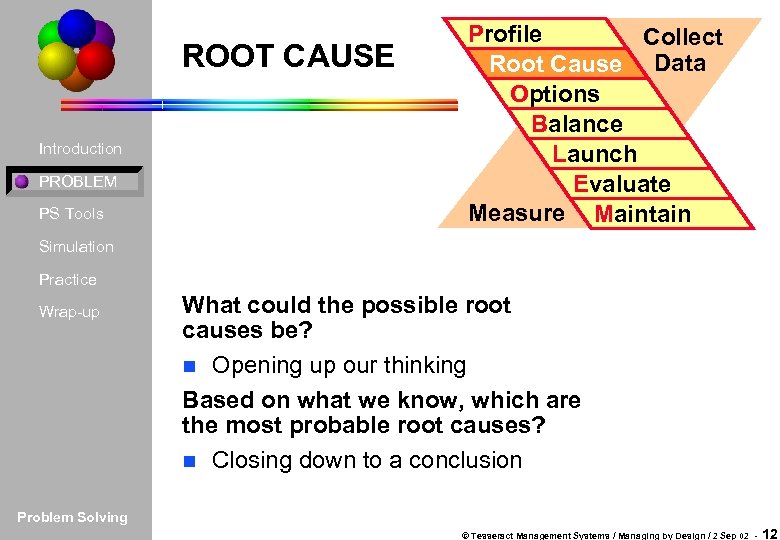
ROOT CAUSE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up What could the possible root causes be? n Opening up our thinking Based on what we know, which are the most probable root causes? n Closing down to a conclusion Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 12
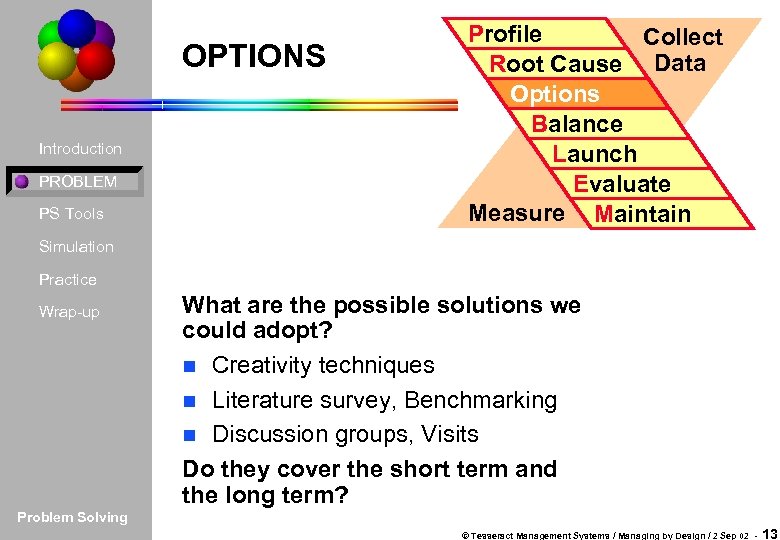
OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up What are the possible solutions we could adopt? n Creativity techniques n Literature survey, Benchmarking n Discussion groups, Visits Do they cover the short term and the long term? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 13
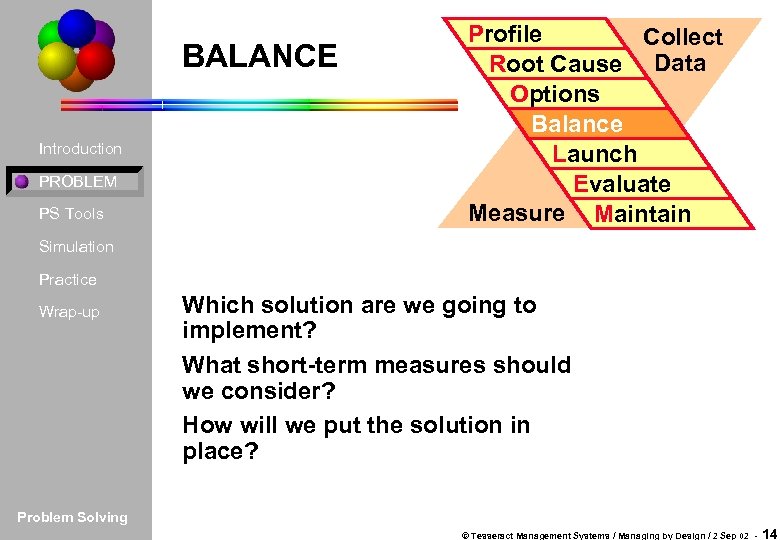
BALANCE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up Which solution are we going to implement? What short-term measures should we consider? How will we put the solution in place? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 14
LAUNCH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up How will we manage the implementation? How will we ensure the quality of the solution? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 15
EVALUATE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up How do we make sure we know we have improved the situation? How do we improve our own approach in these improvement activities? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 16
MAINTAIN Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up How do ensure a ‘permanent fix’? How do we make sure others know of our success? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 17
DATA/MEASURE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Simulation Practice Wrap-up And most important of all… Get the FACTS! In God we trust, all others bring data! Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 18
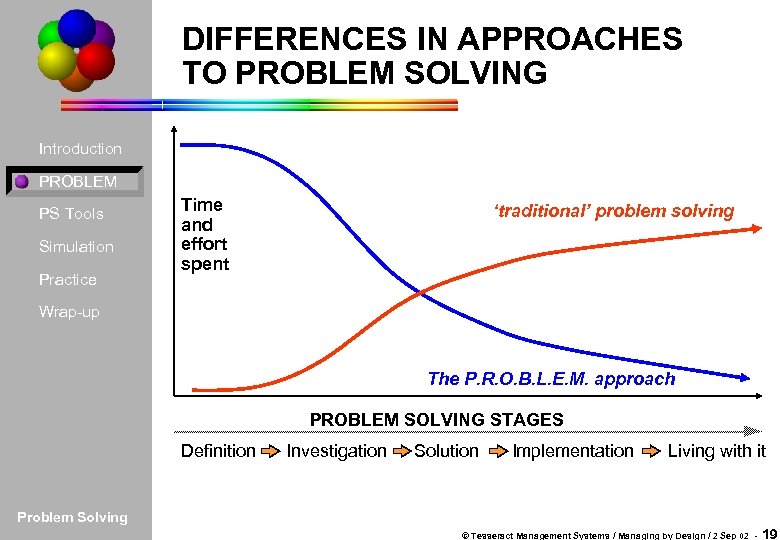
DIFFERENCES IN APPROACHES TO PROBLEM SOLVING Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Time and effort spent ‘traditional’ problem solving Wrap-up The P. R. O. B. L. E. M. approach PROBLEM SOLVING STAGES Definition Investigation Solution Implementation Living with it Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 19
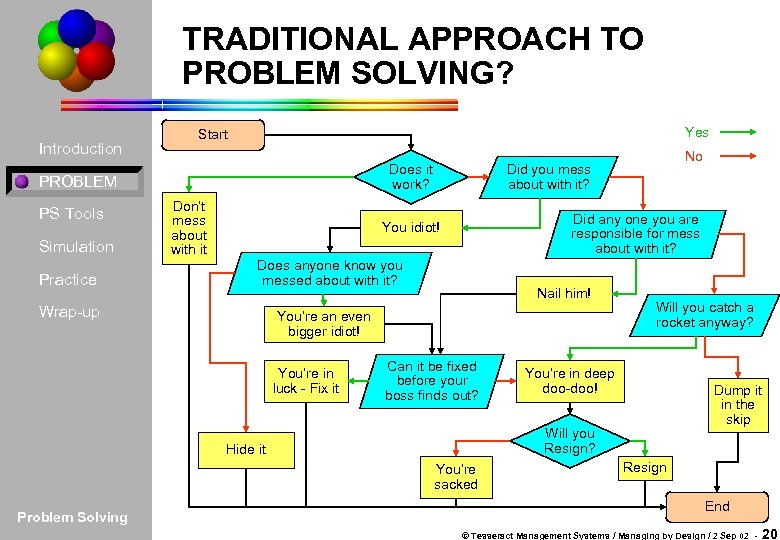
TRADITIONAL APPROACH TO PROBLEM SOLVING? Introduction Yes Start Does it work? PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Don’t mess about with it Did any one you are responsible for mess about with it? You idiot! Does anyone know you messed about with it? Wrap-up Nail him! You’re an even bigger idiot! You’re in luck - Fix it Can it be fixed before your boss finds out? Will you catch a rocket anyway? You’re in deep doo-doo! Dump it in the skip Will you Resign? Hide it You’re sacked Problem Solving No Did you mess about with it? Resign End © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 20
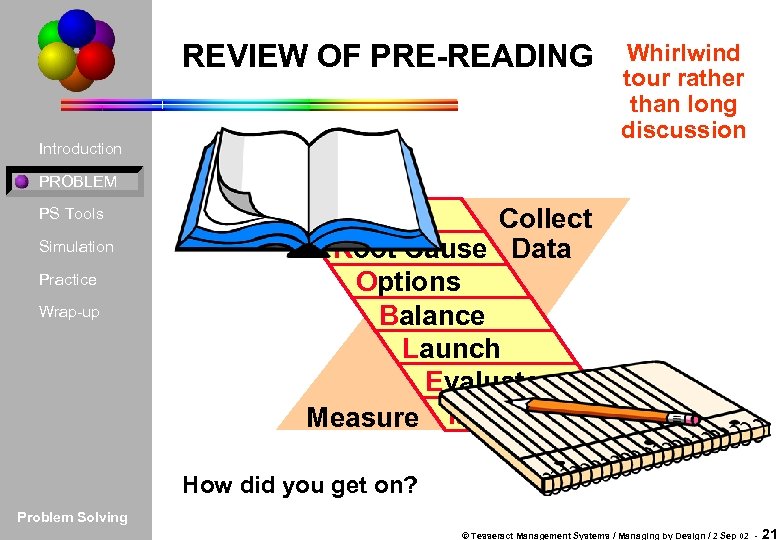
REVIEW OF PRE-READING Introduction Whirlwind tour rather than long discussion PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain How did you get on? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 21

PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 4 Exercise 5 Quote Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To arrive at a clear definition of a workable and owned problem, which everyone involved understands and is based on hard facts Output n A statement of the situation as it is now and of the situation as it will be when the problem has been resolved. A clearly identified problem owner and quantification of the impact of resolving the problem Process n Identify the detail of the problem area/process /people; current output; problem owner; flowcharting; measures; quantification of benefit. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 22
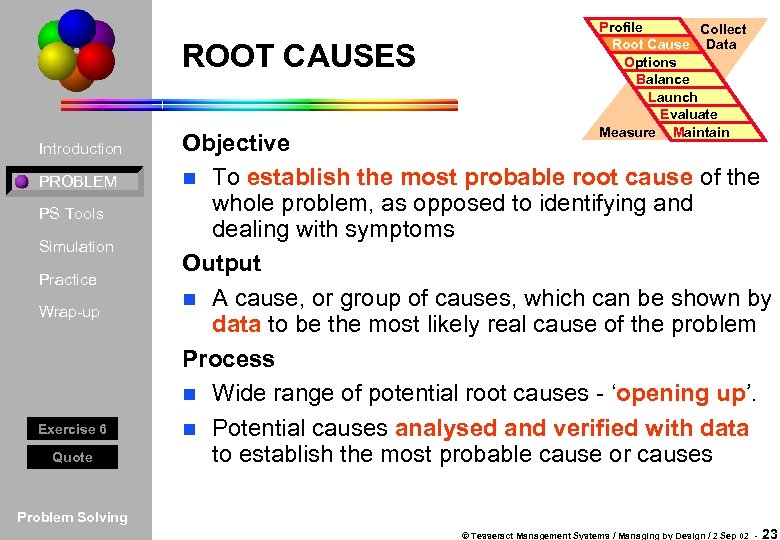
ROOT CAUSES Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 6 Quote Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To establish the most probable root cause of the whole problem, as opposed to identifying and dealing with symptoms Output n A cause, or group of causes, which can be shown by data to be the most likely real cause of the problem Process n Wide range of potential root causes - ‘opening up’. n Potential causes analysed and verified with data to establish the most probable cause or causes Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 23
OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 7 Exercise 8 Quote Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To identify a range of possible solutions which would eliminate the chosen root cause or causes, and which reflect an understanding of best practice. Output n A list of possible solutions to the problem. Process n Brainstorming sessions; use of creative design tools; literature survey; visiting companies with similar processes; canvassing opinions of others n Options as to how the solution will be implemented, or whethere needs to be a long-term ‘ideal’ solution in conjunction with a short-term ‘fix’. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 24
BALANCE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 9 Quote Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To develop a comprehensive, efficient and detailed solution to the problem being addressed. Output n A complete solution, possibly with an associated short-term fix, & associated implementation plans. Process n Gathering and using data to weigh up which solution to implement; interim short-term measures; means of implementation; forward plan (training; communication; pilot; changes to procedures/ manuals; purchased items); flowchart of ‘new’ process. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 25

LAUNCH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 10 Quote Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To ensure that the implementation of the chosen solution is adequately resourced, & runs to plan. Output n The solution implemented with minimum disruption. Process n Executing implementation plan, including any preparation and purchasing activity; clearly defined owners; plotting progress against activities and milestones; analysing deviations; correction of progress issues; piloting solution; ensuring quality of the solution; change management Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 26
EVALUATE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 11 Quote Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To establish whether or not the chosen solution has eliminated the root cause of the problem. To review and improve the teams performance. Output n Data against specific measures to identify change of process output. Learning points for the team, individuals and the problem solving process itself. Process n Planned schedule of regular measurement; presentation and display of data n Review meeting; recommendations to amend the process. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 27
MAINTAIN Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 12 Quote Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To ensure that the implemented solution becomes the new way of working and that the problem, as defined, remains permanently fixed Output n A new set of standard operating procedures and, where relevant, a training and/or communication plan. Process n Re-writing procedures, standards and guidelines; training and education; measurement re-established; targets set for improvement; n Communication; recognition. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 28

CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Exercise 2: Continuous Improvement How do you see Continuous Improvement as differing from Problem Solving? Simulation Practice Wrap-up Why do we want to generate “a continuous supply of problems”? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 29
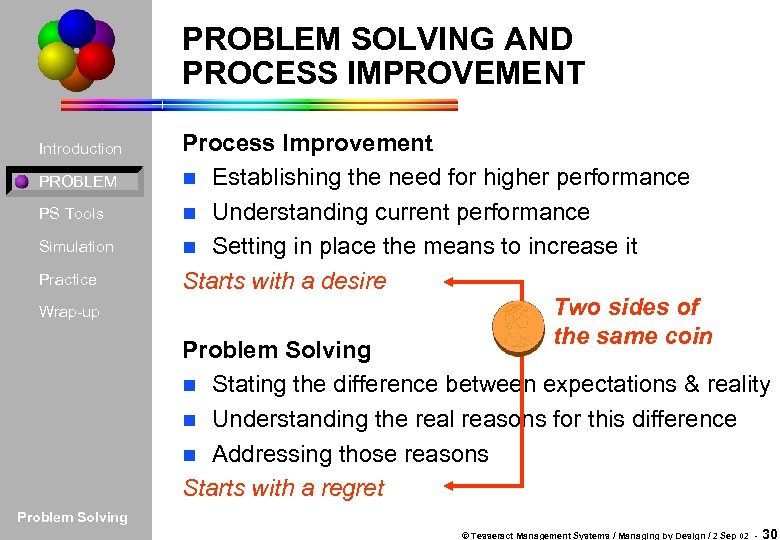
PROBLEM SOLVING AND PROCESS IMPROVEMENT Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Process Improvement n Establishing the need for higher performance n Understanding current performance n Setting in place the means to increase it Starts with a desire Two sides of the same coin Problem Solving n Stating the difference between expectations & reality n Understanding the real reasons for this difference n Addressing those reasons Starts with a regret Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 30
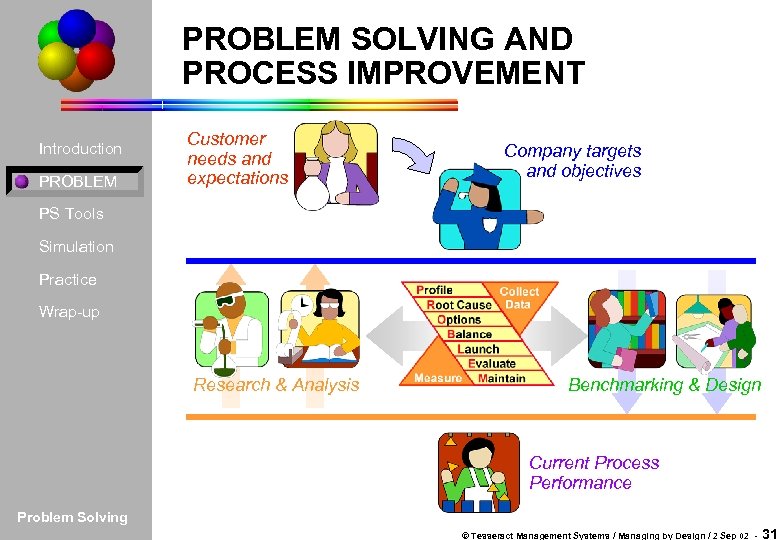
PROBLEM SOLVING AND PROCESS IMPROVEMENT Introduction PROBLEM Customer needs and expectations Company targets and objectives PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Research & Analysis Benchmarking & Design Current Process Performance Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 31
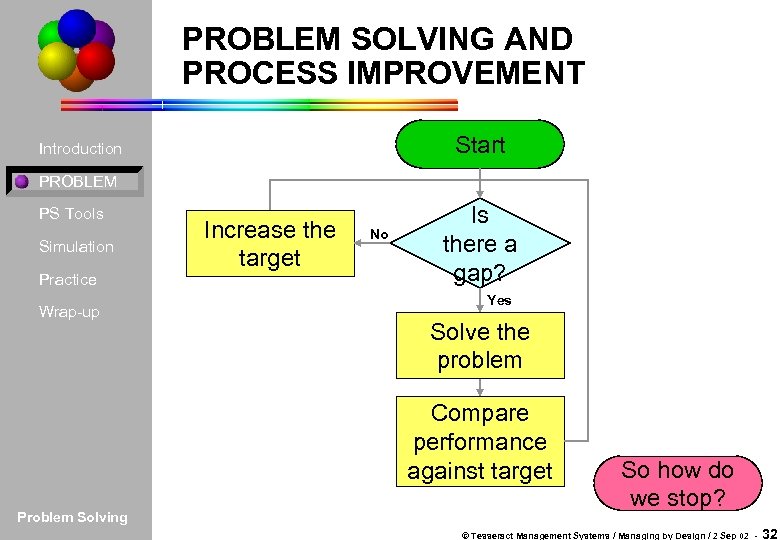
PROBLEM SOLVING AND PROCESS IMPROVEMENT Start Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Increase the target No Is there a gap? Yes Solve the problem Compare performance against target Problem Solving So how do we stop? © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 32
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up "Some men see things as they are and say why? I dream things that never were and say 'Why not? '” Robert F Kennedy, American Politician "All progress is based upon a universal innate desire on the part of every organism to live beyond its income. ” Samuel Butler, English Novelist Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 33
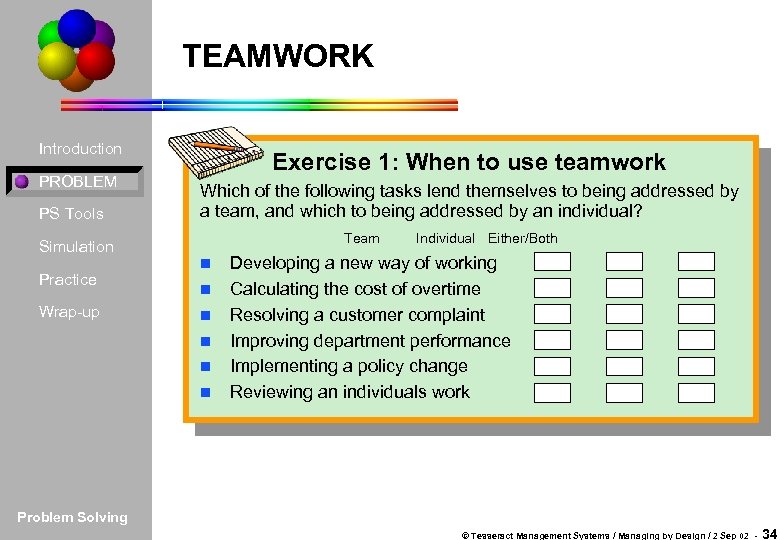
TEAMWORK Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Exercise 1: When to use teamwork Which of the following tasks lend themselves to being addressed by a team, and which to being addressed by an individual? Team Simulation Practice Wrap-up n n n Individual Either/Both Developing a new way of working Calculating the cost of overtime Resolving a customer complaint Improving department performance Implementing a policy change Reviewing an individuals work Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 34
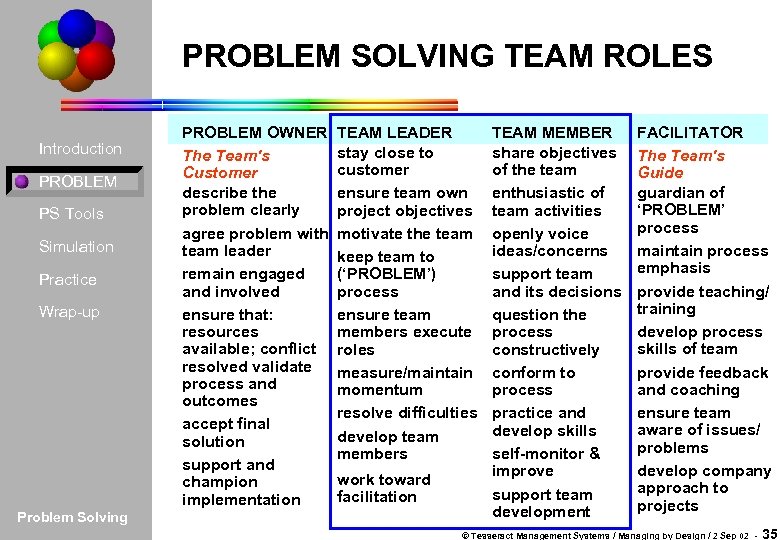
PROBLEM SOLVING TEAM ROLES Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving PROBLEM OWNER The Team's Customer describe the problem clearly agree problem with team leader remain engaged and involved ensure that: resources available; conflict resolved validate process and outcomes accept final solution support and champion implementation TEAM LEADER stay close to customer ensure team own project objectives motivate the team keep team to (‘PROBLEM’) process ensure team members execute roles measure/maintain momentum resolve difficulties develop team members work toward facilitation TEAM MEMBER share objectives of the team enthusiastic of team activities openly voice ideas/concerns support team and its decisions question the process constructively conform to process practice and develop skills self-monitor & improve support team development FACILITATOR The Team's Guide guardian of ‘PROBLEM’ process maintain process emphasis provide teaching/ training develop process skills of team provide feedback and coaching ensure team aware of issues/ problems develop company approach to projects © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 35
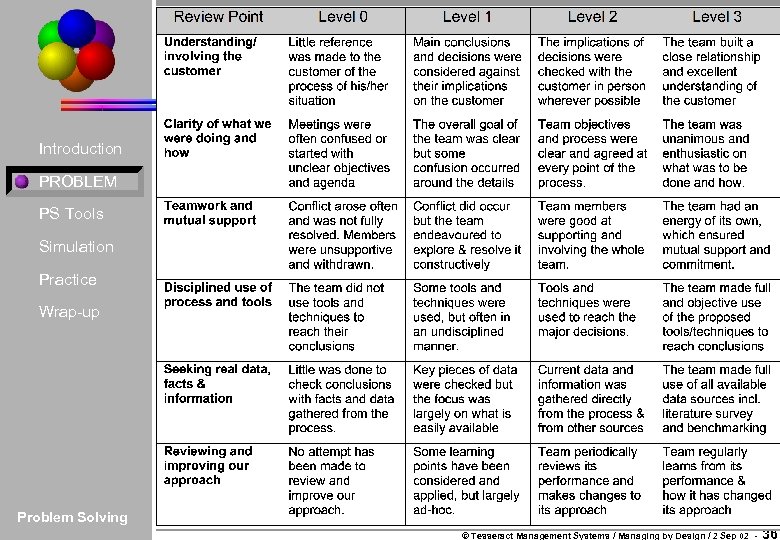
Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 36
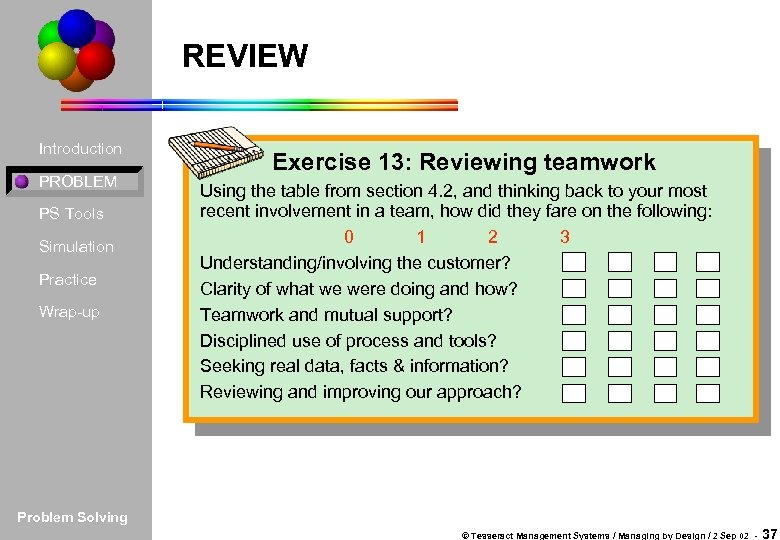
REVIEW Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 13: Reviewing teamwork Using the table from section 4. 2, and thinking back to your most recent involvement in a team, how did they fare on the following: 0 1 2 3 Understanding/involving the customer? Clarity of what we were doing and how? Teamwork and mutual support? Disciplined use of process and tools? Seeking real data, facts & information? Reviewing and improving our approach? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 37

TEAMWORK Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up "Revolutions need directions and exemplary leadership, but not heroes. Heroes subvert the fact that change comes about by lots of people taking action” Bill Harris, American Radical 1976 Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 38
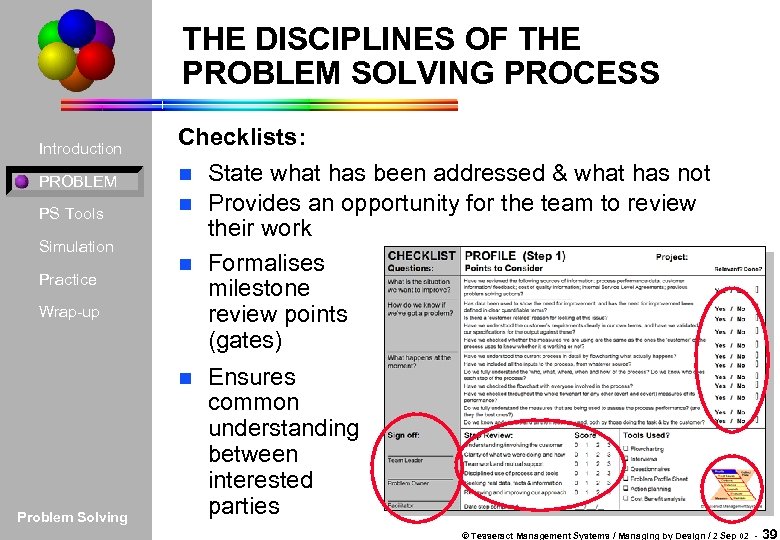
THE DISCIPLINES OF THE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Checklists: n State what has been addressed & what has not n Provides an opportunity for the team to review their work n Formalises milestone review points (gates) n Problem Solving Ensures common understanding between interested parties © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 39
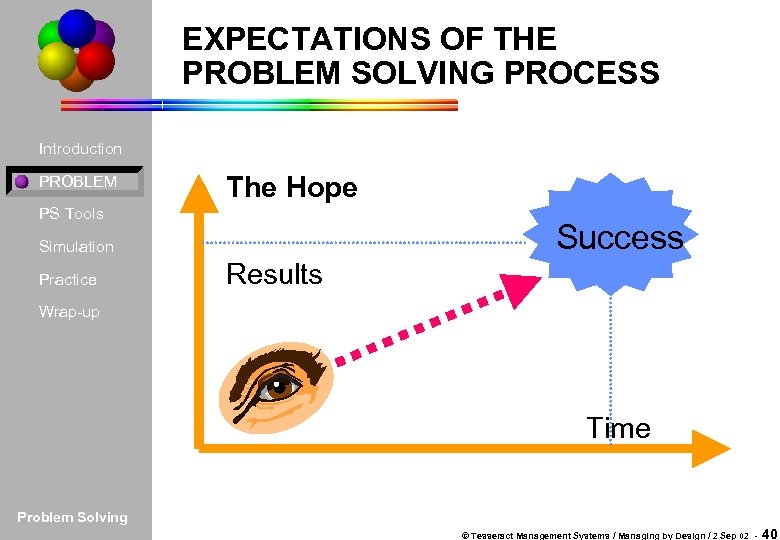
EXPECTATIONS OF THE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM The Hope PS Tools Success Simulation Practice Results Wrap-up Time Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 40
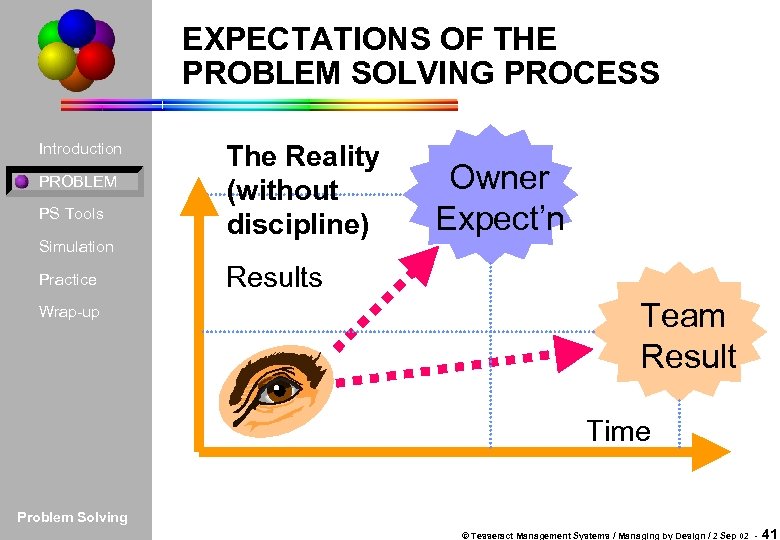
EXPECTATIONS OF THE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up The Reality (without discipline) Owner Expect’n Results Team Result Time Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 41
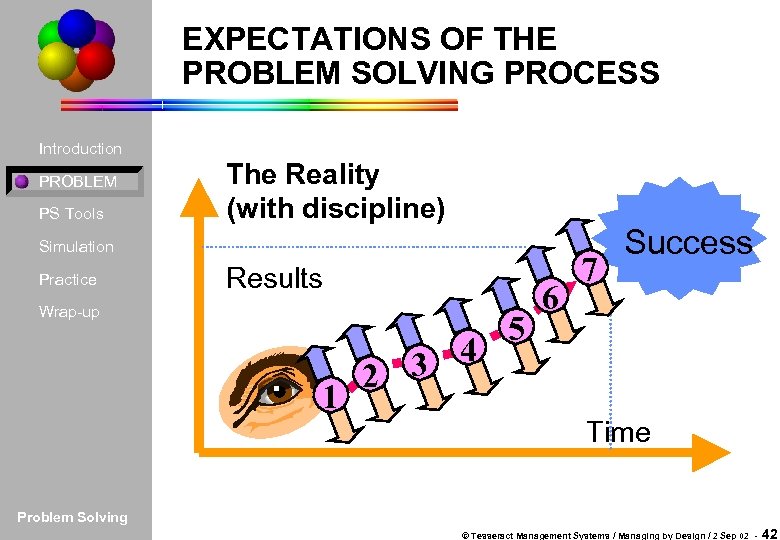
EXPECTATIONS OF THE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools The Reality (with discipline) Simulation Practice Results Wrap-up 1 3 4 2 5 6 7 Success Time Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 42
PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS Introduction People What of the standard problem solving tools can you name? Equipment Aged Children Fine Tuning Lodger PROBLEM UHF Cable Type of Complaint Dying picture tube Tally VHF Total Bad TV picture Interference (blender) PS Tools Station Product Defect Power Source Simulation Practice Wrap-up Service Buildings Distance Other Stations Geography Signal Building 2 Shipping Error 10 YES 40 20 Who is Affected? 30 TRAIN MONITOR PROGRESS Lower Insurance Lower Rent __________ MOVE Cost Time OFFICE 0 R. O. I. Vehicles Closer Aesthetics Customers B G A D H C E F 20 Alternatives More rooms Buy press 4 4 Processing 1 3 3 2 1 Contract out how many? Total Private work Do nothing how much? Effect 30 Protected Parking Cost of Moving Recondition Quantification EQUIPMENT MONEY Upkeep _____ Criteria The best problem solving tools are usually: n Simple n Flipchart based MAYBE NO Desired Situation 20 0 A B C D E F G H 10 Where Does it Occur? APPROVAL GET NEW INFORMATION END OF PROJECT Simple Description of the Problem When Does it Occur? 8 WRITE NEW PROCEDURE 30 Totals Current Situation 6 PRESENT TO MANAGING DIRECTOR Hills Billing Error 30 GROUP DECISION 14 1 2 Meetings More Space Work Disrupted 9 Wheel Chair Easier Access PEOPLE Wk No. 13 14 15 16 17 10 12 Buy Machine Suspected Cause 4 Install Machine 7 0 3 Test 6 Systems 5 10 15 20 25 30 Write Procedures Train Users 2 Activity 8 METHODS Why? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 43
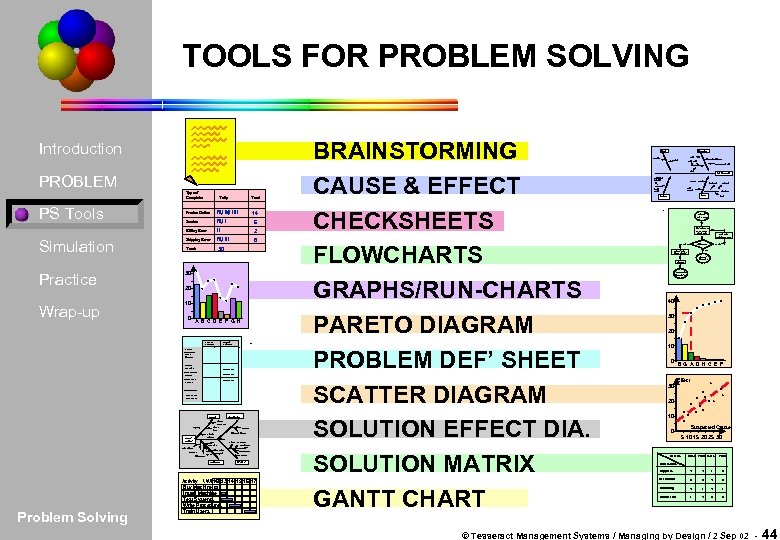
TOOLS FOR PROBLEM SOLVING Introduction PROBLEM Type of Complaint PS Tools Tally Total 14 Product Defect 6 Billing Error Simulation Service 2 Shipping Error 8 30 Totals Practice 30 Wrap-up 10 20 0 A B C D E F G H Current Situation Desired Situation Simple Description of the Problem Who is Affected? _____ When Does it Occur? _____ Where Does it Occur? _____ Quantification how much? how many? EQUIPMENT MONEY Lower Insurance Upkeep Lower Vehicles Rent Protected Parking Cost of Moving MOVE OFFICE Private work More rooms Meetings Processing More Space Work Disrupted METHODS Problem Solving Closer Aesthetics Customers Wheel Chair Easier Access PEOPLE Activity Wk 12 13 14 15 16 17 No. Buy Machine Install Machine Test Systems Write Procedures Train Users BRAINSTORMING CAUSE & EFFECT CHECKSHEETS FLOWCHARTS GRAPHS/RUN-CHARTS PARETO DIAGRAM PROBLEM DEF’ SHEET SCATTER DIAGRAM SOLUTION EFFECT DIA. SOLUTION MATRIX GANTT CHART People Children Equipment Aged Fine Tuning Lodger UHF Cable Dying picture tube VHF Interference (blender) Bad TV picture Station Buildings Other Stations Power Source Distance Geography Signal Building Hills GROUP DECISION PRESENT TO MANAGING DIRECTOR YES GET NEW INFORMATION APPROVAL MAYBE NO WRITE NEW PROCEDURE END OF PROJECT TRAIN MONITOR PROGRESS 40 30 20 10 0 B G A D H C E F Effect 30 20 10 0 Suspected Cause 5 10 15 20 25 30 Criteria Cost Time R. O. I. Total Alternatives Buy press 4 4 1 9 Recondition 3 3 2 8 Do nothing 2 1 4 7 Contract out 1 2 3 6 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 44
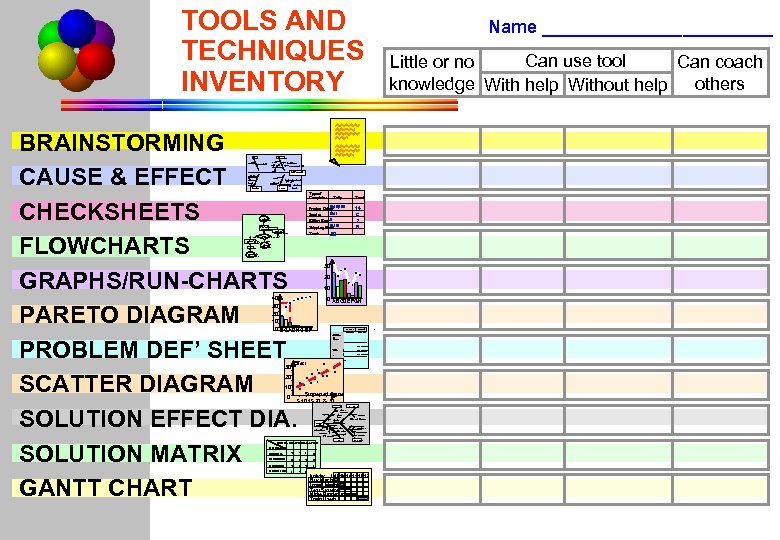
TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES INVENTORY BRAINSTORMING Introduction CAUSE & EFFECT PROBLEM PS Tools CHECKSHEETS Simulation FLOWCHARTS Practice GRAPHS/RUN-CHARTS Wrap-up PARETO DIAGRAM PROBLEM DEF’ SHEET SCATTER DIAGRAM SOLUTION EFFECT DIA. SOLUTION MATRIX GANTT CHART People Children Fine Tuning UHF Cable Dying picture tube VHF Bad TV picture Station Buildings Distance Other Stations Power Source Geography Signal Building Hills Type of Complaint TRAIN Tally Total 14 6 2 8 Product Defect Service GROUP DECISION PRESENT TO MANAGING DIRECTOR YES Can use tool Little or no Can coach knowledge With help Without help others Equipment Aged Lodger Interference (blender) WRITE NEW PROCEDURE Name ____________ Billing Error Shipping Error GET NEW INFORMATION 30 Totals APPROVAL MAYBE NO END OF PROJECT MONITOR PROGRESS 30 20 10 40 0 ABCDEFGH 30 20 10 0 BGAD HC E F Simp Effect 30 Current Situation Descripti le of on Proble the m Who Affecte is d? When Occuit Does r? Where it Does Occur ? Quantification Desired Situation __________ how much? many? 20 10 Suspected Cause 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 MONEY Upkeep MOVE OFFICE Private work More rooms Meetings Work More Disrupted Space Processing Criteria Cost Time R. O. I. Total EQUIPMENT Lower Insurance Lower Vehicles Rent Protected Parking Cost of Moving METHODS Closer. Aesthetics Customers Wheel Chair Easier Access PEOPLE Alternatives Buy press 4 4 1 9 Recondition 3 3 2 8 Do nothing 2 1 4 Contract out 1 2 3 7 6 Activity Wk No. 121314151617 Buy Machine Install Machine Test Systems Write Procedures Train Users Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 45
BRAINSTORMING Introduction n PROBLEM PS Tools n Simulation Practice n Wrap-up n n Problem Solving Rapid listing of ideas on a flipchart Done in groups around a theme eg “How can we solve. . . ” Ideas spring out of other people’s suggestions (crossfertilizing) All suggestions are listed, and evaluation/discussion discouraged so as not to suppress creativity. Called “brainwriting” if done individually © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 46
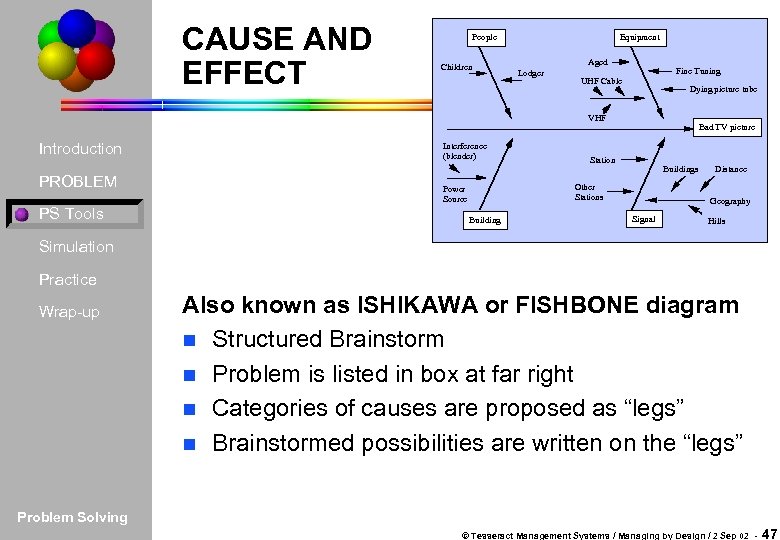
CAUSE AND EFFECT People Children Equipment Aged Lodger Fine Tuning UHF Cable Dying picture tube VHF Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Interference (blender) Bad TV picture Station Buildings Other Stations Power Source Building Distance Geography Signal Hills Simulation Practice Wrap-up Also known as ISHIKAWA or FISHBONE diagram n Structured Brainstorm n Problem is listed in box at far right n Categories of causes are proposed as “legs” n Brainstormed possibilities are written on the “legs” Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 47
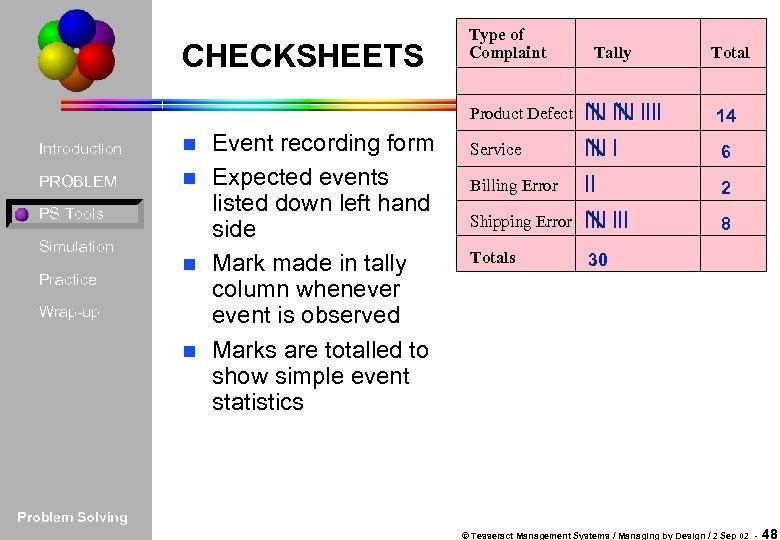
CHECKSHEETS Type of Complaint Tally Total Product Defect Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Event recording form n Expected events listed down left hand side n Mark made in tally column whenever event is observed n Marks are totalled to show simple event statistics n 14 Service 6 Billing Error 2 Shipping Error 8 Totals 30 Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 48
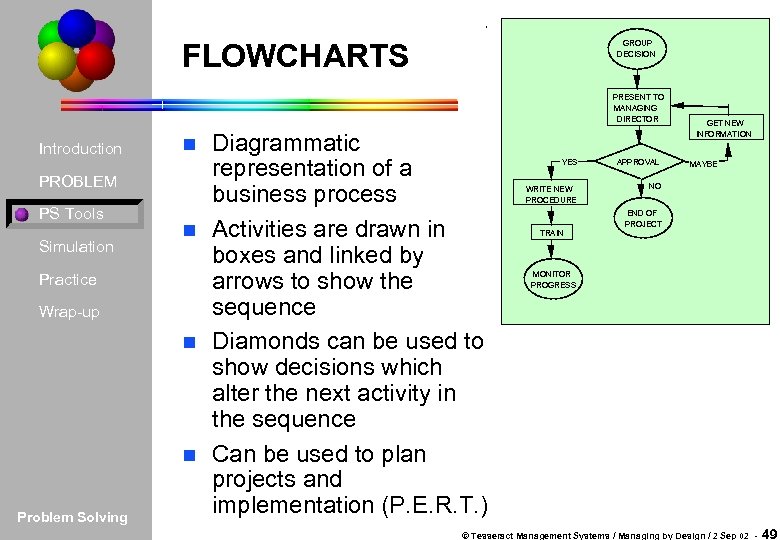
FLOWCHARTS GROUP DECISION PRESENT TO MANAGING DIRECTOR Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Diagrammatic representation of a business process n Activities are drawn in boxes and linked by arrows to show the sequence n Diamonds can be used to show decisions which alter the next activity in the sequence n Can be used to plan projects and implementation (P. E. R. T. ) n YES APPROVAL WRITE NEW PROCEDURE GET NEW INFORMATION NO MAYBE END OF PROJECT TRAIN MONITOR PROGRESS © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 49
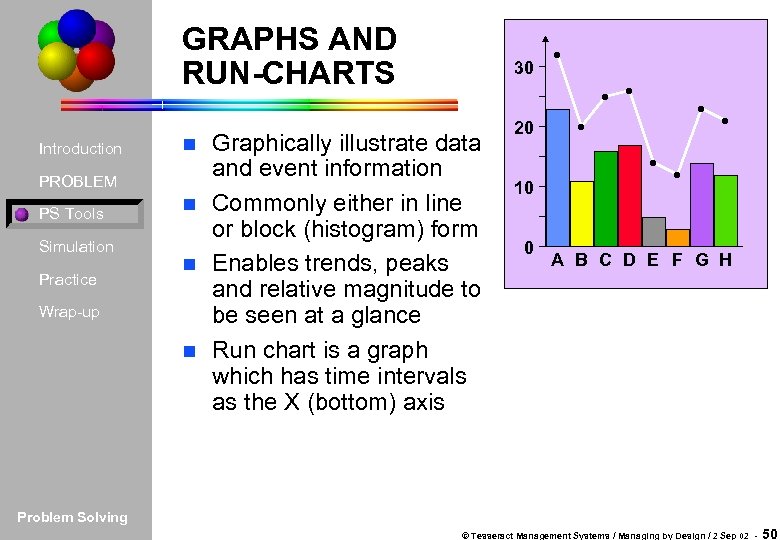
GRAPHS AND RUN-CHARTS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up 30 Graphically illustrate data and event information n Commonly either in line or block (histogram) form n Enables trends, peaks and relative magnitude to be seen at a glance n Run chart is a graph which has time intervals as the X (bottom) axis n 20 10 0 A B C D E F G H Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 50
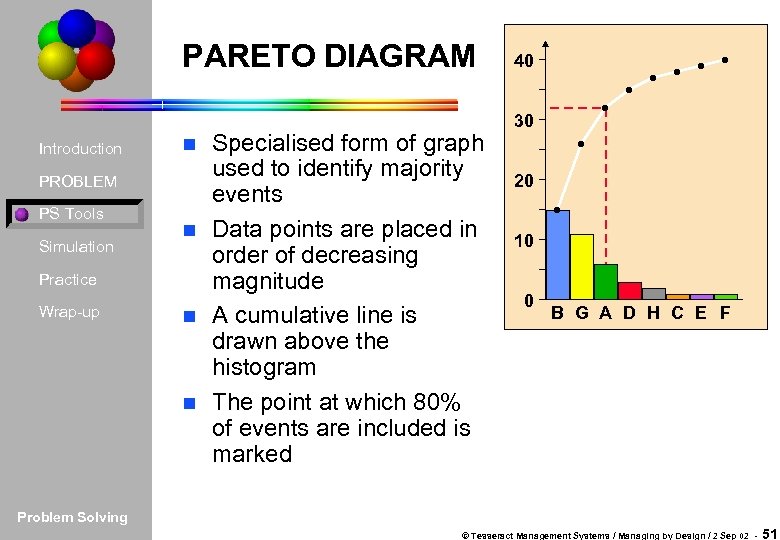
PARETO DIAGRAM Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Specialised form of graph used to identify majority events n Data points are placed in order of decreasing magnitude n A cumulative line is drawn above the histogram n The point at which 80% of events are included is marked 40 30 n 20 10 0 B G A D H C E F Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 51
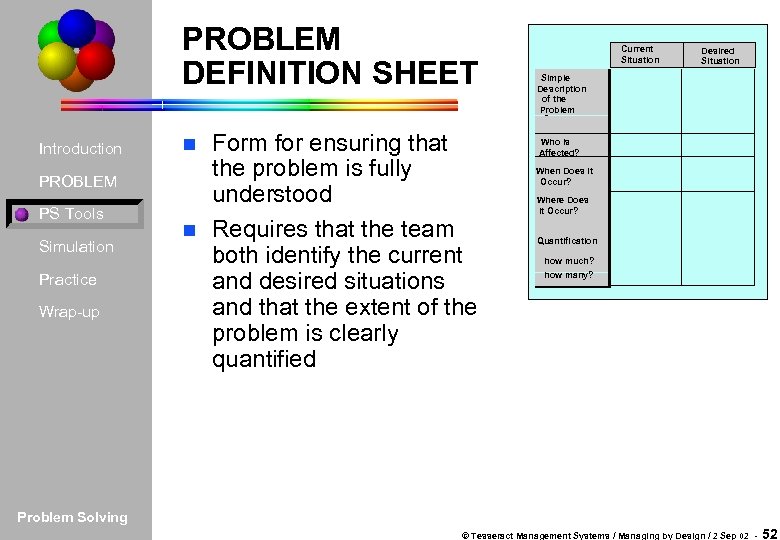
PROBLEM DEFINITION SHEET Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Form for ensuring that the problem is fully understood n Requires that the team both identify the current and desired situations and that the extent of the problem is clearly quantified n Current Situation Desired Situation Simple Description of the Problem Who is Affected? When Does it Occur? Where Does it Occur? Quantification how much? how many? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 52
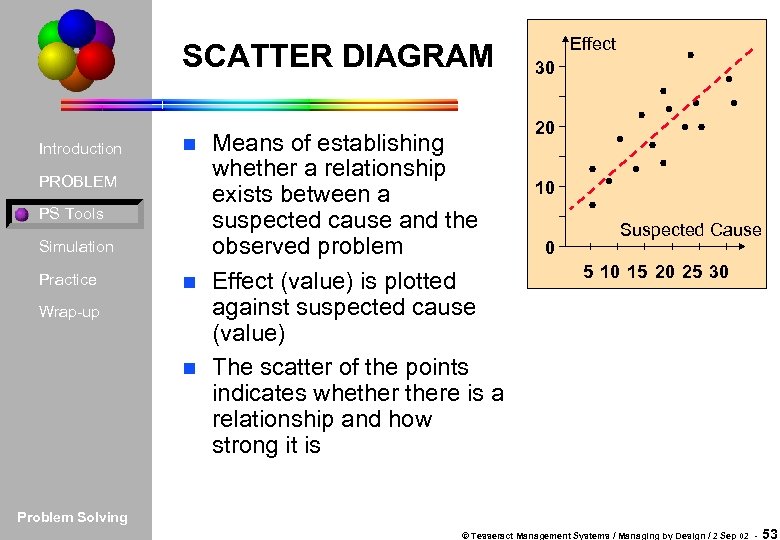
SCATTER DIAGRAM Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Means of establishing whether a relationship exists between a suspected cause and the observed problem n Effect (value) is plotted against suspected cause (value) n The scatter of the points indicates whethere is a relationship and how strong it is n Effect 30 20 10 0 Suspected Cause 5 10 15 20 25 30 Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 53
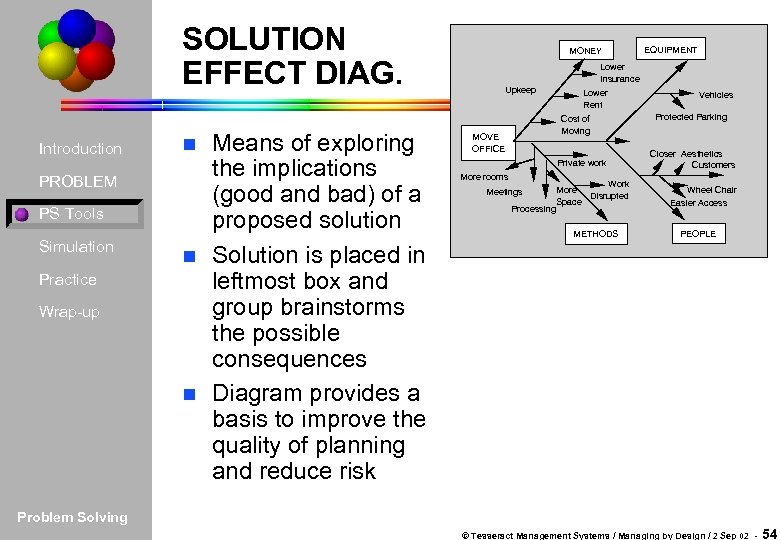
SOLUTION EFFECT DIAG. Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Means of exploring the implications (good and bad) of a proposed solution n Solution is placed in leftmost box and group brainstorms the possible consequences n Diagram provides a basis to improve the quality of planning and reduce risk n MONEY EQUIPMENT Lower Insurance Upkeep Lower Rent Cost of Moving MOVE OFFICE Private work More rooms Meetings Processing Work More Disrupted Space METHODS Vehicles Protected Parking Closer Aesthetics Customers Wheel Chair Easier Access PEOPLE Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 54
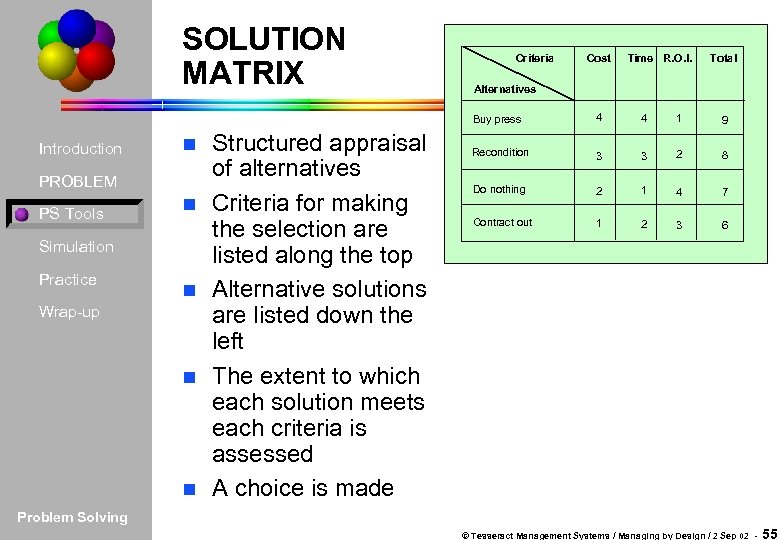
SOLUTION MATRIX Criteria Cost Time R. O. I. Total Alternatives Buy press Introduction n PROBLEM PS Tools n Simulation Practice n Wrap-up n n Structured appraisal of alternatives Criteria for making the selection are listed along the top Alternative solutions are listed down the left The extent to which each solution meets each criteria is assessed A choice is made 4 4 1 9 Recondition 3 3 2 8 Do nothing 2 1 4 7 Contract out 1 2 3 6 Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 55
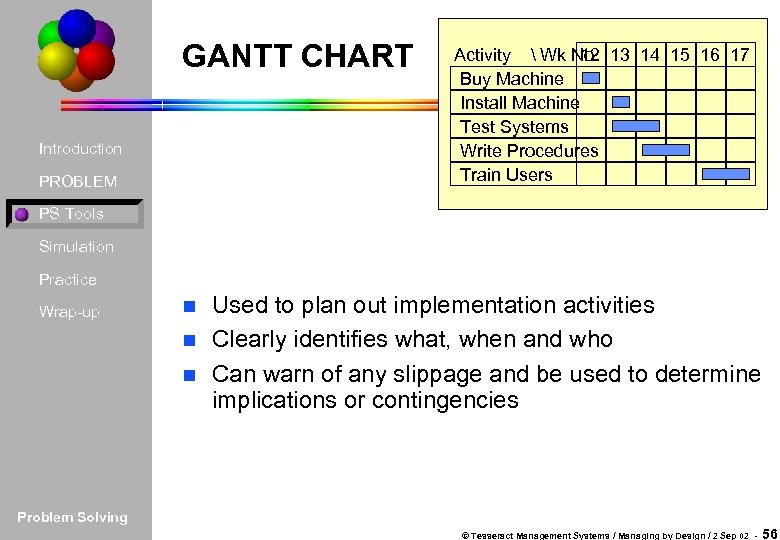
GANTT CHART Introduction PROBLEM Activity Wk No. 13 14 15 16 17 12 Buy Machine Install Machine Test Systems Write Procedures Train Users PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Used to plan out implementation activities n Clearly identifies what, when and who n Can warn of any slippage and be used to determine implications or contingencies n Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 56
WHERE TO USE THE PS TOOLS Introduction People Equipment Aged Children Lodger Fine Tuning UHF Cable Dying picture tube VHF PROBLEM Interference (blender) Bad TV picture Station Buildings Distance Other Stations Power Source Type of Building Complaint Geography Tally Total Hills Signal 14 6 2 8 Product Defect PS Tools Service Billing Error 30 Totals APPROVAL WRITE NEW PROCEDURE TRAIN GET NEW INFORMATION MAYBE NO END OF PROJECT MONITOR PROGRESS 30 Wrap-up PRESENT TO MANAGING DIRECTOR YES Simulation Practice GROUP DECISION Shipping Error 20 10 40 0 ABCD E F GH 30 20 10 Current Situation Simple Description of the Problem Desired Situation 0 BGADHC E F Who is Affected? _____ When Does it Occur? _____ Where Does it Occur? _____ Quantification how much? how many? 30 Effect 20 10 0 Upkeep MOVE OFFICE Suspected Cause MONEY EQUIPMENT 51015202530 Lower Insurance Lower Vehicles Rent Protected Parking Cost of Moving Private work Closer. Aesthetics Customers More rooms Meetings Work More Disrupted Space Processing Wheel Chair Easier Access Criteria Cost Time. R. O. I. Total METHODS PEOPLE Alternatives Buy press 4 4 1 9 Recondition 3 3 2 8 Do nothing 2 1 4 7 Contract out 1 2 3 6 Activity Wk No. 2 13 14 15 16 17 1 Buy Machine Install Machine Test Systems Write Procedures Train Users Problem Solving 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BRAINSTORMING CAUSE AND EFFECT CHECKSHEETS FLOWCHARTS GRAPHS/RUNCHARTS PARETO DIAGRAM PROBLEM DEF’ SHEET SCATTER DIAGRAM SOLUTION EFFECT DIA. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 57
INTRODUCING TESSECART plc World famous producers of racing chariots Introduction PROBLEM The Tessecart Mk 1 Prizewinning Chariot! PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 58
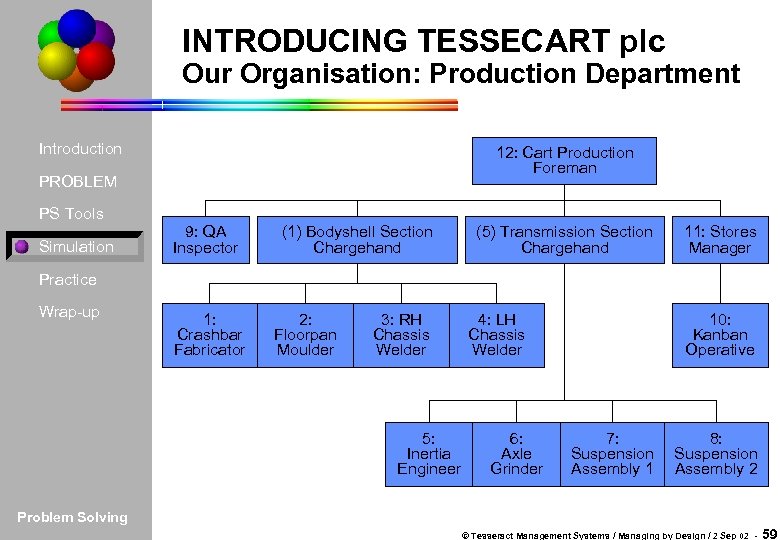
INTRODUCING TESSECART plc Our Organisation: Production Department Introduction 12: Cart Production Foreman PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation 9: QA Inspector (1) Bodyshell Section Chargehand (5) Transmission Section Chargehand 11: Stores Manager Practice Wrap-up 1: Crashbar Fabricator 2: Floorpan Moulder 3: RH Chassis Welder 5: Inertia Engineer 4: LH Chassis Welder 6: Axle Grinder 10: Kanban Operative 7: Suspension Assembly 1 8: Suspension Assembly 2 Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 59
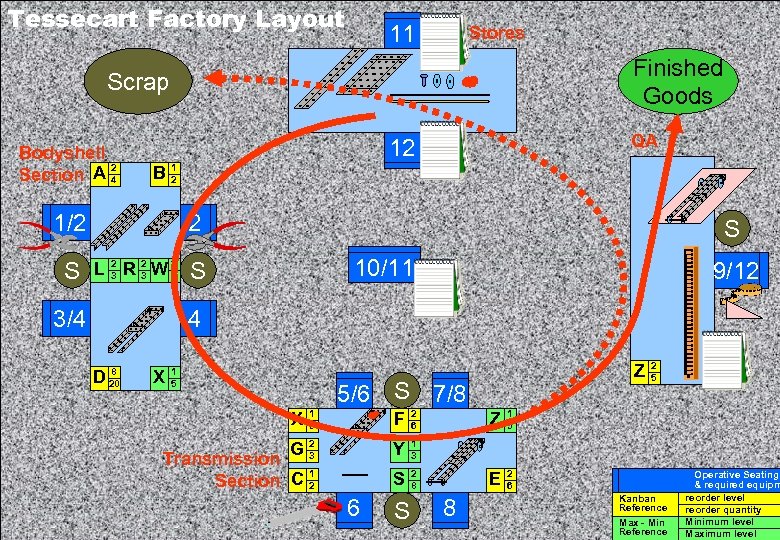
Tessecart Factory Layout 11 Stores Finished Goods Scrap QA 12 Introduction Bodyshell 2 Section A 4 PROBLEM B 1 2 PS Tools 1/2 2 S Simulation 10/11 S L R 3 W 3 S Practice 3 2 2 2 Wrap-up 3/4 8 D 20 4 X 1 5 Z 5/6 S 7/8 1 5 F 2 6 G 2 3 Y 1 2 S 2 8 Transmission Section C 6 S Z 8 1 5 E 2 6 2 5 1 3 X Problem Solving 9/12 Operative Seating & required equipm reorder level Kanban Reference reorder quantity Minimum level Max - Min Reference Maximum level © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 60
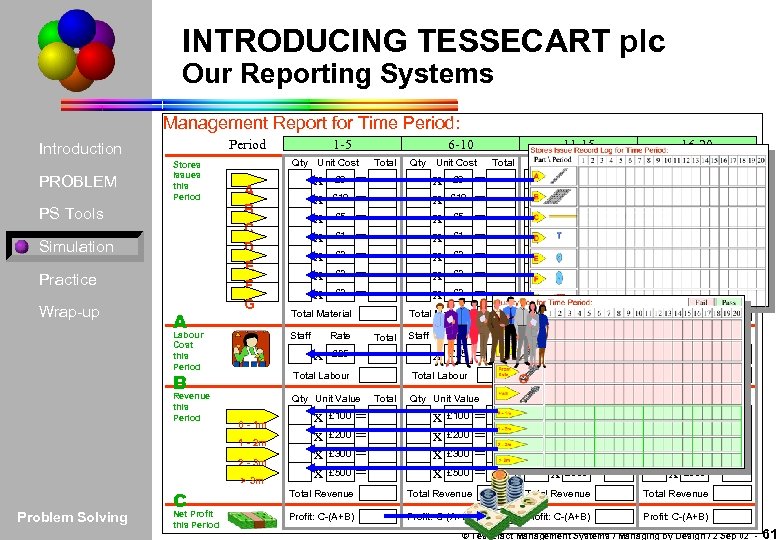
INTRODUCING TESSECART plc Our Reporting Systems Management Report for Time Period: PROBLEM Stores Issues this Period PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up 1 -5 Period Introduction A 6 -10 Qty Unit Cost A B C D E F G x x x x £ 6 £ 10 £ 5 £ 1 £ 2 £ 3 Revenue this Period Qty Unit Value 0 - 1 m 2 - 3 m > 3 m Net Profit this Period Total = x x = £ 200 = £ 300 = £ 500 = £ 100 Staff £ 10 £ 5 £ 1 £ 2 £ 3 £ 25 x x x x Total = Qty Unit Value x x = £ 200 = £ 300 = £ 500 = £ 100 £ 6 £ 10 £ 5 £ 1 £ 2 £ 3 16 -20 Total Staff x x x x £ 25 Total = Qty Unit Value x x = £ 200 = £ 300 = £ 500 = £ 100 Staff £ 10 £ 5 £ 1 £ 2 £ 3 = = = = Rate x Total Labour Total £ 6 Total Material Rate x Qty Unit Cost = = = = Total Material Total Labour Total Qty Unit Cost = = = = Rate x Total Labour 1 - 2 m Problem Solving Rate £ 25 £ 6 Total Material Staff C x x x x Total Material x Qty Unit Cost = = = = Labour Cost this Period B Total 11 -15 £ 25 Total = Total Labour Total Qty Unit Value x x Total = £ 200 = £ 300 = £ 500 = £ 100 Total Revenue Profit: C-(A+B) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 61
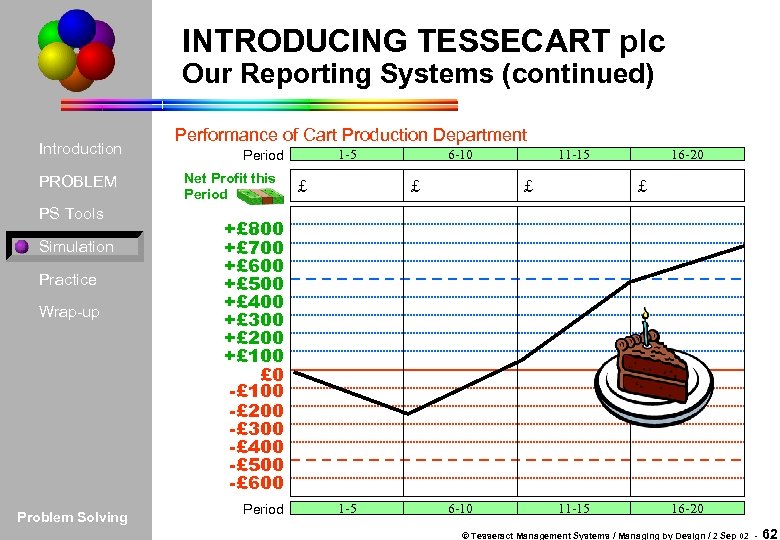
INTRODUCING TESSECART plc Our Reporting Systems (continued) Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Performance of Cart Production Department 1 -5 Period Net Profit this Period £ 6 -10 £ 11 -15 £ 16 -20 £ +£ 800 +£ 700 +£ 600 +£ 500 +£ 400 +£ 300 +£ 200 +£ 100 £ 0 -£ 100 -£ 200 -£ 300 -£ 400 -£ 500 -£ 600 Period 1 -5 6 -10 11 -15 16 -20 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 62
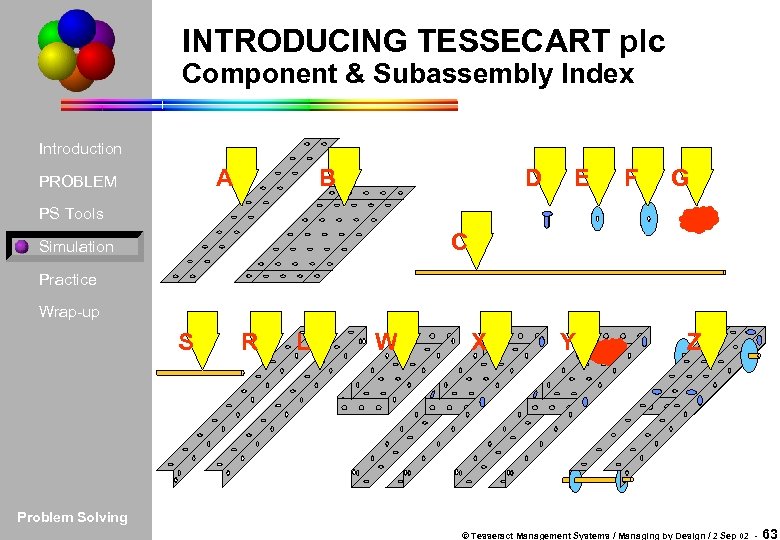
INTRODUCING TESSECART plc Component & Subassembly Index Introduction A PROBLEM B D E F G PS Tools C Simulation Practice Wrap-up S R L W X Y Z Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 63
TESSECART plc World famous producers of racing chariots Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up So how did we do? n Volume? n Quality? n Profit? n Morale? n …? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 64

From the Office of the Managing Director TESSECART plc C art To Cart Production Foreman (whoever you are) me World famous producers of Subject Y. A. Q. (yet another quality) Initiative racing chariots m o Dear (please fill in your own name) Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up I am pleased to inform you that after careful consideration (of all those managers who didn’t make themselves scarce) we have selected you to pilot the new YAQ initiative. During your production run tomorrow afternoon you will be required to dramatically improve the performance of your process at no cost to us – or you will be fired. We have had some air-head consultants demonstrate how poor our current management is (and that of course means you) and we have been persuaded to let them help you through some improvement process before we fire you. So buck up man (or woman – are you sure we employ women Miss Cranshawe? – not as management surely? – what is the world coming to) and appreciate how much we are doing for you – no other company would give you this opportunity – it never happened in my day. Yours condescendingly (Fawn at this point) Problem Solving Hiram N. Firam XVII Senior. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 65
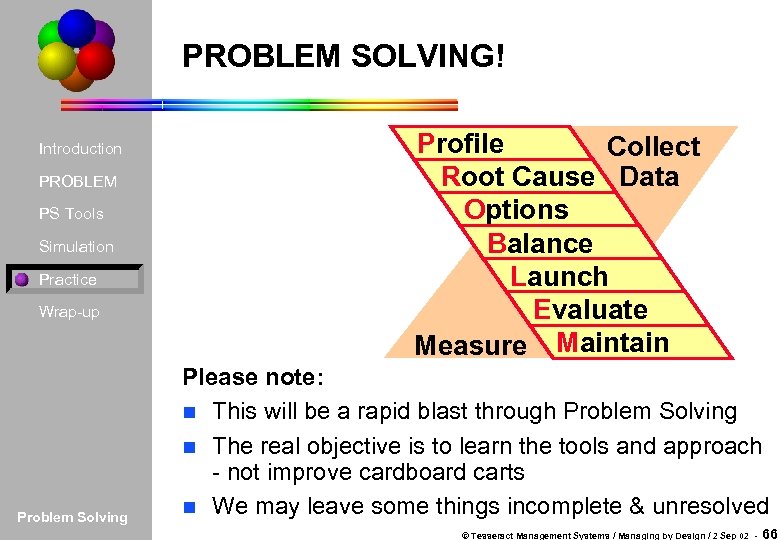
PROBLEM SOLVING! Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Please note: n This will be a rapid blast through Problem Solving n The real objective is to learn the tools and approach - not improve cardboard carts n We may leave some things incomplete & unresolved © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 66
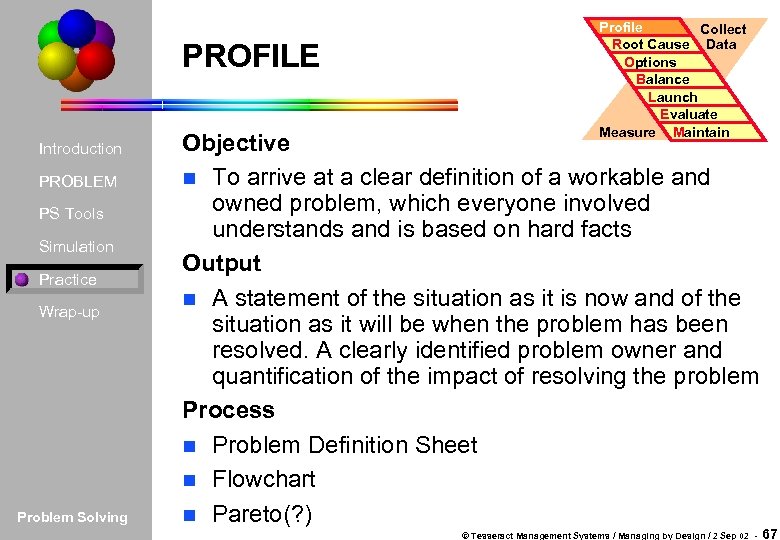
PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To arrive at a clear definition of a workable and owned problem, which everyone involved understands and is based on hard facts Output n A statement of the situation as it is now and of the situation as it will be when the problem has been resolved. A clearly identified problem owner and quantification of the impact of resolving the problem Process n Problem Definition Sheet n Flowchart n Pareto(? ) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 67
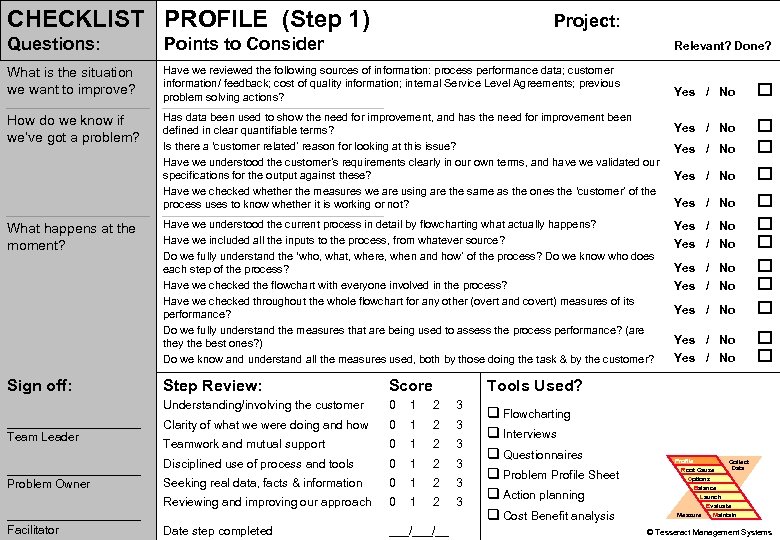
CHECKLIST PROFILE (Step 1) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Relevant? Done? What is the situation we want to improve? Have we reviewed the following sources of information: process performance data; customer information/ feedback; cost of quality information; internal Service Level Agreements; previous problem solving actions? Yes / No How do we know if we’ve got a problem? Has data been used to show the need for improvement, and has the need for improvement been defined in clear quantifiable terms? Is there a ‘customer related’ reason for looking at this issue? Have we understood the customer’s requirements clearly in our own terms, and have we validated our specifications for the output against these? Have we checked whether the measures we are using are the same as the ones the ‘customer’ of the process uses to know whether it is working or not? Yes / No Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools What happens at the moment? Simulation Practice Wrap-up Sign off: Have we understood the current process in detail by flowcharting what actually happens? Have we included all the inputs to the process, from whatever source? Do we fully understand the ‘who, what, where, when and how’ of the process? Do we know who does each step of the process? Have we checked the flowchart with everyone involved in the process? Have we checked throughout the whole flowchart for any other (overt and covert) measures of its performance? Do we fully understand the measures that are being used to assess the process performance? (are they the best ones? ) Do we know and understand all the measures used, both by those doing the task & by the customer? __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 Date step completed ___/__ Yes / No Yes / No Yes / No Tools Used? q Flowcharting q Interviews q Questionnaires q Problem Profile Sheet q Action planning q Cost Benefit analysis Profile Root Cause Options Collect Data Balance Launch Measure Evaluate Maintain 68 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
ROOT CAUSES Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To establish the most probable root cause of the whole problem, as opposed to identifying and dealing with symptoms Output n A cause, or group of causes, which can be shown by data to be the most likely real cause of the problem Process n Cause & Effect Diagram n Checksheet n Pareto n Scatter Diagram (? ) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 69
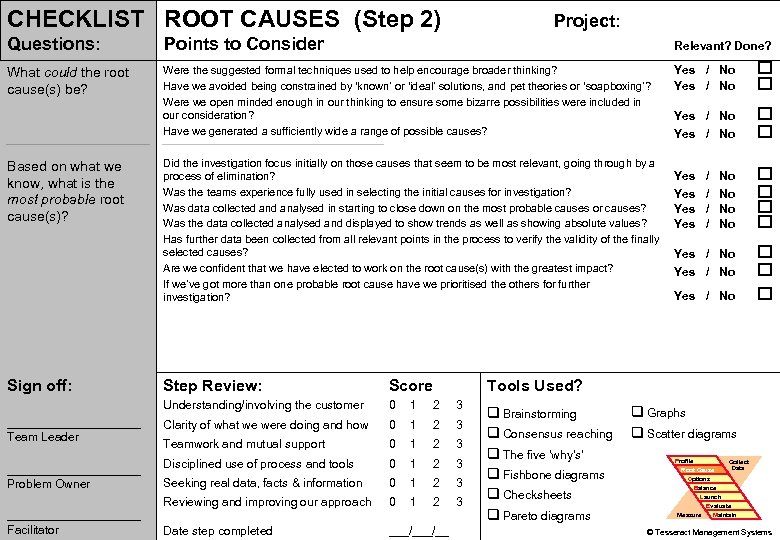
CHECKLIST ROOT CAUSES (Step 2) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Relevant? Done? What could the root cause(s) be? Were the suggested formal techniques used to help encourage broader thinking? Have we avoided being constrained by ‘known’ or ‘ideal’ solutions, and pet theories or ‘soapboxing’? Were we open minded enough in our thinking to ensure some bizarre possibilities were included in our consideration? Have we generated a sufficiently wide a range of possible causes? Yes / No Yes Yes No No Yes / No Introduction Based on what we PROBLEM know, what is the most probable root PS Tools cause(s)? Simulation Practice Wrap-up Sign off: Did the investigation focus initially on those causes that seem to be most relevant, going through by a process of elimination? Was the teams experience fully used in selecting the initial causes for investigation? Was data collected analysed in starting to close down on the most probable causes or causes? Was the data collected analysed and displayed to show trends as well as showing absolute values? Has further data been collected from all relevant points in the process to verify the validity of the finally selected causes? Are we confident that we have elected to work on the root cause(s) with the greatest impact? If we’ve got more than one probable root cause have we prioritised the others for further investigation? __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 Date step completed ___/__ / / Yes / No Tools Used? q Brainstorming q Consensus reaching q The five ‘why’s’ q Fishbone diagrams q Checksheets q Pareto diagrams q Graphs q Scatter diagrams Profile Root Cause Options Collect Data Balance Launch Measure Evaluate Maintain 70 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To identify a range of possible solutions which would eliminate the chosen root cause or causes, and which reflect an understanding of best practice. Output n A list of possible solutions to the problem. Process n Brainstorming n Affinity Diagram n Hurdling n Trying things out - experimenting n (Low-hanging fruit? ) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 71
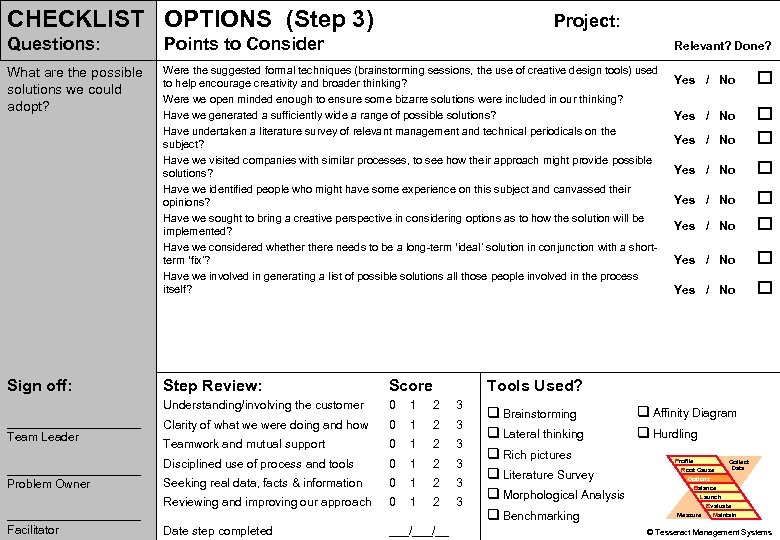
CHECKLIST OPTIONS (Step 3) Project: Questions: Points to Consider What are the possible solutions we could adopt? Were the suggested formal techniques (brainstorming sessions, the use of creative design tools) used to help encourage creativity and broader thinking? Were we open minded enough to ensure some bizarre solutions were included in our thinking? Have we generated a sufficiently wide a range of possible solutions? Have undertaken a literature survey of relevant management and technical periodicals on the subject? Have we visited companies with similar processes, to see how their approach might provide possible solutions? Have we identified people who might have some experience on this subject and canvassed their opinions? Have we sought to bring a creative perspective in considering options as to how the solution will be implemented? Have we considered whethere needs to be a long-term ‘ideal’ solution in conjunction with a shortterm ‘fix’? Have we involved in generating a list of possible solutions all those people involved in the process itself? Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Relevant? Done? Yes / No Yes / No Wrap-up Sign off: __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: Tools Used? 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 Date step completed ___/__ q Affinity Diagram q Brainstorming q Hurdling q Lateral thinking q Rich pictures Profile Collect Data Root Cause q Literature Survey Options Balance Launch q Morphological Analysis Evaluate Maintain Measure q Benchmarking 72 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
BALANCE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To develop a comprehensive, efficient and detailed solution to the problem being addressed. Output n A complete solution, possibly with an associated short-term fix, & associated implementation plans. Process n Selection matrix n Gantt Chart n Potential Problem Analysis Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 73
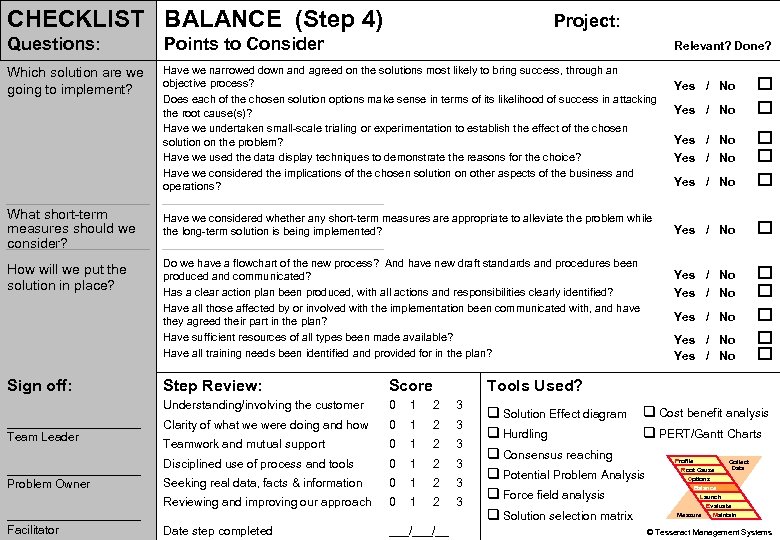
CHECKLIST BALANCE (Step 4) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Which solution are we going to implement? Have we narrowed down and agreed on the solutions most likely to bring success, through an objective process? Does each of the chosen solution options make sense in terms of its likelihood of success in attacking the root cause(s)? Have we undertaken small-scale trialing or experimentation to establish the effect of the chosen solution on the problem? Have we used the data display techniques to demonstrate the reasons for the choice? Have we considered the implications of the chosen solution on other aspects of the business and operations? Introduction PROBLEM What. PS Tools short-term measures should we consider? Simulation How will we put the Practice solution in place? Wrap-up Sign off: Relevant? Done? __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 Date step completed ___/__ Yes / No Yes / No Have we considered whether any short-term measures are appropriate to alleviate the problem while the long-term solution is being implemented? Do we have a flowchart of the new process? And have new draft standards and procedures been produced and communicated? Has a clear action plan been produced, with all actions and responsibilities clearly identified? Have all those affected by or involved with the implementation been communicated with, and have they agreed their part in the plan? Have sufficient resources of all types been made available? Have all training needs been identified and provided for in the plan? Yes / No Yes / No Tools Used? q Solution Effect diagram q Cost benefit analysis q PERT/Gantt Charts q Hurdling q Consensus reaching Profile Collect Data Root Cause q Potential Problem Analysis Options Balance Launch q Force field analysis Evaluate Maintain Measure q Solution selection matrix 74 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
LAUNCH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To ensure that the implementation of the chosen solution is adequately resourced, & runs to plan. Output n The solution implemented with minimum disruption. Process n Executing implementation plan n Plotting progress against activities and milestones n Correction of progress issues Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 75
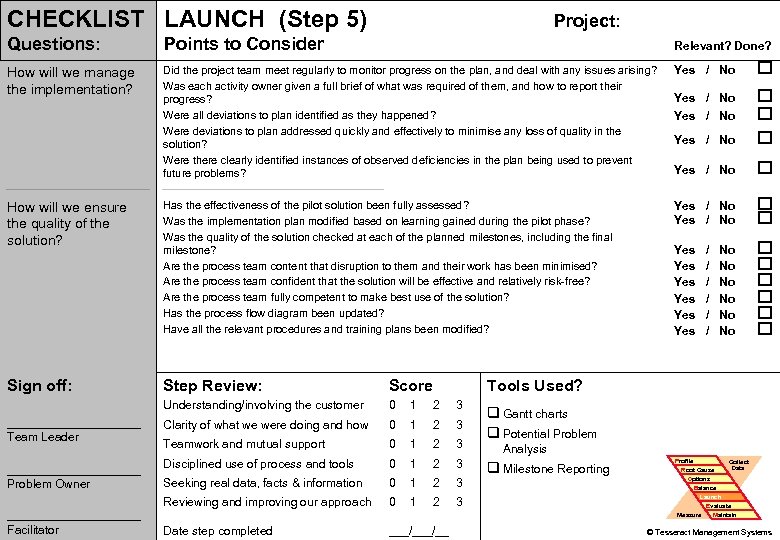
CHECKLIST LAUNCH (Step 5) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Relevant? Done? How will we manage the implementation? Did the project team meet regularly to monitor progress on the plan, and deal with any issues arising? Was each activity owner given a full brief of what was required of them, and how to report their progress? Were all deviations to plan identified as they happened? Were deviations to plan addressed quickly and effectively to minimise any loss of quality in the solution? Were there clearly identified instances of observed deficiencies in the plan being used to prevent future problems? Yes / No Yes / No Has the effectiveness of the pilot solution been fully assessed? Was the implementation plan modified based on learning gained during the pilot phase? Was the quality of the solution checked at each of the planned milestones, including the final milestone? Are the process team content that disruption to them and their work has been minimised? Are the process team confident that the solution will be effective and relatively risk-free? Are the process team fully competent to make best use of the solution? Has the process flow diagram been updated? Have all the relevant procedures and training plans been modified? Yes / No Yes Yes Yes Introduction PROBLEM How will we ensure PS Tools the quality of the solution? Simulation Practice Wrap-up Sign off: __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 ___/__ No No No Tools Used? q Gantt charts q Potential Problem Analysis q Milestone Reporting Profile Root Cause Options Collect Data Balance Launch Measure Date step completed / / / Evaluate Maintain 76 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
CHANDELIER (from Only Fools and Horses) Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools n What did you think of the level of Potential Problem Analysis demonstrated. Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 77
EVALUATE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To establish whether or not the chosen solution has eliminated the root cause of the problem. To review and improve the teams performance. Output n Data against specific measures to identify change of process output. Learning points for the team, individuals and the problem solving process itself. Process n Run the new process n Planned schedule of regular measurement n Review meeting Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 78
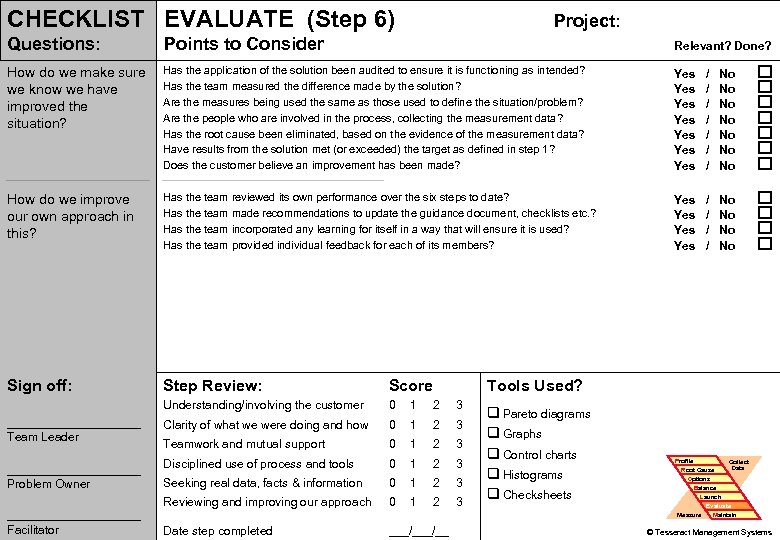
CHECKLIST EVALUATE (Step 6) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Relevant? Done? How do we make sure we know we have improved the situation? Has the application of the solution been audited to ensure it is functioning as intended? Has the team measured the difference made by the solution? Are the measures being used the same as those used to define the situation/problem? Are the people who are involved in the process, collecting the measurement data? Has the root cause been eliminated, based on the evidence of the measurement data? Have results from the solution met (or exceeded) the target as defined in step 1? Does the customer believe an improvement has been made? Yes Yes / / / / No No Has the team reviewed its own performance over the six steps to date? Has the team made recommendations to update the guidance document, checklists etc. ? Has the team incorporated any learning for itself in a way that will ensure it is used? Has the team provided individual feedback for each of its members? Yes Yes / / No No Introduction PROBLEM How do we improve PS Tools our own approach in this? Simulation Practice Wrap-up Sign off: __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: Tools Used? 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 q Pareto diagrams q Graphs q Control charts q Histograms q Checksheets Profile Root Cause Options Balance Launch Measure Date step completed ___/__ Collect Data Evaluate Maintain 79 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
MAINTAIN Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Objective n To ensure that the implemented solution becomes the new way of working and that the problem, as defined, remains permanently fixed Output n A new set of standard operating procedures and, where relevant, a training and/or communication plan. Process n Re-writing procedures etc. n New targets set for improvement n Recognition. Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 80
CHECKLIST MAINTAIN (Step 7) Project: Questions: Points to Consider Relevant? Done? How do we ensure a ‘permanent fix’? Does everyone involved fully understand the new standards and procedures? Has all the ‘support’ for the old process been removed? Has a schedule of checks and audits been set up to monitor the new process? Have the outcomes of the complete exercise and the benefits been widely communicated? Yes Yes No No How Introduction do we make sure others know of our PROBLEM success? Are there similar issues elsewhere which might benefit from taking the same approach? Yes / No / / PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Sign off: __________ Problem Owner __________ Problem Solving Facilitator Score Understanding/involving the customer __________ Team Leader Step Review: Tools Used? 0 1 2 3 Clarity of what we were doing and how 0 1 2 3 Teamwork and mutual support 0 1 2 3 Disciplined use of process and tools 0 1 2 3 Seeking real data, facts & information 0 1 2 3 Reviewing and improving our approach 0 1 2 3 q Standard operating procedures q Service Level Agreements q Training plans q Briefing notes Profile Root Cause Options Balance Launch Measure Date step completed ___/__ Collect Data Evaluate Maintain 81 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 -
RECAP ON THE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up How should we summarise the problem solving process? Reflecting back: n How do we now feel about our answers to the syndicate? How do we want to take Problem Solving forward? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 82

WRAP UP Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Any remaining questions n Clear the Car Park n Session assessment n Meeting Review n Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 83

Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 84

PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Exercise 4: Problem Definition (A) Develop a single sentence to define accurately and specifically the current problem concerning Northern Ireland as you see it? Practice Wrap-up And by the definition, literally as it is written above, what specifically would be delivered if the problem was to be solved as stated? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 85

PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Exercise 5: Problem Definition (B) For the problem definition you wrote down in part A, to what extent would the following conditions be met by it? Y N ? n The problem is clearly and unambiguously defined n Those who need to contribute to the solution will agree it n The statement will be interpreted in the same way by all n Success in solving it can be judged objectively Can you see ways in which your statement may be improved? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 86

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain PROFILE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up "If you accept your limitations you go beyond them” Brendan Francis, Writer ”It isn’t that they can’t see the solution, it is that they can’t see the problem” GK Chesterton, Writer Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 87

ROOT CAUSE Introduction Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 6: Quality of Root Cause Below are listed two statements of the root cause to a production problem in a biscuit making plant: A) 37% of waste is generated by inaccurate placing on the belt B) People are not properly trained to undertake their tasks Which do you see as the better Root Cause statement? A? B? Why? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 88

ROOT CAUSE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain "The question is one of fighting the causes and not just being satisfied with getting rid of the effects” Ernesto 'Che' Guevara, Bolivian Radical 1953 "Philosophers are adults who persist in asking childish questions” Sir Isaiah Berlin, British Philosopher Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 89

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Exercise 7: Brainstorming Ideas On a separate sheet of paper, spend the next five minutes brainstorming possible solutions to the problem of road congestion. Review your list of ideas using the following questions: Y n n n N ? Do you have a long list of ideas (more than ten)? Do you have a number of silly or bizarre ideas? Have your ideas covered many different aspects? The answer to each of the above should be ‘yes’. How could you improve your brainstorming approach further? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 90

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Exercise 8: Learning from others In seeking to identify new ideas or solutions to improve your work, how often has your group done any of the following? Often Practice Wrap-up n n n Rarely Never Shared ideas in the group on ways to improve Visited other companies to learn new techniques Attended conferences & shared the outputs Undertaken a literature survey & discussed it Invited speakers in from similar operations Had new starters present their ideas & history Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 91

OPTIONS Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain "The human mind is like an umbrella - it functions best when open” Walter Gropius, German Architect "The 'silly' question is often the first intimation of some totally new development” Alfred North Whitehead, British Philosopher Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 92

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain BALANCE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Exercise 9: Building a solution package Which of the following situations may benefit from a short term fix (STF), and/or a Pilot of the solution? Pilot Practice Wrap-up STF Injuries occurring from poorly maintained machine guards n Implementing flexi-time in the department n Introduction of a new machine n Valuable and experienced people leaving the company n From your answers can you derive any general principles as to when an STF or a Pilot might be desirable? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 93
Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain BALANCE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation "Circumstances? I make circumstances!” Napoleon Bonaparte, Emperor of Practice France Wrap-up "Is it progress if a cannibal uses a fork? ” Stanislaw J. Lec, Polish Poet Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 94

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain LAUNCH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Exercise 10: Managing Change How does your department fare on the following aspects of Change Management: Yes Practice Wrap-up n n n No Using a clearly defined and updated milestone plan? Ensuring people really believe in the need for change? The Boss is clearly keen for the ‘Change’ to happen? People are trained to get full benefit from the change? Progress is reviewed regularly, and issues addressed? People are rewarded for supporting the ‘Change’? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 95

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain LAUNCH Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up "Anyone who proposes to do good must not expect people to roll stones out of his way, but must accept his lot calmly if they even roll a few more upon it” Albert Schweitzer, German Missionary "It does not matter how small you are if you have faith and a plan of action” Fidel Castro, Cuban Leader Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 96

EVALUATE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Exercise 11: Measuring Impact Identify the 3 most recent changes in your area & list them below: 1: 2: 3: For each of these can you determine, in quantitative terms, the performance or financial benefit that they achieved? And can you say accurately how their performance in delivery improved/declined in the 6 months after implementation? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 97

EVALUATE Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation "An error is simply a failure to adjust immediately from a preconception to an actuality” John Cage, American Musician Practice Wrap-up Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain "The ability to learn faster than your competitors may be the only sustainable competitive advantage. ” Arie P. de Geus, Head of Planning at Shell Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 98

MAINTAIN Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain Exercise 12: Keeping it going List below, all the mechanisms that determine, control, support and influence how things are done in your area? Practice Wrap-up How do these get reviewed when a new change is introduced? Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 99

Profile Collect Root Cause Data Options Balance Launch Evaluate Measure Maintain MAINTAIN Introduction PROBLEM PS Tools Simulation Practice Wrap-up "The art of progress is to preserve order amid change and to preserve change amid order” Alfred North Whitehead, British Philosopher "To improve is to change; to be perfect is to change often. ” Winston Churchill, English Prime Minister Problem Solving © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2 Sep 02 - 100
717b3001ea3772fee56e5070241a4fac.ppt