35c74e3f15ea51960ad405cd4ecb0532.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Introduction & Overview “the continuum towards a modern TVET system” Presentation to TVET Conference, Beijing for Ministries of Finance / Education / Labour and Social Security 18 th May 2006 Ron Perkinson Principal Education Specialist International Finance Corporation World Bank Group www. ifc. org
Introduction & Overview “the continuum towards a modern TVET system” Presentation to TVET Conference, Beijing for Ministries of Finance / Education / Labour and Social Security 18 th May 2006 Ron Perkinson Principal Education Specialist International Finance Corporation World Bank Group www. ifc. org
 Purpose of Case Studies • Create awareness of international best practice characteristics for TVET systems • Discuss and debate best practice characteristics for a modern TVET system • Target discussion at a broad policy level
Purpose of Case Studies • Create awareness of international best practice characteristics for TVET systems • Discuss and debate best practice characteristics for a modern TVET system • Target discussion at a broad policy level
 IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET • • • Blueprint of perfect TVET system doesn’t exist! IFC’s best practice criteria are not absolute! Best practice characteristics are used to provide benchmarks for comparisons (China and internationally) • All of the best practice criteria do not apply to all Industry sectors • They are provided to foster discussion and debate – to create the vision for a more modern system Hand-outs are DRAFT only
IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET • • • Blueprint of perfect TVET system doesn’t exist! IFC’s best practice criteria are not absolute! Best practice characteristics are used to provide benchmarks for comparisons (China and internationally) • All of the best practice criteria do not apply to all Industry sectors • They are provided to foster discussion and debate – to create the vision for a more modern system Hand-outs are DRAFT only
 IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET Systems Important Characteristics include: • Where the needs of the Industry and business are driving training policies, standards and delivery; • Frameworks and systems (national or provincial) that are fostering career pathways for working adults and for the unemployed, from entry level in to the workforce – and beyond; • Systems that cater for apprentices and different kinds of lifelong learners, where all age groups can benefit; • Systems where vocational education and training can be modular and flexible – and where certified credits can be transferable nationally across institutions and provincial borders in to higher studies; • Where delivery is through accredited post secondary institutions, public or private, with both accorded equal treatment by governing TVET authorities;
IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET Systems Important Characteristics include: • Where the needs of the Industry and business are driving training policies, standards and delivery; • Frameworks and systems (national or provincial) that are fostering career pathways for working adults and for the unemployed, from entry level in to the workforce – and beyond; • Systems that cater for apprentices and different kinds of lifelong learners, where all age groups can benefit; • Systems where vocational education and training can be modular and flexible – and where certified credits can be transferable nationally across institutions and provincial borders in to higher studies; • Where delivery is through accredited post secondary institutions, public or private, with both accorded equal treatment by governing TVET authorities;
 IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET Systems 2 • Systems that foster competency and skills based training - without time constraints and where national competency standards, guidelines and qualifications are Industry-led rather than government controlled; • Where national and regional industry training advisory councils have a majority of private sector representation; • Government and / or sub-government bodies who are responsible for ensuring that Industry Training Councils implement and maintain effective Quality Management Systems; • An effective registration and accrediting body for licensing public and private TVET institutions; • Minimum experience or qualifications for approved training providers.
IFC’s 10 International Best Practices Characteristics in TVET Systems 2 • Systems that foster competency and skills based training - without time constraints and where national competency standards, guidelines and qualifications are Industry-led rather than government controlled; • Where national and regional industry training advisory councils have a majority of private sector representation; • Government and / or sub-government bodies who are responsible for ensuring that Industry Training Councils implement and maintain effective Quality Management Systems; • An effective registration and accrediting body for licensing public and private TVET institutions; • Minimum experience or qualifications for approved training providers.
 Education Expenditure Comparatives 2003 -04 Global GDP Public education spending is 5% of global GDP OECD spend 6. 1% of GDP on education (2005) China Total Public Expenditure Current Private Expenditure 3. 2% of GDP 1. 6% of GDP Total (Public & Private) = 4. 8% of GDP China needs over 50% increase on public expenditure to reach world average
Education Expenditure Comparatives 2003 -04 Global GDP Public education spending is 5% of global GDP OECD spend 6. 1% of GDP on education (2005) China Total Public Expenditure Current Private Expenditure 3. 2% of GDP 1. 6% of GDP Total (Public & Private) = 4. 8% of GDP China needs over 50% increase on public expenditure to reach world average
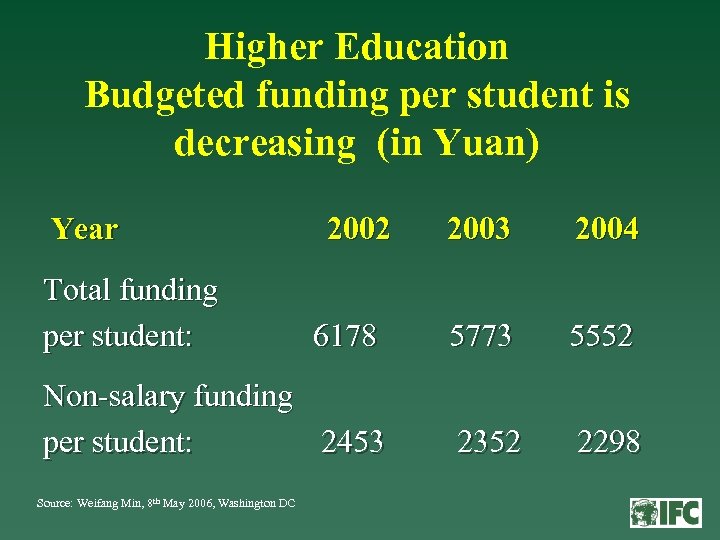 Higher Education Budgeted funding per student is decreasing (in Yuan) Year 2003 2004 6178 5773 5552 Non-salary funding per student: 2453 2352 2298 Total funding per student: Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC 2002
Higher Education Budgeted funding per student is decreasing (in Yuan) Year 2003 2004 6178 5773 5552 Non-salary funding per student: 2453 2352 2298 Total funding per student: Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC 2002
 The Development of Higher Education in China • In 2005 total enrollment in Chinese higher education was 23, 000. • Gross enrollment ratio went from 9. 8% in 1998 to around 20% in 2005. • Estimated enrollment in 2006: Undergrad: 5, 300, 000 Graduate: 400, 000 of which are Doctoral: 56, 000 Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC
The Development of Higher Education in China • In 2005 total enrollment in Chinese higher education was 23, 000. • Gross enrollment ratio went from 9. 8% in 1998 to around 20% in 2005. • Estimated enrollment in 2006: Undergrad: 5, 300, 000 Graduate: 400, 000 of which are Doctoral: 56, 000 Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC
 Estimated Enrollment Numbers by 2010 and 2020 • In the past 6 years the annual growth rate = 16%. • Even if the annual growth rates slow down to 5%, • Higher Education Enrollment would be be 27, 000 by 2010 44, 000 by 2020 How will China finance such predicted numbers? Alternative forms of financing will be necessary Building new capacity in TVET will be critical Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC
Estimated Enrollment Numbers by 2010 and 2020 • In the past 6 years the annual growth rate = 16%. • Even if the annual growth rates slow down to 5%, • Higher Education Enrollment would be be 27, 000 by 2010 44, 000 by 2020 How will China finance such predicted numbers? Alternative forms of financing will be necessary Building new capacity in TVET will be critical Source: Weifang Min, 8 th May 2006, Washington DC
 TVET. . . more integrated in to the formal education system • No longer practical to leave growing areas of TVET outside of the formal higher education system of credentials and qualifications – constantly changing technologies – shorter life cycles of new products and services – need for new kinds of skilled workers (lifelong learners) – need for developing career pathways
TVET. . . more integrated in to the formal education system • No longer practical to leave growing areas of TVET outside of the formal higher education system of credentials and qualifications – constantly changing technologies – shorter life cycles of new products and services – need for new kinds of skilled workers (lifelong learners) – need for developing career pathways
 How will China’s Policy Makers. . . • Mobilize private sector resources to help fill the demand gap? • Develop new policies for a more modern TVET system? • Create policies that will meet The 11 th Five-Year Plan (2005) – with a focus on quality improvement – achieving internationalized participation in education and TVET – responsiveness to needs of the labour market and employers – preparing students for new occupations and employment – combining workplace practice and production with study
How will China’s Policy Makers. . . • Mobilize private sector resources to help fill the demand gap? • Develop new policies for a more modern TVET system? • Create policies that will meet The 11 th Five-Year Plan (2005) – with a focus on quality improvement – achieving internationalized participation in education and TVET – responsiveness to needs of the labour market and employers – preparing students for new occupations and employment – combining workplace practice and production with study
 Conference Case Studies • Systems (China, Finland, Sweden, Denmark & Australia) • Industries (Finance, Automotive, Power, Airline, Engineering, Customs, Health) • Institutions (Finance, Power, Automotive, Health/Medical/Distance, Airline, Customs, Engineering) Conference Feedback – then Draft Reports will be completed and published
Conference Case Studies • Systems (China, Finland, Sweden, Denmark & Australia) • Industries (Finance, Automotive, Power, Airline, Engineering, Customs, Health) • Institutions (Finance, Power, Automotive, Health/Medical/Distance, Airline, Customs, Engineering) Conference Feedback – then Draft Reports will be completed and published


